Paleochannel distribution, delta development and paleoenvironment evolution in Bohai Bay since the Late Pleistocene
-
摘要:
渤海湾及其沿岸是中国海洋地质与第四纪地质研究程度最高的地区之一。虽然研究成果众多,但仍有一些基础的地质问题亟待解决。比如,晚更新世晚期黄河是否流经渤海湾?全新世黄河在渤海湾及其沿岸形成的多期次三角洲叶瓣在海域如何展布?以上问题一直是中国海洋地质研究中备受关注的热点话题。借助2016-2017年在渤海湾获取的约2000 km的浅地层剖面数据、2个30 m左右的取芯钻孔(BXZK2017-1和BXZK2017-2孔)及相应的AMS 14C和OSL测年数据,同时结合前人的一些浅剖数据和钻孔的研究成果,将渤海湾中部晚更新世以来的地层自上而下划分出4个地震单元(SU1~SU4)和6个沉积单元(DU1-DU6),分别对应前三角洲相、潮坪与浅海、泛滥平原、河道相、海陆交互相、湖沼相。在此基础上综合探讨渤海湾晚更新世晚期以来总体的地层框架和沉积演化特征。研究表明:黄河可能在21.8~9 cal ka BP,由近东西向流经渤海湾北部进入渤海中部盆地;全新世以来,渤海湾从西北侧至南侧,依次分布4期次的三角洲叶瓣,对应的发育时间可能分别是1400 AD~现在、11~1128 AD、700 BC~11 AD和1855~现在;渤海湾西侧最北两期次的水下三角洲可能主要与海河有关,而南侧其余2期次三角洲叶瓣则可能分别对应岐口超级叶瓣以及现代黄河三角洲超级叶瓣。加深了解渤海湾晚更新世晚期以来的地层序列演化、古河道发育以及全新世三角洲在渤海湾的展布情况,将有助于渤海湾海岸带开发、海底工程建设以及地质灾害防范等。
Abstract:The Bohai Bay and its coastal area are one of the most attractive hotspots for the studies of marine geology and Quaternary geology in China. Although many achievements have been made, some fundamental geological questions still remain unsolved. For example, did the Yellow River flow through Bohai Bay during the Late Pleistocene? How was the multi-stage delta lobes of the Yellow River Delta distribute in the Bohai Bay? Those questions have been attracting great attentions from marine geologists in China. Based upon ~2000 km seismic profile data, two ~30m-length boreholes (BHZK2017-1 and BHZK2017-2) in Bohai Bay during 2016-2017, numerous AMS 14C and OSL dating results and previous achievements of seismic profiles and boreholes, the stratigraphic sequences was divided into four seismic units (SU1-SU4) and six sedimentary units (DU1-DU6) in descending order, namely prodelta, tidal flat, floodplain, river channel, land-sea interaction facies and lacustrine/marsh facies, respectively. The general stratigraphic framework and sedimentary evolution of Bohai Bay since the Late Pleistocene were accordingly analyzed. It is revealed that the Yellow River likely flowed from near the East-West to the central basin of the Bohai Sea through the northern part of the Bohai Bay during 21.8-9 cal ka BP. Moreover, four subaqueous delta lobes distributed from the northwest to the south of the Bohai Bay since the Holocene were formed during 1400 AD-present, 1048-1128 AD, 700 BC-11 AD and 1855-present, respectively. Two northern subaqueous delta lobes were mainly related to the Haihe River, and the other two southern delta lobes were likely to be the Qikou superlobe and the modern Yellow River Delta superlobe respectively. The studies upon the sedimentary evolutions, paleochannel development and the subaqueous delta distribution since the Late Pleistocene would be conducive to the layout of coastal engineering programs and the mitigation of geological hazards in Bohai Bay.
-
1. 引言
淮河流域是中国中东部地区重要的商品粮主产区及能源资源供应区,流域内交错叠加了淮河生态经济区、山东半岛蓝色经济区、长江三角洲一体化发展区等重要国家战略规划,地理位置极其重要。1970年代以前淮河流域地下水长期处于自然因素主导的补排平衡状态,70年代中后期人工开采量增大,世纪之交达到巅峰并持续了十多年(葛伟亚,2007)。长期过量开采造成了诸多环境地质问题:地下水位持续下降、地面沉降、水质劣化(文冬光等,2012;陆徐荣等,2014),据2020年统计资料,流域浅层地下水位强下降区面积超过30000 km2。过量开采地下水造成的环境地质问题制约着区域社会经济发展,需要深入、持续开展地下水资源评价与开发利用潜力研究,为流域经济可持续发展提供地质数据支撑及解决方案。
流域地下水资源评价及研究工作在欧美起步较早,1930年代美国已经陆续开展了流域尺度地下水资源研究工作,德国中南部开展了持续的地下水要素评价、监测、示踪研究工作。20世纪中叶,以海河流域及淮河流域北部地区为首的流域地下水资源相关研究逐步开展。淮河流域已开展3次地下水资源评价工作,基本查明了不同时序、动态要素制约下的阶段性地下水资源禀赋。基于供水安全目的的流域尺度地下水化学特征调查开展多次,基本查明了流域地下水分布特征及水质现状❶(张炎斋和吴培任,2005;水艳和张炎斋,2009)。针对地下水开采引发的环境地质问题专项调查开展多次,如地面沉降调查、劣质水区地方病环境地质问题调查、苏北沿海环境地质问题综合调查等,阶段性查明流域环境地质问题,并建立了部分水文要素监测设施(陶月赞和岳文君,2003)。总之,淮河流域地下水相关调查及研究积累了大量的数据及成果,为区域水资源可持续开发利用提供了相当丰硕的参考依据,但也存在一定的讨论空间:一是更高生态约束条件下的地下水资源评价和开发潜力研究尚需深入开展工作;二是地下水资源动态平衡特征需要进一步研究。本文数据基于“沙颍河-涡河流域水文地质调查”项目,在第二次全国地下水资源评价数据基础上,利用区内20年来开展的1∶5万水文地质调查成果、蚌埠和郑州水文试验站试验成果、2019年以来的流域专项水文试验成果,校核更新了流域水文地质参数,重点参考2019、2020年水均衡要素数据,在流域新的生态约束条件下开了淮河流域地下水资源特征和开发潜力研究。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 范围
淮河流域(包括山东半岛)位于111°55′~122°45′E、30°55′~38°05′N,面积约33万km2,流域主要覆盖河南、安徽、江苏、山东四省(图 1)。
2.2 降水特征
淮河流域处于中国南北气候过渡带,流域内多年平均降水量600~1400 mm,空间上降水量由南向北递减。降雨量的年际、年内分布极不均匀,差异较大,汛期(6—9月)降水占全年降水的50%~70%(图 2)。
2.3 含水系统
淮河流域地下水主要分为松散岩类孔隙水、碳酸盐岩类裂隙岩溶水和基岩裂隙水3种类型。其中分布最广的为松散岩类孔隙水,其次为岩溶水和基岩裂隙水,但有供水意义的主要为孔隙水和岩溶水。
平原区松散岩类孔隙水在区内分布最为广泛,按其埋藏深度可分为浅层地下水和深层地下水。在流域内平原区地表下30~55 m,区域上广泛分布有一层14~20 m厚的黏性土层,因此,传统上大致以地表下50 m为界限,将埋深小于和大于50 m的松散岩类孔隙含水层组分别划分为浅层含水岩组和深层含水岩组(葛伟亚,2006)。
淮河流域上游地区地下水基本是由西北流向东南,南部西部则由西向东流。北部岗状平原区浅层孔隙地下水水位埋深一般大于6 m;北部低缓平原区地下水水位埋深大部分为2~4 m;南部地下水水位埋深大部分小于2 m。浅层孔隙地下水水位主要受降水和蒸发及地表水影响,水位变幅一般为1.5~2.5 m。淮河流域深层地下水整体流向为从山前向平原径流,整体水位稳定,受季节影响较小,在阜阳—太和、亳州等地形成地下水位降落漏斗,江苏省盐城市附近深层地下水位呈逐年上升趋势。
3. 研究方法及数据来源
3.1 评价方法
山区采用径流模数法进行地下水资源评价,平原区采用均衡法进行评价。平原区地下水以孔隙水为主要评价本体。流域内承压孔隙水补给条件艰苛,深层承压孔隙地下水年龄均在25 ka以上(龚建师,2005),目前生态约束条件下,认为该层地下水为不可更新地下水,未做资源评价。
地下水质量评价依据《地下水质量标准》(GB/T14848-2017), 采用单因子综合评价法,对35项常规无机化学指标进行评价。
地下水开采潜力评价参照《地下水潜力评价技术要求》(GWI-D4)开展相关评价,潜力表征参数为开采潜力系数,该系数为可采量与现状开采量的比值,系数≥1.4,表示潜力大,1.2~1.4表示潜力较大,1.0~1.2,表示潜力较小,系数<1.0表示无潜力。
3.2 数据来源
以第二次地下水资源评价数据为基础,汇总域内2000年以来开展的120余幅1∶5万水文地质调查工作成果、城市地质调查成果,参考域内两个水文试验站相关试验成果,结合“沙颍河—涡河流域水文地质调查”项目野外实验,校核更新了流域的降雨入渗系数、含水层导水系数、山丘区地下水径流模数、山前侧向补给系数、弹性释水系数、渠系入渗系数等水文地质参数。
通过收集气象部门数据,汇总更新了流域降水、蒸发数据。
通过收集水利公报数据,结合野外典型断面校核实测数据,融合汇总了流域水文参数及地下水资源开发利用数据。
4. 结果与分析
4.1 水循环要素演变
4.1.1 降水补给要素变化
降雨量按照多年平均降雨量统计,统计结果如图 3所示。结果显示,不同阶段淮河流域多年平均降雨量差异不大,1980年以前为2390亿m3/a,1980—1999年为2317亿m3/a,2000—2018年为2339.8亿m3/a。
4.1.2 蒸散发排泄要素变化
2000年以前的蒸散发量按《淮河流域水污染治理与水资源可持续利用》中给出的蒸散发量进行统计,2000—2018年蒸散发量按照降雨量、产流、入渗、其他排泄量等进行计算(吴祖成,2016;薛阳等,2017)。淮河流域多年平均蒸散发量变化如图 4所示。1980年以前,流域多年平均蒸散发量1560.67亿m3/a,1980—1999年多年平均蒸散发量1538.49亿m3/a,2000—2018年多年平均蒸散发量为1529.6亿m3/a。数值差异不大,但呈持续微弱下降趋势。
4.1.3 人工开采要素变化
淮河流域开发利用地下水历史较早,以开采平原区浅层地下水用于农业灌溉为主。建国初期,只有少量的土井开采地下水用作农灌和居民生活,工业用水开采地下水很少。
从淮河流域开采量历史变化(图 5)可以看出,30多年来地下水开采量增长迅速。20世纪70年代地下水开采量约79.81亿m3/a,80年代地下水开采量约87.28亿m3/a,90年代地下水开采量约为131.28亿m3/a,到了2000—2004年年均地下水开采量增加到138.03亿m3/a。70年代、80年代开采量变化不大,到了90年代跨越式增长,2000—2018年开采量呈波动稳定状态。通过上述数据,结合流域社会经济发展阶段,以及2000年加大治淮力度等时间节点,可以把淮河流域人工开采地下水历史划为3个典型阶段,即1980年以前,1980—1999年,2000—2018年3个阶段(图 6)。
4.1.4 地下水位变化
淮河流域地下水循环条件演化的主导因素为人工开采,在流域内人工开采最严重的为豫东平原、鲁西南地区、皖北平原、苏北平原。据2005年及2020年流域地下水位统测数据,淮河流域浅层地下水水位大部分呈下降趋势,15年来浅层地下水明显下降区面积达3.2万km2。
4.2 地下水资源状况
4.2.1 地下水资源评价分区
根据统一性、系统性、层次性、继承性原则,结合淮河流域特殊的地理、气象、地质地貌背景,有针对性的对淮河流域进行地下水资源分区。淮河流域可划分为1个一级分区、3个二级分区、6个三级分区、15个四级分区(表 1、图 8)。
表 1 淮河流域水文地质单元划分表Table 1. Hydrogeological unit division of Huaihe River Basin
4.2.2 地下水资源及空间分布
流域浅层天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a,其中平原区天然资源量为234.8502亿m3/a,山丘区天然资源量为94.6929亿m3/a,山丘和平原区重复计算量为2.5775亿m3/a。按地下水四级区统计,南四湖水系平原天然资源量为17.91亿m3/a;淮河水系近代黄泛平原区天然资源量为31.68亿m3/a;南四湖水系山区天然资源量为4.11亿m3/a;鲁北诸河水系平原区天然资源量为5.69亿m3/a;沂沭河水系平原区天然资源量为40.31亿m3/a;沂沭河水系山区天然资源量为23.61亿m3/a;胶东低山丘陵南坡诸河水系区天然资源量为10.20亿m3/a;胶东低山丘陵北坡诸河水系区天然资源量为5.56亿m3/a;鲁北诸河水系山区天然资源量为14.00亿m3/a;淮河水系波状平原天然资源量为13.86亿m3/a;淮河水系与长江水系过渡区天然资源量为13.73亿m3/a;黄淮冲积、海积平原天然资源量为84.10亿m3/a;淮河流域大别山区天然资源量为21.89亿m3/a;淮河水系山前平原天然资源量为22.89亿m3/a;淮河流域伏牛山区天然资源量为17.41亿m3/a。按省统计,山东天然资源量为82.515亿m3/a;河南天然资源量为83.203亿m3/a;安徽天然资源量为71.134亿m3/a;江苏天然资源量为87.755亿m3/a,湖北浅层水天然资源量为2.359亿m3/a(图 9、图 10)。
4.3 地下水质量现状
利用2019年国家地下水监测工程780个测孔测试数据及2019年区域460组水化学测试数据,基于35个常规无机化学指标,开展流域主要平原地区地下水质量评价。结果显示,淮河流域地下水质量总体一般,浅层地下水Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比6.7%,Ⅳ~Ⅴ类水样品占比93.3%,深层地下水Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水占比8.5%,Ⅳ~Ⅴ类水样品占比91.5%。浅层地下水和深层地下水主要影响因子均为铁、锰、硬度等指标,淮北平原、苏北局部地区、豫东鲁西南局部地区深层地下水砷、氟超标严重。
与2005、2010年淮河流域地下水质量评价结果对比,现状浅层地下水质量在经历了2005—2010年显著恶化后,近年在地表水质量总体好转的情况下,仍在趋于恶化,总体超标水比例增加了4.3%,但Ⅴ类水降低了6.2%(图 11)。
深层水超标率从2005年的51.6%到2010年65.9%,近年呈现出显著恶化趋势,2019年超标水比例已上升25.6%,达2005—2010年恶化趋势的1.8倍,且Ⅳ、Ⅴ均呈大幅上升趋势。
4.4 地下水开采潜力
采用开采潜力系数法进行区域地下水开采潜力评价。由于区域深层地下水在新的生态约束条件下无可利用资源量,故现状深层地下水开采区均为无潜力区。
浅层地下水(含基岩裂隙水)开采潜力总体上南部大于北部,山区-平原复合行政区大于纯平原行政区。其中江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区、河南南部地区浅层地下水开采潜力较大,豫东地区、山东大部分地区开采潜力小,郑州、开封、许昌、漯河、商丘、周口、济宁、淄博、菏泽超采严重,已无潜力(表 2)。
表 2 浅层地下水开采潜力状况(108m3/a)Table 2. Exploitation potential of shallow groundwater (108 m3/a)
5. 讨论与建议
淮河流域人均水资源量为475 m3,不足全国人均水资源量(2012年,2100 m3)的1/4,加上水质劣化,使得水资源供需矛盾更加突出。南水北调中线工程对豫东供水、东线工程对苏皖鲁供水一定程度缓解了域内缺水问题,但在新时期高质量发展导向的生态约束条件下,水资源供需形势仍然严峻。且一定程度的人工干预水资源配置造成了水文要素异化反馈,亟待开展相关科学研究。为进一步缓解淮河流域水资源供需矛盾,优化水资源配置问题,提出以下建议:
(1)深入开展流域尺度地下水地表水一体化调查研究,逐步寻求科学途径,解决流域水资源配置现状。目前,流域内重地表水配置、轻地下水参与,如2001—2019年,地表水利用率达65.2%,地下水利用率为53.1%,应合理配置不同时空条件下的地表水、地下水利用占比。
(2)开展劣质水区地下水资源系统调查,提出基于水质安全的可持续供水建议。淮河流域地下水质量问题是困扰流域浅层地下水开发的主要问题,部分地区高氟、高砷、高碘地下水造成的地方病在区内仍有发生,2019年测试数据显示豫东皖北苏北等地浅层地下水样本氟化物含量超标占比26.22%,碘化物超标占比20.64%,豫东皖北苏北等地深层水样本氟化物含量超标率27.92%,碘化物超标47.17%。安全供水需求导向的水资源调查工作需要深入开展。
(3)南水北调东线工程、引江济淮工程在改善北方缺水地区水资源利用问题的同时,也造成了沿线部分受水区水位不稳定变化,由此引起一定生态响应,如土壤盐渍化、水质变化等,需要加强沿线受水影响区水文要素监测工作,为水资源配置精细化管理、生态响应科学问题研究提供支撑。
6. 结论
(1)受人工开采持续增大影响,流域地下水循环特征发生变化,浅层地下水位持续下降,豫东、鲁西南地区2005年以来浅层地下水位下降5 m以上面积超过30000 km2。浅层地下水位下降导致有效蒸发强度变弱,蒸发量持续下降,多年平均有效蒸发强度从2000年前的1538.49 mm降至近期的1529.6 mm。
(2)淮河流域浅层地下水天然资源量为326.97亿m3/a,人均171.19亿m3/a,地下水资源相对一般。
(3)淮河流域平原地区地下水总体一般,浅层、深层孔隙水Ⅴ类水占比分别达47.7%、44.9%;与2005年、2010年历史数据相比,水质呈劣化趋势,2019年测试数据显示区域地下水中高氟水、高碘水占比仍在20%以上,深层地下水碘化物超标近半。
(4)浅层地下水开发盈余量总体南多北少、山区多平原少;江苏全域、安徽沿淮地区总体开采潜力大,可采系数均在1.0以上,最大达103.92×108 m3/a,豫东、鲁西南地区开采潜力小,部分地市如漯河、周口、菏泽等地超采严重,已无潜力。
注释
❶叶念军,葛伟亚,龚建师,杨则东,左正金,陆徐荣,徐建国,王献坤,杨小双,彭玉怀,王付军,赵华荣,刘红樱,朱恒华,陆华,杨佩明,徐华,陈秀其,杨磊,程生平,周锴锷,邢怀学,穆倩,朱春芳,陈鸿汉,李炳华. 2012. 淮河流域环境地质调查报告[R]. 南京:中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心.
致谢: 感谢项目组成员赵广明、丁喜桂、王锦以及山东科技大学博士生凌子龙,研究生郭若舜和贵州大学研究生金宗玮在野外调查、室内分析和论文写作过程中给予的帮助。 -
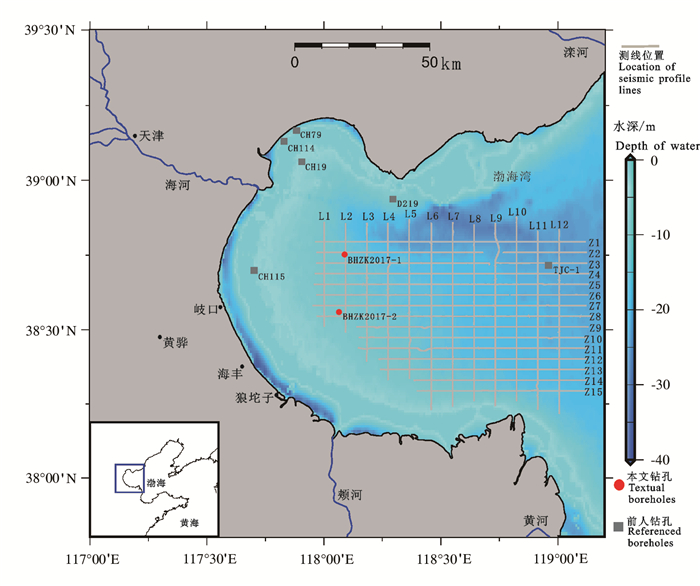
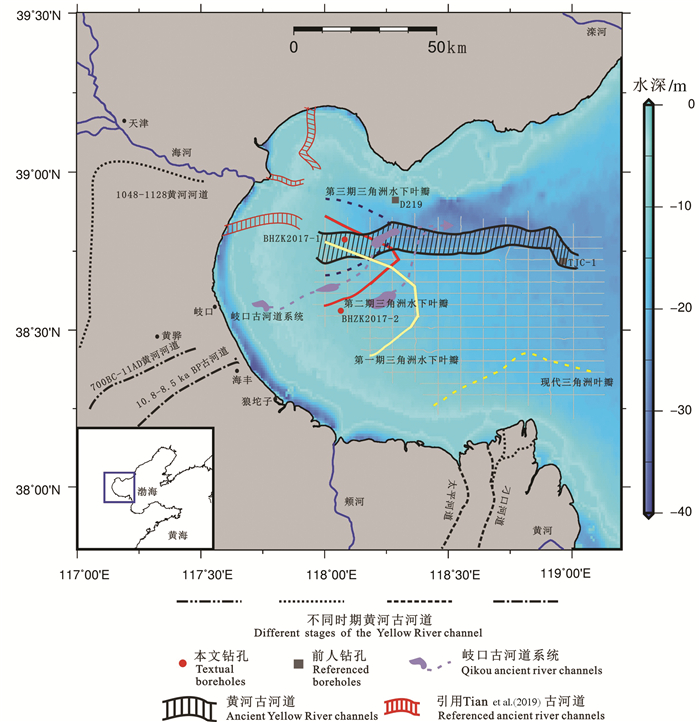
图 1 渤海湾浅地层剖面测线和钻孔位置分布图
钻孔CH19、CH79、CH114和CH115引自Tian et al., 2017;钻孔TJC-1李杰等,2018;钻孔D219胡广元等,2017
Figure 1. Location of boreholes and seismic profile lines in Bohai Bay
Boreholes CH19, CH79, CH114 and CH115 were cited from Tian et al., 2017; Borehole TJC-1 is introduced from Li Jie et al., 2018; Borehole D219 is quoted from Hu Guangyuan et al., 2017
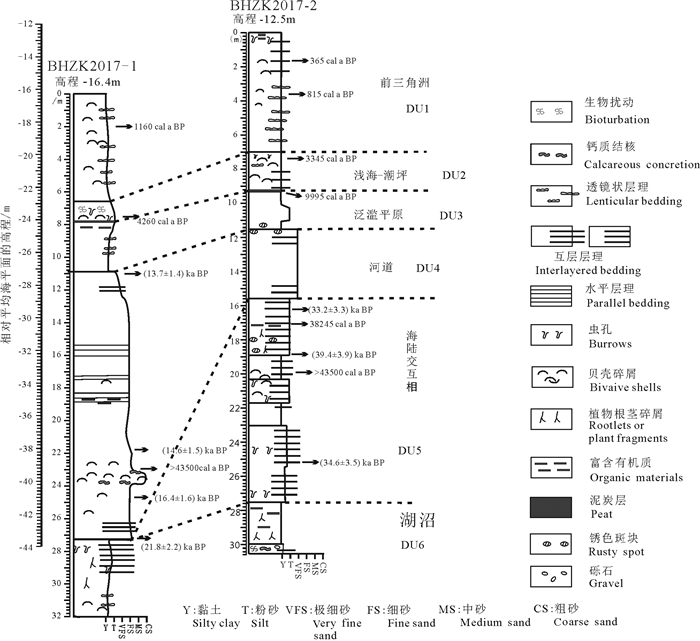
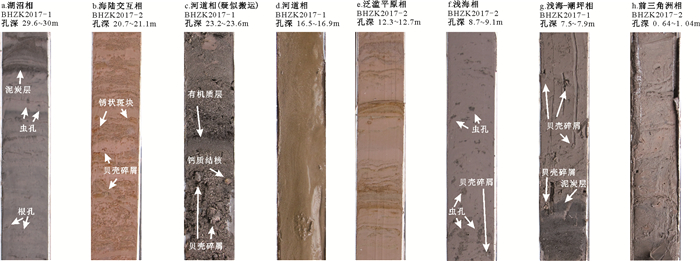
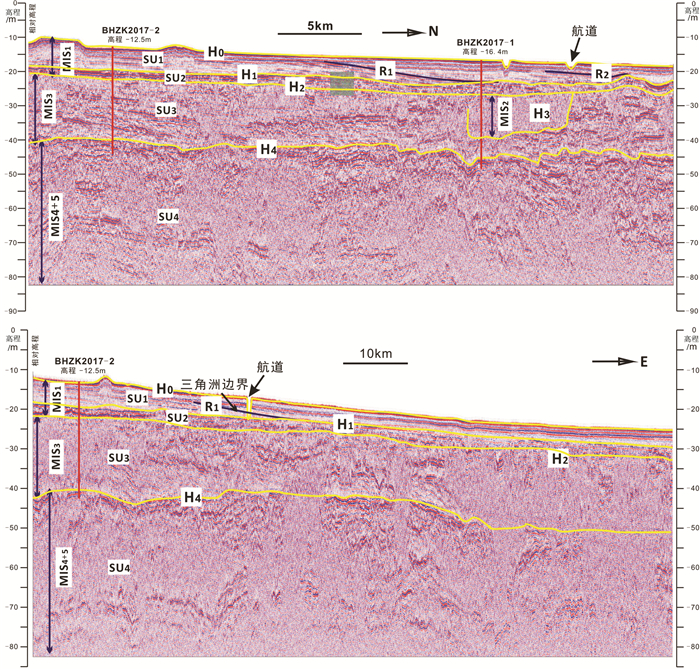
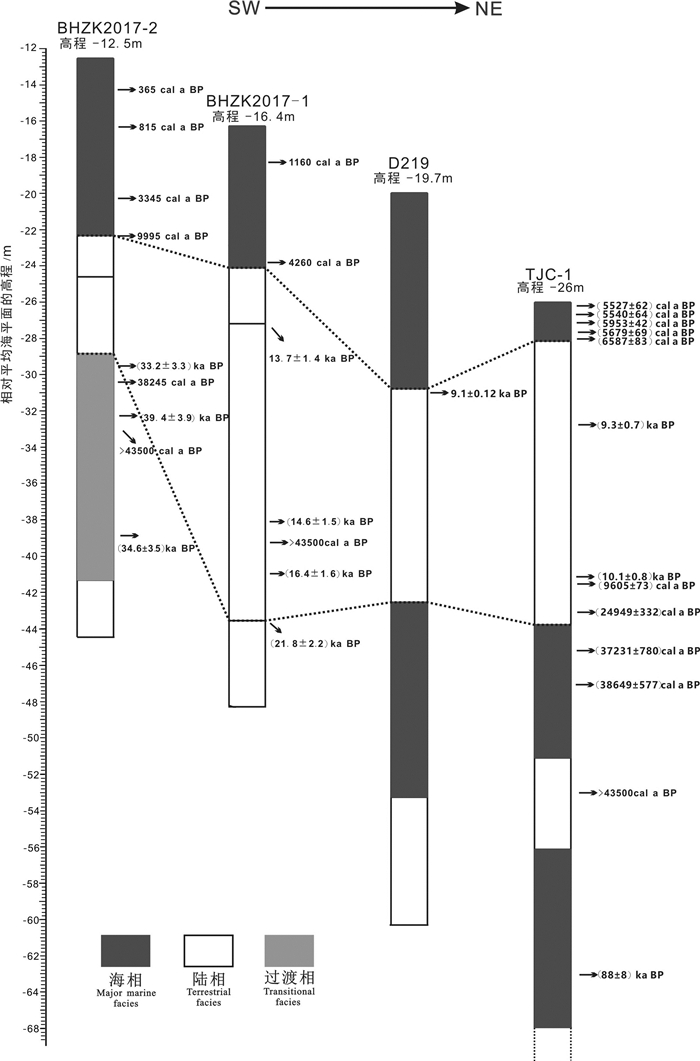
图 7 渤海湾钻孔晚更新世以来的区域地层对比
D219钻孔胡广元等,2017;TJC-1钻孔李杰等,2018
Figure 7. Regional comparison of the strata in the boreholes of Bohai Bay since the Late Pleistocene
Borehole D219 is quoted from Hu Guangyuan et al., 2017; borehole TJC-1 is quoted from Li Jie et al., 2018
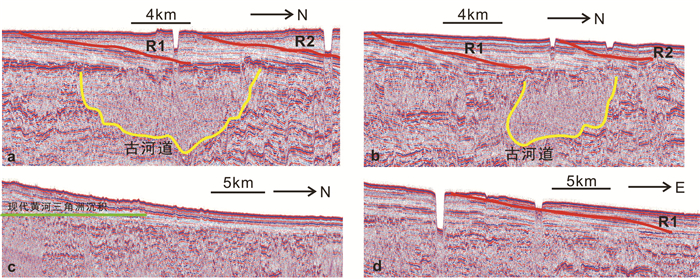
图 8 渤海湾古河道及水下三角洲范围分布图
海河入海口附近红色古河道段引自Tian et al., 2017;岐口古河道系统胡广元等,2017;10.8~8.5 ka BP古河道段引自Xu et al., 2015;700BC—11AD黄河河道、1048—1128黄河河道、太平河道和刁口河道薛春汀等,2003
Figure 8. Distribution of ancient river channels and phases of subaqueous deltas in Bohai Bay
The red ancient river section near the Haihe River estuary is cited from Tian et al., 2017; the Qikou ancient river system is cited from Hu Guangyuan et al., 2017; the 10.8 ~ 8.5 ka BP ancient river section is cited from Xu et al., 2015; the 700BC-11AD Yellow River, 1048-1128 Yellow River, Taiping River and Diaokou River are cited from Xue Chunting et al., 2003
表 1 渤海湾地区钻孔位置
Table 1 Location of boreholes in Bohai Bay

表 2 渤海湾钻孔AMS 14C测年数据
Table 2 List of AMS 14C ages from boreholes in Bohai Bay

表 3 渤海湾钻孔光释光(OSL)测年数据
Table 3 List of OSL ages from boreholes in Bohai Bay

-
Chen Yongsheng, Wang Fu, Tian Lizhu, Li Jianfen, Shang Zhiwen, Wang Hong, Qi Wuyun. 2014. Holocene sedimentation rates and their response to fluvial supply on thewest coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(10): 1582-1590 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286006410_Holocene_sedimentation_rates_and_their_response_to_fluvial_supply_on_the_west_coast_of_Bohai_Bay
Cheng Guodong, Ren Yucan, Li Shaoquan, Li Guangxue, Dong Wan. 1986. Evolution andvertical sequence of river channels in the modern Yellow River delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 6(2): 3-17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng Guodong, Xue Chunting. 1997. Sedimentary Geology of Yellow River Delta[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-8 (in Chinese).
Coast Studies Group, Department of Geography. 1974. The subaqueous delta of the Hai-Ho and silting problem of Tientsin New Port[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natual Science), (1): 80-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-NJDZ197401007.htm
Dong Lixian, Su Jilan, Wang Kangshan. 1989. Tide current in the Yellow Sea and its relationship with sediment transport[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 11: 102-114. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303140951_Tide_current_in_the_Yellow_Sea_and_its_relationship_with_sediment_transport
Du Ruizhi, Liu Guoxian, Yang Songlin, Zhou Yihua, Zhang Bing. 1990. Modern sedimentation rate and sedimentation process in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 10(3): 15-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ199003001.htm
Fu Zhaohui, Chen Fajing, Li Min, Shi Pitong, Min feiqiong. 2008. Sedimentary characteristics of the Xinbei oilfield and their controls on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Geology in China, 35(4): 691-698 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200804014.htm
Gao Ruiqi, Zhao Wenzhi, Kong Fanxian. 2004. The Young Explorers Discussed Ptroleum Geology of Bohai Bay Basin[M]. Beijing: Ptroleum Industy Press (in Chinese).
Gao Shanming. 1981. Sedimentary model in Luanhe river[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 26: 895-896 (in Chinese).
He Lei, Xue Chunting, Ye Siyuan, Alessandro Amorosi, Yuan Hongming, Yang Shixiong, Edward A Laws. 2019. New evidence on the spatial-temporal distribution of superlobes in the Yellow River Delta Complex[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 214: 117-138. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.05.003
He Lei, Ye Siyuan, Yuan Hongming, Xue Chunting. 2019. Rethinking the spatio-temporal distribution of Lijin superlobei n the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 74(1): 146-616 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/333192045_Rethinking_the_spatio-temporal_distribution_of_Lijin_superlobe_in_the_Yellow_River_Delta
Hori Kazuaki, Saito Yoshiki. 2007. An early Holocene sea-level jump and delta initiation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(18): L18401. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031029
Hu Guangyuan, Zhuang Zhenye, Yin Ping, Zhao Dongpo, Liu Shuang, Wang Ling. 2017. The hole D219 and the Late Quarternary paleogeographic environments in the northern Bohai Bay, China[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(6): 16-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201706003.htm
Institute of Oceanography. 1985. Chinese Academy of Sciences. Geology of Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985 (in Chinese).
Li Guangxue., Wei Helong, Yue Shuhong, Cheng Yiji, Han Yeshen. 1998. Sedimentation in the Yellow River delta, part Ⅱ: Suspended sediment dispersal and deposition on the subaqueous delta[J]. Marine Geology, 149: 113-131. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00032-2
Li Jie, Li Rihui, Yang Shixiong, Chen Xiaohui, Chen Shanshan. 2018. Pollenspore assemblages and induced palaeoenvironmental changes in the western Bohai Seasince Late Pleistoene[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 38(2): 115-128 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201802012.htm
Liu Chuncheng, Dai Fugui, Yang Jin, Yang Kesheng. 2010. Seismic interpretation of Eogene-Neogene geological structures and tectonic styles in the sea area of Bohai Gulf basin[J]. Geology in China, 37(6): 1545-1558 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201006002.htm
Liu J Paul, John D Milliman, Gao Shu, Cheng Peng. 2004. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, north Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 209(1/4): 45-67. http://ieg.or.kr/include/file_down.php?save_path=/data1/ref&filename=00310209001000045.pdf&filename2=00310209001000045.pdf
Liu Jian, Wang Hong, Wang Feifei, Qiu Jiandong, Saito Yoshiki, Lu Jingfang, Zhou Liangyong, Xu Gang, Du Xiaolei, Chen Qiang. 2016. Sedimentary evolution during the last ~1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 451: 84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.03.012
Liu Jian, Zhang Xunhua, Mei Xi, Zhao Quanhong, Guo Xingwei, Zhao Weina, Liu Jianxing, Yoshiki Saito, Wu Zhiqiang, Li Jie, Zhu Xiaoqing, Chu Hongxian. 2018. The sedimentary succession of the last ~3.50 Myr in the western South Yellow Sea: Paleoenvironmental and tectonic implications[J]. Marine Geology, 399: 47-65. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.11.005
Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Du Jun, Xia Dongxing, Li Ping, Xue Zuo, Hu Weifen, Yu xiaoxiao. 2014. Evolution of the buried channel systems under the modern Yellow River Delta since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary International, 349: 327-338. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.061
Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Liu Chenguang, Zheng Yanpeng, Li Peiying, Zhang Zhiwei. 2019. Seismic stratigraphy and morphology of the Holocene progradational system beneath Bohai Bay, Bohai Sea: Lobate evolution of a multi-sourced subaqueous fluvidelataic comlpex[J]. Marine Geology, 409: 31-47. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.12.009
Liu Yanxia, Huang Haijun, Dong Huijun, Qi Yali, Zhang Yi. 2015. Geomorphic charateristicsnd location of the maximum Holocene trangression boundary in the southwestern coast of the Bohai Sea[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 35(2): 340-353 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Qiu Jiandong, Liu Jian, Saito Yoshiki, Wang Hong, Yang Zigeng, Nakashima Rei. 2014. Sedimentary evolution ofthe Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Southern Shandong Peninsula in theWestern South Yellow Sea[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 13 (5): 747-760. doi: 10.1007/s11802-014-2227-z
Reimer Paula J, Bard Edouard, Bayliss Alex, Beck J Warren, Blackwell Paul G, Ramsey Christopher Bronk, Buck Caitlin E, Cheng Hai, Edwards R Lawrence, Friedrich Michael, Grootes Pieter M, Guilderson Thomas P, Haflidason Haflidi, Hajdas Irka, Hatte Christine, Heaton Timothy J, Hoffmann Dirk L, Hogg Alan G, Hughen Konrad A, Kaiser K Felix, Kromer Bernd, Manning Sturt M, Niu Mu, Reimer Ron W, Richards David A, Scott E Marian, Southon John R, Staff Richard A, Turney Christian S M, Plicht Johannes van der. 2013. IntCal13 and marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0-50000 years cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 55: 1869-1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947
Saito Yoshiki, Wei Helong, Zhou Yongqing, Akira Nishimura, Yoshio Sato, Setsuya Yokota. 2000. Delta progradation and chenier formation in the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18: 489-497. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00080-2
Southon John, Kashgarian Michaele, Fontugne Michel, Merivier Bernard, Yim Wyss. 2002. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia[J]. Radiocarbon, 44: 167-180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778
Su Shengwei, Shang Zhiwen, Wang Haifeng, Wang Hong. 2011. Holocene cheniers: Spatial and temporal distribution and sea levelindicators in Bohai Bay[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(9): 1382-1395 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201109007.htm
Tan Qixiang. 1981. The lower reaches of the Yellow River before the Western Han Dynasty[J]. Historical Geography, (1): 48-64(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tian Lizhu, Chen Yanping, Jiang Xingyu, Wang Fu, Pei Yandong, Chen Yongsheng, Shang Zhiwei, Li Jianfen, Li Yan, Wang Hong. 2017. Post-glacial sequence and sedimentation in the western Bohai Sea, China, and its linkageto global sea-level changes[J]. Marine Geology, 388: 12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.04.006
Wang F, Li J, Chen Y, Fang J, Zong Y, Shang Z, Wang H. 2015. The record of Mid-holocene maximum landward marine transgression in the west coast of Bohai Bay[J]. China Marine Geology, 359: 89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.11.013
Wang Haifeng, Pei Yandong, Liu Huimin, Fan Changfu, Wang Hong. 2011. Holocene cheniers: Spatial and temporal distribution and sea levelindicators in Bohai Bay[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(9): 1396-1404 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201109007.htm
Wang Hong. 1996. Paleoenvironment of the Holocene cheniers and oysterreefs in the Bohai Bay, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 16: 71-79 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ601.007.htm
Wang Houjie, Yang Zuosheng, Saito Yoshiki, J. Paul Liu, Sun Xiaoxia, Wang Yan. 2007. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950-2005): Impactsof climate change and human activities[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 57: 331-354. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.003
Wang Qiang, Li Fenglin. 1983. Changes of Quaternary sea and landin the west coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 3: 85-91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Qiqiang, Yuan Guibang, Zhang Shu, Liu Zengshou, Wang Weidong, Liu Zhijie, Zhuang Zhenye. 2007. Shelly ridge accumulation and sea-land interaction on the west coast ofthe Bohai Bay[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 27(5): 775-786 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1571344
Wang Weiwei, Fu Yuanbin, Li Shutong, Li Peiying. 2013. Distribution on surface sediment and sedimentary divisions in the middle part of Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 31(3): 478-485 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201303011.htm
Wintle Ann G. 1997. Luminescence dating: Laboratory procedures and protocols[J]. Radiat. Meas., 27: 769-817. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00220-5
Wu Chen, Hu Jingrong, Wang Zihui. 1982. Transgression of the west coast of Bohai Bay in the middle Holocene[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 6: 26-31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xing Huanzheng. 2003. Evolution Haihe Rrver port line and analysis of sedimentsource[J]. Haihe Water Resources, (2): 28-30 (in Chinese).
Xu Fengshan, Zhang Suping. 2008. An Illustrated Bivalvia Mollusca Fauna of China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Qinmian, Yang Jilong, Yuan Guibang, Chu Zhongxin, Zhang Zhenke. 2015. Stratigraphic sequence and episodes of the ancient Huanghe Delta along the southwesternbohai bay since the LGM[J]. Marine Geology, 367: 69-82. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.05.008
Xue Chunting, Cheng Guodong. 1989. Shelly ridges in west coast of Bohai Sea and Holocene Yellow River delta system[C]//Yang Zigeng, Lin Hemao(eds. ). Quaternary Processes and Events in China Offshore and Onshore Areas. Beijing: China Ocean Press: 117-125 (in Chinese).
Xue Chunting. 1993. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 113: 321-330. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90025-Q
Xue Chunting. 1994. Dicisionand recorgnition of modern Yellow River delta lobes[J]. Geographical Research, 13(2): 59-66 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313366720_Division_and_recognition_of_modern_Yellow_River_Delta_lobes
Xue Chunting, Zhu Xionghua, Lin Hemao. 1995. Holocene sedimentary sequence, foraminifera and ostracodain westcoastal lowland of BohaiSea, China[J]. Quaternary Science Review, 14: 521-530. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(95)00013-F
Xue Chunting, Zhou Yongqing, Wang Guiling. 2003. Reviews of the Yellow River delta superlobes since 700BC[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 23(3): 23-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200303005.htm
Xue Chunting, Zhou Yongqing, Zhu Xionghua. 2004. The Yellow River course and delta from end of Late Pleistocene to the 7th century BC[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 26(1): 48-61 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC200401006.htm
Xue Chunting, Ding Dong. 2008. Weihe River-Mihe River Delta in south coast of Bohai Sea, China: Sedimentary sequenceand architecture[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 28(5): 672-676 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284976932_Weihe_River-Mihe_river_delta_in_south_coast_of_Bohai_Sea_China_sedimentary_sequence_and_architecture
Xue Chunting. 2009. Historical changes of coastlines on west and south coasts of Bohai Sea since 7000 a B. P[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 29(2): 217-222 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200902011.htm
Xue Chunting. 2016. Extents, type and evolution of Luanhe river fan-delta system, China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 36(6): 13-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201606004.htm
Yang Huairen, Wang Jian. 1990. Quaternary trangression and coastline changes in Huanghe River (Yellow River) Delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 10: 1-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yao Zhengquan, Shi Xuefa, Qiao Shuqing, Liu Qingsong, Selvaraj Kandasamy, Liu jianxing, Liu Yanguang, Liu Jihua, Fang Xisheng, Gao Jingjing, Dou Yanguang. 2017. Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least ~880 ka ago[J]. Scientific Reports. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040015777410_d44f.html
Zhang Jin, Wan Shiming, Peter D Clift, Huang Jie, Zhang Kaidi, Mei Xi, Liu Jian, Nan Qingyun, Zhao Debo, Li Anchun, Chen Lihui, Zheng Hongbo, Yang Shouye, Li Tiegang, Zhang Xunhua. 2019. History of Yellow River and Yangtze River delivering sediment to the Yellow Sea since 3.5 Ma: Tectonic or climate forcing?[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 216: 74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.06.002
Zhang Suping. 2008. Atlas of Marine Mollusks in China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese).
Zhang Yifeng, Li Xinfeng. 1983. The characteristics of material component and the material resources in Huanhe(Yellow) River, Luanhe River[J]. Marine Sciences, 3: 15-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://epub.cnki.net/grid2008/docdown/docdownload.aspx?filename=HYKX198303005&dbcode=CJFD&year=1983&dflag=pdfdown
Zhao Baoren, Zhuang Guoqiang, Cao Deming, Lei Fanghui. 1995. The circulation and tidal residual current of Bohai Sea and their influence on sediment disribution[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 26(5): 466-473 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Songling, Yang Guangfu, Cang Shuxi, Zhang Hongcai, Huang Qingfu, Xia Dongxing, Wang Yongji, Liu Fushou, Liu Chengfu. 1978. On the Marine stratigraphy and coastlines of the western coast of the gulf of Bohai[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 9: 15-25(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197801001.htm
Zhao Xitao, Geng Xiushan, Zhang Jingwen. 1979. Sea level change in eastern China over 20000 years[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1: 269-281 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Xitao, Zhang Jingwen, Jiao Wenqiang, Li Guiying. 1980. Shelly ridge on the west coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 25: 279-281 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1980-25-6-279
Zhao Xitao, Chen Zongyong, Zhu Jiwen. 1996. Sea Level Changes in China[M]. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang Zhenye, Xu Weidong, Li Xuelun. 1991. The coastline evolution on the south coast of the Bohai Sea since 6 ka B. P[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 21(2): 99-110 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-qdhy199102009.htm
Zou Yilin, Tan Qixiang, Shi Nianhai. 1982. Yellow River, Changes of river system in China history[C]//Physical Geography of China, Historical Physical. Beijing: Science Press, 38-86 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈永胜, 王福, 田立柱, 李建芬, 商志文, 王宏, 齐乌云. 2014. 渤海湾西岸全新世沉积速率对河流供给的响应[J]. 地质通报, 33(10): 1582-1590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.015 成国栋, 任于灿, 李绍全, 李广雪, 董万. 1986. 现代黄河三角洲河道演变及垂向序列[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 6(2): 3-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198602000.htm 成国栋, 薛春汀. 1997. 黄河三角洲沉积地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-8. 地理系海岸研究组. 1974. 海河水下三角洲的演变特征和天津新港泥沙来源的初步探讨[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), (1): 80-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ197401007.htm 董礼先, 苏纪兰, 王康墡. 1989. 黄渤海潮流场及其与沉积物搬运的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 11, 102-114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.1989.01.004 杜瑞芝, 刘国贤, 杨松林, 周义华, 张兵. 1990. 渤海湾现代沉积速率和沉积过程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 10(3): 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ199003001.htm 付兆辉, 陈发景, 李敏, 时丕同, 闵飞琼. 2008. 新北油田沉积特征及对油气成藏的影响[J]. 中国地质, 35(4): 691-698 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.04.013 高瑞琪, 赵文智, 孔凡仙. 2004. 青年勘探家论渤海湾盆地石油地质[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社. 高善明. 1981. 滦河三角洲沉积模式[J]. 科学通报, 26: 895-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198114023.htm 何磊, 叶思源, 袁红明, 薛春汀. 2019. 黄河三角洲利津超级叶瓣时空范围的再认识[J]. 地理学报, 74(1): 146-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201901012.htm 胡广元, 庄振业, 印萍, 赵东坡, 刘爽, 王玲. 2017. D219孔和渤海湾北部晚第四纪地质环境[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 33(6): 16-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201706003.htm 李杰, 李日辉, 杨士雄, 陈晓辉, 陈姗姗. 2018. 渤海西部海域晚更新世以来的孢粉组合及古环境变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(2): 115-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201802012.htm 刘春成, 戴富贵, 杨津, 杨克绳. 2010. 渤海湾盆地海域古近系-新近系地质结构和构造样式地震解译[J]. 中国地质, 37(6): 1545-1558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.001 刘艳霞, 黄海军, 董慧君, 祁雅莉, 张翼. 2015. 渤海西南岸全新世最大海侵界线及其地貌特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 35(2): 340-353. 苏盛伟, 商志文, 王福, 王宏. 2011. 渤海湾全新世贝壳堤: 时空分布和海面变化标志点[J]. 地质通报, 30(9): 1382-1395. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.007 谭其骧. 1981. 西汉以前的黄河下游河道[J]. 历史地理, (1): 48-64. 王海峰, 裴艳东, 刘会敏, 范昌福, 王宏. 2011. 渤海湾全新世牡蛎礁: 时空分布和海面变化标志点[J]. 地质通报, 30: 1396-1404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.008 王宏. 1996. 渤海湾全新世贝壳堤和牡蛎礁的古环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 16: 71-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1996.01.008 王强, 李凤林. 1983. 渤海湾西岸第四纪海陆变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 3: 85-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198304012.htm 王强, 袁桂邦, 张熟, 刘增寿, 王卫东, 刘志杰, 庄振业. 2007. 渤海湾西岸贝壳堤堆积与海陆相互作用[J]. 第四纪研究, 27(5): 775-786. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.019 王伟伟, 付元宾, 李树同, 李培英. 2013. 渤海中部表层沉积物分布特征与粒度分区[J]. 沉积学报, 31(3): 478-485. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201303011.htm 吴忱, 胡镜荣, 王子惠. 1982. 全新世中期渤海湾西岸的海侵[J]. 海洋通报, 6;26-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB198206004.htm 邢焕政. 2003. 海河口岸线演变及泥沙来源分析[J]. 海河水利, (2): 28-30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7328.2003.02.010 徐凤山, 张素萍. 2008. 中国海产双壳类图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 薛春汀, 成国栋. 1989. 渤海西岸贝壳堤及全新世黄河三角洲体系[C]//杨子赓, 林和茂主编. 中国沿海及近海地区第四纪进程与事件[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 117-125. 薛春汀. 1994. 现代黄河三角洲叶瓣的划分和识别[J]. 地理研究, 13(2): 59-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ199402008.htm 薛春汀, 周永青, 王桂玲. 2003. 古黄河三角洲若干问题的思考[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 23(3): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200303005.htm 薛春汀, 周永青, 朱雄华. 2004. 晚更新世末至公元前7世纪的黄河流向和黄河三角洲[J]. 海洋学报, 26(1): 48-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.01.006 薛春汀, 丁东. 2008. 渤海莱州湾南岸潍河-弥河三角洲: 沉积序列和沉积格架[J]. 地理科学, 28(5): 672-676. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2008.05.014 薛春汀. 2009. 7000年来渤海西岸、南岸海岸线变迁[J]. 地理科学, 29(2): 217-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2009.02.012 薛春汀. 2016. 滦河冲积扇-三角洲的范围和类型及其演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(6): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201606004.htm 杨怀仁, 王建. 1990. 黄河三角洲地区第四纪海进与岸线变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 10: 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ199003000.htm 张素萍. 2008. 中国海洋贝类图鉴[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. 张义丰, 李凤新. 1983. 黄河、滦河三角洲的物质组成及其来源[J]. 海洋科学, 3: 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX198303005.htm 赵保仁, 庄国文, 曹德明, 雷方辉. 1995. 渤海的环流、潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 26(5): 466-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003 赵松龄, 杨光复, 苍树溪, 张宏才, 黄庆福, 夏东兴, 王永吉, 刘福寿, 刘成福. 1978. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 9: 15-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197801001.htm 赵希涛, 耿秀山, 张景文. 1979. 中国东部20000年来的海平面变化[J]. 海洋学报, 1: 269-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC197902007.htm 赵希涛, 张景文, 焦文强, 李桂英. 1980. 渤海湾西岸的贝壳堤[J]. 科学通报, 25: 279-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198006012.htm 赵希涛, 陈宗镛, 朱季文. 1996. 中国海面变化[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社. 中国科学院海洋研究所. 1985. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 庄振业, 许卫东, 李学伦. 1991. 渤海南岸6000年来的岸线演变[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 21(2): 99-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY199102009.htm 邹逸麟, 谭其骧, 史念海. 1982. 历史时期的水系变迁, 黄河[C]//中国自然地理, 历史自然地理. 北京: 科学出版社: 38-86.




 下载:
下载: