Natural attenuation monitoring of 1,2,3-trichloropropane and benzene in the groundwater of organic pollution sites, Tianjin chemical plant and its environmental restoration suggestions
-
摘要:研究目的
氯代烃、苯系物等有机污染物对中国地下水环境造成重要威胁,监控自然衰减技术在场地污染修复中发挥着重要作用,研究监控自然衰减技术,有利于推动地下水有机污染控制与环境修复技术发展。
研究方法本文通过对某化工污染场地地下水中1,2,3-三氯丙烷(TCP)和苯3年的长期监测,对地下水污染物浓度、氧化还原电位(ORP)、硝酸盐浓度的变化及微生物多样性进行分析,研究了场地不同含水层TCP和苯的自然衰减特征,并采用一级衰减动力学方程,计算了污染源区TCP和苯自然衰减能力。
研究结果结果表明:研究区地下水存在不同程度的TCP和苯的自然衰减;潜水及承压含水层地下水ORP值分别为-225~-57 mV和-182~-3 mV,为中—强还原环境,具备有机污染物厌氧生物降解基础环境条件;与非污染源区、承压含水层相比,污染源区、潜水含水层地下水微生物自然衰减作用更强,其中,污染源区MMW02监测井潜水含水层地下水TCP和苯的降解率分别为80.00%和77.88%;潜水含水层TCP和苯的衰减速率分别为0.0018 d-1和0.0016 d-1,承压含水层TCP和苯的衰减速率分别为0.001 d-1和0.0015 d-1。
结论针对地下水污染程度的不同,将监控自然衰减技术单独使用或与其他方法、技术联合使用,是低成本、高效率修复该类工业污染场地地下水有机污染的有效方法。
创新点:采用化学指标与微生物指标相结合的评价方法,从时间和区域角度,揭示实际污染场地地下水氯代烃和苯系物的自然衰减特征,并对其衰减潜力进行定量评价和预测。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveOrganic pollutants, such as chlorinated hydrocarbons and BTEX, have an important threat to groundwater environment in China. Natural attenuation monitoring plays an important role in contaminated sites remediation. Researches on natural attenuation monitoring will be conductive to promoting the development of groundwater organic pollution control and environmental remediation technologies.
MethodsIn order to study the natural attenuation of 1,2,3-trichloropropane (TCP) and benzene in different aquifers groundwater, the 3-year monitoring data of TCP, benzene, oxidation reduction potential (ORP), nitrate (NO3-) and biodiversity in an organic contaminated site has been collected and analyzed. Natural attenuation capacity of the pollution source area of the site was calculated using first order attenuation kinetic equation.
ResultsThe results show that the natural attenuation of TCP and benzene occurred in the aquifer for different degrees, and ORP values of the groundwater in phreatic and confined aquifer were -225~-57 mV and -182~-3 mV, respectively, which were medium-high reducing environment with basic environmental conditions for anaerobic biodegradation of organic pollutants. Moreover, the effect of microbial degradation was stronger in the pollution source area and phreatic aquifer than that in non-pollution source area and confined aquifer, and the degradation rates of TCP and benzene in the phreatic aquifer of MMW02 monitoring well were 80.00% and 77.88%, respectively. The attenuation rate of TCP and benzene were 0.0018 d-1 and 0.0016 d-1 in phreatic aquifer, and 0.001 d-1 and 0.0015 d-1 in confined aquifer.
ConclusionsAccording to the different degree of groundwater pollution, the natural attenuation monitoring technology can be used alone or combined with other remediation methods and technologies, which is a low cost and high efficiency method to reduce groundwater organic pollution for this kind of industrial contaminated sites.
-
1. 引言
中国的土壤和地下水污染形势严峻,仅东部平原及沿海地区,就存在数十万个潜在污染场地,其中有许多为有机污染场地,尤以氯代烃和芳香烃等有机溶剂污染最为突出(石建省等,2011; Yang et al., 2019)。《华北平原地下水有机污染调查评价》初步分析结果表明,氯代烃的检出率占总有机污染物的30%左右,芳香烃的检出率占所有有机污染物的25%左右(张兆吉等,2009)。
监测自然衰减技术是利用环境中自然发生的物理、化学及生物过程,降低土壤或地下水中污染浓度或毒性并长期监测其变化(Flynn et al., 2004; Weatherill et al., 2018; 李元杰等,2018)。对地下水有机溶剂污染,监测自然衰减是进行地下水污染恢复与控制的有效方法之一,也是目前在有机污染广泛、治理困难、资金受约束的现状条件下大多数场地可直接采用的可行技术(赵勇胜等,2010; 陈然然等,2015)。美国超基金项目实施统计显示,2005—2008年实施修复的场地中采用或部分采用监测自然衰减技术的场地高达56%(Leipe et al., 2005;Serrano et al., 2006;Nijenhuis et al., 2007;Baldwin et al., 2008),因此,监测自然衰减法是污染场地修复,尤其是有机污染场地修复与控制的重要方法。
而在中国,对有机污染的自然衰减研究尚处于起步阶段,相关研究主要侧重于室内模拟试验,如周睿等(2009)通过室内模拟柱实验研究了BTEX在地下水中的自然衰减过程,发现BTEX在地下环境中各组分均能发生自然衰减,但衰减的速度不同;吴玉成等(1999, 2000)研究了地下水中苯和甲苯在厌氧反硝化条件下的降解去除情况,结果表明在污染地下水中土著微生物能够以硝酸盐(NO3-)为电子受体降解苯和甲苯。在实际污染场地应用研究方面,吕航(2014)通过对某石油污染场地地下水、土中的污染物、地球化学、同位素、微生物等指标的监测,证实了石油烃污染物自然衰减作用的有效性并预测了污染物浓度、分布的发展趋势;贾慧(2011)针对加油站包气带石油污染自然衰减的研究,利用土壤中氧气和二氧化碳的含量分布规律对污染物衰减能力进行了评价;刘明柱等(2005)对北方某城市浅层地下水水质进行监测和数值模拟研究,发现研究区三氯乙烯(TCE)和四氯乙烯(PCE)存在生物降解作用,但是反应速率很小。此外,2008年吉林大学水资源环境研究所(焦珣,2010;路莹,2013)针对松原某石油污染场地,开展了监控自然衰减联合微生物原位强化修复技术研究,取得了较好的修复效果,联合技术的应用进一步拓展了监控自然衰减的适用范围。但总体而言,中国现阶段关于实际污染场地监测自然衰减技术的调查、分析和研究仍十分有限,且有限的研究多针对于石油污染物,尤以BTEX研究居多,对于氯代烃监测自然衰减的调查研究相对缺乏。
基于此,本文以天津某有机污染场地地下水中1,2,3-三氯丙烷(TCP)和苯为研究对象,通过近3年的长期监测数据,从污染物的生物降解自然衰减机制角度出发,分析污染物浓度和地球化学指标的变化趋势和空间分布,结合微生物多样性分析,评价验证自然衰减的发生,并对污染场地的自然衰减潜力进行评估;在此基础上,针对场地污染及自然衰减特点,提出有机污染地下水环境修复建议,为当地地下水环境改善及监测自然衰减技术的应用提供参考和借鉴。
2. 材料与方法
2.1 研究区概况
研究对象为天津蓟县某化工污染场地及其下游位置,面积约2000 m2,位于蓟运河冲洪积扇上部,蓟县境内最大的河流州河附近,地貌上属于燕山山脉向滨海平原的过渡地带,属山前平原全淡水区,地势总体平坦。研究区属暖温带半湿润大陆性季风气候,具有冬冷少雨雪,春旱多风沙,夏热多雨水,秋爽温差大,四季分明的特点,年平均气温11~12.3℃,降雨量北多南少,多年平均降雨量约为600 mm,陆地蒸发量约550 mm。
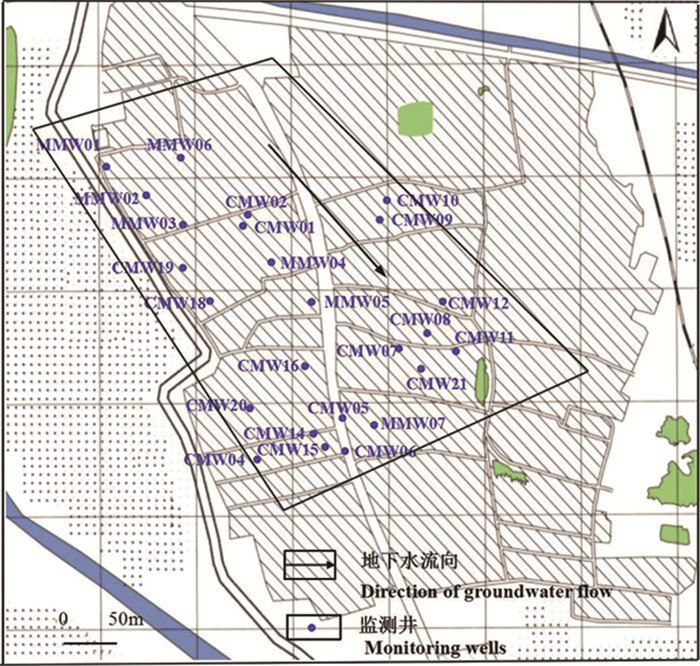
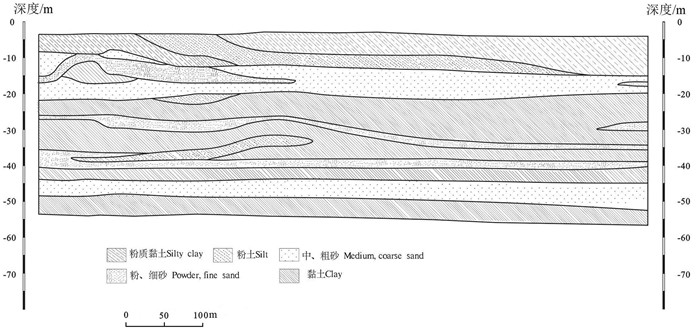
研究区表层岩性为第四系松散堆积物,向下分为四层,第一层为杂填土,第二层为粉质黏土层,第三层为中粗砂层夹粉细砂,第四层为黏土层。50 m之上可以划分4个主要含水层,第一层埋深为5~18 m,局部存在隔水透镜体,该深度内含水砂层分布较厚,含水量丰富,地下水类型为潜水;第二层埋深22~24 m,含水层厚度较薄,岩性以中砂为主;第三层埋深34~37 m,岩性以粉细砂为主;第四层埋深42~45 m,岩性以粗砂为主(图 1)。地下水潜水含水层主要受降雨入渗、蒸发及开采的影响,地下水位年变化幅度1~4 m,水力坡度1‰左右,水力滞缓,局部受人为开采影响较大,总体流向为由西北向东南。
该场地污染源为一小型化工厂,该厂运行时间为3年,于1979年关闭,运行期间主要收集国内其他化工厂的下脚料重新进行蒸馏分解,提纯获取低沸点化工原料。收集的下脚料种类复杂,约数十种,提纯的化工物料主要包括TCP、苯系物(BTEX)等物质。
2.2 监测井布设
在研究区布设24口监测井,包括沿地下水流向构建了7口分层多级监测井(Multistage Monitoring well,MMW)以及筛选民井(Civil Monitoring Well,CMW)中的8口浅层潜水井、9口承压地下水井进行了地下水取样分析。多级监测井基本情况如表 1所示,监测井分布情况如图 2所示。
表 1 多级监测井基本情况Table 1. Basic information of multistage monitoring wells
2.3 监测期及监测指标
本研究监测期为2014年5月至2017年3月,在此期间,对研究区地下水多次取样,进行有机污染物及相关地球化学指标的测试分析。根据前期调研取得的认识,本次研究选择该场地两种特征类型污染物——TCP和苯作为地下水有机污染物自然衰减识别的代表性监测指标,并选择氧化还原电位和硝酸盐作为环境监测指标,同时在监测末期采集研究区地下水微生物样品进行宏基因组测序分析,辅助识别微生物自然衰减作用。
2.4 地下水样品采集
多级监测井和单层监测井采用气囊泵或蠕动泵进行小流量采样,并在采样前进行充分洗井,待现场常规水质参数稳定后取样。地下水样品采集在2 h内完成。采集样品于40 mL棕色顶空瓶(有机分析)、500 mL饮用纯净水瓶(无机分析)和1.5 L棕色瓶(微生物分析),并置于4℃便携式冰箱中保存并送往苏伊士环境检测技术(上海)有限公司和生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行检测。测试过程进行加标、平行等质控处理。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 地下水污染物的分布特征
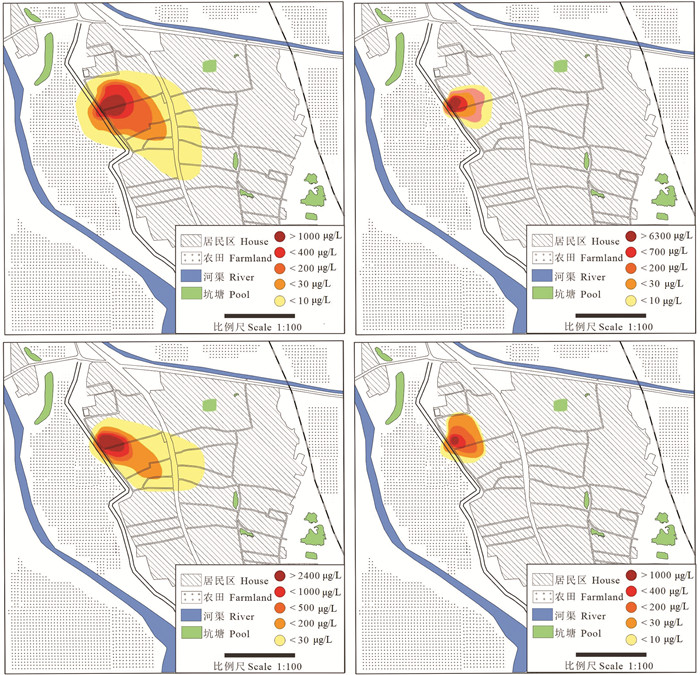
地下水监测重点为研究区50 m之上含水层,通过监测井及民井进行地下水取样,并绘制了污染物分布图,其中,15 m潜水含水层和45 m承压含水层TCP和苯污染分布如图 3所示。由图可知,场地潜水含水层和承压含水层均受到不同程度的有机污染,潜水污染主要由于污染物地表径流下渗造成,而深层承压地下水受污染的原因主要是当地民井多采用全滤水管,封层止水效果较差,造成上部污染地下水串层,进而污染下层地下水。由图还可以看出,TCP和苯的高浓度点分布于土地所范围内,并以此为中心随地下水流向下游扩散;对于两种污染物,潜水含水层中浓度均明显高于承压含水层;不同含水层中TCP污染浓度及污染羽范围都均大于苯,这是因为TCP在水体中具有较高的溶解度,一旦下渗进入地下水中,在地下水流驱动下会很快向下游迁移。此外,其属于重质非水相液体(DNAPL),当相邻含水层之间存在联系时,会进一步向下迁移至承压乃至深层地下水,导致其在深层含水层中扩散范围较大,而苯其属于轻质非水相液体(LNAPL),且亨利常数较高,更易挥发,因此,其不易于向下污染微承压或者深层含水层。
3.2 污染物浓度的时间变化趋势
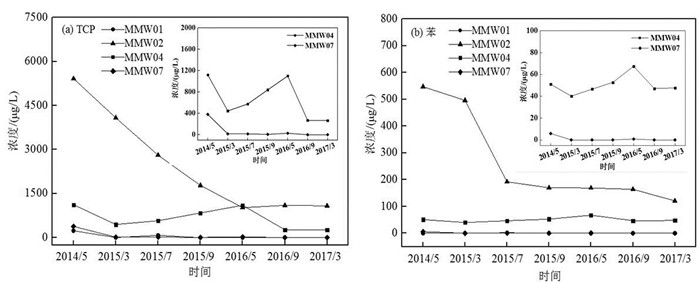
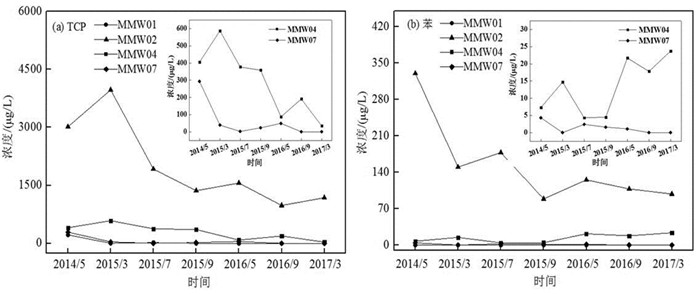
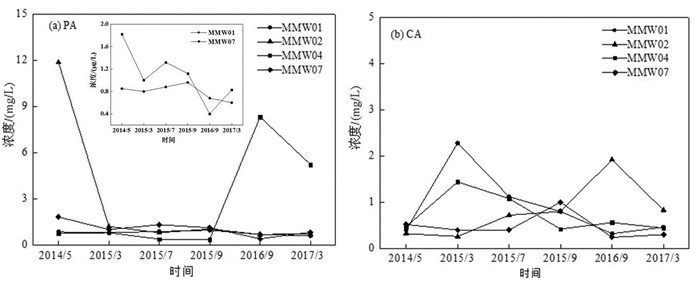
为分析研究区地下水中TCP和苯浓度的时间变化规律,沿地下水流方向选取MMW01、MMW02、MMW04和MMW07这4口监测井的15 m潜水含水层和45 m承压含水层监测数据进行详细研究,结果见 图 4和图 5。对于潜水含水层,MMW01、MMW02监测井地下水TCP和苯浓度呈现明显递减趋势,相较于2014年5月,2017年3月MMW01监测井地下水TCP浓度下降了99.39%,苯初始浓度未检出;MMW02监测井地下水TCP和苯浓度分别下降80.00%和77.88%;MMW04和MMW07监测井地下水污染物浓度呈现波动性下降趋势,MMW04监测井地下水TCP浓度下降了76.25%,苯浓度变化不大;MMW07地下水TCP和苯浓度均下降了100%。
在无人为干预的情况下,地下水中污染物浓度的降低可归结为自然衰减作用。自然衰减作用主要包括土壤颗粒的吸附、污染物质的微生物降解和地下水的稀释和弥散作用等(费宇红等,2022)。而对于有机污染物来说,微生物降解是最重要的自然衰减过程,因为它是能够真正减少或去除有机污染物的过程(赵勇胜,2015)。在该场地中,监测井MMW02和MMW04分别位于污染源区中心及其下游较近区域,污染物浓度较高,碳源和能源充足,因此推测微生物降解可能是该区域自然衰减的主要作用,但另一方面,地下水中有机污染物浓度很高甚至存在NAPL相时,则不适用于自然衰减修复,因为污染物初始浓度越大,自然衰减达到预期目标需要的时间就越长;MMW01和MMW07监测井分别位于污染源上游和下游较远区域,污染程度较轻,相对来说微生物降解速率较低(宁卓等,2018),因此,地下水稀释扩散可能是污染物自然衰减的主要作用。
对于承压含水层由图 5结果可以看出,整个研究期内,MMW01、MMW04和MMW07监测井地下水污染物浓度变化规律与潜水含水层相似,而污染源区的MMW02监测井地下水TCP和苯浓度则呈现波动性变化,这可能是由于水位的变化影响了地下水中污染物浓度。研究区的高水位一般在每年6—9月份,低水位一般在每年11月至次年3月,水位升高时,地下水中污染物浓度降低,水位降低时,地下水中污染物浓度升高。潜水含水层污染物浓度高于承压含水层,且其溶解氧、硝酸盐、硫酸盐等电子受体可通过包气带从土壤中得到一定程度的补充(Margalef-Marti et al., 2021; Aftabtalab et al., 2022),因此微生物自然衰减作用较强,TCP和苯的浓度受水位影响相对较小,呈现持续性递减趋势,而承压含水层污染物则呈现波动性变化。相较于2014年5月,2017年3月地下水中TCP和苯的浓度分别下降了60.87%和70.26%。
姜伟男(2020)通过1年的监测数据研究了某石油化工污染场地地下水中苯和1,2-二氯乙烯的浓度变化,发现苯和1,2-二氯乙烯浓度也是呈现波动变化,并不是单调递减,高水位期污染物的浓度低于低水位期的浓度,监测末期苯和1,2-二氯乙烯的浓度低于监测初期的浓度,推断地下水中污染物发生了自然衰减,这一研究结果与本研究具有一致性。
3.3 地下水氧化还原环境变化
地下水中微生物利用有机污染物作为碳源和能源,同时以环境中的溶解氧、硝酸盐、锰氧化物等作为电子受体生长、繁殖,导致环境中的氧化还原条件发生变化。氧化还原电位(ORP)是宏观反映氧化还原性的指标,可以初步判断地下水中有机物微生物降解过程,获得研究区有机污染物发生自然衰减的证据(Landmeyer et al., 2003; 何泽等,2019)。
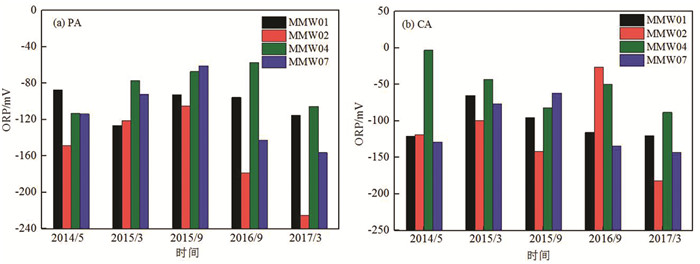
由不同监测井地下水ORP变化情况(图 6)可知,研究区2014年5月至2017年3月各监测井潜水含水层和承压含水层ORP值的变化范围分别为-225~-57 mV和-182~-3 mV,均为负值,说明研究区地下水中ORP值较低,总体处于偏还原的环境。
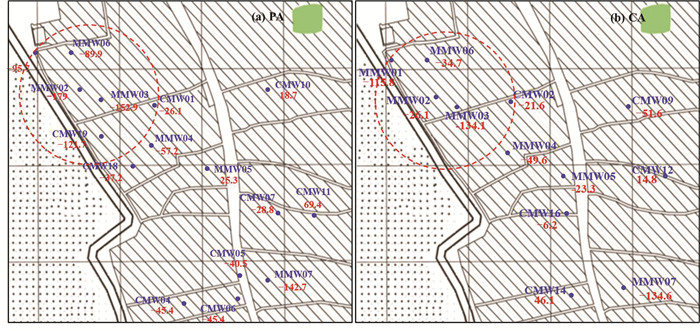
图 7为2016年研究区地下水ORP值的空间分布,由图可以看出,污染源区地下水ORP值明显低于非污染源区,因此可以推测未受污染时,该场地地下水可能为弱还原环境或氧化环境,而氯代烃和苯系物污染导致地下水氧化还原环境发生变化,转化为较强的还原环境。已有研究表明,电子受体争夺电子能力大小不同,使其被微生物利用顺序不同,一般来说,微生物会先利用氧作为电子受体,而后依次利用硝酸盐、锰氧化物等电子受体(Meckenstock et al., 2015),研究区地下水污染区域显示强还原环境,由此可以证明,地下水受污染初期,存在有机污染物的好氧微生物降解,溶解氧作为电子受体被优先利用,使得地下水氧化还原环境发生明显改变。
3.4 地下水NO3-浓度变化
地下水微生物在氧化环境中以O2为电子受体,而在兼性或弱还原环境中,会利用其他电子受体进行有机污染物的降解,NO3-作为厌氧微生物降解过程最主要的电子受体,其浓度的变化情况可间接反映出污染物的微生物降解情况。
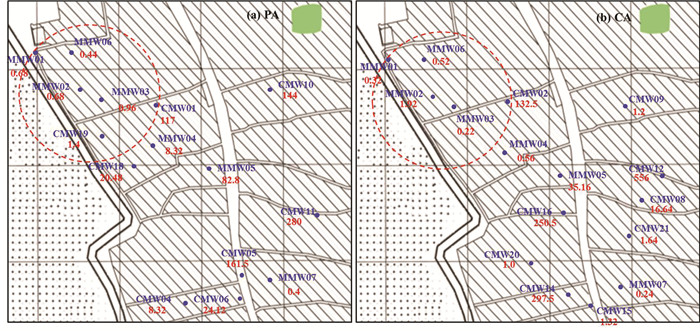
图 8为不同监测井中地下水NO3-浓度变化情况,由图可知,整个研究期内,MMW02监测井潜水层NO3-浓度呈现下降趋势,说明该含水层存在微生物反硝化作用,其他各监测井NO3-浓度变化不大,说明承压含水层及非污染源区潜水层的反硝化作用较弱,整体来看,潜水及承压含水层NO3-浓度均较低,这是因为该场地污染历史久远,含水层微生物自然衰减作用已进行数十年,O2和NO3-作为电子受体被优先利用,因此在微生物降解作用强烈的区域,NO3-浓度较低,结合图 9结果可以看出,位于地下水流向上的MMW01、MMW02、MMW04和MMW07监测井中NO3-浓度较其他监测井浓度较低,这可能是因为地下水主要流动方向上,电子受体更新速度快,可以得到较快补充,因此微生物降解作用更加强烈;此外,由图 9还可以看出,污染源区地下水中NO3-浓度普遍低于附近井中浓度,说明相对于非污染源区,污染源区域有机物微生物反硝化降解作用强烈。
3.5 地下水中微生物群落分析
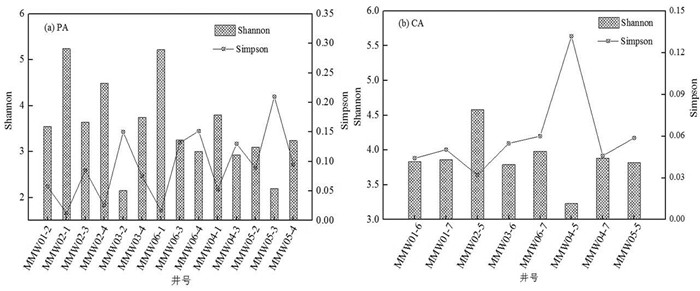
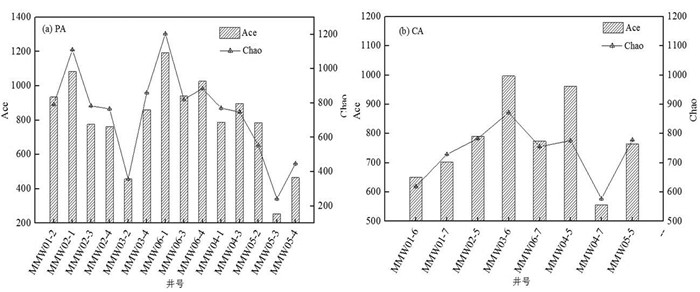
Shannon指数和Simpson指数是衡量微生物多样性的重要指标,Shannon指数值越高说明微生物多样性越高,Simpson指数与其相反,指数值越高说明多样性越低。此外,Ace指数与Chao指数常用来估计物种总数,指数值越大则物种总数越多,反之则物种总数越少(李洋等,2022)。通过多级监测井,对该场地不同深度潜水含水层和承压含水层地下水微生物样品进行测序分析,并采用QIIME软件包计算得到各样品的微生物多样性指数,结果如图 10和图 11所示。
由图 10可以看出,在潜水含水层中,除MMW03-2(-X,代表多级监测井层位)样品外,污染源区及其下游紧邻区域监测井(MMW02、MMW03和MMW06)地下水的Shannon指数总体上较污染源上游(MMW01)及下游较远区(MMW04和MMW05)要高,Simpson指数则与之相反,说明污染源区及其下游紧邻区域内地下水中的微生物较其上游及下游较远区丰富。物种总数统计结果与多样性结果类似,MMW02和MMW06监测井地下水Ace指数与Chao指数相对较高,MMW04和MMW05监测井地下水Ace指数与Chao指数相对较低,说明相对于污染源下游较远区域,污染源区及其下游紧邻区域地下水微生物更丰富。综上所述,污染源区的MMW02和MMW06监测井地下水微生物多样且较丰富,下游较远区微生物多样性和物种丰富程度都较为均一。这一结果说明微生物以有机污染物作为电子供体,进行生长和繁殖,同时有机污染物被氧化降解,污染源区与非污染源区微生物种群多样性和总数的差异再次证明了有机污染物微生物自然衰减作用的存在。
相对于潜水含水层,承压含水层Shannon指数的空间分布总体上较均一,最高值为4.58(MMW02),最低值为3.23(MMW04),其他监测井地下水Shannon指数均在3.8~4.8,相应地,除MMW04-5监测井地下水Simpson指数高于0.12外,其他监测井地下水Simpson指数均低于0.1,这说明研究区承压含水层地下水中,微生物种类较均匀,即受有机污染引起的地下水微生物多样性变化相对较小。承压含水层地下水Ace指数和Chao指数也呈现出污染源区及紧邻区域较高、污染源区上游及下游较远区域较低的规律。上述结果说明,相对于潜水含水层,承压含水层地下水有机污染浓度较低,因此微生物多样性及总数空间差异性较低,即存在一定程度的微生物自然衰减作用,但相对较弱。
3.6 研究区自然衰减能力评价
已有研究表明(Newell et al., 2002; Silva et al., 2013),BTEX等有机污染物的自然衰减符合一级衰减方程,一级衰减模型见式(1):

(1) 式中,C0为有机物的初始浓度,mg/L;Ct为有机物衰减后的浓度,mg/L;k为有机物的衰减速率常数,d-1,k值越大,表示物质衰减速度越快;t为衰减时间,d。
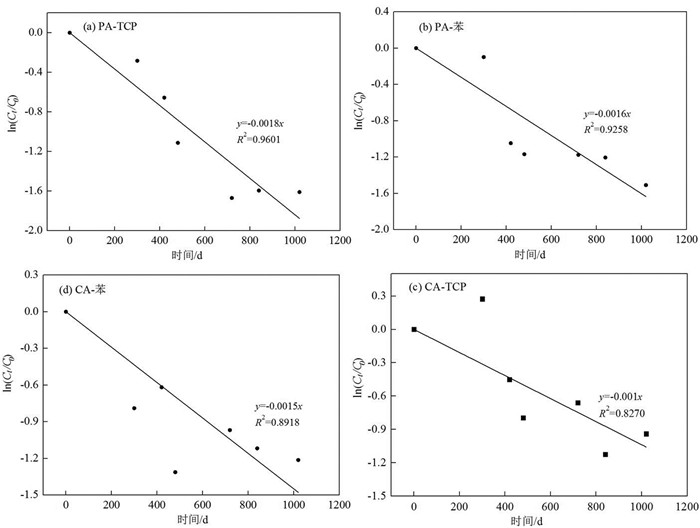
以污染源区MMW02监测井为例,对地下水中TCP和苯浓度的自然对数与时间进行线性拟合(图 12),得到的函数斜率即为该监测井污染物的衰减速率常数,以此来评价研究区自然衰减速率和趋势。
![]() 图 12 污染源区地下水TCP和苯自然衰减动力学拟合曲线a—潜水含水层中的TCP;b—潜水含水层中的苯;c—承压含水层中的TCP;d—承压含水层中的苯Figure 12. Dynamic fitting curves of natural attenuation of TCP and benzene in the groundwater of source pollution areaa-TCP in phreatic aquife (PA); b-Benzene in phreatic aquife (PA); c-TCP in confined aquife (CA); d-Benzene in confined aquife (CA)
图 12 污染源区地下水TCP和苯自然衰减动力学拟合曲线a—潜水含水层中的TCP;b—潜水含水层中的苯;c—承压含水层中的TCP;d—承压含水层中的苯Figure 12. Dynamic fitting curves of natural attenuation of TCP and benzene in the groundwater of source pollution areaa-TCP in phreatic aquife (PA); b-Benzene in phreatic aquife (PA); c-TCP in confined aquife (CA); d-Benzene in confined aquife (CA)有机物的半衰期与衰减速率常数的公示如式(2):

(2) 由图拟合结果,结合公式(2)计算可知,MMW02监测井潜水含水层TCP和苯的衰减速率分别为0.0018 d-1和0.0016 d-1,半衰期分别为385 d和433 d;承压含水层TCP和苯的衰减速率分别为0.001 d-1和0.0015 d-1,半衰期分别为693 d和462 d。贾慧等(2011)关于某通过现场试验计算的某石油类污染场地苯系物的降解速率为0.015 d-1,朱瑞利等(2015)通过模拟计算某场地浅层地下水氯代烃的自然衰减速率为0.005 d-1,不同场地条件的差异性及复杂性,可能会导致自然衰减程度的差异,利用一级衰减速率系数只能反映特定场地条件及周期内污染物的衰减速率,即本研究得出的衰减速率只是基于在本研究期内的场地自然衰减能力评价结果。
3.7 有机污染场地地下水环境修复建议
综合上述研究结果可知,针对该有机污染场地的非污染源区或污染较轻区域,可开展持续性的地下水环境监测,通过监控自然衰减,尤其是微生物自然衰减过程,可在合理的时间范围内,达到有机污染修复的目的;针对污染源区或污染较重区域,场地单纯依靠监控自然衰减的修复时间可能需要数年甚至更长,因此可以与其他治理方法联合使用以缩短治理时间,例如可采用人工抽水、截流、帷幕注浆等措施,快速排出或屏蔽被污染地下水,防止污染羽继续扩展;再通过异位或原位的吸附沉淀、化学氧化还原、微生物降解等方法,去除部分有机污染物;最后再通过监控自然衰减,以较低的成本实现有机污染地下水的修复;此外,当地相关部门应加强地下水资源管理,严格控制开采量,严禁乱开乱采,对已有串层混合开采井有计划地进行关堵封停,合理布设新增井,并对结构设计严格把关,避免人为“天窗”发生,加剧深层地下水污染。
4. 结论
(1)场地不同深度含水层均存在TCP和苯污染,并以污染源为中心随地下水流向下游扩散,污染羽呈西北-东南分布,且潜水含水层中污染浓度高于承压含水层。
(2)研究区不同监测井地下水污染物基本呈现下降趋势,即存在不同程度的自然衰减作用;潜水及承压含水层地下水ORP值分别为-225~-57 mV和-182~-3 mV,为中—强还原环境,具备有机污染物发生厌氧生物降解的基础环境条件,且污染源区、潜水含水层地下水ORP值、硝酸盐浓度和微生物多样性和丰富性指数均明显低于非污染源区、承压含水层地下水,说明污染源区、潜水含水层地下水微生物自然衰减作用更强,其中,污染源区MMW02监测井潜水含水层地下水TCP和苯的降解率分别为80.00%和77.88%。
(3)修复建议:污染源区潜水含水层TCP和苯的衰减速率分别为0.0018 d-1和0.0016 d-1,半衰期分别为385 d和433 d;承压含水层TCP和苯的衰减速率分别为0.001 d-1和0.0015 d-1,半衰期分别为693 d和462 d,氯代烃和苯系物自然衰减速率较低,因此可以与其他治理方法联合使用以缩短治理时间,例如采用人工抽水、截流、帷幕注浆等措施,快速排出或屏蔽污染源区被污染地下水,防止污染范围继续扩展;再通过异位或原位的吸附沉淀、化学氧化还原、微生物降解等方法,去除部分有机污染物;最后再通过监控自然衰减,以相对较低的成本实现有机污染地下水的修复。
-
图 12 污染源区地下水TCP和苯自然衰减动力学拟合曲线
a—潜水含水层中的TCP;b—潜水含水层中的苯;c—承压含水层中的TCP;d—承压含水层中的苯
Figure 12. Dynamic fitting curves of natural attenuation of TCP and benzene in the groundwater of source pollution area
a-TCP in phreatic aquife (PA); b-Benzene in phreatic aquife (PA); c-TCP in confined aquife (CA); d-Benzene in confined aquife (CA)
表 1 多级监测井基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of multistage monitoring wells

-
Aftabtalab A, Rinklebe J, Shaheen S M, Niazi N K, Moreno-Jimenez E, Schaller J, Knorr K. 2022. Review on the interactions of arsenic, iron (oxy) (hydr)oxides, and dissolved organic matter in soils, sediments, and groundwater in a ternary system[J]. Chemosphere, 286: 131790-131801. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131790
Baldwin B R, Nakatsu C H, Nies L. 2008. Enumeration of aromatic oxygenase genes to evaluate monitored natural attenuation at gasoline-contaminated sites[J]. Water Research, 42(3): 723-731. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.07.052
Chen Ranran, Zhu Xin, Lin Yusuo, Yu Ran, Long Tao. 2015. Preliminary inquiry of monitored natural attenuation remediation of chlorinated organic compounds contaminated site[J]. Chemistry Journal, 66(7): 2361-2369.
Fei Yuhong, Liu Yaci, Li Yasong, Bao Xilin, Zhang Pengwei. 2022. Prospect of groundwater pollution remediation methods and technologies in China[J]. Geology in China, 49(2): 420-434 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Flynn R M, Rossi P, Hunkeler D. 2004. Investigation of virus attenuation mechanisms in a fluvioglacial sand using column experiments[J]. Microbiology Ecology, 49: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.femsec.2003.08.017
He Ze, Ning Zhuo, Huang Guanxing, Liu Dandan, Zhang Qianqian, Sun Jichao. 2019. The response characteristics of microbial diversity to shallow groundwater contamination in the piedmont of the Taihang Mountains using molecular biotechnologies: A case study of groundwater of Hutuo River Basin[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 290-301 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jia Hui. 2011. Research on natural attenuation of oil contaminant in the vadose zone[J]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jia Hui, Wu Xiaofeng, Hu Liming, Liu Peibin. 2011. Research of the natural attenuation capacity of oil pollutants based on in-situ experiment[J]. Environmental Science, 32(12): 3699-3703 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Weinan. 2020. Study on Identification of Natural Attenuation of Pollutants in Groundwater in Petrochemical Contaminated Site[D]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiao Xun. 2010. Research on MNA Remediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminants in Groundwater [D]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Landmeyer J E, Bradley P M. 2003. Effect of hydrologic and geochemical conditions on oxygen-enhanced bioremediation in a gasoline-contaminated aquifer[J]. Bioremediation Journal, 7: 165-177. doi: 10.1080/713607983
Liu Mingzhu, Chen Honghan, Hu Liqin. 2005. Numerical modeling of transport of organic pollutants in shallow groundwater in a certain city of northern China[J]. Geology in China, 32(3): 507-511 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2005.03.022
Li Yuanjie, Wang Senjie, Zhang Min, He Ze, Zhang Wei. 2018. Research progress of monitored natural attenuation remediation technology for soil and groundwater pollution[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(3): 1185-1193.
Li Yang, Luo Jiayi, Lin Feng, Mao Ruifeng, Li Kai. 2022. Analysis of microbial diversity of red vinasse acid in Wuhan area of Guangxi[J]. China Condiment, 47(1): 14-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu Ying. 2013. Mechanism of Natural Biodegradation in Petroleum Contaminated Shallow Groundwater System[D]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lü Hang. 2014. Research on Biodegradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminants and Enhanced In-Situ Remediation in Groundwater[D]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract)
Margalef-Marti R, Llovet L, Carrey R, Ribas A, Domene X, Mattana S, Chin-Pampillo J, Mondini C, Alcaniz J M, Soler A, Otero N. 2021. Impact of fertilization with pig slurry on the isotopic composition of nitrate retained in soil and leached to groundwater in agricultural areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 125: 104832-104840. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104832
Meckenstock R U, Elsner M, Griebler C. 2015. Biodegradation: Updating the concepts of control for microbial cleanup in contaminated aquifers[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(12): 7073-7081. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b00715
Newell C J, Rifai H S, Wilson J T, Connor J A, Aziz J A, Suarez M P. 2002. Calculation and use of first- order rate constants for monitored natural attenuation studies[R]. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Nijenhuis I, Nikolausz M, Köth A, Felföldi T, Weiss H, Drangmeister J, Grossmann J, Kästner M, Richnowl H. 2007. Assessment of the natural attenuation of chlorinated ethenes in an anaerobic contaminated aquifer in the Bitterfeld/Wolfen area using stable isotope techniques, microcosm studies and molecular biomarkers[J]. Chemosphere, 67(2): 300-311. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.084
Ning Zhuo, Guo Caijuan, Cai Pingping, Zhang Min, Chen Zongyu, He Ze. 2018. Geochemical evaluation of biodegradation capacity in a petroleum contaminated aquifer[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(11): 4068-4074 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.11.010
Serrano A, Gallego M, González J L. 2006. Assessment of natural attenuation of volatile aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soil contaminated with diesel fuel[J]. Environmental Pollution, 144(1): 203-209. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.031
Shi Jiansheng, Wang Zhao, Zhang Zhaoji, Fei Yuhong, Zhang Fenge, Li Yasong, Chen Jingsheng, Qian Yong. 2011. Preliminary analysis on the organic contamination of groundwater in the Notth China Plain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Science, 20(11): 1695-1699(in Chinese with English abstract).
Silva M L, Gomez D E, Alvarez P J J. 2013. Analytical model for BTEX natural attenuation in the presence of fuel ethanol and its anaerobic metabolite acetate[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 146: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.12.006
Yang S, Ge W Y, Chen H H, Xu W L. 2019. Investigation of soil and groundwater environment in urban area during post-industrial era: A case study of brownfield in Zhenjiang, Jiangsu Province, China[J]. China Geology, 2(4): 501-511.
Weatherill J J, Atashgahi S, Schneidewind U, Krause S, Ullah S, Cassidy N, Rivettfg M O. 2018. Natural attenuation of chlorinated ethenes in hyporheic zones: A review of key biogeochemical processes and in-situ transformation potential[J]. Water Research, 128: 362-382. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.10.059
Wu Yucheng, Zhong Zuoshen, Chen Liang. 2000. Removal of aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants from groundwater: Laboratory aquifer column studies[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 30(1): 61-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Yucheng, Zhong Zuoshen, Zhang Jianli. 1999. Microbial degradation of benzene and toluene in groundwater under enhanced denitrifying condition[J]. China Environmental Science, 19(6): 505-509 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.1999.06.007
Zhang Zhaoji, Fei Yuhong, Zhang Liansheng. 2009. Investigation and evaluation of groundwater pollution in North China Plain[C]//Data Compilation of New Advances in Geological Science and Technology and New Achievements in Geological Prospecting in China. 2009. Beijing: China Geological Education Press (in Chinese).
Zhao Yongsheng. 2015. Control and Remediation of Groundwater Contamination Sites[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1-397 (in Chinese).
Zhao Yongsheng, Wang Bing, Qu Zhiui, Zheng Wei, Jia Xu, Sun Meng. 2010. Natural attenuation of diesel pollution in sand layer of vadose zone[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 40(2): 389-393 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Rui, Zhao Yongsheng, Ren Hejun, Dong Jun, Hu Guiquan, Zhao Yan, Hua Fei. 2009. Natural attenuation of BTEX in the underground environment[J]. Environmental Science, 30(9): 2804-2808 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Ruili, Zhang Shiyang, Li Hui, Lin Kuangfei, Lü Shuguang. 2015. Natural attenuation simulation of 1,1,1-trichloroethane in shallow groundwater at a contaminated site in Pudong, Shanghai[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 41(3): 42-348 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈然然, 祝欣, 林玉锁, 余冉, 龙涛. 2015. 氯代有机物污染场地的监控自然衰减修复初探[J]. 化工学报, 66(7): 2361-2369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201507001.htm 费宇红, 刘雅慈, 李亚松, 包锡麟, 张鹏伟. 2022. 中国地下水污染修复方法和技术应用展望[J]. 中国地质, 49(2): 420-434. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220206?st=search 何泽, 宁卓, 黄冠星, 刘丹丹, 张千千, 孙继朝. 2019. 太行山前平原浅层地下水污染的分子生物学响应特征——以滹沱河流域为例[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 290-301. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20190206?st=search 贾慧. 2011. 非饱和区石油污染的自然衰减研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学. 贾慧, 武晓峰, 胡黎明, 刘培斌. 2011. 基于现场试验的石油类污染物自然衰减能力研究[J]. 环境科学, 32(12): 3699-3703. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201112048.htm 姜伟男. 2020. 某石油化工污染场地地下水中污染物自然衰减识别研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学. 焦珣. 2010. 地下水石油类污染MNA修复研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 李洋, 罗佳沂, 林凤, 毛瑞丰, 李凯. 2022. 广西武宣地区红糟酸微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国调味品, 47(1): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTW202201003.htm 李元杰, 王森杰, 张敏, 何泽, 张巍. 2018. 土壤和地下水污染的监控自然衰减修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(3): 1185-1193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201803052.htm 刘明柱, 陈鸿汉, 胡丽琴. 2005. 北方某城市浅层地下水中有机污染物迁移转化的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国地质, 32(3): 507-511. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20050322?st=search 路莹. 2013. 浅层地下水系统石油类污染物的生物降解机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学. 吕航. 2014. 地下水石油烃污染物的微生物降解过程及其原位强化修复研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学. 宁卓, 郭彩娟, 蔡萍萍, 张敏, 陈宗宇, 何泽. 2018. 某石油污染含水层降解能力地球化学评估[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(11): 4068-4074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201811012.htm 石建省, 王昭, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 张凤娥, 李亚松, 陈京生, 钱永. 2011. 华北平原地下水有机污染特征初步分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(11): 1695-1699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201111020.htm 吴玉成, 钟佐燊, 陈亮. 2000. 去除地下水芳香烃污染物: 实验室含水层土柱研究[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 30(1): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200001015.htm 吴玉成, 钟佐燊, 张建立. 1999. 反硝化条件下微生物降解地下水中的苯和甲苯[J]. 中国环境科学, 19(6): 505-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ199906010.htm 张兆吉, 费宇红, 张连胜. 2009. 华北平原地下水污染调查评价[C]//2009年度中国地质科技新进展和地质找矿新成果资料汇编. 北京: 中国地质教育出版社. 赵勇胜, 王冰, 屈智慧, 郑苇, 贾旭, 孙猛. 2010. 柴油污染包气带砂层中的自然衰减作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 40(2): 389-393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201002023.htm 赵勇胜. 2015. 地下水污染场地的控制与修复[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-397. 周睿, 赵勇胜, 任何军, 董军, 胡桂全, 赵妍, 花菲. 2009. BTEX在地下水环境中的自然衰减[J]. 环境科学, 30(9): 2804-2808. 朱瑞利, 张施阳, 李辉, 林匡飞, 吕树光. 2015. 上海浦东浅层地下水环境三氯乙烷自然衰减规律及过程模拟[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 41(3): 42-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLDX201503011.htm -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 汪思颖,韩绮,张立秋,封莉. 中国地下水污染防治技术研究进展与展望. 环境污染与防治. 2024(12): 1834-1840 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: