Mineral saturation index characteristics, sources of Sr2+, SO42− and development potential of strontium−rich karst water in Xintian County, Hunan Province
-
摘要:研究目的
湖南新田县发现大型富锶矿泉水田,然而锶元素来源及锶矿泉开发利用潜力研究相对薄弱,此外探究富锶岩溶水水化学特征及锶元素来源可为岩溶区寻找富锶地下水提供一定的理论支撑。
研究方法通过开展水文地质调查,富锶地下水水化学指标检测分析,利用PHREEQC软件、水化学计量法、端元法、水文地质参数等揭示富锶岩溶水矿物饱和指数特征,Sr2+、SO42−来源及富锶地下水开发潜力。
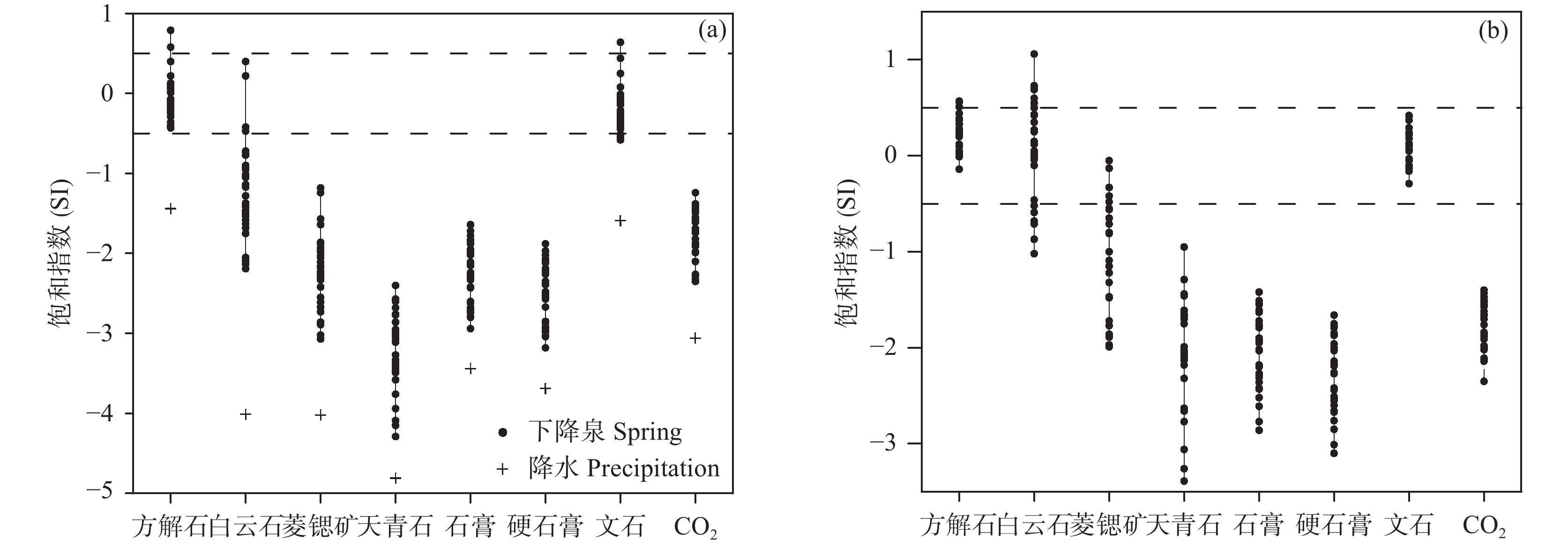
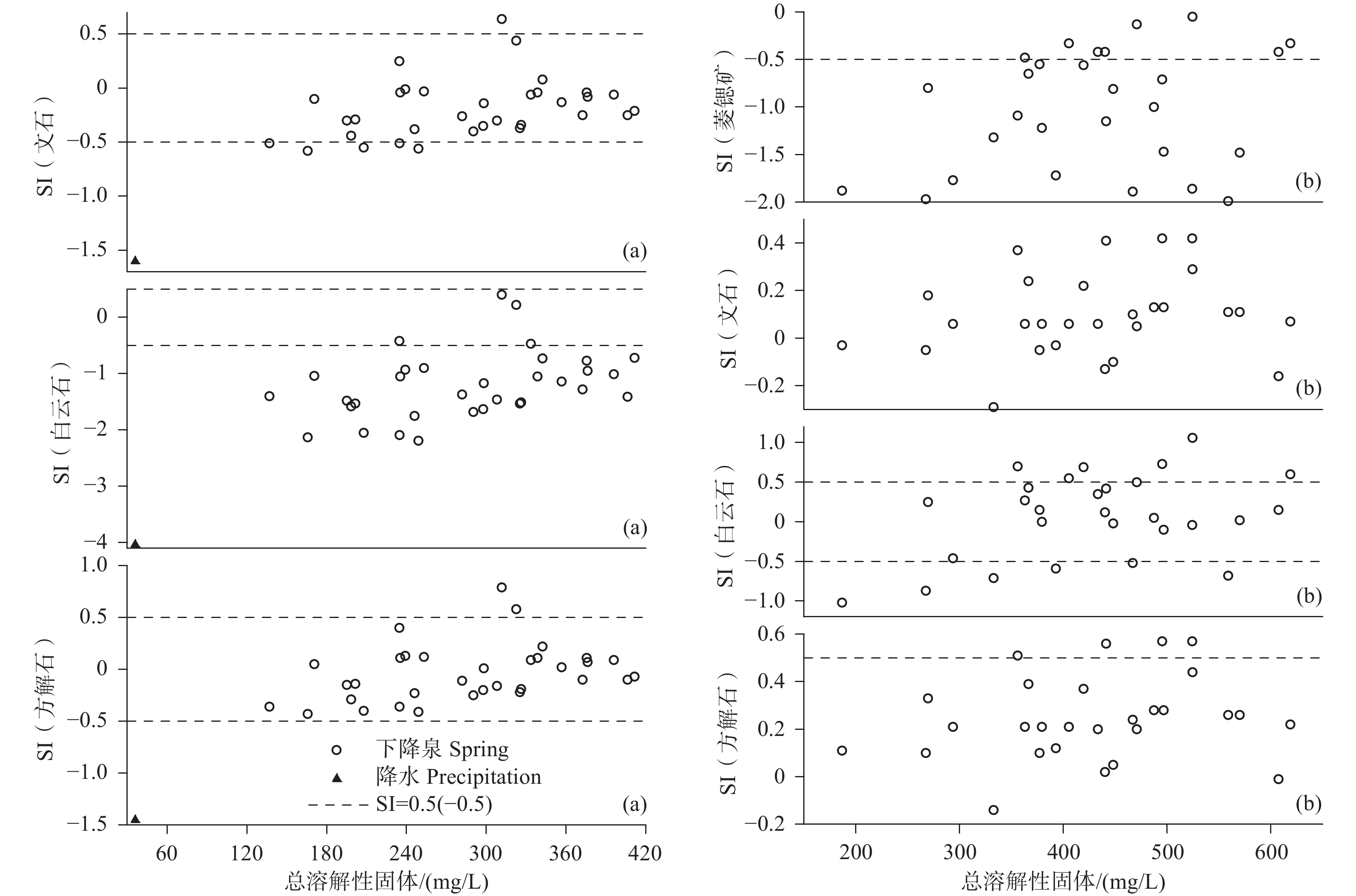
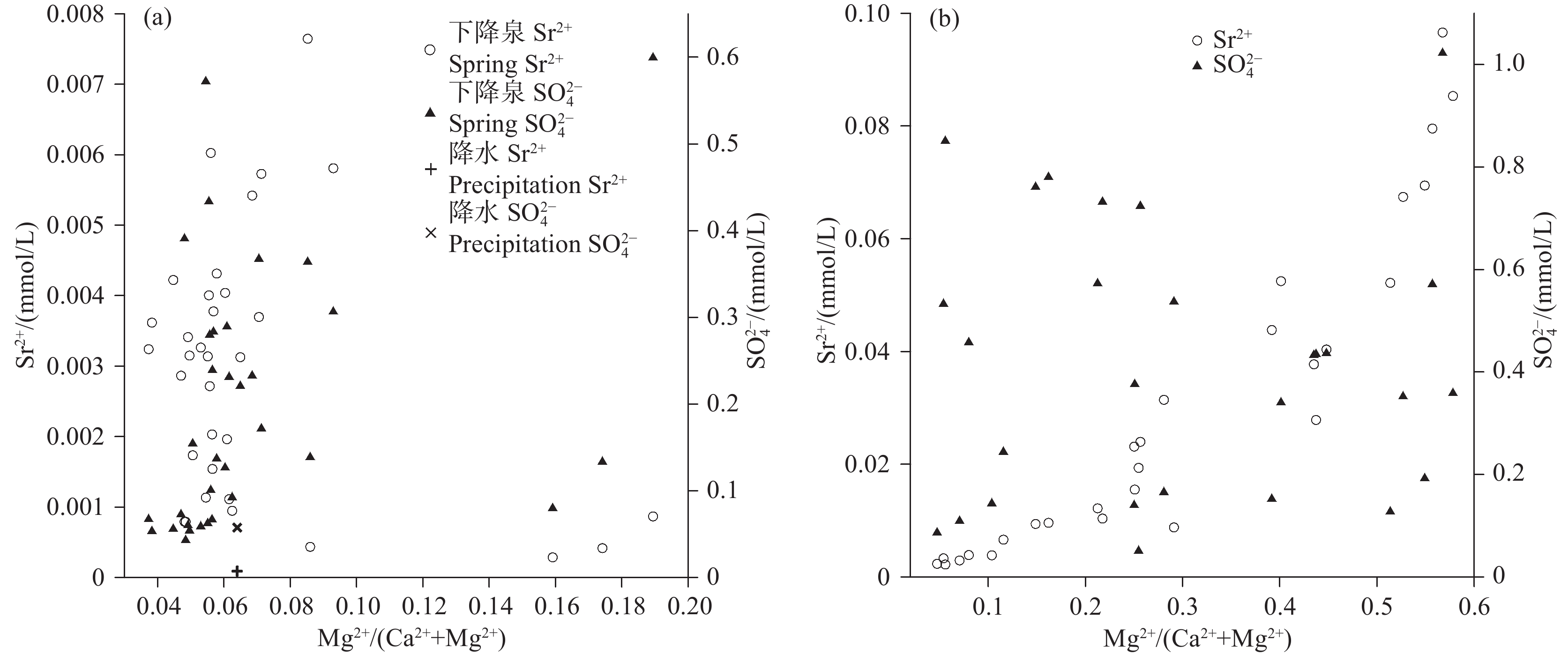
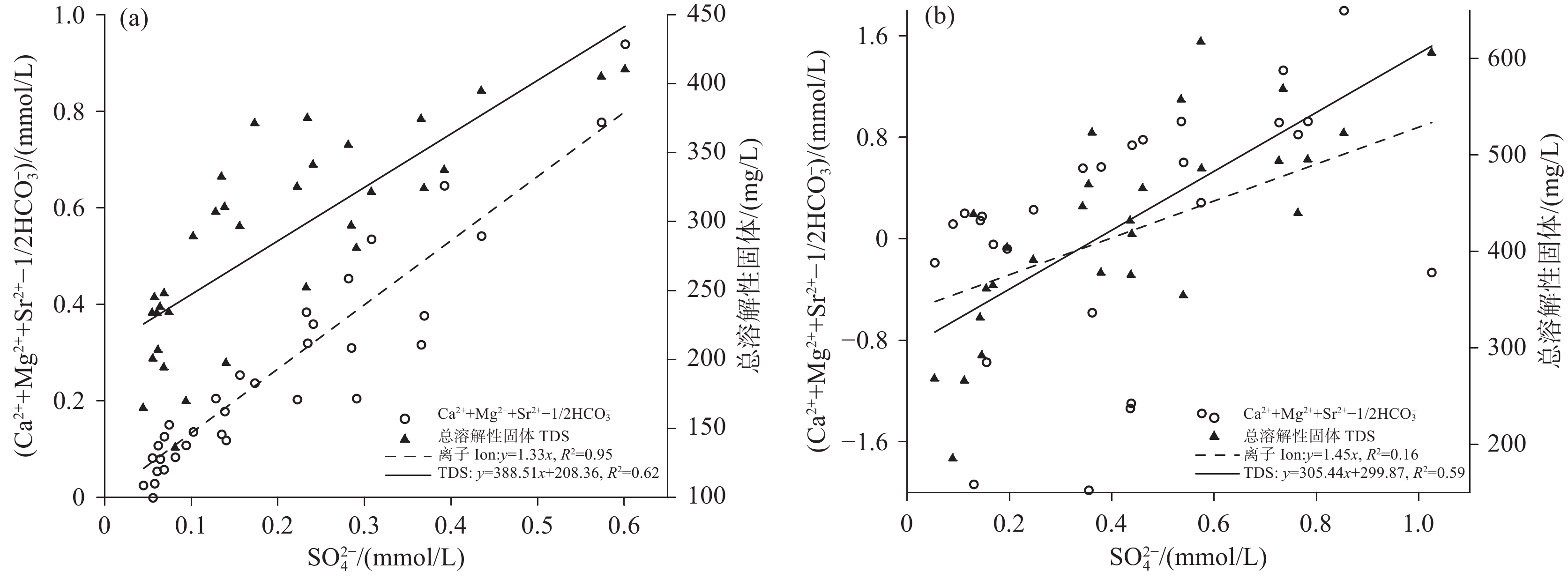
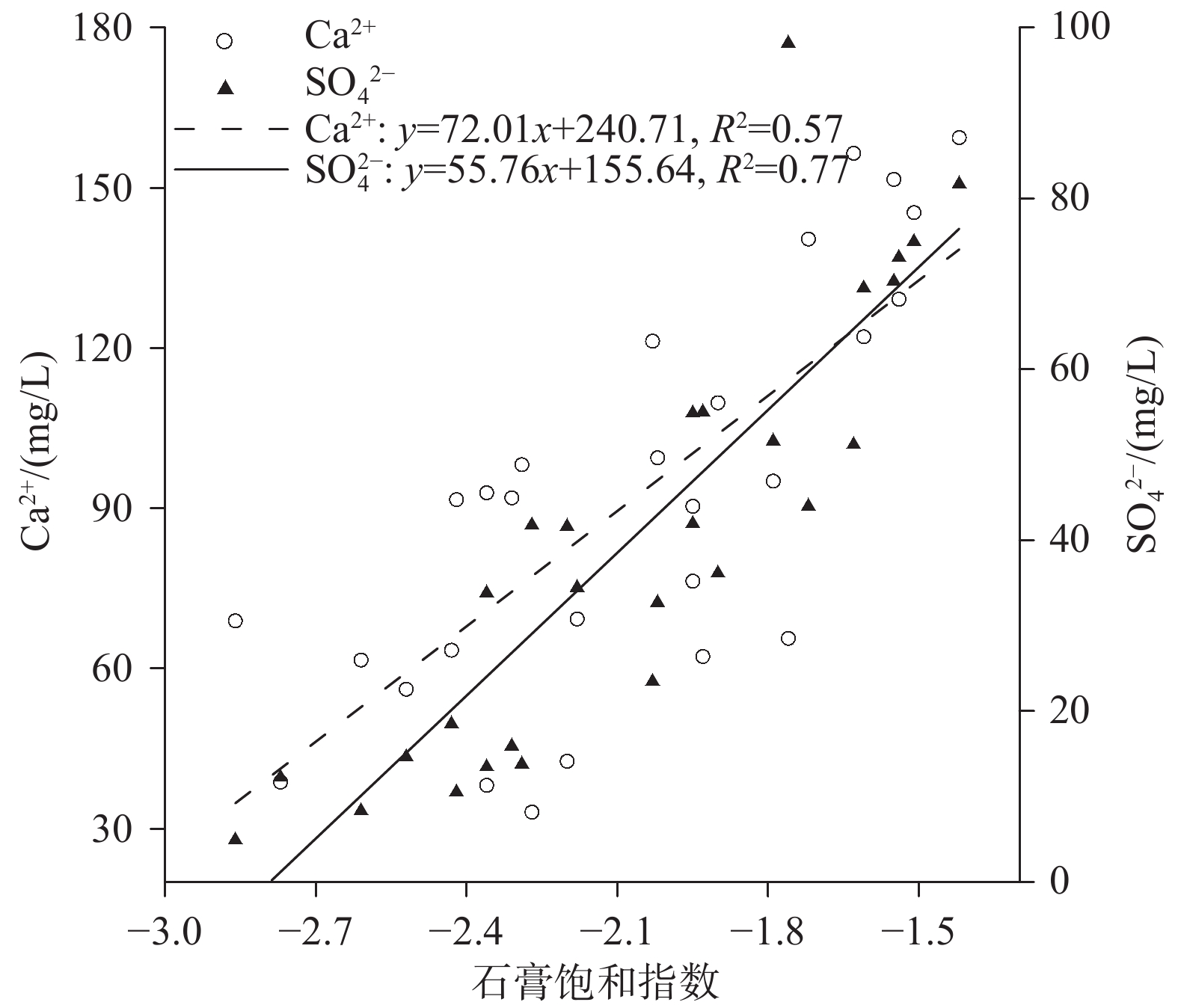
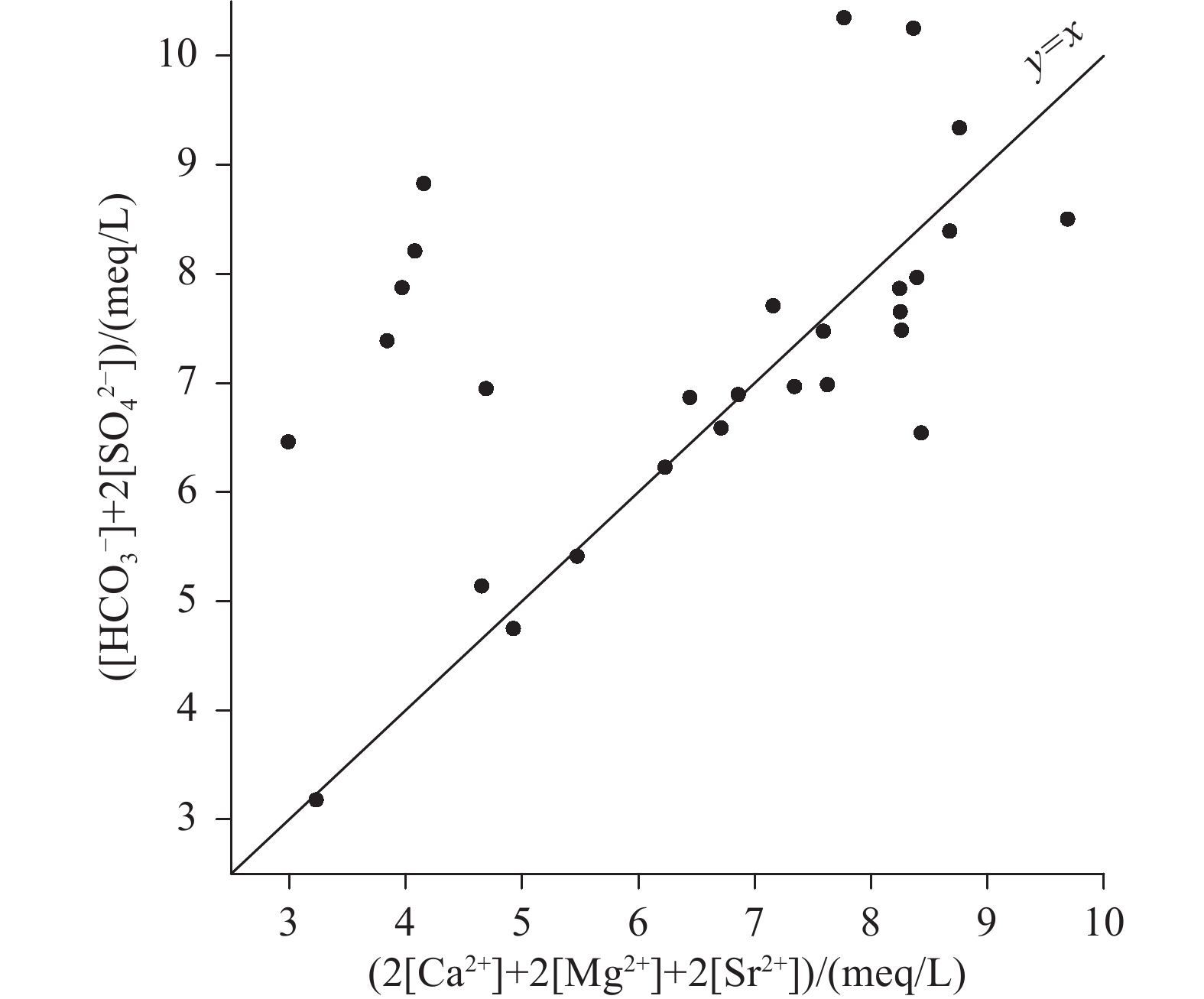
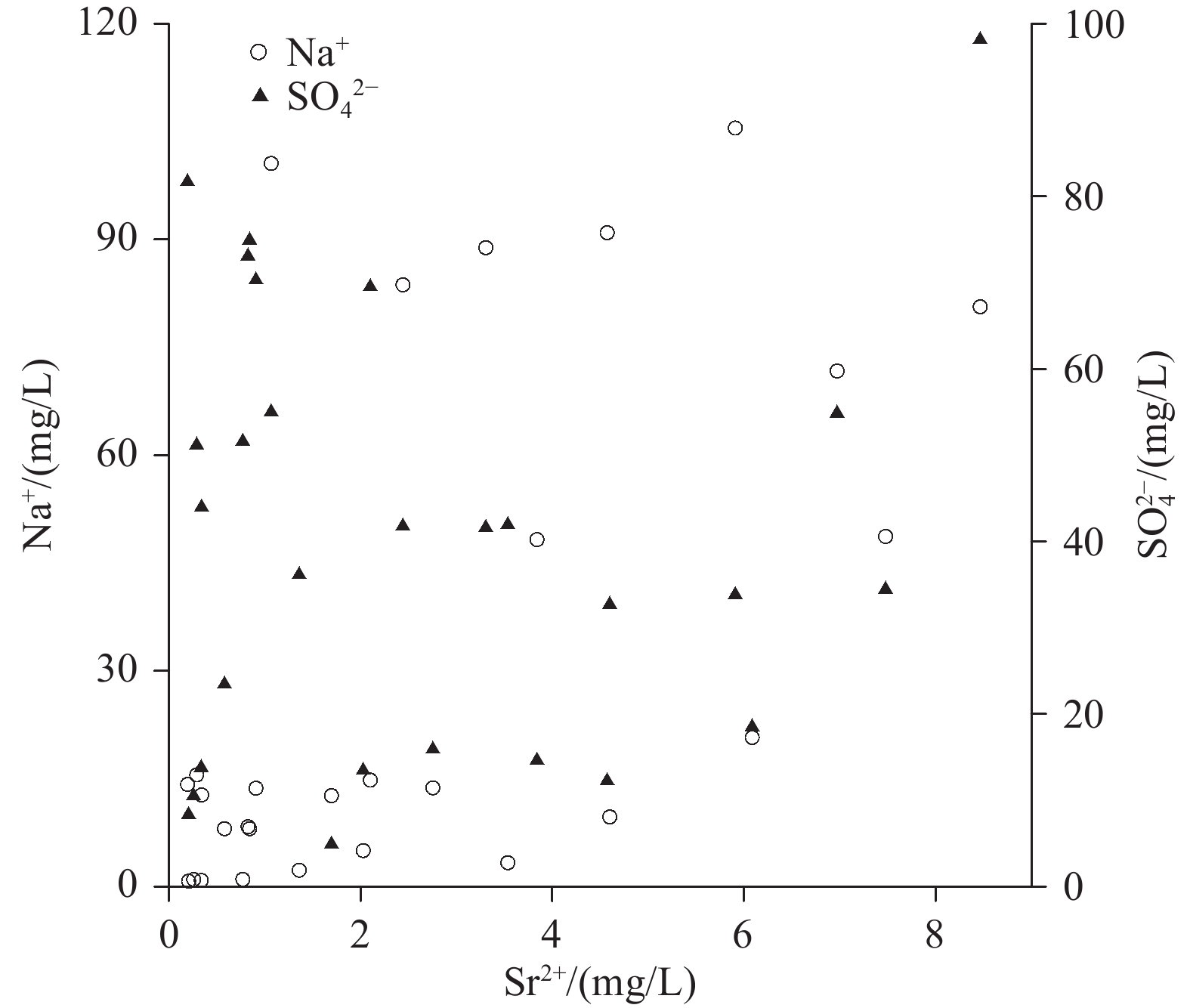
研究结果方解石在下降泉和机井中均主要处于饱和状态,白云石由下降泉中未饱和状态转为机井中的饱和状态,菱锶矿在机井中出现饱和状态,石膏在下降泉和机井中均为未饱和状态。下降泉中矿物饱和指数随泉水溶解性总固体增加而升高,两者呈较好的正相关关系,但在机井中两者相关性较差。下降泉SO42−和大气降水SO42−具有较好的拟合关系,根据Ca2+、Mg2+、Sr2+、HCO3−、SO42−化学计量关系,机井中SO42−可能来源于石膏溶解。下降泉中Sr2+主要来源于石灰岩中以类质同像置换钙的锶,机井中Sr2+较大可能来源于含水层中菱锶矿。研究区85.2%水点的地下水符合国家生活饮用水卫生标准,超标水点多为单指标超标。经计算,枯水年富锶地下水天然补给资源量、可开采资源量和地下水资源潜力分别为3.83×107 m3/a、1.05×107 m3/a、7.28×106 m3/a。
结论新田县富锶地下水中锶主要来源于泥盆系佘田桥组地层含锶矿物(类质同像置换钙的锶和菱锶矿)的溶解,富锶地下水资源量及资源潜力可观,具有较大的开发利用潜力与价值。
创新点:(1)运用矿物饱和指数、水化学计量法、端元法探究岩溶地下水中Sr2+、SO42−来源及贡献量;(2)根据新田县气象水文资料、研究区可开采地下水现状,分析富锶地下水资源量及资源潜力,评价富锶地下水开发潜力与价值。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survey engineering.
ObjectiveThere is limited research on the sources of strontium elementand the potential for the development and utilization of karst water in the large−scale strontium rich mineral water field in Xintian County, Hunan Province. Exploring the hydrochemical characteristics of strontium−rich karst water and the sources of strontium element can provide theoretical support for searching for strontium rich groundwater in karst areas.
MethodsPHREEQC software, water stoichiometry, end element method and hydrogeological parameters were used in this study to reveal the mineral saturation index characteristicsof strontium−rich karst water, as well as the sources of Sr2+ and SO42− and its development potential through the hydrogeological investigation and hydrochemical testson groundwater in this strontium−rich mineral water field.
ResultsCalcite is mainly saturated both in the springs and shafts, while dolomite changes from unsaturated in the springs to saturate in the shafts. Strontium is saturated in the shafts, and gypsum is unsaturated both in the springs and the shafts. In the springs, mineral saturation index increases with the total dissolved solids, and they areof a good positive correlation, but of a poor correlation in the shafts. The correlation of SO42− betweenthe springs and shaftsare positive. According to the stoichiometric relation of Ca2+, Mg2+, Sr2+, HCO3− and SO42−, SO42− in the shafts may come from gypsum dissolution. The Sr2+ in the springsare mainly derived from strontium which replaces calcium with isomorphism in limestone, while Sr2+ in the shafts probably come from strontium siderite in the aquifer. 85.2% of the groundwatersamplings in the research area meet the national standard for drinking water quality, and the excess water samplings are mostly single indicator exceeding the standard. Through calculation, the natural recharge resources, exploitable resources and groundwater resource potential of strontium−rich groundwater in dry years are 3.83×107 m3/a、1.05×107 m3/a、7.28×106 m3/a respectively.
ConclusionsStrontium in the strontium−rich groundwater in Xintian County is mainly derived from the dissolution of strontium−containing minerals in Shetianqiao Formation strata of Devonian. Those minerals, including strontianite, were form by isomorphicly substitute of calcium with strontium. The amount and resource potential of strontium−rich groundwater are considerable, with a great value for development and utilization.
Highlights:(1) The sources and contributions of Sr2+ and SO42− in karst groundwater were studied by using mineral saturation index, water stoichiometry and end element method; (2) The amount and development potential of strontium−rich groundwater in the research area are analyzed based on the meteorological and hydrological information and the current exploitable groundwater resource.
-
1. 引言
玄武岩原生岩浆来自于上地幔,成分与地幔源岩关系十分密切,其岩浆的产生往往又与裂谷扩张、板块俯冲消减、地幔的深部作用等过程有关(徐义刚,2006;Nielsen et al., 2006;Campbell, 2007;厉子龙等,2008)。碱性玄武岩因其产出的特殊构造背景而备受关注(王岳军等,2004;余心起等,2005;陈立辉等,2012;赵慧等,2015)。华南印支期岩浆岩以发育强过铝—过铝质花岗岩为特征,同期基性火山岩极少出露,代表的有湖南道县虎子岩玻基辉橄岩40Ar-39Ar坪年龄为204 Ma(赵振华等,1998)、宁远碱性玄武岩年龄为212.3 Ma(刘勇等,2010)及武夷山地区霓辉石正长岩年龄为242 Ma(Wang et al., 2003)。
马山杂岩为一个多次岩浆活动形成由超基性、基性、中酸性岩组成的中生带复杂岩体(王晓地,2013)。玄武岩分布于杂岩体的北部,由浅层相的玄武玢岩逐步过渡到喷出相的玄武岩,因其侵入泥盆系,同时又被早燕山期花岗斑岩侵入,故认为其时代为印支期。但目前还没有与之相协调的同位素精确年龄。前人对马山杂岩也做过系统研究,但存在一定的分歧,吴根耀和李曰俊(2011)认为马山杂岩中的印支期玄武岩属亚速尔型洋岛玄武岩,为沿灵山断裂曾发育过洋盆提供了直接的地质依据,成为恢复现已消失了的洋盆的一个重要判据;广西壮族自治区区域地质调查研究院(2006)❶认为马山复式岩体为板内型钾玄岩,其形成构造环境与岛弧无关;郭新生等(2001)认为马山基性岩源区为交代地幔的辉长岩浆在地壳深部分异而形成的,马山花岗岩由幔源岩浆加热地壳使之熔融的壳源岩浆形成并伴有与幔源岩浆的混合;Li et al.(2000)认为马山玄武岩是典型的板内岩浆岩,与岛弧环境不存在成因联系,表明桂东南钾玄质岩石很可能是亏损的软流圈地幔和富集的岩石圈地幔岩浆混合的产物。本文拟报道桂东南马山玄武岩锆石U-Pb精确年龄,结合地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素资料,探讨其岩石成因和形成的构造背景,为华南地区印支期的动力学背景研究提供依据。
2. 岩体地质特征
马山杂岩位于桂东南六万大山,出露面积约为93 km2(图 1),大地构造上位于特提斯构造域和环太平洋构造域的交汇处,同时又处于扬子与华夏两大块体接合部位即“钦杭结合带”内。岩体侵位于寒武系、泥盆系和印支期大容山岩体中,为一个多次岩浆活动形成由超基性、基性、中酸性岩组成的中生代复杂岩体(王晓地,2013)。玄武岩分布于岩体的北部,由浅层相的玄武玢岩逐步过渡到喷出相的玄武岩,出露面积约30 km2。
![]() 图 1 马山杂岩体地质图(据广西壮族自治区区域地质调查研究院,2006❶修改)1—全新统;2—茅口组;3—黄龙组;4—大埔组;5—榴江组;6—东岗岭组;7—郁江组;8—那高岭组;9—莲花山组;10—黄洞口组;11—花岗斑岩;12—正长岩;13—石英二长岩;14—闪长岩;15—辉石岩;16—玄武岩;17—花岗闪长岩;18—二长花岗岩;19—断层;20—地质界线;21—角度不整合界线;22—角岩、矽卡岩化;23—玄武岩年龄采样点Figure 1. Geological map of the Mashan Complex (modified from the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Institute of Regional Geological Survey, 2006❶)1-Holocene; 2-Maokou Formation; 3-Huanglong Formation; 4-Dapu Formation; 5-Liujiang Formation; 6-Donggangling Formation; 7-Yujiang Formation; 8-Nagaoling Formation; 9-Lianhuashan Formation; 10-Huangdongkou Formation; 11-Granite porphyry; 12-Syenite; 13-Quartz monzonite; 14-Diorite; 15-Pyroxenite; 16-Basalt; 17-Granodiorite; 18-Monzogranite; 19-Fault; 20-Geological boundary; 21-Angular unconformity; 22-Hornfels, skarnization; 23-Sampling location
图 1 马山杂岩体地质图(据广西壮族自治区区域地质调查研究院,2006❶修改)1—全新统;2—茅口组;3—黄龙组;4—大埔组;5—榴江组;6—东岗岭组;7—郁江组;8—那高岭组;9—莲花山组;10—黄洞口组;11—花岗斑岩;12—正长岩;13—石英二长岩;14—闪长岩;15—辉石岩;16—玄武岩;17—花岗闪长岩;18—二长花岗岩;19—断层;20—地质界线;21—角度不整合界线;22—角岩、矽卡岩化;23—玄武岩年龄采样点Figure 1. Geological map of the Mashan Complex (modified from the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Institute of Regional Geological Survey, 2006❶)1-Holocene; 2-Maokou Formation; 3-Huanglong Formation; 4-Dapu Formation; 5-Liujiang Formation; 6-Donggangling Formation; 7-Yujiang Formation; 8-Nagaoling Formation; 9-Lianhuashan Formation; 10-Huangdongkou Formation; 11-Granite porphyry; 12-Syenite; 13-Quartz monzonite; 14-Diorite; 15-Pyroxenite; 16-Basalt; 17-Granodiorite; 18-Monzogranite; 19-Fault; 20-Geological boundary; 21-Angular unconformity; 22-Hornfels, skarnization; 23-Sampling location玄武岩为深灰色,具斑状结构、基质具间粒间隐结构,以块状和气孔状构造为主。斑晶为斜长石(30%)、辉石(15%)、少量橄榄石及角闪石,基质为斜长石(35%)、辉石(15%)与金属矿物(4%),含少量副矿物。斜长石斑晶呈半自形板状、常见聚片双晶、卡钠复合双晶;辉石斑晶呈粒状、短柱状,被碳酸盐化只保留轮廓;橄榄石斑晶呈粒状,被伊丁石化只保留轮廓;角闪石斑晶呈柱状、粒状,绿泥石化只保留轮廓。基质中斜长石呈板条状、粒状,具有聚片双晶,辉石呈粒状分布在长石间隙中,由于碳酸盐化,只保留辉石轮廓。金属矿物主要以磁铁矿为主,副矿物为磷灰石、锆石(图 2)。
3. 锆石同位素测年
锆石测年选择玄武岩(Mszy-7)为测试对象,年代学样品采自南宁市横县步头村(地理坐标为22° 45′33″N,109°35′22″E),锆石样品挑选由国土资源部河北省地质矿产局廊坊实验室完成,锆石阴极发光(CL)照相在中国地质大学JXA-8100电子探针仪上完成。LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄测定在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室的Agilent7500型ICPMS上进行。仪器分析步骤及分析结果数据处理参照文献(Yuan et al., 2003)。
玄武岩锆石多数呈长柱状,晶形较完好,颗粒大小一般为50 μm×100 μm,韵律环带发育。在CL图像上大部分核部和边部差异不明显(图 3)。所测锆石的18个分析点中Th含量为191×10-6~838×10-6,U含量为508×10-6~3348×10-6,Th/U比值为0.16~1.19,均表现出岩浆锆石的特点。其中12和15号点为老锆石,207Pb/206Pb年龄分别为1070 Ma和1650 Ma,与206Pb/238U年龄不一致,可能为部分Pb丢失所致;3号点年龄偏老,206Pb/238U年龄为464 Ma;2、16、17和19号点的206Pb/238U年龄变化于262~288 Ma,可能代表了早期的岩浆活动;5号点的206Pb/238U年龄偏低,为133 Ma,可能与区内早白垩世的变质作用有关。所测试的其余10个分析点206Pb/238U年龄相对集中,主体变化于245~248 Ma,落在U-Pb谐和线上或其附近(图 3),获得206Pb/238U年龄的加权平均值为(246.7±1.5)Ma,MSWD=0.16,代表了玄武岩的形成年龄(表 1)。同时玄武岩侵入泥盆纪地层,又被早燕山期时代为185.2 Ma的花岗斑岩侵入(王晓地,2013),故认为其形成时代为印支期。
表 1 马山玄武岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素分析数据Table 1. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb isotopic data of the Mashan basalt
4. 岩石地球化学特征
玄武岩的主量元素分析在中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心完成(表 2),分析方法为:Si和烧失量采用重量法,Al和Fe2+采用容量法,Fe3+、Ti和P采用分光光度法,K、Na、Ca、Mg和Mn采用原子吸收光谱法;微量元素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成,微量元素采用HR-ICP-MS (Element Ⅰ)分析完成(表 2);Sr、Nd同位素分析用中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心MAT261及Triton质谱仪分析完成(表 3),实验流程以及标准样品测定按照Sm-Nd同位素实验方法完成(王银喜等,1988)。
表 2 马山玄武岩主量元素(%)和稀土及微量元素(10−6)分析结果及参数Table 2. Compositions and parameters of major elements(%), rare earth and trace element(10−6) in the Mashan basalt 表 3 马山玄武岩Sr-Nd同位素组成分析结果Table 3. Sr-Nd isotopic data of the Mashan basalt
表 3 马山玄武岩Sr-Nd同位素组成分析结果Table 3. Sr-Nd isotopic data of the Mashan basalt
4.1 主量元素
玄武岩呈基性(SiO2=46.02%~51.56%),碱性程度较强(δ=5.21~8.02),岩石总体富碱(ALK=5.21%~8.02%)、富钾(K2O=2.59%~4.96%)、K2O大于Na2O(个别样品除外)(K2O/Na2O=1.07~1.62),铝含量较高(Al2O3=12.01%~14.88%),Mg#值高(35.11~56.09),钛含量高(TiO2=1.24%~2.15%),铁含量较高((FeO+Fe2O3)=10.80%~12.66%)。在火山岩TAS分类图解中主要落在粗面玄武岩区、少数落在玄武粗安岩及碱玄岩区(图 4a),SiO2-K2O图解落在钾玄质系列岩石范围内(图 4b),岩石属钾质粗面玄武岩。
![]() Figure 4. Classifications diagrams of the Mashan basalt (a after Le Bas et al., 1986; b after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)
Figure 4. Classifications diagrams of the Mashan basalt (a after Le Bas et al., 1986; b after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)4.2 稀土元素
玄武岩稀土元素总量(∑REE)为150.98×10-6~254.89×10-6,轻稀土元素富集,稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图上表现为右倾趋势(图 5a),轻、重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)为6.94~9.87,(La/Yb)N值介于8.43~14.75;具轻微的Eu负异常,δEu值介于0.85~0.95。
![]() 图 5 马山玄武岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(标准化数值据Sun and Mcdonough, 1989)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spider diagrams of the Mashan basalt (normalized values are from Sun and McDonough, 1989)
图 5 马山玄武岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(标准化数值据Sun and Mcdonough, 1989)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spider diagrams of the Mashan basalt (normalized values are from Sun and McDonough, 1989)4.3 微量元素
在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图上(图 5b),玄武岩均表现为富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs,Rb、Ba、K、Pb、LREE),亏损高场强元素(HFSE,Nb、Ta、P、Ti、HREE),而无明显的Zr亏损。
4.4 Sr-Nd同位素
玄武岩全岩Sr-Nd同位素计算使用Geokit软件完成(路远发和李文霞,2021)。Sr-Nd同位素组成相对变化较大(表 3),Sr同位素组成较均一,ISr=0.704597~0.704834;Nd同位素变化较大,εNd(t) = 0.42~2.05,相应的两阶段Nd模式年龄(tDM2)变化于0.86~0.99 Ga。在ISr-εNd(t)图中样品主要落在亏损地幔(DM)与富集地幔(EM Ⅱ)之间且靠近EM Ⅱ区域,与EM Ⅱ地幔具有亲源性(图 6)。
![]() 图 6 马山玄武岩ISr-εNd(t)关系图(底图据Zinder and Hart, 1986)DM—亏损地幔;HIUM—高U/Pb比值地幔;EM Ⅰ—Ⅰ型富集地幔;EM Ⅱ—Ⅱ型富集地幔Figure 6. ISr-εNd(t) diagram of the Mashan basalt (after Zinder and Hart, 1986)DM-Depleted mantle; HIUM-High U/Pb ratio mantle; EM Ⅰ-Enriched mantle Ⅰ; EM Ⅱ-Enriched mantle Ⅱ
图 6 马山玄武岩ISr-εNd(t)关系图(底图据Zinder and Hart, 1986)DM—亏损地幔;HIUM—高U/Pb比值地幔;EM Ⅰ—Ⅰ型富集地幔;EM Ⅱ—Ⅱ型富集地幔Figure 6. ISr-εNd(t) diagram of the Mashan basalt (after Zinder and Hart, 1986)DM-Depleted mantle; HIUM-High U/Pb ratio mantle; EM Ⅰ-Enriched mantle Ⅰ; EM Ⅱ-Enriched mantle Ⅱ5. 讨论
5.1 玄武岩岩石成因
分离结晶作用在玄武岩岩浆的演化过程中具有非常重要的作用。马山玄武岩的SiO2与TiO2、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO和P2O5呈良好的负相关关系,SiO2与Al2O3呈正相关关系;MgO与TiO2、FeOT、CaO及P2O5呈良好的正相关关系,MgO与Al2O3、(Na2O+K2O)呈良好的负相关关系。同时岩石样品具有低的MgO(3.29%~7.58%)、Ni(5.79×10-6~67.89×10-6)、Cr(7.47×10-6~295×10-6)、Sc(19.80×10-6~41.18×10-6)含量,表明样品中橄榄石、辉石的分离结晶作用显著;在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图上均表现有弱的Ti和P亏损,表明有钛铁矿和磷灰石分离结晶;SiO2与Al2O3呈正相关关系,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图中缺乏明显的Eu异常,表明没有斜长石的结晶分离。
马山玄武岩的地球化学特征以富集大离子亲石元素(K、Ba、Rb、Sr、Th、U、LREE),亏损HREE,无明显的Nb、Ta异常为特征,显示可能受到地壳混染作用。但从另一方面,玄武岩Mg#值较高,为35.11~56.69,接近于洋中脊拉斑玄武岩的Mg#值(60±,Beard and Lofgren, 1991),玄武岩Nb/Ta平均值为16.44,Zr/Hf平均值为36.97,与原始地幔值(Nb/Ta=17.5、Zr/Hf=36.27)相近,高于大陆地壳平均值(Nb/Ta=11、Zr/Hf=33,Taylor and McLennan, 1985;Stolz et al., 1996)。Th/La平均值为0.18,明显低于大陆地壳的平均值(0.28),稍高于下地壳的Th/ La比值(0.15),说明玄武质岩浆上升侵位过程中受到地壳大规模混染程度较小;同位素显示有低ISr和高εNd(t)等反映幔源的特征,随着SiO2含量的增加,ISr几乎没有变化,也反映幔源岩浆上侵定位过程中没有发生地壳混染。马山玄武岩具有高的Sr含量(平均值为663.05×10-6),杨祝良等(1999)和曹建劲(2006)分别对浙闽沿海出露的早白垩世玄武岩及广东沿海地区及海南岛基性岩研究发现它们也具有较高的Sr含量,也排除了地壳混染作用。因此,可以判断马山玄武岩其源区主要来自地幔,无明显的地壳混染。
马山玄武岩Nb/U平均值为18.44、Ce/Pb平均值为10.24,明显低于MORB(洋中脊玄武岩)和OIB(洋岛玄武岩)的Nb/U和Ce/Pb比值(分别为40和255,Hofmann et al., 1988),这表明马山玄武岩不可能直接由软流圈地幔部分熔融产生,同时玄武岩的地球化学特征以富集大离子亲石元素(K、Ba、Rb、Sr、Th、U、LREE),亏损Nb、Ta和HREE为特征,同位素显示低ISr和高εNd(t),与EM Ⅱ地幔具有亲源性。一般认为EM Ⅱ型地幔是俯冲带陆源物质进入上地幔再循环的结果,因为大陆沉积物的同位素特征对于EM Ⅱ地幔的形成最为理想(Zinder and Hart, 1986)。因此玄武岩的源区可能与早期俯冲作用带入部分地壳物质进入地幔后,释放流体交代的富集岩石圈地幔有关。Rb、Ba在金云母中为相容元素(LaTourette et al., 1995),Rb、Sr、Ba在角闪石中适度相容(Adam et al., 1993;LaTourette et al., 1995),Nb在角闪石中比在金云母中更相容(LaTourette et al., 1995; Ionov et al., 1997)。所以可以根据金云母和角闪石中微量元素的差异性,来判断岩浆熔融的岩石圈源区是角闪石还是金云母(Furman and Graham, 1999; Yang et al., 2005; Xia and Xu, 2005)。Ba/Rb-Rb/Sr和Nb/Th-Rb/Sr图解显示,马山玄武岩样品几乎都落在金云母的趋势范围(图 7),说明玄武岩的源区主要的含水矿物相为金云母。微量元素HREE、Y在石榴石中强烈富集,而角闪石相对富集中稀土元素(MREE)(Green, 1994),尖晶石则强烈亏损REE及Y(Glaser et al., 1999)。因此,马山玄武岩亏损HREE,表明其源区残留相主要是石榴石,判断马山玄武岩的岩浆来源于石榴石相地幔的部分熔融。在地幔中尖晶石相转变为石榴石相的转换深度约为60~80 km,石榴石相的稳定上限为70~80 km、角闪石相稳定下限约为80 km(Wendlant and Eggler, 1980; Olafsson and Eggler, 1983),因此马山玄武岩的源区成分为含金云母石榴石橄榄岩,源区深度应大于80 km,对含金云母的矿物集合体稳定性评估实验证明,熔体形成于近3000~3500 MPa,或者说深度90~100 km(Olafsson and Eggler, 1983; Wallace and Green, 1988; Lloyd et al., 1991; Sato et al., 1997)。因此玄武质岩浆可能起源于约80~100 km。
![]() 图 7 马山玄武岩Ba/Rb-Rb/Sr和Nb/Th-Rb/Sr图解(底图据Furman and Graham, 1999)Figure 7. Ba/Rb-Rb/Sr and Nb/Th-Rb/Sr diagrams of the Mashan basalt (after Furman and Graham, 1999)
图 7 马山玄武岩Ba/Rb-Rb/Sr和Nb/Th-Rb/Sr图解(底图据Furman and Graham, 1999)Figure 7. Ba/Rb-Rb/Sr and Nb/Th-Rb/Sr diagrams of the Mashan basalt (after Furman and Graham, 1999)5.2 构造意义
马山玄武岩样品在Zr-Zr/Y玄武岩判断图解上主要落在板内玄武岩区(图 8a),在玄武岩类Ta/ Hf-Th/Hf大地构造环境判别图落在陆内裂谷碱性玄武岩区(图 8b),因此可以判断马山玄武岩产于板内环境。
![]() A—板内玄武岩区;B—岛弧玄武岩区;C—洋中脊玄武岩区;Ⅰ—板块发散边缘N-MORB区;Ⅱ—板块汇聚边缘(Ⅱ1—大洋岛弧玄武岩区;Ⅱ2—陆缘岛弧及陆缘火山弧玄武岩区);Ⅲ—大洋板内洋岛、海山玄武岩区及T-MORB、E-MORB区;Ⅳ—大陆板内(Ⅳ1—陆内裂谷及陆缘裂谷拉斑玄武岩区;Ⅳ2—陆内裂谷碱性玄武岩区;Ⅳ3—大陆拉张带(或初始裂谷)玄武岩区);Ⅴ—地幔热柱玄武岩区Figure 8. Tectonic setting discrimination diagrams of the Mashan basalt (a after Pearce and Norry, 1979; b after Wang Yunliang et al., 2001)A-Within-plate basalt; B-Island arc basalt; C-Mid-ocean ridge basalt; Ⅰ-N-MORB; Ⅱ-Plate convergence margin (Ⅱ1-Oceanic island basalt; Ⅱ2-Volcanic arc basalt); Ⅲ-Oceanic intraplate island basalt, seamount basalt and T-MORB, E-MORB; Ⅳ-Intraplate basalt (Ⅳ1-Intracontinental rift basalt and continental margin rift tholeiite; Ⅳ2-Alkali basalt; Ⅳ3-Incipient rift basalt); Ⅴ-Mantle plume basalt
A—板内玄武岩区;B—岛弧玄武岩区;C—洋中脊玄武岩区;Ⅰ—板块发散边缘N-MORB区;Ⅱ—板块汇聚边缘(Ⅱ1—大洋岛弧玄武岩区;Ⅱ2—陆缘岛弧及陆缘火山弧玄武岩区);Ⅲ—大洋板内洋岛、海山玄武岩区及T-MORB、E-MORB区;Ⅳ—大陆板内(Ⅳ1—陆内裂谷及陆缘裂谷拉斑玄武岩区;Ⅳ2—陆内裂谷碱性玄武岩区;Ⅳ3—大陆拉张带(或初始裂谷)玄武岩区);Ⅴ—地幔热柱玄武岩区Figure 8. Tectonic setting discrimination diagrams of the Mashan basalt (a after Pearce and Norry, 1979; b after Wang Yunliang et al., 2001)A-Within-plate basalt; B-Island arc basalt; C-Mid-ocean ridge basalt; Ⅰ-N-MORB; Ⅱ-Plate convergence margin (Ⅱ1-Oceanic island basalt; Ⅱ2-Volcanic arc basalt); Ⅲ-Oceanic intraplate island basalt, seamount basalt and T-MORB, E-MORB; Ⅳ-Intraplate basalt (Ⅳ1-Intracontinental rift basalt and continental margin rift tholeiite; Ⅳ2-Alkali basalt; Ⅳ3-Incipient rift basalt); Ⅴ-Mantle plume basalt扬子和华夏地块在新元古代(约820 Ma)拼合之后直到晚古生代—早中生代华南地区再无新的洋壳打开,华南自约820 Ma后进入板内或陆内演化阶段(舒良树,2006;Wang et al., 2010; Li et al., 2010),印支期造山为板内或陆内造山,但其造山机制或驱动力还有待进一步研究。印支期发育的含石榴石堇青石强过铝S型花岗岩只出露于桂东南十万大山—大容山一带,而华南其他地区出露的印支期花岗岩只是一些过铝质花岗岩(周岱等,2021)。S型过铝质花岗岩被认为不仅与碰撞挤压环境下的地壳加厚有关,也是后碰撞伸展环境的标志。Guo et al.(1997)认为湖南印支期花岗岩的形成可能与区内印支期幔源玄武质岩浆对中下地壳的烘烤所导致的地壳重熔有关,并非碰撞挤压所形成。Wang et al.(2002)认为湖南印支期过铝质花岗岩的形成与玄武质岩浆的底侵有关。Wang et al.(2003)认为武夷山洋坊242 Ma的霓辉石正长岩形成于印支期伸展环境。Sibumasu地块向印支-华南地块斜向汇聚的主碰撞期为243~258 Ma(Carter et al., 2001),马山玄武岩的LA-ICPMS锆石的U-Pb年龄为(246.7±1.5)Ma,其时代与印支运动结束的时代基本一致,地球化学特征显示其为钾玄质岩石,构造环境判断其产于板内裂谷环境,同时又远离Song ma碰撞缝合带及古太平洋板块向华南大陆之下俯冲带,所以其形成机制和印支板块碰撞及太平洋板块的俯冲作用可能关系不大。桂东南地区灵山断裂、岑溪—博白断裂、罗定—广宁断裂、信宜—廉江断裂、吴川—四会断裂等印支期的逆冲-推覆构造十分发育,云开大山周边断裂带的同位素测年为200~256 Ma(彭少梅等,1995;Wang et al., 2007)。因此,马山玄武岩更可能与桂东南地区逆冲-推覆构造后期的伸展作用有关,由于伸展作用产生有利空间,造成玄武质岩浆上侵并喷发,形成马山玄武岩。
6. 结论
(1)马山玄武岩形成年龄为(246.7±1.5)Ma,为早三叠世印支期玄武岩。
(2)马山玄武岩富碱、富钾,为钾质粗面玄武岩。稀土元素特征为轻稀土富集型,微量元素特征为富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素,为钾玄岩系列岩石。其岩浆作用以分离结晶为主,无明显的地壳混染。Sr-Nd同位素显示具有EM Ⅱ富集地幔端元的特征,其源区为早期俯冲作用带入的部分地壳物质进入地幔后,经流体交代作用形成含金云母石榴石的富集地幔(> 80 km)源区。
(3)马山玄武岩产于板内环境,其形成可能与桂东南地区印支期逆冲-推覆构造后期的伸展作用有关,由于伸展作用产生有利空间,造成玄武岩浆上侵并喷发并形成玄武岩。
注释
❶广西壮族自治区区域地质调查研究院. 2006. 广西1∶25万玉林市幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 1-687.
-
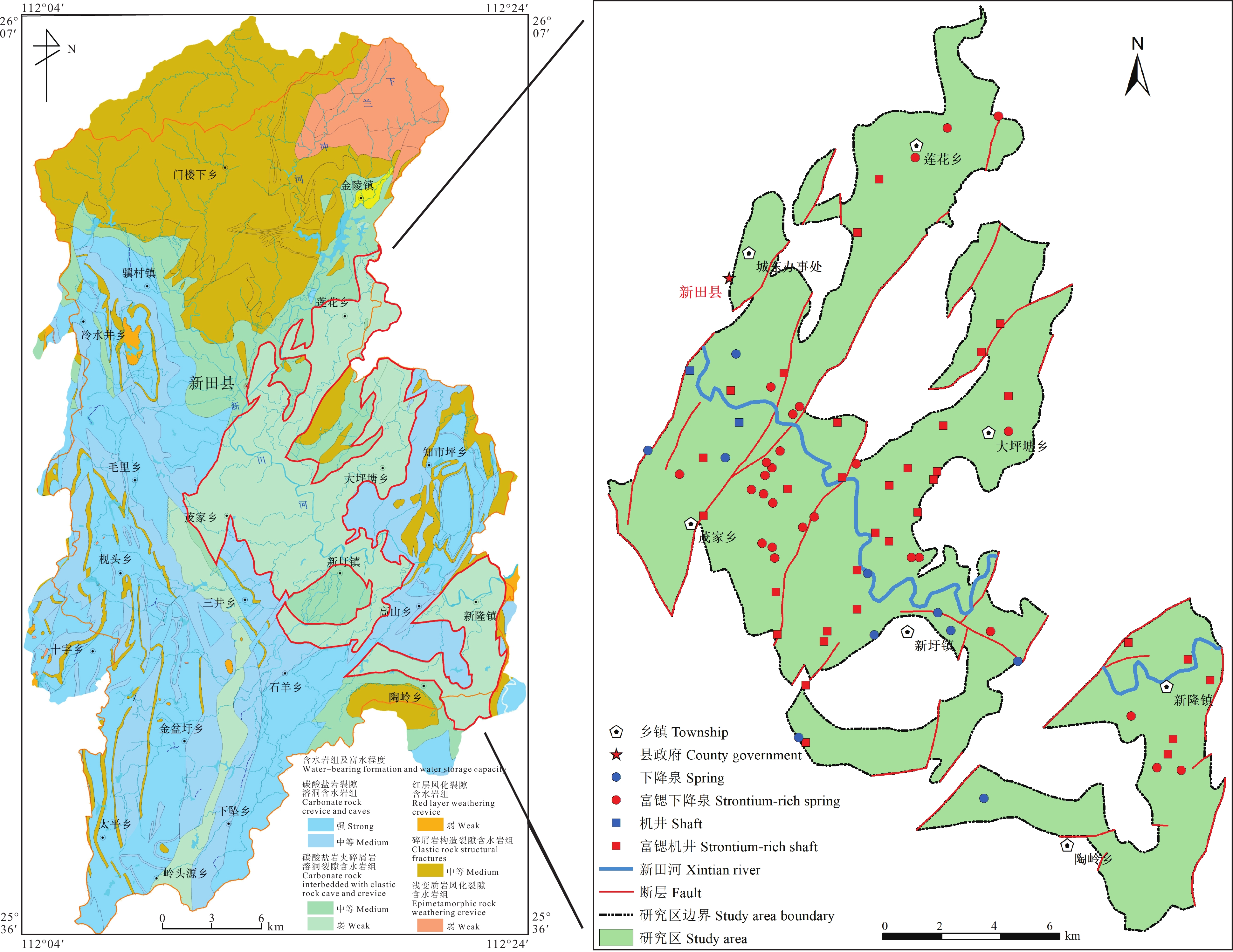
图 1 湖南新田县富锶地下水采样点分布图(据夏日元等, 2017修改)
Figure 1. Map showing distribution of sampling sites of strontium−rich groundwater in Xintian County, Hunan Province (modified from Xia Riyuan et al., 2017)
表 1 湖南新田县大气降水、下降泉、机井水化学指标含量统计结果
Table 1 Statistics of hydrochemical indicator content in springs, shafts and precipitation
分类 统计量 pH Sr2+ K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ HCO3− SO42− Cl− TDS 下
降
泉最小值 6.76 0.03 0.07 0.37 39.38 1.73 132.50 4.29 1.40 136.91 最大值 7.81 0.67 16.44 15.68 131.14 13.41 398.43 57.71 27.45 411.50 平均值 7.13 0.26 1.69 3.39 94.31 4.27 277.41 19.19 6.10 286.00 标准差 0.27 0.16 2.94 4.14 22.76 2.66 62.59 14.55 6.12 74.65 机
井最小值 6.90 0.20 0.28 0.76 33.10 1.86 182.98 5.18 1.68 186.56 最大值 7.62 8.47 16.04 105.52 159.42 58.22 581.31 98.43 88.78 618.82 平均值 7.33 2.64 2.57 31.63 91.83 22.92 393.74 40.36 19.96 428.27 标准差 0.21 2.48 2.94 35.96 37.79 16.31 80.89 25.33 22.00 105.02 大气降水 7.53 0.00771 0.77 0.19 8.92 0.37 31.49 5.53 0.9 36.27 注:除pH外所有指标含量单位均为mg/L;大气降水样品数1组,下降泉样品数33组,机井样品数28组。 表 2 富锶地下水部分常规指标含量统计结果
Table 2 Statistics of some conventional indexes content in strontium−rich groundwater
指标 下降泉 机井 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 Al/(μg/L) 178 / − 670 / − Cu/(μg/L) 1.52 / − 8.66 / − Pb/(μg/L) 0.76 0.42 0.25 15 1.85 0.32 Zn/(μg/L) 15.8 / − 437 / − Cr/(μg/L) 10.4 5.41 1.47 8.99 6.19 2.36 Cd/(μg/L) 0.2 / − 0.4 / − Mn/(μg/L) 190 / − 571 / − As/(μg/L) 1.38 / − 5.03 / − Hg/(μg/L) 0.14 / − 1.87 / − Se/(μg/L) 1.98 / − 2.04 / − Fe/(mg/L) 0.27 / − 1.1 / − NO3−−N/(mg/L) 78.94 / − 64.46 / − CODMn/(mg/L) 2.51 / − 1.37 / − 注:“−”表示含量低于检测线;“/”表示无数据。 -
[1] Acheampong S Y, Hess J W. 1998. Hydrogeologic and hydrochemical framework of the shallow groundwater system in the southern Voltaian sedimentary basin, Ghana[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, (6): 527−537.
[2] Banner J L. 1995. Application of the trace element and isotope geochemistry of strontium to studies of carbonate diagenesis[J]. Sedimentology, 42(5): 805−824. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1995.tb00410.x
[3] Bao Zhenxin. 2010. Parameter Estimation on Curve–Fitting Methodology in Hydrologic Frequency Analysis[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, 1–81(in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Cao Jianwen, Xia Riyuan, Tang Zhonghua, Zhao Liangjie, Wang Zhe, Luan Song, Wang Song. 2021. Groundwater resources in Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao greater bay area and its development potential[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1075−1093 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] China Geological Survey. 2012. Handbook of Hydrogeology (Second Edition)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 686–694(in Chinese).
[6] Fan Wei, Yang Yuesuo, Ye Xueyan, Lu Ying. 2010. Hydrogeochemical and environmental characteristics of strontium–enrichment in groundwater and its genesis in Qingken lake area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 40(2): 349−355 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Gao Xubo, Xiang Xuanli, Hou Baojun, Gao Liebo, Zhang Jianyou, Zhang Songtao, Li Chengcheng, Jiang Chunfang. 2020. Application of hydrochemistry coupled with stable isotopes in the study of karst water hydrogeology[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 39(5): 629−636 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Guo Qinghai, Wang Yanxin. 2006. Hydrogeochemistry as an indicator for karst groundwater flow: A case study in the Shentou karst water system, Shanxi, China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 25(3): 85−88 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Huang Q B, Qin X Q, Yang Q Y, Liu P Y, Zhang J S. 2016. Identification of dissolved sulfate sources and the role of sulfuric acid in carbonate weathering using δ13CDIC and δ34S in karst area, northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(1): 51. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4869-6
[10] Huang Qibo, Kang Zhiqiang, Qin Xiaoqun, Yu Jianguo, Su Chuntian. 2011. Distribution characteristics of Sr2+, Sr/Mg, Sr/Ca and its applications in karst water system of Xishui County[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 30(4): 98−103 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Huang Qibo, Qin Xiaoqun, Liu Pengyu, Tang Pingping. 2014. The characteristics and influencing factors of SO42– and sulfate isotope (δ34S) in different types of groundwater in Fenyang, Shanxi Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 34(2): 364−371 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Huang Qibo. 2019. The Carbon Sequestration Effect in Semi–Arid Karst Area: A Case Study of Liuling Spring Catchment, Shanxi Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1−130 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Jiang Zhongcheng, Xia Riyuan, Shi Jian, Pei Jianguo, He Shiyi, Liang Bin. 2006. The application effects and exploitation capacity of karst underground water resources in Southwest China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 27(5): 495−502 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Li Yilian, Wang Yanxin, Zhang Jianghua, Gao Hongbo. 2000. Geochemical modeling of sulfate pollution in karst water of Niangziguan region, Shanxi Province, China[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 25(5): 467−471 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li Yilian, Wang Yanxin, Zhou Lairu, Gao Hongbo, Zhang Jianghua. 2002. Hydrogeochemical modeling on saturation of minerals in groundwater: A case study at Niangziguang, northern China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 21(1): 32−36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Liu Congqiang. 2007. Biogeochemical Processes and Cycling of the Nutrients in the Earth’s Surface–Chemical Erosion and Nutrient Cycling in Karstic Catchment, Southwest China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 311–314(in Chinese).
[17] Liu C Q, Lang Y C, Satake H, Wu J H, Li S L. 2008. Identification of anthropogenic and natural inputs of sulfate and chloride into the karstic ground water of Guiyang, SW China: Combined δ37Cl and δ34S approach[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(15): 5421−5427.
[18] Liu Qingxuan, Wang Guiling, Zhang Fawang. 2004. Geochemical environment of trace element strontium (Sr) enriched in mineral waters[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 31(6): 19−23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Ma Zhiyuan, Fan Jijiao. 2005. Sulfate forming from groundwater in eastern Weibei karst area, Shanxi Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 33(3): 45−48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Nai Weihua, Wang Wenke, Wang Yixing, Duan Lei, Shi Jie, Li Bin. 2018. Sulfate distribution and source of groundwater from Kashgar plain[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 36(1): 120−123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Odum H T. 1957. Strontium in natural waters[J]. Publications of the Institute of Marine Science, University of Texas, 4(2): 22–37.
[22] Plummer L N, Busby J F, Lee R W, Hanshaw B B. 1990. Geochemical modeling of the Madison aquifer in parts of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dokata[J]. Water Resource Research, 26(9): 1981−2014. doi: 10.1029/WR026i009p01981
[23] Qian Hui, Ma Zhiyuan, Li Peiyue. 2012. Hydrogeochemistry (Second Edition)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 47–48(in Chinese).
[24] Ren Kun, Pan Xiaodong, Lan Ganjiang, Peng Cong, Liang Jiapeng, Zeng Jie. 2021. Seasonal variation and sources identification of dissolved sulfate in a typical karst subterranean stream basin using sulfur and oxygen isotopes[J]. Environmental Science, 42(9): 4267−4274 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Shawan S D, Andrew L H. 2002. Strontium and carbon isotope constraints on carbonate–solution interactions and inter–aquifer mixing in groundwaters of the semi–arid Murray Basin, Australia[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 262: 50−67. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00021-5
[26] Shen Zhaoli, Zhu Wanhua, Zhong Zuoshen. 1993. Fundamentals of Hydrogeochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 96–97(in Chinese).
[27] Siegel D I, Bickford M E, Orrell S E. 2000. The use of strontium and lead isotopes to identify sources of water beneath the Fresh Kills landfill, Staten Island, New York, USA[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 15(4): 493−500. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00063-3
[28] Su Chuntian, Huang Chenhui, Zou Shengzhang, Xie Daixing, Zhao Guangshuai, Tang Jiansheng, Luo Fei, Yang Yang. 2017a. Enrichment environment and sources of strontium of groundwater in Xintian county, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 36(5): 678−683 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Su Chuntian, Zhang Fawang, Xia Riyuan, Yao Xin, Zou Shengzhang, Luo Fei, Zhao Guangshuai, Yang Yang, Ba Junjie, Li Xiaopan. 2017b. A study of the water–rock interaction of large rich Sr mineral spring in Xintian, Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(5): 1029−1030 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Su Chuntian, Tang Jiansheng, Luo Fei, Li Zhaolin. 2020. Investigation and Study on Groundwater in Xintian River Karst Basin, Hunan Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 131–153(in Chinese).
[31] Wang Yanxin, Sun Lianfa, Luo Chaohui, Gao Hongbo, Sun Zhihong. 1997. The analyse of hydrochemical and istopic information indicating the dynamic environment of Niangziguan springs[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 24(3): 1−5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wang Yu. 2020. Evaluation status and problems of groundwater resource potential in Yunnan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 39(2): 137−146 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Wang Zengyin, Liu Juan, Cui Yinxiang, Wang Tao, Guo Tianyuan. 2003. Distribution characteristics of Sr/Mg、Sr/Ca and applications in Yanhe spring karst water system[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 30(2): 15−19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Xia Riyuan, Jiang Zhongcheng, Zou Shengzhang, Cao Jianhua, Qin Xiaoqun, Su Chuntian, Luo Weiqun, Zhou Lixin. 2017. Progress of hydrogeology and environmental geology comprehensive survey in karst area[J]. Geological Survey of China, 4(1): 1−10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Xia Riyuan, Lu Haiping, Cao Jianwen, Zhao Liangjie, Wang Zhe, Luan Song. 2022. Characteristics of groundwater resources of karst areas in the Southern China and water resources guarantee countermeasures[J]. Geology in China, 49(4): 1139−1153 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Ye Ping, Zhou Aiguo, Liu Cunfu, Wu Jinbo. 2007. New water–rock interaction evidence for groundwater in the Hebei plain: Characteristics of Sr isotope tracer[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 34(4): 41−43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Zhang Jianghua, Liang Yongping, Wang Weitai, Han Xingrui, Hou Guangcai. 2009. A practical use of 34S in the investigation of karst groundwater resource in North China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 28(3): 235−241 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Zhao Guangshuai, Su Chuntian, Pan Xiaodong, Xie Daixing, Luo Fei, Yang Yang, Ba Junjie, Li Xiaopan, Bi Benteng. 2019. Hydrogeochemical zoning characteristics of the strontium mineral spring in Xintian county, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 38(6): 858−866 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Zhao Liangjie, Wang Ying, Zhou Yan, Cao Jianwen, Yang Yang, Wang Zhe. 2022. Groundwater resources evaluation in the Pearl River basin based on SWAT model[J/OL]. Earth Science, 1−19. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220119.1634.006.html(in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] 鲍振鑫. 2010. 水文频率分析适线法参数估计研究[D]. 南京: 南京水利科学研究院, 1–81. [41] 曹建文, 夏日元, 唐仲华, 赵良杰, 王喆, 栾松, 王松. 2021. 粤港澳大湾区地下水资源特征及开发潜力[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1075−1093. doi: 10.12029/gc20210407 [42] 范伟, 杨悦锁, 冶雪艳, 路莹. 2010. 青肯泡地区地下水中锶富集的水文地球化学环境特征及成因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 40(2): 349−355. [43] 高旭波, 向绚丽, 侯保俊, 高列波, 张建友, 张松涛, 李成城, 姜春芳. 2020. 水化学–稳定同位素技术在岩溶水文地质研究中的应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 39(5): 629−636. doi: 10.11932/karst2020y26 [44] 郭清海, 王焰新. 2006. 水文地球化学信息对岩溶地下水流动系统特征的指示意义—以山西神头泉域为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 25(3): 85−88. [45] 黄奇波, 康志强, 覃小群, 俞建国, 苏春田. 2011. 习水县岩溶水系统ρ(Sr2+)、ρ(Sr)/ρ(Ca)、ρ(Sr)/ρ(Mg)分布特征及其应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 30(4): 98−103. [46] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 唐萍苹. 2014. 汾阳地区不同类型地下水SO42–、δ34S的特征及影响因素[J]. 第四纪研究, 34(2): 364−371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.02.10 [47] 黄奇波. 2019. 北方半干旱岩溶区岩溶碳汇过程及效应研究—以山西柳林泉岩溶流域为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 1−130. [48] 蒋忠诚, 夏日元, 时坚, 裴建国, 何师意, 梁彬. 2006. 西南岩溶地下水资源开发利用效应与潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 27(5): 495−502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.012 [49] 李义连, 王焰新, 张江华, 高红波. 2000. 娘子关泉域岩溶水硫酸盐污染的地球化学模拟分析[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 25(5): 467−471. [50] 李义连, 王焰新, 周来茹, 高红波, 张江华. 2002. 地下水矿物饱和度的水文地球化学模拟分析—以娘子关泉域岩溶水为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 21(1): 32−36. [51] 刘丛强. 2007. 生物地球化学过程与地表物质循环—西南喀斯特流域侵蚀与生源要素循环[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 311–314. [52] 刘庆宣, 王贵玲, 张发旺. 2004. 矿泉水中微量元素锶富集的地球化学环境[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 31(6): 19−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2004.06.004 [53] 马致远, 范基姣. 2005. 陕西渭北东部岩溶地下水中硫酸盐的形成[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 33(3): 45−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2005.03.014 [54] 乃尉华, 王文科, 王艺星, 段磊, 史杰, 李斌. 2018. 喀什平原区地下水硫酸盐分布特征及来源[J]. 新疆地质, 36(1): 120−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2018.01.019 [55] 钱会, 马致远, 李培月. 2012. 水文地球化学(第二版) [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 47–48. [56] 任坤, 潘晓东, 兰干江, 彭聪, 梁嘉鹏, 曾杰. 2021. 硫氧同位素解析典型岩溶地下河流域硫酸盐季节变化特征和来源[J]. 环境科学, 42(9): 4267−4274. [57] 沈照理, 朱宛华, 钟佐燊. 1993. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 96–97. [58] 苏春田, 黄晨晖, 邹胜章, 谢代兴, 赵光帅, 唐建生, 罗飞, 杨杨. 2017a. 新田县地下水锶富集环境及来源分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 36(5): 678−683. [59] 苏春田, 张发旺, 夏日元, 姚昕, 邹胜章, 罗飞, 赵光帅, 杨杨, 巴俊杰, 李小盼. 2017b. 湖南新田发现大型富锶矿泉水及机理研究[J]. 中国地质, 44(5): 1029−1030. doi: 10.12029/gc20170515 [60] 苏春田, 唐建生, 罗飞, 李兆林. 2020. 湖南新田河岩溶流域地下水调查研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 131–153. [61] 王焰新, 孙连发, 罗朝晖, 高红波, 孙志鸿. 1997. 指示娘子关泉群水动力环境的水化学–同位素信息分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 24(3): 1−5. [62] 王宇. 2020. 云南省地下水资源潜力评价现状与问题分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 39(2): 137−146. doi: 10.11932/karst20200201 [63] 王增银, 刘娟, 崔银祥, 王涛, 郭天元. 2003. 延河泉岩溶水系统Sr/Mg、Sr/Ca分布特征及其应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 30(2): 15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.02.004 [64] 夏日元, 蒋忠诚, 邹胜章, 曹建华, 覃小群, 苏春田, 罗为群, 周立新. 2017. 岩溶地区水文地质环境地质综合调查工程进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 4(1): 1−10. [65] 夏日元, 卢海平, 曹建文, 赵良杰, 王喆, 栾崧. 2022. 南方岩溶区地下水资源特征与水资源保障对策[J]. 中国地质, 49(4): 1139−1153. doi: 10.12029/gc20220408 [66] 叶萍, 周爱国, 刘存富, 武金博. 2007. 河北平原地下水水––岩作用新证据—锶同位素示踪演变特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 34(4): 41−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.04.011 [67] 张江华, 梁永平, 王维泰, 韩行瑞, 候光才. 2009. 硫同位素技术在北方岩溶水资源调查中的应用实例[J]. 中国岩溶, 28(3): 235−241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.03.002 [68] 赵光帅, 苏春田, 潘晓东, 谢代兴, 罗飞, 杨杨, 巴俊杰, 李小盼, 毕奔腾. 2019. 湖南新田锶矿泉水文地球化学分带特征分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 38(6): 858−866. doi: 10.11932/karst20190603 [69] 赵良杰, 王莹, 周妍, 曹建文, 杨杨, 王喆. 2022. 基于SWAT模型的珠江流域地下水资源评价研究[J/OL]. 地球科学, 1−19. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220119.1634.006.html [70] 中国地质调查局. 2012. 水文地质手册[M]. 第二版, 北京: 地质出版社, 686–694. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 覃悦,蔡永丰,刘军,刘希军,周云,李政林,杨栎娅. 古特提斯演化的岩浆作用记录:来自桂东南印支期火山岩证据. 地球科学. 2024(09): 3140-3154 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: