-
摘要:
铌、钽矿产分布较广。内生铌钽矿成矿类型主要为伟晶岩型、稀有金属花岗岩型、碳酸岩型和碱性岩型;外生矿床多为内生矿床经过风化和沉积等外生作用发生二次富集的风化壳型和残坡积、冲积砂矿型。从成矿时代来看,伟晶岩型矿床成矿时代跨度较大,从3.08 Ga到0.19 Ga;碱性岩型矿床主要成矿期分别在2.25~1.35 Ga和0.75~0.19 Ga;碳酸岩型矿床成矿期主要分布在0.75~0.6 Ga和0.4~0.35 Ga;花岗岩型主要分布在0.75~0.19 Ga的中晚期。碳酸岩型铌矿床和伟晶岩型钽矿床是目前勘探的主要目标。
Abstract:Niobium and tantalum resources are widely distributed in the world. Their endogenous metallogenic deposits are mainly hosted in pegmatite, rare-metal granite, carbonatite, and alkaline rocks. Their exogenetic deposits are mostly the products of secondary enrichment through exogenous processes such as weathering and deposition from endogenous deposits. The metallogenic epoch of pegmatite-hosted deposits has a large span from 3.08 Ga to 0.19 Ga; alkaline rock-hosted deposits are at 2.25-1.35 Ga and 0.75-0.19 Ga respectively; carbonatite-hosted deposits are mainly in 0.75-0.6 Ga and 0.4-0.35 Ga; and granite-hosted deposits are mainly distributed in the middle and late stages of 0.75-0.19 Ga. At present, carbonatite-hosted niobium deposits and pegmatite-hosted tantalum deposits are the main exploration targets.
-
1. 引言
赣南地区位于南岭成矿带的东段,享有“世界钨都”之称,分布有包括西华山、漂塘、大吉山、画眉坳、盘古山等在内的与燕山期花岗岩有密切成因联系的钨锡多金属矿床(陈毓川等,1989;陈郑辉等,2006;毛景文等,2007;郭春丽等,2007;许建祥等,2008;刘善宝等,2010;方桂聪等,2014;刘丽君等,2017)。与石英脉型钨锡矿床有成因联系的花岗岩大多属于富含Li、F的高分异花岗岩(陈毓川等,1989;张文兰等,2006;王登红,2019;杨斌等,2021;秦拯纬等,2022),且通常伴有铍铌钽等稀有金属矿产,如大吉山矿区69号钽矿体(袁忠信等,1981)、画眉坳钨铍矿床、淘锡坑烂梗子区段的钨铍矿体等(刘善宝,2008)。这些高分异花岗岩与中国西部伟晶岩型锂铍稀有金属成矿花岗岩属于同一成因类型(袁忠信等,1981;李建康,2012;李建康等,2014;王登红等,2017;王成辉等,2019;Wang et al., 2020),但赣南地区石英脉型钨锡矿床是否共伴生有锂金属矿产却鲜有报道。本次工作在南岭东段赣南石雷矿区深部发现了云英岩型锂矿,证实了赣南石英脉型钨锡矿集区也有找锂矿的巨大潜力,这为进一步丰富研究赣南地区钨锡锂矿成矿理论研究和拓展岩体型锂矿找矿勘查空间提供了新思路。
2. 矿区地质特征
赣南位于南岭成矿带的东段,东邻武夷山成矿带,西接南北向的诸广山—万洋山岩浆岩带,由崇义—大余—上犹、于都—赣县、全南—定南—龙南等5个矿集区组成(图 1a)。石雷矿区位于赣南的西南部崇义—大余—上犹钨锡矿集区东段,北北东向的西华山—漂塘—茅坪矿田的中部(图 1b)。整个矿田长度约30 km,十余个矿床呈等间距分布(间距3~5 km),致矿花岗岩具有多阶段演化分异、多阶段侵入和多阶段成矿特征(毛景文等, 1998, 2007;裴荣富和熊群尧,1999;刘善宝等,2010)。
石雷矿区主要出露古生代碎屑岩地层。其中,寒武系类复理石建造分布广泛,且遭受了加里东期强烈褶皱,形成了西部正常东部倒转的复式向斜。泥盆系灰白色巨厚层状砾岩夹紫红色含砾砂岩及石英砂岩层零星分布,与下伏寒武系呈角度不整合接触。矿区中部地表主要出露加里东期石英闪长岩,呈北西展布,形成于434~439 Ma(He et al., 2010)。花岗岩是石雷矿区的主要致矿和赋矿地质体,侵入于石英闪长岩之中,并在接触带形成矽卡岩和似伟晶岩壳。花岗岩为隐伏岩体,钻孔揭露到花岗岩顶面最低标高为-52.93 m (ZK4901),最高标高162.87 m (ZK1107),与漂塘矿区的隐伏花岗岩体(岩凸最高标高为300 m)连为一体。岩相由早到晚依次是黑云母花岗岩((160±0.7)Ma)→二云母花岗岩((159.6±0.7)Ma)→白云母花岗岩((159.9±0.4)Ma),呈逐渐过渡关系,没有明显侵入界限(Zhang et al., 2017)。
矿区共发育7个脉带组,呈北东东走向,倾向北北西,倾角变化在69°~85°,矿脉带长度变化在500~ 1700 m,宽度变化在100~300 m,最大深度超过700 m;除中带脉带组产于加里东期石英闪长岩外,其余脉带均产于寒武系砂岩中,自上而下具有典型的“五层楼”分带特征。本次工作在对矿区11勘探线钻孔进行系统编录过程中,发现深部隐伏花岗岩顶部存在广泛的云英岩带。对钻孔ZKn11-11部分云英岩进行采样测试分析,其中的Li2O变化于0.204% ~0.514%(表 1)。根据其产状和矿物组成,含锂云英岩可以划分为石英脉(±钾长石)+云英岩、云母脉+ 云英岩等两种类型。
表 1 ZKn11-11云英岩W、Sn、Li测试分析结果Table 1. The W, Sn, Li analysis results of greisen samples of ZKn11-11
(1)石英脉(±钾长石)+云英岩复合型锂矿化体:该类型的矿化广泛分布于花岗岩体和围岩(角岩带)中(图 2)。产于角岩带中的石英脉+云英岩复合脉位于隐伏花岗岩体的上部,主要由早期的角岩化、黑云母化和晚期的石英脉复合叠加而成,上部石英呈团块状,下部石英呈脉状穿插于角岩之中(图 2a)。产于花岗岩内接触带二云母花岗岩内石英(±钾长石)+云英岩型锂矿化体以石英脉为中心,其两侧围岩发生云英岩化蚀变,云英岩与二云母花岗岩呈逐渐过渡关系(图 2b)。
![]() 图 2 石雷矿区钨锡锂多金属矿体特征a、e、f—产于角岩化砂岩中的石英脉与黑云母石英复合脉; b、c、g、h—产于二云母花岗岩中的石英脉+云英岩复合脉复合型钨锡锂矿体; i、j—产于二云母花岗岩中的长石石英脉; d、k、l—产于二云母花岗岩中云母脉+云英岩(含钨锡矿化)复合脉; Bt—黑云母; Qtz—石英; Mus—白云母; Kfs—钾长石; Wf—黑钨矿; Py—黄铁矿Figure 2. Characteristics of tungsten, tin and lithium polymetallic ore bodies in the Shilei mining areaa, e, f-Quartz vein and biotite quartz composite vein occurring in hornfelized sandstone; b, c, g, h-Composite W-Sn-Li ore body of Quartz vein and greisen composite vein occurring in mica granite; i, j-Feldspar quartz veins occurring in mica granite; d, k, l-Mica vein+greisen (containing tungsten tin mineralization) composite vein occurred in two mica granite; Bt-Biotite; Qtz-Quartz; Mus-Muscovite; Kfs-K-feldspar; WfWolframite; Py-Pyrite
图 2 石雷矿区钨锡锂多金属矿体特征a、e、f—产于角岩化砂岩中的石英脉与黑云母石英复合脉; b、c、g、h—产于二云母花岗岩中的石英脉+云英岩复合脉复合型钨锡锂矿体; i、j—产于二云母花岗岩中的长石石英脉; d、k、l—产于二云母花岗岩中云母脉+云英岩(含钨锡矿化)复合脉; Bt—黑云母; Qtz—石英; Mus—白云母; Kfs—钾长石; Wf—黑钨矿; Py—黄铁矿Figure 2. Characteristics of tungsten, tin and lithium polymetallic ore bodies in the Shilei mining areaa, e, f-Quartz vein and biotite quartz composite vein occurring in hornfelized sandstone; b, c, g, h-Composite W-Sn-Li ore body of Quartz vein and greisen composite vein occurring in mica granite; i, j-Feldspar quartz veins occurring in mica granite; d, k, l-Mica vein+greisen (containing tungsten tin mineralization) composite vein occurred in two mica granite; Bt-Biotite; Qtz-Quartz; Mus-Muscovite; Kfs-K-feldspar; WfWolframite; Py-Pyrite(2)云母脉+云英岩复合型钨锡锂矿体:产于花岗岩体内接触带的二云母花岗岩中(图 2c),含钨锡石英脉穿插于云英岩中,脉两侧的云英岩中也有浸染状的细粒黑钨矿和锡石产出。
3. 含锂云母成分分析和初步认识
本次研究对11号勘探线两个坑内钻孔ZK11-09、ZK11-10(图 3)中的3件样品进行了分析。将钻孔样品制备为为厚度为30 μm的探针片,然后在国家地质测试实验中心,通过激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)分析出云母的成分。分析结果见于表 2。石雷矿区云英岩中的云母中Li2O的含量介于0.18%~0.89%。其中,ZK11-10-B2样品中Li2O的平均含量为0.30%;ZK11-10-B4样品中Li2O的平均含量为0.43%;ZK11-09-B9样品中Li2O的平均含量为0.52%。根据云母的Fetot+Mn+Ti-AlⅥ-Mg-Li图解(图 4),石雷矿区云英岩中的云母应属于白云母—多硅白云母(Guggenhim and Bailey, 1977; Tischendorf et al., 1977; Brigatti et al., 2001)。
表 2 石雷矿区云英岩中云母LA-ICP-MS原位分析结果Table 2. LA-ICP-MS in-situ analysis results of mica of greisen in the Shilei mining area
云英岩是由花岗岩经高温热液作用形成的蚀变岩石,作为钨锡矿重要找矿标志,广泛发育于南岭钨锡矿床之中(陈毓川等,1989)。近年来,关于南岭成矿带及其邻区的钨锡矿床中云英岩带中富锂云母发现的报道陆续出现。不少的研究认为伴生于该类型的锂矿化主要赋存于铁锂云母-锂云母之中,例如栗木矿区的锂云母(李胜虎等,2015),大湖塘、香花岭、茅坪、漂塘、大厂矿区的铁锂云母(Legros et al., 2016, 2018;王正军等,2018;张勇等,2020;Guo et al., 2022)。石雷矿区云英岩中云母类型主要为Li含量较低的白云母—多硅白云母。根据矿山提供的钻孔样品测试分析结果,矿区深部、隐伏岩体顶部的云英岩化具有普遍性,其中仅中矿带角岩化砂岩中的云英岩的Li2O含量可达0.25%(视厚度为2.3 m);二云母花岗岩中发育视厚度为3.08 m,Li2O含量为0.15%~0.27%(平均0.21%)的石英(长石)脉—云英岩复合型锂矿化体;二云母花岗岩中发育的含云母脉云英岩连续4个样品(视厚度为3.08 m)的WO3含量为0.022%~2.61%,Sn为0.013%~ 0.93%;Li2O为0.14%~0.33%(平均0.22%),均达到共伴生品位要求,具有潜在的综合利用价值。该类型伴生的锂矿化的发现证实,钨锡矿中低锂含量云母的大量富集也可形成具有工业价值的锂矿体。此外,富锂云英岩主要发育于晚期的二云母花岗岩之中,其成矿来源显然不可能来自于稍早形成的黑云母花岗岩,但其成矿母岩是否为高分异的锂氟花岗岩,且钨锡矿与锂等稀有金属成矿关系如何依然有待进一步研究(Legros et al., 2018)。总之,该发现丰富了钨锡矿床的成矿理论,拓宽了区域云英岩型锂矿的找矿勘查思路,并为进一步该类型矿床的找矿空间提供了依据。
4. 南岭钨锡矿中云英岩型锂矿成矿潜力及找矿方向
随着锂云母提锂技术的逐渐成熟,赣西北九岭地区岩体型锂矿的找矿突破(李仁泽等,2020),赣南石英脉型钨锡矿床深部及外围云英岩型锂矿的引起了同行的关注(王学求等,2020;娄德波等,2022)。已有的资料表明(陈毓川等,1989),云英岩是岩浆气液交代花岗岩的产物,依据其形态,云英岩可以划分为岩体型和脉带型。岩体型云英岩主要分布于白云母花岗岩体的岩凸部位,如崇义县茅坪钨矿床,云英岩上部产有石英脉型钨锡矿脉带,其下是石英脉+云英岩脉带,呈“草帽”状,是岩体型和脉带型的复合型,主要含锂矿物为铁锂云母和含锂白云母,具有形成大型锂矿床的潜力;脉带型云英岩主要分布在花岗岩与围岩的内接触带上,如九龙脑岩体内洪水寨钨钼锂矿床,西华山钨矿床、张天堂岩体内塘飘孜钨矿床等,其赋矿围岩均为黑云母花岗岩,具有形成中型锂矿床的潜力。
以往的地质勘查工作仅评价云英岩中的钨锡矿,其共伴生云英岩中锂没有进行系统的评价。初步的野外地质调查表明,赣南地区已发现含锂矿物有铁锂云母(茅坪钨矿床、淘锡坝锡矿床等)、含锂多硅白云母(石雷钨锡矿床)、锂云母(铁山垅钨矿床外围),以铁锂云母为主,云英岩中锂含量的高低与含锂云母成正相关,现已发现铁锂云母脉的Li2O含量最高可达1.04%(淘锡坝)。西华山—漂塘—茅坪—塘漂孜钨矿带分布著名的西华山、漂塘、茅坪等大型钨锡矿床,其共伴生的云英岩均有不同程度锂矿化显示,个别矿床具有形成大型锂矿床的潜力。除对已知石英脉型钨锡矿床深部及外围云英岩开展锂矿地质勘查及评价工作外,需要注重对赣南地区花岗岩型锂矿床地质找矿工作部署。目前,龙南九曲地区已经新发现了白云母钠长石锂矿体,这为赣南地区寻找宜春“414”岩体型锂钽矿床提供了很好的线索。
总体上,南岭地区从早古生代特别到中生代强烈的断块运动及相伴随的岩浆活动,对内生稀有元素成矿起着主要作用,稀有元素成矿一般发生在多期活动的晚期岩体之中。随着国家科技水平不断提高, 新一轮科技革命的不断发展, 锂等战略性新兴产业矿产需求量将保持较快增长态势(王登红,2019;陈其慎等,2021;王成辉等,2022),南岭地区云英岩型锂矿的成矿作用研究和找矿勘查也将进一步得到重视。下一步工作中,需要开展同步的成矿理论研究工作,特别是一些复式岩体晚阶段岩浆作用与锂矿化的关系值得高度关注。
5. 结论
南岭东段石雷石英脉钨锡矿深部识别出云英岩型锂矿,含锂矿物主要为白云母-多硅白云母。其中,产于角岩化砂岩中的云英岩Li2O含量平均可达0.25%,二云母花岗岩中石英(长石)脉-云英岩Li2O含量平均为0.21%,二云母花岗岩中发育的含云母脉云英岩Li2O平均为0.22%,具有潜在的综合利用价值。南岭地区具有良好的岩体型锂矿成矿潜力和巨大的找矿前景,石英脉型钨锡矿深部及外围发育的云英岩是主要的找矿目标。
致谢: 南京地质调查中心陈世忠研究员对文稿进行了认真审阅和修改;审稿专家和编辑提出了宝贵修改意见。在此一并表示诚挚的感谢。 -
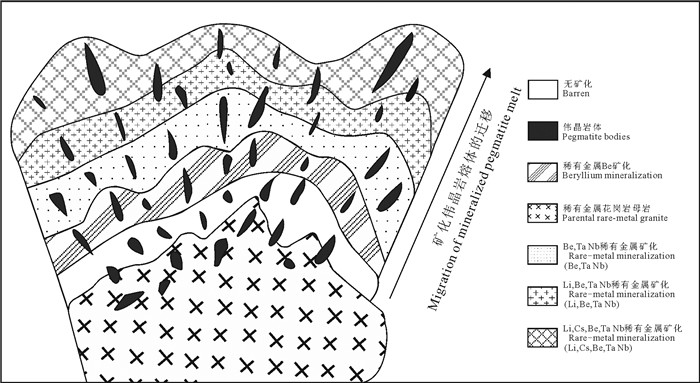
图 1 稀有金属花岗岩母岩之上含LCT伟晶岩分带及矿化示意图(改自Černý, 1991)
Figure 1. Schematic representation of LCT pegmatite zoning and mineralization above a parental granite (modified from Černý, 1991)
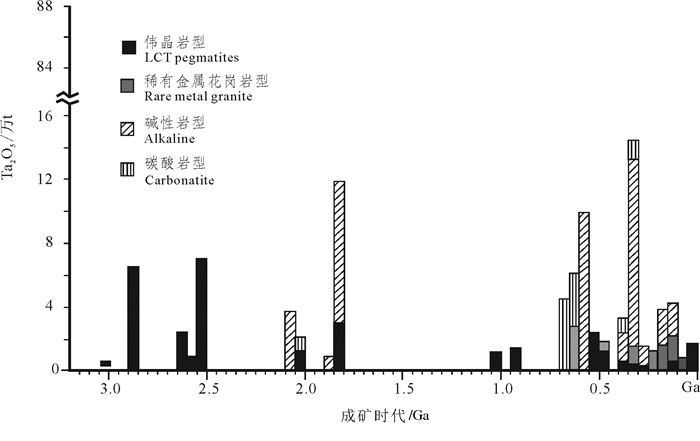
图 2 不同成矿类型钽矿成矿时代分布图(改自Tkachev et al., 2019)
Figure 2. Mineralization epoch distribution of different Ta metallogenic types (modified from Tkachev et al., 2019)
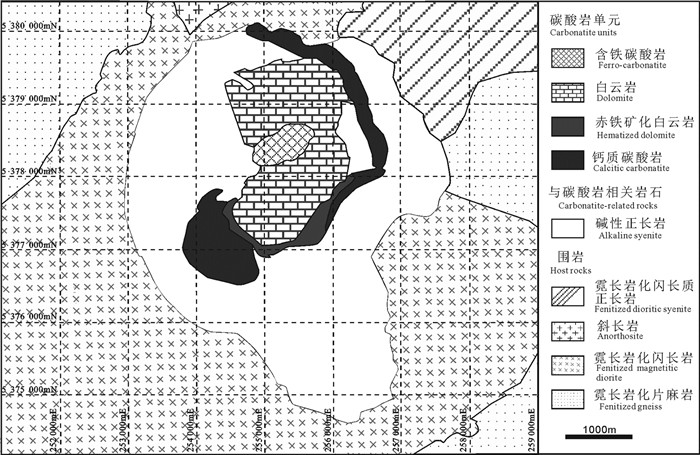
图 3 圣—奥能瑞碱性杂岩体示意图(改自Tremblay et al., 2017)
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of Saint-Honoré alkaline complex (modified from Tremblay et al., 2017)
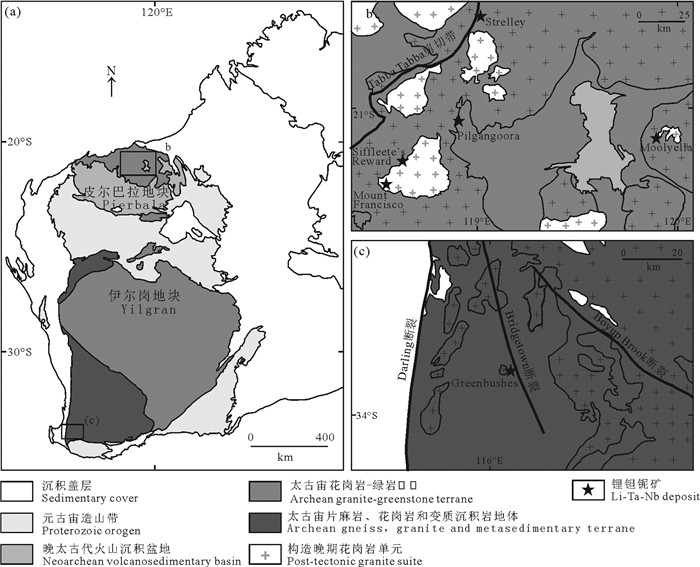
图 4 西澳克拉通伟晶岩型锂矿地质概况(据Kendall-Langley et al., 2020)
Figure 4. Distribution of lithium pegmatite deposits in Western Australia Craton (after Kendall-Langley et al., 2020)
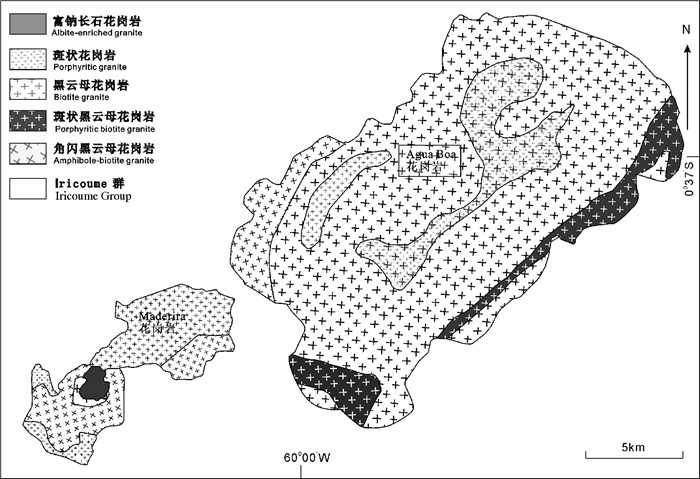
图 5 皮廷加成矿省Madeira花岗岩和Agua Boa花岗岩地质图(据Costi et al., 2002)
Figure 5. Geology map of Madeira granite and Agua Boa granite in Pitinga (after Costi et al., 2002)
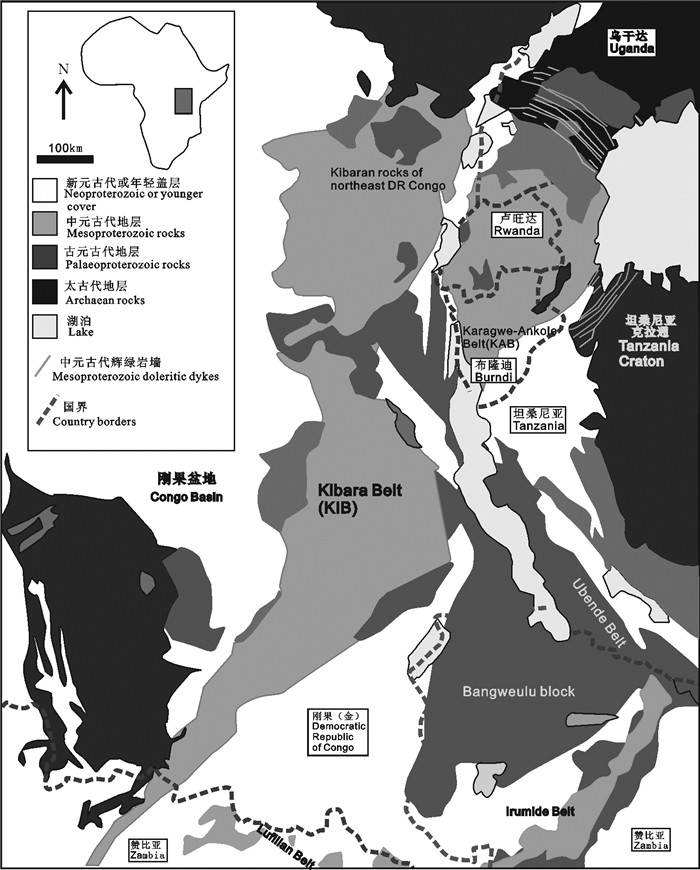
图 6 基巴拉褶皱带地质略图(改自Fernandez-Alonso et al., 2012)
Figure 6. Simplified geological map of Kibara fold belt(modified from Fernandez-Alonso et al., 2012)
表 1 铌钽矿床类型划分(据British Geological Survey, 2011)
Table 1 Classification of global Nb-Ta deposits(after British Geological Survey, 2011)

-
Bleiwas D I, Papp J F, Yager T R. 2015. Shift in Global Tantalum Mine Production, 2000-2014: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2015-3079[R]. 6.
Bradley D, McCauley A. 2013. A Preliminary Deposit Model for Lithium-Cesium-Tantalum (LCT) Pegmatites[R]. U.S. Geological Survey Open- File Report.
British Geological Survey. 2011. Nature environment research council[R]. Nottingham.
Cai Xiao, Song Yang, Wang Denghong, Li Jiankang, Zhou Wei, Ding Haiyang. 2013. Distribution rules and metallogenic geological characteristics of important foreign niobium-tantalum deposits[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica(Supp. ), 193-194(in Chinese).
Cao Fei, Yang Huipan, Zhang Liang, Wang Wei. 2019. Current situation and trend analysis of global tantalum and niobium mineral resources[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 39(5): 56-89 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Černý P. 1991. Rare-element granitic pegmatites, part II-Regional to global environments and petrogenesis[J]. Geoscience Canada, 18(2): 68-81. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285711507_rare-element_granitic_pegmatites_part_ii_regional_to_global_environments_and_petrogenesis
Černý P, Ercit T S. 2005. The classification of granitic pegmatites revisited[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 43: 2005-2026. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.43.6.2005
Costi H T, Dall Agnol R, Borges R M K, Minuzzi O R R. 2002. Tin-bearing sodic episyenites associated with the Proterozoic, A-type Agua Boa granite, Pitinga Mine, Amazonian Craton, Brazil[J]. Gondwana Research, 5(2): 435-451. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70734-6
Costi H T. 2009. The peralkaline tin-mineralized madeira cryolite albite-rich granite of Pitinga, Amazonian Craton, Brazil: Petrography, mineralogy, and crystallization processes[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 47: 1301-1327. doi: 10.3749/canmin.47.6.1301
Dewaele S, Tack L, Fernandez Alonso M, Boyce A J. 2008. Geology and mineralisation of the Gatumba area, Rwanda: Present state of knowledge[J]. Etudes Rwandaises, 16: 6-24. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/264542184_Geology_and_mineralization_at_the_Gatumba_area_Present_state_of_knowledge
Dewaele S, Henjes-Kunst F, Melcher F, Sitnikova M, Burgess R, Gerdes A, Fernandez M A, Clercq F D, Muchez P, Lehmann B. 2011. Late Neoproterozoic overprinting of the cassiterite and columbite-tantalite bearing pegmatites of the Gatumba area, Rwanda (Central Africa)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 61(1): 10-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2011.04.004
Dewaele S, Hulsbosch N, Cryns Y, Boyce A J. 2015. Geological setting and timing of the world-class Sn, Nb-Ta and Li mineralization of Manono-Kitotolo (Katanga, Democratic Republic of Congo)[J]. Ore Geology Review, 72: 373-390. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Niels_Hulsbosch2/publication/282563504_Geological_setting_and_timing_of_the_world-class_Sn_Nb-Ta_and_Li_mineralization_of_Manono-Kitotolo_Katanga_Democratic_Republic_of_Congo/links/576265b508ae2b8d20ed6efa.pdf
Doig R, Barton J M. 1968. Ages of carbonatites and other alkaline rock in Québec[J]. Canada Journal of Earth Science, 7: 22-28. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036855565210_20fa.html
Dorion J F, Hosseini Z. 2013. Implementation of a seismic system at Niobec Mine[C]//47th U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium. San Francisco, California.
Fernandez-Alonso M, Cutten H, De Waele B De, Tack L, Tahon A, Baudet D, Barritt S D. 2012. The Mesoproterozoic Karagwe-Ankole Belt (formerly the NE Kibara Belt): The result of prolonged extensional intracratonic basin development punctuated by two short-lived far-field compressional events[J]. Precambrian Research, 216-219: 63-86. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.06.007
Fetherston J M. 2004. Tantalum in western Australia[J]. Mineral Re-sources Bulletin, 22: 63-89.
Hulsbosch N, Hertogen J, Dewaele S, Andre L, Muchez P. 2014. Alkali metal and rare earth element evolution of rock-forming minerals from the Gatumba area pegmatites (Rwanda): Quantitative assessment of crystal-melt fractionation in the regional zonation of pegmatite groups[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 132: 349-374. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.006
Hulsbosch N, Boiron M C, Dewaele S, Muchez P. 2016. Fluid fractionation of tungsten during granite-pegmatite differentiation and the metal source of peribatholitic W quartz veins: Evidence from the Karagwe-Ankole Belt (Rwanda)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 175: 299-318. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.11.020
Jacobson M I, Calderwood M A, Grguric B A. 2007. Guidebook to the Pegmatites of Western Australia[M]. Carlisle W A: Hes-perian Press.
Kaeter D, Barros R, Menuge J F, Chew D M. 2018. The magmatic-hydrothermal transition in rare-element pegmatites from southeast Ireland: LA-ICP-MS chemical mapping of muscovite and columbite-tantalite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 240: 98-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.024
Kendall-Langley L A, Kemp A I S, Grigson J L, Hammerli J. 2020. U-Pb and reconnaissance Lu-Hf isotope analysis of cassiterite and columbite group minerals from Archean Li-Cs-Ta type pegmatites of Western Australia[J]. Lithos, 352-353: 105-231. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/ChlQZXJpb2RpY2FsRW5nTmV3UzIwMjEwMzAyEiAzYWY0MmFiNTZlODIwNzNhNDFhZjUyMmFkYzBiODM1NxoIdmVkOXUyaDE%3D
Küster D. 2009. Granitoid-hosted Ta mineralization in the Arabian-Nubian Shield-ore deposit types, tectono-metallogenetic setting and petrogenetic framework[J]. Ore Geology Review, 35: 68-86. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.09.008
Lehmann B, Halder S, Ruzindana Munana J, Ngizimana J P, Biryabarema M. 2014. The geochemical signature of rare-metal pegmatites in Central Africa: Magmatic rocks in the Gatumba tin-tantalum mining district, Rwanda[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144 (Part C): 528-538. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036044284810_564b.html
Li Jiankang, Li Peng, Wang Denghong, Li Xiangjie. 2019. A review of niobium and tantalum metallogenic regularity in China[J]. Chinese Sciences Bulletin, 64(15): 1545-1566 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/N972018-00933
Mackay D A R, Simandl G J. 2014. Geology, market and supply chain of niobium and tantalum——A review[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 49: 1025-1047. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0551-2
Makanga J F, Edou-Minko A. 2003. Etude petrographique et geochimique du complexe annulaire de mabounie (Ga-bon)[J]. African Journal of Science and Technology, 4(1): 67-77. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/272339342_Etude_Petrographique_et_Geochimique_du_Complexe_Annulaire_de_Mabounie_Gabon
McCausland P J, Pisarevsky S, Jourdan F, Higgins M. 2009. Laurentia at 571 Ma: Preliminary paleomagnetism and Ar-Ar age of the Ediacaran St Honore alkali intrusion, Quebec[C]//Proceedings, American Geophysical Union-Geological Association of Canada-Mineralogical Association of Canada-Canadian Geophysical Union, Joint Assembly, Toronto, Abstract GA12A-01.
Melcher F, Graupner T, Gäbler H-E, Sitnkova M, Henjes-Kunst F, Oberthus T, Gerdes A, Dewaele S. 2015. Tan-talum-(niobium-tin) mineralization in African pegmatites and rare metal granites: Constraints from Ta-Nb oxide mineralogy, geochemistry and U-Pb geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Review, 64: 667-719. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.003
Mitchell R H. 2005. Mineralogical and experimental constraints on the origions of niobium mineralization in carbonatites[G]//Linnen R L, Samson I M(eds. ). Rare-element Geochemistry and Mineral Deposits: Geological Association of Canada Short Course Notes.
Nicolas D K. 1962. The economic geology of columbium (Niobium) and of tantalum[J]. Economic Geology, 57(3): 377-404. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.57.3.377
Partington G A, McNaughton N J, Williams I S. 1995. A review of the geology, mineralization, and geochronology of the Greenbushes pegmatite, Western Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 90: 616-635. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.3.616
Pirajno F, González-álvarez I, Border A, Porter M. 2017. Mount Weld and Gifford Creek Rare Earth Elements Carbon-Atites[R]. Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (AusIMM), Monograph, 32: 163-166.
Pohl W L, Biryabarema M, Lehmann B. 2013. Early Neoproterozoic rare metal (Sn, Ta, W) and gold metallogeny of the Central Africa Region: A review[J]. Applied Earth Science, 122(2): 66-82. doi: 10.1179/1743275813Y.0000000033
Saeidi A, Heidarzadeh S, Lalancette S, Rouleau A. 2020. The effects of in situ stress uncertainties on the assessment of open stope stability: Case study at the Niobec Mine, Quebec(Canada)[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 25: 1-13. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352380820300460
Schulz K J, Piatak N M, Papp J F. 2017. Niobium and tantalum, chapter M of critical mineral resources of the United States: economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply[R]. USGS Professional Paper 1802, M1-M34.
Simandl G J, Burr R O, Trueman D L, Paradis S. 2018. Tantalum and niobium: Deposits, resources, exploration methods and market-a primer for geoscientists[J]. Journal of the Geological Association of Canada, 85-96. doi: 10.1002/9781118755341.ch15
Sweetapple M T, Holmes J, Young J, Grigson M W. 2017. Pilgangoora Lithium-Tantalum Pegmatite Deposit[R]. Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (AusIMM), Monograph 32: 339-342.
Sweetapple M T, Collins P L F. 2002. Genetic framework for the classification and distribution of Archean rare metal peg-matites in the North Pilbara craton, western Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 97: 873-895. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.97.4.873
Tkachev A V, Rundqvist D V, Vishnevskaya N A. 2019. Global metallogny of tantalum through geological time[J]. Geology of Ore Deposit, 61(6): 512-529. doi: 10.1134/S1075701519060060
Tassinari C C G, Macambira M J B. 1999. Geochronological provinces of the Amazonian craton[J]. Episodes, 22: 174-182. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1999/v22i3/004
Tremblay J, Bedard L P, Matton G. 2017. Columbitization of fluorcalciopyrochlore by hydrothermalism at the Saint- Honore alkaline complex, Quebec(Canada): new insights on halite in carbonatites[J]. Ore Geology Review, 91: 695-707. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.027
Trumbull R B. 1993. A petrological and Rb/Sr isotopic study of an early Archean fertile granite-pegmatite system: the Sinceni Pluton in Swaziland[J]. Precambrian Research, 61: 89-116. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(93)90059-B
Wang Wei, Hou Kejun, Wang Denghong, Yuan Linping, Liu Lijun, Lu Bingting. 2020. Columbite -Tantalite U-Pb dating of Yanshanina rare metal mineralization in western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 47(3): 890-891(in Chinese with English abstract).
Woolley A R, Kjarsgaard B A. 2008. Carbonatite occurrences of the world-Map and database[R]. Geological Survey of Canada Open File, 579-628.
Wu Xuemin, Zhou Minjuan, Luo Xicheng, Zhou Jianting. 2016. The metallogenic conditions and prospection potential of lithium and rare metals in northwestern Jiangxi[J]. East China Geology, 37(4): 275-283(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201604008.htm
Yang Yuandong, Li Jiye, Zhu Yongping, Liu Junyuan. 2020. Geological characteristics of a pegmatite niobium and tantalum deposit in the east of Manono, Congo[J]. Mineral Exploration, 11(7): 1428-1435(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Yong, Guo Weiming, Yao Chunyan, Zheng Di, Liu Junan, Xu Ming, Shen Mangting, Shen Xuehua. 2020. The Characteristics and Mineralization Potential of South American Craton Mineral Resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 203-205(in Chinese).
曹飞, 杨卉芃, 张亮, 王威. 2019. 全球钽铌矿产资源开发利用现状及趋势[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 39(5): 56-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH201905007.htm 蔡肖, 宋扬, 王登红, 李健康, 周伟, 丁海洋. 2013. 国外重要铌钽矿床分布规律及成矿地质特征[J]. 矿物学报(增刊), 193-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2013S2108.htm 李健康, 李鹏, 王登红, 李兴杰. 2019. 中国铌钽矿成矿规律[J]. 科学通报, 64(15): 1545-1566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201915002.htm 王伟, 侯可军, 王登红, 袁蔺平, 刘丽君, 吕秉廷. 2020. 川西燕山期稀有金属铌钽铁矿U-Pb年龄报道[J]. 中国地质, 47(3): 890-891. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200328&flag=1 吴学敏, 周敏娟, 罗喜成, 周建廷. 2016. 江西西北部锂及稀有金属成矿条件及找矿潜力分析[J]. 华东地质, 37(4): 275-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201604008.htm 杨远东, 李继业, 祝永平, 刘均沅. 2020. 刚果(金)马诺诺(Manono)东部某伟晶岩型铌钽矿地质特征[J]. 矿产勘查, 11(7): 1428-1435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2020.07.015 曾勇, 郭维民, 姚春彦, 郑镝, 刘君安, 徐鸣, 沈莽庭, 沈雪华. 2020. 南美克拉通矿产资源特征与成矿潜力[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 203-205. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张学艳,许强平. 安徽省无为市浪尖山黑色熔剂用石灰岩矿地质特征及开采技术条件分析. 地下水. 2025(01): 209-211 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 沈东升,鲍祺祺,邱钧健,古佛全,龙於洋. 氧化钙对危险废物焚烧飞灰热处理过程中铅释放的抑制. 环境科学学报. 2022(09): 238-244 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陆世才,农良春,叶胜,江沙,龙鹏,聂继绩,陈俊宏. 广西平广林场那厘矿区熔剂用石灰岩矿矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 现代矿业. 2022(08): 65-67+72 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: