Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of surface evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain in recent 20 years
-
摘要:
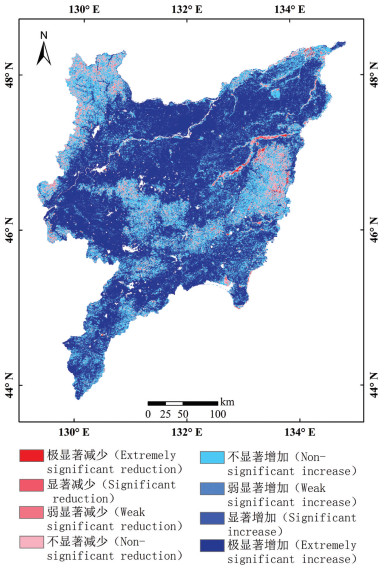
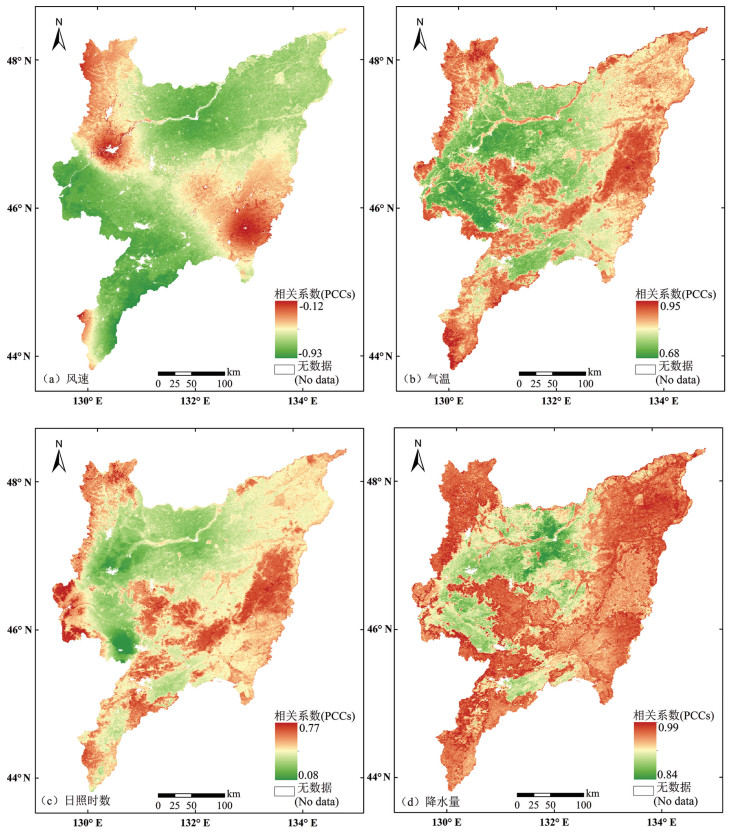
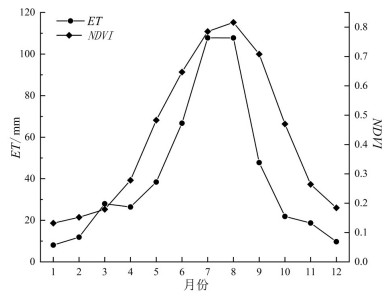
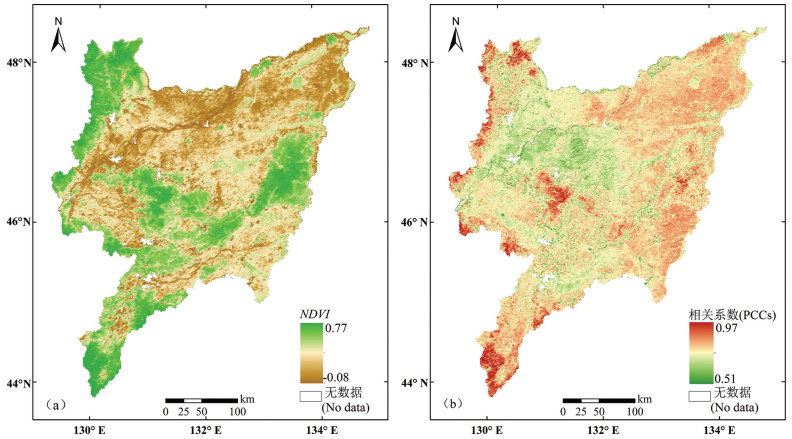
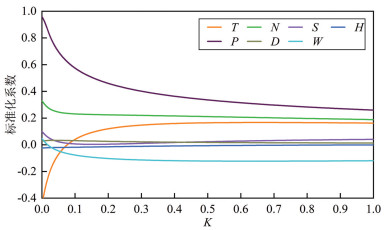
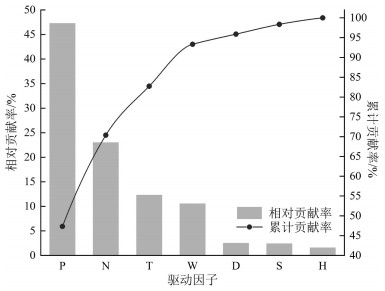
分析地表蒸散发时空变化规律及驱动因素,对促进区域水资源的科学分配、做好生态系统水源保护具有重要意义。本文基于MOD16蒸散发遥感数据产品,采用趋势分析及显著性检验法,深入分析了近20年三江平原地表蒸散量的时空变化特征,根据Penman-Monteith公式选取与地表蒸散量(ET)相关的驱动因子,分析各驱动因子对地表蒸散量变化的影响,并构建岭回归统计模型,分析研究地表蒸散量变化的主要驱动因子及其相对贡献率。结果表明:近20年三江平原地表蒸散发(ET)年际起伏特征明显,整体呈上升趋势;研究区内91.53%的地区ET呈增加趋势,且ET分布的地域差异逐年缩小;年内ET呈单峰型周期性变化,季节差异性明显;研究区坡度对ET有正向影响,高程和风速对ET有负向影响;气温、日照时数、降水量及NDVI与ET均呈正相关性,其中降水量与ET相关性最为显著;构建岭回归驱动分析模型的决定系数R2为0.823,能够有效解释各驱动因素与ET的关系。模型计算结果表明:降水量和植被覆盖度对三江平原地表蒸散量影响较大,是影响地表蒸散量变化的主要驱动力。
Abstract:It is of great significance for analyzing the spatiotemporal variation law of surface evapotranspiration and its driving factors to promote the scientific allocation of regional water resources and to do a good job of ecological water source protection. Based on MOD16 ET remote sensing data, trend analysis and significance test method were adopted to analyze the spatial-temporal variation characteristics of surface evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain in recent 20 years. According to Penman-Monteith formula, driving factors related to surface evapotranspiration (ET) were selected to analyze the influence of driving factors on the change of surface evapotranspiration. Ridge regression statistical model was built to analyze the main driving factors of evapotranspiration change and their relative contribution rates. The results show that the interannual fluctuation characteristics of surface evapotranspiration (ET) in the Sanjiang Plain were obvious in recent 20 years, and the overall trend of ET was increasing. ET in 91.53% of the study area shows an increasing trend, and the regional differences of ET distribution decreased year by year. The annual ET shows unimodal periodical variation, and the seasonal difference is obvious. Slope in the study area has a positive effect on ET, while elevation and wind speed have a negative effect. Temperature, sunshine duration, precipitation and NDVI are positively correlated with ET, and precipitation has the most significant correlation with ET. The determination coefficient R2 of ridge regression driving analysis model is 0.823, which can effectively explain the relationship between various driving factors and ET. The results of model calculation show that precipitation and vegetation coverage have a great influence on the surface evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain and are the main driving forces for the change of surface evapotranspiration.
-
-
表 1 研究数据来源
Table 1 Introduction of research data sources

表 2 高程分级地表蒸散量统计
Table 2 Statistics of surface evapotranspiration in elevation classification

表 3 坡度分级地表蒸散量统计
Table 3 Statistics of surface evapotranspiration by slope classification

表 4 驱动因子共线性诊断
Table 4 Driving factors collinearity diagnosis

表 5 岭回归分析结果
Table 5 Ridge regression analysis results

-
Cai Bofeng, Yu Rong. 2009. Advance and evaluation in the long time series vegetation trends research based on remote sensing[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 13(6): 1170-1186(in Chinese with English abstract). http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=32217608
Chen Shaodan, Zhang Liping, Tian Xiangyong, Tang Rouxin, Liu Xin. 2019. Comparative analysis of potential evapotranspiration estimation between Penman-Monteith model and MOD16 data in Middle and Lower Yangtze River Basin[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 52(4): 283-289, 296(in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng Xingyao, Liu Yang, Liu Zhihui, Yao Junqiang. 2017. Temporal-spatial dynamic change characteristics of evapotranspiration in arid region of Northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(9): 2994-3008(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong Q, Zhan C, Wang H, Wang F, Zhu M. 2015. A review on evapotranspiration data assimilation based on hydrological models[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 26(2): 230-242.
Du Guoming, Liu Wenqi, Yu Jiaxing, Zhang Shuang. 2019. Influence of paddy field and dry field distribution on local surfacetemperature by remote sensing inversion in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(5): 259- 267 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fang Li, Wang Wenjie, Jiang Weiguo, Chen Min, Wang Yong, Jia Kai, Li Yansen. 2017. Vegetation cover, spatio-temporal change and its response to climate change in the Heilongjiang River Basin (China) from 2000 to 2014[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 37(11): 1745-1754(in Chinese).
Fan Jianzhong, Li Dengke, Gao Maosheng. 2014. Spatio-temporal variations of evapotranspiration in Shaanxi Province using MOD16 products[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(09): 1536-1543(in Chinese with English abstract).
Feng Fei, Yao Yunjun, Zhang Yanbing, Li Xianglan. 2015. Spatio-temporal variations of evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain using MOD16 products[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(11): 1858-1864(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Kui, Lu Yimin, Wei Zheng, Chen He, Zhang Baozhong, Ma Wenjin. 2019. Effects of land use and climate change on spatiotemporal changes of evapotranspiration in Haihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 21(12): 1888-1902(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXX201912008.htm
Hu Meng, Feng Qi, Xi Haiyang. 2013. Progress of monitoring soil moisture by remote sensing in Arid Areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 44(5): 1270-1275(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Qiuxiang, Zhang Shunkai, Zhang Xu, Wang Zilong. 2020. Assessment of variations and driving factors of water resources development and utilization in the Sanjiang Plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 18(1): 74-81(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jung M, Reichstein M, Ciais P, Seneviratne S I, Sheffield J, Goulden ML, Bonan G, Cescatti A, Chen J, Jeu R D. 2010. Recent decline in the global land evapotranspiration trend due to limited moisture supply[J]. Nature, 467(7318): 951-954. doi: 10.1038/nature09396
Liu Chunyu, Zhao Jun, Liu Yingying, Wei Wei. 2011. Remote sensing estimation of evapotranspiration quantity and analysis of space-time structure over Shiyang River Basin[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, (3): 117-122(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201103023.htm
Liu Guodong, Zhang Li, Yang Ze, Dai Huimin, Zhao Chuandong. 2021. Distribution characteristics of heavy metal in the water and suspended substance of Nenjiang River Basin: Environmental Implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 30(1): 53-61(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Jing, Liu Tiejun, Du Xiaofeng, Wu Yongsheng, Bao Yulong. 2020. Simulation on spatio-temporal stability of ET based on MOD16A2 in Mu Us sandy land[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 38(2): 243-250(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Suhua, Tian Jing, Mi Sujuan. 2016. Review of methods on estimation of daily evapotranspiration from one time-of-day remotely sensed transient evapotranspiration[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 28(4): 10-17(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.gtzyyg.com/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=2031
Liu Weipeng, Cui Huqun, Liu Weipo, Cheng Xuxue, Li Zhihong. 2021. An analysis of the evolution trend and influencing factors of the groundwater flow field in the Sanjiang Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(1): 10-17(in Chinese with English abstract).
Meng Yu, Dan Wenhong, Wang Huan. 2020. Spatiotemporal characteristics of evapotranspiration and its affecting factors in Wujiang Basin based on MOD16[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(6): 139-145(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mu Q, Zhao M, Running S W. 2011. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115(8): 1781-1800. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.02.019
Nishida K, Nemani R R, Glassy J M, Running SW. 2003. Development of an evapotranspiration index from Aqua/MODIS for monitoring surface moisture status[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 41(2): 493-501. http://secure.ntsg.umt.edu/publications/2003/NNGR03a/41tgrs02-nishida-proof.pdf
Sharma V, Kilic A, Irmak S. 2016. Impact of scale/resolution on evapotranspiration from Landsat and MODIS images[J]. Water Resources Research, 52(3): 1207-1221. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Vivek_Sharma78/publication/295090175_Impact_of_scaleresolution_on_evapotranspiration_from_Landsat_and_MODIS_images/links/579a84e308ae7b940a8aa0f7.pdf
Shi Xiaoliang, Wu Mengyue, Zhang Na, Ding Hao. 2020. Spatial and temporal variation of vegetation water use efficiency and its response to meteorological factors in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(5): 1651-1663(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shukla J, Mintz Y. 1982. Influence of Land-Surface Evapotranspiration on the Earth's climate[J]. Science, 215(4539): 1498-1501. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4539.1498
Tian Yichao, Liang Mingzhong, Hu Baoqing. 2015. Temporal-spatial dynamic change characteristics of evapotranspiration in Beibu Gulf Coastal Zone during 2000-2013[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 46(8): 146-158(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Haibo, Ma Mingguo. 2014. Estimation of transpiration and evaporation of different ecosystems in an inland river basin using remote sensing data and the Penman-Monteith equation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(19): 5617-5626(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Haifeng, Zhang Zhitao, Karnieli Arnon, Chen Junying, Han Wenting. 2018. Hyperspectral estimation of desert soil organic matter content based on gray correlation-ridge regression model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 34(14): 124-131(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/328799191_Hyperspectral_estimation_of_desert_soil_organic_matter_content_based_on_gray_correlation-ridge_regression_model
Wang Huan, Mei Zaimei. 2020. Spatiotemporal changes of evapotranspiration and their relationship with climate factors in Guizhou Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(5): 221-229(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Tong, Tang Ronglin, Li Zhaoliang, Jiang Yazhen, Liu Meng, Tang Bohui, Wu Hua. 2019. Temporal upscaling methods for daily evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed instantaneous observations[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 23(5): 813-830(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Ying, Zhang Lei, Wang Jinsong. 2016. Response of the hydrological process to land-use/cover change in Taohe River basin[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 38(1): 200-210(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-BCDT201601023.htm
Wei Hejie, Zhang Yanfang, Zhu Ni, Wang Pengtao, Yu Yuan. 2015. Spatial and temporal characteristic of ET in the Weihe River Basin Based on MOD16 Data[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 35(2): 414-422(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97197X/201502/1005689294.html
Wen Yuanyuan, Zhao Jun, Wang Yanqiang, Wang Yuchun, Wang Jianbang. 2020. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of surface evapotranspiration in Shanxi Province based on MOD16[J]. Progress in Geography, 39(2): 255-264(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.007
Xu Ligang, Xu Jiaxing, Dong Lei, Feng Wenjuan, Jiang Jiahu. 2013. Research advance in process and modeling of water transfer in soil-plant-atmosphere continuum[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 31(1): 242-248(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jiajia, Zhang Yihe, Feng Yulin, Gao Tie, Xiao Hongye, Liu yang, Yang ze, Wei Minghui, Zhang Zhehuan. 2020. Patiotemporal dynamic change analysis of land use in eastern songnen plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 29(06): 627-634, 602(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Nan. 2004. The unique role of ridge regression analysis in solving the multicollinearity problem[J]. Statistics & Decision, (3): 14-15(in Chinese).
Yang Xiuqin, Wang Lei, Wang Kai. 2015. Spatio-temporal distribution of terrestrial evapotranspiration in Huaihe River basin based on MOD16 ET data[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 37(5): 1343-1352(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201505022.htm
Yuan Lihua, Jiang Weiguo, Shen Wenming, Liu Yinghui, Wang Wenjie, Tao Liangliang, Zheng Hua, Liu Xiaofu. 2013. The spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2010[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(24): 7798-7806(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Baozhong, Xu Di, Liu Yu, Chen He. 2015. Review of multi-scale evapotranspiration estimation and spatio-temporal scale expansion[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(6): 8-16(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/tcsae/tcsae/2015/00000031/00000006/art00002
Zhang Yongqiang, Kong Dongdong, Zhang Xuanze, Tian Jing, Li Congcong. 2021. Impacts of vegetation changes on global evapotranspiration in the period 2003-2017[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(3): 584-594(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zhitao, Wang Haifeng, Karnieli Arnon, Chen Junying, Han Wenting. 2018. Inversion of soil moisture content from hyperspectra based on ridge regression[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 49(5): 240-248(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_nyjxxb201805028.aspx
蔡博峰, 于嵘. 2009. 基于遥感的植被长时序趋势特征研究进展及评价[J]. 遥感学报, 13(6): 1170-1186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB200906015.htm 陈少丹, 张利平, 田祥勇, 汤柔馨, 柳鑫. 2019. 基于P-M模型和MOD16数据的长江中下游潜在蒸散量比较分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 52(4): 283-289, 296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201904001.htm 邓兴耀, 刘洋, 刘志辉, 姚俊强. 2017. 中国西北干旱区蒸散发时空动态特征[J]. 生态学报, 37(9): 2994-3008. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201709014.htm 杜国明, 刘文琦, 于佳兴, 张爽. 2019. 三江平原水旱田分布对遥感反演局地地表温度的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(5): 259-267+320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYGU201905032.htm 范建忠, 李登科, 高茂盛. 2014. 基于MOD16的陕西省蒸散量时空分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(9): 1536-1543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.09.022 方利, 王文杰, 蒋卫国, 陈民, 王永, 贾凯, 李延森. 2017. 2000-2014年黑龙江流域(中国)植被覆盖时空变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 地理科学, 37(11): 1745-1754. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201711017.htm 冯飞, 姚云军, 张彦彬, 李香兰. 2015. 基于MOD16产品的三江平原蒸散量时空分布特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(11): 1858-1864. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201511016.htm 胡猛, 冯起, 席海洋. 2013. 遥感技术监测干旱区土壤水分研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 44(5): 1270-1275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201305041.htm 黄葵, 卢毅敏, 魏征, 陈鹤, 张宝忠, 马文津. 2019. 土地利用和气候变化对海河流域蒸散发时空变化的影响[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 21(12): 1888-1902. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2019.190269 姜秋香, 张舜凯, 张旭, 王子龙. 2020. 三江平原水资源开发利用程度变化与驱动因素[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 18(1): 74-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202001013.htm 刘国栋, 张立, 杨泽, 戴慧敏, 赵传冬. 2021. 嫩江流域水体及悬浮物重金属元素分布特征及环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 30(01): 53-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202101008.htm 刘春雨, 赵军, 刘英英, 魏伟. 2011石羊河流域蒸散发量遥感估算及时空格局分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, (3): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201103023.htm 刘静, 刘铁军, 杜晓峰, 吴永胜, 包玉龙. 2020. 基于MOD16A2的毛乌素沙地实际蒸散量时空稳定性模拟[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 38(2): 243-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDQ202002035.htm 刘素华, 田静, 米素娟. 2016. 遥感估算蒸散发量的日尺度扩展方法综述[J]. 国土资源遥感, 28(4): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201604002.htm 刘伟朋, 崔虎群, 刘伟坡, 程旭学, 李志红. 2021. 三江平原地下水流场演化趋势及影响因素[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(1): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202101002.htm 蒙雨, 但文红, 王焕. 2020. 基于MOD16的乌江流域地表蒸散发时空特征及影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究, 27(6): 139-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY202006021.htm 史晓亮, 吴梦月, 张娜, 丁皓. 2020. 三江平原植被水分利用效率时空变化及其对气象因子变化的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(5): 1651-1663. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ202005028.htm 田义超, 梁铭忠, 胡宝清. 2015. 2000-2013年北部湾海岸带蒸散量时空动态特征[J]. 农业机械学报, 46(8): 146-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJX201508021.htm 王海波, 马明国. 2014. 基于遥感和Penman-Monteith模型的内陆河流域不同生态系统蒸散发估算[J]. 生态学报, 34(19): 5617-5626. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201419030.htm 王海峰, 张智韬, Arnon Karnieli, 陈俊英, 韩文霆. 2018. 基于灰度关联——岭回归的荒漠土壤有机质含量高光谱估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 34(14): 124-131. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.016 王焕, 梅再美. 2020. 贵州省地表蒸散发时空变化及其与气候因子的关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 27(5): 221-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY202005033.htm 王桐, 唐荣林, 李召良, 姜亚珍, 刘萌, 唐伯惠, 吴骅. 2019. 遥感反演蒸散发的日尺度扩展方法研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 23(5): 813-830. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201905002.htm 王莺, 张雷, 王劲松. 2016. 洮河流域土地利用/覆被变化的水文过程响应[J]. 冰川冻土, 38(1): 200-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201601023.htm 位贺杰, 张艳芳, 朱妮, 王鹏涛, 喻元. 2015. 基于MOD16数据的渭河流域地表实际蒸散发时空特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 35(2): 414-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS201502021.htm 温媛媛, 赵军, 王炎强, 王玉纯, 王建邦. 2020. 基于MOD16的山西省地表蒸散发时空变化特征分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 39(2): 255-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ202002007.htm 徐力刚, 许加星, 董磊, 冯文娟, 姜加虎. 2013. 土壤-植物-大气界面中水分迁移过程及模拟研究进展[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 31(1): 242-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7601.2013.01.044 杨佳佳, 张一鹤, 冯雨林, 高铁, 肖红叶, 刘洋, 杨泽, 魏明辉, 张哲寰. 2020. 松嫩平原东部土地利用时空动态变化分析[J]. 地质与资源, 29(06): 627-634+602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202006020.htm 杨楠. 2004. 岭回归分析在解决多重共线性问题中的独特作用[J]. 统计与决策, (3): 14-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6487.2004.03.007 杨秀芹, 王磊, 王凯. 2015. 基于MOD16产品的淮河流域实际蒸散发时空分布[J]. 冰川冻土, 37(5): 1343-1352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201505022.htm 袁丽华, 蒋卫国, 申文明, 刘颖慧, 王文杰, 陶亮亮, 郑华, 刘孝富. 2013. 2000-2010年黄河流域植被覆盖的时空变化[J]. 生态学报, 33(24): 7798-7806. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201324021.htm 张宝忠, 许迪, 刘钰, 陈鹤. 2015. 多尺度蒸散发估测与时空尺度拓展方法研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报, 31(6): 8-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYGU201506002.htm 张永强, 孔冬冬, 张选泽, 田静, 李聪聪. 2021. 2003-2017年植被变化对全球陆面蒸散发的影响[J]. 地理学报, 76(3): 584-594. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB202103008.htm 张智韬, 王海峰, KARNIELI Arnon, 陈俊英, 韩文霆. 2018. 基于岭回归的土壤含水率高光谱反演研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 49(5): 240-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJX201805028.htm




 下载:
下载: