Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Sanheshan pluton in southwest of Jiaodong: Evidence from geochronology, geochemistry and Sr−Nd−Pb−Hf isotopes
-
摘要:研究目的
胶东地区是中国最大的金矿矿集区,也是山东省最为重要的铜钼多金属矿成矿区。加强中生代花岗岩的岩相学、岩石地球化学和年代学等方面的研究,有利于进一步促进该区金及多金属矿的找矿工作。
研究方法本文以胶东半岛西南部三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩为研究对象,开展系统的岩相学、LA−ICP−MS 锆石U−Pb 年代学、主微量元素地球化学、全岩Sr−Nd−Pb 同位素及锆石Lu−Hf 同位素研究,旨在探讨其岩石成因、岩浆源区性质和构造背景。
研究结果LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年结果表明,中细粒二长花岗岩的成岩年龄为(115.42±0.27)Ma,花岗斑岩的形成年龄为(115.21±0.25)Ma,形成时代均属中生代早白垩晚期;岩石地球化学特征表明,中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩均属高钾钙碱性I型花岗质岩石,LREE较HREE分馏明显,具弱Ce负异常和明显Eu中等负异常,富集Rb、K、Zr和Hf,亏损Sr、Ba、Nb、P、Ti;全岩Sr−Nd−Pb及锆石Hf同位素分析结果表明,三合山岩体起源于重熔的下地壳,并受到了幔源物质的混染。
结论三合山岩体形成于早白垩世太平洋板块相对欧亚板块俯冲导致的陆内伸展背景下,为中国东部岩石圈减薄过程中壳幔相互作用的产物。
创新点:(1)厘定了三合山岩体的侵入时序;(2)填补了胶东西南部中生代花岗岩的空缺;(3)为胶东西南部早白垩世晚期构造岩浆活动提供了新的佐证和理想的成岩成矿研究对象。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveJiaodong area is the largest gold ore concentration area in China and the most important copper−molybdenum polymetallic ore deposit area in Shandong Province. Strengthening the study of petrography, petrogeochemistry and chronology of Mesozoic granites is conducive to further promoting the prospecting of gold and polymetallic deposits in this area.
MethodsTaking the medium−fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry as the main research object, this study primarily carried onlaser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA−ICP−MS) U−Pb chronology on the zircon, whole−rock geochemistry,whole−rock Sr−Nd−Pb and zircon Hf isotopic study, aiming to confirm the timing and discuss the petrogenesis and tectonic settings of the Sanheshan pluton in Southwest Jiaodong.
ResultsThe results of LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb show that the medium−fine grained monzogranite was formed in (115.42 ± 0.27) Ma and the granite porphyry was formed in (115.21±0.25) Ma, both of which are belonging to the Late Early Cretaceous of Mesozoic. Geocahemical research shows that the medium−fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry are both belong to themetaluminous high−K calc−alkaline series I−type granites; LREE are more obvious than HREE,with weak Ce negative anomaly and obvious Eu moderate negative anomaly; trace elements enriched in Rb, K, Zr and Hf, depleted in Sr, Ba, Nb, P and Ti. The whole rock Sr−Nd−Pb and zircon Hf isotope analysis results show that the Sanheshan pluton was originated from the remelting lower crust, and was contaminated by mantle materials.
ConclusionsThe Sanheshanpluton was formed in the continental extension background caused by the subduction of the Pacific plate relative to the Eurasian plate in the Early Cretaceous, which was the product of crust−mantle interaction during the lithospheric thinning in eastern China.
-
Keywords:
- geochemistry /
- geochronology /
- Sr−Nd−Pb−Hf isotope /
- geological survey engineering /
- Jiaodong /
- Shandong Province
Highlights:(1) The intrusive timing of Sanheshanpluton is determined; (2) It fills the vacancy of Mesozoic granites in the southwest of Jiaodong; (3) It provides new evidence and ideal research object for regional tectonic magmatic activity in Late Early Cretaceous.
-
1. 引 言
位于华北克拉通东南缘的胶东地区是中国最大的金矿矿集区,也是山东省最为重要的铜钼多金属矿成矿区(丁正江等,2012;李杰,2012;Song et al.,2021;宋明春等,2022;韩小梦等,2024)。以往该地区地质找矿和科研工作主要围绕金矿展开,其他矿种勘查和研究程度相对较低。尤其是该区可观的铜钼多金属矿化,其潜力被金矿的光芒所掩盖(文博杰等,2015)。近年来,随着福山邢家山钨钼矿(大型)、王家庄铜矿(中型)、栖霞尚家庄钼矿床(中型))、香夼铅锌矿床(中型)、荣成冷家钼矿(小型)和威海大邓格金多金属矿(小型)等一系列铜钼多金属矿床勘查、研究工作的不断深入(李杰等,2013;丁正江等,2015;李杰等,2016;郭晶等,2019;Liu et al.,2022),丁正江等(2013)、宋明春(2014)认为,金矿、铜钼多金属矿与伟德山期花岗岩关系密切,二者是同一构造背景、同一时代形成的产于不同构造部位、不同围岩条件的不同矿床类型,属同一成矿系列;以壳幔同熔型花岗岩(伟德山花岗岩)为中心,由近及远依次产出钼矿、钼钨矿→铜矿、银矿、铅锌矿、多金属矿→金矿。
本次研究的三合山岩体地处胶东半岛的西南部,胶莱盆地的西北缘,其内部及边缘发育金、钼、铅锌等多金属矿化(孙璐伟和王光良,2014)。由于缺少岩石地球化学和同位素测年数据支持,三合山岩体成岩时代的划分存在较大的争议,相关论文引用亦较为混乱:董银峰等(2015)根据区域岩浆岩分布特征,将其划为晚侏罗世玲珑期侵入岩;田杰鹏等(2016)、万中杰(2017)、曾凡玉(2019)将其划入中生代燕山晚期(雨山序列、崂山序列)侵入岩。三合山岩体形成于什么时代?产出于何种构造背景?岩体与金、铜钼多金属矿成矿关系如何?这些问题不仅制约了对该岩体岩浆演化进程和序列的探索研究,还限制了对赋存在其中的矿床的形成构造背景和成矿过程的厘定。鉴于此,本文以三合山岩体的中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩为研究对象,利用LA−ICP−MS 锆石U−Pb 年代学、主微量元素地球化学、全岩Sr−Nd−Pb 同位素及锆石Lu−Hf 同位素分析等手段,确定了三合山岩体的岩石地球化学类型,厘定了侵入时序,揭示了成岩构造环境,填补了胶东西南部中生代花岗岩的空缺,为区域早白垩世晚期构造岩浆活动提供了新的佐证和理想的成岩成矿研究对象。
2. 区域地质背景
胶东地区位于华北克拉通的东南缘,横跨华北板块和秦岭—大别—苏鲁造山带两个Ⅰ级构造单元(图1),包含胶北隆起、威海隆起和胶莱盆地三个Ⅲ级构造单元(宋明春等,2020)。胶北隆起结晶基底以新太古界胶东岩群为主,其次为古元古界荆山群、粉子山群,盖层为中元古界蓬莱群;威海隆起结晶基底为含超高压榴辉岩的花岗质片麻岩;胶莱盆地基底以胶东群、粉子山群和荆山群为主,盖层以中生界青山群、莱阳群和王氏群为主。区域岩浆岩活动剧烈,主要集中发育于新太古代、元古代和中生代。其中新太古代侵入岩受基底构造控制整体呈近东西向展布,元古宙侵入岩受区域韧性变形带控制呈北北东—北东向展布,中生代侵入岩受北北东—北东向断裂构造严格控制(丁正江等,2015)。区域构造以近东西向褶皱、韧性剪切带构造体系和NE—NNE向郯庐断裂带羽状断裂构造体系为主。
![]() Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Jiaodong (a) and distribution map of gold-polymetallic deposits (b) (modified from Ding Zhengjiang et al.,2013; Yang Liqiang et al.,2014)
Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Jiaodong (a) and distribution map of gold-polymetallic deposits (b) (modified from Ding Zhengjiang et al.,2013; Yang Liqiang et al.,2014)胶东地区金及多金属矿产资源极为丰富。金矿主要赋存在NE—NNE向脆性断裂中,自西向东可划分为三山岛成矿带,焦家成矿带、招平成矿带,栖霞成矿带和牟乳成矿带,断裂构造距郯庐断裂的远近与断裂内金矿体的规模呈负相关性(李洪奎等,2017)。多金属矿受伟德山期花岗岩控制明显,大致围绕岩体形成了内部钼‒中边部铜银‒外部铅锌多金属的分布环带(宋明春等,2015)。
3. 研究区地质概况
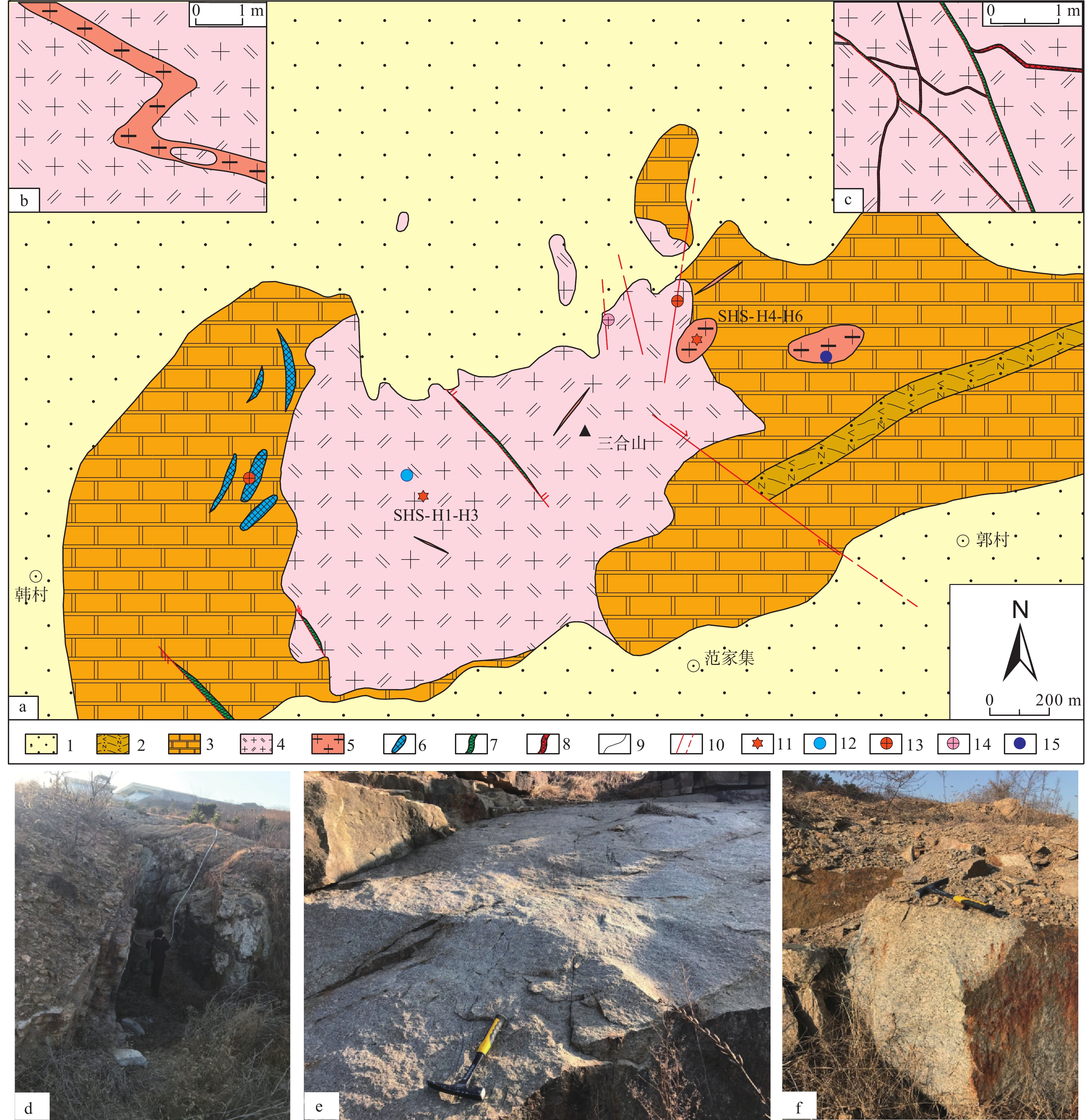
研究区地处浅覆盖区,地层、岩浆岩仅在中部的三合山及其四周出露(图2a)。
![]() 图 2 三合山岩体地质略图及野外露头照片(据山东省地质矿产勘查开发局第四地质大队,1992
图 2 三合山岩体地质略图及野外露头照片(据山东省地质矿产勘查开发局第四地质大队,19921 修改)a—三合山地质略图;b—岩性穿插关系;c—矿脉穿插关系;d—民采老硐;e—二长花岗岩野外露头;f—花岗斑岩野外露头;1—第四系;2—荆山群野头组;3—荆山群陡崖组;4—中细粒二长花岗岩;5—花岗斑岩;6—矽卡岩;7—萤石−重晶石脉;8—石英-辉钼矿脉;9—地质界线;10—实测/推测断裂;11—采样位置;12—辉钼矿点;13.—金矿点;14—银矿点;15—铅矿点Figure 2. Geological map and field photos of Sanheshanpluton (modified from Shandong Provincial No.4 Institute of Geological and Mineral Survey,19921 )a–Sketch geological map of Sanheshan; b–Lithology interspersed relation; c–Ore veins interspersed relation; d–Civilian mines; e–Field outcrops of monzogranite; f–Field outcrop of granite porphyry; 1–Quaternary; 2–Yetou Formation of Jingshan Group; 3–Douya Formation of Jingshan Group; 4–Medium−fine grained monzogranite; 5–Granite porphyry; 6–Skarn; 7–Fluorite−barite veins; 8–Quartz−molybdenite vein; 9–Geological boundary; 10–Measured/presumed fault; 11–Sampling location; 12–Molybdenite points; 13–Gold sites; 14–Silver ore points; 15–Lead ore points地层以古元古代荆山群野头组和陡崖组为主:野头组岩性以斜长角闪岩、透灰岩、长石石英岩和大理岩为主,陡崖组岩性以石墨黑云变粒岩、斜长片麻岩和混合岩化花岗岩为主。
三合山岩体是区内主要侵入岩,呈小岩株状侵入古元古代荆山群中,占据了整个三合山。岩体平面呈近东西向椭圆状,东西长1.5 km,南北宽0.8~1.2 km,出露面积约1.5 km2。侵入岩包含中深成相和浅成相岩石两类岩石。中生代燕山晚期,中深成相的中细粒二长花岗岩侵位固结后,岩石圈发生拆沉和减薄,浅成相的花岗斑岩沿断裂和构造薄弱部位侵位于斑状二长花岗岩和古元古代地层中。野外可在花岗斑岩中见到中细粒二长花岗岩捕虏体(图2b)。
区内控矿构造活动主要分为两期:早期裂隙(节理)构造,在侵入岩冷凝过程形成,按裂隙走向可化为20°~30°、345°~355°、80°~115°三组,裂隙宽1~5 mm,倾角60°~80°,呈平行“裂隙束”和“交叉状裂隙”呈现,内部充填辉钼矿石英脉和辉钼矿脉;晚期构造以北西向和近东西向断裂构造为主,断裂长200~700 m,宽1~2 m,切割早期形成的含钼裂隙构造(图2c),内部充填重晶石、萤石矿脉和含金、银、铅石英脉。地表见多处沿断裂构造采掘的民采老硐(图2d)。
4. 样品采集与岩相学特征
本次共采集地球化学测试样品6件,其中细粒二长花岗岩样品3件(SHS-H1-H3),采集于三合山西北部采坑(图2e),地理坐标36°44′22″N,119°33′39″E;花岗斑岩样品3件(SHS-H4-H6),采集于三合山东北部花岗岩采坑(图2f),地理坐标36°44′39″N,119°34′16″E。
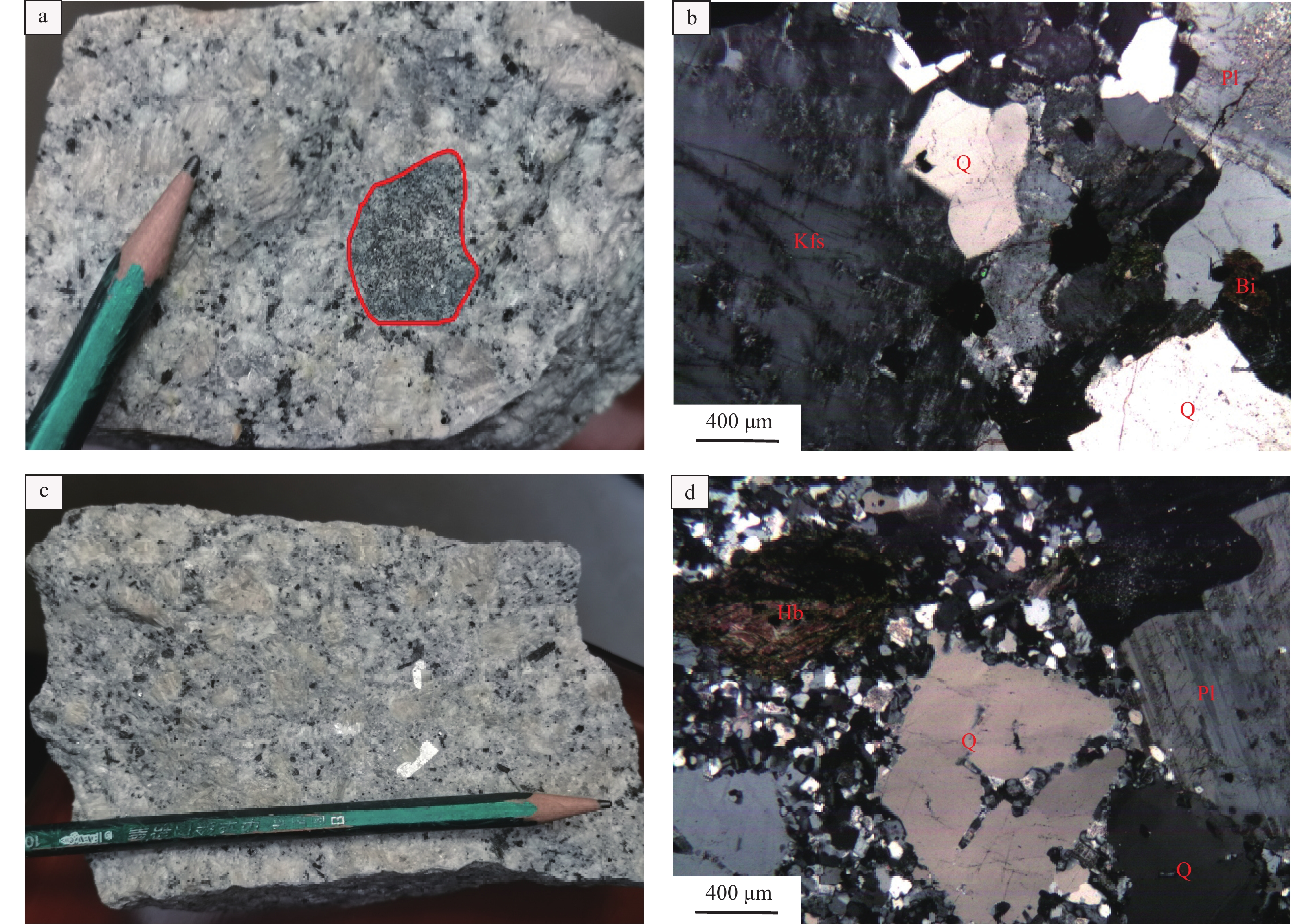
中细粒二长花岗岩呈岩株状产出,风化岩石呈灰白色,新鲜岩石呈浅灰色−肉红色,似斑状结构,块状构造(图3a),内部可见暗色闪长质包体。主要矿物为钾长石(35%~40%)、斜长石(30%~35%)、石英(20%~25%),次要矿物为黑云母(1%~5%)和角闪石(1%~5%),副矿物为锆石、榍石、磷灰石及极少量不透明矿物。斑晶主要由钾长石和斜长石组成,偶见石英(图3b),粒径一般2~5 mm,基质由斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母、角闪石组成,粒径一般0.5~1 mm。斜长石呈自形—半自形板状,聚片双晶发育,部分大颗粒可见环带构造,局部发育绢云母化;钾长石呈半自形板状—他形粒状,局部可见轻微高岭土化;石英呈他形粒状分布于钾长石和斜长石颗粒间,构成细粒花岗结构。黑云母呈片状,星散状分布,具绿泥石化;角闪石呈半自形柱状,星散状分布。
![]() 图 3 三合山岩体手标本及显微镜照片a—中细粒二长花岗岩及其内部暗色包体;b—花岗斑岩;c—花岗结构;d—斑状结构;Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Bi—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Hb—角闪石Figure 3. Field and micrograph of Sanheshan plutona–Medium−fine grained monzogranite and its internal dark inclusion; b–Granite porphyry; c–Granitic texture; d–Porphyric texture; Q–Quartz; Kfs–Potash feldspar; Bi–Biotite; Pl–Plagioclase; Hb–Hornblende
图 3 三合山岩体手标本及显微镜照片a—中细粒二长花岗岩及其内部暗色包体;b—花岗斑岩;c—花岗结构;d—斑状结构;Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Bi—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Hb—角闪石Figure 3. Field and micrograph of Sanheshan plutona–Medium−fine grained monzogranite and its internal dark inclusion; b–Granite porphyry; c–Granitic texture; d–Porphyric texture; Q–Quartz; Kfs–Potash feldspar; Bi–Biotite; Pl–Plagioclase; Hb–Hornblende花岗斑岩呈脉状、小岩株状侵入中细粒二长花岗岩和古元古代荆山群中。风化岩石呈灰白色,新鲜岩石呈浅灰色,斑状结构,块状构造(图3c)。主要由斜长石(40%~45%)、钾长石(35%~40%)、石英(20%~25%)、黑云母(1%~5%)和少量角闪石组成,副矿物为锆石和磷灰石。斑晶为斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母及角闪石(图3d),均为半自形晶,粒径一般2~7 mm,斜长石呈自形—半自形板状,可见聚片双晶、卡钠复合双晶,部分可见环带,发育绢云母化;钾长石呈板状,可见格子双晶及钠质条纹,局部具轻微高岭土化;石英呈他形粒状,可见港湾、穿孔状熔蚀;黑云母多呈片状,角闪石呈柱状,具绿泥石化蚀变。基质为斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母,粒径一般0.1~0.2 mm。
5. 测试方法
5.1 全岩主、微量元素分析
主、微量元素测试工作是在北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司完成。首先将岩石粉碎粗碎至厘米级的块体,选取无蚀变及脉体穿插的新鲜样品用纯化水冲洗干净,烘干并粉碎至200目以供测试使用。
主量元素测试首先将粉末样品(200目)称量后加Li2B4O7(1:8)助熔剂混合,并使用融样机加热至1150℃,使其在金铂坩埚中熔融成均一玻璃片体,后使用XRF(Zetium,PANalytical)测试。测试精度优于1%。其中Fe2O3T为荧光光谱仪测试分析全铁的含量,FeO含量通过湿化学分析方法得到。
微量元素测试首先将粉末样品(200目)称量并置放入聚四氟乙烯溶样罐,并加入HF+HNO3,在干燥箱中将高压消解罐保持在190℃温度72 h,取出后用盐酸稀释定容后放置于仪器中分析。测试使用ICP−MS(M90,analytikjena)完成,所测数据根据监控标样GSR-2显示误差小于5%,部分挥发性元素及极低含量元素的分析误差小于10%。
5.2 全岩Sr−Nd−Pb同位素
Sr−Nd−Pb同位素测试在北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司完成。样品经过消解及同位素分离后,使用Thermo Fisher Scientific多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪Neptune Plus MC−ICP−MS分别测定87Sr/86Sr值和143Nd/144Nd值,根据88Sr/86Sr值(8.373209)和143Nd/144Nd值(0.7218)对测定的87Sr/86Sr值和143Nd/144Nd值进行仪器分馏校正。使用Tl(205Tl/203Tl=0.23875)对Pb同位素进行分馏校正。在样品测试的整个过程中,所测定的BHVO-1标样和BCR-2标样的Nd−Sr同位素比值分别为143Nd/144Nd=0.0.512984±0.000006(±2σ)、87Sr/86Sr=0.703485±0.000006(±2σ),143Nd/144Nd =0.0.512626±0.000006(±2σ)、87Sr/86Sr=0.705074±0.000009(±2σ)。实验详细的分析步骤见文献(张立仕等,2021)。
5.3 锆石LA−ICP−MS U−Pb定年
锆石单矿物分选由廊坊市拓轩岩矿检测服务有限公司完成。首先将待测年岩石样品粉碎至80~100目,接着采用常规和磁选方法进行初步分选,再在双目显微镜下手工挑选出锆石颗粒。将晶型和透明度较好的颗粒整齐地粘在双面胶上,用环氧树脂灌注成激光样品靶,然后抛磨至锆石的核部出露。锆石的反射光、透射光和阴极发光(CL)图像同样在廊坊市拓轩岩矿检测服务有限公司完成。
锆石U−Pb同位素定年和微量元素含量在北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司利用LA−ICP−MS同时分析完成。激光剥蚀系统为NWR193(Elemental Scientific Lasers LLC),ICP−MS为德国耶拿M90。激光剥蚀过程中采用氦气作载气、氩气为补偿气以调节灵敏度,二者在进入ICP之前通过一个Y型接头混合。每个样品点分析数据包括20~30 s的空白信号和50 s的样品信号。U−Pb 同位素定年中采用锆石标准91500和PLEsovice作外标进行同位素分馏校正,每分析5~10个样品点,分析2次91500,并对PLEsovice分析一次作为监控。锆石微量元素含量利用SRM610作为多外标、Si作内标的方法进行定量计算。分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U−Th−Pb同位素比值和年龄计算),采用软件ZSkits完成。锆石样品的U−Pb年龄谐和图绘制和年龄权重平均计算均采用Isoplot/Ex_ver3 (Ludwig,2003)完成。本次测试的91500及PLEsovice标样均符合推荐值(Black et al.,2003;Sláma et al.,2008)。
5.4 锆石Lu−Hf同位素
锆石Lu−Hf同位素分析的锆石点均挑选于LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年中的有效点,每件样品20点,共计40点。锆石Hf同位素分析在北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司实验室完成。分析过程中采用美国热电(Nepture-plus MC−ICP−MS)多接收电感耦合等离子质谱仪和NWR193激光烧蚀进样系统进行测定。测试步骤与校准方法参照Wu et al.(2006)。锆石剥蚀使用频率为8 Hz,能量为16 J/cm2的激光剥蚀31s,剥蚀出直径约30 μm的剥蚀坑。测试时,由于锆石中的176Lu/177Hf比值极其低(小于0.002),176Lu对176Hf的同位素干扰可以忽略不计。每个测试点的172Yb/173Yb平均值用于计算Yb的分馏系数,然后再扣除176Yb对176Hf的同质异位素干扰。172Yb/173Yb的同位素比值为1.35274(Chu et al.,2002)。数据处理采用软件ICP-MSDataCal完成。91500和Plesovice两个国际锆石标准与样品同时分析,91500进行外标校正,Plesovice作为监控标样。
6. 测试结果
6.1 岩石地球化学特征
选取三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩各3件样品进行了地球化学分析,其主微量和稀土元素组成见表1。较低的烧失量(LOI)数值,表明采集岩石新鲜,基本未经蚀变,数据可靠性高。
表 1 三合山岩体主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)测试结果Table 1. Major (%) and trace elements (10−6) data of Sanheshan pluton样号 SHS-H1 SHS-H2 SHS-H3 SHS-H4 SHS-H5 SHS-H6 样号 SHS-H1 SHS-H2 SHS-H3 SHS-H4 SHS-H5 SHS-H6 岩性 中细粒二长花岗岩 花岗斑岩 岩性 中细粒二长花岗岩 花岗斑岩 Al2O3 13.61 13.90 14.01 13.91 14.40 14.50 Cd 0.15 1.50 0.22 0.11 0.13 0.11 SiO2 72.50 72.13 71.39 71.34 69.95 70.94 In 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 CaO 1.17 1.05 1.30 1.40 1.46 1.45 Sb 0.16 0.86 0.44 0.22 0.23 0.18 K2O 4.80 5.12 5.09 4.72 5.15 5.09 Cs 0.96 0.88 1.27 1.27 1.21 1.41 Fe2O3T 2.15 2.30 2.46 2.57 2.50 2.50 Ba 479.20 635.43 711.47 652.29 960.24 853.53 FeO* 1.13 1.17 1.26 1.36 1.28 1.30 Ta 3.35 2.47 2.85 2.07 2.15 2.24 MgO 0.43 0.46 0.49 0.60 0.64 0.58 W 3.89 3.41 2.92 0.76 1.74 0.72 MnO 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.06 Re 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 Na2O 4.01 4.09 4.12 4.07 4.12 4.17 Tl 0.59 0.63 0.72 0.60 0.63 0.64 P2O5 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.12 0.12 0.12 Pb 17.19 18.23 20.02 17.67 18.54 19.80 TiO2 0.31 0.36 0.39 0.42 0.40 0.41 Bi 0.17 0.13 2.69 0.05 0.02 0.02 LOI 0.99 0.71 0.72 0.69 0.79 0.61 Th 18.10 15.34 15.77 17.15 14.74 16.45 Total 100.10 100.27 100.13 99.91 99.58 100.41 U 3.90 3.03 3.43 7.03 3.88 4.59 DI 89.85 90.58 89.48 88 87.56 88.6 Hf 4.83 5.02 6.14 5.20 4.85 4.62 SI 3.83 3.89 4.09 5.10 5.24 4.77 La 41.76 42.73 54.53 51.60 50.03 46.71 A/NK 1.15 1.13 1.14 1.18 1.17 1.17 Ce 80.86 81.09 99.04 89.69 86.72 83.07 A/CNK 0.98 0.98 0.96 0.97 0.96 0.97 Pr 7.89 7.83 9.64 8.17 8.32 7.67 AR 3.37 3.42 3.33 3.27 3.16 3.19 Nd 30.04 29.37 36.60 30.28 30.18 28.76 σ 2.63 2.91 2.99 2.73 3.19 3.07 Sm 5.28 4.68 5.96 4.64 4.68 4.52 Mg# 28.41 28.45 28.31 31.63 33.62 31.46 Eu 0.69 0.75 0.83 0.79 0.88 0.81 Li 10.91 7.90 10.87 15.89 16.53 15.96 Gd 4.63 4.41 5.29 4.35 4.21 4.07 Be 5.98 4.86 5.85 4.62 4.50 4.63 Tb 0.72 0.59 0.80 0.57 0.57 0.58 Sc 2.29 2.39 3.42 2.68 2.88 2.59 Dy 3.96 3.09 4.06 2.87 3.02 2.96 Ti 2223.66 2637.78 3036.49 3174.67 3064.32 3122.98 Ho 0.67 0.52 0.73 0.48 0.50 0.49 V 12.34 12.27 14.87 19.51 19.22 19.42 Er 2.23 1.67 2.39 1.60 1.64 1.63 Cr 9.44 10.69 3.15 14.88 7.56 14.15 Tm 0.41 0.30 0.41 0.28 0.29 0.29 Mn 349.94 409.02 461.86 425.79 469.52 419.42 Yb 2.63 2.10 2.64 1.97 2.06 2.02 Co 2.04 3.20 4.81 5.30 4.47 4.34 Lu 0.39 0.31 0.40 0.29 0.29 0.29 Ni 1.37 27.64 80.79 39.74 21.85 22.43 ∑REE 182.16 179.44 223.32 197.58 193.39 183.87 Cu 8.86 31.81 15.33 10.52 10.65 16.48 LREE 166.52 166.45 206.60 185.17 180.81 171.54 Zn 36.18 286.83 37.00 42.62 36.40 38.14 HREE 15.64 12.99 16.72 12.41 12.58 12.33 Ga 18.50 17.74 19.92 18.64 18.57 19.46 L/H 10.65 12.81 12.36 14.92 14.37 13.91 As 1.36 2.68 2.03 1.77 1.65 1.60 δEu 0.42 0.50 0.44 0.53 0.59 0.57 Rb 184.80 173.34 193.80 180.07 187.87 194.07 δCe 1.00 0.99 0.96 0.95 0.93 0.96 Sr 152.11 149.54 176.50 243.13 276.10 275.48 (La/Sm)N 4.98 5.74 5.76 7.00 6.72 6.50 Y 21.85 16.42 23.75 15.49 15.86 16.05 (La/Yb)N 10.71 13.72 13.93 17.66 16.37 15.59 Zr 195.03 225.33 276.03 210.21 194.88 187.26 (Sm/Nd)N 0.54 0.49 0.50 0.47 0.48 0.48 Nb 27.91 27.23 32.75 24.73 24.62 25.10 (Gd/Yb)N 1.42 1.69 1.62 1.78 1.65 1.63 Mo 1.87 13.57 14.46 9.00 8.67 5.96 T/℃ 796 808 823 799 790 787 6.1.1 主量元素
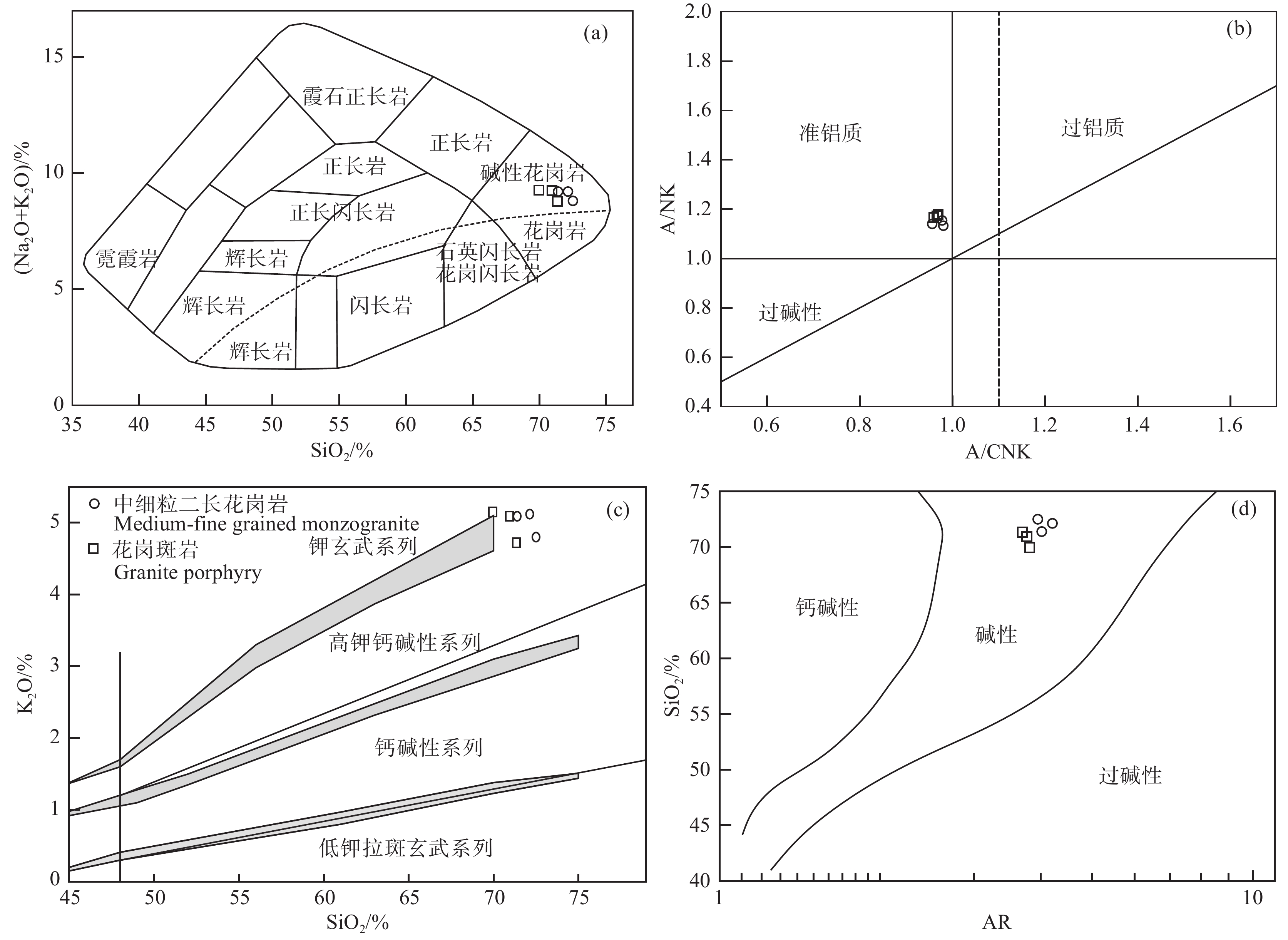
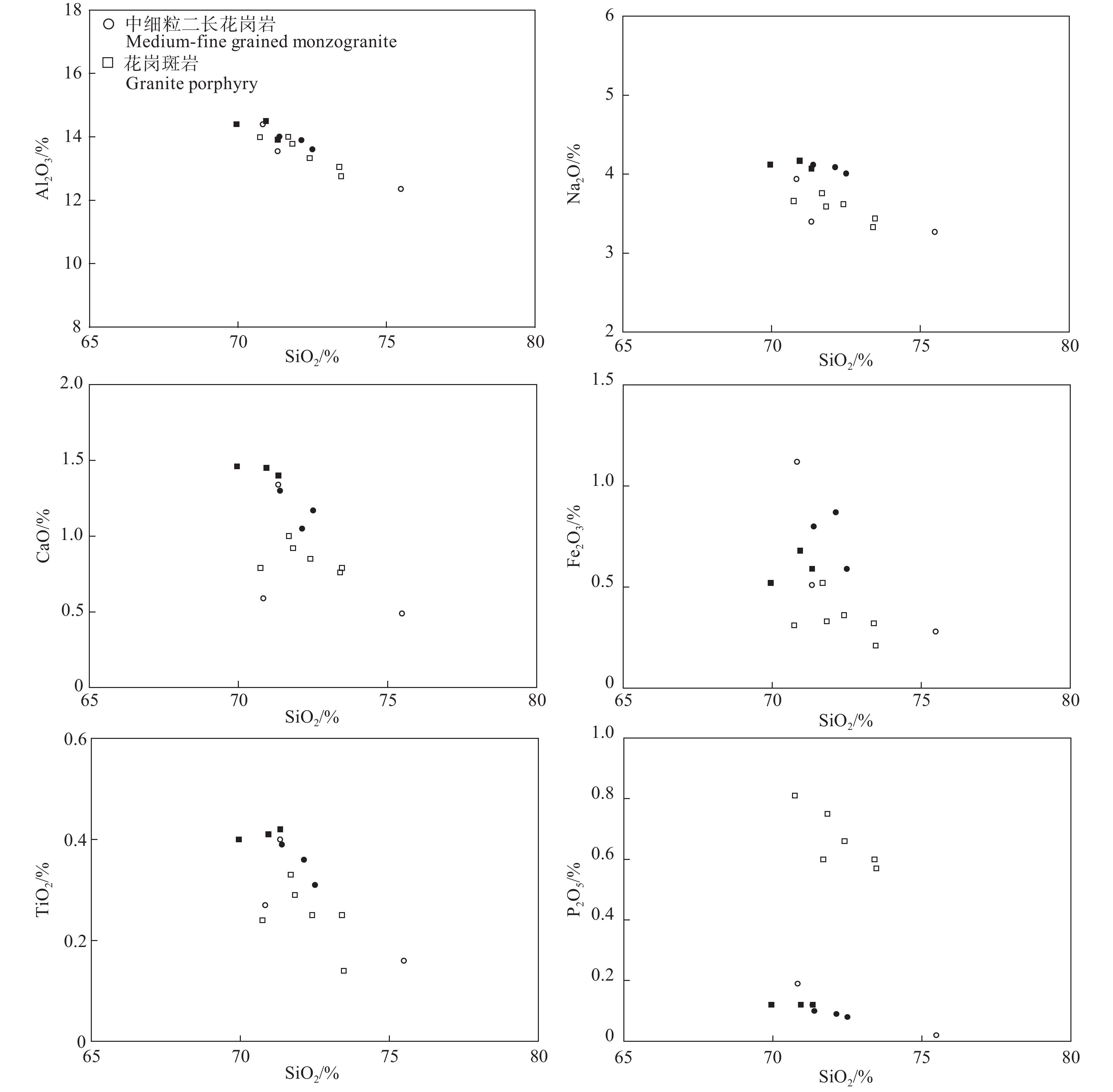
三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩具有相似的地球化学特征:SiO2含量69.95%~72.50%,平均71.38%,属酸性岩范畴;K2O含量4.80%~5.15%,平均5.00%,Na2O含量4.01%~4.17%,平均4.10%,全碱含量(K2O+Na2O)介于8.79%~9.27%,平均9.09%,在TAS图解中(图4a),样品点主要位于碱性趋势线之上的碱性花岗岩区域,与野外及薄片观察结果一致。K2O/Na2O比值1.16~1.25,平均1.22,为钙碱性岩石系列,在SiO2–K2O判别图上(图4b),样品点主要落入高钾钙碱性岩区。Al2O3含量13.61%~14.01%,平均13.84%,铝饱和指数A/CNK=0.97~0.99,平均为0.98,显示准铝质特征(图4c)。MgO含量为0.43%~0.64%,具有较低的Mg#(28.61~33.62)。P2O5和TiO2含量较低,分别为0.08%~0.12%和0.31%~0.42%。σ值为2.63~2.99,AR值为3.16~3.42,在AR−SiO2图解上落入碱性区域(图4d)。岩石的分异指数(DI)为87.56~90.58,表明本区花岗岩分异演化彻底。岩石的固结指数(SI)为3.77~5.03,反映岩浆酸性程度较高。
![]() 图 4 三合山岩体花岗岩TAS图解(a)(据Wilson,1989)、A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(据Maniar and Piccoli,1989)、SiO2−K2O图解(c)(据Le Maitre,1989; Rickwood,1989)及AR−SiO2图解(d)(据Wright,1969)Figure 4. Granite TAS diagram of Sanheshanpluton (a) (after Wilson, 1989), A/CNK−A/NK diagram (b) (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989), SiO2−K2O diagram (c) (after Le Maitre, 1989; Rickwood, 1989) and AR−SiO2 diagram (d) (after Wright,1969)
图 4 三合山岩体花岗岩TAS图解(a)(据Wilson,1989)、A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(据Maniar and Piccoli,1989)、SiO2−K2O图解(c)(据Le Maitre,1989; Rickwood,1989)及AR−SiO2图解(d)(据Wright,1969)Figure 4. Granite TAS diagram of Sanheshanpluton (a) (after Wilson, 1989), A/CNK−A/NK diagram (b) (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989), SiO2−K2O diagram (c) (after Le Maitre, 1989; Rickwood, 1989) and AR−SiO2 diagram (d) (after Wright,1969)6.1.2 稀土元素
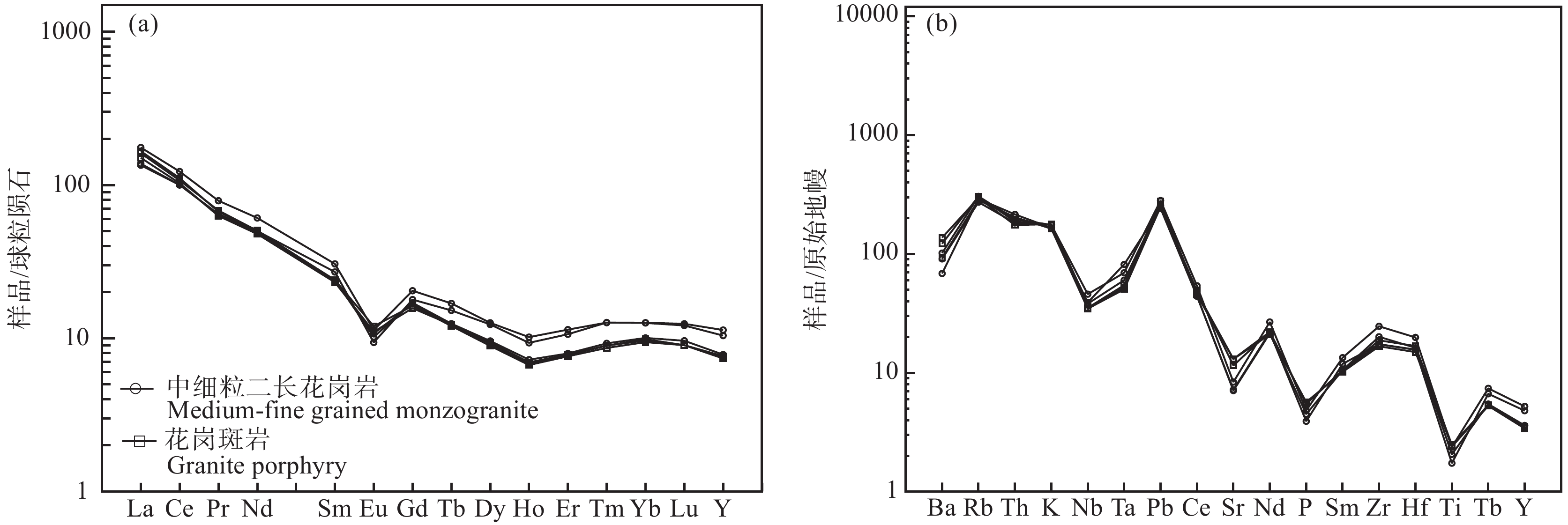
三合山岩体稀土总量相对较低,∑REE为179.44×10−6~223.32×10−6,平均193.29×10−6。相对富集LREE,亏损HREE;LREE为166.45×10−6~206.60×10−6,平均179.52×10−6,HREE为12.33×10−6~15.64×10−6,平均13.78×10−6,LREE/HREE为10.65~14.92,(La/Yb)N值为10.71~17.66,平均14.66。(La/Sm)N=4.98~7.00,平均为6.12,轻稀土分异较强烈,(Gb/Yb)N=1.42~1.78,平均为1.63,重稀土分异相对较弱,在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分配模式图(图5a)中,各样品配分曲线基本一致,均向右倾斜,δCe表现为无异常的范围(介于0.93~1.00,平均0.97),δEu显示为中等负异常(介于0.42~0.59,平均0.51)。
![]() 图 5 三合山岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化数据:a据Boynton,1984;b据Sun and Mcdonough,1989)Figure 5. Chondrite−normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle−normalized trace element spider diagrams(normalization data: a after Boynton, 1984; b after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
图 5 三合山岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化数据:a据Boynton,1984;b据Sun and Mcdonough,1989)Figure 5. Chondrite−normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle−normalized trace element spider diagrams(normalization data: a after Boynton, 1984; b after Sun and McDonough, 1989)6.1.3 微量元素
在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图中(图5b),所有样品显示较为一致的微量元素地球化学特征:蛛网图解曲线呈现一致向右陡倾的特征,表明随着元素不相容性的增加,岩石的富集度呈几何级增加。Rb、K、Pb、Nd、Zr和Hf元素富集程度较强,表现为明显的峰,大离子亲石元素Sr、Ba和高场强元素Nb、P、Ti相对亏损,表现为谷。
6.2 全岩Sr−Nd−Pb同位素
对三合山岩体中的中细粒二长花岗岩(SHS-H1、SHS-H2)和花岗斑岩(SHS-H4、SHS-H5)共计4件样品进行了Sr−Nd−Pb同位素测试分析,实验结果列于表2和表3。分析结果表明,三合山岩体二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩的Sr−Nd−Pb同位素特征比较相似,显示了同源岩浆的特性;Sr、Nd含量分别为156.4×10−6~338.2×10−6、27.47×10−6~31.15×10−6;87Rb/86Sr、87Sr/86Sr比值分别为1.34~3.09、0.712558~0.714895;147Sm/144Nd、143Nd/144Nd比值分别为0.95839~0.114550、0.511770~0.511877;岩石中Pb同位素组成较为均一,富含放射成因Pb;208Pb/204Pb、207Pb/204Pb和206Pb/204Pb值分别为39.8582~39.9679、15.4656~15.4709和17.3563~17.4478。利用中细粒二长花岗岩(115.42 Ma)和花岗斑岩(115.21 Ma)的加权平均结晶年龄校正Sr、Nd同位素组成后,得到ISr与INd初始值分别为0.70984~0.71084、0.511698~0.511800,对应的εNd(t)值为−15.45~−13.46;初始(208Pb/204Pb)i、(207Pb/204Pb)i和(206Pb/204Pb)i分别为37.5196~37.6835、15.4491~15.4572和17.0150~17.1799;Nd亏损地幔二阶段模式年龄TDM2为2005~2167 Ma。
表 2 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩全岩Sr−Nd同位素分析结果Table 2. Sr−Nd isotope date of whole rock of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton样品
编号岩性 t/Ma Rb Sr 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ Sm Nd 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ ISr(t) INd(t) εNd(t) TDM2/Ma /10−6 /10−6 SHS-H1 中细
粒二
长花
岗岩115.42 167.0 156.4 3.09 0.714895 0.000004 5.21 27.47 0.114550 0.511863 0.000009 0.70984 0.511777 −13.91 2041 SHS-H2 115.42 168.8 170.9 2.86 0.714753 0.000004 5.04 29.86 0.102043 0.511877 0.000009 0.71008 0.511800 −13.46 2005 SHS-H4 花岗
斑岩115.21 152.2 295.4 1.49 0.713277 0.000004 4.94 31.15 0.095839 0.511770 0.000009 0.71084 0.511698 −15.45 2167 SHS-H5 115.21 156.2 338.2 1.34 0.712558 0.000005 4.90 30.49 0.097061 0.511793 0.000009 0.71037 0.511720 −15.02 2132 表 3 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩全岩Pb同位素分析结果Table 3. Pbisotope date of whole rock of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton样品
编号岩性 t/Ma Th U Pb 206Pb/204Pb 2σ 207Pb/204Pb 2σ 208Pb/204Pb 2σ (206Pb/204Pb)i (207Pb/204Pb)i (208Pb/204Pb)i /10−6 SHS-H1 中细粒二长
花岗岩115.42 16.9 5.16 21.4 17.4478 0.0003 15.4702 0.0003 37.9679 0.0007 17.1799 15.4572 37.6805 SHS-H2 115.42 35.4 14.1 45.9 17.3563 0.0003 15.4656 0.0003 37.8582 0.0008 17.0150 15.4491 37.5775 SHS-H4 花岗斑岩 115.21 31.9 7.27 26.4 17.4101 0.0003 15.4709 0.0003 37.9594 0.0007 17.1041 15.4561 37.5196 SHS-H5 115.21 28.7 8.71 40.8 17.3811 0.0003 15.4656 0.0002 37.9395 0.0006 17.1440 15.4541 37.6835 6.3 锆石U−Pb年代学
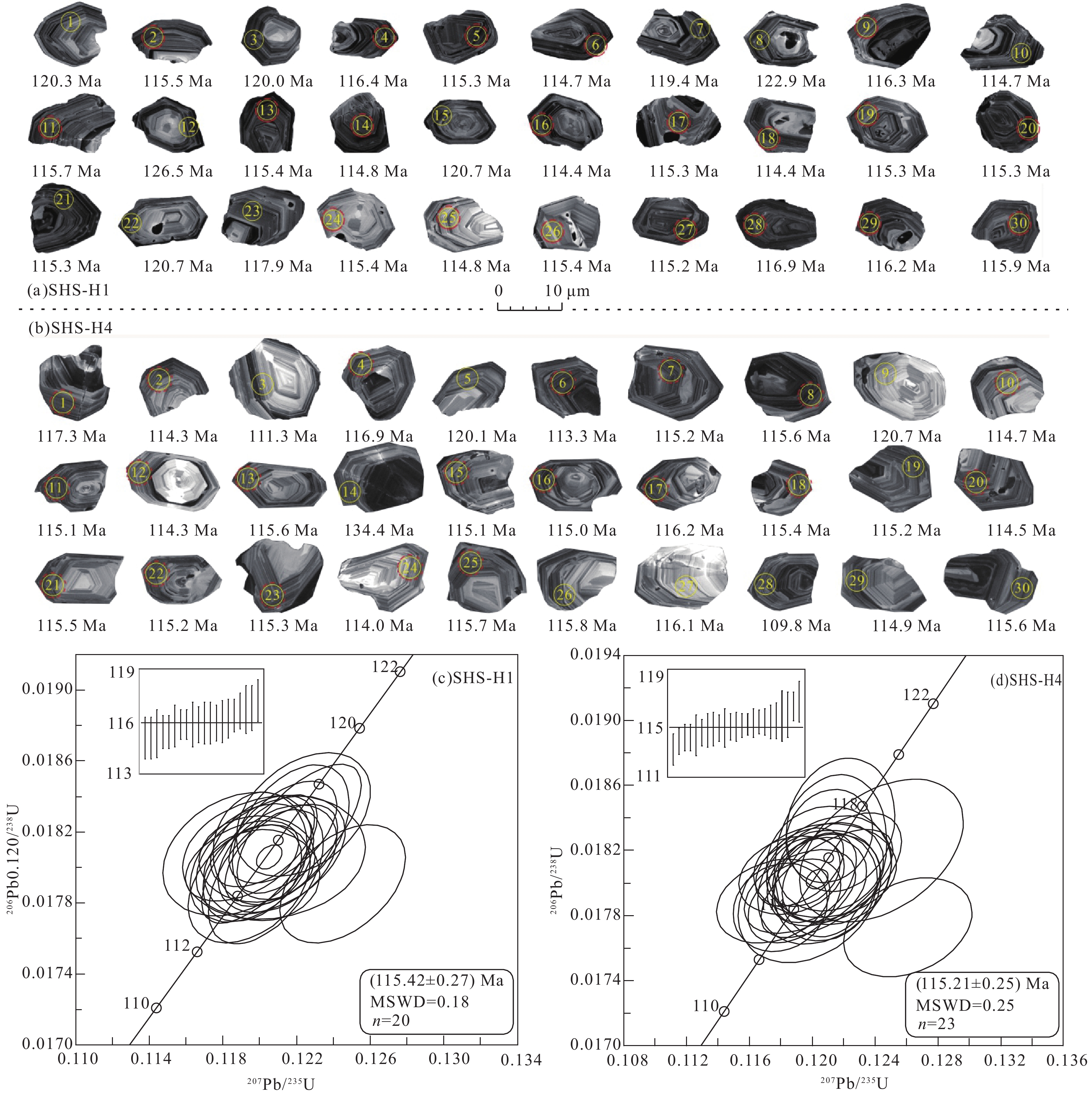
中细粒二长花岗岩(SHS-H1)与花岗斑岩(SHS-H4)中锆石特征较为一致,多为近等轴粒状、短柱状,少数呈长柱状,粒度一般为100~150 μm,少数颗粒长轴可达200 μm,长宽比为1∶1~2∶1。锆石晶面完整,晶棱清晰。从阴极发光(CL)图像上看,锆石发育明显的震荡韵律环带(图6),具有岩浆锆石的特征。锆石U、Th含量分别为174.13×10−6~1294.89×10−6、138.16×10−6~847.75×10−6,Th/U比值为0.42~0.94,平均0.67,明显大于变质锆石的Th/U值(<0.1),而与岩浆锆石的Th/U值相当(吴元保和郑永飞,2004),表明所测锆石为典型的岩浆成因锆石。
![]() 图 6 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩(a、c)和花岗斑岩(b、d)锆石阴极发光图像和锆石U−Pb年龄谐和图(黄圈为锆石U−Pb测量位置,红圈为锆石Lu−Hf测量位置)Figure 6. Cathodoluminescence images and zircon U−Pb age concordance diagram of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton(The yellow circle represents the measurement location of zircon U−Pb, the red circle represents the measurement location of zircon Lu−Hf)
图 6 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩(a、c)和花岗斑岩(b、d)锆石阴极发光图像和锆石U−Pb年龄谐和图(黄圈为锆石U−Pb测量位置,红圈为锆石Lu−Hf测量位置)Figure 6. Cathodoluminescence images and zircon U−Pb age concordance diagram of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton(The yellow circle represents the measurement location of zircon U−Pb, the red circle represents the measurement location of zircon Lu−Hf)SHS-H1样品的20个测点的206Pb/238U年龄为114.4~116.9 Ma,其加权平均值为(115.42±0.27)Ma(MSWD=0.18);SHS-H4样品的23个测点的206Pb/238U年龄为113.3~117.3 Ma,加权平均值为(115.21±0.25)Ma(MSWD=0.25)(表4)。
表 4 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩LA−ICP−MS U−Pb 分析结果Table 4. LA−ICP−MS zircons U−Pb isotope date of medium−fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton样品编号 含量/10−6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 谐和度
/%Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ SHS-H1-01 298.08 550.69 0.54 0.04884 0.00099 0.12673 0.00256 0.01884 0.00015 140.4 47.6 121.2 2.3 120.3 1 99.29 SHS-H1-02 436.92 495.22 0.88 0.04773 0.00105 0.11878 0.00265 0.01808 0.00023 86.1 52.4 114 2.4 115.5 1.4 98.65 SHS-H1-03 274.80 525.30 0.52 0.04893 0.00112 0.12683 0.00313 0.01879 0.0002 144.3 53.8 121.2 2.8 120 1.2 98.97 SHS-H1-04 543.04 771.30 0.70 0.04848 0.00066 0.12216 0.00224 0.01822 0.00024 122.9 32.1 117 2 116.4 1.5 99.46 SHS-H1-05 461.77 704.41 0.66 0.0486 0.00081 0.12099 0.00214 0.01805 0.0002 128.8 39.5 116 1.9 115.3 1.2 99.45 SHS-H1-06 778.55 897.44 0.87 0.04864 0.00075 0.12036 0.00206 0.01795 0.00025 130.3 36.2 115.4 1.9 114.7 1.6 99.38 SHS-H1-07 388.93 602.59 0.65 0.04892 0.00078 0.12619 0.00211 0.01869 0.00013 144 37.2 120.7 1.9 119.4 0.8 98.94 SHS-H1-08 584.03 909.03 0.64 0.05177 0.00061 0.13748 0.00214 0.01925 0.00023 275.4 26.8 130.8 1.9 122.9 1.5 93.95 SHS-H1-09 299.49 584.38 0.51 0.0486 0.00081 0.1217 0.00209 0.0182 0.00025 128.6 39.1 116.6 1.9 116.3 1.6 99.71 SHS-H1-10 721.04 1079.50 0.67 0.05068 0.00071 0.12576 0.00235 0.01796 0.00023 226.5 32.2 120.3 2.1 114.7 1.5 95.38 SHS-H1-11 342.01 560.97 0.61 0.04823 0.00084 0.12004 0.00168 0.01811 0.00021 110.4 41.1 115.1 1.5 115.7 1.3 99.51 SHS-H1-12 382.91 496.64 0.77 0.0492 0.00086 0.13447 0.00259 0.01982 0.00024 157.1 41.1 128.1 2.3 126.5 1.5 98.74 SHS-H1-13 646.64 817.67 0.79 0.04843 0.00099 0.12063 0.00267 0.01807 0.00022 120.2 48.2 115.6 2.4 115.4 1.4 99.81 SHS-H1-14 672.97 809.51 0.83 0.04835 0.00071 0.1196 0.00177 0.01797 0.00018 116.4 34.9 114.7 1.6 114.8 1.1 99.89 SHS-H1-15 503.59 775.33 0.65 0.04885 0.00085 0.12743 0.00213 0.01891 0.00021 140.5 40.8 121.8 1.9 120.7 1.3 99.14 SHS-H1-16 799.18 1008.37 0.79 0.05048 0.00085 0.12453 0.00225 0.01791 0.00022 217.2 38.8 119.2 2 114.4 1.4 96.01 SHS-H1-17 291.41 530.44 0.55 0.04783 0.00073 0.11906 0.00203 0.01804 0.00015 91 36.3 114.2 1.8 115.3 1 99.07 SHS-H1-18 369.34 460.87 0.80 0.04843 0.00085 0.11945 0.00219 0.01791 0.00022 120.5 41.6 114.6 2 114.4 1.4 99.86 SHS-H1-19 506.22 705.33 0.72 0.04825 0.00096 0.11987 0.00208 0.01805 0.00016 111.6 47 115 1.9 115.3 1 99.66 SHS-H1-20 580.28 802.42 0.72 0.04836 0.00063 0.12 0.00207 0.01805 0.00024 116.8 30.7 115.1 1.9 115.3 1.5 99.77 SHS-H1-21 520.20 690.67 0.75 0.05056 0.00088 0.13097 0.00247 0.01884 0.0003 220.7 40.1 125 2.2 120.3 1.9 96.27 SHS-H1-22 312.05 466.17 0.67 0.04793 0.00078 0.12474 0.00197 0.0189 0.00022 96 38.5 119.4 1.8 120.7 1.4 98.87 SHS-H1-23 331.44 525.58 0.63 0.0519 0.00082 0.13187 0.00202 0.01846 0.00017 281.1 36.2 125.8 1.8 117.9 1.1 93.73 SHS-H1-24 138.16 174.13 0.79 0.0488 0.00137 0.1208 0.00328 0.01806 0.00023 138.4 65.9 115.8 3 115.4 1.4 99.62 SHS-H1-25 358.83 432.95 0.83 0.0487 0.00098 0.12014 0.00209 0.01796 0.00017 133.4 47.2 115.2 1.9 114.8 1.1 99.63 SHS-H1-26 299.95 400.79 0.75 0.0487 0.00068 0.12119 0.00202 0.01807 0.00019 133.2 32.9 116.2 1.8 115.4 1.2 99.39 SHS-H1-27 404.64 640.94 0.63 0.04823 0.00086 0.11961 0.00222 0.01803 0.00022 110.4 42.3 114.7 2 115.2 1.4 99.58 SHS-H1-28 464.66 704.26 0.66 0.04856 0.00092 0.1224 0.0024 0.0183 0.00023 126.4 44.6 117.2 2.2 116.9 1.4 99.72 SHS-H1-29 664.74 757.28 0.88 0.04838 0.00065 0.12128 0.00194 0.0182 0.00019 118 31.8 116.2 1.8 116.2 1.2 99.99 SHS-H1-30 417.79 644.51 0.65 0.04805 0.00067 0.12017 0.00187 0.01815 0.00017 101.9 33 115.2 1.7 115.9 1.1 99.38 SHS-H4-01 404.97 634.56 0.61 0.04823 0.00107 0.12184 0.00229 0.01836 0.00027 110.8 52.2 116.7 2.1 117.3 1.7 99.51 SHS-H4-02 221.91 363.68 0.59 0.04769 0.00095 0.11753 0.00238 0.01789 0.00017 83.9 47.5 112.8 2.2 114.3 1.1 98.71 SHS-H4-03 662.61 785.21 0.81 0.0484 0.00069 0.11611 0.00148 0.01741 0.00014 119.1 33.8 111.5 1.3 111.3 0.9 99.76 SHS-H4-04 359.95 606.30 0.57 0.04815 0.00082 0.12113 0.00182 0.01829 0.00019 106.4 40.1 116.1 1.6 116.9 1.2 99.34 SHS-H4-05 499.70 1199.82 0.42 0.0496 0.00097 0.12807 0.00239 0.01881 0.00028 176.1 45.4 122.4 2.2 120.1 1.8 98.18 SHS-H4-06 353.63 584.96 0.6 0.0516 0.00108 0.12611 0.00271 0.01773 0.0002 267.5 48.2 120.6 2.4 113.3 1.3 93.94 SHS-H4-07 606.58 728.31 0.82 0.04841 0.00067 0.12016 0.00176 0.01803 0.00018 119.5 32.7 115.2 1.6 115.2 1.1 99.98 SHS-H4-08 547.19 940.08 0.57 0.04884 0.0009 0.1219 0.00252 0.0181 0.00022 140 43.2 116.8 2.3 115.6 1.4 99 SHS-H4-09 162.49 218.28 0.72 0.0976 0.00581 0.26322 0.01747 0.0189 0.00028 1578.7 111.5 237.3 14 120.7 1.8 50.88 SHS-H4-10 219.02 316.83 0.67 0.0481 0.00087 0.11923 0.00235 0.01795 0.00017 104.3 42.7 114.4 2.1 114.7 1.1 99.7 SHS-H4-11 492.39 669.39 0.73 0.04854 0.00088 0.12031 0.0021 0.01801 0.00018 125.7 42.4 115.4 1.9 115.1 1.1 99.74 SHS-H4-12 485.68 769.69 0.62 0.0482 0.00075 0.1189 0.00195 0.01789 0.00017 108.9 36.6 114.1 1.8 114.3 1.1 99.78 SHS-H4-13 332.11 449.72 0.73 0.04777 0.00067 0.11921 0.00184 0.0181 0.00016 87.7 33.4 114.4 1.7 115.6 1 98.91 SHS-H4-14 373.12 576.05 0.63 0.12877 0.00986 0.38418 0.03117 0.02106 0.00033 2081.3 134.7 330.1 22.9 134.4 2.1 40.7 SHS-H4-15 384.84 655.90 0.57 0.04871 0.00113 0.12081 0.00281 0.01802 0.00026 133.9 54.7 115.8 2.5 115.1 1.6 99.42 SHS-H4-16 652.15 675.30 0.94 0.04863 0.00089 0.12097 0.00278 0.018 0.00022 130.1 42.8 116 2.5 115 1.4 99.17 SHS-H4-17 403.25 600.87 0.65 0.04963 0.00128 0.12442 0.00344 0.0182 0.00029 177.8 60 119.1 3.1 116.2 1.9 97.63 SHS-H4-18 336.63 669.29 0.49 0.04799 0.00064 0.11944 0.00155 0.01807 0.00014 98.6 31.6 114.6 1.4 115.4 0.9 99.25 SHS-H4-19 313.74 524.55 0.59 0.06444 0.00112 0.15985 0.00253 0.01804 0.00016 756.2 36.5 150.6 2.2 115.2 1 76.53 SHS-H4-20 352.20 569.94 0.6 0.04851 0.00123 0.11984 0.00301 0.01792 0.00027 124 59.5 114.9 2.7 114.5 1.7 99.62 SHS-H4-21 159.20 238.15 0.67 0.04871 0.00126 0.12083 0.003 0.01808 0.00019 133.7 60.6 115.8 2.7 115.5 1.2 99.7 SHS-H4-22 381.55 517.41 0.72 0.04875 0.00097 0.12092 0.00227 0.01803 0.00018 136 46.5 115.9 2.1 115.2 1.2 99.38 SHS-H4-23 388.39 602.39 0.62 0.04775 0.0009 0.1187 0.00221 0.01805 0.00016 87 44.6 113.9 2 115.3 1 98.76 SHS-H4-24 266.55 379.52 0.69 0.04811 0.00088 0.11798 0.00197 0.01785 0.00018 104.8 43.1 113.2 1.8 114 1.1 99.31 SHS-H4-25 368.31 609.97 0.58 0.04864 0.00125 0.1211 0.00263 0.01811 0.00024 130.6 60.3 116.1 2.4 115.7 1.5 99.68 SHS-H4-26 223.64 335.62 0.66 0.0525 0.00113 0.13084 0.0029 0.01812 0.00023 307.3 49.1 124.8 2.6 115.8 1.4 92.73 SHS-H4-27 226.31 323.53 0.68 0.04887 0.00141 0.12122 0.00236 0.01817 0.00033 141.7 67.9 116.2 2.1 116.1 2.1 99.89 SHS-H4-28 847.75 1294.89 0.63 0.04854 0.00056 0.11494 0.00138 0.01718 0.00017 125.7 27.3 110.5 1.3 109.8 1.1 99.41 SHS-H4-29 520.32 623.94 0.81 0.04883 0.00099 0.12087 0.00217 0.01798 0.00022 139.7 47.6 115.9 2 114.9 1.4 99.15 SHS-H4-30 307.92 557.81 0.53 0.04868 0.00094 0.1212 0.00221 0.0181 0.00018 132.6 45.4 116.2 2 115.6 1.1 99.54 6.4 锆石Lu−Hf同位素
所有测试点的176Lu/177Hf比值介于0.000482~0.001942,小于0.002,表明锆石在岩体形成之后漫长的演化历程中具有较低的放射成因Hf积累,因而可以用锆石176Lu/177Hf比值探索岩体形成时的成因信息(吴福元等,2007;徐义刚等,2007;孙金凤,2009)。另外,所有测试点的fLu/Hf值介于−0.98~−0.94,明显小于铁镁质地壳(−0.34)和硅铝质地壳(−0.72)(Vervoort et al., 1996;Amelin et al., 2000),故二阶段模式年龄更能反映其源区物质从亏损地幔被抽取的时间或其源区物质在地壳的平均存留年龄。
中细粒二长花岗岩样品锆石的176Hf/177Hf比值变化于0.282124~0.282419,平均为0.282221;εHf(t)值为−20.39~−9.95,平均为−16.97;亏损地幔二阶段模式年龄TDM2为1807~2466 Ma,平均为2250 Ma。花岗斑岩样品锆石的176Hf/177Hf比值变化于0.282135~0.282323,平均为0.282219;εHf(t)值为−20.10~−13.42,平均为−17.12;亏损地幔二阶段模式年龄TDM2为2028~2447 Ma,平均为2260 Ma(表5)。
表 5 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩锆石Lu−Hf分析结果Table 5. Zircon Lu−Hf isotope date of medium−fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton样品编号 T/Ma 176Yb/178Hf 2σ 176Lu/178Hf 2σ 176Hf/178Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM/Ma TDM2/Ma fLu/Hf SHS-H1-002 115.5 0.034365 0.000136 0.001259 0.000005 0.282244 0.000016 −18.67 −16.25 1431 2204 −0.96 SHS-H1-004 116.4 0.040687 0.000423 0.001395 0.000013 0.282230 0.000014 −19.17 −16.72 1456 2235 −0.96 SHS-H1-005 115.3 0.035505 0.000181 0.001268 0.000007 0.282195 0.000015 −20.40 −17.95 1500 2313 −0.96 SHS-H1-006 114.7 0.055793 0.000178 0.001942 0.000014 0.282288 0.000017 −17.12 −14.74 1395 2109 −0.94 SHS-H1-009 116.3 0.034779 0.000340 0.001231 0.000007 0.282220 0.000014 −19.53 −17.08 1464 2257 −0.96 SHS-H1-011 115.7 0.041548 0.001231 0.001526 0.000035 0.282209 0.000014 −19.93 −17.52 1492 2284 −0.95 SHS-H1-013 115.4 0.043584 0.000611 0.001507 0.000017 0.282239 0.000016 −18.84 −16.43 1448 2216 −0.95 SHS-H1-014 114.8 0.042933 0.000181 0.001555 0.000004 0.282223 0.000018 −19.42 −17.01 1473 2253 −0.95 SHS-H1-016 114.4 0.048977 0.001296 0.001710 0.000035 0.282156 0.000021 −21.78 −19.42 1574 2403 −0.95 SHS-H1-017 115.3 0.035244 0.000354 0.001233 0.000017 0.282241 0.000016 −18.77 −16.32 1434 2210 −0.96 SHS-H1-018 114.4 0.053518 0.001327 0.001771 0.000035 0.282183 0.000019 −20.81 −18.43 1537 2341 −0.95 SHS-H1-019 115.3 0.035349 0.000213 0.001262 0.000008 0.282268 0.000015 −17.82 −15.40 1398 2151 −0.96 SHS-H1-020 115.3 0.051387 0.000848 0.001737 0.000025 0.282208 0.000014 −19.94 −17.56 1501 2286 −0.95 SHS-H1-024 115.4 0.023987 0.000194 0.000814 0.000007 0.282252 0.000016 −18.41 −15.93 1404 2185 −0.98 SHS-H1-025 114.8 0.032159 0.000260 0.001121 0.000016 0.282159 0.000018 −21.66 −19.23 1544 2392 −0.97 SHS-H1-026 115.4 0.048079 0.000216 0.001565 0.000011 0.282422 0.000019 −12.36 −9.95 1190 1807 −0.95 SHS-H1-027 115.2 0.048379 0.000880 0.001646 0.000028 0.282127 0.000018 −22.80 −20.39 1612 2466 −0.95 SHS-H1-028 116.9 0.038652 0.000438 0.001333 0.000015 0.282171 0.000016 −21.25 −18.80 1537 2366 −0.96 SHS-H1-029 116.2 0.048147 0.001031 0.001636 0.000036 0.282198 0.000016 −20.31 −17.90 1512 2309 −0.95 SHS-H1-030 115.9 0.036768 0.000498 0.001304 0.000015 0.282243 0.000014 −18.72 −16.27 1435 2207 −0.96 SHS-H4-001 117.3 0.056976 0.001736 0.001836 0.000057 0.282135 0.000018 −22.51 −20.10 1608 2447 −0.94 SHS-H4-002 114.3 0.034185 0.000795 0.001206 0.000020 0.282180 0.000013 −20.94 −18.54 1519 2347 −0.96 SHS-H4-004 116.9 0.036438 0.000215 0.001309 0.000007 0.282242 0.000023 −18.75 −16.29 1437 2209 −0.96 SHS-H4-006 113.3 0.035037 0.000510 0.001240 0.000021 0.282261 0.000015 −18.07 −15.69 1407 2168 −0.96 SHS-H4-007 115.2 0.057145 0.001128 0.001917 0.000035 0.282225 0.000015 −19.35 −16.96 1484 2249 −0.94 SHS-H4-008 115.6 0.036822 0.000405 0.001276 0.000013 0.282240 0.000014 −18.82 −16.39 1438 2214 −0.96 SHS-H4-010 114.7 0.029173 0.000118 0.001025 0.000005 0.282227 0.000016 −19.28 −16.83 1447 2243 −0.97 SHS-H4-011 115.1 0.039391 0.000574 0.001368 0.000010 0.282199 0.000017 −20.26 −17.85 1499 2305 −0.96 SHS-H4-012 114.3 0.038626 0.000294 0.001350 0.000015 0.282247 0.000015 −18.57 −16.17 1431 2199 −0.96 SHS-H4-013 115.6 0.037094 0.000262 0.001278 0.000007 0.282163 0.000015 −21.55 −19.11 1546 2385 −0.96 SHS-H4-015 115.1 0.040294 0.000423 0.001421 0.000020 0.282200 0.000015 −20.24 −17.81 1500 2304 −0.96 SHS-H4-016 115 0.046511 0.000306 0.001610 0.000006 0.282194 0.000017 −20.45 −18.06 1516 2318 −0.95 SHS-H4-017 116.2 0.040350 0.000583 0.001369 0.000014 0.282184 0.000018 −20.79 −18.36 1520 2338 −0.96 SHS-H4-018 115.4 0.037646 0.000760 0.001252 0.000021 0.282323 0.000014 −15.87 −13.42 1320 2028 −0.96 SHS-H4-020 114.5 0.030983 0.000654 0.001083 0.000025 0.282260 0.000015 −18.11 −15.67 1402 2168 −0.97 SHS-H4-021 115.5 0.028978 0.000462 0.000996 0.000014 0.282208 0.000016 −19.95 −17.49 1472 2284 −0.97 SHS-H4-022 115.2 0.042578 0.000377 0.001447 0.000013 0.282173 0.000015 −21.17 −18.77 1538 2362 −0.96 SHS-H4-023 115.3 0.022154 0.000350 0.000765 0.000013 0.282259 0.000014 −18.14 −15.69 1392 2169 −0.98 SHS-H4-024 114 0.035765 0.000751 0.001215 0.000020 0.282183 0.000016 −20.85 −18.44 1516 2342 −0.96 SHS-H4-025 115.7 0.035741 0.000105 0.001236 0.000004 0.282283 0.000015 −17.29 −14.83 1376 2117 −0.96 7. 讨 论
7.1 成岩年龄及意义
胶东中生代岩发育玲珑期(146~166 Ma,S型)、郭家岭期(123~135 Ma,I型)、伟德山期(110~123 Ma,I型)和崂山期(108~118 Ma,A型)4期花岗岩(王来明等,2021),其中伟德山期花岗岩因与胶东金及多金属矿矿成矿关系密切而备受关注。大量研究资料(表6)表明,伟德山期花岗岩主要分布在胶东中、东部地区和胶西北艾山—大泽山一带,西南部尚无中生代花岗岩年龄的报道。胶东中、东部伟德山期花岗岩多沿北东向断裂断续分布,岩石类型丰富,岩体结构完整,多呈规模较大的环带状的复式岩体,主要有伟德山岩体(112~114.2 Ma)、三佛山岩体(114.2~119.6 Ma)、泽头岩体(114~116 Ma)和牙山—院格庄岩体(118.1~118.8 Ma)。胶西北伟德山期花岗岩规模较小,岩体结构、岩石类型简单,多呈小岩株状产出(Li et al., 2012),主要有艾山岩体(113~122 Ma)、南宿岩体(121.3 Ma)和秦姑庵岩体(119.9 Ma)。三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩的的锆石LA−ICP−MS U−Pb加权平均年龄分别为(115.42±0.27)Ma和(115.21±0.25)Ma,岩石地球化学特征显示I型花岗岩的特征。根据王来明等(2021)对胶东地区中生代花岗岩的划分方案,三合山岩体应划入伟德山期花岗岩。
表 6 胶东伟德山期花岗岩同位素年龄表(LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb)Table 6. Isotope chronology of the Weideshan granite in Jiaodong( LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb )岩体名称 样品编号 地理位置 岩性 年龄/Ma 资料来源 伟德山 GZ 威海市崮庄村 细粒石英闪长岩 112±1 李杰等,2013 SSD-1/1B 荣成冷家 中细粒钾长花岗岩 113. 4±1.8 丁正江等,2013 GZ 荣成南台 中细粒碎裂花岗岩 114. 2±2.1 三佛山 D04-1 乳山市三佛山 细粒正长花岗岩 119.6± 1.0 李增达等,2018 D09-1 中细粒二长花岗岩 111.4± 2.2 D11-2 中粗粒二长花岗岩 115.7± 1.7 泽头 06SD01 海阳辛安 中粒二长花岗岩 114±3 郭敬辉等,2005 06SD17 乳山市高家台村 中粗粒二长花岗岩 116±3 ZT-1-01 文登泽头 中粒黑云角闪石英二长岩 115.6±1.1 董学等,2020 牙山—
院格庄2017N1 院格庄 中粒含角闪二长花岗岩 118.10±0.66 邹键等,2021 2017N2 含巨斑状细中粒二长花岗岩 118.52±0.78 2017N3 巨斑状中粒含角闪二长花岗岩 118.80±0.67 艾山 16SD-33 蓬莱艾山 斑状角闪花岗闪长岩 116.7±1.7 胡波,2019 WDS07/1B 蓬莱张家沟村 含斑中粗粒二长花岗岩 122±1 任天龙等,2021 JD48 栖霞市前寨村 斑状中粗粒二长花岗岩 119±1 JD87 蓬莱市邓格庄村 含斑中粗粒二长花岗岩 113±1 南宿 LM06/1b 莱州市西姜家村 中粒二长花岗岩 121.3±2.1 胡波,2019 秦姑庵 JD151 莱州市秦姑庵 斑状中粒二长花岗岩 119.9±1.3 李秀章等,2021 三合山 SHS-H1 平度市三合山 中细粒二长花岗岩 115.42±0.27 本文 SHS-H4 平度市三合山 花岗斑岩 115.21±0.25 20世纪80年代至今,山东省第四地质矿产勘查院在三合山地区开展了大量金及多金属矿勘查工作,不仅在三合山岩体的原生裂隙中发现大量钼矿化信息(单孔最大见矿厚度97.28 m,平均品位0.047%),还在三合山岩体边部及外围的断裂构造中发现了大量金(1.09~2.19 g/t)、铅(16.39%~52.66%)成矿信息。金及多金属矿成矿明显受岩体侵位的制约。三合山岩体与胶东东部伟德山岩体侵位时间大致相当(中生代燕山晚期115 Ma),矿化特征类似(内部钼、外部金及多金属矿),指示胶东西南部同样存在115~125 Ma贵金属、有色金属成矿事件(丁正江等,2013)。三合山岩体侵入时间的准确厘定,不仅填补了胶东西南部中生代花岗岩的空缺,更为该区下一步矿产勘查工作提供了新的思路和方向。
7.2 岩石成因类型
花岗岩成因类型的识别是研究花岗岩岩浆起源与演化、成岩构造背景等内容的前提。目前,大家较推崇且应用较广泛的是ISAM分类法。通常认为I型花岗岩为壳幔混源产物,S型花岗岩来源于地壳熔融,M型花岗岩来源于地幔,A型花岗岩与源岩无关,代表产于伸展构造背景中高温无水的花岗岩(华北等,2020)。
三合山岩体SiO2含量69.95%~72.50%,平均71.38%,而地幔岩部分熔融不可能形成SiO2含量70 % 左右的花岗岩(张旗等,2008),故排除为M型花岗岩的可能。铝饱和指数A/CNK=0.97~0.99,平均为0.98,显示准铝质特征,镜下未见富铝矿物,与S型花岗岩A/CNK>1.1,常见堇青石等富铝矿物有明显区别。在Harker图解上,随SiO2含量增加TiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、Na2O、CaO、P2O5呈线性下降(图7),与I型花岗岩演化趋势一致,同样排除了三合山岩体为S型花岗岩的可能,指示三合山岩体成因类型应属I型或A型。
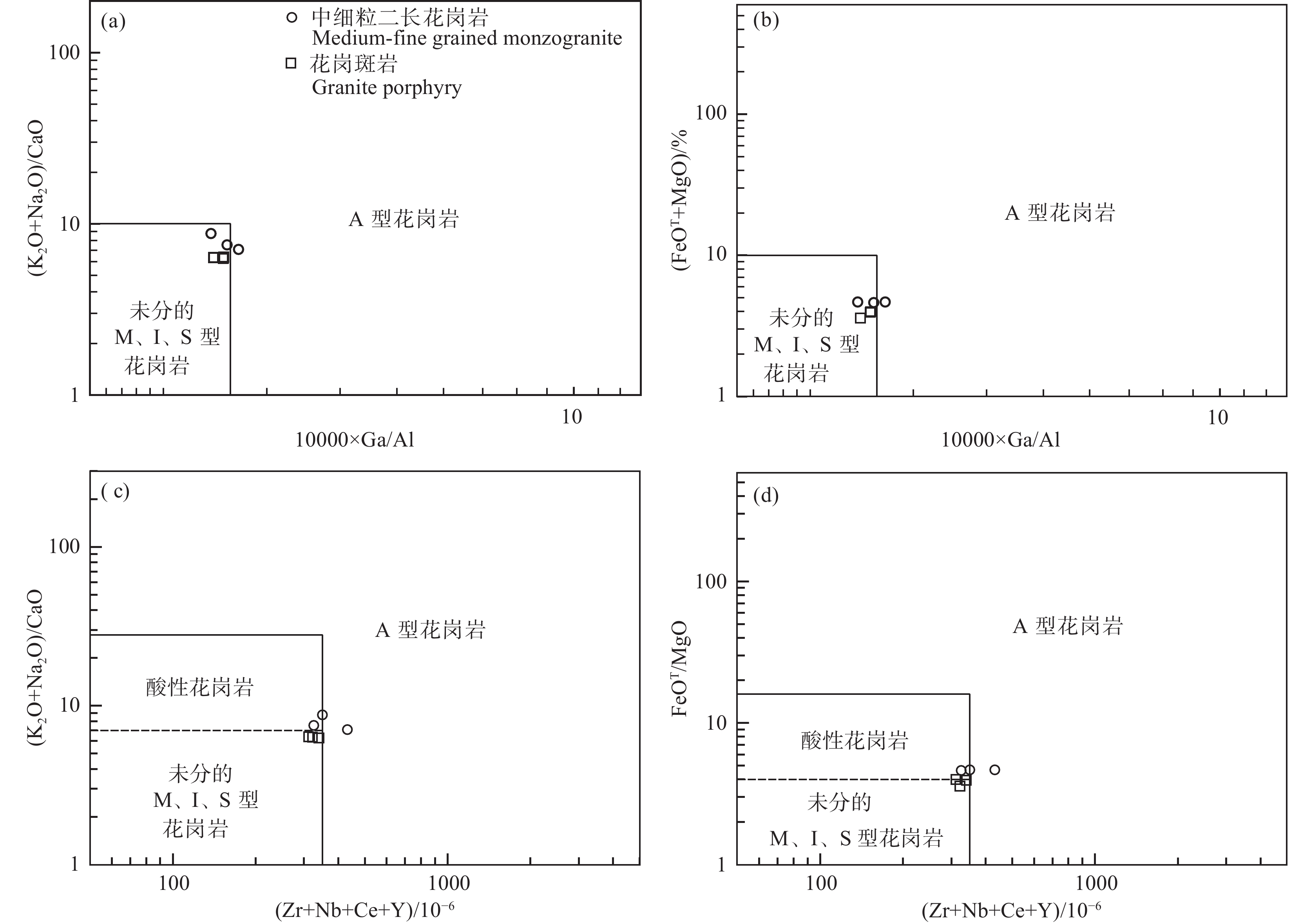
A 型花岗岩具有钠闪石−钠铁闪石、霓石−霓辉石、铁橄榄石等碱性暗色矿物组成的特征性矿物组合,并且在地球化学成分上具有富集Si、K 和Nb、Ta、Zr、Ga 等高场强元素组合的特征(Whalen et al.,1987)。岩相学及全岩地球化学的研究表明:(1)三合山岩体矿物组合主要为钾长石、斜长石、石英、黑云母和角闪石,并不具有A 型花岗岩中典型的碱性暗色矿物组合;(2)在地球化学化学成分上,明显亏损大离子亲石元素Sr、Ba和高场强元素Nb、Ta、P、Ti,可区别于A型花岗岩;(3)利用Watson and Harrison(1983)提出的全岩锆石饱和温度计算公式,可得三合山岩体成岩温度介于787~823℃,平均为800℃,略低于A型花岗岩的平均成岩温度833℃(Whalen et al.,1987)。在Ga/Al比值和Zr+Nb+Ce+Y为基础的多种花岗岩成因判别图解中(图8),所有样品偏离A 型花岗岩区域,而集中分布在分异I型花岗岩和未分的I、S、M型花岗岩之间。
![]() 图 8 三合山岩体花岗岩成因判别图解(底图据Whalen et al., 1987)Figure 8. Genetic discrimination diagram of granite in Sanheshanpluton (basemap from Whalen et al., 1987)
图 8 三合山岩体花岗岩成因判别图解(底图据Whalen et al., 1987)Figure 8. Genetic discrimination diagram of granite in Sanheshanpluton (basemap from Whalen et al., 1987)综合以上分析成果,结合在显微镜下观察到角闪石,三合山岩体应属未分异−分异的I型花岗岩。
7.3 岩浆源区性质
花岗岩的岩浆源区性质是花岗岩研究中最令人关注的问题之一,地球不同源区微量元素和同位素组成的差异性和同位素组成的继承性是示踪物质来源的基础。
三合山岩体岩石的Nb/Ta比值8.32~11.93,平均10.91,总体位于大陆地壳范围内(Nb/Ta=10~14,赵振华等,2008),Nb/La比值0.48~0.67,介于原始地幔(1.06)和下地壳(0.45)之间(Jochum et al., 1989;Green,1995),Zr/Hf比值40.18~44.98,平均41.89,略高于中国东部大陆地壳的37(Gao et al.,1998),以上微量元素比值表明三合山岩体岩浆源区以陆壳物质为主,并在成岩过程中受到地幔物质的混染。
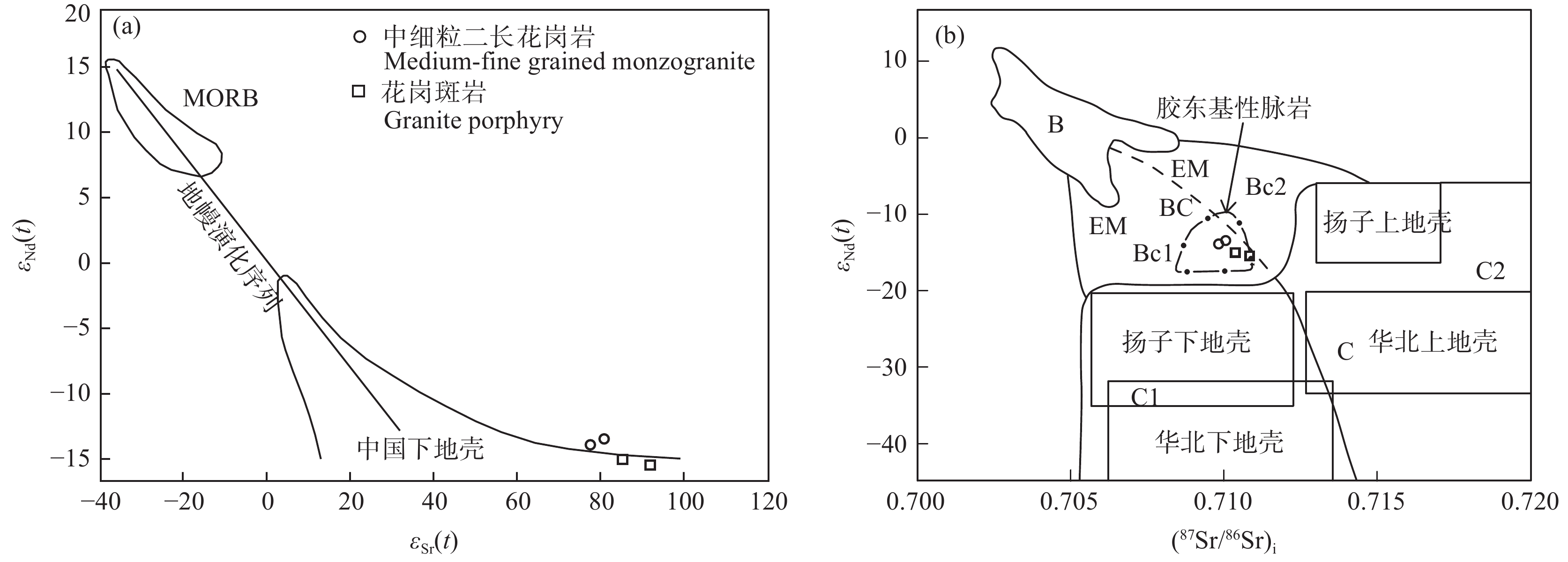
三合山岩体初始锶(0.70984~0.71084)相对较低(现代大陆硅铝质岩ISr平均值为0.719)、εNd(t)值(−15.45~−13.46)较小,TDM2介于2005~2167 Ma,与古元古代荆山群和粉子山群的同位素年龄一致(宋明春和王沛成,2003)。对此最为直接的解释为岩浆起源于古元古代地壳物质的部分熔融。在εNd(t)–εSr(t)图解中,所有样品均落在中国下地壳附近,在εNd(t)–(87Sr/86Sr)i图解中,所有样品落入低Sr初始值的玄武岩源区和壳源区之间的过度源区BC1内(张旗等,2008),且位于胶东基性脉岩范围内(图9b),指示岩浆源区具有壳幔混源性质(Yang et al.,2012)。本文通过矿床学研究方法(温春齐和多吉,1999)中的岩体壳幔混源程度计算公式(Pm=100×(0.70945−0.000255×t−R0)/(0.00559−0.000149×t),式中Pm为幔源成分百分比,t为花岗岩的成岩年龄(亿年),R0为中初始比值的花岗岩的87Sr/86Sr的初始值(0.708)),计算了三合山岩体幔源成分比例。计算结果表明,三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩幔源成分比例基本一致,幔源成分占比21.44%。这与宋明春和严庆利(2000)计算的伟德山花岗岩母岩浆是由30.38%的幔源基性岩浆与69.62%的壳源酸性岩浆经混合作用形成的结论大致相当。
![]() 图 9 三合山岩体花岗岩Sr−Nd同位素图解a—εNd(t)−εSr(t)图解(据Zhu et al. 2001);b—εNd(t)−(87Sr/86Sr)i图解(据Jahn et al.,1999;盖永升等,2015修改;基性脉岩范围据Yang et al.,2012);MORB—洋中脊型玄武岩;B—玄武岩源区;Bc—过渡源区;C—陆壳源区Figure 9. Sr−Nd isotope diagram of granite in Sanheshan plutona−εNd(t)−εSr(t)diagram (modified from Zhu et al., 2001); b−εNd(t) − (87Sr/86Sr)i diagram (modified from Jahn et al., 1999; Gai Yongsheng et al., 2015; basic dike range by Yang et al., 2012); MORB–Mid ocean ridge basalt; B–Origin of basalt; Bc–Origin of transitional mantle; C–Continental source
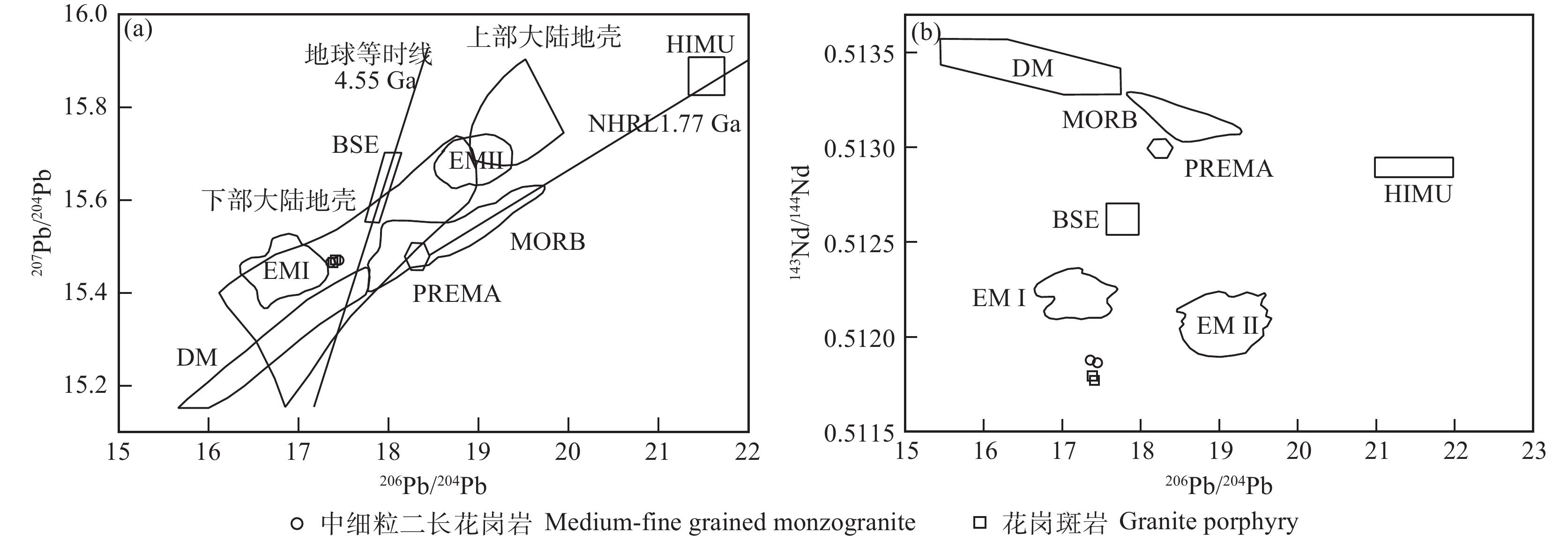
图 9 三合山岩体花岗岩Sr−Nd同位素图解a—εNd(t)−εSr(t)图解(据Zhu et al. 2001);b—εNd(t)−(87Sr/86Sr)i图解(据Jahn et al.,1999;盖永升等,2015修改;基性脉岩范围据Yang et al.,2012);MORB—洋中脊型玄武岩;B—玄武岩源区;Bc—过渡源区;C—陆壳源区Figure 9. Sr−Nd isotope diagram of granite in Sanheshan plutona−εNd(t)−εSr(t)diagram (modified from Zhu et al., 2001); b−εNd(t) − (87Sr/86Sr)i diagram (modified from Jahn et al., 1999; Gai Yongsheng et al., 2015; basic dike range by Yang et al., 2012); MORB–Mid ocean ridge basalt; B–Origin of basalt; Bc–Origin of transitional mantle; C–Continental sourcePb同位素具有质量大、同位素之间相对质量小,且同位素组成基本不受外界环境变化影响的特点,可作为追索岩浆源区的有效手段(Hart,1984)。三合山岩体所有样品显示较为一致的Pb同位素组成特征,在207Pb/204Pb−206Pb/204Pb(图10a)和207Pb/204Pb−143Nd/143Nd(图10b)图解中,所有样品均落在下部大陆壳范围内,且靠近EMⅠ富集地幔。表明岩浆主要来源于古老地壳部分熔融,并受到过幔源物质的混染。
![]() 图 10 三合山岩体花岗岩Pb同位素207Pb/204Pb–206Pb/204Pb相关曲线(a,据Allègre,1988)、206Pb/204Pb–143Nd/144Pb相关图解(b,据Zindler and Hart,1986)PREMA—原始地幔;DM—亏损地幔;EMⅠ—Ⅰ型富集地幔;EMⅡ—Ⅱ型富集地幔;HIMU—高μ值地幔;MORB—洋中脊型玄武岩;BSE—全硅酸盐地球Figure 10. 207Pb / 204Pb–206Pb / 204Pb curve (a, after Allègre, 1988) and 143 Nd/144Nd–206Pb/204Pb isotopic diagram (b, after Zindler and Hart, 1986 ) of granite in Sanheshan plutonPREMA–Primitive mantle; DM–Depleted mantle; EMⅠ–Enriched mantle Ⅰ; EMⅡ–Enriched mantle Ⅱ; HIMU–High μ mantle; MORB–Mid ocean ridge basalt; BSE–Bulk silicate earth
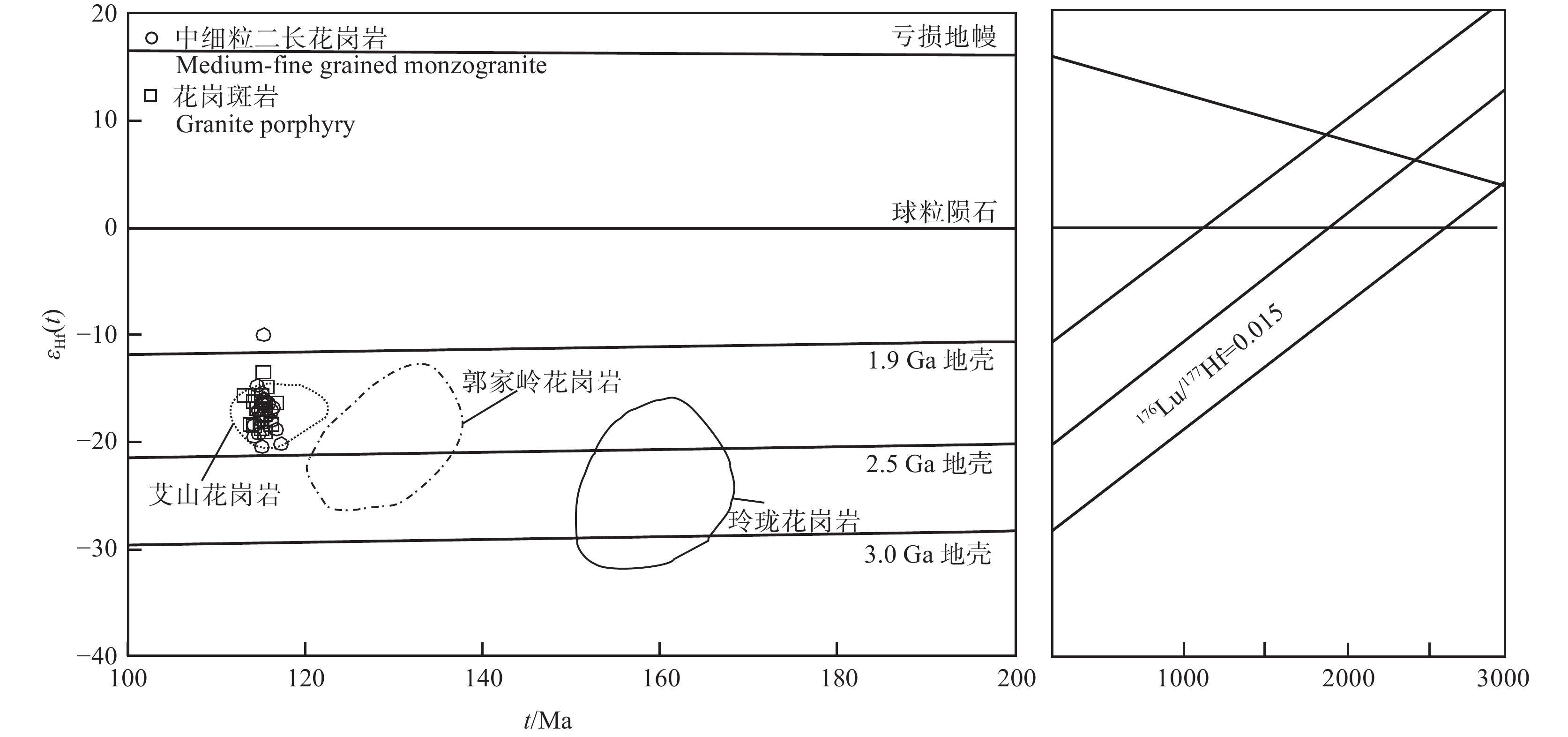
图 10 三合山岩体花岗岩Pb同位素207Pb/204Pb–206Pb/204Pb相关曲线(a,据Allègre,1988)、206Pb/204Pb–143Nd/144Pb相关图解(b,据Zindler and Hart,1986)PREMA—原始地幔;DM—亏损地幔;EMⅠ—Ⅰ型富集地幔;EMⅡ—Ⅱ型富集地幔;HIMU—高μ值地幔;MORB—洋中脊型玄武岩;BSE—全硅酸盐地球Figure 10. 207Pb / 204Pb–206Pb / 204Pb curve (a, after Allègre, 1988) and 143 Nd/144Nd–206Pb/204Pb isotopic diagram (b, after Zindler and Hart, 1986 ) of granite in Sanheshan plutonPREMA–Primitive mantle; DM–Depleted mantle; EMⅠ–Enriched mantle Ⅰ; EMⅡ–Enriched mantle Ⅱ; HIMU–High μ mantle; MORB–Mid ocean ridge basalt; BSE–Bulk silicate earthHf同位素分析结果显示,三合山岩体两类岩石的锆石具有变化较大的εHf(t)值(−20.10~−9.95,平均为−17.05),在εHf(t)−t图解中均落入球粒陨石Hf同位素演化线以下(图11),不同于玲珑花岗岩和郭家岭花岗岩,而与伟德山期艾山花岗岩大部分重叠。εHf(t)和εHf(0)均为负值,表明三合山岩体主要来自古老地壳物质的熔融。三合山岩体锆石Hf同位素二阶模式年龄TDM2介于1807~2466 Ma,这与胶东西北部艾山岩体(锆石Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄2180~2420 Ma)和胶东东部三佛山岩体(全岩Nd同位素二阶模式年龄2143~2447 Ma、锆石Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄2096~2385 Ma)接近(李秀章等,2022),指示伟德山期花岗岩的放射成因同位素具有一致性。
![]() 图 11 三合山岩体花岗岩锆石εHf(t)−t图解(据李秀章等, 2022)Figure 11. εHf(t)−t diagram of zircons of granite in Sanheshan pluton (modified from Li Xiuzhang et al., 2022)
图 11 三合山岩体花岗岩锆石εHf(t)−t图解(据李秀章等, 2022)Figure 11. εHf(t)−t diagram of zircons of granite in Sanheshan pluton (modified from Li Xiuzhang et al., 2022)综合以上全岩Sr–Nd–Pb 及锆石Hf同位素分析结果认为,三合山岩体起源于重熔的下地壳,并受到了幔源物质的混染。
7.4 成岩构造环境
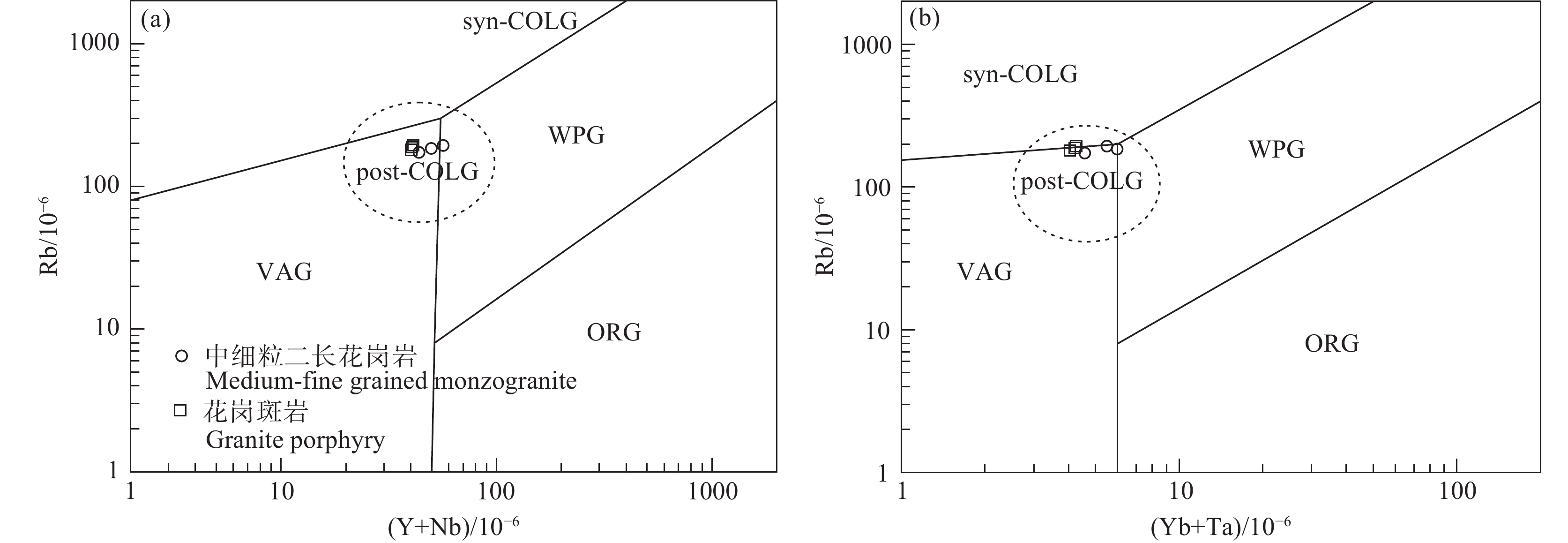
主量元素特征显示,三合山属于高钾钙碱性花岗−钾玄武岩系列,表明岩体形成于俯冲或者同碰撞的环境(钱青等,2002)。稀土元素和微量元素特征方面,三合山岩体富集Rb、K、La、Zr和Hf,亏损大离子亲石元素Sr、Ba和高场强元素Nb、P、Ti,显示与俯冲背景有关的特征(Kelemen et al.,2007)。此外,元素Rb、Y、Yb、Nb和Ta活动性较弱,在漫长的构造演化过程中变化较小,能有效区分不同构造环境下形成的花岗岩类,包括火山弧花岗岩、同碰撞花岗岩、板内花岗岩和洋脊花岗岩等。在(Y+Nb)−Rb、(Yb+Ta)−Rb微量元素构造环境判别图中(图12a、b),中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩主要落入后碰撞花岗岩区域,表明其形成于胶东区域伸展的构造动力学背景下。
![]() 图 12 三合山岩体构造环境判别图解(底图据Pearce et al.,1984)syn−COLG—同碰撞型;VAG—火山弧型;WPG—板内型;ORG—洋中脊型;post−COLG—后碰撞型Figure 12. Tectonic environment discrimination diagram of the Sanheshan pluton (modified from Pearce et al.,1984)syn−COLG−Syn−collision granite; VAG−Volcanic arc granite; WPG−Within plate granite; ORG−Oceanic ridge granite; post−COLG−Post−collision granite
图 12 三合山岩体构造环境判别图解(底图据Pearce et al.,1984)syn−COLG—同碰撞型;VAG—火山弧型;WPG—板内型;ORG—洋中脊型;post−COLG—后碰撞型Figure 12. Tectonic environment discrimination diagram of the Sanheshan pluton (modified from Pearce et al.,1984)syn−COLG−Syn−collision granite; VAG−Volcanic arc granite; WPG−Within plate granite; ORG−Oceanic ridge granite; post−COLG−Post−collision granite中生代早白垩世晚期,受太平洋板块后撤式俯冲影响,中国东部处于陆内伸展背景下,胶东地区发生了岩石圈减薄,地幔上涌等地质事件,主要表现为胶莱盆地(拉分盆地)的形成和大规模I–A型岩浆(伟德山期花岗岩和崂山期花岗岩)沿断裂构造侵位(王来明等,2021)。作为伟德山期花岗岩的一员,三合山岩体初始的壳幔混合岩浆沿郯庐断裂带的次级断裂上涌,并不断萃取围岩中的成矿元素,当岩浆中挥发分达到饱和时发生流体相和熔体相的分离,熔体相侵位冷凝形成三合山岩体,而后流体相富钼岩浆热液沿节理、沿裂隙充填,并在演化过程中发生沸腾作用,大量钼元素沉淀,形成三合山斑岩型钼矿。
综上所述,三合山岩体及相关的斑岩型钼矿形成于早白垩世太平洋板块相对欧亚板块俯冲导致的弧后扩张环境下,为中国东部岩石圈减薄过程中壳幔相互作用的产物。
8. 结 论
(1)三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩的LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄分别为(115.42±0.27)Ma和(115.21±0.25)Ma,指示三合山岩体形成于中生代白垩世晚期,应属伟德山期花岗岩。
(2)三合山岩体岩石为准铝质高钾钙碱性系列,轻稀土元素分馏明显,重稀土分馏较弱,具中等Eu中等负异常;富集Rb、K、Pb、Nd、Zr和Hf元素,亏损大离子亲石元素Sr、Ba和高场强元素Nb、P、Ti,成因类型为未分异—分异的I型花岗岩。
(3)较低的锶初始值,负的εNd(t)和εHf(t),指示三合山岩体起源于下地壳重熔,并受到了幔源物质的混染。三合山岩体形成于早白垩世太平洋板块相对欧亚板块俯冲导致的陆内伸展背景下,为中国东部岩石圈减薄过程中壳幔相互作用的产物。
致谢: 北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司汪欢博士在试验测试工作方面给予了帮助;中国地质大学(北京)董学博士在论文的写作和修改过程中给予了帮助;主编郝梓国老师对论文提出了宝贵的修改意见;在此一并表示感谢。
1 ➊山东省地质矿产勘查开发局第四地质大队.1992.1/5万沙河、新河、辛安、郭家店地质调查报告[R]. -
图 1 胶东大地构造位置( a) 与金−多金属矿床分布图(b)(据丁正江等,2013;杨立强等,2014修改)
Figure 1. Schematic tectonic map of Jiaodong (a) and distribution map of gold-polymetallic deposits (b) (modified from Ding Zhengjiang et al.,2013; Yang Liqiang et al.,2014)
图 2 三合山岩体地质略图及野外露头照片(据山东省地质矿产勘查开发局第四地质大队,1992
1 修改)a—三合山地质略图;b—岩性穿插关系;c—矿脉穿插关系;d—民采老硐;e—二长花岗岩野外露头;f—花岗斑岩野外露头;1—第四系;2—荆山群野头组;3—荆山群陡崖组;4—中细粒二长花岗岩;5—花岗斑岩;6—矽卡岩;7—萤石−重晶石脉;8—石英-辉钼矿脉;9—地质界线;10—实测/推测断裂;11—采样位置;12—辉钼矿点;13.—金矿点;14—银矿点;15—铅矿点
Figure 2. Geological map and field photos of Sanheshanpluton (modified from Shandong Provincial No.4 Institute of Geological and Mineral Survey,1992
1 )a–Sketch geological map of Sanheshan; b–Lithology interspersed relation; c–Ore veins interspersed relation; d–Civilian mines; e–Field outcrops of monzogranite; f–Field outcrop of granite porphyry; 1–Quaternary; 2–Yetou Formation of Jingshan Group; 3–Douya Formation of Jingshan Group; 4–Medium−fine grained monzogranite; 5–Granite porphyry; 6–Skarn; 7–Fluorite−barite veins; 8–Quartz−molybdenite vein; 9–Geological boundary; 10–Measured/presumed fault; 11–Sampling location; 12–Molybdenite points; 13–Gold sites; 14–Silver ore points; 15–Lead ore points
图 3 三合山岩体手标本及显微镜照片
a—中细粒二长花岗岩及其内部暗色包体;b—花岗斑岩;c—花岗结构;d—斑状结构;Q—石英;Kfs—钾长石;Bi—黑云母;Pl—斜长石;Hb—角闪石
Figure 3. Field and micrograph of Sanheshan pluton
a–Medium−fine grained monzogranite and its internal dark inclusion; b–Granite porphyry; c–Granitic texture; d–Porphyric texture; Q–Quartz; Kfs–Potash feldspar; Bi–Biotite; Pl–Plagioclase; Hb–Hornblende
图 4 三合山岩体花岗岩TAS图解(a)(据Wilson,1989)、A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(据Maniar and Piccoli,1989)、SiO2−K2O图解(c)(据Le Maitre,1989; Rickwood,1989)及AR−SiO2图解(d)(据Wright,1969)
Figure 4. Granite TAS diagram of Sanheshanpluton (a) (after Wilson, 1989), A/CNK−A/NK diagram (b) (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989), SiO2−K2O diagram (c) (after Le Maitre, 1989; Rickwood, 1989) and AR−SiO2 diagram (d) (after Wright,1969)
图 5 三合山岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)
(标准化数据:a据Boynton,1984;b据Sun and Mcdonough,1989)
Figure 5. Chondrite−normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle−normalized trace element spider diagrams
(normalization data: a after Boynton, 1984; b after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
图 6 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩(a、c)和花岗斑岩(b、d)锆石阴极发光图像和锆石U−Pb年龄谐和图
(黄圈为锆石U−Pb测量位置,红圈为锆石Lu−Hf测量位置)
Figure 6. Cathodoluminescence images and zircon U−Pb age concordance diagram of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton
(The yellow circle represents the measurement location of zircon U−Pb, the red circle represents the measurement location of zircon Lu−Hf)
图 8 三合山岩体花岗岩成因判别图解(底图据Whalen et al., 1987)
Figure 8. Genetic discrimination diagram of granite in Sanheshanpluton (basemap from Whalen et al., 1987)
图 9 三合山岩体花岗岩Sr−Nd同位素图解
a—εNd(t)−εSr(t)图解(据Zhu et al. 2001);b—εNd(t)−(87Sr/86Sr)i图解(据Jahn et al.,1999;盖永升等,2015修改;基性脉岩范围据Yang et al.,2012);MORB—洋中脊型玄武岩;B—玄武岩源区;Bc—过渡源区;C—陆壳源区
Figure 9. Sr−Nd isotope diagram of granite in Sanheshan pluton
a−εNd(t)−εSr(t)diagram (modified from Zhu et al., 2001); b−εNd(t) − (87Sr/86Sr)i diagram (modified from Jahn et al., 1999; Gai Yongsheng et al., 2015; basic dike range by Yang et al., 2012); MORB–Mid ocean ridge basalt; B–Origin of basalt; Bc–Origin of transitional mantle; C–Continental source
图 10 三合山岩体花岗岩Pb同位素207Pb/204Pb–206Pb/204Pb相关曲线(a,据Allègre,1988)、206Pb/204Pb–143Nd/144Pb相关图解(b,据Zindler and Hart,1986)
PREMA—原始地幔;DM—亏损地幔;EMⅠ—Ⅰ型富集地幔;EMⅡ—Ⅱ型富集地幔;HIMU—高μ值地幔;MORB—洋中脊型玄武岩;BSE—全硅酸盐地球
Figure 10. 207Pb / 204Pb–206Pb / 204Pb curve (a, after Allègre, 1988) and 143 Nd/144Nd–206Pb/204Pb isotopic diagram (b, after Zindler and Hart, 1986 ) of granite in Sanheshan pluton
PREMA–Primitive mantle; DM–Depleted mantle; EMⅠ–Enriched mantle Ⅰ; EMⅡ–Enriched mantle Ⅱ; HIMU–High μ mantle; MORB–Mid ocean ridge basalt; BSE–Bulk silicate earth
图 11 三合山岩体花岗岩锆石εHf(t)−t图解(据李秀章等, 2022)
Figure 11. εHf(t)−t diagram of zircons of granite in Sanheshan pluton (modified from Li Xiuzhang et al., 2022)
图 12 三合山岩体构造环境判别图解(底图据Pearce et al.,1984)
syn−COLG—同碰撞型;VAG—火山弧型;WPG—板内型;ORG—洋中脊型;post−COLG—后碰撞型
Figure 12. Tectonic environment discrimination diagram of the Sanheshan pluton (modified from Pearce et al.,1984)
syn−COLG−Syn−collision granite; VAG−Volcanic arc granite; WPG−Within plate granite; ORG−Oceanic ridge granite; post−COLG−Post−collision granite
表 1 三合山岩体主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)测试结果
Table 1 Major (%) and trace elements (10−6) data of Sanheshan pluton
样号 SHS-H1 SHS-H2 SHS-H3 SHS-H4 SHS-H5 SHS-H6 样号 SHS-H1 SHS-H2 SHS-H3 SHS-H4 SHS-H5 SHS-H6 岩性 中细粒二长花岗岩 花岗斑岩 岩性 中细粒二长花岗岩 花岗斑岩 Al2O3 13.61 13.90 14.01 13.91 14.40 14.50 Cd 0.15 1.50 0.22 0.11 0.13 0.11 SiO2 72.50 72.13 71.39 71.34 69.95 70.94 In 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 CaO 1.17 1.05 1.30 1.40 1.46 1.45 Sb 0.16 0.86 0.44 0.22 0.23 0.18 K2O 4.80 5.12 5.09 4.72 5.15 5.09 Cs 0.96 0.88 1.27 1.27 1.21 1.41 Fe2O3T 2.15 2.30 2.46 2.57 2.50 2.50 Ba 479.20 635.43 711.47 652.29 960.24 853.53 FeO* 1.13 1.17 1.26 1.36 1.28 1.30 Ta 3.35 2.47 2.85 2.07 2.15 2.24 MgO 0.43 0.46 0.49 0.60 0.64 0.58 W 3.89 3.41 2.92 0.76 1.74 0.72 MnO 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.06 Re 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 Na2O 4.01 4.09 4.12 4.07 4.12 4.17 Tl 0.59 0.63 0.72 0.60 0.63 0.64 P2O5 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.12 0.12 0.12 Pb 17.19 18.23 20.02 17.67 18.54 19.80 TiO2 0.31 0.36 0.39 0.42 0.40 0.41 Bi 0.17 0.13 2.69 0.05 0.02 0.02 LOI 0.99 0.71 0.72 0.69 0.79 0.61 Th 18.10 15.34 15.77 17.15 14.74 16.45 Total 100.10 100.27 100.13 99.91 99.58 100.41 U 3.90 3.03 3.43 7.03 3.88 4.59 DI 89.85 90.58 89.48 88 87.56 88.6 Hf 4.83 5.02 6.14 5.20 4.85 4.62 SI 3.83 3.89 4.09 5.10 5.24 4.77 La 41.76 42.73 54.53 51.60 50.03 46.71 A/NK 1.15 1.13 1.14 1.18 1.17 1.17 Ce 80.86 81.09 99.04 89.69 86.72 83.07 A/CNK 0.98 0.98 0.96 0.97 0.96 0.97 Pr 7.89 7.83 9.64 8.17 8.32 7.67 AR 3.37 3.42 3.33 3.27 3.16 3.19 Nd 30.04 29.37 36.60 30.28 30.18 28.76 σ 2.63 2.91 2.99 2.73 3.19 3.07 Sm 5.28 4.68 5.96 4.64 4.68 4.52 Mg# 28.41 28.45 28.31 31.63 33.62 31.46 Eu 0.69 0.75 0.83 0.79 0.88 0.81 Li 10.91 7.90 10.87 15.89 16.53 15.96 Gd 4.63 4.41 5.29 4.35 4.21 4.07 Be 5.98 4.86 5.85 4.62 4.50 4.63 Tb 0.72 0.59 0.80 0.57 0.57 0.58 Sc 2.29 2.39 3.42 2.68 2.88 2.59 Dy 3.96 3.09 4.06 2.87 3.02 2.96 Ti 2223.66 2637.78 3036.49 3174.67 3064.32 3122.98 Ho 0.67 0.52 0.73 0.48 0.50 0.49 V 12.34 12.27 14.87 19.51 19.22 19.42 Er 2.23 1.67 2.39 1.60 1.64 1.63 Cr 9.44 10.69 3.15 14.88 7.56 14.15 Tm 0.41 0.30 0.41 0.28 0.29 0.29 Mn 349.94 409.02 461.86 425.79 469.52 419.42 Yb 2.63 2.10 2.64 1.97 2.06 2.02 Co 2.04 3.20 4.81 5.30 4.47 4.34 Lu 0.39 0.31 0.40 0.29 0.29 0.29 Ni 1.37 27.64 80.79 39.74 21.85 22.43 ∑REE 182.16 179.44 223.32 197.58 193.39 183.87 Cu 8.86 31.81 15.33 10.52 10.65 16.48 LREE 166.52 166.45 206.60 185.17 180.81 171.54 Zn 36.18 286.83 37.00 42.62 36.40 38.14 HREE 15.64 12.99 16.72 12.41 12.58 12.33 Ga 18.50 17.74 19.92 18.64 18.57 19.46 L/H 10.65 12.81 12.36 14.92 14.37 13.91 As 1.36 2.68 2.03 1.77 1.65 1.60 δEu 0.42 0.50 0.44 0.53 0.59 0.57 Rb 184.80 173.34 193.80 180.07 187.87 194.07 δCe 1.00 0.99 0.96 0.95 0.93 0.96 Sr 152.11 149.54 176.50 243.13 276.10 275.48 (La/Sm)N 4.98 5.74 5.76 7.00 6.72 6.50 Y 21.85 16.42 23.75 15.49 15.86 16.05 (La/Yb)N 10.71 13.72 13.93 17.66 16.37 15.59 Zr 195.03 225.33 276.03 210.21 194.88 187.26 (Sm/Nd)N 0.54 0.49 0.50 0.47 0.48 0.48 Nb 27.91 27.23 32.75 24.73 24.62 25.10 (Gd/Yb)N 1.42 1.69 1.62 1.78 1.65 1.63 Mo 1.87 13.57 14.46 9.00 8.67 5.96 T/℃ 796 808 823 799 790 787 表 2 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩全岩Sr−Nd同位素分析结果
Table 2 Sr−Nd isotope date of whole rock of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton
样品
编号岩性 t/Ma Rb Sr 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ Sm Nd 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ ISr(t) INd(t) εNd(t) TDM2/Ma /10−6 /10−6 SHS-H1 中细
粒二
长花
岗岩115.42 167.0 156.4 3.09 0.714895 0.000004 5.21 27.47 0.114550 0.511863 0.000009 0.70984 0.511777 −13.91 2041 SHS-H2 115.42 168.8 170.9 2.86 0.714753 0.000004 5.04 29.86 0.102043 0.511877 0.000009 0.71008 0.511800 −13.46 2005 SHS-H4 花岗
斑岩115.21 152.2 295.4 1.49 0.713277 0.000004 4.94 31.15 0.095839 0.511770 0.000009 0.71084 0.511698 −15.45 2167 SHS-H5 115.21 156.2 338.2 1.34 0.712558 0.000005 4.90 30.49 0.097061 0.511793 0.000009 0.71037 0.511720 −15.02 2132 表 3 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩全岩Pb同位素分析结果
Table 3 Pbisotope date of whole rock of medium-fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton
样品
编号岩性 t/Ma Th U Pb 206Pb/204Pb 2σ 207Pb/204Pb 2σ 208Pb/204Pb 2σ (206Pb/204Pb)i (207Pb/204Pb)i (208Pb/204Pb)i /10−6 SHS-H1 中细粒二长
花岗岩115.42 16.9 5.16 21.4 17.4478 0.0003 15.4702 0.0003 37.9679 0.0007 17.1799 15.4572 37.6805 SHS-H2 115.42 35.4 14.1 45.9 17.3563 0.0003 15.4656 0.0003 37.8582 0.0008 17.0150 15.4491 37.5775 SHS-H4 花岗斑岩 115.21 31.9 7.27 26.4 17.4101 0.0003 15.4709 0.0003 37.9594 0.0007 17.1041 15.4561 37.5196 SHS-H5 115.21 28.7 8.71 40.8 17.3811 0.0003 15.4656 0.0002 37.9395 0.0006 17.1440 15.4541 37.6835 表 4 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩LA−ICP−MS U−Pb 分析结果
Table 4 LA−ICP−MS zircons U−Pb isotope date of medium−fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton
样品编号 含量/10−6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 谐和度
/%Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ SHS-H1-01 298.08 550.69 0.54 0.04884 0.00099 0.12673 0.00256 0.01884 0.00015 140.4 47.6 121.2 2.3 120.3 1 99.29 SHS-H1-02 436.92 495.22 0.88 0.04773 0.00105 0.11878 0.00265 0.01808 0.00023 86.1 52.4 114 2.4 115.5 1.4 98.65 SHS-H1-03 274.80 525.30 0.52 0.04893 0.00112 0.12683 0.00313 0.01879 0.0002 144.3 53.8 121.2 2.8 120 1.2 98.97 SHS-H1-04 543.04 771.30 0.70 0.04848 0.00066 0.12216 0.00224 0.01822 0.00024 122.9 32.1 117 2 116.4 1.5 99.46 SHS-H1-05 461.77 704.41 0.66 0.0486 0.00081 0.12099 0.00214 0.01805 0.0002 128.8 39.5 116 1.9 115.3 1.2 99.45 SHS-H1-06 778.55 897.44 0.87 0.04864 0.00075 0.12036 0.00206 0.01795 0.00025 130.3 36.2 115.4 1.9 114.7 1.6 99.38 SHS-H1-07 388.93 602.59 0.65 0.04892 0.00078 0.12619 0.00211 0.01869 0.00013 144 37.2 120.7 1.9 119.4 0.8 98.94 SHS-H1-08 584.03 909.03 0.64 0.05177 0.00061 0.13748 0.00214 0.01925 0.00023 275.4 26.8 130.8 1.9 122.9 1.5 93.95 SHS-H1-09 299.49 584.38 0.51 0.0486 0.00081 0.1217 0.00209 0.0182 0.00025 128.6 39.1 116.6 1.9 116.3 1.6 99.71 SHS-H1-10 721.04 1079.50 0.67 0.05068 0.00071 0.12576 0.00235 0.01796 0.00023 226.5 32.2 120.3 2.1 114.7 1.5 95.38 SHS-H1-11 342.01 560.97 0.61 0.04823 0.00084 0.12004 0.00168 0.01811 0.00021 110.4 41.1 115.1 1.5 115.7 1.3 99.51 SHS-H1-12 382.91 496.64 0.77 0.0492 0.00086 0.13447 0.00259 0.01982 0.00024 157.1 41.1 128.1 2.3 126.5 1.5 98.74 SHS-H1-13 646.64 817.67 0.79 0.04843 0.00099 0.12063 0.00267 0.01807 0.00022 120.2 48.2 115.6 2.4 115.4 1.4 99.81 SHS-H1-14 672.97 809.51 0.83 0.04835 0.00071 0.1196 0.00177 0.01797 0.00018 116.4 34.9 114.7 1.6 114.8 1.1 99.89 SHS-H1-15 503.59 775.33 0.65 0.04885 0.00085 0.12743 0.00213 0.01891 0.00021 140.5 40.8 121.8 1.9 120.7 1.3 99.14 SHS-H1-16 799.18 1008.37 0.79 0.05048 0.00085 0.12453 0.00225 0.01791 0.00022 217.2 38.8 119.2 2 114.4 1.4 96.01 SHS-H1-17 291.41 530.44 0.55 0.04783 0.00073 0.11906 0.00203 0.01804 0.00015 91 36.3 114.2 1.8 115.3 1 99.07 SHS-H1-18 369.34 460.87 0.80 0.04843 0.00085 0.11945 0.00219 0.01791 0.00022 120.5 41.6 114.6 2 114.4 1.4 99.86 SHS-H1-19 506.22 705.33 0.72 0.04825 0.00096 0.11987 0.00208 0.01805 0.00016 111.6 47 115 1.9 115.3 1 99.66 SHS-H1-20 580.28 802.42 0.72 0.04836 0.00063 0.12 0.00207 0.01805 0.00024 116.8 30.7 115.1 1.9 115.3 1.5 99.77 SHS-H1-21 520.20 690.67 0.75 0.05056 0.00088 0.13097 0.00247 0.01884 0.0003 220.7 40.1 125 2.2 120.3 1.9 96.27 SHS-H1-22 312.05 466.17 0.67 0.04793 0.00078 0.12474 0.00197 0.0189 0.00022 96 38.5 119.4 1.8 120.7 1.4 98.87 SHS-H1-23 331.44 525.58 0.63 0.0519 0.00082 0.13187 0.00202 0.01846 0.00017 281.1 36.2 125.8 1.8 117.9 1.1 93.73 SHS-H1-24 138.16 174.13 0.79 0.0488 0.00137 0.1208 0.00328 0.01806 0.00023 138.4 65.9 115.8 3 115.4 1.4 99.62 SHS-H1-25 358.83 432.95 0.83 0.0487 0.00098 0.12014 0.00209 0.01796 0.00017 133.4 47.2 115.2 1.9 114.8 1.1 99.63 SHS-H1-26 299.95 400.79 0.75 0.0487 0.00068 0.12119 0.00202 0.01807 0.00019 133.2 32.9 116.2 1.8 115.4 1.2 99.39 SHS-H1-27 404.64 640.94 0.63 0.04823 0.00086 0.11961 0.00222 0.01803 0.00022 110.4 42.3 114.7 2 115.2 1.4 99.58 SHS-H1-28 464.66 704.26 0.66 0.04856 0.00092 0.1224 0.0024 0.0183 0.00023 126.4 44.6 117.2 2.2 116.9 1.4 99.72 SHS-H1-29 664.74 757.28 0.88 0.04838 0.00065 0.12128 0.00194 0.0182 0.00019 118 31.8 116.2 1.8 116.2 1.2 99.99 SHS-H1-30 417.79 644.51 0.65 0.04805 0.00067 0.12017 0.00187 0.01815 0.00017 101.9 33 115.2 1.7 115.9 1.1 99.38 SHS-H4-01 404.97 634.56 0.61 0.04823 0.00107 0.12184 0.00229 0.01836 0.00027 110.8 52.2 116.7 2.1 117.3 1.7 99.51 SHS-H4-02 221.91 363.68 0.59 0.04769 0.00095 0.11753 0.00238 0.01789 0.00017 83.9 47.5 112.8 2.2 114.3 1.1 98.71 SHS-H4-03 662.61 785.21 0.81 0.0484 0.00069 0.11611 0.00148 0.01741 0.00014 119.1 33.8 111.5 1.3 111.3 0.9 99.76 SHS-H4-04 359.95 606.30 0.57 0.04815 0.00082 0.12113 0.00182 0.01829 0.00019 106.4 40.1 116.1 1.6 116.9 1.2 99.34 SHS-H4-05 499.70 1199.82 0.42 0.0496 0.00097 0.12807 0.00239 0.01881 0.00028 176.1 45.4 122.4 2.2 120.1 1.8 98.18 SHS-H4-06 353.63 584.96 0.6 0.0516 0.00108 0.12611 0.00271 0.01773 0.0002 267.5 48.2 120.6 2.4 113.3 1.3 93.94 SHS-H4-07 606.58 728.31 0.82 0.04841 0.00067 0.12016 0.00176 0.01803 0.00018 119.5 32.7 115.2 1.6 115.2 1.1 99.98 SHS-H4-08 547.19 940.08 0.57 0.04884 0.0009 0.1219 0.00252 0.0181 0.00022 140 43.2 116.8 2.3 115.6 1.4 99 SHS-H4-09 162.49 218.28 0.72 0.0976 0.00581 0.26322 0.01747 0.0189 0.00028 1578.7 111.5 237.3 14 120.7 1.8 50.88 SHS-H4-10 219.02 316.83 0.67 0.0481 0.00087 0.11923 0.00235 0.01795 0.00017 104.3 42.7 114.4 2.1 114.7 1.1 99.7 SHS-H4-11 492.39 669.39 0.73 0.04854 0.00088 0.12031 0.0021 0.01801 0.00018 125.7 42.4 115.4 1.9 115.1 1.1 99.74 SHS-H4-12 485.68 769.69 0.62 0.0482 0.00075 0.1189 0.00195 0.01789 0.00017 108.9 36.6 114.1 1.8 114.3 1.1 99.78 SHS-H4-13 332.11 449.72 0.73 0.04777 0.00067 0.11921 0.00184 0.0181 0.00016 87.7 33.4 114.4 1.7 115.6 1 98.91 SHS-H4-14 373.12 576.05 0.63 0.12877 0.00986 0.38418 0.03117 0.02106 0.00033 2081.3 134.7 330.1 22.9 134.4 2.1 40.7 SHS-H4-15 384.84 655.90 0.57 0.04871 0.00113 0.12081 0.00281 0.01802 0.00026 133.9 54.7 115.8 2.5 115.1 1.6 99.42 SHS-H4-16 652.15 675.30 0.94 0.04863 0.00089 0.12097 0.00278 0.018 0.00022 130.1 42.8 116 2.5 115 1.4 99.17 SHS-H4-17 403.25 600.87 0.65 0.04963 0.00128 0.12442 0.00344 0.0182 0.00029 177.8 60 119.1 3.1 116.2 1.9 97.63 SHS-H4-18 336.63 669.29 0.49 0.04799 0.00064 0.11944 0.00155 0.01807 0.00014 98.6 31.6 114.6 1.4 115.4 0.9 99.25 SHS-H4-19 313.74 524.55 0.59 0.06444 0.00112 0.15985 0.00253 0.01804 0.00016 756.2 36.5 150.6 2.2 115.2 1 76.53 SHS-H4-20 352.20 569.94 0.6 0.04851 0.00123 0.11984 0.00301 0.01792 0.00027 124 59.5 114.9 2.7 114.5 1.7 99.62 SHS-H4-21 159.20 238.15 0.67 0.04871 0.00126 0.12083 0.003 0.01808 0.00019 133.7 60.6 115.8 2.7 115.5 1.2 99.7 SHS-H4-22 381.55 517.41 0.72 0.04875 0.00097 0.12092 0.00227 0.01803 0.00018 136 46.5 115.9 2.1 115.2 1.2 99.38 SHS-H4-23 388.39 602.39 0.62 0.04775 0.0009 0.1187 0.00221 0.01805 0.00016 87 44.6 113.9 2 115.3 1 98.76 SHS-H4-24 266.55 379.52 0.69 0.04811 0.00088 0.11798 0.00197 0.01785 0.00018 104.8 43.1 113.2 1.8 114 1.1 99.31 SHS-H4-25 368.31 609.97 0.58 0.04864 0.00125 0.1211 0.00263 0.01811 0.00024 130.6 60.3 116.1 2.4 115.7 1.5 99.68 SHS-H4-26 223.64 335.62 0.66 0.0525 0.00113 0.13084 0.0029 0.01812 0.00023 307.3 49.1 124.8 2.6 115.8 1.4 92.73 SHS-H4-27 226.31 323.53 0.68 0.04887 0.00141 0.12122 0.00236 0.01817 0.00033 141.7 67.9 116.2 2.1 116.1 2.1 99.89 SHS-H4-28 847.75 1294.89 0.63 0.04854 0.00056 0.11494 0.00138 0.01718 0.00017 125.7 27.3 110.5 1.3 109.8 1.1 99.41 SHS-H4-29 520.32 623.94 0.81 0.04883 0.00099 0.12087 0.00217 0.01798 0.00022 139.7 47.6 115.9 2 114.9 1.4 99.15 SHS-H4-30 307.92 557.81 0.53 0.04868 0.00094 0.1212 0.00221 0.0181 0.00018 132.6 45.4 116.2 2 115.6 1.1 99.54 表 5 三合山岩体中细粒二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩锆石Lu−Hf分析结果
Table 5 Zircon Lu−Hf isotope date of medium−fine grained monzogranite and granite porphyry in Sanheshan pluton
样品编号 T/Ma 176Yb/178Hf 2σ 176Lu/178Hf 2σ 176Hf/178Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM/Ma TDM2/Ma fLu/Hf SHS-H1-002 115.5 0.034365 0.000136 0.001259 0.000005 0.282244 0.000016 −18.67 −16.25 1431 2204 −0.96 SHS-H1-004 116.4 0.040687 0.000423 0.001395 0.000013 0.282230 0.000014 −19.17 −16.72 1456 2235 −0.96 SHS-H1-005 115.3 0.035505 0.000181 0.001268 0.000007 0.282195 0.000015 −20.40 −17.95 1500 2313 −0.96 SHS-H1-006 114.7 0.055793 0.000178 0.001942 0.000014 0.282288 0.000017 −17.12 −14.74 1395 2109 −0.94 SHS-H1-009 116.3 0.034779 0.000340 0.001231 0.000007 0.282220 0.000014 −19.53 −17.08 1464 2257 −0.96 SHS-H1-011 115.7 0.041548 0.001231 0.001526 0.000035 0.282209 0.000014 −19.93 −17.52 1492 2284 −0.95 SHS-H1-013 115.4 0.043584 0.000611 0.001507 0.000017 0.282239 0.000016 −18.84 −16.43 1448 2216 −0.95 SHS-H1-014 114.8 0.042933 0.000181 0.001555 0.000004 0.282223 0.000018 −19.42 −17.01 1473 2253 −0.95 SHS-H1-016 114.4 0.048977 0.001296 0.001710 0.000035 0.282156 0.000021 −21.78 −19.42 1574 2403 −0.95 SHS-H1-017 115.3 0.035244 0.000354 0.001233 0.000017 0.282241 0.000016 −18.77 −16.32 1434 2210 −0.96 SHS-H1-018 114.4 0.053518 0.001327 0.001771 0.000035 0.282183 0.000019 −20.81 −18.43 1537 2341 −0.95 SHS-H1-019 115.3 0.035349 0.000213 0.001262 0.000008 0.282268 0.000015 −17.82 −15.40 1398 2151 −0.96 SHS-H1-020 115.3 0.051387 0.000848 0.001737 0.000025 0.282208 0.000014 −19.94 −17.56 1501 2286 −0.95 SHS-H1-024 115.4 0.023987 0.000194 0.000814 0.000007 0.282252 0.000016 −18.41 −15.93 1404 2185 −0.98 SHS-H1-025 114.8 0.032159 0.000260 0.001121 0.000016 0.282159 0.000018 −21.66 −19.23 1544 2392 −0.97 SHS-H1-026 115.4 0.048079 0.000216 0.001565 0.000011 0.282422 0.000019 −12.36 −9.95 1190 1807 −0.95 SHS-H1-027 115.2 0.048379 0.000880 0.001646 0.000028 0.282127 0.000018 −22.80 −20.39 1612 2466 −0.95 SHS-H1-028 116.9 0.038652 0.000438 0.001333 0.000015 0.282171 0.000016 −21.25 −18.80 1537 2366 −0.96 SHS-H1-029 116.2 0.048147 0.001031 0.001636 0.000036 0.282198 0.000016 −20.31 −17.90 1512 2309 −0.95 SHS-H1-030 115.9 0.036768 0.000498 0.001304 0.000015 0.282243 0.000014 −18.72 −16.27 1435 2207 −0.96 SHS-H4-001 117.3 0.056976 0.001736 0.001836 0.000057 0.282135 0.000018 −22.51 −20.10 1608 2447 −0.94 SHS-H4-002 114.3 0.034185 0.000795 0.001206 0.000020 0.282180 0.000013 −20.94 −18.54 1519 2347 −0.96 SHS-H4-004 116.9 0.036438 0.000215 0.001309 0.000007 0.282242 0.000023 −18.75 −16.29 1437 2209 −0.96 SHS-H4-006 113.3 0.035037 0.000510 0.001240 0.000021 0.282261 0.000015 −18.07 −15.69 1407 2168 −0.96 SHS-H4-007 115.2 0.057145 0.001128 0.001917 0.000035 0.282225 0.000015 −19.35 −16.96 1484 2249 −0.94 SHS-H4-008 115.6 0.036822 0.000405 0.001276 0.000013 0.282240 0.000014 −18.82 −16.39 1438 2214 −0.96 SHS-H4-010 114.7 0.029173 0.000118 0.001025 0.000005 0.282227 0.000016 −19.28 −16.83 1447 2243 −0.97 SHS-H4-011 115.1 0.039391 0.000574 0.001368 0.000010 0.282199 0.000017 −20.26 −17.85 1499 2305 −0.96 SHS-H4-012 114.3 0.038626 0.000294 0.001350 0.000015 0.282247 0.000015 −18.57 −16.17 1431 2199 −0.96 SHS-H4-013 115.6 0.037094 0.000262 0.001278 0.000007 0.282163 0.000015 −21.55 −19.11 1546 2385 −0.96 SHS-H4-015 115.1 0.040294 0.000423 0.001421 0.000020 0.282200 0.000015 −20.24 −17.81 1500 2304 −0.96 SHS-H4-016 115 0.046511 0.000306 0.001610 0.000006 0.282194 0.000017 −20.45 −18.06 1516 2318 −0.95 SHS-H4-017 116.2 0.040350 0.000583 0.001369 0.000014 0.282184 0.000018 −20.79 −18.36 1520 2338 −0.96 SHS-H4-018 115.4 0.037646 0.000760 0.001252 0.000021 0.282323 0.000014 −15.87 −13.42 1320 2028 −0.96 SHS-H4-020 114.5 0.030983 0.000654 0.001083 0.000025 0.282260 0.000015 −18.11 −15.67 1402 2168 −0.97 SHS-H4-021 115.5 0.028978 0.000462 0.000996 0.000014 0.282208 0.000016 −19.95 −17.49 1472 2284 −0.97 SHS-H4-022 115.2 0.042578 0.000377 0.001447 0.000013 0.282173 0.000015 −21.17 −18.77 1538 2362 −0.96 SHS-H4-023 115.3 0.022154 0.000350 0.000765 0.000013 0.282259 0.000014 −18.14 −15.69 1392 2169 −0.98 SHS-H4-024 114 0.035765 0.000751 0.001215 0.000020 0.282183 0.000016 −20.85 −18.44 1516 2342 −0.96 SHS-H4-025 115.7 0.035741 0.000105 0.001236 0.000004 0.282283 0.000015 −17.29 −14.83 1376 2117 −0.96 表 6 胶东伟德山期花岗岩同位素年龄表(LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb)
Table 6 Isotope chronology of the Weideshan granite in Jiaodong( LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb )
岩体名称 样品编号 地理位置 岩性 年龄/Ma 资料来源 伟德山 GZ 威海市崮庄村 细粒石英闪长岩 112±1 李杰等,2013 SSD-1/1B 荣成冷家 中细粒钾长花岗岩 113. 4±1.8 丁正江等,2013 GZ 荣成南台 中细粒碎裂花岗岩 114. 2±2.1 三佛山 D04-1 乳山市三佛山 细粒正长花岗岩 119.6± 1.0 李增达等,2018 D09-1 中细粒二长花岗岩 111.4± 2.2 D11-2 中粗粒二长花岗岩 115.7± 1.7 泽头 06SD01 海阳辛安 中粒二长花岗岩 114±3 郭敬辉等,2005 06SD17 乳山市高家台村 中粗粒二长花岗岩 116±3 ZT-1-01 文登泽头 中粒黑云角闪石英二长岩 115.6±1.1 董学等,2020 牙山—
院格庄2017N1 院格庄 中粒含角闪二长花岗岩 118.10±0.66 邹键等,2021 2017N2 含巨斑状细中粒二长花岗岩 118.52±0.78 2017N3 巨斑状中粒含角闪二长花岗岩 118.80±0.67 艾山 16SD-33 蓬莱艾山 斑状角闪花岗闪长岩 116.7±1.7 胡波,2019 WDS07/1B 蓬莱张家沟村 含斑中粗粒二长花岗岩 122±1 任天龙等,2021 JD48 栖霞市前寨村 斑状中粗粒二长花岗岩 119±1 JD87 蓬莱市邓格庄村 含斑中粗粒二长花岗岩 113±1 南宿 LM06/1b 莱州市西姜家村 中粒二长花岗岩 121.3±2.1 胡波,2019 秦姑庵 JD151 莱州市秦姑庵 斑状中粒二长花岗岩 119.9±1.3 李秀章等,2021 三合山 SHS-H1 平度市三合山 中细粒二长花岗岩 115.42±0.27 本文 SHS-H4 平度市三合山 花岗斑岩 115.21±0.25 -
[1] Allègre C J, Lewin E, Dupré B. 1988. A coherent crust−mantle model for the uranium−thorium–lead isotopic system[J]. Chemical Geology, 70(3): 211−234. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90094-0
[2] Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N. 2000. Early−middle archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu−Hf and U−Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(24): 4205−4225. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2
[3] Black L P, Kamo S L, Allen C M, Aleinikoff J N, Davis D W, Korsch R J, Foudoulis C. 2003. TEMORA 1: A new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U−Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 200(1/2): 155–170.
[4] Boynton W V. 1984. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 63–114.
[5] Chu N C, Taylor R N, Valérie Chavagnac, Nesbitt R W, Boella R M, Milton J A, German C R, Bayon G, Burton K. 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi−collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17: 1567−1574. doi: 10.1039/b206707b
[6] Ding Zhengjiang, Sun Fengyue, Liu Fulai, Liu Jianhui, Liu Dianhaop, Zhang Peijian, Du Shengxian, Li Bing. 2013. U–Pb dating of zircons from the Weideshan molybdenum copper polymetallic deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula, China, and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(2): 607−618
[7] Ding Zhengjiang, Sun Fengyue, Liu Jianhui, Liu Dianhao, Li Bile, Zhang Peijian, Qian Ye, Li Jie. 2012. Re–Os dating of molybdenites from the Xingjiashan molybdenum–tungsten deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula, China and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(9): 2721−2732 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Ding Zhengjiang, Sun Fengyue, Li Guohua, Ji Pan, Kong Yan. 2015. Accurate zircon U–Pb dating of Early Yanshanian molybdenum–tungsten mother rocks in Xingjiashan area of Jiaodong Peninsula and its significance[J]. Geology in China, 42(2): 556−569 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Dong Xue, Li Dapeng, Zhao Rui, Wang Xinran, Wang Qingfei. 2020. Zircon U–Pb chronology and petrogenesis of Zetou pluton in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Implications for regional petrogenesis and mineralization in the Aptian to Albian[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1501−1514 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.11
[10] Dong Yinfeng, Xu Jinxin, Zhao Jin, Li Mingbo, Du Zhenming. 2015. Metallogenic regularity of laizhou–Anqiu iron ore–forming belt in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 31(5): 7−12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Gai Yongsheng, Liu Liang, Kang Lei, Yang Wenqiang, Liao Xiaoying, Wang Yawei. 2015. The origin and geologic significance of plagiogranite inophiolite belt at North Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(9): 2549−2565 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Gao S, Luo T C, Zhang B R, Zhang H F, Han Y W, Zhao Z D, Hu Y K. 1998. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(11): 1959−1975. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00121-5
[13] Green T H. 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust–mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 120(3/4): 347−359.
[14] Guo Jing, Zhu Xueqiang, Ren Tianlong, Dai Guangkai. 2019. Discovery and significance of cryptoexplosive intrusive breccia in Xiangkuang polymetallic sulfide deposit in Qixia Area of Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 35(1): 19−24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Guo Jinghui, Chen Fukun, Siebel W, Zhai Mingguo. 2005. Evolution of syn− to post−collisional magmatism from north Sulu UHP belt, eastern China: Zircon U−Pb geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(4): 1281–1301 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Han Xiaomeng, Duan Liu'an, Zhao Pengfei, Wang Jiantian, Guo Yuncheng. 2024. Pyrite Rb−Sr isochron age of the Qianchuiliu gold deposit on northeastern margin of Jiaolai Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 366−367 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Hart S R. 1984. A large–scale isotope anomaly in the southern hemisphere mantle[J]. Nature, 309(5971): 753−757. doi: 10.1038/309753a0
[18] Hua Bei, Gao Xue, Hu Zhaoguo, Mei Zhenhua, Zhang Zhiwu, Meng Yinsheng, Zhang Baotao, Zhao Lei. 2020. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Wuzhuxinwusu granite, western Xing–Meng Orogenic Belt: Evidences from geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1426−1444 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.07
[19] Hu Bo. 2019. Chronology, Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of the Aishan–Nansu Pluton in Jiaodong[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University, 1–63(in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Jahn B M ,Wu F Y, Lo C H, Tsai C H. 1999. Crust−mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: Geochemical and Sr–Nd isotopic evidence from post−collisional mafic–ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China[J]. Chemical Geology, 157(1/2): 119–146.
[21] Jochum K P, Mcdonough W F, Palme H, Spettel B. 1989. Compositional constraints on the continental lithospheric mantle from trace elements in spinel peridotite xenoliths[J]. Nature, 340(6234): 548−550. doi: 10.1038/340548a0
[22] Kelemen P B, Hanghj K, Greene A R. 2007. One view of the geochemistry of subduction–related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 3: 1−70.
[23] Le Maitre R W. 1989. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and a Glossary of Terms: Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Sub–Commision on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks[M]. Blackwell, Oxford.
[24] Li Hongkui, Zhuo Chuanyuan, Geng Ke, Liang Taitao. 2017. Intra–continental extensional tectonics of the Tan–Lu fault zone: An example from the appearance characteristics of the Yishu fault zone[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(2): 73−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Li Jie. 2012. The Study on Metallization and Metallogenetic Model of Mo–Cu–Pb–Zn Complex Deposits and Comparison with Gold Metallization in Jiaodong Area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1–127(in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Li Jie, Song Mingchun, Li Shiyong, Zhou Mingling, Ni Shijun, Zhang Chengjiang, Ding Zhengjiang, Yue Yuepo. 2013. Geological and geochemical features of the Dadengge gold polymetallic deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geology in China, 43(1): 221−237 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Li Jie, Song Mingchun, Li Shiyong, Zhou Xiaojian, Song Yingxin, Ding Zhengjiang, Yang Lixin, Wang Shanshan, Jiang Fan, Li Qian. 2016. Geological and geochemical features of the Dadengge gold polymetallic deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geology in China, 43(1): 221−237 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Li Xiuzhang, Liu Handong, Yu Xiaowei, Wang Ligong, Zhu Peigang, Guo Ruipeng. 2021. Petrogenesis element geochenistry Zircon U–Pb Chronology and Lu–Hf isotopic constraints of Qinguan granite body in northwestern Jiaozhou area[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 37(12): 1−16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Li Xiuzhang, Wang Ligong, Li Yixin, Wang Yingpeng, Yu Xiaowei, Zhang Wen, Guo Ruipeng, Liu Handong. 2022. Geochemistry, Zircon U–Pb chronology and Lu–Hf isotope characteristics of monzogranites from Aishan Pluton in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geoscience, 36(1): 333−346. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Li Zengda, Yu Xiaofei, Wang Qunming, Du Zezhong, Cao Qiang, Shi Yuanming, Wang Ran. 2018. Petrogenesis of Sanfoshan granite, Jiaodong: Diagenetic physical and chemical conditions, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Sr–Nd isotope constraints[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(2): 447−468 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Liu A D, Yun C G, Xiao M H, Jian T W, Peng F Z, Li P W, You F W. 2022. Discovery of a medium–scale tectonic altered rock type gold deposit (13.5 t) on the northeastern margin of Jiaolai Basin, Shandong Province, China and its new application of exploration direction[J]. China Geology, 5: 543−545.
[32] Ludwig K R. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication.
[33] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101: 635−643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[34] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25: 956–983.
[35] Qian Qing, Zhong Sunlin, Li Tongyi, Wen Daren. 2002. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of the Badaling high Ba–Sr granitoids: A comparison of igneous rocks from North China and the Dabie–Sulu Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(3): 275−292 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Ren Tianlong, Wang Laiming, Zhu Xueqiang, Yu Xiaowei, Yang Zhenyi, Liu Handong, Guo Ruipeng, Tao Youbing. 2021. Early Cretaceous Weideshan Period granite in Jiaodong Area[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 37(10): 1−12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Rickwood P C. 1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 22(4): 247–263.
[38] Sláma J, Košler Condon D J, Crowley J L, Gerdes A, Hanchar J M, Horstwood M S, Morris G A, Nasdala L, Norberg N. 2008. Plešovice zircon: A new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 249: 1−35. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
[39] Song Mingchun, Yan Qingli. 2000. Characteristics of dioritic inclusions in Weideshan superunit and its magma origin in Jiaonan Area[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, (4): 16−21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Song Mingchun, Wang Peicheng. 2003. Regional Geology of Shandong Province[M]. Jinan: Shandong Map Publishing House, 1–970 (in Chinese).
[41] Song Mingchun. 2014. Jiaodong gold deposit and its tectonic magmatic background for mineralization[J]. Mineral Deposits, 33(S1): 131−132 (in Chinese).
[42] Song Mingchun, Song Yingxin, Li Jie, Li Shiyong. 2015. Metallogenic series of gold and nonferrous metal deposits related to Cretaceous granites in eastern Shandong Peninsula, China[J]. Geotectonica et Etallogenia, 39(5): 828−843 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Song Mingchun, Lin Shaoyi, Yang Liqiang, Song Yingxin, Ding Zhengjiang, Li Jie, Li Shiyong, Zhou Mingling. 2020. Metallogenic model of Jiaodong Peninsula gold deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 39(2): 215−236 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Song Mingchun, Song Yingxin, Li Jie, Cao Chunguo, Ding Zhengjiang, Liu Xiao, Zhou Mingling, Li Shiyong. 2022. Stepwise prospecting method for deep–seated deposits: Take deep prospecting of ore concentration area of gold in Jiaodong Peninsula, China as an example[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 1−15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Song M C, Ding Z J, Zhang J J, Song Y X, Bo J W, Wang Y Q , Liu H B, Li S Y, Li J, Li R X, Wang B, Liu X D, Zhang L L, Dong L L, Li J, He C Y. 2021. Geology and mineralization of the sanshandao supergiant gold deposit (1200 t) in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A review[J]. China Geology, 4(4): 686–719.
[46] Sun Jinfeng, Yang Jinhui, Wu Fuyuan. 2009. Application of in–situ isotopic analysis to granite genesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(2): 129−139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Sun Luwei, Wang Guangliang. 2014. Geological characteristics and ore prospecting directions of xingshabei molybdenum deposit in Yantai area of Jiaodong peninsula in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 30(4): 41−45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 42: 313−345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[49] Tian Jiepeng, Tian Jingxiang, Guo Ruipeng, Wei Cangshan, Wang Ligong, Yu Xiaowei, Li Xiuzhang, Huang Yongbo, Zhang Chunchi, Liu Handong, Zhu Peigang. 2016. Jiaodong–type gold deposit related to crust source remelting layered granite and crust–mantle mixed granodiorite[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(5): 987−996.
[50] Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Gehrels G E, Nutman A P. 1996. Constraints on early earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 379(6566): 624−627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0
[51] Wan Zhongjie. 2017. Analysis on geological characteristics and the origin of Nanren iron deposit in Changyi City of Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 33(8): 27−32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[52] Wang Laiming, Ren Tianlong, Liu Handong, Ning Zhenguo, Yu Xiaowei, Guo Ruipeng, Hou Jianhua, Zhu Xueqiang. 2021. Division of Mesozoic granites in Jiaodong Area[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 37(8): 1−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[53] Watson E B, Harrison T M. 1983. zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. earth planet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2): 295−304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
[54] Wen Bojie, Fan Hongrui, Hu Fangfang, Yang Kuifeng, Liu Xuan, Cai Yachun, Sun Zhifu, Sun Zongfeng. 2015. The genesis of pegmatite–type molybdenum mineralization in Sanshandao, and their implications for molybdenum deposit in Jiaodong, East China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(4): 1002−1014 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[55] Wen Chunqi, Duo Ji. 1999. Methods of Ore Deposit Study[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 1–202 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[56] Whalen J, Currie K, Chappell B. 1987. A–type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, (4): 95.
[57] Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach[M]. London: Chapman & Hall, 466.
[58] Wright J B. 1969. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non–orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 106(4): 370−384. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800058222
[59] Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, Yang J H, Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U–Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 234(1/2): 105−126.
[60] Wu Fuyuan, Li Xianhua, Zheng Yongfei, Gao Shan. 2007. Lu–Hf isotopic systematics and thier applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185−220 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[61] Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei. 2004. Genetic mineralogy of zircon and its constraints on U–Pb age interpretation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16): 1589−1604 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-16-1589
[62] Xu Yigang, Wu Xiangyang, Luo Zhenyu, Ma Jinlong, Huang Xiaolong, Xie Liewen. 2007. Zircon Hf isotope compositions of Middle Jurassic–Early Cretaceous intrusions in Shandong Province and its implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 307−316 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[63] Yang Liqiang, Deng Jun, Wang Zhongliang, Zhang Liang, Guo Linnan, Song Mingchun, Zheng Xiaoli. 2014. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2447−2467 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[64] Yang K F, Fan H R, Santosh M, Hu F F, Wilde S A, Lan T G, Lu L N, Liu Y S. 2012. Reactivation of the archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong terrane, the North China craton[J]. Lithos, 146/147(8): 112−127.
[65] Zeng Fanyu. 2019. Analysis on geological characteristics and the origin of Wazi iron deposit in Shandong[J]. Mineral Exploration, 10(8): 1928−1933 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[66] Zhang Lishi, Sun Fengyue, Li Bile, Qian Ye, Zhang Yajing, Wang Li, Wang Linlin. 2021. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of granitoids in the Fu'anpu molybdenum deposit, Lesser Xing’an–Zhangguangcai range metallogenic belt: Constraints from element geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Sr– Nd– Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(8): 2471−2492 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[67] Zhang Qi, Wang Yan, Pan Guoqiang, Li Cengdong, Jin Weijun. 2008. Sources of granites: Some crucial questions on granite study (4)[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1193−1204.
[68] Zhao Zhenhua, Xiong Xiaolin, Wang Qiang, Qiao Yulou. 2008. Someaspectson geochemistry of Nb and Ta[J]. Geochimica, 37(4): 304−320. (in Chinese with English abstract
[69] Zhu B Q, Zhang J L, Tu X L, Chang X Y, Fan C Y, Liu Y, Liu J Y. 2001. Pb, Sr, and Nd isotopic features in organic matter from China and their implications for petroleum generation and migration[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(15): 2555−2570. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00608-1
[70] Zindler A, Hart S. 1986. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 14: 493−571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
[71] Zou Jian, Tang Wenlong, Ding Zhengjiang, Bo Junwei, LIi Zhiqiang, Yu Sen. 2021. Zircon U–Pb dating of the Yuangezhuang pluton in Muping of Shandong Province and its constraints on mineralization of Cu–Mo deposits[J]. Geology in China, 48(3): 883−899 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.12029/gc20210316
[72] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 刘建辉, 刘殿浩, 张丕建, 杜圣贤, 李兵. 2013. 胶东伟德山地区铜钼多金属矿锆石U–Pb法测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 29(2): 607−618. [73] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘建辉, 刘殿浩, 李碧乐, 张丕建, 钱烨, 李杰. 2012. 胶东邢家山钼钨矿床辉钼矿Re–Os同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 28(9): 2721−2732. [74] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 李国华, 纪攀, 孔彦. 2015. 胶东邢家山地区燕山早期钼钨成矿母岩锆石U–Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 中国地质, 42(2): 556−569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.02.015 [75] 董学, 李大鹏, 赵睿, 王欣然, 王庆飞. 2020. 胶东泽头岩体锆石U–Pb年代学和岩石成因: 对区域早白垩世晚期成岩成矿作用的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1501−1514. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.11 [76] 董银峰, 徐金欣, 赵金, 李明波, 杜振明. 2015. 山东省莱州–安丘铁成矿带成矿规律探析[J]. 山东国土资源, 31(5): 7−12. [77] 盖永升, 刘良, 康磊, 杨文强, 廖小莹, 王亚伟. 2015. 北阿尔金蛇绿混杂岩带中斜长花岗岩的成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 31(9): 2549−2565. [78] 郭晶, 朱学强, 任天龙, 戴广凯. 2019. 山东栖霞香夼地区多金属硫化物矿床外围隐爆–侵入角砾岩的发现及意义[J]. 山东国土资源, 35(1): 19−24. [79] 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, Siebel W, 翟明国. 2005. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞—碰撞后构造过程:锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 21(4): 1281−1301. [80] 韩小梦, 段留安, 赵鹏飞, 王建田, 郭云成. 2024. 山东省胶莱盆地东北缘前垂柳金矿床黄铁矿Rb−Sr等时线年龄[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 366−367. [81] 华北, 高雪, 胡兆国, 梅贞华, 张之武, 孟银生, 张保涛, 赵磊. 2020. 兴蒙造山带西段乌珠新乌苏花岗岩岩石成因和构造背景: 地球化学、U–Pb年代学和Sr–Nd–Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1426−1444. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.07 [82] 胡波. 2019. 胶东艾山–南宿岩体年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 1–63. [83] 李洪奎, 禚传源, 耿科, 梁太涛. 2017. 郯–庐断裂带陆内伸展构造: 以沂沭断裂带的表现特征为例[J]. 地学前缘, 24(2): 73−84. [84] 李杰. 2012. 胶东地区钼−铜−铅锌多金属矿成矿作用及成矿模式[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 1–127. [85] 李杰, 宋明春, 王美云, 李世勇, 周明岭, 倪师军, 张成江, 丁正江, 岳跃破. 2013. 胶东尚家庄钼矿床Re–Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1612−1621. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.024 [86] 李杰, 宋明春, 李世勇, 周晓剑, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 杨立新, 王珊珊, 姜帆, 李倩. 2016. 胶东大邓格金多金属矿床地质地球化学特征及意义[J]. 中国地质, 43(1): 221−237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.016 [87] 李秀章, 刘汉栋, 于晓卫, 王立功, 祝培刚, 郭瑞朋. 2021. 胶西北秦姑庵花岗岩体岩石成因及对金成矿的启示: 元素地球化学、锆石U–Pb 年代学及Lu–Hf同位素制约[J]. 山东国土资源, 37(12): 1−16. doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2021.12.001 [88] 李秀章, 王立功, 李衣鑫, 王英鹏, 于晓卫, 张文, 郭瑞朋, 刘汉栋. 2022. 胶东艾山岩体二长花岗岩地球化学、锆石U–Pb年代学及Lu–Hf同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 36(1): 333−346. [89] 李增达, 于晓飞, 王全明, 杜泽忠, 曹强, 师明元, 王然. 2018. 胶东三佛山花岗岩的成因: 成岩物理化学条件、锆石U–Pb年代学及Sr–Nd同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 34(2): 447−468. [90] 钱青, 钟孙霖, 李通艺, 温大任. 2002. 八达岭基性岩和高Ba–Sr花岗岩地球化学特征及成因探讨: 华北和大别–苏鲁造山带中生代岩浆岩的对比[J]. 岩石学报, 18(3): 275−292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2002.03.002 [91] 任天龙, 王来明, 朱学强, 于晓卫, 杨振毅, 刘汉栋, 郭瑞朋, 陶有兵. 2021. 胶东地区早白垩世伟德山期花岗岩[J]. 山东国土资源, 37(10): 1−12. doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2021.10.001 [92] 宋明春, 严庆利. 2000. 胶南地区伟德山超单元中闪长质包体的特征及岩浆成因[J]. 山东地质, (4): 16−21. [93] 宋明春, 王沛成. 2003. 山东省区域地质[M]. 济南: 山东省地图出版社, 1–970. [94] 宋明春. 2014. 胶东型金矿及其成矿的构造岩浆背景[J]. 矿床地质, 33(S1): 131−132. [95] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 李杰, 李世勇. 2015. 胶东与白垩纪花岗岩有关的金及有色金属矿床成矿系列[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(5): 828−843. [96] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 李杰, 李世勇, 周明岭. 2020. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 39(2): 215−236. [97] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 李杰, 曹春国, 丁正江, 刘晓, 周明岭, 李世勇. 2022. 深部矿阶梯找矿方法: 以胶东金矿集区深部找矿为例[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 1−15. [98] 孙金凤, 杨进辉, 吴福元. 2009. 原位微区同位素分析在花岗岩成因研究中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 16(2): 129−139. [99] 孙璐伟, 王光良. 2014. 胶东半岛烟台地区杏山北钼矿床地质特征及其找矿预测[J]. 山东国土资源, 30(4): 41−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2014.04.009 [100] 田杰鹏, 田京祥, 郭瑞朋, 韦昌山, 王立功, 于晓卫, 李秀章, 黄永波, 张春池, 刘汉栋, 祝培刚. 2016. 胶东型金矿: 与壳源重熔层状花岗岩和壳幔混合花岗闪长岩有关的金矿[J]. 地质学报, 90(5): 987−996. [101] 万中杰. 2017. 山东省昌邑市南任铁矿地质特征及成因初探[J]. 山东国土资源, 33(8): 27−32. [102] 王来明, 任天龙, 刘汉栋, 宁振国, 于晓卫, 郭瑞朋, 侯建华, 朱学强. 2021. 胶东地区中生代花岗岩划分[J]. 山东国土资源, 37(8): 1−14. [103] 文博杰, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋, 刘玄, 蔡亚春, 孙之夫, 孙宗锋. 2015. 胶西北三山岛伟晶岩型脉状钼矿化成因及对胶东钼成矿的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 31(4): 1002−1014. [104] 温春齐, 多吉. 1999. 矿床学研究方法[M]. 成都: 四川科技出版社, 1–202. [105] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu–Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185−220. [106] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U–Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589−1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 [107] 徐义刚, 巫祥阳, 罗震宇, 马金龙, 黄小龙, 谢烈文. 2007. 山东中侏罗世—早白垩世侵入岩的锆石Hf同位素组成及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 23(2): 307−316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.011 [108] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 郭林楠, 宋明春, 郑小礼. 2014. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2447−2467. [109] 曾凡玉. 2019. 山东洼子铁矿地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 矿产勘查, 10(8): 1928−1933. [110] 张立仕, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 钱烨, 张雅静, 王力, 王琳琳. 2021. 小兴安岭–张广才岭成矿带福安堡钼矿区花岗岩类的岩石成因和构造背景: 元素地球化学、锆石U–Pb年龄和Sr–Nd–Hf同位素约束[J]. 地质学报, 95(8): 2471−2492. [111] 张旗, 王焰, 潘国强, 李承东, 金惟俊. 2008. 花岗岩源岩问题——关于花岗岩研究的思考之四[J]. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1193−1204. [112] 赵振华, 熊小林, 王强, 乔玉楼. 2008. 铌与钽的某些地球化学问题[J]. 地球化学, 37(4): 304−320. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.04.005 [113] 邹键, 唐文龙, 丁正江, 薄军委, 李志强, 于森. 2021. 山东牟平院格庄岩体锆石U–Pb年龄及其对周缘铜钼多金属成矿的制约[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 883−899.



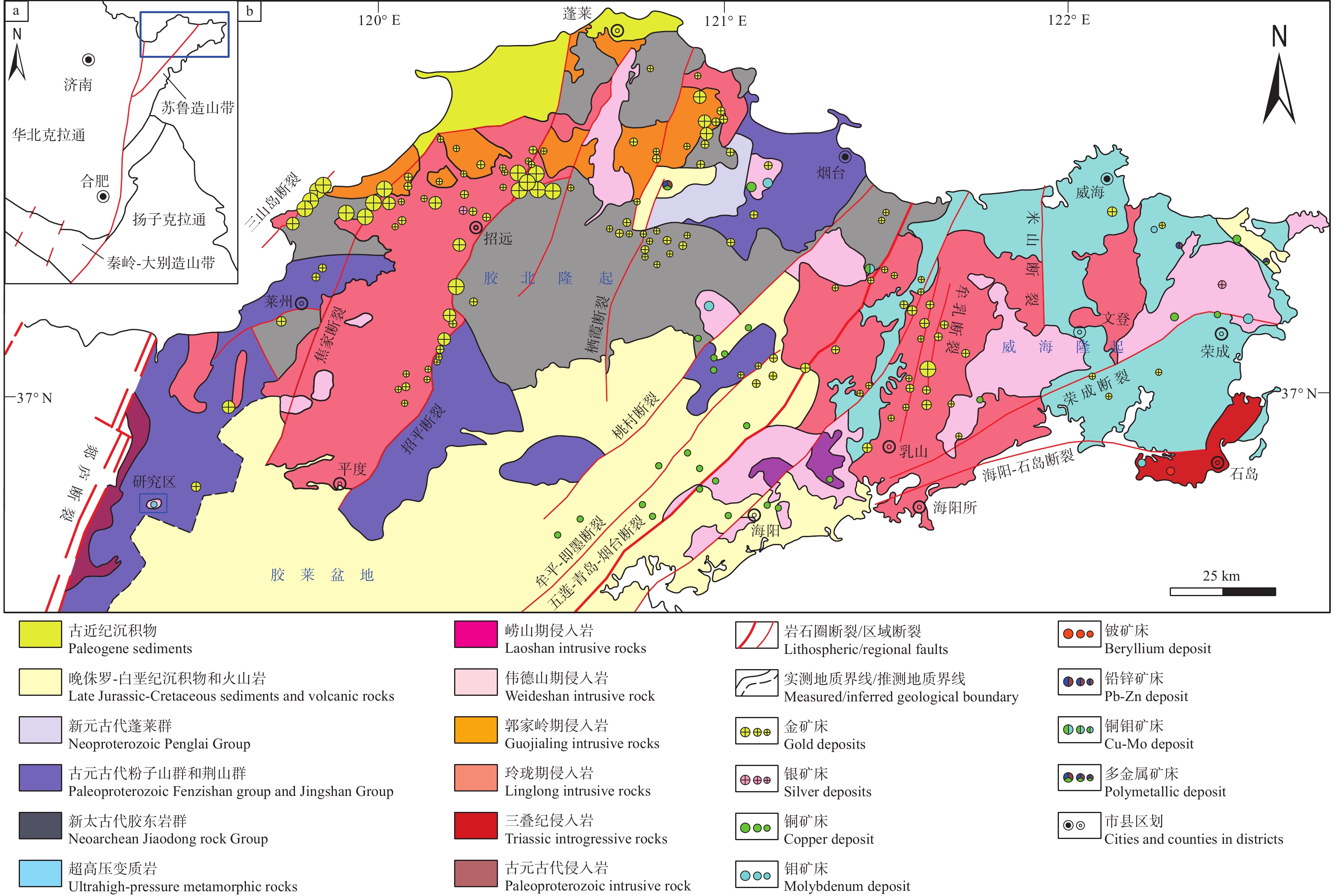
 下载:
下载: