Characteristics and distribution of fault−controlled carbonate reservoirs in Yijianfang Formation of Yueman area, northern Tarim Basin
-
摘要:研究目的
跃满区块位于塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘油田塔里木河南岸地区,其奥陶系一间房组碳酸盐岩储层发育。勘探开发成果显示,该区高产井主要沿区内4条走滑断裂分布,并且沿断裂带表现出油气产量差异,具有较强的非均质性,储层受断裂控制明显,因此明确该类断控型储层特征及分布规律对油气勘探和开发具有重要意义。
研究方法论文综合利用钻测井数据与岩心分析,结合三维地震资料,分析储层岩石学特征、储层类型及其发育规律,探讨优质储层与区内走滑断裂的耦合关系,以明确该类断控型储层的分布规律。
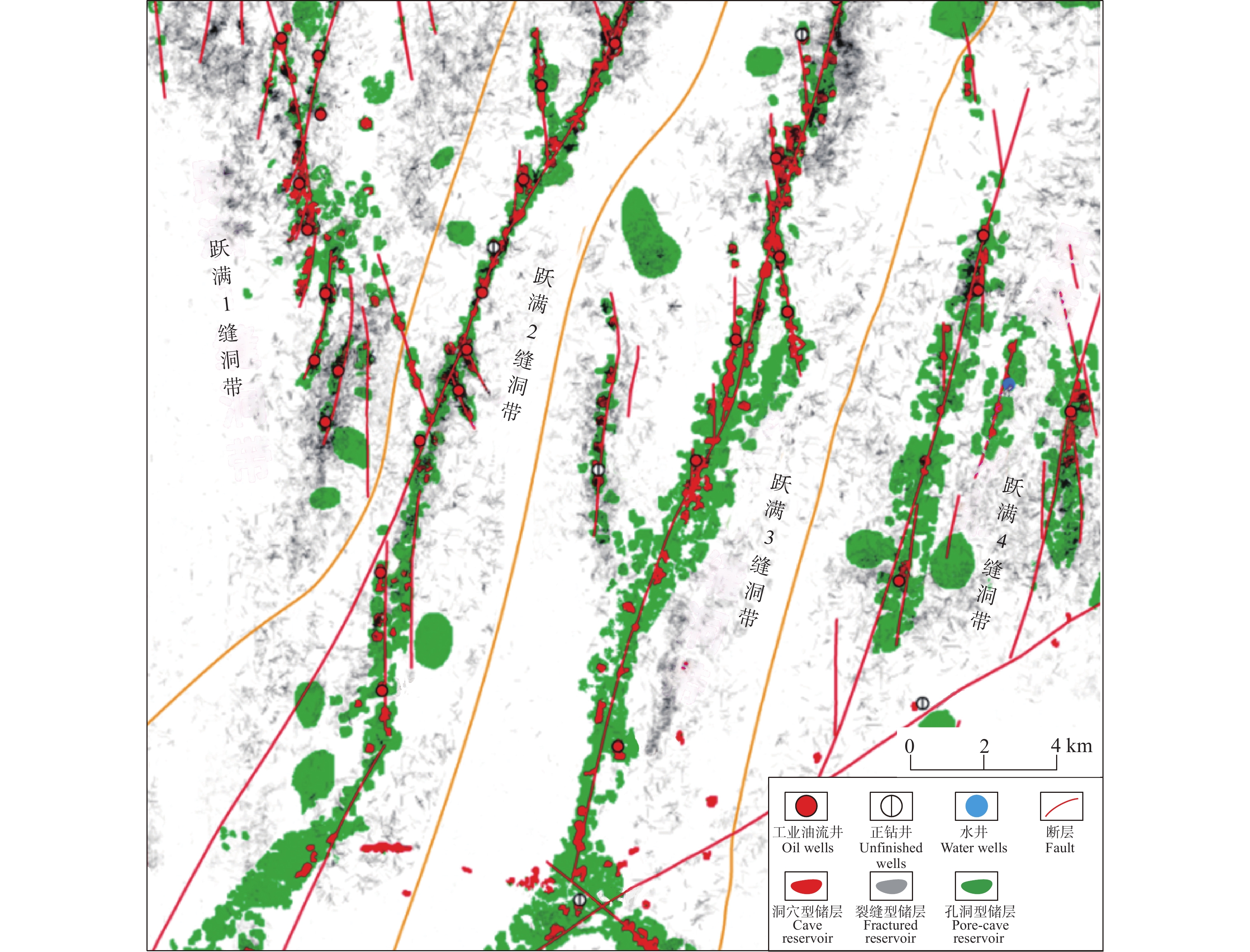
研究结果区内一间房组储集岩类型以生屑灰岩、砂屑灰岩、颗粒灰岩、泥晶灰岩为主,孔隙度与渗透率均较低。根据储集空间类型,储层可分为洞穴型储层、裂缝−孔洞型储层、裂缝型储层与孔洞型储层4类,洞穴型储层垂向上沿主干断层呈串珠状发育,裂缝−孔洞型、裂缝型与孔洞型储层沿断裂带状发育。
结论走滑断裂的分段性控制着优质储层的分布,断裂马尾段、斜列段和叠覆段储层发育最佳,分支断层斜交段发育一般,线性段则发育较差,在此基础上,高能相带叠加区相对非叠加区储层发育更佳。
创新点:(1)基于钻井及地震资料开展储层特征分析和断层刻画,揭示了跃满地区一间房组储层的发育受区内走滑断裂的构造特征控制;(2)阐明了地层应力集中区更复杂的走滑断裂结构,是多期岩溶作用及礁滩体发育的有利条件,更易形成优质储层。
Abstract:This paper is the result of oil and gas geological exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe carbonate reservoirs of the Ordovician Yijianfang Formation are developed in Yueman area, south of Tarim River in Halahatang oilfield, Tarim Basin. The exploration and development results show that the high−producing wells are mainly distributed along four strike−slip faults in the area, and the oil and gas production along the fault zone is different, with strong heterogeneity, and the reservoirs are obviously controlled by faults. Therefore, it is of great significance for oil and gas exploration and development to clarify the characteristics and distribution regularities of fault−controlled reservoirs.
MethodsIn this paper, based on drilling logging data, cores data and 3D seismic data, the petrological characteristics, reservoir types and development regularities are analyzed, and the coupling relationship between high−quality reservoirs and strike−slip faults is discussed to clear the distribution regularities of such fault−controlled reservoirs.
ResultsThe reservoir rock types of Yijianfang Formation in the area are mainly bioclastic limestone, arenaceous limestone, granular limestone and micritic limestone, with low porosity and permeability. According to the types of reservoir space, the reservoirs can be divided into four types: cavernous reservoirs, vuggy reservoirs, fractured reservoirs and fractured−vuggy reservoirs. The cavernous reservoirs develop vertically along the main fault, the vuggy reservoirs, fractured reservoirs and fractured−vuggy reservoirs are banded distributed along the fault.
ConclusionThe structure of strike−slip faults controls the distribution of high−quality reservoirs, and the reservoir stratums in Horsetail, en echelon and overlap sections of faults are the best developed, the oblique intersection sections of branching faults are fair developed, while the linear sections are poorly developed. On this basis, the reservoirs in the superposition area of high−energy facies belts are better developed than those in the non−superposition area.
Highlights:(1) Reservoir characteristics analysis and fault characterization based on drilling and seismic data reveal that the development of the Yijianfang Formation reservoir in Yueman area is controlled by the structure characteristics of strike−slip faults; (2) It is clarified that the more complex strike−slip fault structure in the stress concentration area is a favorable condition for multi-stage karstification and the development of reef flats, and it is easier to form high−quality reservoirs.
-
1. 引 言
塔里木盆地古生界碳酸盐岩储层分布广,厚度大,生储盖空间配置优越(翟光明等, 2004),围绕古隆起发育的塔北油田与塔中油田更是中国陆上碳酸盐岩油气勘探开发研究的重点区块(Yang et al., 2007; 何治亮等, 2016)。塔北油田的开发经历了自北部潜山区向南到顺层改造区的探索,形成了一套以浅层风化壳岩溶及层间岩溶为主控的缝洞体油藏的认识(沈安江等, 2019)。随着勘探开发逐步深入到台缘叠加区,已有油藏体系认知无法对低隆区油藏的开发进行有效指导,开发陷入瓶颈。随着顺北1号与顺北5号深层—超深层奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层取得重大突破(Jiao et al., 2018),受断裂控制的断溶体油气藏逐渐成为油田勘探开发的重点,对油气藏的认识也逐步转变为深大断裂控储、控藏、控富研究(王新新等, 2019; 丁志文等, 2020)。
塔里木盆地地质历史上构造运动强烈,经历多期构造运动,受区域应力场作用,稳定克拉通内部发育一系列陆内短滑距走滑断裂(Han et al., 2017; 邓尚等, 2021),最新三维地震勘探揭示,多期构造作用形成的走滑断裂继承性发育,形成多种构造样式,导致油气分布具有明显的区段性(邬光辉等, 2011)。同时,受断裂控制的断溶体油气藏特征表现出仅沿断裂带含油、且不均匀富集的特点(Wu et al., 2018; Jiao et al., 2018),表明走滑断裂是控制储层的重要因素(Wang et al., 2021),故进一步认识断裂对岩溶性储层的控制作用对碳酸盐岩油气的勘探具有重要意义。
2. 区域地质概况
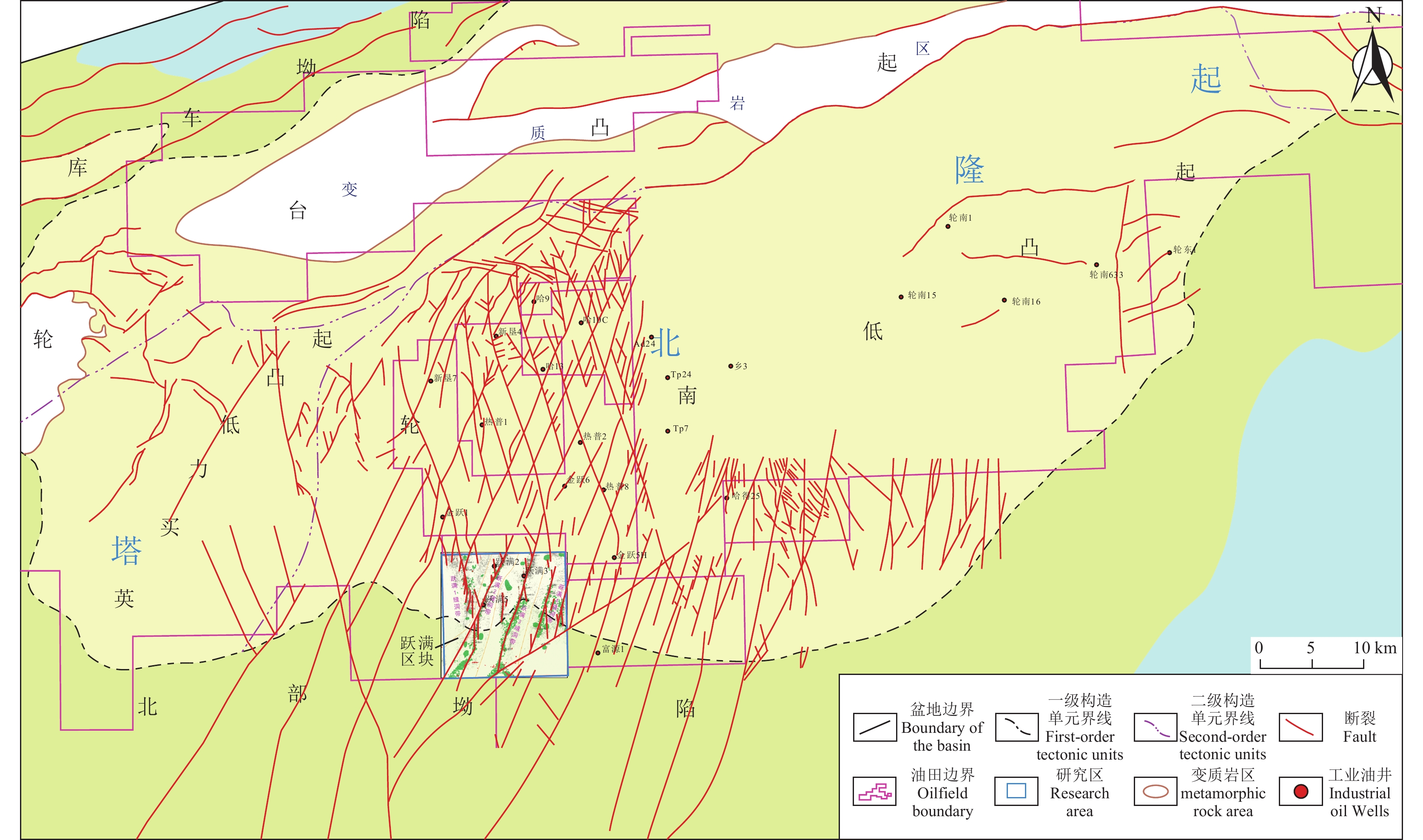
跃满区块构造上位于塔里木盆地塔北隆起轮南低凸起的西部斜坡带(图1),轮南低凸起为一大型潜山背斜,面积15100 km2,主体在轮南油田至塔河油田一带,长轴在东部为北东向,西部为北东东向。跃满区块为向西倾没的哈拉哈塘大型鼻状构造一部分,北接轮台凸起,南衔北部坳陷,西邻英买力低凸起。研究区区域构造演化主要经历了中、晚加里东运动差异抬升期,晚海西—印支运动挤压抬升期,燕山—早喜山运动局部调整期,晚喜山运动至今构造反转期(马德波等, 2020)。
跃满区块地层发育完整,自上而下钻遇新生界第四系,新近系和古近系,中生界白垩系、侏罗系、三叠系,古生界二叠系、石炭系、志留系以及奥陶系。奥陶系可细分为上奥陶统桑塔木组(O3s)、良里塔格组(O3l)、吐木休克组(O3t);中奥陶统一间房组(O2y);中—下奥陶统鹰山组(O1-2y);下奥陶统蓬莱坝组(O1p)(朱光有等, 2011)。勘探开发目的层主要为奥陶系一间房组海相碳酸盐岩地层,上覆吐木休克组为一致密泥灰岩层,可以形成良好的油气封闭条件,有利于下伏一间房组油气成藏。
3. 储层特征
3.1 储层岩石学特征
岩心、薄片和测井资料表明,跃满地区中奥陶统一间房组储集岩以灰岩为主,岩性主要为生屑灰岩、砂屑灰岩、颗粒灰岩、泥晶灰岩(图2),为开阔台地相的台内砂屑、藻屑滩沉积岩类。岩心孔渗分析结果显示孔隙度平均值1.00%、渗透率平均值1.160×10−3 μm2,均为较低水平,且孔隙度与渗透率相关性不明显。
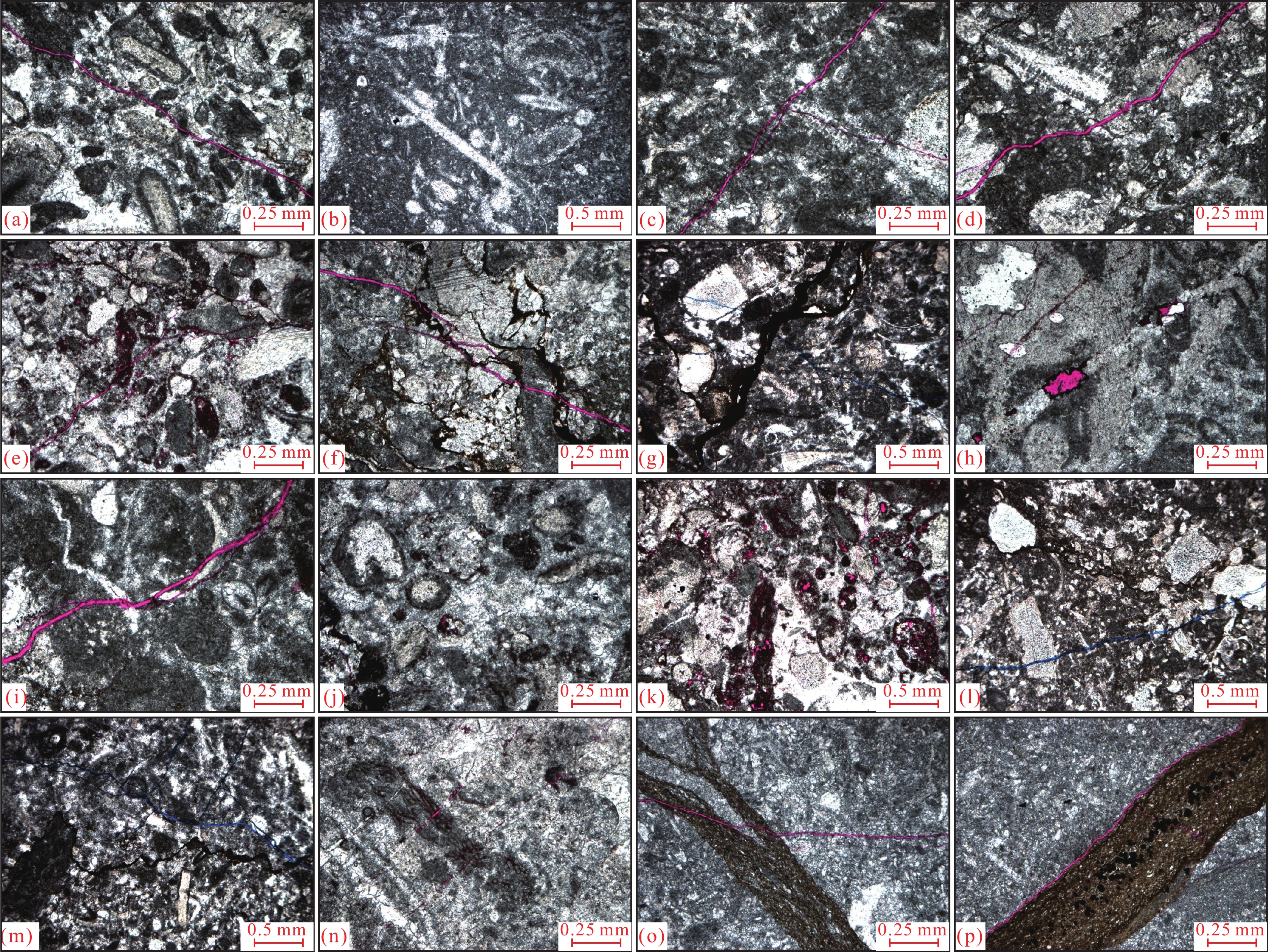
![]() 图 2 跃满地区奥陶系一间房组储层岩性(染色铸体薄片)a—跃满2井,井深:7211.8 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;b—跃满2井,井深:7200.6 m,泥晶生屑灰岩;c—跃满2井,井深:7209.7 m,泥亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;d—跃满2井,井深:7206.7 m,泥粉晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;e—跃满2井,井深:7215.7 m,亮晶藻团块生屑灰岩,构造缝;f—跃满2井,井深:7209.9 m,泥亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝与压溶缝;g—跃满2井,井深:7201.7 m,泥晶生屑灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;h—跃满2井,井深:7210.7 m,方解石和沥青质半充填的构造缝;i—跃满2井,井深:7207.3 m,亮晶藻砂屑灰岩,构造缝,方解石全充填的溶蚀缝;j—跃满2井,井深:7216.7 m,亮晶生屑藻砂屑灰岩,粒内溶孔;k—跃满2井,井深:7217.6 m,泥亮晶生屑藻砂屑灰岩,粒内溶孔;l—跃满2井,井深:7212.6 m,亮晶颗粒灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;m—跃满2井,井深:7213.7 m,亮晶颗粒灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;n—跃满2井,井深:7214.5 m,粉晶颗粒灰岩,方解石半充填构造缝;o—跃满2井,井深:7196.5 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,构造缝;p—跃满2井,井深:7197.5 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,收缩缝Figure 2. Reservoir lithology of Ordovician Yijianfang Formation in Yueman area (dyed cast thin section)a−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7211.8 m, sparry bioclastic limestone, structural fracture; b−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7200.6 m, micrite bioclast limestone; c−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7209.7 m, micrite−sparry bioclast limestone, structural fracture; d−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7206.7 m, micrite−powder bioclast limestone, structural fracture; e−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7215.7 m, sparry clumpy alga bioclastic limestone, structural fracture; f−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7209.9 m, micrite−sparry bioclast limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; g−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7201.7 m, micrite bioclast limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; h−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7210.7 m, structural fracture, half−filled with calcite and asphalt; i−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7207.3 m, sparry algal arenaceous limestone, structural fracture, dissolution fracture, full−filled with calcite; j−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7216.7 m, Sparry bioclastic arenaceous limestone, intragranular dissolved pore; k−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7217.6 m, argillaceous sparry bioclastic arenaceous limestone, intragranular dissolved pore; l−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7212.6 m, sparry granular limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; m−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7213.7 m, sparry granular limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; n−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7214.5 m, silt−grained limestone, half−filled with calcite, structural fracture ; o−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7196.5 m, bioclastic micritic limestone, structural fracture; p−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7197.5 m, bioclastic micritic limestone, shrinkage fracture
图 2 跃满地区奥陶系一间房组储层岩性(染色铸体薄片)a—跃满2井,井深:7211.8 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;b—跃满2井,井深:7200.6 m,泥晶生屑灰岩;c—跃满2井,井深:7209.7 m,泥亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;d—跃满2井,井深:7206.7 m,泥粉晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;e—跃满2井,井深:7215.7 m,亮晶藻团块生屑灰岩,构造缝;f—跃满2井,井深:7209.9 m,泥亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝与压溶缝;g—跃满2井,井深:7201.7 m,泥晶生屑灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;h—跃满2井,井深:7210.7 m,方解石和沥青质半充填的构造缝;i—跃满2井,井深:7207.3 m,亮晶藻砂屑灰岩,构造缝,方解石全充填的溶蚀缝;j—跃满2井,井深:7216.7 m,亮晶生屑藻砂屑灰岩,粒内溶孔;k—跃满2井,井深:7217.6 m,泥亮晶生屑藻砂屑灰岩,粒内溶孔;l—跃满2井,井深:7212.6 m,亮晶颗粒灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;m—跃满2井,井深:7213.7 m,亮晶颗粒灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;n—跃满2井,井深:7214.5 m,粉晶颗粒灰岩,方解石半充填构造缝;o—跃满2井,井深:7196.5 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,构造缝;p—跃满2井,井深:7197.5 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,收缩缝Figure 2. Reservoir lithology of Ordovician Yijianfang Formation in Yueman area (dyed cast thin section)a−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7211.8 m, sparry bioclastic limestone, structural fracture; b−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7200.6 m, micrite bioclast limestone; c−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7209.7 m, micrite−sparry bioclast limestone, structural fracture; d−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7206.7 m, micrite−powder bioclast limestone, structural fracture; e−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7215.7 m, sparry clumpy alga bioclastic limestone, structural fracture; f−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7209.9 m, micrite−sparry bioclast limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; g−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7201.7 m, micrite bioclast limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; h−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7210.7 m, structural fracture, half−filled with calcite and asphalt; i−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7207.3 m, sparry algal arenaceous limestone, structural fracture, dissolution fracture, full−filled with calcite; j−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7216.7 m, Sparry bioclastic arenaceous limestone, intragranular dissolved pore; k−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7217.6 m, argillaceous sparry bioclastic arenaceous limestone, intragranular dissolved pore; l−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7212.6 m, sparry granular limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; m−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7213.7 m, sparry granular limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; n−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7214.5 m, silt−grained limestone, half−filled with calcite, structural fracture ; o−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7196.5 m, bioclastic micritic limestone, structural fracture; p−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7197.5 m, bioclastic micritic limestone, shrinkage fracture3.2 储层类型
薄片、岩心及钻测井资料揭示(图2,图3;表1),研究区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储集空间宏观上以大型溶蚀洞穴、溶蚀孔洞及构造裂缝为主,微观上以孔隙(粒间孔、粒内孔、晶间孔、晶间溶孔)与微裂缝(构造缝、压溶缝、溶蚀缝)为主。根据洞、孔、缝组合特征,储层类型可分为洞穴型储层、裂缝−孔洞型储层、裂缝型储层与孔洞型储层4类,其中洞穴型储层储集能力最强,裂缝孔洞型储层兼具良好的储集与运移能力,分别为区内重点开发的Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类储层发育段,而裂缝型与孔洞型储层储集能力一般但分布广,多为Ⅲ类储层发育段。
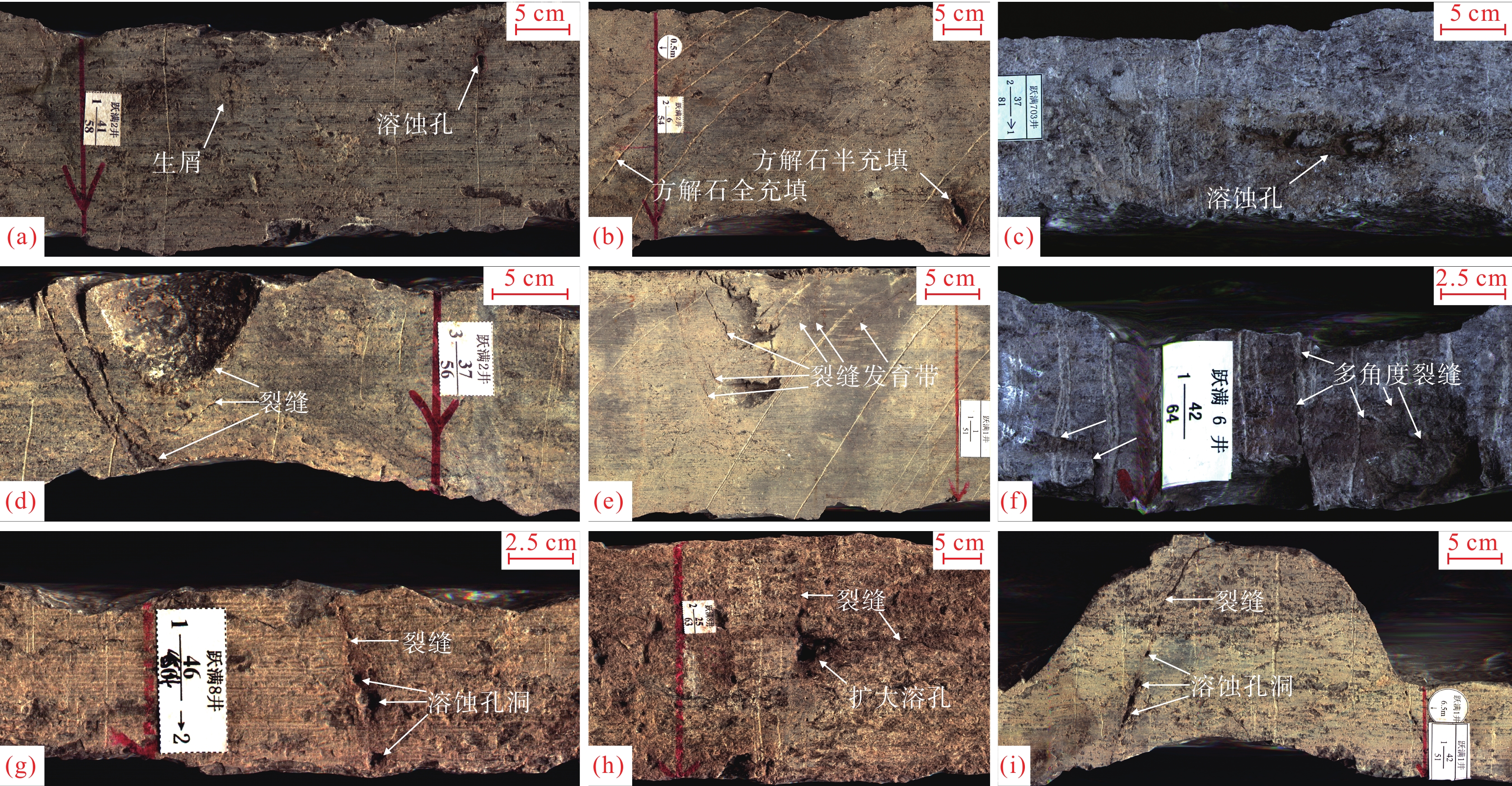
![]() 图 3 跃满地区奥陶系一间房组储层类型(岩心)a—跃满2井,1−58−35,生屑砂屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞;b—跃满2井,2−54−6,生屑砂屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞,方解石全充填、半充填;c—跃满703井,2−81−37,生屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞;d—跃满2井,3−56−37,砂屑生屑灰岩,中高角度缝;e—跃满1井,1−51−1,砂屑灰岩,中高角度缝,沿缝发育溶蚀孔;f—跃满6井,1−64−42,砂屑灰岩,直立缝与水平缝近垂直共轭;g—跃满8井,1−64−46,砂屑灰岩,高角度裂缝,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育,见油斑;h—跃满8井,2−63−25,砂屑灰岩,直立缝与水平缝交汇处溶孔扩大;i—跃满1井,1−51−42,砂屑灰岩,中高角度裂缝,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育Figure 3. Reservoir type of the Yijianfang Formation of Ordovician in Yueman area (cores)a−Well Yueman 2, 1−58−35, bioclastic calcarenite, dissolved pore; b−Well Yueman 2, 2−54−6, bioclastic calcarenite, dissolved pore, full filled or half filled with calcite; c−Well Yueman 703, 2−81−37, bioclastic limestone, dissolved pore; d−Well Yueman 2, 3−56−37, sandy bioclastic limestone, middle−high angle fracture; e−Well Yueman 1, 1−51−1, calcarenite, middle−high angle fracture, dissolved pore; f−Well Yueman 6, 1−64−42, calcarenite, horizontal and vertical fractures; g−Well Yueman 8, 1−64−46, calcarenite, high Angle fracture, dissolved pore, oil patch; h−Well Yueman 8, 2−63−25, calcarenite, horizontal and vertical fractures, dissolved pore increase at fracture intersections; i−Well Yueman 1, 1−51−42, calcarenite, middle−high angle fracture, dissolved pore表 1 跃满区块漏失统计Table 1. Lost circulation statistics in Yueman area
图 3 跃满地区奥陶系一间房组储层类型(岩心)a—跃满2井,1−58−35,生屑砂屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞;b—跃满2井,2−54−6,生屑砂屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞,方解石全充填、半充填;c—跃满703井,2−81−37,生屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞;d—跃满2井,3−56−37,砂屑生屑灰岩,中高角度缝;e—跃满1井,1−51−1,砂屑灰岩,中高角度缝,沿缝发育溶蚀孔;f—跃满6井,1−64−42,砂屑灰岩,直立缝与水平缝近垂直共轭;g—跃满8井,1−64−46,砂屑灰岩,高角度裂缝,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育,见油斑;h—跃满8井,2−63−25,砂屑灰岩,直立缝与水平缝交汇处溶孔扩大;i—跃满1井,1−51−42,砂屑灰岩,中高角度裂缝,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育Figure 3. Reservoir type of the Yijianfang Formation of Ordovician in Yueman area (cores)a−Well Yueman 2, 1−58−35, bioclastic calcarenite, dissolved pore; b−Well Yueman 2, 2−54−6, bioclastic calcarenite, dissolved pore, full filled or half filled with calcite; c−Well Yueman 703, 2−81−37, bioclastic limestone, dissolved pore; d−Well Yueman 2, 3−56−37, sandy bioclastic limestone, middle−high angle fracture; e−Well Yueman 1, 1−51−1, calcarenite, middle−high angle fracture, dissolved pore; f−Well Yueman 6, 1−64−42, calcarenite, horizontal and vertical fractures; g−Well Yueman 8, 1−64−46, calcarenite, high Angle fracture, dissolved pore, oil patch; h−Well Yueman 8, 2−63−25, calcarenite, horizontal and vertical fractures, dissolved pore increase at fracture intersections; i−Well Yueman 1, 1−51−42, calcarenite, middle−high angle fracture, dissolved pore表 1 跃满区块漏失统计Table 1. Lost circulation statistics in Yueman area序号 井号 放空长/m 漏失量/m3 序号 井号 放空长/m 漏失量/m3 1 跃满1 1.92 355 18 跃满5−4X 6.39 659 2 跃满10 0 506.12 19 跃满5−5 1.85 148.4 3 跃满1−1 0 535.7 20 跃满601 0 373.7 4 跃满1−3 0.12 118.24 21 跃满6C 0 215.5 5 跃满1−5 0.76 0 22 跃满701 0 260.4 6 跃满2−2C 0 1200 23 跃满701−H1 1.11 1494.4 7 跃满2−4X 1.41 2049 24 跃满702 0 133.2 8 跃满3 0 253.4 25 跃满703 2.72 252.2 9 跃满3−1 1.49 307.1 26 跃满7−1X 0 1558.11 10 跃满3−2C 0 1063.2 27 跃满7−2X 0.34 1527.19 11 跃满3−3 0.93 348.5 28 跃满7JS 19.1 3231.33 12 跃满3−5 0.74 114.6 29 跃满8 4.02 773.5 13 跃满3−5C 8 1064.6 30 跃满801 2.79 1389.18 14 跃满3−6X 0.96 241.6 31 跃满801−H6 2.59 549.4 15 跃满3−7X 0 9.9 32 跃满802 1.45 329.7 16 跃满4 0 43.8 33 跃满8−1 6.34 286.2 17 跃满5−3 0 269.4 34 跃满9 9.25 811 孔洞型、裂缝型、裂缝−孔洞型储层在区内大量发育。其中孔洞型储层以一间房组开阔台地相台内滩和台地边缘相台缘礁滩体等高能相带为发育基础,层状发育且具有较好的孔隙度与渗透率,储层段岩心薄片可见微观粒间溶孔、铸膜孔、粒内溶孔等(图2e、k),可见部分孔洞被方解石充填,岩心可见不规则溶蚀孔洞发育,部分被方解石半充填、全充填(图3a~c)。裂缝型储层区内普遍发育,连通溶蚀洞穴、孔洞或成组发育的裂缝型储层更为有效,薄片可见沥青与泥质全充填的压溶缝,方解石全充填、半充填的溶蚀缝,未充填的构造缝等(图2f、h、i);岩心显示裂缝以中高角度—高角度构造缝为主,形态总体较规则,缝面较平坦,具成组发育特征(图3d~f)。裂缝−孔洞型储层主要分布于一间房组开阔台地相台内滩颗粒灰岩中,兼具良好的运移与储集能力,岩心显示,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育,且多裂缝交汇处溶蚀孔洞发育更佳(图3g~i)。
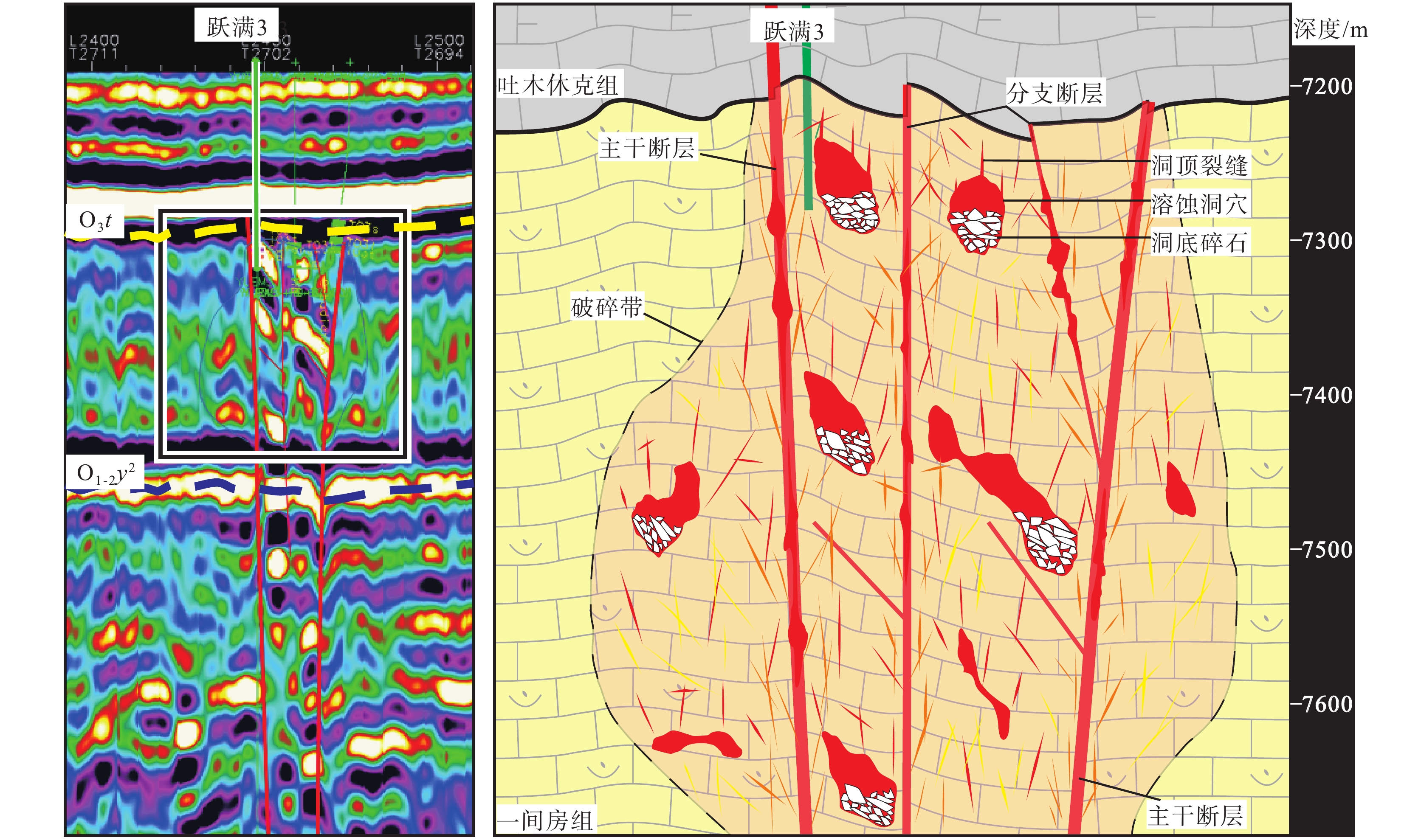
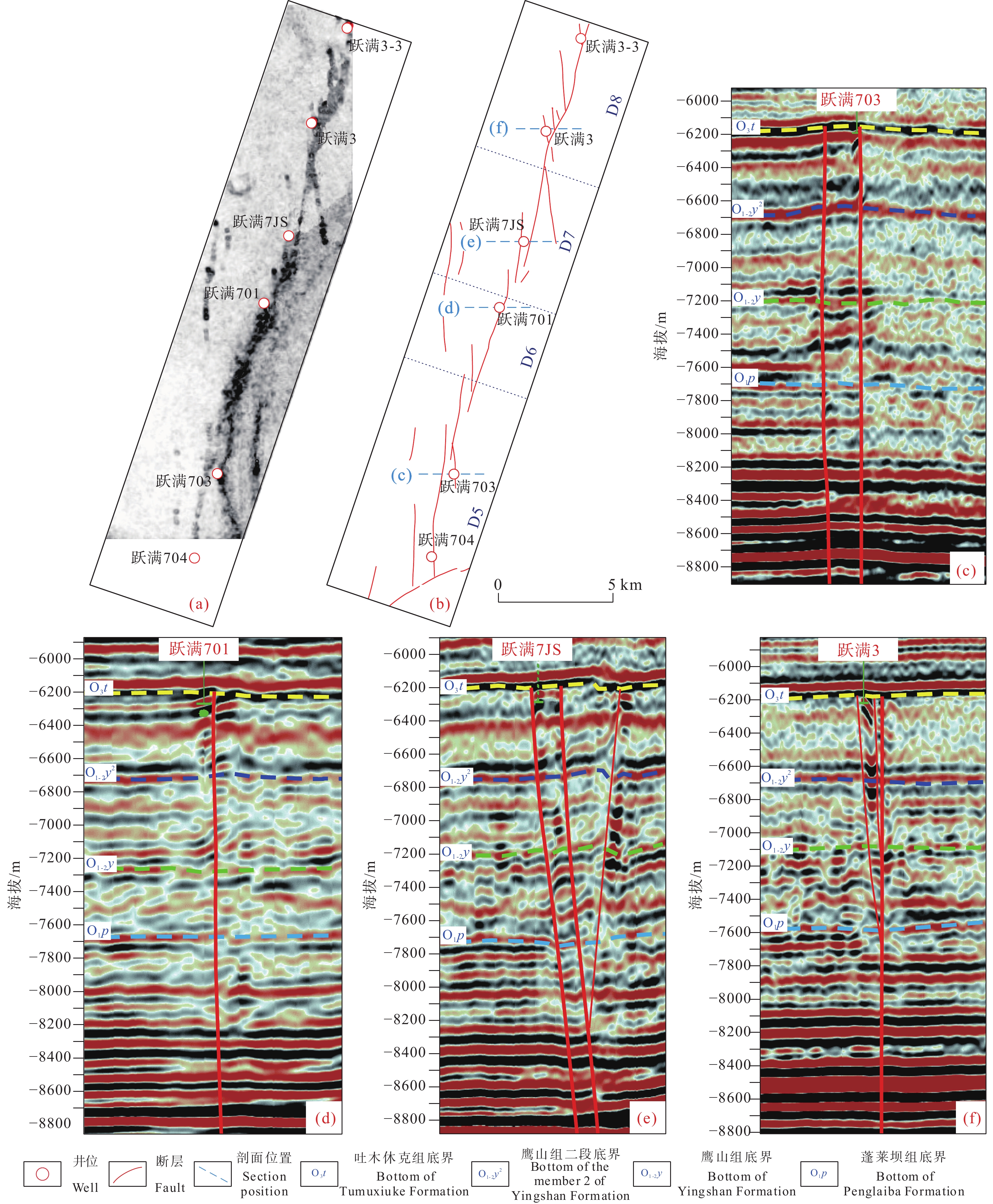
洞穴型储层以大型溶蚀洞穴为主要储集空间,洞穴围岩裂缝及洞底碎石孔隙为次要储集空间,新三维地震资料显示,洞穴在地震剖面上表现出强串珠状反射特征,该类储层主要发育于一间房组上部,沿主干断层或断层两侧垂向发育(图4)。
钻井资料上洞穴型储层表现为放空和漏失,跃满区块已有钻井的放空漏失现象统计显示,区内共完钻51口井,放空21井,占比41.2%,平均放空3.537 m,最长放空跃满7JS井,放空长达19.1 m,最短放空跃满1−3井,仅放空0.12 m;同时总计33井有漏失现象,占比64.7%,平均漏失681.0 m3,最小漏失跃满3−7X井共9.9 m3,最大漏失跃满7JS井共3231 m3(表1),放空漏失现象普遍。
3.3 储层发育规律
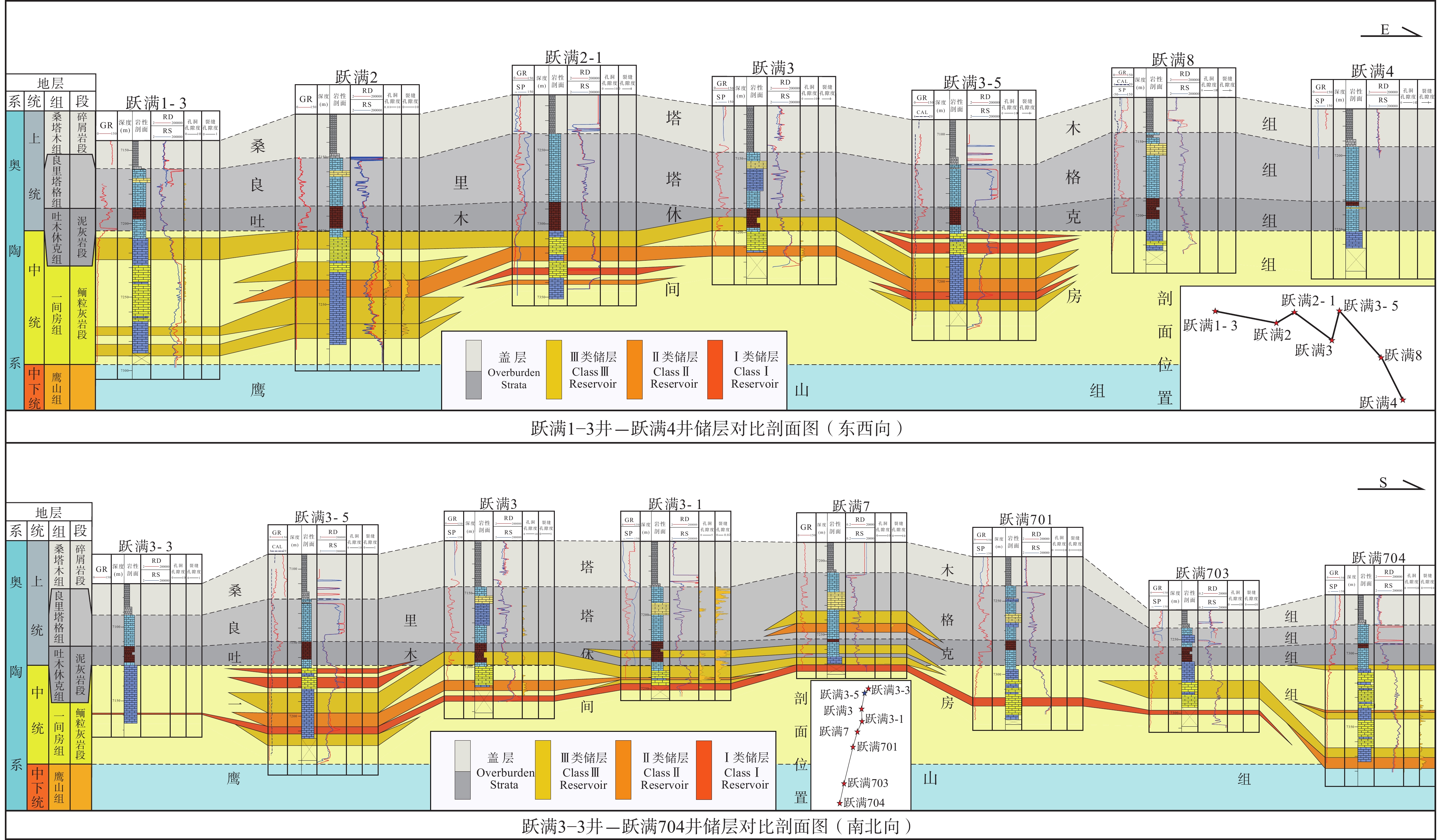
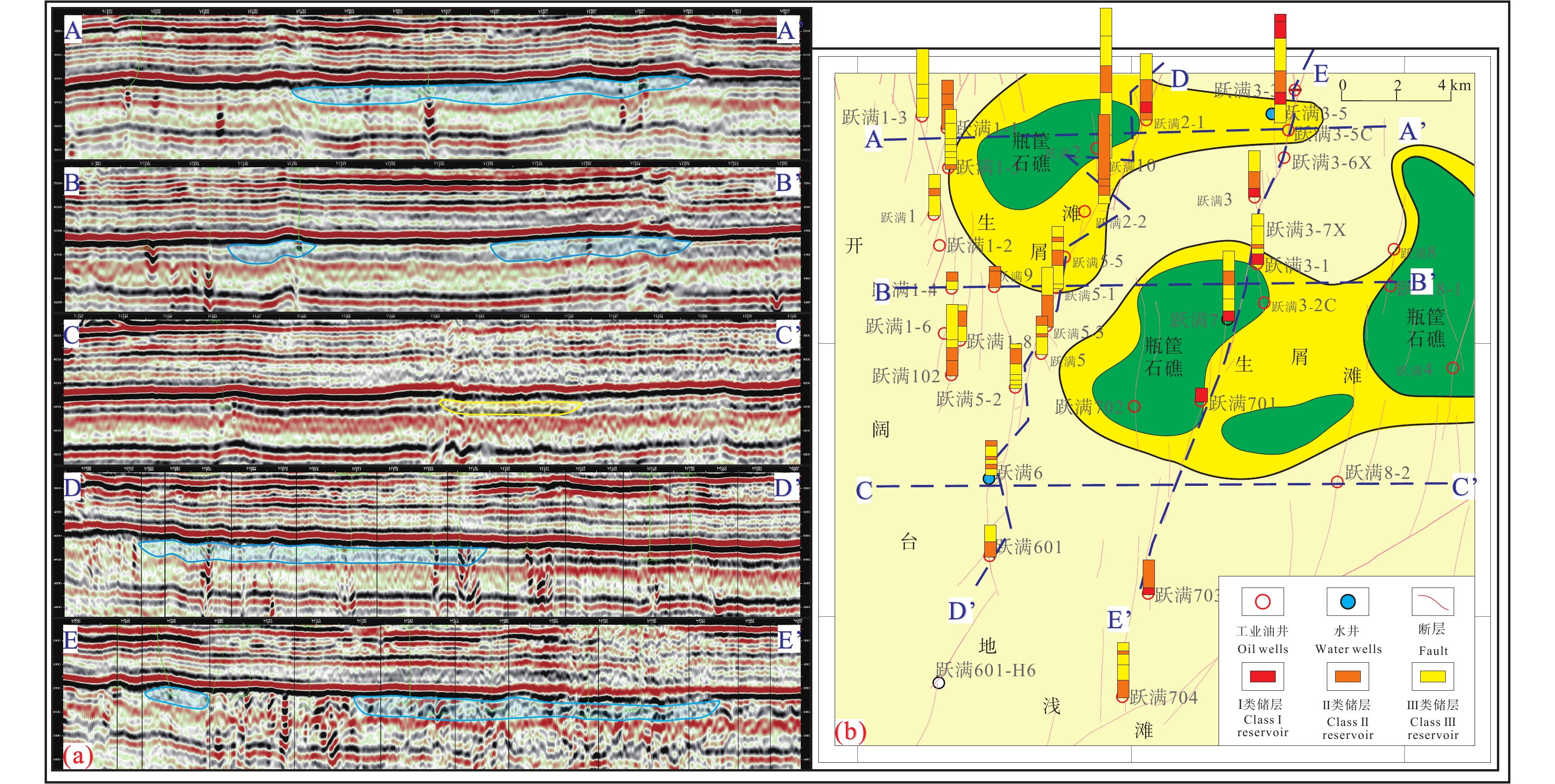
综合钻、测井及三维地震资料,对比东西向与南北向相邻井所揭示的岩性、储层及沉积特征,对区内储层分布特征进行厘定,结果表明,在垂向上,储层主要分布于一间房组顶面以下0~120 m范围之内,少量钻井(跃满3、跃满7)揭示上覆吐木休克组与良里塔格组有少量Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类储层发育;在横向剖面上,储层表现出强非均质性以及低连续性:各井储层类型、储层厚度差异较大,东西向连井对比图显示各井储层连续性差,而在近南北断层走向上,连井对比图显示储层具有一定连续性(图5);在一间房组,洞穴型储层沿断裂孤立发育,孔洞型储层与裂缝型储层沿断裂带状发育,同时,不同断裂构造段内储层发育具有显著差异性,特别是洞穴型储层,往往集中于局部断裂大量发育,显示出强烈的断控特征(图6)。
4. 走滑断裂特征
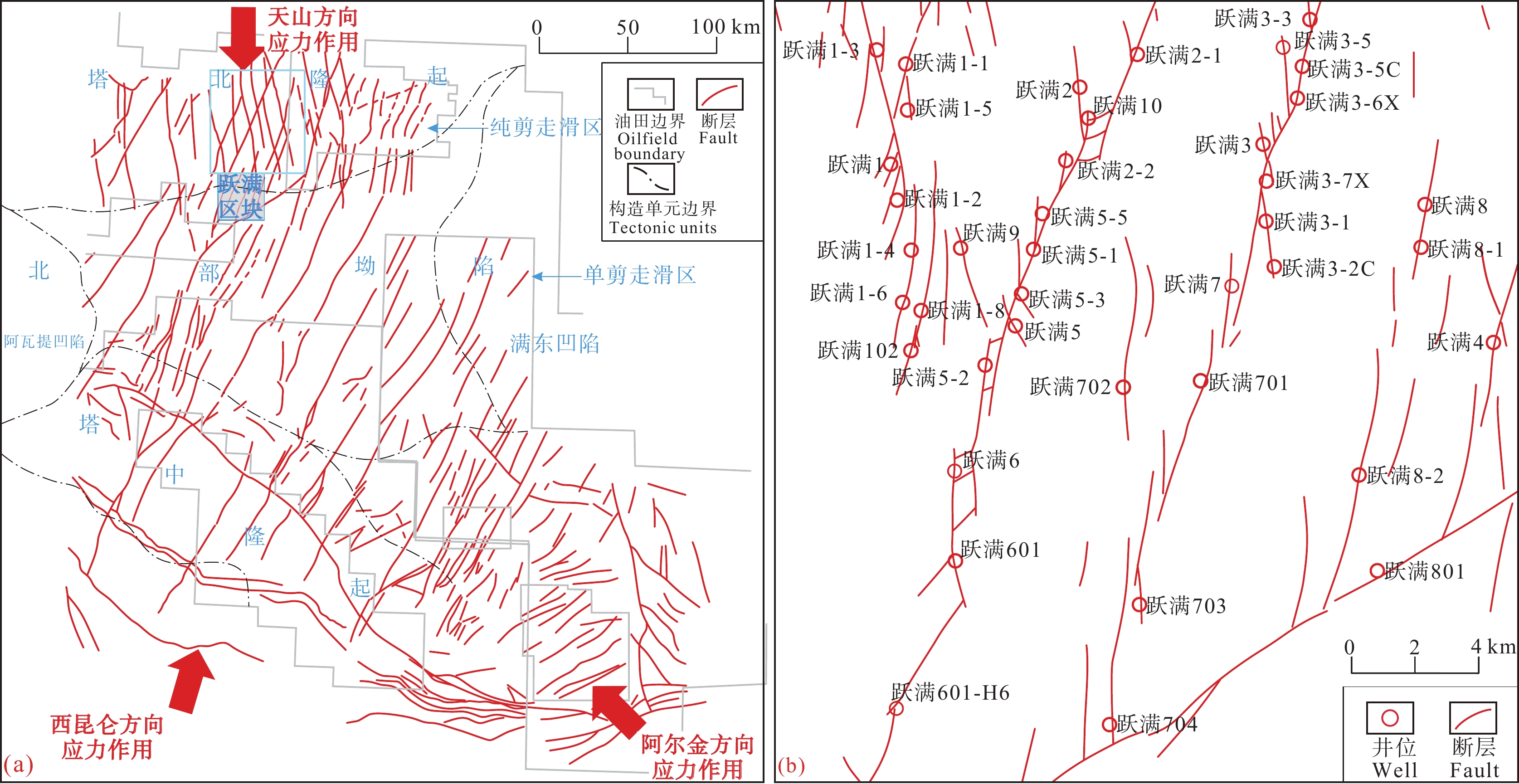
塔里木盆地经历多期不同方向的斜向构造挤压作用,盆内发育多组走滑断裂系统,按形成的力学机制可分为纯剪机制和单剪机制(图7)。研究区受古昆仑洋及阿尔金板块俯冲消解作用,形成多组纯剪机制的“X”型共轭走滑断裂带(Tang et al., 2012; 孙东等, 2015),在此基础上,共轭断层相继滑动、切割调节,形成的不连续断层经过尾端扩张与连接生长,最终形成位移量极少的“小位移”长断裂带。通过断裂带碳酸盐胶结物U−Pb测年结合地震解析,确定塔里木盆地奥陶系碳酸盐岩走滑断裂活动始于距今约460 Ma的中奥陶世末期(Wu et al., 2021)。跃满区块位于塔北哈拉哈塘地区南部,为共轭走滑断裂发育区的边缘地带,区内主要发育一组北北西向与三组北北东向走滑断裂(图7)。
![]() 图 7 塔北至塔中地区(a,据Wu et al., 2021修改)跃满区块(b)走滑断裂体系纲要图Figure 7. Schematic diagram of strike−slip faults in Tabei−Tazhong area (a, modified from Wu et al., 2021) and Yueman area (b)
图 7 塔北至塔中地区(a,据Wu et al., 2021修改)跃满区块(b)走滑断裂体系纲要图Figure 7. Schematic diagram of strike−slip faults in Tabei−Tazhong area (a, modified from Wu et al., 2021) and Yueman area (b)4.1 走滑断裂分段特征
北北西向跃满1−3—跃满102断裂带位于跃满区块西北部,为北部金跃地区向南延伸的一号断裂的末端,具有强烈的应力发散特点,研究区可见有另一北北东向走滑断裂(跃满1−1井所在断裂)终止于该马尾断层。北北东向跃满601—跃满2−1断裂带与跃满704—跃满3−3断裂带位于研究区中部,是研究区油气开发的重点,两条断裂均延伸较长,跃满601—跃满2−1断裂带向南延伸至顺北区块后终止,向北穿过金跃、热普等区块,延伸至哈6区块被共轭北北西向断裂截断;跃满704—跃满3−3断裂带向南终止于北东东向的顺北1号断裂带,向北延伸至金跃区块后被截断。跃满801—跃满8走滑断裂仅在研究区发育,延伸较短、连续性差且前期勘探开发尚不完善,故暂不做分析研究。
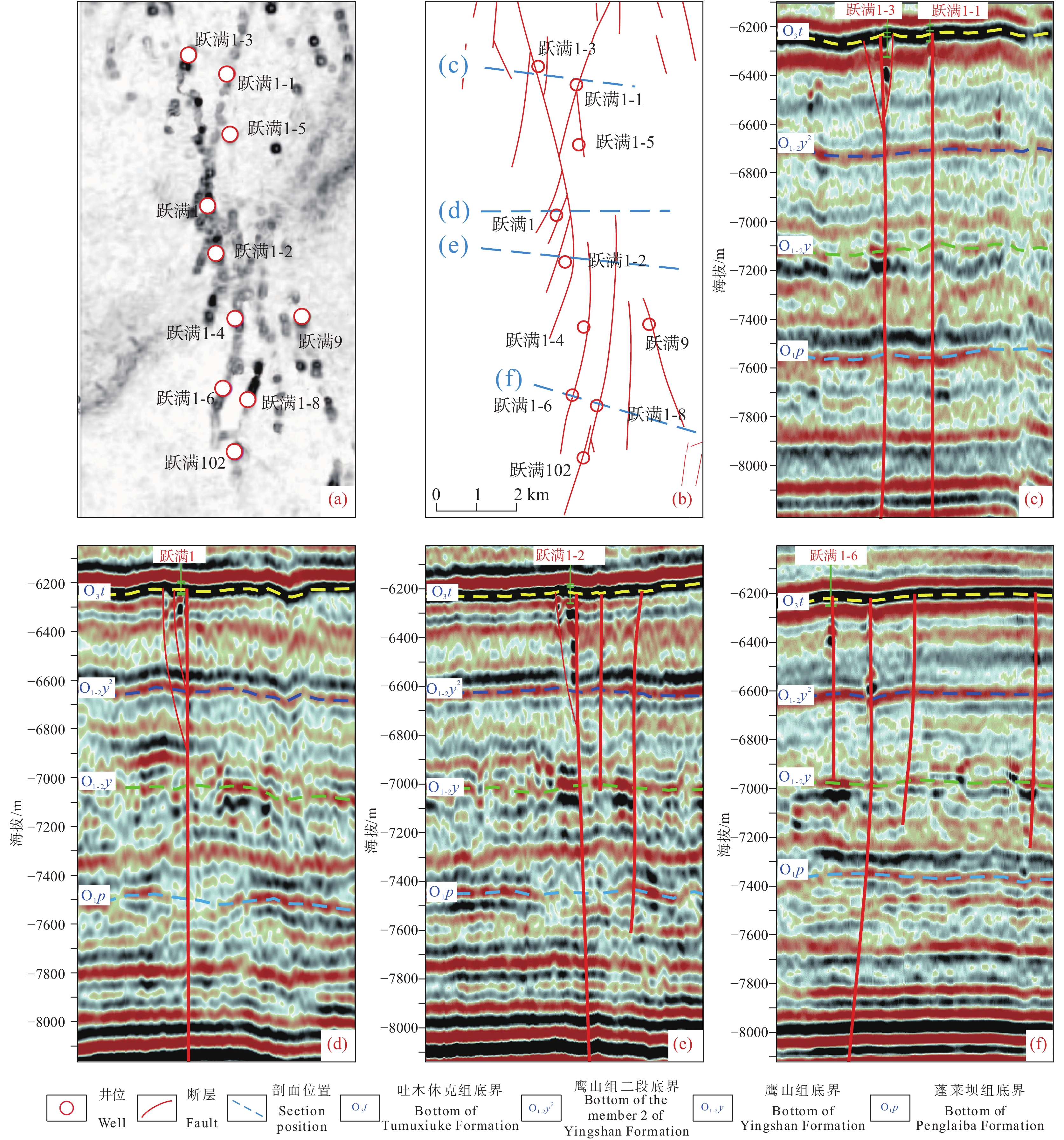
在对区内沿断裂走向的高度差异表征断层应力特征研究的基础上,对断裂构造进行分段性研究,结果显示:跃满1−3—跃满102断裂带为一典型马尾段,平面上由主干断层与若干同向弯曲的短分支断层组成,分支断层向南散开形成典型的马尾状构造,最南端转变为扇形排布的雁列断层,地震剖面上,北部可见平行的主干断层与小的花状构造,中部可见半花状构造,南部多为深大半花状构造(图8)。
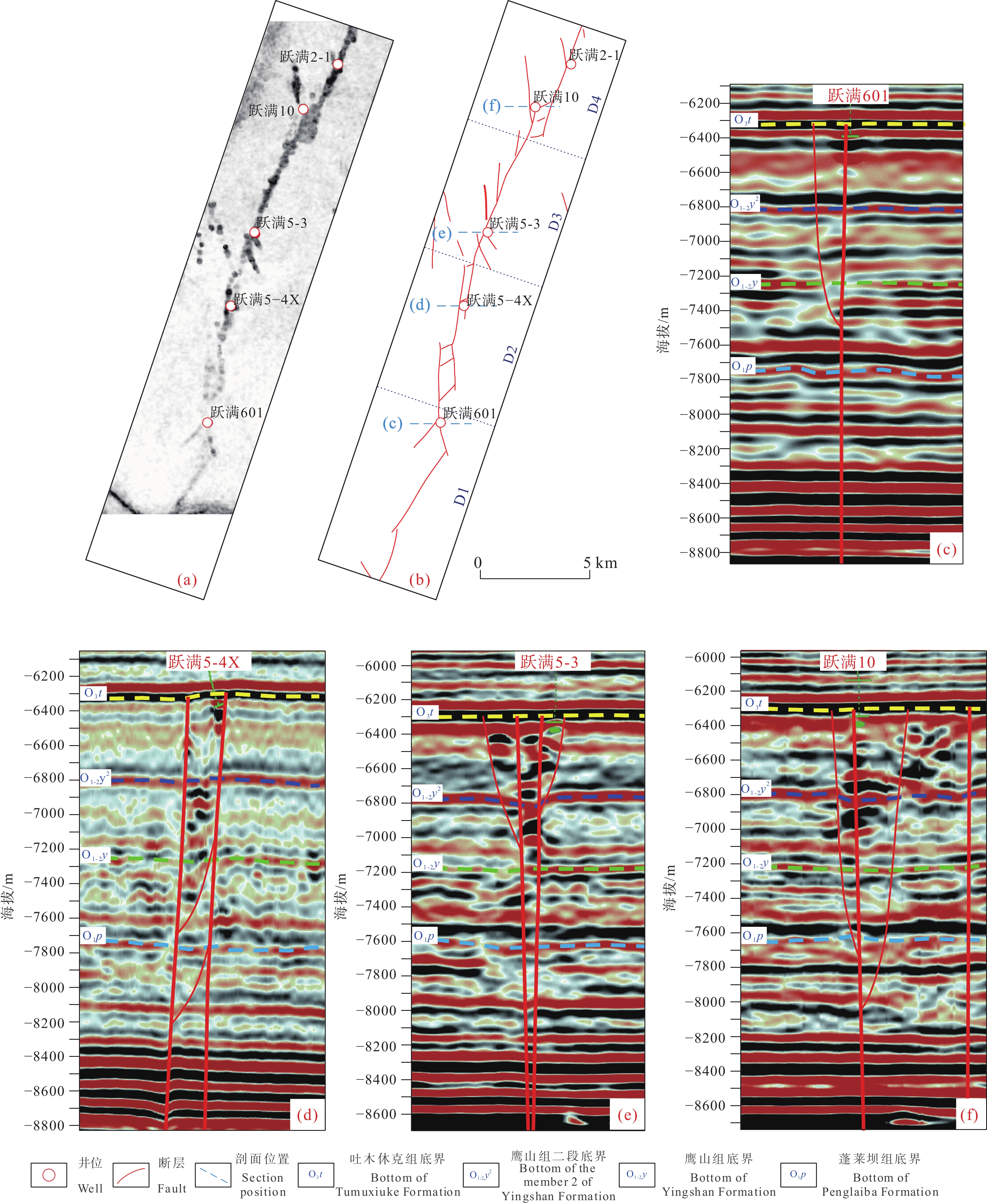
跃满601—跃满2−1断裂带自南向北可划分四段:D1线性段、D2叠覆段、D3斜列段、D4叠覆段。D1线性段为压扭性质,平面上为单条断层线性延伸,剖面上为单条直立断层;D2与D4左行右阶叠覆段均为张扭性质,平面上表现为主干断层错位发育,在断层之间形成条形叠覆区域,叠覆区内受拉张应力作用,发育多条与两主干断层大角度斜交的分支断层,D2段一大一小两个叠覆区连续发育,D4段叠覆区规模居中,剖面上主要表现为两条直立断层伴随半花状构造;D3斜列段中部为压扭性质,靠近叠覆段的两端为张扭性质,平面上由多条断层平行排列组成,剖面上主要表现为两条直立断层(图9)。
跃满704—跃满3−3断裂带自南向北可划分为四段:D5斜列段、D6线性段、D7斜列段、D8斜交段。D5斜列段为压扭性质,D7斜列段为张扭性质,平面上均为多条断层平行排列,与断层整体走向呈低角度交错,剖面上为两条直立断层;D6线性段为D5斜列段至D7斜列段间的过渡段,为张扭性质,平面上为单条主干断层,剖面上为单条陡直断层;D8斜交式断层应力性质表现为压扭与张扭交错,平面上为若干R剪切分支断层与主干断层组成,分支断层主要发育于主干断层以西,剖面上显示为发育在奥陶系内的半花状构造(图10)。
4.2 各构造段储层分布特征
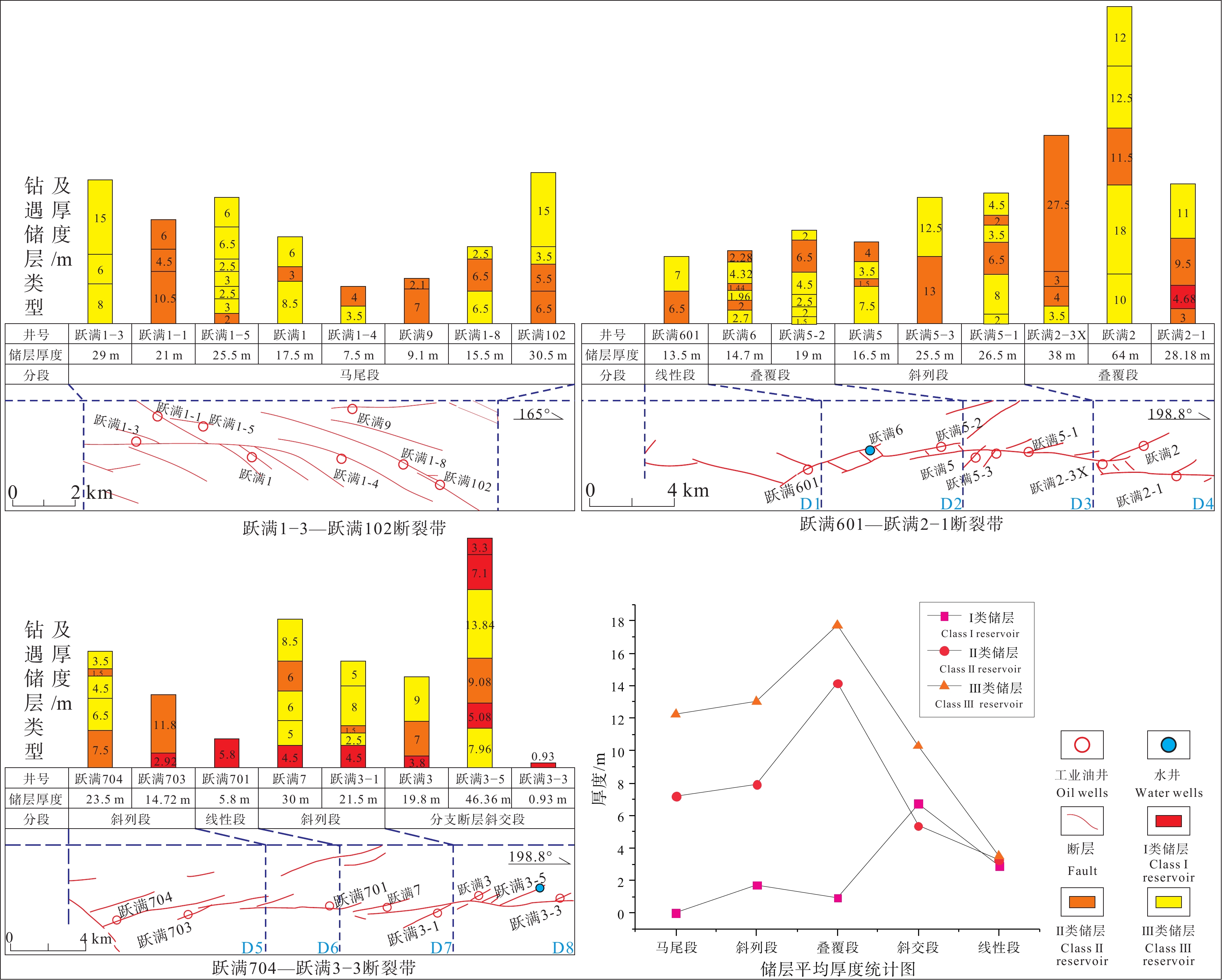
根据三维地震资料揭示的洞穴及缝洞雕刻结果,区内布置并完成了30余口井的钻探工作,并对27口井进行了试采,在钻测井资料对储层的解析基础上,结合走滑断裂的分段特征对断裂不同构造段内储层发育情况进行统计分析(表2,表3,表4),结果表明:马尾段内,储层厚度普遍较厚,储层类型以裂缝型与孔洞型储层为主,裂缝孔洞型储层少量发育,未见洞穴型储层,储层发育整体较好;叠覆段与斜列段内,储层厚度普遍较厚,且各类储层均有发育,储层发育最佳;分支断层斜交段储层发育极不均匀,整体认为储层发育一般;线性段储层发育则普遍较差。
表 2 跃满区块钻井储层统计(跃满1−3—跃满102)Table 2. Reservoir statistics of drilling in Yueman area (Yueman 1−3−Yueman 102)分段 井号 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 马尾段 跃满1−3 7209 7224 15 Ⅲ 7282 7290 8 Ⅲ 7270 7276 6 Ⅲ 跃满1−1 7217 7223 6 Ⅱ 7227.5 7238 10.5 Ⅱ 7223 7227.5 4.5 Ⅱ 跃满1−5 7226 7232 6 Ⅲ 7287 7289.5 2.5 Ⅲ 7255 7261.5 6.5 Ⅲ 7295.5 7298.5 3 Ⅲ 7275.5 7278 2.5 Ⅲ 7301.5 7303.5 2 Ⅱ 7282.5 7285.5 3 Ⅲ 跃满1 7259.5 7265.5 6 Ⅲ 7268.5 7277 8.5 III 7265.5 7268.5 3 II 跃满1−4 7297 7301 4 Ⅱ 7303.5 7307 3.5 Ⅲ 跃满9 7586.8 7588.9 2.1 Ⅱ 7591 7598 7 Ⅱ 跃满1−8 7302.5 7305 2.5 Ⅲ 7343.5 7350 6.5 Ⅲ 7311 7317.5 6.5 Ⅱ 跃满102 7282 7297 15 Ⅲ 7300.5 7306 5.5 Ⅱ 7297 7300.5 3.5 Ⅲ 7306 7312.5 6.5 Ⅱ 表 4 跃满区块钻井储层统计(跃满704—跃满3−3)Table 4. Reservoir statistics of drilling in Yueman area (Yueman 704−Yueman 3−3)分段 井号 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 斜列段 跃满704 7307.5 7311 3.5 Ⅲ 7364 7370.5 6.5 Ⅲ 7338.5 7340 1.5 Ⅱ 7370.5 7378 7.5 Ⅱ 7340 7344.5 4.5 Ⅲ 跃满703 7277.9 7289.7 11.8 Ⅲ 7298 7300.92 2.92 Ⅰ 线性段 跃满701 7315.7 7321.5 5.8 Ⅰ 斜列段 跃满7 7234 7242.5 8.5 Ⅲ 7265.5 7270.5 5 Ⅲ 7242.5 7248.5 6 II 7270.5 7275 4.5 Ⅰ 7257 7263 6 Ⅲ 跃满3−1 7224 7229 5 Ⅲ 7244 7246.5 2.5 Ⅲ 7234.5 7242.5 8 Ⅲ 7246.5 7251 4.5 Ⅰ 7242.5 7244 1.5 Ⅱ 分支断层
斜交段跃满3 7189.5 7198.5 9 Ⅲ 7219.4 7223.2 3.8 Ⅰ 7209 7216 7 Ⅱ 跃满3−5 7167.7 7171 3.3 Ⅰ 7197.88 7206.96 9.08 Ⅱ 7173.8 7180.9 7.1 Ⅰ 7206.96 7212.04 5.08 Ⅰ 7184.04 7197.88 13.84 Ⅲ 7212.04 7220 7.96 Ⅲ 跃满3−3 7158.62 7159.55 0.93 Ⅰ 表 3 跃满区块钻井储层统计(跃满601—跃满2−1)Table 3. Reservoir statistics of drilling in Yueman area (Yueman 601−Yueman 2−1)分段 井号 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 线性段 跃满601 7313 7320 7 Ⅲ 7372.5 7379 6.5 Ⅱ 叠覆段 跃满6 7294 7296.28 2.28 Ⅱ 7302.04 7304 1.96 Ⅲ 7296.28 7300.6 4.32 Ⅲ 7304 7306 2 Ⅱ 7300.6 7302.04 1.44 Ⅱ 7308 7310.7 2.7 Ⅲ 跃满5−2 7277 7279 2 Ⅲ 7301.5 7304 2.5 Ⅲ 7284 7290.5 6.5 Ⅱ 7313 7315 2 Ⅲ 7290.5 7295 4.5 Ⅲ 7318 7319.5 1.5 Ⅲ 斜列段 跃满5 7272.5 7276.5 4 Ⅱ 7280 7281.5 1.5 Ⅱ 7276.5 7280 3.5 Ⅲ 7281.5 7289 7.5 Ⅲ 跃满5−3 7258.5 7271 12.5 Ⅲ 7279 7292 13 Ⅱ 跃满5−1 7248.5 7253 4.5 Ⅲ 7263 7269.5 6.5 Ⅱ 7253 7255 2 Ⅱ 7269.5 7277.5 8 Ⅲ 7255 7258.5 3.5 Ⅲ 7280.5 7282.5 2 Ⅲ 叠覆段 跃满2−3X 7274 7301.5 27.5 Ⅱ 7319 7323 4 Ⅱ 7313 7316 3 Ⅱ 7323 7326.5 3.5 Ⅲ 跃满2 7200.5 7212.5 12 Ⅲ 7245 7263 18 III 7221 7233.5 12.5 Ⅲ 7263 7273 10 Ⅲ 7233.5 7245 11.5 Ⅱ 跃满2−1 7304.5 7315.5 11 Ⅲ 7329.76 7334.44 4.68 Ⅰ 7315.5 7325 9.5 Ⅱ 7338 7341 3 Ⅱ 5. 分析讨论
5.1 断控岩溶作用对储层发育的控制
综上所述,跃满区块走滑断裂分段特征与储层的发育规模具有一定的耦合关系,前人研究认为:塔北哈拉哈塘地区岩溶作用对碳酸盐岩储层具有直接控制作用(Dan et al., 2016; 梁乘鹏等, 2019),岩溶体系又主要受控于低水位期海平面下降、先存断裂及裂缝、地表河流体系(Liang and Jones, 2014; 宁超众等, 2020)。塔北奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层发育可分为四个阶段:一间房组准同生阶段、良里塔格组台缘滩沉积阶段、志留系前潜山岩溶阶段与后期埋藏溶蚀阶段(张学丰等, 2012; 赵学钦等, 2015),而非暴露区跃满区块位于塔北隆起最南缘,隆升幅度最小(廖涛等, 2016),故该区奥陶系储层主要受早期准同生岩溶与后三期埋藏岩溶作用,埋藏岩溶作用主要表现为深部溶蚀性流体沿断裂向上运移,改造一间房组碳酸盐岩,形成有效储集体(郑剑等, 2015; 牛君等, 2017)。分析认为断裂主要通过控制岩溶作用间接控制储层的发育,结合钻井与走滑断裂相对位置关系发现:区内储层发育程度受控于走滑断裂的构造样式及应力特征,构造样式越复杂,应力作用越集中,则岩溶作用更强,相应储层发育更好(图11)。
马尾段是断裂端部应力发散的结果,多条拉张性质的雁列断层与分支断层成组发育,整体构造样式较复杂,中部短马尾分支断层间距小、下切浅,南部长雁列断层间距大、下切深。断层间距越小,单位面积溶蚀作用则越强,而下切越深越有利于溶蚀性流体的上侵,马尾段储层统计显示,整体储层发育较好,平均厚度19.45 m,储层类型多为裂缝型、孔洞型以及裂缝−孔洞型,未见洞穴型储层发育。
斜列段与叠覆段均为应力集中区,且区内构造样式复杂,斜列的主干断层以及连通主干断层的分支断层均可作为流体的运移通道,溶蚀区域面积增大且溶蚀作用强度大幅增强,以主干断层夹持区溶蚀效果最好。区内钻井揭示,区内斜列段与叠覆段储层发育最佳,储层厚度均较厚,各井平均厚度23.46 m,最厚储层38 m(跃满2−3X井),最薄储层14.7 m(跃满6井),储层类型以裂缝孔洞型为主,各井均有多类储层发育。
分支断层斜交段局部应力集中,密集程度不一,多条分支断层逆向发育于断层西侧,分支断层长度不一,与马尾段类似,长分支断层具有更长的流体运移通道,分支断层密集区单位面积溶蚀作用更强,储层统计显示长分支断层储层厚度异常厚,例如跃满3−5井,储层厚46.36 m,各类储层均发育,短分支断层上储层发育一般,且非密集分支断层上的跃满3−3井储层发育极差,整体认为储层发育一般。
线性段均无构造应力集中,且构造样式简单,断层仅作为流体的运移通道,岩溶作用对该段内碳酸盐岩改造作用较弱。线性段内储层发育较差,厚度较薄且储层类型单一。
5.2 断控高能相带对储层发育的控制
研究区一间房组整体为开阔台地相,加里东中期—晚奥陶纪早期(加里东中期Ⅰ幕),塔北发生了一次较大规模的海退,一间房组短暂暴露,准同生岩溶大面积发育(倪新锋等, 2009),中奥陶世末期,走滑断裂开始活动并控制着区内微地貌(Wu et al., 2021),断裂挤压段易形成正地貌,有利于高能礁滩体发育,该类礁滩体受准同生期岩溶作用及自身结构影响,具有更好的孔隙度、渗透率(Zeng et al., 2018; 高达等, 2022),也更易受埋藏岩溶作用溶蚀改造,从而形成有效储集体。
新三维地震资料上不同沉积相带具有不同的地震响应特征:开阔台地相地震反射时差横向变化稳定,成平行、亚平行结构,振幅较强、连续,能量稳定;台内滩地震反射时差增大,反射杂乱,具有下超、上隆的特征,振幅变弱(聂杞连等, 2015)。连井地震剖面显示,区内一间房组顶部发育不规则的高能相带(图12),主要覆盖了跃满601—跃满2−1断裂带北部D3斜列段与D4叠覆段,跃满704—跃满3−3断裂带中北部D6线性段与D7斜列段。对比高能相带叠合区与非叠合区发现,在断裂分段性控制储层发育的基础上,高能相带的叠加区储层发育更好,与高能相带叠加的D4叠覆段相较D2叠覆段储层厚度更厚,叠加高能相带的D3斜列段和D7斜列段储层厚度相近,且储层厚度均高于D5斜列段。
6. 结 论
(1)跃满区块奥陶系一间房组储层发育,储集岩以生屑灰岩、砂屑灰岩、颗粒灰岩、泥晶灰岩为主。根据储集空间组合特征储层可分为洞穴型储层、裂缝−孔洞型储层、裂缝型储层和孔洞型储层四类。各类储层集中发育于一间房组顶部,沿走滑断裂带状分布。
(2)跃满区块位于塔北南坡纯剪走滑区,发育一组北北西向与三组北北东向走滑断裂。区内断裂具有分段性,按平面构造样式可分为马尾段、斜列段、叠覆段、分支断层斜交段和线性段。断裂不同段内平面组合特征、剖面构造特征和应力特征均有区别,马尾段应力发散,构造样式复杂,斜列段与叠覆段应力集中、构造样式复杂,分支断层斜交段局部应力集中、构造样式单一,线性段无构造应力集中,构造样式最简单。
(3)走滑断裂分段性影响埋藏岩溶作用强度及规模,从而控制储层发育程度与分布情况。研究区内马尾段、斜列段和叠覆段储层发育最佳,分支断层斜交段储层发育受控于分支断层长度,整体发育一般,线性段储层发育较差。此外,在断裂分段性控制储层发育的基础上,高能相带叠加区储层更为发育。
致谢: 项目研究过程中,中国石油塔里木油田勘探开发研究院的张银涛高级工程师、康鹏飞工程师,以及西南石油大学地球科学与技术学院的赵星星、崔晓庆、宋玉婷等在前期资料收集、数据处理上提供了指导和帮助,审稿专家与编辑对稿件提出了宝贵的修改意见。在此一并致以诚挚谢意!
1 ➊赵宽志, 马青, 赵学钦, 孙崇浩, 袁力. 2014. 哈拉哈塘地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层精细描述与地质建模[R]. 库尔勒: 中国石油天然气股份有限公司塔里木油田分公司. -
图 2 跃满地区奥陶系一间房组储层岩性(染色铸体薄片)
a—跃满2井,井深:7211.8 m,亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;b—跃满2井,井深:7200.6 m,泥晶生屑灰岩;c—跃满2井,井深:7209.7 m,泥亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;d—跃满2井,井深:7206.7 m,泥粉晶生屑灰岩,构造缝;e—跃满2井,井深:7215.7 m,亮晶藻团块生屑灰岩,构造缝;f—跃满2井,井深:7209.9 m,泥亮晶生屑灰岩,构造缝与压溶缝;g—跃满2井,井深:7201.7 m,泥晶生屑灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;h—跃满2井,井深:7210.7 m,方解石和沥青质半充填的构造缝;i—跃满2井,井深:7207.3 m,亮晶藻砂屑灰岩,构造缝,方解石全充填的溶蚀缝;j—跃满2井,井深:7216.7 m,亮晶生屑藻砂屑灰岩,粒内溶孔;k—跃满2井,井深:7217.6 m,泥亮晶生屑藻砂屑灰岩,粒内溶孔;l—跃满2井,井深:7212.6 m,亮晶颗粒灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;m—跃满2井,井深:7213.7 m,亮晶颗粒灰岩,构造缝,压溶缝;n—跃满2井,井深:7214.5 m,粉晶颗粒灰岩,方解石半充填构造缝;o—跃满2井,井深:7196.5 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,构造缝;p—跃满2井,井深:7197.5 m,生屑泥晶灰岩,收缩缝
Figure 2. Reservoir lithology of Ordovician Yijianfang Formation in Yueman area (dyed cast thin section)
a−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7211.8 m, sparry bioclastic limestone, structural fracture; b−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7200.6 m, micrite bioclast limestone; c−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7209.7 m, micrite−sparry bioclast limestone, structural fracture; d−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7206.7 m, micrite−powder bioclast limestone, structural fracture; e−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7215.7 m, sparry clumpy alga bioclastic limestone, structural fracture; f−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7209.9 m, micrite−sparry bioclast limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; g−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7201.7 m, micrite bioclast limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; h−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7210.7 m, structural fracture, half−filled with calcite and asphalt; i−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7207.3 m, sparry algal arenaceous limestone, structural fracture, dissolution fracture, full−filled with calcite; j−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7216.7 m, Sparry bioclastic arenaceous limestone, intragranular dissolved pore; k−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7217.6 m, argillaceous sparry bioclastic arenaceous limestone, intragranular dissolved pore; l−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7212.6 m, sparry granular limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; m−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7213.7 m, sparry granular limestone, structural fracture, pressolutional fracture; n−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7214.5 m, silt−grained limestone, half−filled with calcite, structural fracture ; o−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7196.5 m, bioclastic micritic limestone, structural fracture; p−Well Yueman 2, depth: 7197.5 m, bioclastic micritic limestone, shrinkage fracture
图 3 跃满地区奥陶系一间房组储层类型(岩心)
a—跃满2井,1−58−35,生屑砂屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞;b—跃满2井,2−54−6,生屑砂屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞,方解石全充填、半充填;c—跃满703井,2−81−37,生屑灰岩,溶蚀孔洞;d—跃满2井,3−56−37,砂屑生屑灰岩,中高角度缝;e—跃满1井,1−51−1,砂屑灰岩,中高角度缝,沿缝发育溶蚀孔;f—跃满6井,1−64−42,砂屑灰岩,直立缝与水平缝近垂直共轭;g—跃满8井,1−64−46,砂屑灰岩,高角度裂缝,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育,见油斑;h—跃满8井,2−63−25,砂屑灰岩,直立缝与水平缝交汇处溶孔扩大;i—跃满1井,1−51−42,砂屑灰岩,中高角度裂缝,沿裂缝溶蚀孔洞发育
Figure 3. Reservoir type of the Yijianfang Formation of Ordovician in Yueman area (cores)
a−Well Yueman 2, 1−58−35, bioclastic calcarenite, dissolved pore; b−Well Yueman 2, 2−54−6, bioclastic calcarenite, dissolved pore, full filled or half filled with calcite; c−Well Yueman 703, 2−81−37, bioclastic limestone, dissolved pore; d−Well Yueman 2, 3−56−37, sandy bioclastic limestone, middle−high angle fracture; e−Well Yueman 1, 1−51−1, calcarenite, middle−high angle fracture, dissolved pore; f−Well Yueman 6, 1−64−42, calcarenite, horizontal and vertical fractures; g−Well Yueman 8, 1−64−46, calcarenite, high Angle fracture, dissolved pore, oil patch; h−Well Yueman 8, 2−63−25, calcarenite, horizontal and vertical fractures, dissolved pore increase at fracture intersections; i−Well Yueman 1, 1−51−42, calcarenite, middle−high angle fracture, dissolved pore
图 7 塔北至塔中地区(a,据Wu et al., 2021修改)跃满区块(b)走滑断裂体系纲要图
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of strike−slip faults in Tabei−Tazhong area (a, modified from Wu et al., 2021) and Yueman area (b)
表 1 跃满区块漏失统计
Table 1 Lost circulation statistics in Yueman area
序号 井号 放空长/m 漏失量/m3 序号 井号 放空长/m 漏失量/m3 1 跃满1 1.92 355 18 跃满5−4X 6.39 659 2 跃满10 0 506.12 19 跃满5−5 1.85 148.4 3 跃满1−1 0 535.7 20 跃满601 0 373.7 4 跃满1−3 0.12 118.24 21 跃满6C 0 215.5 5 跃满1−5 0.76 0 22 跃满701 0 260.4 6 跃满2−2C 0 1200 23 跃满701−H1 1.11 1494.4 7 跃满2−4X 1.41 2049 24 跃满702 0 133.2 8 跃满3 0 253.4 25 跃满703 2.72 252.2 9 跃满3−1 1.49 307.1 26 跃满7−1X 0 1558.11 10 跃满3−2C 0 1063.2 27 跃满7−2X 0.34 1527.19 11 跃满3−3 0.93 348.5 28 跃满7JS 19.1 3231.33 12 跃满3−5 0.74 114.6 29 跃满8 4.02 773.5 13 跃满3−5C 8 1064.6 30 跃满801 2.79 1389.18 14 跃满3−6X 0.96 241.6 31 跃满801−H6 2.59 549.4 15 跃满3−7X 0 9.9 32 跃满802 1.45 329.7 16 跃满4 0 43.8 33 跃满8−1 6.34 286.2 17 跃满5−3 0 269.4 34 跃满9 9.25 811 表 2 跃满区块钻井储层统计(跃满1−3—跃满102)
Table 2 Reservoir statistics of drilling in Yueman area (Yueman 1−3−Yueman 102)
分段 井号 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 马尾段 跃满1−3 7209 7224 15 Ⅲ 7282 7290 8 Ⅲ 7270 7276 6 Ⅲ 跃满1−1 7217 7223 6 Ⅱ 7227.5 7238 10.5 Ⅱ 7223 7227.5 4.5 Ⅱ 跃满1−5 7226 7232 6 Ⅲ 7287 7289.5 2.5 Ⅲ 7255 7261.5 6.5 Ⅲ 7295.5 7298.5 3 Ⅲ 7275.5 7278 2.5 Ⅲ 7301.5 7303.5 2 Ⅱ 7282.5 7285.5 3 Ⅲ 跃满1 7259.5 7265.5 6 Ⅲ 7268.5 7277 8.5 III 7265.5 7268.5 3 II 跃满1−4 7297 7301 4 Ⅱ 7303.5 7307 3.5 Ⅲ 跃满9 7586.8 7588.9 2.1 Ⅱ 7591 7598 7 Ⅱ 跃满1−8 7302.5 7305 2.5 Ⅲ 7343.5 7350 6.5 Ⅲ 7311 7317.5 6.5 Ⅱ 跃满102 7282 7297 15 Ⅲ 7300.5 7306 5.5 Ⅱ 7297 7300.5 3.5 Ⅲ 7306 7312.5 6.5 Ⅱ 表 4 跃满区块钻井储层统计(跃满704—跃满3−3)
Table 4 Reservoir statistics of drilling in Yueman area (Yueman 704−Yueman 3−3)
分段 井号 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 斜列段 跃满704 7307.5 7311 3.5 Ⅲ 7364 7370.5 6.5 Ⅲ 7338.5 7340 1.5 Ⅱ 7370.5 7378 7.5 Ⅱ 7340 7344.5 4.5 Ⅲ 跃满703 7277.9 7289.7 11.8 Ⅲ 7298 7300.92 2.92 Ⅰ 线性段 跃满701 7315.7 7321.5 5.8 Ⅰ 斜列段 跃满7 7234 7242.5 8.5 Ⅲ 7265.5 7270.5 5 Ⅲ 7242.5 7248.5 6 II 7270.5 7275 4.5 Ⅰ 7257 7263 6 Ⅲ 跃满3−1 7224 7229 5 Ⅲ 7244 7246.5 2.5 Ⅲ 7234.5 7242.5 8 Ⅲ 7246.5 7251 4.5 Ⅰ 7242.5 7244 1.5 Ⅱ 分支断层
斜交段跃满3 7189.5 7198.5 9 Ⅲ 7219.4 7223.2 3.8 Ⅰ 7209 7216 7 Ⅱ 跃满3−5 7167.7 7171 3.3 Ⅰ 7197.88 7206.96 9.08 Ⅱ 7173.8 7180.9 7.1 Ⅰ 7206.96 7212.04 5.08 Ⅰ 7184.04 7197.88 13.84 Ⅲ 7212.04 7220 7.96 Ⅲ 跃满3−3 7158.62 7159.55 0.93 Ⅰ 表 3 跃满区块钻井储层统计(跃满601—跃满2−1)
Table 3 Reservoir statistics of drilling in Yueman area (Yueman 601−Yueman 2−1)
分段 井号 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 类型 线性段 跃满601 7313 7320 7 Ⅲ 7372.5 7379 6.5 Ⅱ 叠覆段 跃满6 7294 7296.28 2.28 Ⅱ 7302.04 7304 1.96 Ⅲ 7296.28 7300.6 4.32 Ⅲ 7304 7306 2 Ⅱ 7300.6 7302.04 1.44 Ⅱ 7308 7310.7 2.7 Ⅲ 跃满5−2 7277 7279 2 Ⅲ 7301.5 7304 2.5 Ⅲ 7284 7290.5 6.5 Ⅱ 7313 7315 2 Ⅲ 7290.5 7295 4.5 Ⅲ 7318 7319.5 1.5 Ⅲ 斜列段 跃满5 7272.5 7276.5 4 Ⅱ 7280 7281.5 1.5 Ⅱ 7276.5 7280 3.5 Ⅲ 7281.5 7289 7.5 Ⅲ 跃满5−3 7258.5 7271 12.5 Ⅲ 7279 7292 13 Ⅱ 跃满5−1 7248.5 7253 4.5 Ⅲ 7263 7269.5 6.5 Ⅱ 7253 7255 2 Ⅱ 7269.5 7277.5 8 Ⅲ 7255 7258.5 3.5 Ⅲ 7280.5 7282.5 2 Ⅲ 叠覆段 跃满2−3X 7274 7301.5 27.5 Ⅱ 7319 7323 4 Ⅱ 7313 7316 3 Ⅱ 7323 7326.5 3.5 Ⅲ 跃满2 7200.5 7212.5 12 Ⅲ 7245 7263 18 III 7221 7233.5 12.5 Ⅲ 7263 7273 10 Ⅲ 7233.5 7245 11.5 Ⅱ 跃满2−1 7304.5 7315.5 11 Ⅲ 7329.76 7334.44 4.68 Ⅰ 7315.5 7325 9.5 Ⅱ 7338 7341 3 Ⅱ -
[1] Dan Y, Zou H, Liang B, Zhang Q Y, Cao J W, Li J R, Hao Y Z. 2016. Restoration of multistage paleogeomorphology during Caledonian Period and paleokarst cavernous reservoir prediction in Halahatang area, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 37(3): 304−312.
[2] Deng Shang, Liu Yuqing, Liu Jun, Han Jun, Wang Bin, Zhao Rui. 2021. Structural styles and evolution models of intracratonic strike−slip faults and the implications for reservoir exploration and appraisal: A case study of the Shunbei Area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 45(6): 1111−1126 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Ding Zhiwen, Wang Rujun, Chen Fangfang, Yang Jianping, Zhu Zhongqian, Yang Zhimin, Sun Xiaohui, Xian Bo, Li Erpeng, Shi Tao, Zuo Chao, Li Yang. 2020. Origin, hydrocarbon accumulation and oil−gas enrichment of fault−karst carbonate reservoirs: A case study of Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in South Tahe area of Halahatang oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(2): 286−296 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Gao Da, Wang Mingmin, Tao Ye, Huang Lili, Sun Chuanyan, Huang Xinmiao, Wu Jianwei. 2022. Control of sea level changes on high−frequency sequence and sedimentary evolution of Lianglitage Formation in the Tazhong Area[J]. Geology in China, 49(6): 1936−1950 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Han X Y, Deng S, Tang L J, Cao Z C. 2017. Geometry, kinematics and displacement characteristics of strike−slip faults in the northern slope of Tazhong uplift in Tarim Basin: A study based on 3D seismic data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 88: 410−427.
[6] He Zhiliang, Jin Xiaohui, Wo Yujin, Li Huili, Bai Zhenrui, Jiao Cunli, Zhang Zhongpei. 2016. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and exploration domains of ultra−deep marine carbonates in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 21(1): 3−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Jiao F Z. 2018. Significance and prospect of ultra−deep carbonate fault−karst reservoirs in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 39(2): 207−216.
[8] Liang Chengpeng, Dan Yong, Xu Shenglin, Li Fuxiang, Pang Chunyu, Wei Jiaqi. 2019. Interlayer karst reservoir characteristics and development controlling factors of Ordovician in the Xinken area, Tarim basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 38(3): 427−437 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Liang T, Jones B. 2014. Deciphering the impact of sea−level changes and tectonic movement on erosional sequence boundaries in carbonate successions: A case study from Tertiary strata on Grand Cayman and Cayman Brac, British West Indies[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 305: 17−34.
[10] Liao Tao. Hou Jiagen. Chen Lixin. Ma Ke, Yang Wenming, Dong Yue, Bai Xiaojia. 2016. Fault controlling on non−exposed karst fracture−vug reservoirs of the Ordovician in Halahatang Oilfield, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 18(2): 221−235 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Ma Debo, Cui Wenjuan, Tao Xiaowan, Dong Hongkui, Xu Zhaohui, Li Tingting, Chen Xiuyan. 2020. Structural characteristics and evolution proccess of faults in the Lunnan low uplift, Tabei Uplift in the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 31(5): 647−657 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Ni Xinfeng, Zhang Lijuan, Shen Anjiang, Pang Wenqing, Qiao Zhanfeng. 2009. Paleo−karstification types, karstification periods and superimposition relationship of Ordovician carbonates in northern Tarim Basin[J]. Geology in China, 36(6): 1312−1321 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Nie Qilian, Wang Shenjian, Tong Kailian, Duan Jie, Sun Qingli. 2015. The Research of Seismic Geomorphology on High−energy Ooliti Beach of Feixianguan Formation in the central of Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 12(5): 621−626 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Ning Chaozhong, Hu Suyun, Pan Wenqing, Yao Zixiu, Li Yong, Yuan Wenfang. 2020. Characterization of paleo−topography and karst caves in Ordovician Lianglitage Formation, Halahatang oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(5): 985−995, 1047 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Niu Jun, Huang Wenhui, Liang Fei, Wang Wenyong, Wan Huan, You Shenggang, Zhang Yamei. 2017. Buried Palaeokarst characteristics and favorable reservoir distribution of Ordovician carbonate rock in Yubei area[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 41(6): 74−84,95,124−125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Shen Anjiang, Chen Yana, Meng Shaoxing, Zheng Jianfeng, Qiao Zhanfeng, Ni Xinfeng, Zhang Jianyong, Wu Xingning. 2019. The research progress of marine carbonate reservoirs in China and its significance for oil and gas exploration[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 24(4): 1−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Sun Dong, Yang Lisha, Wang Hongbin, Zheng Duoming, Sun Qinhua, Li Guohui, Dai Dongdong, Fang Qifei. 2015. Strike−slip fault system in Halahatang Area of Tarim Basin and its control on reservoirs of Ordovician marine carbonate rock[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 26(S1): 80−87 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Tang L J, Qi L X, Qiu H J, Yun L, Li M, Xie D Q, Yang Y, Wan G M. 2012. Poly−phase differential fault movement and hydrocarbon accumulation of the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(8): 2569−2583.
[19] Wang W Y, Pang X Q, Chen Z X, Chen D X, Wang Y P, Yang X, Luo B, Zhang W, Zhang X W, Li C R, Wang Q F, Li C J. 2021. Quantitative evaluation of transport efficiency of fault−reservoir composite migration pathway systems in carbonate petroliferous basins[J]. Energy, 222(1): 119983.
[20] Wang Xinxin, Cui Deyu, Sun Chonghao, Zhang Sheng, Fang Lu, Zhang Min. 2019. Characteristics of Strikes−slip fault and its controlling on oil in block A of the Halahatang oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6): 1058−1067 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Wu Guanghui, Cheng Lifang, Liu Yukui, Wang Hai, Qu Tailai, Gao Li. 2011. Strike−slip fault system of the Cambrian−Ordovician and its oil−controlling effect in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjinag Petroleum Geology, 32(3): 239−243 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Wu G H, Gao L H, Zhang Y T, Ning C Z, Xie E. 2018. Fracture attributes in reservoir−scale carbonate fault damage zones and implications for damage zone width and growth in the deep subsurface[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 118: 181−193.
[23] Wu G H, Ma B S, Han J F, Guan B Z, Chen X, Yang P, Xie Z. 2021. Origin and growth mechanisms of strike−slip faults in the central Tarim cratonic basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(3): 595−607.
[24] Yang H J, Hao F, Han J F, Cai Z X, Gu Q Y. 2007. Fault systems and multiple oil−gas accumulation play of the Lunnan lower uplift, Tarm Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, (4): 795−811.
[25] Zeng H L, Zhao W Z, Xu Z H, Fu Q L, Hu S Y, Wang Z C, Li B H. 2018. Carbonate seismic sedimentology: A case study of Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation, Gaoshiti−Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 45(5): 830−839.
[26] Zhai Guangming, He Wenyuan. 2004. An important petroleum exploration region in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 25(1): 7(in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Zhang Xuefeng, Li Ming, Chen Zhiyong, Jiang Hua, Tang Junwei, Liu Bo, Gao Jixian, He Yunlan. 2012. Characteristics and karstification of the Ordovician carbonate reservoir, Halahatang area, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(3): 815−826 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Zhao Xueqin, Yang Haijun, Ma Qin, Zhou Chenggang, Sun Chonghao, Cai Quan, Sun Shiyong. 2015. Syn−sedimentary corrosion mode of carbonate reef−banks in the middle Ordovician Yijianfang Formation within the western Tabei uplift of Tarim Basin[J]. Geology in China, 42(6): 1811−1821 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Zheng Jian, Wang Zhenyu, Yang Haijun, Sun Chonghao, Zhang Yunfeng, Chen Jingshan. 2015. Buried karstification period and contribution to reservoirs of Ordovician Yingshan Formation in Tazhong Area[J]. Geoscience, 29(3): 665−674 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Zhu Guangyou, Yang Haijun, Zhu Yongfeng, Gu Lijing, Lu Yuhong, Su Jin, Zhang Baoshou, Fan Qiuhai. 2011. Study on petroleum geological characteristics and accumulation of carbonate reservoirs in Hanilcatam area, Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(3): 827−844 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] 邓尚, 刘雨晴, 刘军, 韩俊, 王斌, 赵锐. 2021. 克拉通盆地内部走滑断裂发育、演化特征及其石油地质意义: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 45(6): 1111−1126. [32] 丁志文, 汪如军, 陈方方, 阳建平, 朱忠谦, 杨志敏, 孙晓辉, 鲜波, 李二鹏, 史涛, 左超, 李阳. 2020. 断溶体油气藏成因、成藏及油气富集规律——以塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘油田塔河南岸地区奥陶系为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 47(2): 286−296. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.02.07 [33] 高达, 王明敏, 陶叶, 黄理力, 孙春燕, 黄鑫淼, 武建伟. 2022. 塔中地区良里塔格组海平面变化对高频层序和沉积演化的控制[J]. 中国地质, 49(6): 1936−1950. doi: 10.12029/gc20220617 [34] 何治亮, 金晓辉, 沃玉进, 李慧莉, 白振瑞, 焦存礼, 张仲培. 2016. 中国海相超深层碳酸盐岩油气成藏特点及勘探领域[J]. 中国石油勘探, 21(1): 3−14. [35] 梁乘鹏, 淡永, 徐胜林, 李富祥, 庞春雨, 魏家琦. 2019. 塔里木盆地新垦地区奥陶系层间岩溶储层形成机制与控制因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 38(3): 427−437. doi: 10.11932/karst20190301 [36] 廖涛, 侯加根, 陈利新, 马克, 杨文明, 董越, 白晓佳. 2016. 断裂对塔北地区哈拉哈塘油田奥陶系非暴露岩溶缝洞型储集层的控制作用[J]. 古地理学报, 18(2): 221−235. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2016.02.017 [37] 马德波, 崔文娟, 陶小晚, 董洪奎, 徐兆辉, 李婷婷, 陈秀艳. 2020. 塔北隆起轮南低凸起断裂构造特征与形成演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 31(5): 647−657. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2020.04.014 [38] 倪新锋, 张丽娟, 沈安江, 潘文庆, 乔占峰. 2009. 塔北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩古岩溶类型、期次及叠合关系[J]. 中国地质, 36(6): 1312−1321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.06.012 [39] 聂杞连, 王身建, 佟恺林, 段杰, 孙庆莉. 2015. 川中地区飞仙关组高能鲕滩储层的地震地貌学研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 12(5): 621−626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2015.05.009 [40] 宁超众, 胡素云, 潘文庆, 姚子修, 李勇, 袁文芳. 2020. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区奥陶系良里塔格组古地貌与岩溶洞穴特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 41(5): 985−995,1047. doi: 10.11743/ogg20200509 [41] 牛君, 黄文辉, 梁飞, 王文勇, 万欢, 游声刚, 张亚美. 2017. 玉北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩埋藏型岩溶发育特征及有利储层分布[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 41(6): 74−84,95,124−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2017.06.009 [42] 沈安江, 陈娅娜, 蒙绍兴, 郑剑锋, 乔占峰, 倪新锋, 张建勇, 吴兴宁. 2019. 中国海相碳酸盐岩储层研究进展及油气勘探意义[J]. 海相油气地质, 24(4): 1−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.04.001 [43] 孙东, 杨丽莎, 王宏斌, 郑多明, 孙勤华, 李国会, 代冬冬, 房启飞. 2015. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区走滑断裂体系对奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩储层的控制作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 26(S1): 80−87. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2015.S1.0080 [44] 王新新, 崔德育, 孙崇浩, 张晟, 房璐, 张敏. 2019. 哈拉哈塘油田A地区断裂特征及其控油作用[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(6): 1058−1067. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.088 [45] 邬光辉, 成丽芳, 刘玉魁, 汪海, 曲泰来, 高力. 2011. 塔里木盆地寒武—奥陶系走滑断裂系统特征及其控油作用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 32(3): 239−243. [46] 翟光明, 何文渊. 2004. 塔里木盆地石油勘探实现突破的重要方向[J]. 石油学报, 25(1): 7. doi: 10.7623/syxb200401001 [47] 张学丰, 李明, 陈志勇, 姜华, 唐俊伟, 刘波, 高计县, 赫云兰. 2012. 塔北哈拉哈塘奥陶系碳酸盐岩岩溶储层发育特征及主要岩溶期次[J]. 岩石学报, 28(3): 815−826. [48] 赵学钦, 杨海军, 马青, 周成刚, 孙崇浩, 蔡泉, 孙仕勇. 2015. 塔北西部一间房组碳酸盐岩礁滩体同生期暴露溶蚀作用模式[J]. 中国地质, 42(6): 1811−1821. [49] 郑剑, 王振宇, 杨海军, 孙崇浩, 张云峰, 陈景山. 2015. 塔中地区奥陶系鹰山组埋藏岩溶期次及其对储层的贡献[J]. 现代地质, 29(3): 665−674. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.03.018 [50] 朱光有, 杨海军, 朱永峰, 顾礼敬, 卢玉红, 苏劲, 张宝收, 范秋海. 2011. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区碳酸盐岩油气地质特征与富集成藏研究[J]. 岩石学报, 27(3): 827−844. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 乔俊程,常少英,曾溅辉,曹鹏,董科良,王孟修,杨冀宁,刘亚洲,隆辉,安廷,杨睿,文林. 塔里木盆地北部富满地区超深层走滑断裂带碳酸盐岩油气差异成藏成因探讨. 石油与天然气地质. 2024(05): 1226-1246 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: