Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan
-
摘要:研究目的
川西巴塘断裂带地质背景复杂,研究地质灾害发育特征,有利于揭示活动断裂带的地质灾害效应。
研究方法本文在巴塘断裂带地质灾害成灾背景分析和野外调查研究的基础上,剖析了区域地质灾害分布规律与典型滑坡发育特征,探讨了巴塘断裂带的地质灾害效应。
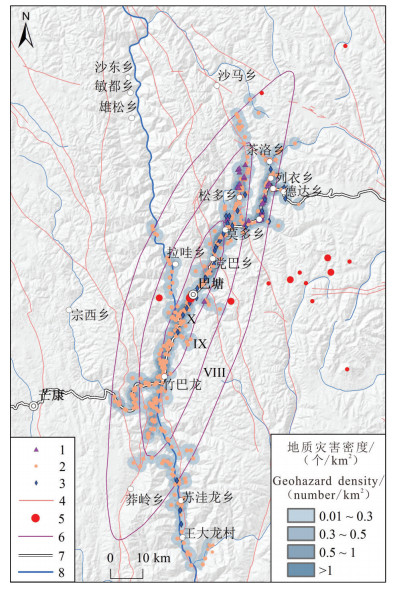
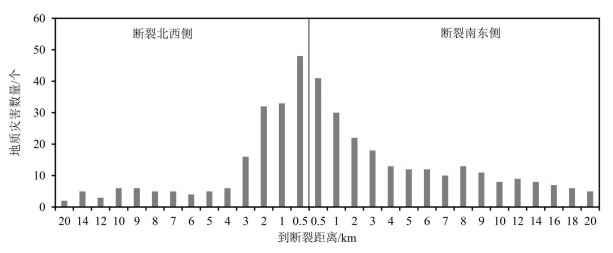
研究结果研究认为:(1)巴塘断裂带附近碎裂岩体结构为地质灾害孕育提供了物质基础,断裂剧烈活动(地震)或蠕滑直接诱发地质灾害,断裂带强烈地质灾害效应主要发生在断裂两侧3000 m范围以内;(2)巴塘断裂带地质灾害具有点多面广、分布不均、局部集中等特点,金沙江干流沿岸深切峡谷区发育大量蠕滑型滑坡和历史地震堵江滑坡;(3)巴塘断裂带地震滑坡和古滑坡发育,部分滑坡直接跨越断层,受断裂、降雨和人类工程等内外动力作用的综合影响,局部复活明显。
结论巴塘断裂带对区域地质灾害发育分布具有显著的控制作用,巴塘断裂带部分居民点和公路存在地质灾害风险,城镇规划区应远离河谷岸坡和泥石流堆积扇等易受地质灾害影响区域。研究成果对于认识青藏高原东缘活动断裂带地质灾害效应和防灾减灾具有重要的科学意义。
创新点:深入剖析了青藏高原东缘巴塘活动断裂带的地质灾害效应和成灾机理。
Abstract:This paper is the result of the geological disaster prevention and control engineering and geological hazard prevention and control engineering.
ObjectiveThe Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan and eastern Tibet Plateau has complex geological settings. The study on the geo-hazard development characteristics is helpful to reveal the geo-hazard effect of active fault zone.
MethodsBased on the forming background analysis and field geo-hazard investigation of the Batang fault zone, this paper analyzes the geo-hazard distribution law and typical landslide development characteristics, and discusses the geo-hazard effects of the Batang fault zone.
ResultsThe study shows that: (1) The fragmented rock mass structure effected by fault activity can promote the development and formation of geo-hazard, and the violent fault activity (earthquake) or the creeping activity can induce geo-hazards, and the strong geo-hazard effects mainly occur with in 3000 m on both sides of the fault. (2) Geo-hazards in the Batang fault zone have the characteristics of wide areas, uneven distribution, local concentration, and so on. There are a large number of creepy landslides and seismic landslides in the deep-cut canyon along the main stream of the Jinsha River. (3) Seismic landslides and ancient landslides are developed in the Batang fault zone, and some landslides directly cross the fault zone. The superimposed influence of internal and external forces such as faults, rainfall and human engineering, has induced some local revival of some landslides.
ConclusionsThe Batang fault has a significant control effect on regional geo-hazard development and distribution.Some residential areas and roads in the Batang fault zone are at geo-hazard risk. The town planning area should be far away from the river valley bank slopes and debris flow accumulation fans and other areas vulnerable to geo-hazard. The research results have important scientific significance for understanding the geo-hazard effects of the active fault zone in the eastern Tibet Plateau and for disaster prevention and mitigation.
-
1. 引言
隐爆角砾岩型矿床一般形成于浅成-超浅成(0.5~3 km)封闭或半封闭环境(唐菊兴, 1995; 卿敏和韩先菊, 2002),引发岩石隐蔽爆破的热液流体以岩浆热液为主,且多分布于浅成-超浅成中酸性侵入岩/次火山岩的顶部(Sillitoe, 1985; 卿敏和韩先菊, 2002; 张西社等, 2015),但也可见远离侵入岩的含矿隐爆角砾岩(Ni et al., 2018),该类型矿床的形成实质包括岩石爆破(气爆或者浆爆)和成矿流体注入过程(黄定华等, 1997; 李生元和马小兵, 1999; 马小兵和李生元, 1999)。隐爆角砾岩型矿床与斑岩型矿床或者浅成低温热液型矿床具有紧密联系(Eaton et al., 1993; Pirajno, 1995),有些学者甚至将其作为深部斑岩型矿床的找矿标志(Silltoe et al., 2003;张会琼等, 2012)。
东南沿海地区属于环太平洋多金属成矿带西南部分,发育许多隐爆角砾岩型Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn、Mo矿床(姜耀辉等, 1994; 濮为民等, 2008; 邓新根和华杰雄, 2010; 陈华, 2011; 林书平等, 2012)。其中,东际金(银)矿床位于闽北政和—建瓯金银矿集区内,具有隐爆角砾岩型矿床特征。2012年储量核实报告表明,该矿床已探明金资源量12.5 t,银资源量135.9 t,为次火山热液型矿床(刘永发, 2011)或者浅成中低温热液型矿床(卢燕等, 2017; 王波涛和严卸平, 2019; 刘日富等, 2019),成矿流体具有中低温(168.4~ 211.4℃)和低盐度(3.22%~ 8.13%NaCleqv)特征(王波涛和严卸平, 2019)。在以往的研究中,该矿床成矿物质来源和成矿时代等问题研究较少,制约了该金矿成矿与区域构造-岩浆事件的关联性研究,不利于进一步探讨此矿床深部找矿潜力。鉴于此,本文开展了黄铁矿硫、铅同位素,电子探针和锆石U-Pb测年等测试分析,试图解决东际金(银)矿床成矿作用方面的问题。
2. 区域地质背景
闽北政和—建瓯金银矿集区位于华夏造山带北部龙泉—政和俯冲增生杂岩和浙闽沿海岩浆弧交界位置。该矿集区内地层主要为新元古代马面山岩群(变质基底)和燕山期陆相火山-沉积岩系(盖层)(图 1)。基底变质岩原岩是一套浊积特征显著并有中-基性火山物质掺杂的巨厚复理石建造,变质程度为绿片岩相。盖层主要为燕山期酸性—中酸性陆相火山岩建造,其中,晚侏罗世南园组火山岩浆活动表现为裂隙式喷发,构成北东向火山岩带,早白垩世晚期石帽山群火山岩浆活动则为中心式喷发,形成了东坑火山盆地(安山岩Rb- Sr年龄(104.4 ± 23)Ma,ISr= 0.7092;熔结凝灰岩Rb-Sr年龄(105.4±3.1)Ma,ISr= 0.7101,谢家莹等, 1994)和仁山火山盆地。
![]() Figure 1. Tectonic location (a) and geological and mineral resources map (b) of the Zhenghe-Jianou gold ore concentration area (a after Zhang Kexin et al., 2015; b after Feng Zhiwen et al., 1991)
Figure 1. Tectonic location (a) and geological and mineral resources map (b) of the Zhenghe-Jianou gold ore concentration area (a after Zhang Kexin et al., 2015; b after Feng Zhiwen et al., 1991)区内侵入岩主要有熊山岩体(闪长岩,Sm-Nd等时线年龄为(585.7±30)Ma;任胜利等, 1997)、林屯岩体(石英闪长岩,锆石U-Pb年龄(433±7)Ma,隰弯弯等,2019)、富美岩体(花岗岩,锆石U-Pb年龄为(369±4)Ma,隰弯弯等,2019)、铁山岩体(燕山期大型钾质交代岩,Chen et al., 2017;也有人称石英正长岩和辉石正长岩,锆石U-Pb年龄为(254±4)Ma,Wang et al., 2005)和铜盆庵岩体(二长花岗岩和正长花岗斑岩,锆石U-Pb年龄为(153.5±1.8)Ma和(153.0±0.8)Ma,李亚楠等, 2015),其次是早白垩世岩脉(有~130 Ma和~100 Ma两期,未发表数据),岩石类型从中酸性—酸性—酸偏碱性皆有,以酸性和中酸性岩为主。区域构造以政和—大埔北东向断裂带为主,其次为浦城—三都澳北西向断裂带,二者交汇区域也是政和—建瓯矿集区的主体位置。该区内已发现东际金(银)矿(刘永发, 2011)、王母山金矿(胡荣华, 2009)、大药坑金矿(肖凡等, 2017)、狮子岗铜矿和夏山铅锌矿等,最近又新发现了井后超大型叶蜡石矿床(卢林, 2018),表明矿集区具有很好的成矿地质条件。
3. 矿区地质特征
东际金(银)矿床位于东坑火山盆地西缘,矿区出露地层有新元古代马面山岩群、晚侏罗世南园组和早白垩世晚期黄坑组,金(银)矿体均赋存于南园组(图 2)。马面山岩群出露于矿区西南角,岩性以片岩为主。南园组出露于矿区北部,岩性主要为流纹质晶屑凝灰(熔)岩夹晶屑凝灰(熔)岩,不整合于马面山岩群之上。黄坑组出露于矿区东南部,不整合覆盖于南园组及马面山岩群之上,上部为凝灰杂砂质砾岩、含砾砂岩,下部为凝灰质角砾岩、火山角砾岩。
![]() 图 2 东际金(银)矿床地质简图(据刘永发, 2011修改)Figure 2. Simplified geological map of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit (after Liu Yongfa, 2011)
图 2 东际金(银)矿床地质简图(据刘永发, 2011修改)Figure 2. Simplified geological map of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit (after Liu Yongfa, 2011)矿区构造以夏山—东际北东向断裂带为主,次为前际—地坪北西向断裂带及次级或派生断裂,均为成矿后断裂。夏山—东际断裂带主体走向北东,往南东陡倾,或为岩脉充填切割矿体,或直接错断矿体,东坑火山盆地边界断裂也是其组成部分。前际—地坪断裂带总体走向北西,向南西陡倾,为花岗斑岩和辉绿玢岩充填,多表现为切割矿体。
矿区侵入岩、次火山岩及脉岩广泛发育,包括中晚志留世细粒花岗岩和燕山晚期花岗斑岩、石英二长斑岩、石英正长斑岩、正长斑岩、闪长玢岩等,沿北东向断裂带及北西向断裂带充填。
矿区隐爆角砾岩和矿体空间关系紧密,在416 m、450 m、501 m、517 m等中段均有出露。以450 m中段为例,此隐爆角砾岩主要由灰白色晶屑凝灰岩角砾和热液胶结物(石英和黄铁矿)组成,角砾彼此之间可拼贴完整,且遭受了硅化和绢云母化等蚀变,往往靠近围岩,角砾化程度降低,热液胶结物含量减少,而在角砾化程度较高位置,几乎全由灰黑色石英和黄铁矿构成,这样的区域也是金品位最高位置。
矿区围岩蚀变主要有硅化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化和碳酸盐化等,其中,以硅化、黄铁矿化和绢云母化分布最为广泛,与成矿关系最为密切,尤以富铝绢云母带与金、银矿化带空间耦合性最好,可作为成矿流体主通道位置的识别标志(卢燕等, 2017)。
4. 矿床地质特征
矿区内共圈定金(银)矿体7个,其中Ⅰ号主矿体占矿床总资源/储量88%。Ⅰ号主矿体赋存于南园组底部,呈似层状产出(图 3),并具有分枝复合特点,矿体沿走向延伸305 m,沿倾向延伸400~500 m,最大为550 m(0#线),矿体走向为北东向(10~60°),倾向南东,倾角25~45°。其他矿体均属于Ⅰ号主矿体顺延伸方向尖灭再现或侧移的小矿体,储存部位及产状特征与Ⅰ号主矿体基本一致。
![]() 图 3 东际金(银)矿0#勘探线地质剖面图(据刘永发, 2011修改)Figure 3. Sketch geological section along 0# geological exploration line of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit (after Liu Yongfa, 2011)
图 3 东际金(银)矿0#勘探线地质剖面图(据刘永发, 2011修改)Figure 3. Sketch geological section along 0# geological exploration line of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit (after Liu Yongfa, 2011)矿石中金属矿物以黄铁矿为主,少量毒砂、黄铜矿、方铅矿和闪锌矿,微量自然金、银金矿、自然银和含银矿物等(图 4)。脉石矿物以石英、绢云母、水云母、绿泥石,少量方解石及绿帘石等。其中,金以自然金和银金矿形式存在,自然金呈他形粒状充填于石英晶粒间,金黄色,粒径5~20 μm,属细-微粒金,银金矿也赋存于石英晶粒间,粒径4~15 μm,呈不规则状和似椭球状。此外,银矿物(如辉银矿和深红银矿)沿黄铁矿裂隙生长,或以包体形式赋存于黄铁矿,粒径10~40 μm。
![]() 图 4 东际金(银)矿床主要金属矿物特征a—自形—半自形粒状结构黄铁矿;b, c—黄铁矿被毒砂交代,黄铜矿沿毒砂颗粒边缘或者微裂隙生长,指示矿物生成顺序由早到晚依次为黄铁矿→毒砂→黄铜矿;d—黄铜矿、方铅矿交代他形粒状黄铁矿;e—银矿物沿黄铁矿裂隙生长(BSE图像);f—银矿物呈包裹体形式产于黄铁矿中(BSE图像);g, h—金矿物生长于石英颗粒间(BSE图像)。矿物代号:Py—黄铁矿;Ccp—黄铜矿;Apy—毒砂;Gn—方铅矿Figure 4. Characteristics of main metal minerals of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposita-Euhedral-subhedral texture pyrite; b, c-Pyrite replaced by arsenopyrite and chalcopyrite, which suggests that the sequence of metal minerals is pyrite, arsenopyrite and chalcopyrite; d-Anhedral texture pyrite replaced by chalcopyrite and galena; e-Ag-bearing mineral growing in the fracture of pyrite (BSE image); f- Ag-bearing mineral occurring as a inclusion in the pyrite (BSE image); g, h-Au-bearing mineral growing in the quartz. Mineral abbreviation: Py-Pyrite; Ccp-Chalcopyrite; Apy-Arsenopyrite; Gn-Galena
图 4 东际金(银)矿床主要金属矿物特征a—自形—半自形粒状结构黄铁矿;b, c—黄铁矿被毒砂交代,黄铜矿沿毒砂颗粒边缘或者微裂隙生长,指示矿物生成顺序由早到晚依次为黄铁矿→毒砂→黄铜矿;d—黄铜矿、方铅矿交代他形粒状黄铁矿;e—银矿物沿黄铁矿裂隙生长(BSE图像);f—银矿物呈包裹体形式产于黄铁矿中(BSE图像);g, h—金矿物生长于石英颗粒间(BSE图像)。矿物代号:Py—黄铁矿;Ccp—黄铜矿;Apy—毒砂;Gn—方铅矿Figure 4. Characteristics of main metal minerals of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposita-Euhedral-subhedral texture pyrite; b, c-Pyrite replaced by arsenopyrite and chalcopyrite, which suggests that the sequence of metal minerals is pyrite, arsenopyrite and chalcopyrite; d-Anhedral texture pyrite replaced by chalcopyrite and galena; e-Ag-bearing mineral growing in the fracture of pyrite (BSE image); f- Ag-bearing mineral occurring as a inclusion in the pyrite (BSE image); g, h-Au-bearing mineral growing in the quartz. Mineral abbreviation: Py-Pyrite; Ccp-Chalcopyrite; Apy-Arsenopyrite; Gn-Galena矿石结构主要有粒状结构、压碎结构、交代残余结构和包含结构(图 4),矿石构造主要有角砾状构造、块状构造、脉状构造和稀疏浸染状构造(图 5),其中角砾状构造最为常见,当角砾变少时可变为块状构造,金品位明显增加,故两种矿石类型在空间上可同时出现,局部可见二者渐变过渡关系。
![]() 图 5 东际金(银)矿床矿化特征a—黄铁矿-石英细脉;b—网脉状黄铁矿细脉;c, d, e—角砾状矿化,其中角砾已发生强烈硅化,胶结物为热液成因石英和黄铁矿;f—角砾状矿化,当岩石角砾变小和变少时,可变化为块状矿石,金含量也随之升高Figure 5. Mineralization characteristics of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposita-Pyrite-bearing quartz vein; b-Stockwork pyrite; c, d, e, f -Breccia mineralization, silicification breccias cemented by hydrothermal quartz and pyrite. The breccias become smaller and less in the breccia zone, whereas the Au grade is higher
图 5 东际金(银)矿床矿化特征a—黄铁矿-石英细脉;b—网脉状黄铁矿细脉;c, d, e—角砾状矿化,其中角砾已发生强烈硅化,胶结物为热液成因石英和黄铁矿;f—角砾状矿化,当岩石角砾变小和变少时,可变化为块状矿石,金含量也随之升高Figure 5. Mineralization characteristics of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposita-Pyrite-bearing quartz vein; b-Stockwork pyrite; c, d, e, f -Breccia mineralization, silicification breccias cemented by hydrothermal quartz and pyrite. The breccias become smaller and less in the breccia zone, whereas the Au grade is higher5. 样品特征及测试方法
锆石年龄样品为矿区450 m中段角砾状矿石晶屑凝灰岩角砾和穿插矿体的花岗斑岩。晶屑凝灰岩主要由石英晶屑组成,少量岩屑,大小为0.1~ 0.4 mm,大者可至1mm,基质为隐晶质物质,发生了绢云母化蚀变(图 6a、b、c)。花岗斑岩穿插矿(化)体,后者被氧化后呈特征“铁锈色”,花岗斑岩的斑晶矿物为石英、斜长石和黑云母等,含量分别可至20%、35%和5%,大小一般在0.4~0.8 mm,基质由斜长石和微细晶石英组成,总体含量40%(图 6d、e、f)。上述样品经人工破碎至80~100目后,按常规重液和电磁方法分选,并在双目镜下挑选锆石。将锆石颗粒置于环氧树脂制靶,固化抛光,用于阴极发光(CL)照相,并从中选取环带清晰的锆石进行LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年测试分析,实验测试单位为中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心。激光剥蚀系统为美国Conherent公司生产的GeoLasPro 193 nm Arf准分子系统,ICP-MS为Thermo X2。激光剥蚀采样过程以氦气作为载气,束斑直径为30 μm、频率为10Hz、能量密度约为10J/cm3。采样方式为单点剥蚀、跳峰采集。采用Plesovice(年龄为(337 ± 0.4)Ma,Slama et al., 2008)和GJ-1标准锆石作为外标进行基准校正。数据处理采用ICPMSDATACAL软件,锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图、年龄分布频率图和加权平均年龄计算采用Isoplot/Exver 3(Ludwig, 2003)完成。
电子探针实验样品取自450 m中段,分别选取了块状矿石、角砾状矿石、细脉状矿石和稀疏浸染状矿石。切制探针片之后,首先进行黄铁矿岩相学观察,选取生成顺序清晰的黄铁矿作为目标点位,然后送至中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室电子探针实验室进行表面喷碳处理,进而利用配备4道波谱仪的JEOL JXA-8100电子探针完成分析测试,工作加速电压20 kV,加速电流20 nA,束斑直径<1 μm,所有测试数据均进行了ZAF校正处理。
硫、铅同位素样品为富Au角砾状矿石,采样位置为450 m中段和416 m中段1#穿脉位置。首先将矿石粉碎,使用双目镜,挑选黄铁矿单矿物,保证纯度在99%以上。然后使用超声波清洗掉矿物表面粘附粉尘,用玛瑙钵研磨至200目,送澳实分析检测(广州)有限公司实验室测试。其中,硫同位素使用S-ISTP01方法,元素分析仪配套硫同位素质谱仪测δ34S,数据经V-CDT即陨硫铁标准物质标准化。铅同位素使用Pb-IRM01方法,试样加入硝酸、盐酸和氢氟酸,微波消解,然后用扇形磁场等离子体质谱(HR-ICP-SFMS)测试,数据经内标(TI同位素比率)和外部校准(自然铅物质标样)标准化,206Pb/204Pb、207Pb/204Pb、208Pb/204Pb比值相对偏差RSD<0.2%。
6. 结果分析
6.1 硫、铅同位素
当成矿流体fO2较低时,硫主要呈低价态HS-和S2-存在,基本都富集于硫化物中;当成矿流体fO2较高时,硫主要呈高价态SO42-存在,并富集于硫酸盐矿物中,此时硫化物δ34S值低于成矿热液中总δ34S值(Ohmoto, 1972)。通过光薄片观察,东际金(银)矿床不发育硫酸盐矿物,含硫矿物主要为黄铁矿、毒砂、黄铜矿和方铅矿等,说明成矿过程中未发生不同价态含硫矿物之间硫同位素分馏,故本文研究的黄铁矿δ34S值可以反映成矿流体δ34SΣ的特征。东际金(银)矿床角砾状矿石金含量较高,故开展此类矿石中黄铁矿硫、铅同位素示踪,最能反映成矿物质来源。实验结果表明(表 1),416m中段黄铁矿δ34S为-1.8‰,450m中段黄铁矿δ34S为-0.7‰~-6.6‰,不同深度黄铁矿δ34S值相差不大。总体来看。东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿δ34S值为-0.7‰~-6.6‰,极差5.8‰,除一件样品较高外(450 CM0-1),其余样品δ34S值较集中,平均值为-2.03‰。
表 1 东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿硫、铅同位素特征Table 1. Sulfur and lead isotope data of pyrites from the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit
由于金属硫化物U、Th元素含量低,在其结晶以后,通过衰变作用所产生的放射性成因铅含量非常低,对铅同位素组成的影响可以忽略,故硫化物铅同位素是示踪成矿物质来源的有效方法之一(张乾等, 2000)。东际金(银)矿床角砾状矿石黄铁矿206Pb/204Pb为17.9801~18.4303,207Pb/204Pb为15.2689~15.9397,208Pb/204Pb为37.9052~38.7871(表 1),与矿集区内大药坑金矿和邻区金矿矿石铅具有很好线性关系(图 7),与矿区周边马面山岩群变质岩、晚侏罗世南园组晶屑凝灰岩、晚侏罗世石英闪长岩和二长斑岩(发育于东坑火山盆地内,穿切早白垩世晚期火山岩,推测成岩时代为早白垩世晚期或者晚白垩世早期)等岩石的铅同位素相比,该矿床矿石铅与燕山期火山-侵入杂岩的岩石铅更加接近,也与马面山岩群中某些变质岩的铅同位素相似。
![]() 图 7 东际金(银)矿床208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb和207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb图解Figure 7. Plot of 208Pb/204Pb versus 206Pb/204Pb and 207Pb/204Pb versus 206Pb/204Pb of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit(Dayaokeng Au deposit data after Xiao Fan et al., 2017; adjacent Au deposits, crystal tuff, monzonite porphyry and quartz diorite data after Feng Zhiwen et al., 1991; Mamianshan Group metamorphic rock data after Feng Chengyou et al., 2007)
图 7 东际金(银)矿床208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb和207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb图解Figure 7. Plot of 208Pb/204Pb versus 206Pb/204Pb and 207Pb/204Pb versus 206Pb/204Pb of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit(Dayaokeng Au deposit data after Xiao Fan et al., 2017; adjacent Au deposits, crystal tuff, monzonite porphyry and quartz diorite data after Feng Zhiwen et al., 1991; Mamianshan Group metamorphic rock data after Feng Chengyou et al., 2007)6.2 电子探针
依据矿石构造类型、黄铁矿产出状态和晶形特征,黄铁矿可划分出5种类型(分别以Py1、Py2、Py3、Py4和Py5表示)。角砾状矿石黄铁矿有两种形态,Py1颗粒大,粒径0.1~0.4 mm,半自形结构,Py2颗粒小,粒径<0.1 mm,他形结构(图 8a)。浸染状矿石黄铁矿(Py3)颗粒小,粒径0.05~0.1 mm,它形结构,矿物集合体零星分布于晶屑凝灰岩中(图 8b)。细脉浸染状矿石黄铁矿(Py4)颗粒小,粒径<0.05 mm,常与毒砂矿物共生,矿物集合体呈放射状产出(图 8c)。块状矿石黄铁矿(Py5)颗粒大,粒径0.4~0.8 mm,半自形-自形结构,含金、银矿物(图 8d)。
东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿S含量为50.89% ~ 53.42%,平均52.57%,Fe含量为44.38%~46.54%,平均45.83%(表 2),均低于黄铁矿S和Fe的理论含量(分别为53.45%和46.55%,一般沉积型黄铁矿接近理论值),但黄铁矿S/Fe值(原子数比值)为1.99~ 2.02(均值2.01),略高于理论值,说明东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿总体具有富硫贫铁特征。
表 2 东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿电子探针数据(%)Table 2. EPMA data of pyrites from the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit(%)
不同类型黄铁矿具有相似微量元素变化曲线(图 9),表明它们形成于同一热液体系。黄铁矿Au/ Ag比值总体在0.9~5.5,均值2.6,表现出富金贫银特征,但不同类型黄铁矿Au元素含量存在差异,如晶屑凝灰岩中浸染状黄铁矿含有相对均匀的Au含量,而角砾状矿石中黄铁矿含有不均匀的Au含量,这可能反映成矿热液体系物化条件不稳定。研究表明,低温条件下不利于Se元素类质同象置换黄铁矿中S元素(刘英俊等, 1984),Py2贫Se元素且富集低温元素Sb,表明Py2形成温度最低,是角砾状矿石晚期黄铁矿,与岩相学观察基本一致(图 8a),这说明角砾状矿石是多阶段热液流体作用的产物,其金元素富集或许归因于这个地质过程。
6.3 锆石U-Pb
晶屑凝灰岩中锆石颗粒较大,自形程度高,粒径在100~150 μm,成分环带清晰,Th/U值在0.55~ 2.29,均值为0.92,表明岩浆成因锆石。其中,18个锆石点落在谐和线范围,锆石206Pb/238U表面年龄加权平均值为(154±2)Ma(MSWD=2.1,N=18)(图 10,表 3),说明晶屑凝灰岩形成于晚侏罗世。此外,1颗锆石发育“核-边”二元结构,核部锆石206Pb/238U表面年龄为506.6 Ma,发育岩浆成分环带,为岩浆锆石,边部锆石无震荡环带,可能是变质成因,其206Pb/238U表面年龄为402.1 Ma。另一颗锆石发育“核-幔”二元结构,核部锆石呈浑圆状且无岩浆成分环带,可能是变质锆石,其207Pb/206Pb表面年龄为2613 Ma,幔部锆石因较窄而无法进行实验。上述锆石的出现,反映了基底构造演化历史之复杂,可能经历了泛非期、加里东期乃至新太古代等时期的构造-岩浆运动。
表 3 东际金(银)矿床晶屑凝灰岩和花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb数据Table 3. Zircon U-Pb data of crystal tuff and porphyry granite of the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit
花岗斑岩锆石较粗大,自形程度高,粒径在150~250 mm,具有清晰成分环带,Th/U值在0.82~ 2.12,均值为1.27,是岩浆成因锆石。其中,30个锆石点落在谐和线范围,锆石206Pb/238U表面年龄加权平均值为(96.7±0.8)Ma(MSWD=0.65,N=30)(图 11,表 4),说明此斑岩形成于晚白垩世早期。此外,有1颗锆石发育明显“核-幔”二元结构,“核部”锆石呈浑圆状,具有溶蚀残留特征,颜色发黑,但仍可见岩浆成分环带,故认为此锆石也为岩浆成因,其206Pb/238U表面年龄为148 Ma,“幔部”锆石具有清晰岩浆成分环带,也是岩浆成因锆石,其206Pb/238U表面年龄为98 Ma,这种锆石的出现可能是晚白垩世早期岩浆侵位时,捕获了围岩中较老锆石,并以此为核重新结晶生长而成。
表 4 典型金矿床黄铁矿Fe、As、S和Fe/(As+S)含量Table 4. Content of Fe, As, S and Fe/(As+S) of pyrites from typical gold deposits
7. 讨论
7.1 成矿热液性质
黄铁矿Fe常被其同族元素Co和Ni类质同象置换,高温热液条件下,Co比Ni更易替代Fe2+,故不同成因黄铁矿Co/Ni值不一样(Yuan et al., 2018),一般沉积型Co/Ni值小于1且Co含量<100×10-6,变质热液型接近1,岩浆热液型Co/Ni值在1~5,且Co含量>400×10-6,火山热液型Co/Ni值大于5,同时Co含量>500 ×10-6且Ni含量<100 ×10-6(王奎仁, 1987)。东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿Co/Ni值介于3~94,平均值23,Co含量在500×10-6~1070×10-6(均值799×10-6),Ni含量在10×10-6~240×10-6(均值104× 10-6),在黄铁矿Co-Ni图解中(图 12a),落在火山成因区域和岩浆热液成因区域,并以前者为主,与紫金山铜金矿中黄铁矿投点区域重叠,表明东际金(银)矿床中黄铁矿主体为火山作用相关的热液成因,与紫金山铜金矿中黄铁矿成因相同。在黄铁矿As-Co-Ni图解中(图 12b),东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿落在岩浆或火山热液成因区域,与Co-Ni图解中判断一致,成矿热液是与火山作用相关的热液,相对紫金山铜金矿床黄铁矿更富As,一般深循环低温大气水混入较多时,热液体系将更加富As(李红兵和曾凡志, 2005; 曹素巧等, 2014),故东际金(银)矿床成矿热液中含有一定量的大气水。
![]() 图 12 东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿Co-Ni图解和As-Co-Ni图解(紫金山铜金矿黄铁矿数据张文媛等,2014)Figure 12. Plot of Co-Ni and As-Co-Ni of pyrites from the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit(Zijinshan Cu-Au deposit data after Zhang Wenyuan et al., 2014)
图 12 东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿Co-Ni图解和As-Co-Ni图解(紫金山铜金矿黄铁矿数据张文媛等,2014)Figure 12. Plot of Co-Ni and As-Co-Ni of pyrites from the Dongji Au(Ag) deposit(Zijinshan Cu-Au deposit data after Zhang Wenyuan et al., 2014)Au/Ag比值可以指示成矿温度,中低温热液型黄铁矿Au/Ag值>0.5(周学武等, 2005)。东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿Au/Ag值介于0.9~5.5,均值为2.6,说明黄铁矿形成于中低温条件,与王波涛和严卸平(2019)流体包裹体研究结果一致。邻区一些金矿床也具有类似特征,如前际金矿床均一温度为250~ 280℃,小坑金矿床为240~260℃,后坑—翁坑金矿区为260~280℃(冯志文等, 1991)。浅成中低温热液型矿床成矿温度大多在300℃以内(Hedenquist et al., 2000; Pirajno, 2009),如紫金山铜金矿(120~ 240℃)和团结沟金矿(170~230℃)等(毛景文等,2003)。因此,包含东际、前际、小坑等金(银)矿床在内的政和—建瓯金矿集区可能是一个中低温热液型金矿田。
黄铁矿Fe/(S+As)比值与其形成深度具有相关性(周学武等, 2005; 彭丽娜等, 2009; 曹素巧等, 2014;张文媛等, 2014)。东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿Fe/(S+As)值为0.853~0.867(表 4),高于紫金山铜金矿床下部铜矿体中黄铁矿(Fe/(S+As)值平均0.848,张文媛等, 2014, 成矿深度0.5~1.5 km,高天钧, 1999),低于浙东南怀溪铜金矿中黄铁矿(Fe/(S+As)值平均0.881,彭丽娜等, 2009, 成矿压力126.25 × 105~ 295.5×105 Pa,属浅成环境,陶奎元等, 1998),说明东际金(银)矿床成矿深度具有浅成特征。王波涛和严卸平(2019)流体包裹体研究后,也认为该矿床主体成矿深度较浅(0.4~1.1 km)。此外,东际矿区热液蚀变类型以绢云母化和绿泥石化为主,缺失蒙脱石带,金、银矿化主要赋存在以伊利石为主的绢云母化带中,也佐证该矿床形成于浅成热液环境(卢燕等, 2017)。
7.2 成矿物质来源
一般认为自然界有地幔硫、现代海洋硫和沉积(还原)硫三种不同硫来源(郑永飞等, 2000),地幔硫与陨石硫同位素变化于0‰附近,受地壳再循环组分影响,会在-6‰~+6‰变化(Denies, 1995),典型浅成低温热液型铜、金、银矿床δ34S值大都在此范围之内,如紫金山高硫型铜金矿金属硫化物的δ34S值峰值介于-5‰~-1‰(梁清玲等, 2015),悦洋低硫型银矿金属硫化物δ34S值介于- 6.8‰ ~ -1.0‰,平均值-4‰(梁清玲等, 2015),阿希低硫型金矿的黄铁矿δ34S值为-4‰~3.1‰,均值-0.45‰ (翟伟等, 2010)。因此,深源岩浆是浅成低温热液型铜、金、银矿床主要成矿物质来源,可以通过围岩淬取、深源岩浆期后热液或者火山喷气等方式富集。东际金(银)矿床黄铁矿δ34S在-0.7‰~-6.6‰,除样品450 CM0-1的δ34S值为-6.6‰外,其余δ34S值在-0.7‰~-2.3‰(平均值-2.03‰),与同一矿集区内锦屏金矿床(δ34S为0.5‰~2.6‰)和小坑—翁坑金矿化带(δ34S平均值为3.05‰)十分相似,均与幔源硫相似(0±3‰,Chaussidon et al., 1990),指示东际金(银)矿床和相邻金矿床硫源为深部岩浆硫。样品450 CM0-1的δ34S值(-6.6‰)与浙闽地区中生代火山岩中黄铁矿δ34S(4.6‰~6.8‰)和毫石银矿黄铁矿δ34S值(5‰~7‰,此矿床为地热水循环成因,成矿物质主要来源于晚侏罗世火山岩围岩;徐步台等, 1994)十分相近,表明火山岩围岩也是东际金(银)矿床成矿物质来源之一。
除416 m中段黄铁矿,东际金(银)矿床矿石铅μ值在9.27~9.54,均值9.41,位于地幔(8.92)和造山带(10.87)(Doe et al., 1979)之间,ω值为36.22~38.21,均值37.2,超出正常铅范围(35.55±0.59),说明成矿物质具有壳幔混源特征。研究表明,放射性铅同位素“铀铅”(206Pb,207Pb)和“钍铅”(208Pb)含量不同,与物质来源紧密相关,一般化学沉积岩和花岗岩富“铀铅”(206Pb/204Pb>18,207Pb/204Pb>15.3)贫“钍铅”(208Pb/204Pb<39),变质岩铅贫“铀铅”(陈华勇等, 2000)。东际金(银)矿床矿石铅总体富“铀铅”贫“钍铅”型(除样品416 CM1-3外,206Pb/204Pb均值18.335,207Pb/204Pb均值15.565,208Pb/204Pb均值38.584),个别矿石铅贫“铀铅”(样品416 CM1-3的206Pb/204Pb为17.98,207Pb/204Pb为15.269),因此,东际金(银)矿成矿物质具有多源性。在与东际矿区周边马面山岩群变质岩、侵入岩、火山岩和邻区金矿床的铅同位素对比上(图 7),发现东际金(银)矿与邻区金矿矿石铅具有线性关系,与燕山期火山-侵入杂岩接近,也与个别变质岩铅同位素值相似,说明矿集区内金矿床的成矿物质来源相似,主要来自于燕山晚期火山-侵入岩系,变质岩次之。
7.3 成矿时代厘定
东际金(银)矿床角砾状矿石晶屑凝灰岩角砾锆石U-Pb年龄为(154±2)Ma,与德化地区东洋金矿床容矿围岩年龄相近(158~162 Ma,Xu et al., 2018),穿插矿体的花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(96.7±0.8)Ma,因此,该矿床成矿年龄应在上述两个年龄之间。在政和—建瓯金矿集区内,东际金(银)矿与邻区金矿具有相似成矿物质来源,可能反映它们形成于相同成矿构造环境,东坑盆地主体由早白垩世晚期石帽山群火山-沉积岩系构成(安山岩Rb-Sr年龄(104.4±23)Ma,ISr=0.7092;熔结凝灰岩Rb-Sr年龄(105.4±3.1)Ma,ISr=0.7101,谢家莹等, 1994),上山岗金矿、东坑金矿和马仑头金矿等赋存于此地层中,这表明区域金矿化时间应晚于上述时期,据此可进一步约束东际金(银)矿床形成时间为早白垩世晚期。
从区域上来讲,浙闽交界地区三都澳—浦城北西向断裂带是一条铜钼金银多金属成矿带,主要由浦城铜多金属矿集区、政和—建瓯金矿集区和周宁—(福安)铜钼铅锌银矿集区等构成,成矿时代大都集中于100~105 Ma(张克尧等, 2009; 王登红等, 2010),同时也是早白垩世晚期(或称石帽山期)火山盆地分布区域,如东坑盆地、仁山盆地、香炉山盆地等,故该构造-岩浆带是一条早白垩世晚期成岩成矿带,矿床具有相似成矿地质背景和成矿物质来源(冯志文等, 1991),只是因成矿热液物理化学条件不一致,形成了不同成矿类型。因此,将东际金(银)矿床成矿时代限定为早白垩世晚期是可行的,它是区域强烈火山岩浆活动背景下的产物,也是该区大规模成矿的一个缩影。
8. 结论
(1)黄铁矿微量元素特征指示东际金(银)矿床成矿热液具有多阶段性特征,形成于浅成中低温热液条件,成矿热液中含有一定量大气降水。
(2)此矿床黄铁矿硫、铅同位素特征反映成矿物质主要来源于壳幔混源型花岗质岩浆,在岩浆-热液体系演化过程中,活化萃取了变质基底和火山岩围岩中金属元素。
(3)东际金(银)矿区赋矿围岩晶屑凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(154±2)Ma,穿切矿体的花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(96.7±0.8)Ma,结合区域性资料对比分析,可以限定东际金(银)矿床成矿年龄为早白垩世晚期。
致谢: 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所金继军硕士、张怡颖硕士和四川省地质调查院廖维高级工程师、何元宵高级工程师参加了部分野外地质调查工作,在此一并表示感谢。 -
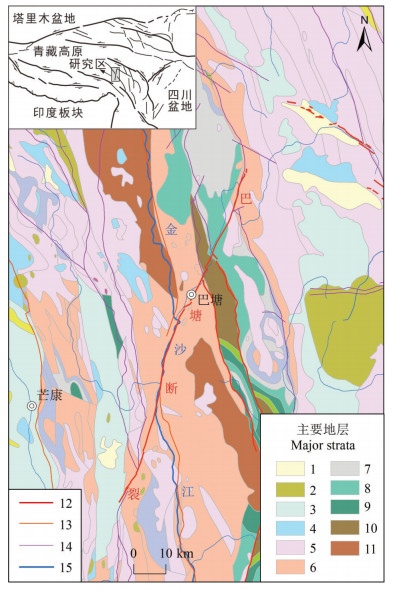
图 1 巴塘断裂带地质背景图
1—第四系;2—古近系;3—白垩系;4—侏罗系;5—三叠系;6—二叠系;7—泥盆系;8—志留系;9—奥陶系;10—震旦系;11—元古宇;12—全新世活动断裂;13—晚更新世活动断裂;14—早—中更新世断裂;15—河流
Figure 1. Geological setting of the Batang fault zone
1-Quaternary; 2-Paleogene; 3-Cretaceous; 4-Jurassic; 5- Triassic; 6-Permian; 7-Devonian; 8-Silurian; 9-Ordovician; 10-Sinian; 11-Proterozoic; 12-Holocene active fault; 13-Late Pleistocene active fault; 14-Early-Middle Pleistocene fault; 15-River
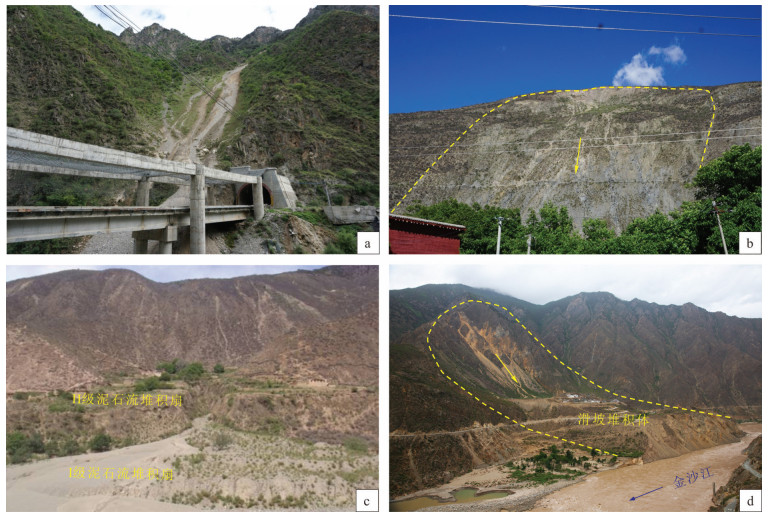
图 5 巴塘断裂带典型地质灾害实例
a—国道G318波戈溪隧道口崩塌;b—巴塘县党巴乡蠕滑型滑坡;c—巴塘县夏邛镇滑雪村泥石流;d—金沙江雪隆囊堵江滑坡
Figure 5. Typical geo-hazards in the Batang fault zone
a-Avalanche at the entrance of Bogexi tunnel of state road 318; b-Creeping landslide in the Dangba Town, Batang County; c-Debris flow in Huaxue Village of Xiaqiong Town, Batang County; d-Xuelongnang landslide in the Jinsha River
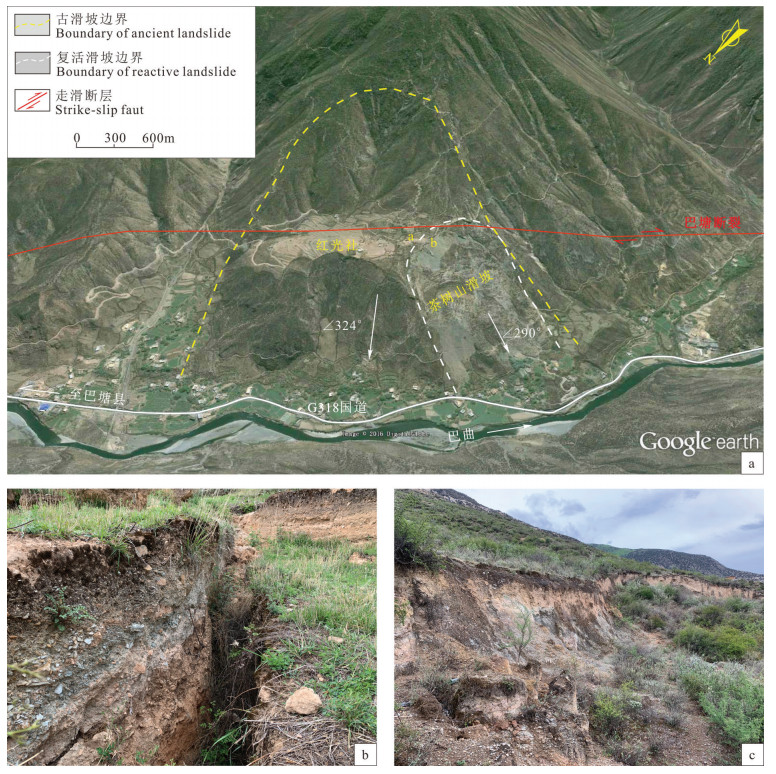
图 6 巴塘县茶树山滑坡发育特征
a—巴塘茶树山滑坡卫星影像图(据Google Earth);b—滑坡拉裂缝(图a中a处);c—滑坡下挫陡坎(图a中b处)
Figure 6. Characteristics of the Chashushan landslide of the Batang County
a-Satellite image of the Chashushan landslide in the Batang county (after the Google Earth); b-Landslide pulled cracks (place a in figure a); c-Landslide falling steep ridge (place b in figure a)
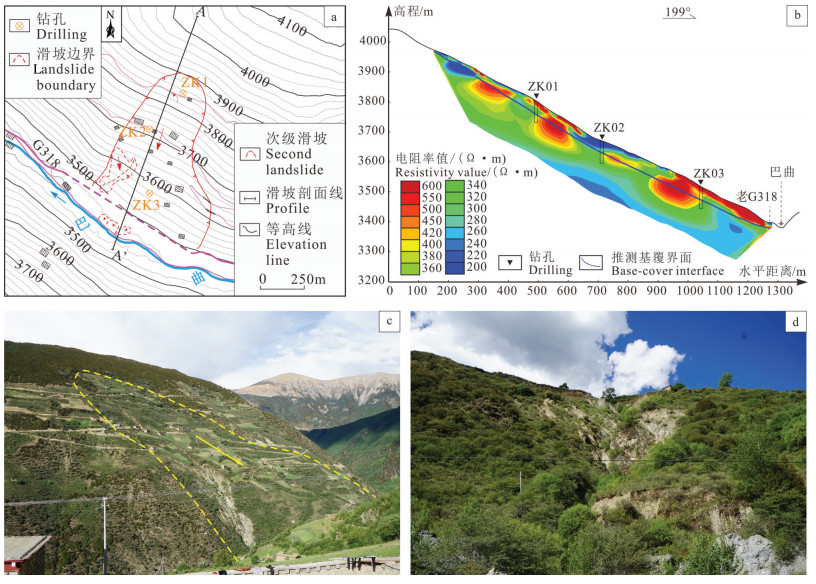
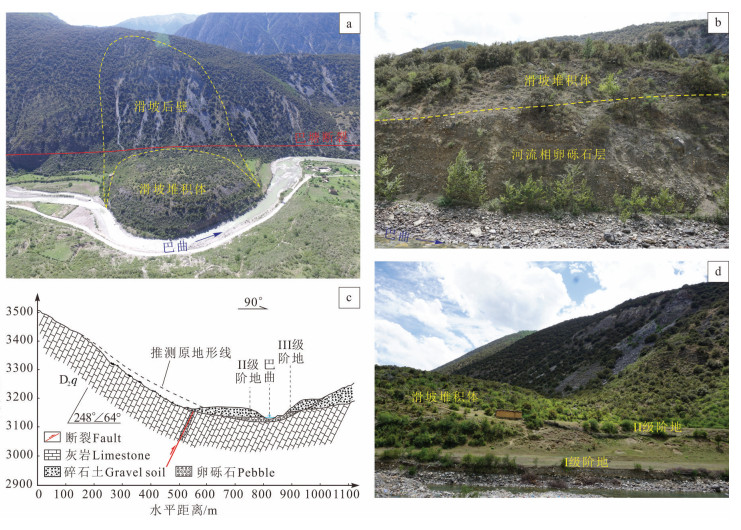
图 8 巴塘特米滑坡发育特征
a—滑坡遥感影像图;b—左岸滑坡堆积体(图a中a处);c—左岸湖相沉积层(图a中b处);d—滑坡后缘拉裂缝;e—滑坡后缘局部垮塌
Figure 8. Characteristics of the Temi landslide in the Batangcounty
a-Remote sensing image of landslide; b-Landslide accumulation on the left bank (place a in figure a); c-Lake sedimentary layer on the left bank (place b in figure a); d-Cracks in the trailing edge of landslide; e-Local collapse in the trailing edge of landslide
-
Bai Yongjian, Li Minghui, Wang Donghui, Gao Yanchao. 2014. Characteristics and disastrous rule research of geohazards in Batang County, the middle reaches of Jinsha River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 25(2): 103—109(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Jian, Dai Fuchu, Lü Tongyan, Cui Zhijiu. 2013. Holocene landslide-dammed lake deposits in the Upper Jinsha River, SE Tibetan Plateauand their ages[J]. Quaternary International, 298: 107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2012.09.018
Chen Jian, Cui Zhijiu. 2015. Discovery of outburst deposits induced by the Xuelongnang paleolandslide-dammed lake in the Upper Jinsha River, China and its environmental and hazard significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 33(2): 275-284(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Jian, Cui Zhijiu, Chen Ruichen, Zheng Xinxin. 2020. The origin and evolution of the Temi Paleo-landslide dammed lake in the upper Jinsha River[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 28(2): 85-93(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng Jia. 2008. Present-day Crustal Deformation of Western Sichuan Inferred from Geodetic Observations[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dai F C, Xu C, Yao X, Xu L, Tu X B, Gong Q M. 2011. Spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the 2008 Ms8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 883-895. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.010
Fan Xuanmei, Xu Qiang, Andres Alonso-Rodriguez, Srikrishnan Siva Subramanian, Li Weile, Zheng Guang, Dong Xiujun, Huang Runqiu. 2019. Successive landsliding and damming of the Jinsha River in eastern Tibet, China: Prime investigation, early warning, and emergency response[J]. Landslides, 16(5): 1003-1020. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01159-x
Guo Jin, Zhang Qingyun, Yuan Canlin. 1990. Disaster and its impact of Batang M6.7 Strong Earthquake Swarm[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, (1): 43-47(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Changbao, Du Yuben, Zhang Yongshuang, Zhang Guangze, Yao Xin, Wang Ke, Liu Jian. 2015. Geohazard effects of the Xianshuihe fault and characteristics of typical landslides in western Sichuan[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 121-134(in Chinese with English abstract).
He Yulin, Zhang Xuqi, Guo Jing. 1997. Investigation on intensity distribution of the 1996 M5.5 Baiyu-Batang Earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, (2): 46-53(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Renqiu. 1997. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, (2): 46-53(in Chinese with English abstract).
Kamp Ulrich, Growley Benjamin J, Khattak Ghazanfar A, Owen Lewis A. 2008. GIS based landslide susceptibility mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region[J]. Geomorphology, 101: 631-642. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.03.003
Keefer David K. 2000. Statistical analysis of an earthquake-induced landslide distribution - the 1989 Loma Prieta, California event[J]. Engineering Geology, 58: 231-249. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00037-5
Li Xiao, Li Shouding, Chen Jian, Liao Qiulin. 2008. Coupling effect mechanism of endogenic and exogenic geological processes of geological hazards evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(9): 1792-1806(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Minghui, Wang Donghui, Gao Yanchao, Bai Yongjian, Liu Xiaoxia. 2010. Report of Detailed Survey on Geological Disasters in the Batang County of Ganzi State[R]. Chengdu Geological Survey Center(in Chinese).
Long Wei, Chen Jian, Wang Pengfei, Xu Chong, Liu Hui, Sun Jinzhong. 2015. Formation mechanism and back analysis of paleoseismic parameters of the Temi large-scale ancient landslide in the upper Jinsha River[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 38(4): 568-575(in Chinese with English abstract).
Martel S J. 2004. Mechanics of landslide initiation as a shear fracture phenomenon [J]. Marine Geology, (23): 319-339.
Ouyang Chaojun, An Huicong, Zhou Shu, Wang Zhongwen, Su Pengcheng, Wang Dongpo, Cheng Duoxiang, She Jinxing. 2019. Insights from the failure and dynamic characteristics of two sequential landslides at Baige village along the Jinsha River, China[J]. Landslides, 16(7): 1397-1414. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01177-9
Ren Sanshao, Guo Changbao, Zhang Yongshuang, Zhou Nengjuan, Du Guoliang. 2017. Development characteristics and formation mechanism of Chashushan landslide in Batang, western Sichuan[J]. Geoscience, 38(4): 568-575(in Chinese with English abstract).
Peng W F, Wang C L, Chen S T, Lee S T. 2009. A seismic landslide hazard analysis with topographic effect, a case study in the 99 Peaks region, Central Taiwan[J]. Environmental Geology, 57(3): 537-549. doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1323-z
Su Lijun, Hu Kaiheng, Zhang Weifeng, Wang Jiao, Lei Yu, Zhang Chonglei, Cui Peng, Alessandro Pasuto, Zheng Quanhong. 2017. Characteristics and triggering mechanism of Xinmo landslide on 24 June 2017 in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 14(9): 1689-1700. doi: 10.1007/s11629-017-4609-3
Tang Huiming, Liu Xiao, Hu Xinli, Griffiths D V. 2015. Evaluation of landslide mechanisms characterized by high-speed mass ejection and long-run-out based on events following the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology, 194: 12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.01.004
Wang Xinmin. 1990. Characteristics of intensity and isoseismic of the 1870 Sichuan Batang Earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, (4): 89-94(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Sijing. 2002. Coupling of earth's endogenic and exogenic geological processes and origins on serious geological disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 10(2): 115-117(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Pengfei, Chen Jian, Dai Fuchu, Long Wei, Xu Chong, Sun Jimin, Cui Zhijiu. 2014. Chronology of relict lake deposits around the Suwalong paleolandslide in the upper Jinsha River, SE Tibetan Plateau: Implications to Holocene tectonic perturbations[J]. Geomorphology, 217: 193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.04.027
Wang Lichao, Wen Mingsheng, Feng Zhen, Sun Weifeng, Wei Yunjie, Li Junfeng, Wang Wenpei. 2019. Researches on the Baige landslide at Jinshajiang River, Tibet, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 30(1): 5-13(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Tao, Liu Jiamei, Li Zetong, Xin Peng, Shi Jusong, Wu Shuren. 2021. Seismic landslide hazard assessment of China and its impact on national territory spatial planning[J]. Geology in China, 48(1): 21-39(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Xiwei, Zhang Peizhen, Wen Xueze, Qin Zunli, Chen Guihua, Zhu Ailan. 2005. Features of active tectonics and recurrence behaviors of strong earthquakes in the western Sichuan Province and its adjacent regions[J]. Seismology and Geology, 27(3): 446 -461(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Xiangning, Li Shengwei. 2005. Risk evaluation and precautionary measures for bank slope instability in the hydroelectric project area on the mainstream of the Jinsha River[J]. Geology in China, 32(1): 155-161(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Yueping, Wang Wenpei, Zhang Nan, Yan Jingkai, Wei Yunjie, Yang Longwei. 2017. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area: A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(5): 827-841(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yongshuang, Guo Changbao, Yao Xin, Yang Zhihua, Wu Ruian, Du Guoliang. 2016. Research on the geohazard effect of active fault on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 37(3): 277-286(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yongshuang, Ba Renji, Ren Sanshao, Li Zongliang. 2019. Analysis on geo-mechanism of the Baige landslide in Jinsha River, Tibet, China[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1637-1645(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Rongjun, Chen Guoxing, Li Yong, Zhou Zhaohui, Gong Yu, He Yulin, Li Xiaogang. 2005. Research on active faults in Litang-Batang region, western Sichuan Province, and the seismogenic structures of the 1989 Batang M6.7 earthquake swarm[J]. Seismology and Geology, 27(1): 31-43(in Chinese with English abstract).
白永健, 李明辉, 王东辉, 高延超. 2014. 金沙江中游巴塘县地质灾害发育特征及成灾规律分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 25(2): 103-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201402023.htm 陈剑, 崔之久. 2015. 金沙江上游雪隆囊古滑坡堰塞湖溃坝堆积体的发现及其环境与灾害意义[J]. 沉积学报, 33(2): 275-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201502007.htm 陈剑, 崔之久, 陈瑞琛, 郑欣欣. 2020. 金沙江上游特米古滑坡堰塞湖成因与演化[J]. 地学前缘, 28(2): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202102008.htm 程佳. 2008. 川西地区现今地壳运动的大地测量观测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. 郭劲, 张庆云, 袁灿林. 1990. 巴塘6.7级强震群灾害及其影响[J]. 四川地震, (1): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHZ199001008.htm 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 张永双, 张广泽, 姚鑫, 王珂, 刘健. 2015. 川西鲜水河断裂带地质灾害发育特征与典型滑坡形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 34(1): 121-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.010 何玉林, 张绪奇, 郭劲. 1997. 1996年12月21日四川白玉、巴塘间5.5级地震烈度考察[J]. 四川地震, (2): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHZ199702006.htm 黄润秋. 2007. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 26(3): 433-451. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001 李晓, 李守定, 陈剑, 廖秋林. 2008. 地质灾害形成的内外动力耦合作用机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 27(9): 1792-1806. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.09.006 李明辉, 王东辉, 高延超, 白永健, 刘小霞. 2010. 甘孜地区(巴塘县)地质灾害详细调查报告[R]. 成都地质调查中心. 龙维, 陈剑, 王鹏飞, 许冲, 刘辉, 孙进忠. 2015. 金沙江上游特米大型古滑坡的成因及古地震参数反分析[J]. 地震研究, 38(4): 568-575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2015.04.007 任三绍, 郭长宝, 张永双, 周能娟, 杜国梁. 2017. 川西巴塘茶树山滑坡发育特征及形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 31(5): 978-989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.05.009 王新民. 1990. 1870年四川巴塘地震的烈度及等震线特征[J]. 四川地震, (4): 89-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHZ199004013.htm 王思敬. 2002. 地球内外动力耦合作用与重大地质灾害的成因初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 10(2): 115-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2002.02.001 王立朝, 温铭生, 冯振, 孙炜锋, 魏云杰, 李俊峰, 王文沛. 2019. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡灾害研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 30(1): 5-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201901001.htm 王涛, 刘甲美, 栗泽桐, 辛鹏, 石菊松, 吴树仁. 2021. 中国地震滑坡危险性评估及其对国土空间规划的影响研究[J]. 中国地质, 48(1): 21-39. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210102&flag=1 徐锡伟, 张培震, 闻学泽, 秦尊丽, 陈桂华, 朱艾斓. 2005. 川西及其邻近地区活动构造基本特征与强震复发模型[J]. 地震地质, 27(3): 446-461. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2005.03.010 许向宁, 李胜伟. 2005. 金沙江干流水电工程区岸坡失稳危险性预测及防治对策[J]. 中国地质, 32(1): 155-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2005.01.021 殷跃平, 王文沛, 张楠, 闫金凯, 魏云杰, 杨龙伟. 2017. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质, 44(5): 827-841. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170501&flag=1 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 杨志华, 吴瑞安, 杜国梁. 2016. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报, 37(3): 277-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603004.htm 张永双, 巴仁基, 任三绍, 李宗亮. 2019. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡的地质成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1637-1645. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200603&flag=1 周荣军, 陈国星, 李勇, 周朝晖, 龚宇, 何玉林, 黎小刚. 2005. 四川西部理塘-巴塘地区的活动断裂与1989年巴塘6.7级震群发震构造研究[J]. 地震地质, 27(1): 31-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2005.01.004 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 王利,梁天意. 内蒙古东部钓鱼台地区火山岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义. 西北地质. 2025(01): 68-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏巍,黄行凯,徐巧,蒋斌斌,刘孜,祝新友,巫锡勇. 大兴安岭中南段哈力黑坝岩体的年代学、地球化学及其构造拆沉作用. 中国地质. 2024(03): 978-994 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 赵利刚,王文龙,高学生,王树庆,许雅雯,胡晓佳. 内蒙古达茂旗北部包尔汉图群时代及中早-中三叠世变质锆石年龄的启示. 华北地质. 2024(02): 1-15+37 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 何鹏,郭硕,苏航. 大兴安岭南段昌图锡力地区白音高老组火山岩年代学、地球化学及构造环境. 华北地质. 2024(02): 16-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨海星,赵胜金,柳志辉,隋海涛,高利东,高玉石,于海洋,张猛. 大兴安岭中南段满克头鄂博组正层型剖面火山岩年代学及地球化学特征. 世界地质. 2023(02): 213-229 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 程泽宇,边伟华,陈崇阳,杨卓龙,高航,王璞珺. 海拉尔盆地嵯岗隆起侏罗系火山岩年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义. 世界地质. 2022(03): 451-464 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵强,汤静如,周青,舒广龙,马鹏,姜迎久,孙振江. 大兴安岭北段满克头鄂博组火山岩形成时代、地球化学特征与大地构造环境. 桂林理工大学学报. 2021(03): 497-509 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: