Evaluation of fault slip probability of geothermal large-scale development: A case study of deep karst geothermal reservoir in Xiong'an New Area
-
摘要:
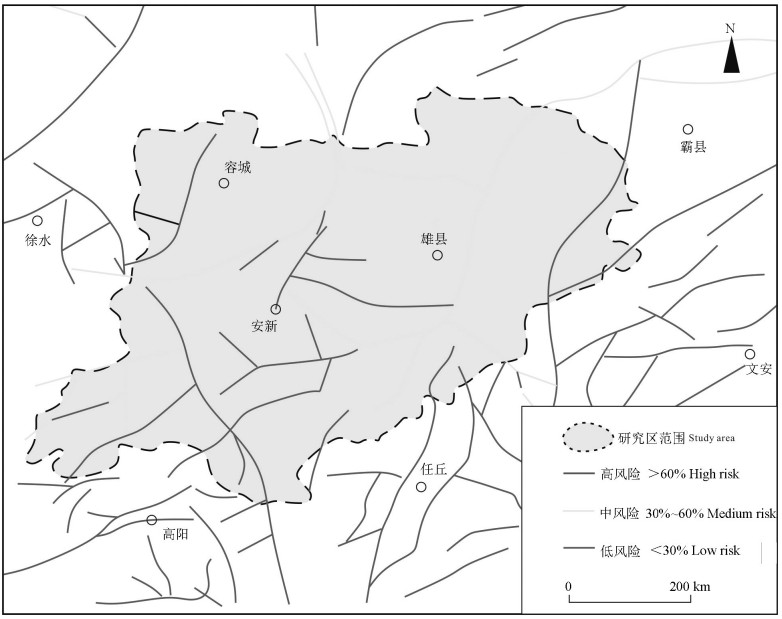
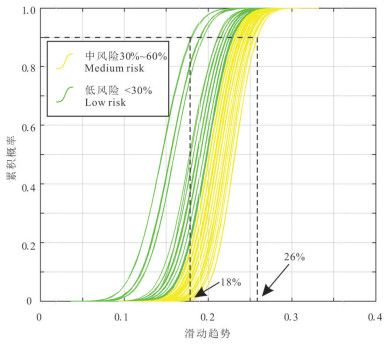
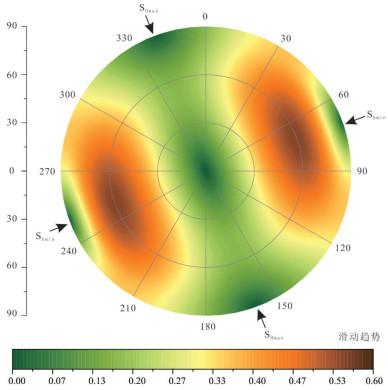
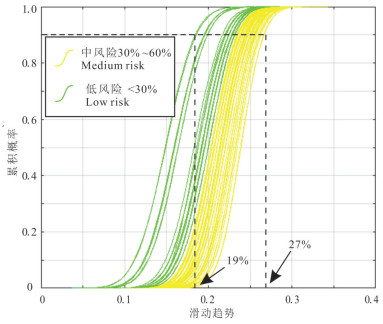
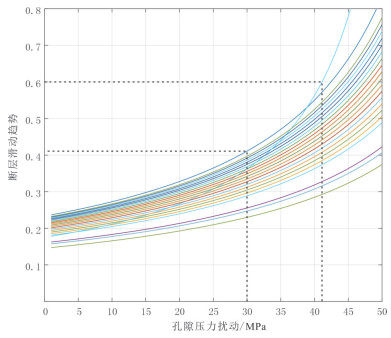
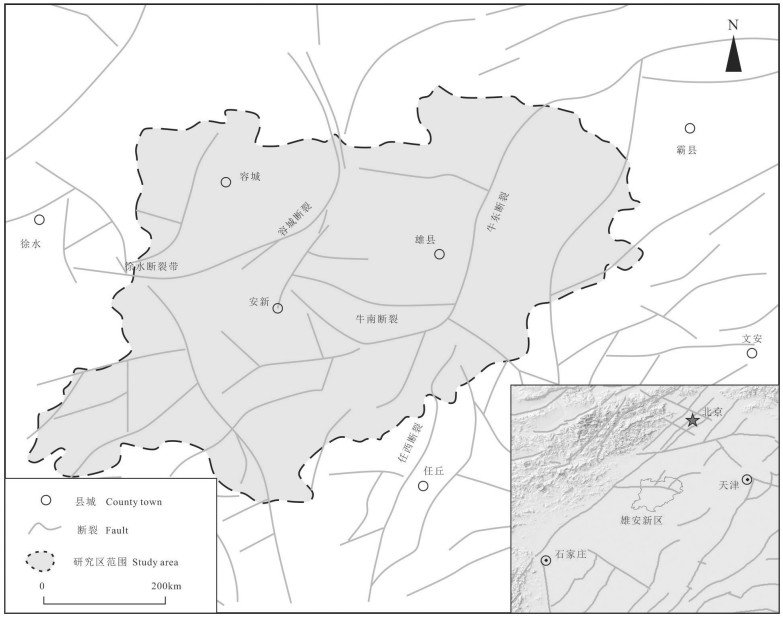
雄安新区地热资源丰富,具有广阔的规模化开发利用前景,对于实现"绿色雄安"具有重要意义。许多学者的研究集中在地质结构探测、地热资源量评价、地壳稳定性等方面,关于深部岩溶热储规模化开发可能引起的断层滑动研究薄弱。本文在地热地质综合调查的基础上,基于地质力学理论,采用蒙特卡罗随机模拟方法,评价雄安新区主要断层特征(走向、倾角、滑动摩擦系数等)、地应力分布(孔隙压力、最大/最小/垂直主应力大小及方向等),量化雄安新区天然断层在规模化开发利用情况下的激活可能性,结果显示已探明断层在天然、规模化回灌和水力压裂条件下的最大滑动趋势分别为0.26、0.27和0.40,地热开发不会引起断层激活。本研究树立了地热规模化开发的信心,可为雄安新区地热资源安全利用提供支撑。
Abstract:Xiongan New Area is rich in geothermal resources and has broad prospects for large-scale development and utilization, which is of great significance to the realization of "green Xiongan". Many scholars have focused their research on geological structure exploration, resource evaluation, crustal stability, etc. However, the study on the possible fault sliding caused by the large-scale development of deep karst thermal storage is weak. On the basis of geomechanical theory and geothermal geological survey, Monte Carlo stochastic simulation method was used to evaluate the characteristics of main faults (strike, dip, slip friction coefficient, etc.) and geostress distribution (pore pressure, maximum/minimum/vertical principal stress magnitude and direction, etc.) in Xiongan New area for quantifying the activation possibility of natural faults under large-scale development and utilization. The results show that the maximum slip trends of proven faults under natural, large-scale recharge and hydraulic fracturing conditions are 0.26, 0.27 and 0.40, respectively. Geothermal development will not cause fault activation. The study establishes confidence in geothermal development and provides support for safe geothermal use in Xiong'an New Area.
-
-
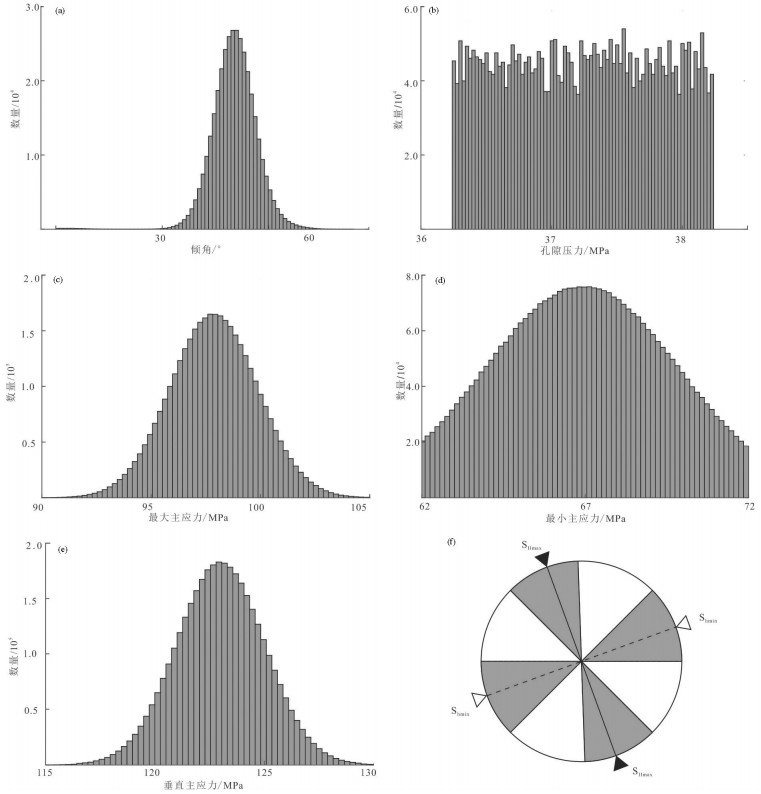
表 1 断层滑动趋势分析参数分布
Table 1 Fault slip trend analysis parameter distribution

-
Blanpied M L, Lockner D A, Byerlee J D. 1995. Frictional slip of granite at hydrothermal conditions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100(B7): 13045-13064. doi: 10.1029/95JB00862
Byerlee J. 1978. Friction of Rocks[M]. Byerlee J D, Wyss M. Basel: Birkhäuser Basel.
Fan Larsheng, Jia Xiaofeng, Wang Guiling, Zhang Tunde, Zhang Ping, Lv Can, Li Junping. 2020. Drilling practice of D03 geothermal exploration well in Xiongan New Area[J]. Exploration Engineering(Rock & Soil Drilling And Tunneling), 47(10): 13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan Yulu, Tan Chengxuan, Zhang Peng, Sun Mingqian, Qi Bangshen, Feng Chengjun, Meng Jing, Wang Huiqing. 2020. A Study of current in-situ stress state and its influence on tectonic stability in the Xiongan New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(4): 481-491 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Feng Chengjun, Qi Bangshen, Wang Xiaoshan, Zhang Peng, Sun Mingqian, Meng Jing, Tan Chengxuan, Chen Qunze. 2019. Study of fault activity risk in typical strong seismic regions in northern China by in-situ stress measurements and the influence on the Xiong'an New Area[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(4): 170-190 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Friberg P, Besana-Ostman G, Dricker I. 2014. Characterization of an earthquake sequence triggered by hydraulic fracturing in Harrison County, Ohio[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 85: 1295-1307. doi: 10.1785/0220140127
He Dengfa, Shan Shuaiqiang, Zhang Yuying, Lu Renqi, Zhang Ruifeng, Cui Yongqian. 2018. 3-D geologic architecture of Xiong'an New Area: Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 48(9): 1207-1222 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG201808002.htm
Heidbach O, Rajabi M, Reiter K. 2016. World Stress Map Database Release 2016. V. 1.1[OL]. GFZ Data Services.
Huang Luyuan, Yang Shuxin, Cui Xiaofeng, Chen Qunce, Yao Rui. 2013. Analysis of characteristics of measured stress and stability of faults in North China[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 34(S1): 204-213 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/287539781_Analysis_of_characteristics_of_measured_stress_and_stability_of_faults_in_North_China
Jaeger J C, Cook N G W, Zimmerman R. 2007. Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics, 4th Edition[M]. US: Wiley-Blackwell.
Ma Zhen, Xia YuBo, Wang Xiaodan, Han Bo, Gao Yihang. 2019. Integration of engineering geological investigation data and construction of a 3D geological structure model in the Xiong'an New Area[J]. Geology in China, 46(S2): 123-129(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Zhen, Xia Yubo, Li Haitao, Han Bo, Yu Xuezhong, Zhou Yalong, Wang Yushan, Guo Xu, Li Hong, Pei Yandong. 2021. Analysis of natural resources and environment eco-geological conditions in the Xiong'an New Area[J]. Geology in China, 48(3): 677-696(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mcgarr A, Barbour A. 2018. Injection-induced moment release can also be aseismic[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45 (11): 5344. doi: 10.1029/2018GL078422
Moeck I, Kwiatek G, Zimmerman Gu. 2009. Slip tendency analysis, fault reactivation potential and induced seismicity in a deep geothermal reservoir[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 31(10): 1174-1182. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2009.06.012
Morris A, Ferrill D, Henderson D. 1996. Slip-tendency analysis and fault reactivation[J]. Geology, 24. http://basin.earth.ncu.edu.tw/Course/SeminarII/abstract2014_1/2014.10.16_Yu-Hsuan%20Chiang/Chiang,%20Yu-%20Hsuan_Geology-1996-Morris-275-8.pdf
Nelson P, Gianoutsos N, Drake II R. 2015. Underpressure in Mesozoic and Paleozoic rock units in the Midcontinent of the United States[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 99: 1861-1892. doi: 10.1306/04171514169
Niu Linlin. 2018. Study on the Tectonic Stress Field and Seismogenic Environment in Beijing Tianjin Hebei Region[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
Norbeck J H, Horne R N. 2018. Maximum magnitude of injection-induced earthquakes: A criterion to assess the influence of pressure migration along faults[J]. Tectonophysics, 733: 108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.01.028
Pang Jumei, Pang Zhonghe, Lü Min, Tian Jiao. 2018. Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of fluids in the Niutuozhen geothermal field, North China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(1): 12. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-7171-y
Seithel R, Gaucher E, Mueller B, Steiner U, Kohl T. 2019. Probability of fault reactivation in the Bavarian Molasse Basin[J]. Geothermics, 82: 81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.06.004
Schoenball M, Walsh F R, Weingarten M. 2018. How faults wake up: The Guthrie-Langston, Oklahoma earthquakes[J]. The Leading Edge, 37(2): 100-106. doi: 10.1190/tle37020100.1
Shang Shijie, Feng Chengjun, Tan Chengxuan, Qi Bangshen, Zhang Peng, Meng Jing, Wang Miaomiao, Sun Mingqian, Wan Jiawei, Wang Huiqing, Xiang Xinxuan. 2019. Quaternary activity study of major buried faults near Xiongan New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 40(6): 836-846 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB201906007.htm
Walsh F R, Zoback M D. 2015. Oklahoma's recent earthquakes and saltwater disposal[J]. Science Advances, 1(5): 1-9. http://www.ourenergypolicy.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/e1500195.full_.pdf
Walsh F R, Zoback M D. 2016. Probabilistic assessment of potential fault slip related to injection-induced earthquakes: Application to north-central Oklahoma, USA[J]. Geology, 44(12): 991-994. doi: 10.1130/G38275.1
Xu Jie, Gao Zhanwu, Song Changqing, Sun Jiangbao. 2000. Tectonic features of the Taihang Mountains pre-mountain rift zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, (2): 111-122(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yi, Dai Junsheng, Wang Ke, Zou Juan, Zhang Dandan. 2014. Characteristics of Paleoproterozoic fracture activity in the Baxian Depression of the Jizhong Depression[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science), 29(1): 27-33, 5(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Xi, Wang Guiling, Ma Feng, Zhang Wei, Zhang Qinglian, Zhang Hanxiong. 2020. Hydrogeochemistry of geothermal maters from Taihang Mountain-Xiong'an New Area and its indicating significance[J]. Earth Science, 46(7): 15(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zoback M D, Harhes H P. 1997. Injection-induced earthquakes and crustal stress at 9 km depth at the KTB deep drilling site, Germany[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B8): 18477-18491(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1029/96JB02814
陈墨香. 1988. 华北地热[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 樊腊生, 贾小丰, 王贵玲, 张统得, 张平, 吕灿, 李俊萍. 2020. 雄安新区D03地热勘探井钻探施工实践[J]. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程), 47(10): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TKGC202010003.htm 范玉璐, 谭成轩, 张鹏, 孙明乾, 戚帮申, 丰成君, 孟静, 王惠卿. 2020. 雄安新区现今地应力环境及其对构造稳定性影响研究[J]. 地球学报, 41(4): 481-491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202004003.htm 丰成君, 戚帮申, 王晓山, 张鹏, 孙明乾, 孟静, 谭成轩, 陈群策. 2019. 基于原地应力实测数据探讨华北典型强震区断裂活动危险性及其对雄安新区的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 26(4): 170-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201904024.htm 何登发, 单帅强, 张煜颖, 鲁人齐, 张锐锋, 崔永谦. 2018. 雄安新区的三维地质结构: 来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(9): 1207-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201809007.htm 胡秋韵, 高俊, 马峰, 赵志宏, 刘桂宏, 王贵玲, 张薇, 朱喜, 张保建, 邢一飞. 2020. 雄安新区容城凸起区地热可采资源量动态预测[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 2013-2025. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.010 黄禄渊, 杨树新, 崔效锋, 陈群策, 姚瑞. 2013. 华北地区实测应力特征与断层稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 34(S1): 204-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2013S1032.htm 马峰, 王贵玲, 张薇, 朱喜, 张汉雄, 岳高凡. 2020. 雄安新区容城地热田热储空间结构及资源潜力[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 1981-1990. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.007 马震, 夏雨波, 王小丹, 韩博, 高伊航. 2019. 雄安新区工程地质勘查数据集成与三维地质结构模型构建[J]. 中国地质, 46(S2): 123-129. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2019S213&flag=1 马震, 夏雨波, 李海涛, 韩博, 余学中, 周亚龙, 王雨山, 郭旭, 李洪, 裴艳东. 2021. 雄安新区自然资源与环境-生态地质条件分析[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 677-696. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210301&flag=1 牛琳琳. 2018. 京津冀地区现代构造应力场与孕震环境研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. 商世杰, 丰成君, 谭成轩, 戚帮申, 张鹏, 孟静, 王苗苗, 孙明乾, 万佳威, 王惠卿, 项歆璇. 2019. 雄安新区附近主要隐伏断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地球学报, 40(6): 836-846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201906007.htm 王贵玲, 高俊, 张保建, 邢一飞, 张薇, 马峰. 2020. 雄安新区高阳低凸起区雾迷山组热储特征与高产能地热井参数研究[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 1970-1980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.006 王贵玲, 蔺文静. 2020. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 1923-1937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002 吴爱民, 马峰, 王贵玲, 刘金侠, 胡秋韵, 苗青壮. 2018. 雄安新区深部岩溶热储探测与高产能地热井参数研究[J]. 地球学报, 39(5): 523-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805002.htm 徐杰, 高战武, 宋长青, 孙建宝. 2000. 太行山山前断裂带的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, (2): 111-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.02.003 张薇, 王贵玲, 刘峰, 邢林啸, 李曼. 2019. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 255-268. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190204&flag=1 张艺, 戴俊生, 王珂, 邹娟, 张丹丹. 2014. 冀中坳陷霸县凹陷古近纪断裂活动特征[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 29(1): 27-33, 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2014.01.005 赵佳怡. 2020. 雄安新区深部热储空间结构与水热分异过程研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. 朱喜, 王贵玲, 马峰, 张薇, 张庆莲, 张汉雄. 2020. 太行山-雄安新区蓟县系含水层水文地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地球科学, 46(7): 15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202107025.htm -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. Jian-yu Liu,Hong-feng Nie,Liang Xu,Chun-lei Xiao,Wei Li,Guo-li Yuan,Yan-peng Huang,Xin-yang Ji,Tian-qi Li. Assessment of ecological geological vulnerability in Mu Us Sandy Land based on GIS and suggestions of ecological protection and restoration. China Geology. 2025(01): 117-143 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 祝晓松,裴小龙,王伟,张中跃,孙伟涛,倪舒博,公为鑫. 山丘区地表基质空间异质性特征及其对植被生态影响. 地质通报. 2024(09): 1544-1554 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘洪,李文昌,欧阳渊,张景华,张腾蛟,李佑国,黄瀚霄,黄勇,李富,陈敏华,李樋,吴君毅. 基于地质建造的西南山区生态地质编图探索与实践——以邛海—泸山地区为例. 地质学报. 2023(02): 623-638 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 息朝庄,吴林锋,张鹏飞,杨茗钛,范云飞,夏浩东,邓会娟. 贵州省惠水土壤-灌溉水-雨水-大气降尘中Cd、As等微量元素特征及来源讨论. 中国地质. 2023(01): 192-205 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王东晓,袁德志. 锶在土壤-作物中迁移富集机制及作物富锶标准探讨:以河南固始史河一带为例. 现代地质. 2023(03): 767-777 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 唐智明. 水肥一体化技术及其在柑橘种植上的应用. 现代农业科技. 2022(01): 73-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 习文勇,傅佩红. 基于模糊数学的柑橘种植土地适宜性评价. 浙江农业学报. 2022(01): 141-152 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张哲寰,杨佳佳,宋运红,贺鹏飞. 黑龙江省讷河市土壤质量与绿色产地适宜性评价. 地质与资源. 2022(02): 183-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 贾磊,刘洪,欧阳渊,张伟,窦磊,刘子宁,莫滨,陈恩,张腾蛟. 基于地质建造的南方山地-丘陵区地表基质填图单元划分方案——以珠三角新会—台山地区为例. 西北地质. 2022(04): 140-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李海山. 柑橘种植与机械化节水灌溉技术探讨. 农业开发与装备. 2021(10): 225-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 欧阳渊,张景华,刘洪,黄瀚霄,张腾蛟,黄勇. 基于地质建造的西南山区成土母质分类方案——以大凉山区为例. 中国地质调查. 2021(06): 50-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: