Structural deformation and fluid evolution associated with the formation of the Sawayardun gold deposit in Southwestern Tianshan Orogen
-
摘要:研究目的
构造-流体与成矿的耦合关系属于目前矿床学研究的前沿问题,造山型金矿作为典型受构造变形控制的热液矿床,是窥探构造-流体与成矿作用内在联系的理想研究对象。
研究方法萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床是西南天山地区规模最大的造山型金矿,通过野外构造解析,流体包裹体和C-H-O-S同位素地球化学数据,研究矿区的构造变形特征,分析成矿流体性质及其成矿物质来源。
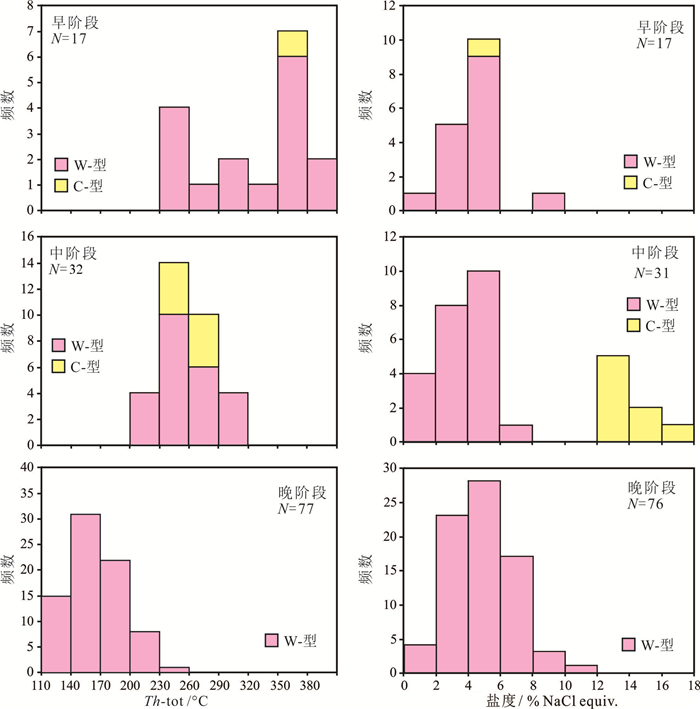
研究结果矿区变形可分3期:早期为韧性变形、中期为脆-韧性变形、晚期为脆性变形。根据脉体穿切关系和变形特征,识别出3期与构造相对应的石英脉(Qz1,Qz2,Qz3),其中Qz2为含金石英脉体,金矿主要形成于第二期的脆-韧性变形期。室内观测发现,早、中期石英中发育CO2-H2O型、纯CO2型和H2O溶液型3种类型流体包裹体,晚期仅发育水溶液型包裹体。早期石英中包裹体均一温度为237~386℃,盐度为1.4%~9.2% NaCl equiv.;中期石英获得CO2-H2O和水溶液包裹体均一温度为204~310℃,盐度为0.5%~16.6% NaCl equiv.;晚期水溶液包裹体具有较低的均一温度(125~235℃)和盐度(0.2%~10.6% NaCl equiv.)。根据CO2-H2O型包裹体计算早、中期的流体压力分别为267 MPa和208~253 MPa,对应形成的深度分别为10 km,8~9 km。同位素分析结果揭示,成矿的流体具有变质流体以及大气降水的特征,成矿物质主要来源于赋矿地层-古生代碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩建造。
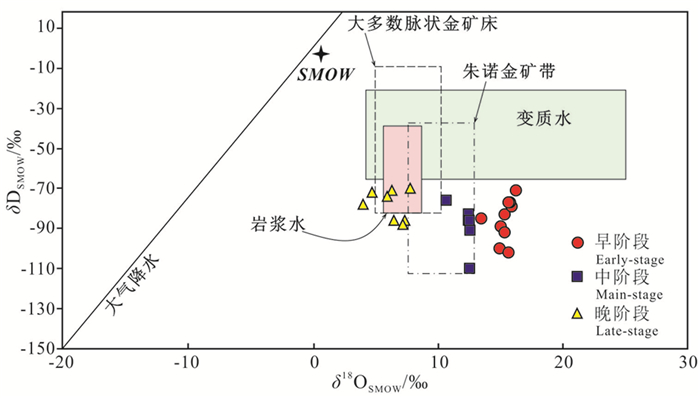
结论萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床晚古生代经历了早期挤压向晚期走滑伸展的转变;早期NW-SE向的挤压作用促使地层变质脱水产生了大量富CO2、低盐度的变质流体,形成无矿石英脉;在构造变形转向走滑伸展时,造山带抬升剥蚀,流体压力降低并发生不混溶或沸腾作用,CO2等气体逃逸,诱发浅源大气降水加入并与变质热液混合,导致大量成矿物质快速沉淀成矿。
创新点: 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿晚古生代经历了两期变形作用,成矿主要与晚期变形密切相关;结合成矿作用特征研究,建立了萨瓦亚尔顿金矿构造-流体与成矿模式图。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe relationship between structure-fluid and mineralization is a frontier problem in modern study of mineral deposit. The orogenic-type gold deposits are hosted in fault zone, and are representative target to study structural deformation and fluid evolution responsible for mineralization process.
MethodsThe Sawayardun orogenic-type gold lode system is the largest gold deposit in the Southwestern Tianshan Orogen, northwestern China. Basing on results of structural analysis, fluid inclusions and C-H-O-S isotope, natures of ore-controlling structure and ore-fluid, and metal source were studied.
ResultsThe structural deformation at the Sawayardun mine can be divided into the early ductile, middle ductile-brittle, and late brittle stages, according to the crosscutting relationships of veins, and macro and micro structures. The three-stage deformation process associated with three kinds of quartz veins (Qz1, Qz2, Qz3) from early to late, with gold mineralization being mainly introduced in middle stage. Quartz formed in the early and middle stages (Qz1 and Qz2) contains three compositional types of fluid inclusions, i.e. pure CO2, CO2-H2O and NaCl-H2O, but the late-stage minerals only contain the NaCl-H2O inclusions. The inclusions trapped in the early, middle and late stages yield total homogenization temperatures of 237℃-386℃, 204℃ -310℃, and 125℃-235℃, respectively, with corresponding salinities of 1.4-9.2, 0.5-16.6, and 0.2%-10.6% NaCl equiv., respectively. The minimum trapping pressures estimated from CO2-H2O inclusions are 267 MPa and 208-253 MPa in the early and middle stages, corresponding to lithostatic depths of 10 km and 8~9 km, respectively. The isotope systematics shows the nature of metamorphic and meteoric fluids and the hostrocks (Palaeozoic clastic and carbonate sediments) to be a significant source of ore metals.
ConclusionsThe structural deformation features at Sawayardun indicate that the mineralization was associated with the tectonic transition from the early NW-SE-trending compression to the late strike-slip extension. The early compression caused the metamorphism and metamorphic dehydration of the Palaeozoic clastic and carbonate sedimentary rocks, resulting in the formation of the low salinity, CO2-rich fluids and the early-stage barren quartz veins. Coupling with the tectonic transition from compression to strike-slip extension, the crust was rapidly uplifted and eroded, the fluid system depressurized and boiled, and mixed with and input by and mixed with the meteoric water, causing rapid escape of gases such as CO2 and deposition of ore-metals such as Au.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
勘探实践证明,志留系是我国目前最为有利、最有前景的页岩气勘探开发层系,已在四川盆地的涪陵、长宁—威远等地区取得了页岩气重大突破,进入商业开发阶段。基础地质调查表明,四川盆地周缘地区志留系黑色页岩发育,尤其是鄂西—渝东北地区,志留系底部龙马溪组富含笔石黑色页岩发育,厚度大,页岩有机质丰度高,生烃潜力大。20世纪80年代以来,中石化、中石油实施的常规油气钻井,在志留系龙马溪组均见到了不同程度的页岩气显示,展示了其良好的页岩气勘探前景,但目前尚未取得突破性的进展。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
通过野外地质调查、老井复查、分析测试及综合研究,结合区域构造特征、岩相古地理、目的层埋深等条件,对鄂西—渝东北地区志留系龙马溪组页岩气成藏地质条件进行了系统的研究,以保存条件为核心,优选鄂西建始—巴东志留系页岩气勘查有利区,在建始龙坪背斜南翼部署实施了1口地质调查井——建地1井,全井段进行了取心、气测录井,和测井工作。通过对建地1井志留系龙马溪组、新滩组、罗惹坪组岩心样品进行系统采样,测试了有机地化、岩石矿物学、储层物性和含气性等评价参数,建立了志留系页岩气综合地质剖面。
3. 研究结果(Results)
建地1井钻探资料揭示志留系自上而下发育纱帽组、罗惹坪组、新滩组和龙马溪组。其中龙马溪组和下伏上奥陶统五峰组为一套富含笔石的黑色页岩,厚度为43.7 m。实验测试分析表明,五峰—龙马溪组页岩有机质丰度高,介于0.2% ~11.24%,平均为4.39%,其中TOC>2%的页岩厚度至少25 m,主要位于龙马溪组底部和五峰组(图 1)。页岩有机质类型为Ⅰ-Ⅱ1型,热成熟度(Ro)介于2.5%~2.9%,处于过成熟早期阶段。新滩组为一套薄—中层状灰色—深灰色粉砂岩或泥质粉砂岩。岩心储层物性研究数据表明,粉砂岩孔隙度介于5.6%~11.24%,储层空气渗透率介于0.0455~1.6712 mD,平均为0.777 mD,为典型的致密砂岩储层。其上覆罗惹坪组为一套厚层状深灰绿色泥岩,渗透率普遍低于10-6mD。综合以上,建始地区志留系发育一套五峰—龙马溪组(生)-新滩组(储)-罗惹坪组(盖)致密砂岩气的生储盖组合,具有龙马溪组页岩气、新滩组致密砂岩气同生共存的成藏组合。
建地1井随钻气测录井资料显示,该井钻至1345 m下志留统新滩组深灰色泥页岩地层时,气测全烃0.09%↑21.5%,甲烷0.087%↑19.89%,现场泥浆脱离气点火成功。其中1190~1738 m全烃异常值大于大于2%的地层累计厚93 m(图 1),综合解释为含气层。这是鄂西—渝东北复杂构造区志留系首次获得致密砂岩气发现,有望打开该地区油气勘探开发新局面。另外,该井钻至井深1738.55~1782.25 m五峰龙马溪组黑色页岩时,全烃异常值0.93%~ 11.07%,甲烷0.55%~9.70%。黑色页岩富含笔石化石,岩心浸水气泡明显,21个岩心样品现场解析含气量平均达0.92 m3(不含损失气、残余气)。建地1井钻探证实了建始地区志留系具有致密砂岩气和页岩气兼探合采的勘查开发前景。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)建地1井钻探揭示湖北建始地区发育一套五峰—龙马溪组(生)-新滩组(储)-罗惹坪组(盖)的致密砂岩气生储盖组合。五峰—龙马溪组富有机质页岩厚度大、有机质丰度高,热成熟度适中,生烃能力好;新滩组为典型的致密砂岩储层。志留系具有龙马溪组页岩气、新滩组致密砂岩气共存的特点。
(2)随钻气测录井资料显示,建地1井新滩组致密砂岩储层、五峰—龙马溪组页岩储层均见到良好的油气显示,揭示建始地区志留系具有致密砂岩气和页岩气兼探合采的勘查开发前景。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
本文为中国地质调查项目鄂西页岩气示范基地拓展区战略调查(DD20189812)资助的成果。感谢翟刚毅、石砥石教授级高工的指导和帮助。
致谢: 野外工作得到的新疆自治区305项目办公室领导和同事的大力支持; 实验工作得到中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所张增杰博士的帮助; 三位评审人提出了宝贵的修改意见,特致谢意! -
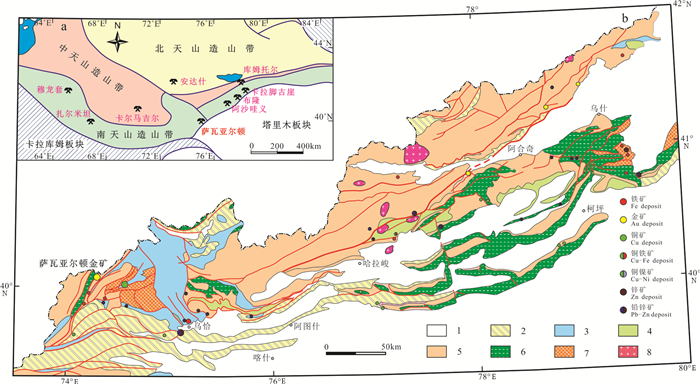
图 1 天山造山带构造简图(a,据Zhang et al., 2017修改)及西南天山区域地质及矿床分布示意图(b)
1—第四系;2—新近系—古近系;3—中生界;4—二叠系;5—石炭—泥盆系;6—下古生界;7—前寒武系;8—花岗岩
Figure 1. Tectonic map of deposits of the Tianshan Orogen (a, modified from Zhang et al., 2017) and geology and distribution of deposits of the Southwestern Tianshan Orogen (b)
1-Quaternary; 2-Neogene-Paleogene; 3-Mesozoic; 4-Permain; 5-Carboniferous-Devonian; 6-Lower Paleozoic; 7-Precambrian; 8-Granite
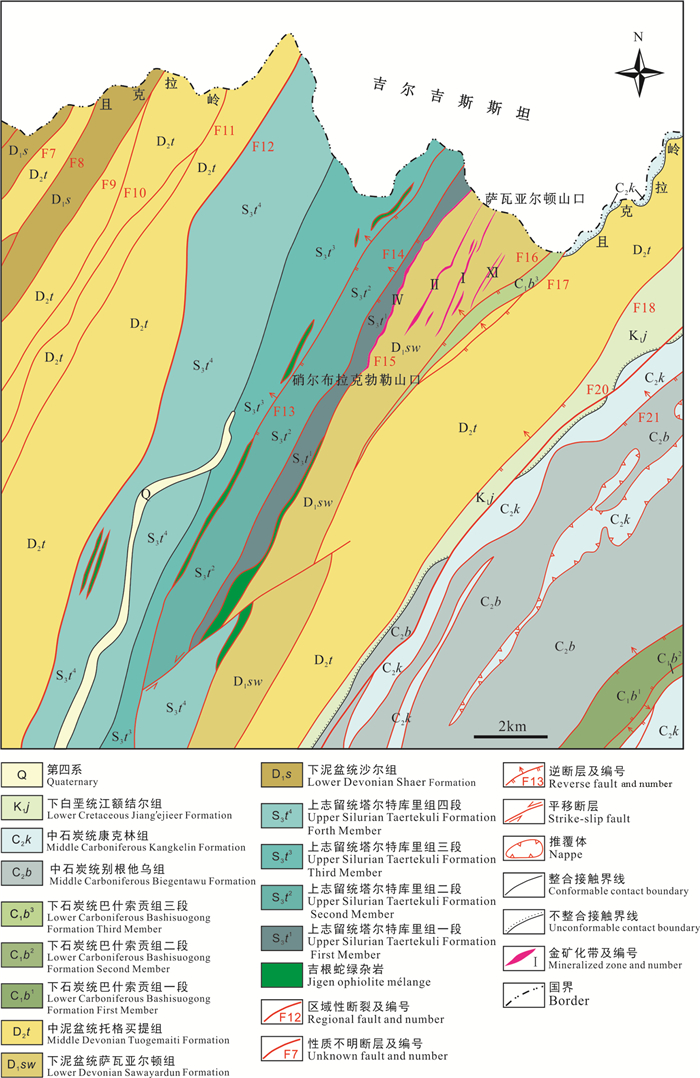
图 2 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿区地质简图
(据新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第二地质大队, 2015, 有修改)
Figure 2. Simplified geological map of the Sawayardun gold deposit
(modified from Geological Team No. 2, Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, 2015)
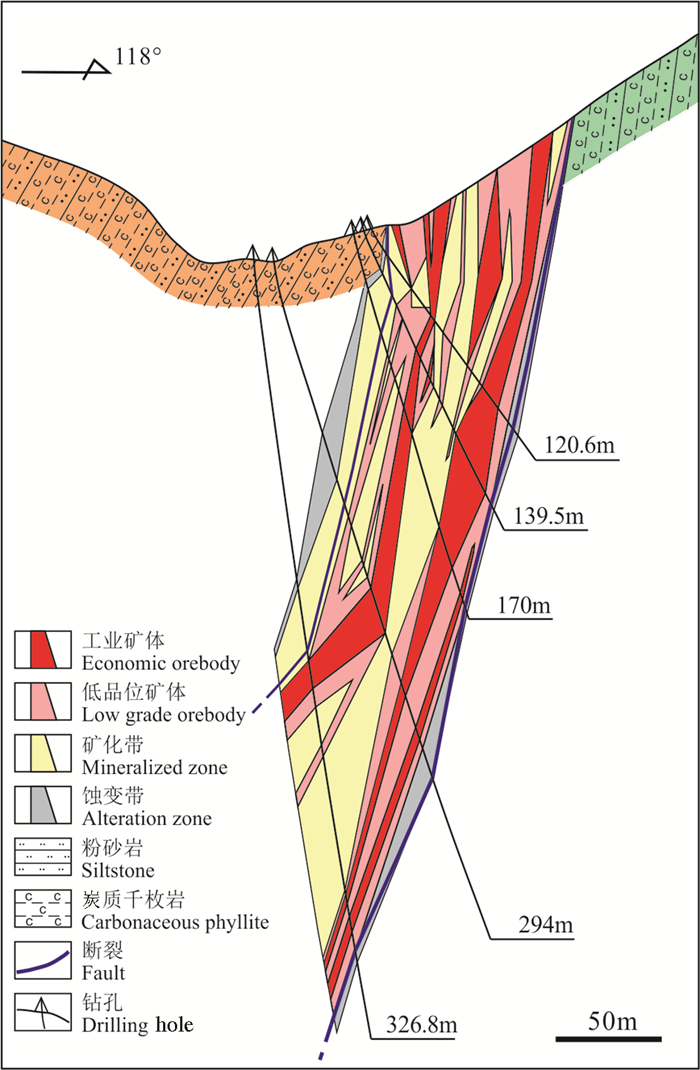
图 3 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿Ⅳ号矿化带23勘探线剖面图
(据新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第二地质大队, 2015, 有修改)
Figure 3. Geological section of No.23 prospecting line of No. Ⅳ mineralized zone at the Sawayardun gold deposit
modified from (Geological Team No. 2, Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, 2015)
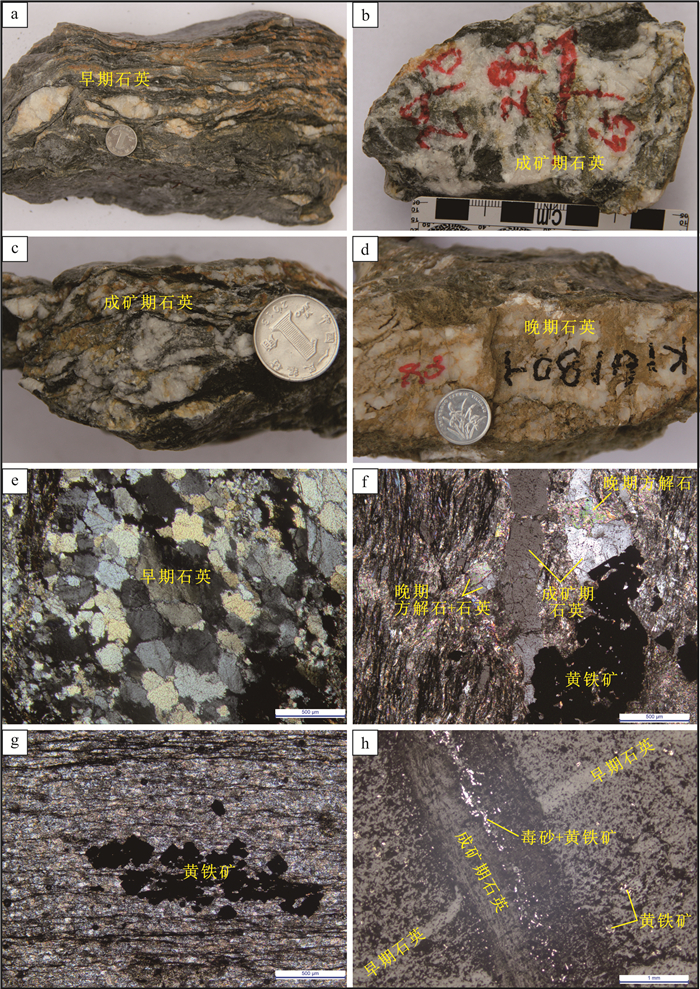
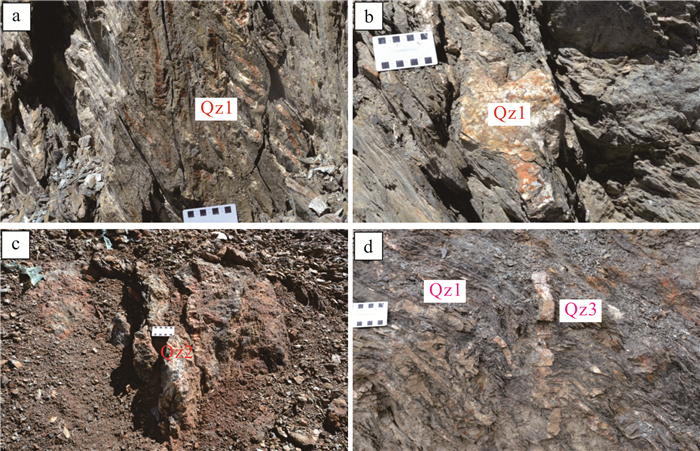
图 4 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿野外照片
a—韧性变形的炭质千枚岩,早期石英脉变形呈小褶皱(镜头朝向北东);b—早期韧性变形的强片理化千枚岩及内部发育的早期石英脉;c—成矿期韧脆性矿化蚀变带;d—晚期脆性变形,发育石英细脉切穿前期构造
Figure 4. Field photos of the Sawayardun gold deposit
a- Ductile deformed carbonaceous phyllite with small folds of early quartz vein deformation (camera faces northeast); b- Early- stage quartz occurring in carbonaceous phyllite in early ductile deformation stage; c- Ductile and brittle mineralized alteration zone during gold metallogenic period; d-Quartz veinlets crosscutting the earlier formed quartz veins in late brittle deformation stage
图 5 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿矿石岩相学照片
a—早期石英脉;b, c—成矿期石英-多金属硫化物脉;d—晚期石英-碳酸盐细脉;e—早期石英亚颗粒、不均匀消光;f—成矿期石英-多金属硫化物脉和晚期石英-碳酸盐细脉;g—早期黄铁矿集合体形成透镜体;h—早期石英-黄铁矿脉和成矿期石英-多金属硫化物脉
Figure 5. Photos showing ore petrography of the Sawayardun gold deposit
a-Early-stage quartz vein; b, c-Middle-stage quartz-polymetallic sulfide vein; d-Late-stage carbonate-quartz veinlet; e-Early-stage quartz showing subgrain structure and wavy extinction; f-Middle-stage quartz-polymetallic sulfide vein and late-stage carbonate-quartz veinlet; gEarly-stage pyrite aggregate showing lens; h-Early-stage quartz-pyrite vein and middle-stage quartz-polymetallic sulfide vein
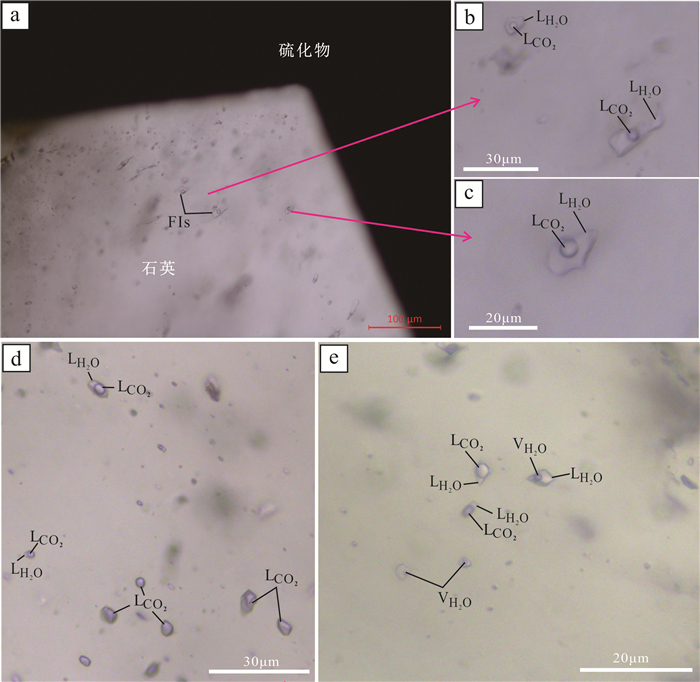
图 6 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床流体包裹体岩相学特征
a—与硫化物共生石英中的包裹体;b, c—富液相的C2型包裹体;d—共存的富气相C1型和PC型包裹体;e—共存的C型和W型包裹体,显示流体不混溶或沸腾特征;VH2O —气相H2O;LH2O —液相H2O;VCO2 —气相CO2;LCO2 —液相CO2;FIs—流体包裹体
Figure 6. Photomicrographs of fluid inclusions in quartz from the Sawayardun gold deposit.
a-Fluid inclusions in sulfide-coexisting quartz of main-stage; b, c-CO2-poor fluid inclusions (C2 type); d-Coexisting C-type and PC-type fluid inclusions in main-stage quartz; e-Coexistence of the W-type and C-type fluid inclusions, implying for fluid boiling; VCO2-vapor CO2; LCO2, -liquid CO2; VH2O -vapor H2O; LH2O - liquid H2O; FIs- fluid inclusions
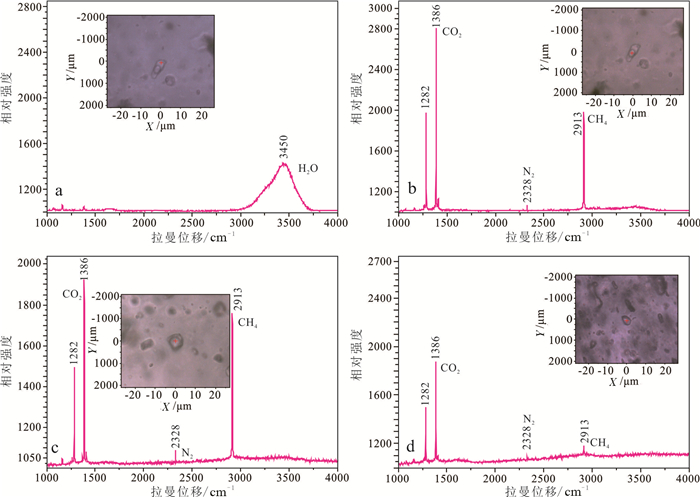
图 8 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿流体包裹体拉曼图谱
a—CO2-H2O包裹体液相中的H2O;b—贫CO2包裹体(C1型)气相成分含N2和CH4;c—富CO2包裹体(C2型)气相成分含N2和CH4;d—纯CO2包裹体气相成分含N2和CH4
Figure 8. Representative raman spectra of fluid inclusions of the Sawayardun gold deposit.
a-Spectrum for liquid bubbles of CO2-H2O inclusions; b- Spectrum for vapor bubbles of CO2- poor fluid inclusions (C1 type), containing variable contents of N2 and CH4, in addition to CO2; c-Spectrum for vapor bubbles of CO2-rich fluid inclusions (C2 type), showing variable contents of N2 and CH4, in addition to CO2; d-Spectrum for pure CO2 inclusions, containing variable CH4 and N2, in addition to CO2
图 9 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿成矿流体的δ18O-δD组成(底图据Taylor, 1997, 其他矿床数据引用文献见正文)
Figure 9. δ18O-δD plots of the ore fluids at the Sawayardun gold deposit (Domains for metamorphic and magmatic fluids are cited from Taylor (1997), and other deposits data are cited in the text)
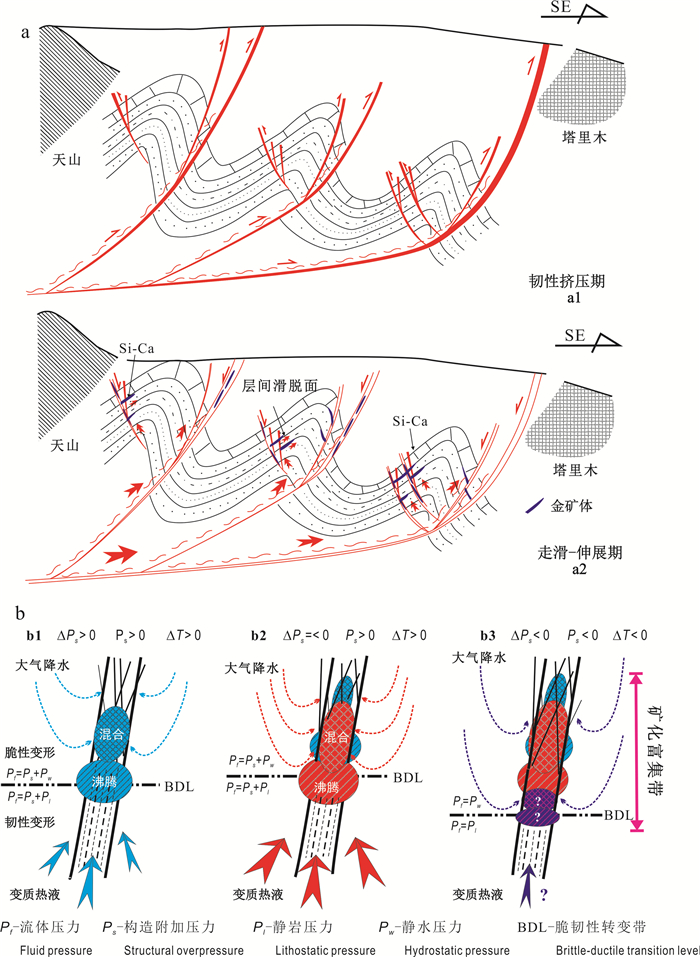
图 11 西南天山萨瓦亚尔顿金矿构造-流体与成矿模式图(b据陈衍景等, 2008; 陈衍景, 2013)
Figure 11. Structure-fluid and metallogenic model for the Sawayardun deposit, Southwestern Tianshan Orogen (modified from Chen Yanjing et al., 2008; Chen Yanjing, 2013)
表 1 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床石英流体包裹体显微测温结果
Table 1 Microthermometric data for fluid inclusions in quartz from the Sawayardun gold deposit

表 2 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿流体的δ18O,δD和δ13C(‰)
Table 2 The δ18O, δD and δ13C ratios (‰) of the Sawayardun gold deposit

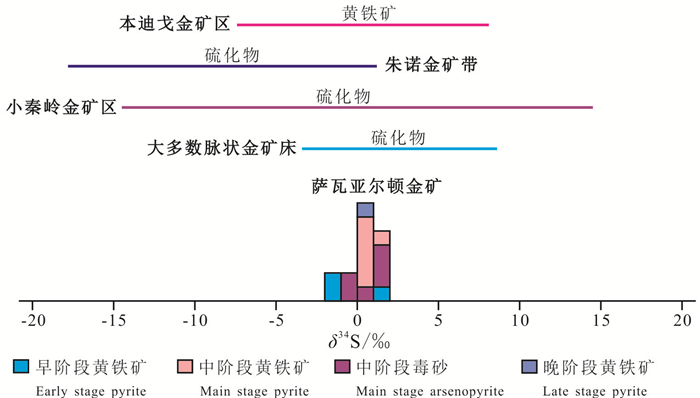
表 3 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿硫同位素分析结果
Table 3 The δ134S values of sulfides at the Sawayardun gold deposit

-
Bodnar R J. 1993. Reviced equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 57: 683-684. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90378-A
Brown P E. 1989. Flincor: A microcomputer program for the reduction and investigation of fluid inclusion data[J]. American Mineralogist, 74: 1390-1393. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279895263_FLINCOR_a_microcomputer_program_for_the_reduction_and_investigation_of_fluid-inclusion_data
Chen Fuwen, Li Huaqin. 2003. Metallogenic chronology of the Sawayaerdun gold-antimony deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 24(6): 563-567 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Huayong, Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Zhang Zengjie. 2004. Fluid inclusion study of the Sawayardun deposit in Southern Tianshan, China: Implication for ore genesis and exploration[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 24(3): 46-54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Huayong, Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Zhang Li, Zhang Zengjie. 2007. Chemical composition of fluid inclusions of the Sawayardun gold deposit, Xinjiang: Implications for oregenesis and prediction[J]. Acta Petroglogica Sinica, 23(9): 2189-2197 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283288544_Chemical_composition_of_fluid_inclusions_of_the_Sawayardun_gold_deposit_Xinjiang_and_its_implications_for_metallgeny_and_exploration
Chen H Y, Chen Y J, Baker M J. 2012a. Evolution of ore-forming fluids in the Sawayaerdun gold deposit in the Southwestern Chinese Tianshan metallogenic belt, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 131-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.05.011
Chen H Y, Chen Y J, Baker M J. 2012b. Isotopic geochemistry of the Sawayaerdun orogenic-type gold deposit, Tianshan, northwest China: Implications for ore genesis and mineral exploration[J]. Chemical Geology, 310/311: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.03.026
Chen Y J, Pirajno F, Qi J P, Li J, Wang H H. 2006. Ore geology, fluid geochemistry and genesis of the Shanggong gold deposit, eastern Qinling Orogen, China[J]. Resource Geology, 56(2): 99-116. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2006.tb00272.x
Chen Y J, Pirajno F, Qi J P. 2005. Origin of gold metallogeny and sources of ore-forming fluids in the Jiaodong Province, eastern China[J]. International Geology Review, 47: 530-549. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.47.5.530
Chen Y J, Pirajno F, Sui Y H. 2004. Isotope geochemistry of the Tieluping silver deposit, Henan, China: A case study of orogenic silver deposits and related tectonic setting[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 39: 560-575. doi: 10.1007/s00126-004-0429-9
Chen Yanjing, Fu Shigu. 1992. Gold Mineralization in West Henan, China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 234 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Fan Hongrui, Pirajno F, Lai Yong, Su Wenchao and Zhang Hui. 2007. Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types hydrothermal gold deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2085-2108 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yanjing, Xiao Wenjiao, Zhang Jinjiang. 2008. Ore-system as a geodynamic probe[J]. Geology in China, 35 (6): 1059-1073 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268519254_Ore-system_as_a_geodynamic_probe
Chen Yanjing, Zhang Jing, Zhang Fuxin, Pirajno F, Li Chao. 2004. Carlin and Carlin-like gold deposits in Western Qinling Mountains and their metallogenic time, tectonic setting and model[J]. Geological Review, 50: 134-152 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274565354_Carlin_and_Carlin-like_Gold_Deposits_in_Western_Qinling_Mountains_and_Their_Metallogenic_Time_Tectonic_Setting_and_Model
Chen Yanjing. 2006. Orogenic-type deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential[J]. Geology in China, 33(6): 1181-1196 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268518982_Orogenic-type_deposits_and_their_metallogenic_model_and_exploration_potential
Chen Yanjing. 2010. Indosinian tectonic setting, magmatism and metallogenesis in Qinling Orogen, central China[J]. Geology in China, 37(4): 854-865 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268518857_Indosinian_tectonic_setting_magmatism_and_metallogenesis_in_Qinling_Orogen_central_China
Chen Yanjing. 2013. The development of continental collsion metallogeny and its application[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(1): 1-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235990978_The_development_of_continental_collision_metallogeny_and_its_application
Chen Z L, Wang Z X, Han F B, Zhang W G, Zhang Q, Zhou Z J, Wang X H, Xiao W F, Han S Q, Yu X Q, Sun Y, Nurgazy T, Latysheve N, Zailabidin H. 2017. Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic uplift, deformation, and erosion of the SW Tianshan Mountains in Kyrgyzstan and Western China[J]. International Geology Review, 60: 1-19.
Clayton R N, O'Neil J R, Mayeda T K. 1972. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 77: 3057-3067. doi: 10.1029/JB077i017p03057
Collins P L F. 1979. Gas hydrates in CO2-bearing fluid inclusions and use of freezing data for estimation of salinity[J]. Economic Geology, 74: 1435-1444. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.74.6.1435
Cox S F, Sun S S, Etheridge M A, Wall V J, Potter T F. 1995. Structural and geochemical controls on the development of turbidite-hosted gold quartz vein deposits, Wattle Gully Mine, Central Victoria, Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 90: 1722-1746. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.6.1722
Deng Jun, Yang Liqiang, Zhai Yusheng, Sun Zhongshi, Chen Xueming. 2000. Theoretical framework and methodological system of tectonics-fluids-mineralization system and dynamics[J]. Earth Science, 25(1): 71-78 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287661255_Theoretical_framework_and_methodological_system_of_tectonics-fluids-mineralization_system_and_dynamics
Deng Xiaohua, Li Wenbo, Li Nuo, Mi Mei, Zhang Ying. 2008. Fluid inclusions constrains on the origin of the Zhifang Mo deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(9): 2133-2148(in Chinese with English Abstract).
Fan H R, Xie Y H, Zhao R, Wang Y L. 2000. Dual origions of Xiaoqinling gold-bearing quartz veins: Fluid inclusion evidences[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45 (5): 537-542. doi: 10.1360/csb2000-45-5-537
Fan H R, Zhai M G, Xie Y H, Yang J H. 2003. Ore-forming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 38 (6): 739-750. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0368-x
Faure G. 1986. Principles of Isotope Geology[M]. 2nd edition. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 589 pp.
Gao Z L, Kwak T. 1995. Turbidite-hosted gold deposits in the Bendigo-Ballarat and Melbourne Zones, Australia. I. geology, mineralization, stable isotopes, and implications for exploration[J]. International Geology Review, 37: 910-944. doi: 10.1080/00206819509465433
Geological Team No. 2 (Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources). 2015. Prospecting report of the Sawayaerdun gold deposit, Wuqia County, Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang[R]. 1-302 (in Chinese).
Goldfarb R J, Leach D L, Rose S C, Landis G P. 1989. Fluid inclusion geochemistry of gold-bearing quartz veins of the Juneau gold belt, southeastern Alaska: Implications for ore genesis[J]. Economic Geology Monograph, 6: 363-375. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/segweb/books/book/1209/chapter/107016282/Fluid-Inclusion-Geochemistry-of-Gold-Bearing
Goldfarb R J, Newberry R J, Pickthorn W J, Gent C A. 1991. Oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur isotope studies in the Juneau gold deposit, southeastern Alaska: Constraints on the origin of hydrothermal fluids[J]. Economic Geology, 86: 66-80. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.86.1.66
Hagemann S G, Luders V. 2003. P-T-X conditions of hydrothermal fluids and precipitation mechanism of stibnite-gold mineralization at the Wiluna lode-gold deposits, Western Australia: Conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 38: 936-952 doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0351-6
Hoefs J. 1997. Stable Isotope Geochemistry[M]. 4th edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 201.
Hofes J. 2009. Stable Isotope Geochemistry[M]. Berlin, Springer, 1-285.
Jia Y, Li X, Kerrich R. 2001. Stable isotope (O, H, S, C and N) systematics of quartz vein systems in the tubidite-hosted Central and North Deborah gold deposits of the Bendigo gold field, Central Victoria, Australia: Constraints on the origin of oreforming fluids[J]. Economic Geology, 96: 705-721. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.96.4.705
Kerrich R, Fryer B J, King R W, Willmore L M, Hees E. 1987. Crustal outgassing and LILE enrichment in major lithosphere structures, Archean Abitibi greenstone belt: Evidence on the source reservoir from strontium and carbon isotope tracers[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 97: 156-168. doi: 10.1007/BF00371236
Kerrich R. 1987. The stable isotope geochemistry of Au-Ag vein deposits in metamorphic rocks[C]//Kyser T K (ed.). Stable Isotope Geochemistry of Low Temperature Fluids: Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course, 13: 287-336.
Liu Benpei, Wang Ziqiang, Zhang Chuanheng, Ma Hongwen, Zhou Hongrui, Zhu Hong. 1996. Tectonic Framework and Evolution in Southwest Tianshan Mountains, China[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geoscience Press, 1-120 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jiajun, Zheng Minghua, Long Xunrong, Zhang Shouting, Song Xiehuo, Gu Tuan. 1999. Redefinition of ore-bearing strata age of Sawaya'erdun gold deposit in Xinjiang and its significant[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(6): 653-656 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1999-44-6-653
Liu Jiajun, Zheng Minghua, Long Xunrong, Yin Huaixin, Wang Jiangzhen, Li Endong, Wang Jin. 2002. Metallogenic characteristics of Sawayaerdun gold deposit in Xinjiang, and their similarities to and differences from those of Muruntau-type gold deposits[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 22(1): 54-61 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu Huanzhang, Fan Hongrui, Ni Pei, Ou Guangxi, Shen Kun, Zhang Wenhuai. 2004. Fluid Inclusion[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 208-222 (in Chinese).
Ma Tianlin, Sun Liqian, Chen Xuanhua, Zhou Jianhai, Zhang Xinli. 1999. Study of Orefield Structure of Sawayaerdun Gold Deposit, Wuqia (Ulugqat) County, Xinjiang[R]. 1-107 (in Chinese).
McCuaig T C, Kerrich R. 1998. P-T-t deformation-fluid characteristics of lode gold deposits: Evidence from alteration systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 12: 381-454. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136898800024
Ohmoto H, Goldhaber M B. 1997. Sulfur and carbon isotopes[C]//Barnes H L (ed.). Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Wiley Interscience, New York, 435-486.
Ohmoto H, Rye R O. 1979. Isotopes of sulphur and carbon[C]//Barnes H L (ed). Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. New York, John Wiley, 509-567.
Ridley J R, Diamond L W. 2000. Fluid chemistry of orogenic lode gold deposits and implications for genetic models[C]//Hagemann S G, Brown P E (eds.). Reviews in Economic Geology, 13: 141-162.
Schidlowski M. 1998. Beginning of terrestrial life: Problems of the early record and implications for extraterrestrial scenarios[J]. Instruments, methods, and missions for astrobiology, SPIE 3441, 149-157.
Sengör A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 364: 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Sibson R H, Robert F, Poulsen H. 1988. High angle reverse faults, fluid pressure cycling and mesothermal gold quartz deposits[J]. Geology, 16: 551-555. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article-abstract/16/6/551/190624/High-angle-reverse-faults-fluid-pressure-cycling
Taylor H P. 1997. Oxygen and hydrogen isotope relationships in hydrothermal mineral deposits[C]//Barnes H L (ed.). Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Wiley and Sons, New York, 229-302.
Wang Deigui. 2000. Characteristics of ophiolite complex in the Sawayaerdun area, Xinjiang and its tectonic significance[C]//Wang Futong (ed.). Proceeding for the Fourth Tianshan Geology, Mineral Resources, 504-509 (in Chinese).
Wulff K, Dziggel A, Kolb J, Vennemann T, Bottcher M E, Meyer F M. 2010. Origin of mineralizing fluids of the sediment-hosted Navachab gold mine, Namibia: Constraints from stable(O, H, C, S) isotopes[J]. Economic Geology. 105(2): 285-302. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.2.285
Xu Xueyi, Ma Zhongping, Li Xiangmin, He Shiping, Yang Junlu. 2003. The discovery of P-MORB in Jigen area of southwest Tianshan Mountains and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 22(3): 245-253(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xue Chunji, Zhao Xiaobo, Mo Xuanxue, Dong Lianhui, Gu Xuexiang, Nurtaev B, Pak N, Zhang Zhaochong, Wang Xinli, Zu Bo, Zhang Guozhen, Feng Bo, Liu Jiaying. 2014. Asian gold belt in western Tianshan and its dynamic setting, metallogenic control and exploration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(5): 28-155 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xue Chunji, Zhao Xiaobo, Zhang Guozhen, Mo Xuanxue, Gu Xuexiang, Dong Lianhui, Zhao Shuming, Mi Dengjiang, Nurtaev B, Pak N, Li Zhidan, Wang Xinli, Zu Bo, Yaxiaer Yalikun, Feng Bo. 2015. Metallogenic environments, oreforming types and prospecting potential of Au-Cu-Zn-Pb resources in Western Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geology in China 42(3): 381-410 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283028040_Metallogenic_environments_ore-forming_types_and_prospecting_potential_of_Au-Cu-Zn-Pb_resources_in_Western_Tianshan_Mountains
Yang Fuquan, Wang Liben, Wang Yitian, Xia Haodong, Deng Hujuan, Ma Boyong. 2004. Ore-forming prospects of gold-antimony metallogenic belt in Southwestern Tianshan Mountain of Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 31(4): 338-344 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Fuquan, Mao Jingwen, Wang Yitian, Li Mengwen, Ye Huishou, Ye Jinhua. 2005. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of Sawayaerdun gold deposit in southwest Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(3): 206-227 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Fuquan, Mao Jingwen, Wang Yitian, Ye Huishou, Chen Wen. 2006. Chronology and geochemical characteristics of helium, argon, carbon and oxygen isotope in fluid inclusion of the Sawayaerdun gold deposit, Xinjiang, Northwestern China and their significance[J]. Geological Review, 52(3): 341-351(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Fuquan, Mao Jingwen, Wang Yitian, Zhao Caisheng, Zhang Yan, Liu Yaling. 2007. Major types, characteristics and metallogenese of gold deposits in southwest Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 26(4): 361-379(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232696998_Major_Types_and_Characteristics_of_Late_Paleozoic_Ore_Deposits_East_Tianshan_Northwest_China
Ye Qingtong, Wu Yiping, Fu Xujie, Chen Mingyong, Ye Jinhua, Zhuang Daoze, Yang Fuquan, Bai Honghai. 1999. Ore-Forming Conditions and Metallogenic Prognosis of Gold and Nonferrous Metallic Resources in Southwestern Tianshan Mountains[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-201(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zacharias J, Paterova B, Pudilova M. 2009. Mineralogy, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope constraints on the genesis of the Roudny Au-Ag deposit, Bohemian Massif[J]. Economic Geology, 104: 53-72. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.1.53
Zhai Yusheng. 1996. Problems in the study of structure-fluid-ore-forming processes[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 3(3/4): 230-236(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang G Z, Xue C J, Chi G X, Liu J Y, Zhao X B, Zu B, Zhao Y. 2017. Multiple-stage mineralization in the Sawayaerdun orogenic gold deposit, western Tianshan, Xinjiang: Constraints from paragenesis, EMPA analyses, Re-Os dating of pyrite (arsenopyrite) and U-Pb dating of zircon from the host rocks[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 81: 326-341. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.038
Zhang Zhaochong, Dong Shuyun, Huang He, Ma Letian, Zhang Dongyang, Zhang Shu, Xue Chunji. 2009. Geology and geochemistry of the Permian intermediate-acid intrusions in the southwestern Tianshan, Xinjiang, China: Implications for petrogenesis and tectonics[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1827-1839(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279764604_Geology_and_geochemistry_of_the_Permian_intermediate-acid_intrusions_in_the_southwestern_Tianshan_Xinjiang_China_Implications_for_petrogenesis_and_tectonics
Zheng Minghua, Liu Jiajun, Zhang Shouting, Long Xunrong. 2002. Isotopic composition and genetic indication of Sawaya'erdun gold deposit, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 29(3): 237-245 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Y F, Hoefs J C. 1993. Effects of mineral precipitation on the sulfur isotope composition of hydrothermal solutions[J]. Chemical Geology, 105(4): 259-269. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90130-B
Zhou Z J, Chen Y J, Jiang S Y, Hu C J, Qin Y, Zhao H X. 2015. Isotope and fluid inclusion geochemistry and ore genesis of the Qiangma gold deposit, Xiaoqinling gold field, Qinling Orogen, southern margin of North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 66: 47-64. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.020
Zhou Z J, Chen Y J, Jiang S Y, Zhao H X, Qin Y, Hu C J. 2014a. Geology, geochemistry and ore genesis of the Wenyu gold deposit, Xiaoqinling gold field, southern margin of North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 59: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.12.001
Zhou Z J, Chen Z L, Han F B, Han S Q, Wang Z X, Xiao W F, Shen T, Wu J F. 2018. Fluid inclusion and isotope geochemistry of the Atebayue Sb deposit, South Tianshan Orogen, Kyrgyzstan[J]. Geological Journal, 53: 1050-1060. doi: 10.1002/gj.2943
Zhou Z J, Liu Z W, Qin, Y. 2014b. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Huachanggou gold deposit, western Qinling Orogen, central China[J]. Geological Journal, 49: 424-441. doi: 10.1002/gj.2557
陈富文, 李华芹. 2003. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿金锑矿床成矿作用同位素地质年代学[J]. 地球学报, 24(6): 563-567. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.06.016 陈华勇, 陈衍景, 倪培, 张增杰. 2004. 南天山萨瓦亚尔顿金矿流体包裹体研究: 矿床成因和勘探意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 24(3): 46-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2004.03.006 陈华勇, 陈衍景, 倪培, 张莉, 张增杰. 2007. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿金矿流体包裹体成分、矿床成因和成矿预测[J]. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2189-2197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.017 陈衍景, 富士谷. 1992. 豫西金矿成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1-234. 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, F Pirajno, 赖勇, 苏文超, 张辉. 2007. 不同类型热液金矿床的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2085-2108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.009 陈衍景, 肖文交, 张进江. 2008. 成矿系统: 地球动力学的有效探针[J]. 中国地质, 35(6): 1059-1073. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.06.004 陈衍景, 张静, 张复新, Pirajno F, 李超. 2004. 西秦岭地区卡林-类卡林金矿床及其成矿时间、构造背景和模式[J]. 地质论评, 50(2): 134-152. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.02.004 陈衍景. 2006. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 33 (6): 1181-1196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.001 陈衍景. 2010. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 37(4): 854-865. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.003 陈衍景. 2013. 大陆碰撞成矿理论的创建及应用[J]. 岩石学报, 29(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201301002.htm 邓军, 杨立强, 翟裕生, 孙忠实, 陈学明. 2000. 构造-流体-成矿系统及其动力学的理论格架与方法体系[J]. 地球科学, 25(1): 71-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200001015.htm 邓小华, 李文博, 李诺, 糜梅, 张颖. 2008. 河南嵩县纸房钼矿床流体包裹体研究及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 24(9): 2133 -2148. 刘本培, 王自强, 张传恒, 马鸿文, 周洪瑞, 朱鸿. 1996. 西南天山构造格局与演化[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1-120. 刘家军, 郑明华, 龙训荣, 尹怀信, 王奖臻, 李恩东, 王进. 2002. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床成矿特征及其与穆龙套型金矿床的异同性[J]. 矿物学报, 22(1): 54-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2002.01.010 刘家军, 郑明华, 龙训荣, 张寿庭, 宋谢火, 谷团. 1999. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床赋矿地层时代的重新厘定及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 44(6): 653-656. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.06.018 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 欧光习, 沈昆, 张文淮. 2004. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 208-222. 马天林, 孙立倩, 陈宣华, 周建海, 张新利. 1999. 新疆西南天山萨瓦亚尔顿金矿矿田构造研究[R]. 1-107. 王德贵. 2000. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿地区蛇绿杂岩的特征及构造意义[C]//王福同. 第四届天山地质矿产资源学术讨论会论文集, 504-509. 新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第二地质大队, 2015. 新疆维吾尔自治区乌恰县萨瓦亚尔顿金矿勘探报告[R]. 1-302. 徐学义, 马中平, 李向民, 何世平, 杨军录. 2003. 西南天山吉根地区P-MORB残片的发现及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 22(3): 245-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2003.03.006 薛春纪, 赵晓波, 莫宣学, 董连慧, 顾雪祥, Bakhtiar Nurtaev, Nikolay Pak, 张招崇, 王新利, 俎波, 张国震, 冯博, 刘家瑛. 2014. 西天山"亚洲金腰带"及其动力背景和成矿控制与找矿[J]. 地学前缘, 21 (5): 128-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201405015.htm 薛春纪, 赵晓波, 张国震, 莫宣学, 顾雪祥, 董连慧, 赵树铭, 米登江, Bakhtiar Nurtaev, Nikolay Pak, 李志丹, 王新利, 俎波, 亚夏尔亚力坤, 冯博. 2015. 西天山金铜多金属重要成矿类型、成矿环境及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 42(3): 381-410. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.03.002 杨富全, 王立本, 王义天, 夏浩东, 邓会娟, 马伯永. 2004. 西南天山金锑成矿带成矿远景[J]. 成都理工大学学报. 31(4): 338-344. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2004.04.002 杨富全, 毛景文, 王义天, 李蒙文, 叶会寿, 叶锦华. 2005. 新疆西南天山萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 24(3): 206-227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.002 杨富全, 毛景文, 王义天, 赵财胜, 叶会寿, 陈文. 2006. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床年代学、氦氩碳氧同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 52(3): 341-351. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.03.015 杨富全, 毛景文, 王义天, 赵财胜, 张岩, 刘亚玲. 2007. 新疆西南天山金矿床主要类型、特征及成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 26(4): 361-379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.04.002 叶庆同, 吴一平, 傅旭杰, 陈明勇, 叶锦华, 庄道泽, 杨富全, 白洪海. 1999. 西南天山金和有色金属矿床成矿条件和矿床预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-201. 翟裕生. 1996. 关于构造-流体-成矿作用研究的几个问题[J]. 地学前缘, 3(3/4): 230-236. 张招崇, 董书云, 黄河, 马乐天, 张东阳, 张舒, 薛春纪. 2009. 西南天山二叠纪中酸性侵入岩的地质学和地球化学: 岩石成因和构造背景[J]. 地质通报, 28(12): 1827-1839. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.015 郑明华, 刘家军, 张寿庭, 龙训荣. 2002. 萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床的同位素组成特征及其成因意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自科版), 29(3): 237-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200203001.htm




 下载:
下载: