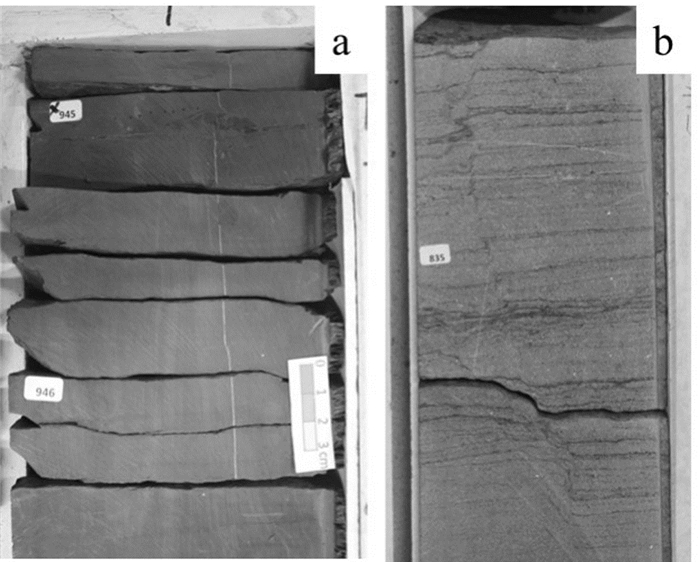
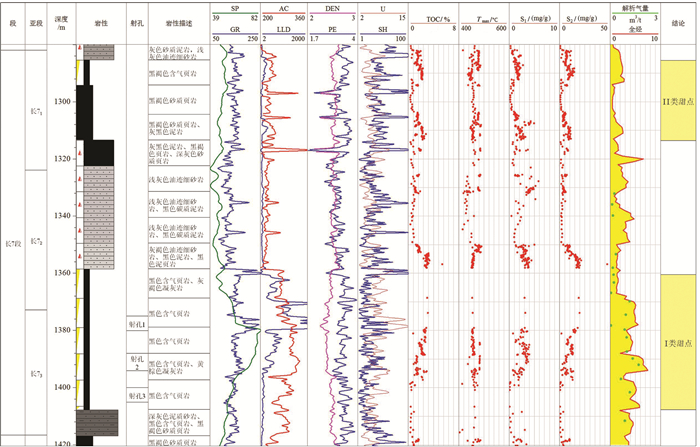
The enrichment conditions and model of shale gas reservoir in the Chang 7 member of Mesozoic Yanchang Formation in Yan'an, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:研究目的
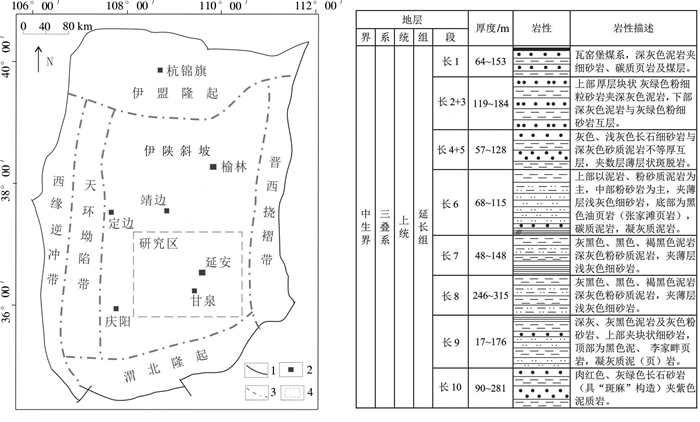
鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组长7段页岩具有岩性岩相、沉积厚度变化快、有机质丰度高但成熟度偏低、黏土含量高、地层普遍低压—常压的特点,对长7段页岩开展页岩气富集条件及发育模式的研究,利于探寻适合长7页岩气勘探开发的地质理论,以期对该地区下一步勘探工作提供指导,进一步完善陆相页岩气地质理论。
研究方法基于钻井、岩心和分析测试资料,从生烃条件、储集条件、保存条件等方面,对长7段页岩气成藏富集条件进行了系统研究,建立页岩气富集发育模式。
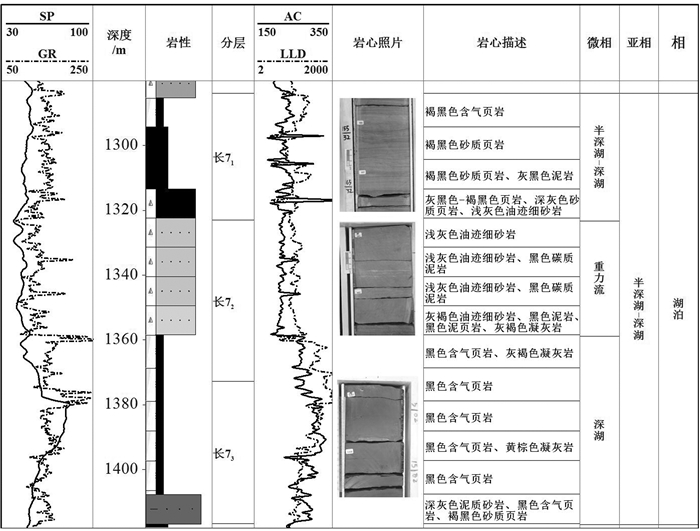
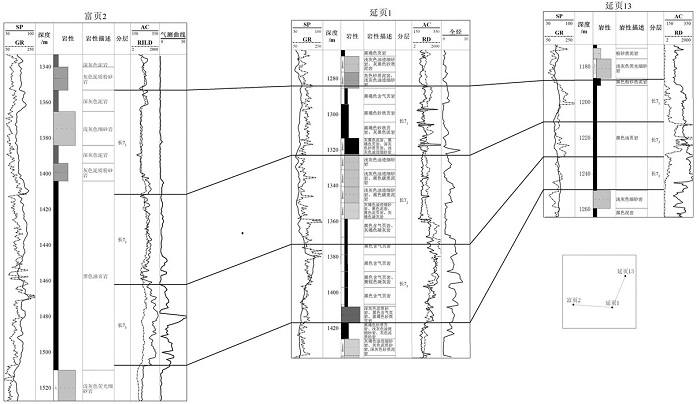
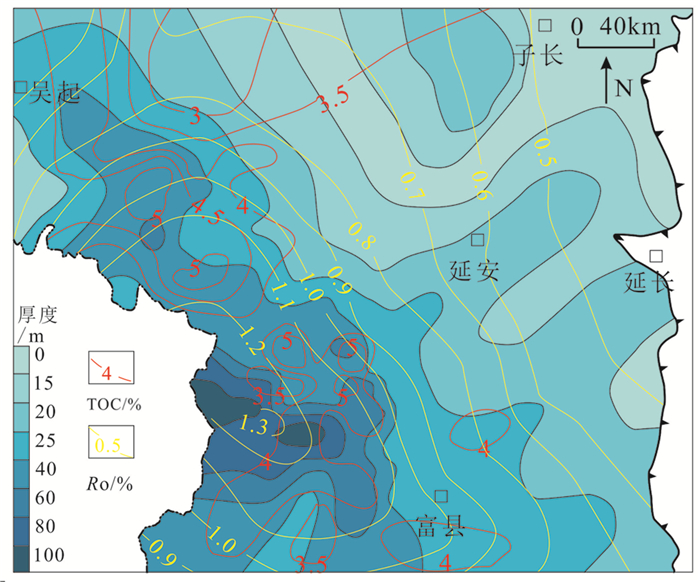
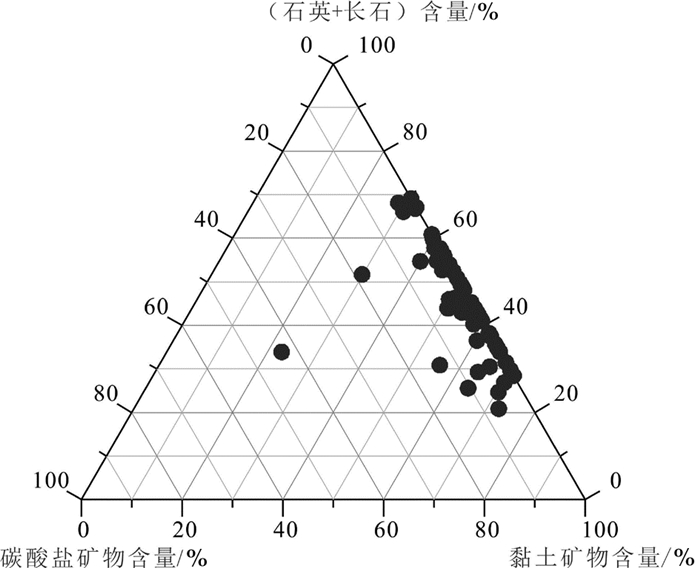
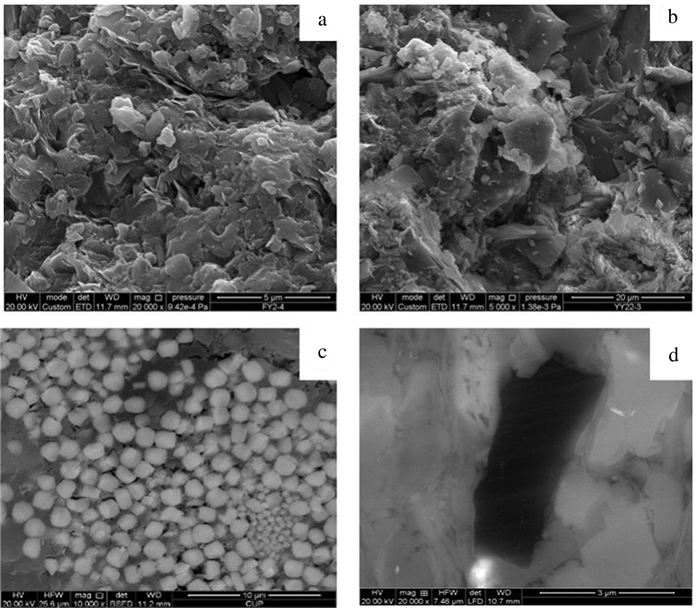
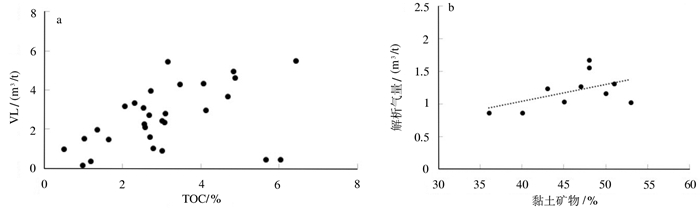
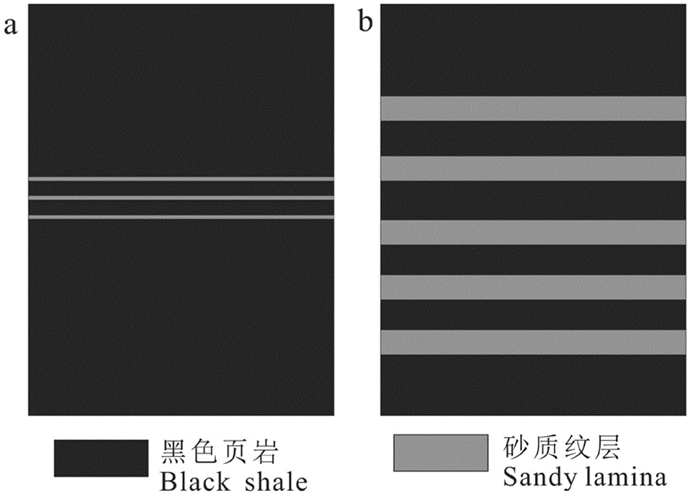
研究结果研究认为:(1)研究区长7页岩有机质丰度高,TOC基本大于1.5%,且处于大量生油气阶段,Ro基本在0.8%~1.3%,生气潜力较大;(2)黏土矿物含量高,基本在40%~60%,利于页岩气吸附,具有吸附气产出的特征;(3)相对稳定的构造背景是页岩气得以保存的重要条件;(4)页岩气富集模式可分为页岩与砂质纹层互层式和厚层富有机质页岩式两种模式,砂质纹层有效改善页岩储层物性,连续沉积的厚层富有机质页岩是气保存的重要形式。
结论依据对长7页岩气富集特征的解剖,将长7页岩气富集规律总结为“两大一多”的特征:生气潜力大、连续厚度大、砂质纹层多。
创新点:总结长7段页岩气成藏富集条件,建立长7段页岩气富集发育模式。
Abstract:This paper is the result of oil and gas exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe Chang 7 shale of Mesozoic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin is characterized by rapid changes of lithologies and lithofacies, thick, high abundance but low maturity of organic matter, high clay content and low-normal strata pressure. The study on shale gas enrichment conditions and development model of the Chang 7 shale is beneficial to explore the geological theory suitable for the exploration and development of Chang 7 shale gas, in order to provide guidance for the next exploration work in the region and further improve the geological theory of continental shale gas.
MethodsBased on drilling, core analysis, and test data, the accumulation and enrichment conditions of the Chang 7 shale gas were systematically studied from the aspects of hydrocarbon generation conditions, reservoir conditions and preservation conditions, and the enrichment and development model of shale gas was established.
ResultsThe results show that: (1) Chang 7 shale in the study area has high organic matter abundance, TOC is basically greater than 1.5%, and is in the oil and gas generation window, Ro is basically between 0.8% and 1.3%, and has the geological conditions of shale gas generation; (2) The clay mineral content is high, basically 40%-60%, which is beneficial to shale gas adsorption and has a certain adsorbed gas production; (3) The relatively stable tectonic background is an important condition for the preservation of shale gas; (4) The enrichment model of shale gas can be divided into two types: interbedded shale and sandy lamina type, and thick organic-rich shale type. The sandy lamina effectively improves the physical properties of shale reservoirs. The thick organic-rich shale deposited continuously is an important form of gas preservation.
ResultsBased on the dissection of the enrichment characteristics of Chang 7 shale gas, the enrichment law of Chang 7 shale gas is summarized as "two large and one many": large gas generation potential, large continuous thickness and many sandy laminas.
-
1. 引言
印度—欧亚板块之间的碰撞是新生代以来最具全球性意义的地质事件,它直接导致了喜马拉雅造山带的形成以及青藏高原的快速抬升,并伴随有强烈的构造-岩浆-变质-成矿作用(潘桂棠等,2006;侯增谦等, 2006;莫宣学,2011;许志琴等, 2011, 2016;任继舜等, 2017;赵亚云等,2022)。受新特提斯洋闭合以及印度-欧亚板块陆陆碰撞过程的影响,在拉萨地块的南缘爆发了大规模的岩浆作用,这些岩浆岩为示踪岩浆源区物质组成、探讨造山带深部大陆动力学过程提供了理想的研究对象(Chung et al., 2003;赵志丹等,2006;莫宣学,2011;孟元库等, 2015, 2018;汪斌等,2022)。
研究表明始新世是新特提斯洋消亡后、印度-欧亚板块之间陆陆碰撞的初始期,拉萨地块南缘大规模发育的林子宗群以及同时期侵入岩被认为是该事件最为直接的岩浆记录,国内外学者已经对该期岩浆作用进行了大量的研究工作,在岩浆岩时空格架、岩石成因、深部动力学机制等方面取得了重要的进展(Chung et al., 2003, 2005;赵志丹等,2006;Zhu et al., 2015,2018)。然而以往的研究工作主要集中在岩浆岩发育的拉萨地块南缘,而在远离印度-欧亚板块碰撞带的西藏中部地区,始新世岩浆活动弱,研究程度较低。近年来,西藏中部局部地区陆续报道了始新世岩浆岩资料,但是这些岩浆岩以中酸性岩石为主,难以准确约束成岩构造背景,不同学者对该期岩浆作用的深部动力学机制仍存在不同的认识,部分学者认为是新特提斯洋北向俯冲板片断离机制下的岩浆产物,而也有部分学者则认为是印度-欧亚板块碰撞导致班公湖—怒江缝合带再次活动的产物(付文春等,2014;魏永峰等,2018;张耀玲等,2018)。可以看出,西藏中部始新世岩浆活动的深部动力学机制仍存有争议,其与南侧大规模发育的同时期岩浆作用之间的成因联系尚不明确,亟待进一步研究。
本文对西藏中部聂尔错地区新识别的辉绿岩脉进行了锆石U-Pb测年与全岩地球化学研究工作,以此查明辉绿岩的形成时代与岩石成因,进一步探讨成岩深部动力学机制、约束印度-欧亚板块之间的汇聚过程。
2. 地质概况与岩石学特征
青藏高原经历了不同时期特提斯洋多期次开合以及板块汇聚过程,形成了近东西向展布的多个构造缝合带,这些缝合带从南至北依次将青藏高原划分为喜马拉雅、拉萨、羌塘、松潘甘孜和祁连—昆仑等地块(Yin and Harrison, 2000; 潘桂堂等, 2006; 许志琴等, 2011; 任纪舜等, 2017)。其中拉萨地块南侧以雅鲁藏布缝合带为界,北侧以班公湖—怒江缝合带为界,其内部又以米拉山断裂和狮泉河—永珠—嘉黎缝合带进一步划分为南、中、北三个次级地块(图 1)(Zhu et al., 2011)。
![]() 图 1 青藏高原南部构造单元划分图(a)和聂尔错地区地质简图及采样位置(b)LSSZ—龙木错—双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖—怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河—纳木错混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆—米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—雅鲁藏布缝合带Figure 1. Tectonic subdivision of the southern Tibetan Plateau (a) and simplified geological map of the Nie'erco area and samples location (b)LSSZ-Longmuco-Shuanghu suture zone; BNSZ-Bangonghu-Nujiang suture zone; SNMZ-Shiquan River-Namsto melange zone; LMF-Luobadui-Milashan Fault; IYZSZ-Indus-Yarlung Zangbo River suture zone
图 1 青藏高原南部构造单元划分图(a)和聂尔错地区地质简图及采样位置(b)LSSZ—龙木错—双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖—怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河—纳木错混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆—米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—雅鲁藏布缝合带Figure 1. Tectonic subdivision of the southern Tibetan Plateau (a) and simplified geological map of the Nie'erco area and samples location (b)LSSZ-Longmuco-Shuanghu suture zone; BNSZ-Bangonghu-Nujiang suture zone; SNMZ-Shiquan River-Namsto melange zone; LMF-Luobadui-Milashan Fault; IYZSZ-Indus-Yarlung Zangbo River suture zone受南侧新特提斯洋北向俯冲以及印度-欧亚板块碰撞过程的影响,在中南拉萨地块上广泛发育着的中—新生代的弧型岩浆活动(Chung et al., 2003, 2005; 莫宣学, 2011; Zhu et al., 2015, 2018; 孟元库等, 2018);而北拉萨地块上岩浆岩主要形成于中生代晚期,一般认为是班公湖—怒江洋俯冲消减以及拉萨—羌塘板块碰撞等构造演化过程的记录(Zhu et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2019a, b;Yu et al., 2022;吴浩等,2022)。由于远离南侧的雅鲁藏布缝合带,西藏中部受新特提斯洋俯冲以及印度—欧亚板块碰撞的影响相对较弱,新生代岩浆活动出露规模较小。近年来,在西藏中部陆续报道了始新世岩浆岩资料,这些岩浆岩多为壳源成因的中酸性火山岩,主要为区域上广泛分布的美苏组火山岩(E1-2m),最新的测年结果显示其形成时代与南侧始新世岩浆爆发的时间相一致(魏永峰等, 2018; 张耀玲等, 2018)。
本文研究区位于聂尔错以东约20 km(图 1),大地构造位置处于北拉萨地块之上,区内地层以侏罗系木嘎岗日岩群(JM)、上侏罗统—下白垩统沙木罗组(J3K1s)以及下白垩统郎山组(K1l)和多尼组(K1d)为主,规模巨大的早白垩世盐湖花岗岩体出露于研究区北部。在研究区中部的侏罗系—白垩系中沿构造裂隙发育着大量的中基性岩脉,然而这些岩脉的形成时代与成因不明,缺乏年代学与地球化学数据约束。本次研究的辉绿岩脉侵位于沙木罗组(J3K1s)砂岩之中,岩脉宽1 m左右,近东西向延伸达百米(图 2a),岩石呈灰白色,块状构造(图 2b),辉绿结构,岩石发生一定程度蚀变,矿物组成以辉石和基性斜长石为主,粒径一般0.5 mm左右,次要矿物见少量角闪石和黑云母等,副矿物有磁铁矿和磷灰石等(图 2c)。
3. 测试方法与结果
本次共采集1件年代学和4件地球化学样品进行年代学与全岩地球化学分析研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测定在吉林大学东北亚矿产资源评价国土资源部重点实验室利用Agilent 7900型ICP-MS仪器完成,测试结果见表 1。全岩主微量元素含量在武汉上谱分析科技有限责任公司完成,测试结果见表 2。主量元素含量利用日本理学PrimusⅡ X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)分析完成,微量元素含量利用Agilent 7700e ICP-MS分析完成。
表 1 聂尔错辉绿岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of Nie'erco diabases 表 2 聂尔错辉绿岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果Table 2. Analytical results of major (%) and trace elements(10-6)of Nie'erco diabases
表 2 聂尔错辉绿岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果Table 2. Analytical results of major (%) and trace elements(10-6)of Nie'erco diabases
3.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
辉绿岩锆石整体呈无色透明的短柱或长柱状,晶形完好,粒径100~200 μm,长宽比在2∶1左右(图 3)。本次共对17颗锆石进行测试分析工作,除去4颗99 Ma、101 Ma、115 Ma和180 Ma的古老捕获锆石外,13颗年轻锆石测点206Pb/238U年龄集中在50~52 Ma,在谐和图上(图 3)所有测点都落在谐和线上或其附近区域,获得13颗年轻锆石206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为(50.8±0.6)Ma(MSWD=0.64),此年龄代表了辉绿岩的形成时代。
3.2 全岩地球化学
辉绿岩样品整体具有低的SiO2(51.1%~54.6%),高的全碱(Na2O+K2O=5.93%~6.86%)、MgO(3.64%~4.46%)、Al2O3(16.9%~17.3%)和TiO2(1.14%~1.49%)含量。在岩石分类Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2图解中(图 4),大部分辉绿岩样品落在碱性玄武岩区域。在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线中,辉绿岩样品呈富集轻稀土元素、亏损重稀土元素的右倾模式((La/Yb)N=12~17),Eu负异常不明显(δEu=0.83~0.95)(图 5a)。在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中(图 5b),辉绿岩样品显示Rb、Ba等大离子亲石元素(LILEs)的富集以及Nb、Ta等高场强元素(HFSEs)的亏损。
![]() 图 4 Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2图解(a,据Pearce, 1996)和SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(b)(数据引自D'Orazio et al., 2001; Gorring et al., 2003; Espinoza et al., 2005; Ji et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2019a)Figure 4. Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2 diagram (a, after Pearce, 1996) and SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) diagram (b) (Data is from D'Orazio et al., 2001; Gorring et al., 2003; Espinoza et al., 2005; Ji et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2019a)
图 4 Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2图解(a,据Pearce, 1996)和SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(b)(数据引自D'Orazio et al., 2001; Gorring et al., 2003; Espinoza et al., 2005; Ji et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2019a)Figure 4. Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2 diagram (a, after Pearce, 1996) and SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) diagram (b) (Data is from D'Orazio et al., 2001; Gorring et al., 2003; Espinoza et al., 2005; Ji et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2019a)![]() 图 5 球粒陨石标准化稀土元素模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(OIB、E-MORB、N-MORB的平均值与微量元素的标准化值引自Sun and McDonough(1989),其他数据引用同图 4)OIB—洋岛玄武岩;N-MORB—亏损型洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋中脊玄武岩Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (b) (the average of OIB, E-MORB, N-MORB and normalized values of REE and trace elements are from Sun and McDonough (1989), other cited data is the same as Fig. 4)OIB-Oceanic island basalt; N-MORB-Normal mid-ocean ridge basalt; E-MORB-Enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt
图 5 球粒陨石标准化稀土元素模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(OIB、E-MORB、N-MORB的平均值与微量元素的标准化值引自Sun and McDonough(1989),其他数据引用同图 4)OIB—洋岛玄武岩;N-MORB—亏损型洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋中脊玄武岩Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (b) (the average of OIB, E-MORB, N-MORB and normalized values of REE and trace elements are from Sun and McDonough (1989), other cited data is the same as Fig. 4)OIB-Oceanic island basalt; N-MORB-Normal mid-ocean ridge basalt; E-MORB-Enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt4. 讨论
4.1 岩石成因
辉绿岩样品具有低硅、富铁、镁、钙的主量元素含量以及高铬、镍等微量元素含量,显示幔源岩浆岩的地球化学特征,幔源岩浆在上升侵位及岩浆房内演化的过程中会受到地壳物质的混染作用(Castillo et al., 1999),因此地壳混染是探讨辉绿岩岩石成因不可回避的问题。锆石中古老捕获锆石的出现指示岩浆在上升过程中受到围岩物质的混染。此外,地壳组分通常具有低的MgO含量、高La/Nb、Th/Nb比值以及明显的Nb、Ta亏损(Rudnick and Fountain, 1995),因此地壳混染过程往往会导致原始岩浆成分向地壳端元演化,在(La/Nb)N-(Th/Nb)N和Nb/U-Nd/Pb图解中(图 6),辉绿岩均表现出地壳成分参与成岩的特征,地壳混染也合理解释了辉长岩样品中明显的Nb、Ta亏损(Rudnick and Gao, 2003)。因此,地球化学特征指示聂尔错辉绿岩在侵位过程中应该经历了一定程度的地壳混染作用。
![]() PM—原始地幔;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;N-MORB—亏损型洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;LC—下地壳;MC—中地壳;UC—上地壳;CC—大陆地壳Figure 6. (La/Nb)N-(Th/Nb)N diagram (a, after Frey et al., 2002) and Nb/U-Nd/Pb diagram (b, after Ji et al., 2016) (the cited data is the same as Fig. 4)PM-Primitive Mantle; OIB-Oceanic island basalt; N-MORB-Normal mid-ocean ridge basalt; E-MORB-Enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt; LC-Lower crust; MC-Middle crust; UC-Upper crust; CC-Continental crust
PM—原始地幔;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;N-MORB—亏损型洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;LC—下地壳;MC—中地壳;UC—上地壳;CC—大陆地壳Figure 6. (La/Nb)N-(Th/Nb)N diagram (a, after Frey et al., 2002) and Nb/U-Nd/Pb diagram (b, after Ji et al., 2016) (the cited data is the same as Fig. 4)PM-Primitive Mantle; OIB-Oceanic island basalt; N-MORB-Normal mid-ocean ridge basalt; E-MORB-Enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt; LC-Lower crust; MC-Middle crust; UC-Upper crust; CC-Continental crust聂尔错辉绿岩具有明显的轻重稀土分异特征,显示OIB型岩石的地球化学亲缘性。在Ti-V图解中(图 7a),辉绿岩样品显示与典型OIB型岩石相似的特征;在TiO2-MnO-P2O5图解中(图 7b),辉绿岩样品同样落在洋岛碱性玄武岩区域。碱性洋岛型岩石通常起源与相对富集的地幔源区,是深部软流圈地幔上涌熔融的产物(Ferrari et al., 2001; Gorring et al., 2003; Sklyarov et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2019a)。近年来,西藏南部陆续报道了大量的始新世基性岩浆作用,这些基性岩石同样具有OIB型的地球化学特征,研究认为起源于深部的软流圈地幔(Ji et al., 2016)。因此,本文认为聂尔错辉绿岩同样是深部软流圈地幔部分熔融的产物。
![]() IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;OFB—大洋溢流玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;OIT—洋岛拉斑玄武岩;OIA—洋岛碱性玄武岩;CAB—钙碱性玄武岩Figure 7. Ti-V diagram (a, after Shervais, 1982) and TiO2-MnO-P2O5 diagram (b, after Mullen, 1983) (the cited data is the same as Fig. 4)IAT-Island arc tholeiite; MORB—Mid-ocean ridge basalt; OFB—Oceanic flood basalt; OIB—Oceanic island basalt; OIT—Oceanic island tholeiite; OIA—Oceanic island alkali basalt; CAB—Calc-alkaline basalt
IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;OFB—大洋溢流玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;OIT—洋岛拉斑玄武岩;OIA—洋岛碱性玄武岩;CAB—钙碱性玄武岩Figure 7. Ti-V diagram (a, after Shervais, 1982) and TiO2-MnO-P2O5 diagram (b, after Mullen, 1983) (the cited data is the same as Fig. 4)IAT-Island arc tholeiite; MORB—Mid-ocean ridge basalt; OFB—Oceanic flood basalt; OIB—Oceanic island basalt; OIT—Oceanic island tholeiite; OIA—Oceanic island alkali basalt; CAB—Calc-alkaline basalt4.2 构造背景
青藏高原岩浆岩广泛发育,其时空展布具有明显的规律性,是深部动力学过程的重要岩石学记录(Chung et al., 2003, 2005; 莫宣学, 2011; Zhu et al., 2011)。研究区位于西藏中部的北拉萨地块之上,区域上岩浆活动以早白垩世晚期—晚白垩世为主,其深部构造演化主要受到班公湖—怒江洋俯冲消减以及拉萨—羌塘陆陆碰撞过程的影响(Zhu et al., 2011, 2016; Pan et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2018, 2019a, b; Liu et al., 2019),大量的研究资料支持班公湖—怒江洋在早白垩世早期已经消亡(Kapp et al., 2007; Raterman et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2017; Li et al., 2018),而早白垩世晚期—晚白垩世大规模的岩浆爆发应该形成于碰撞后伸展背景,其深部动力学机制与洋盆闭合后的板片断离与增厚岩石圈拆沉相关(Zhu et al., 2011, 2016; Wu et al., 2018, 2019a, b)。在晚白垩世之后区域岩浆活动减弱,拉萨地块与羌塘板块拼合成为一体,西藏中部进入板内演化阶段。在Zr-Zr/Y图解和Nb-Zr-Y图解中(图 8),聂尔错辉绿岩样品均落在板内玄武岩区域,进一步表明西藏中部在始新世处于相对稳定的板内环境。
![]() AI—板内碱性玄武岩;AII—板内碱性和拉斑玄武岩;B—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;C—板内拉斑和弧型玄武岩;D—亏损型洋中脊玄武岩和弧型玄武岩Figure 8. Zr-Zr/Y diagram (a, after Pearce and Norry, 1979) and Nb×2-Zr/4-Y diagram (b, after Meschede, 1986) (the cited data is the same as Fig. 4)AI-Within-plate basalt; AII-Within-plate alkaline and within-plate tholeiite; B-Enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt; C-Within-plate basalt and volcanic arc basalt; D-Normal mid-ocean ridge basalt and volcanic arc basalt
AI—板内碱性玄武岩;AII—板内碱性和拉斑玄武岩;B—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;C—板内拉斑和弧型玄武岩;D—亏损型洋中脊玄武岩和弧型玄武岩Figure 8. Zr-Zr/Y diagram (a, after Pearce and Norry, 1979) and Nb×2-Zr/4-Y diagram (b, after Meschede, 1986) (the cited data is the same as Fig. 4)AI-Within-plate basalt; AII-Within-plate alkaline and within-plate tholeiite; B-Enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt; C-Within-plate basalt and volcanic arc basalt; D-Normal mid-ocean ridge basalt and volcanic arc basalt4.3 地球动力学机制
新特提斯洋构造演化史的研究一直是国内外学者关注的热点,其中印度-欧亚大陆的陆陆碰撞时限是众多学者关注的热点问题(Garzanti et al., 1987; Dewey et al., 1989; Yin and Harrison, 2000; Hu et al., 2016)。大量的年代学数据指示拉萨地块南缘在始新世早期(约50 Ma)存在大规模的岩浆爆发活动,其岩石地球化学特征以中酸性钙碱性岩石为主(孟元库等, 2015, 2018),早期的研究提出该期岩浆作用是新特提斯洋北向俯冲引发的弧形岩浆作用(Schärer et al., 1984; Searle et al., 1987),而近年来综合不同学科的研究资料揭示始新世早期岩浆爆发应该是印度—欧亚板块陆陆碰撞过程的产物(Wen et al., 2008;Ji et al., 2009,2016;莫宣学,2011;Zhu et al., 2015,2018;陈兰朴等,2019)。
近年来,众多学者在拉萨地块南缘识别了大量的基性岩浆活动(Dong et al., 2005;岳亚慧和丁林,2006;Ji et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2017;王旭辉等,2019),测年结果显示这些基性岩浆作用同样形成于始新世早期(57~47 Ma),地球化学特征显示OIB型岩石的亲缘性。OIB型岩石的形成通常与深部软流圈地幔上涌相关,可以形成于地幔柱或者板片窗等构造背景(Hole et al., 1991;Ferrari et al., 2001;Hawkesworth and Schersten, 2007;Wu et al., 2019a),考虑到始新世岩浆作用在西藏南部呈条带状展布,而且在西藏中部零星出露,这与地幔柱引发的岩浆岩展布形态并不相符。而在陆陆碰撞过程中,俯冲板片的前缘发生断离以及增厚的岩石圈发生拆沉均会导致深部软流圈地幔上涌并发生减压熔融,形成具有OIB型岩石(Ji et al., 2016;Wu et al., 2019a)。通常增厚岩石圈拆沉会伴随着大规模的埃达克质岩浆爆发,而大量的岩浆岩年代学与地球化学数据指示印度—欧亚板块碰撞形成的增厚岩石圈于渐新世发生拆沉(Chung et al., 2003,2009)。大陆动力学研究提出在板块汇聚带陆陆碰撞过程中,高密度的洋壳会拖曳低密度的陆壳进入地幔深度,而二者之间的浮力差会导致洋壳最终会从陆壳边缘发生断离,并在深部形成板片窗,即板片断离过程(Davies and von Blanckenburg,1995;van Hunen and Allen, 2011; Wu et al., 2016, 2019a)。板片窗的打开会直接导致深部软流圈地幔上涌,同时诱导上覆岩石圈发生熔融,形成平行于板块缝合带的带状岩浆活动,这与拉萨地块南缘近东西向发育的始新世林子宗火山岩相一致(潘桂棠等, 2006; 莫宣学,2011; 朱弟成等, 2017)。此外,重力和远源地震数据指示印度大陆岩石圈边缘并不存在大洋岩石圈板片(Jin et al., 1996),表明俯冲前缘洋壳已经从陆壳边缘发生断离(朱弟成等, 2017)。因此,本文认为板片断离机制是拉萨地块上始新世岩浆活动最为合理的深部地球动力学解释(图 9)。
![]() 图 9 青藏高原始新世构造-岩浆演化示意图(修改自Ji et al., 2016)Figure 9. Schematic illustration of the Eocene tectonic-magmatic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau(modified from Ji et al., 2016)
图 9 青藏高原始新世构造-岩浆演化示意图(修改自Ji et al., 2016)Figure 9. Schematic illustration of the Eocene tectonic-magmatic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau(modified from Ji et al., 2016)尽管远离雅鲁藏布缝合带,本次在北拉萨地块上新获得的辉绿岩资料表明印度—欧亚板块碰撞过程对西藏中部地区的构造-岩浆作用同样产生了一定的影响。最近,在西南天山柯坪地区识别的萨尔干基性岩脉中同样获得了始新世早期的年龄信息((49.1±0.8)Ma),其地球化学组成同样显示OIB型岩石的特征(霍海龙等, 2019)。这些远离俯冲带的OIB型岩石的识别表明新特提斯洋俯冲前缘洋壳在始新世早期板片断离之后,深部软流圈地幔从板片窗快速上涌并逐渐向北运移,不仅在拉萨地块南部形成了岩浆爆发事件,同样在西藏中部乃至天山地区同样引发了一定程度的岩浆活动,最终形成了在青藏高原上广泛发育的始新世岩浆岩。
5. 结论
(1)西藏中部聂尔错地区新识别的辉绿岩中获得了(50.8±0.6)Ma的锆石U-Pb谐和年龄,与藏南地区始新世早期岩浆作用时代相一致。
(2)辉绿岩样品整体显示碱性OIB型岩石的地球化学特征,是深部软流圈地幔上涌减压熔融的产物,其深部动力学机制应该与南侧印度—欧亚板块碰撞后深俯冲的新特提斯洋洋壳板片断离过程相关。
(3)聂尔错地区始新世早期OIB型辉绿岩的识别,结合近年来同时期岩浆作用的报道,指示新特提斯洋板片断离过程对西藏中部构造-岩浆作用同样产生了重要的影响。
-
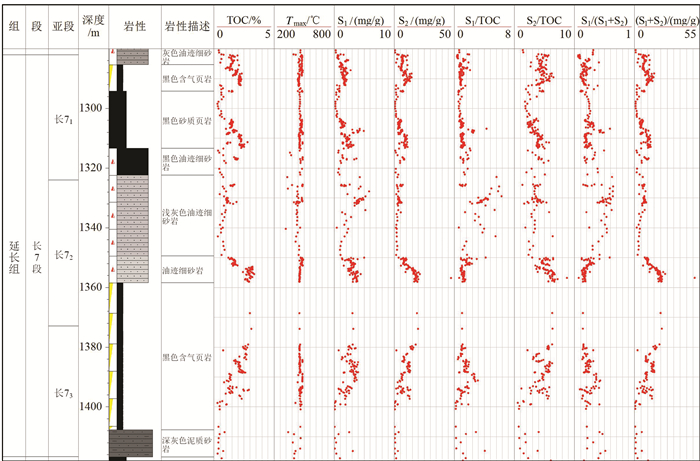
表 1 延安地区延长组长7段页岩岩样抽提分析
Table 1 Extraction analysis of Chang 7 shale samples of Yanchang Formation in Yan'an area

-
Chalmers G R L, Bustin R M. 2007. The organic matter distribution and methane capacity of the Lower Cretaceous strata of northeastern British Columbia[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 70: 223-239. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2006.05.001
Cheng Ming, Luo Xiaorong, Lei Yuhong, Wang Xiangzeng, Yu Yuxi, Zang Lixia, Jiang Chengfu, Sun Binghua, Zhang Likuan. 2015. The distribution, fractal characteristic and thickness estimation of silty laminae and beds in the Zhangjiatan shale, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 26(5): 845-854 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Curtis M E, Sondergeld C H, Ambrose R J. 2012. Microstructural investigation of gas shales in two and three dimensions using nanometer-scale resolution imaging [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 96(4): 665-677. doi: 10.1306/08151110188
Curtis M Erman, Ambrose R J, Sondergeld C H. 2011. Investigation of the relationship between organic porosity and thermal maturity in the Marcellus Shale[R]. SPE 144370.
Fan Bojiang, Wang Xiangzeng, Wu Xiaobin. 2017. Desorption analysis of shale and its geochemical characteristics: A case study of the Chang 7 member shale in the central south Ordos basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 46(3): 554-562, 577 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fishman N S, Lowers H A, Hackley P C, Hill R J, Egenhoff S O. 2012. Porosity in shales of the organic-rich Kimmeridge clay formation(Upper Jurassic), offshore United Kingdom[R]. Long Beach, California: AAPG Annual Convention and Exhibition.
Guo Tonglou, Zhang Hanrong. 2014. Formation and enrichment mode of Jiaoshiba shale gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(1): 28-36(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Xusheng, Hu Dongfeng, Wen Zhidong, Liu Ruobing. 2014. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity in marine shale gas in the Lower Paleozoic of Sichuan Basin and its periphery: A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation of Jiaoshiba area[J]. Geology in China, 41(3): 893-901(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.03.016
He Zhiliang, Nie Haikuan, Zhang Yuying. 2016. The main factors of shale gas enrichment of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(2): 8-17(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Chengfu, Cheng Yuqun, Fan Bojiang, Gao Shengli. 2014. Progress in and challenges to geologic research of terrestrial shale in China: A case study from the 7th member of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Fm in the Yanchang exploration block, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(2): 27-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.02.004
Jin Zhijun, Hu Zongquan, Gao Bo, Zhao Jianhua. 2016. Controlling factors on the enrichment and high productivity of shale gas in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lei Yuhong, Luo Xiaorong, Wang Xiangzeng, Zhang Lixia, Jiang Chengfu, Yang Wan, Yu Yuxi, Cheng Ming, Zhang Likuan. 2015. Characteristics of silty laminae in Zhangjiatan Shale of southeastern Ordos Basin, China: Implications for shale gas formationc[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 99 (4): 661-687. doi: 10.1306/09301414059
Li Qianwen, Pang Xiongqi, Tang Ling, Chen Gang, Shao Xinhe, Jia Nan. 2018. Occurrence features and gas content analysis of marine and continental shales: A comparative study of Longmaxi Formation and Yanchang Formation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 56: 504-522. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.06.019
Li Yanjun, Liu Huan, Liu Jiaxia, Cao Lichun, Jia Xuecheng. 2011. Geological regional selection and an evaluation method of resource potential of shale gas[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University, 33(2): 28-34. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2011.02.004
Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, Jarvie D M. 2009. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the mississippian barnett shale[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 79: 848-861. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.092
Lu Longfei, Qin Jianzhong, Shen Baojian, Tenger, Liu Weixin, Zhang Qingzhen. 2018. The origin of biogenic silica in siliceous shale from Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in the Middle and Upper Yangtze region and its relationship with shale gas enrichment[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(4): 226-236(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Yongsheng, Cai Xunyu, Zhao Peirong. 2018. China's shale gas exploration and development: Understanding and practice[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(4): 561-574(in Chinese with English abstract).
Modica C J, Lapierre S G. 2012. Estimation of kerogen porosity in source rocks as a function of thermal transformation: Example from the Mowry Shale in the Powder River Basin of Wyoming[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 96(1): 87-108. doi: 10.1306/04111110201
Orozco D, Aguilera R. 2015. A material balance equation for stress-sensitive shale gas reservoirs considering the contribution of free, adsorbed and dissolved gas[C]//SPE/CSUR Unconventional Resources Conference. Society of Petroleum Engineers.
Pan Renfang, Gong Qin, Yan Jie, Jin Jineng. 2016. Elements and gas enrichment laws of sweet spots in shale gas reservoir: A case study of the Longmaxi Fm in Changning Block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 36(2): 7-13(in Chinese with English abstract).
Pollastro R M. 2007. Total petroleum system assessment of undiscovered resources in the giant Barnett Shale continuous(unconventional) gas accumulation, Fort Worth Basin, Texas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 91(4): 551-578. doi: 10.1306/06200606007
Pu Boling, Wang Fengqin, Dong Dazhong, Sun Jianbo. 2021. Challenges of terrestrial shale gas exploration & development from Chang 7 shale in the Ordos Basin[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14: 644. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-06914-w
Ross D J K, Bustin R M. 2008. Characterizing the shale gas resource potential of Devonian Mississippian strata in the Western Canada sedimentary basin: Application of an integrated formation evaluation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 92(1): 87-125. doi: 10.1306/09040707048
Schieber J. 2010. Common themes in the formation and preservation of intrinsic porosity in shales and mudstones-illustrated with examples across the Phanerozoic[C]//Proceedings of SPE Unconventional Gas Conference. Allen, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineerings, SPE 132370.
Wang Pengfei, Lü Peng, Jiang Zhenxue, Jin Can, Li Xin, Zhang Kun, Huang Pu, Wang Yi. 2018. Comparison of organic matter pores of marine and continental facies shale in China: based on Focused Ion Beam Helium Ion Microscopy(FIB-HIM) [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 40(5): 739-748(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Shejiao, Yang Tao, Zhang Guosheng, Li Denghua, Chen Xiaoming. 2012. Shale gas enrichment factors and the selection and evaluation of the core area[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 14(6): 94-100 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.06.013
Wang Xiangzeng. 2016. Advances in unconventional gas exploration and development of Yanchang Petroleum Group[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(1): 137-144 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiangzeng, Gao Chao. 2014. The hydrocarbon generation process of the Mesozoic Chang 7 lacustrine shale in south of Ordos Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 1(1): 2-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiangzeng, Gao Shengli, Gao Chao. 2014. Geological features of Mesozoic continental shale gas in south of Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(3): 294-304(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(14)60035-5
Wang Xiangzeng, Hao Jin, Jiang Zhenxue, Guo Chao, Xing Jinyan, Li Zhuo, Tang Xianglu. 2015. Influencing factors and distributions of the oil dissolved shale gas content of member Chang 7 shale in Xiasiwan Area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 26(4): 744-753 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiangzeng, Ren Laiyi. 2016. Advances in theory and practice of hydrocarbon exploration in Yanchang exploration area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(1): 79-86(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yongwei, Gao Shengli, Gao Chao. 2014. Continental shale gas exploration and discussion on Issues related to geological theory in Yanchang exploration area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 33(6): 88-98 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Songtao, Zhu Rukai, Cui Jinggang, Cui Jingwei, Bai Bin, Zhang Xiangxiang, Jin Xu, Zhu Desheng, You Jianchang. 2015. Characteristics of lacustrine shale porosity evolution, Triassic Chang 7 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(2): 167-176(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(15)30003-3
Xie Jun, Zhao Shengxian, Shi Xuewen, Zhang Jian. 2017. Main geological factors controlling high production of horizontal shale gas wells in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 37(7): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan Wei, Liu Guangdi, Xu Liming, Niu Xiaobing. 2019. Main controlling factors for organic matter enrichment in Chang 7 member of the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 40(2): 326-334(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Weite, Zhang Jinchuan, Ding Wenlong, Wang Xiangzeng, Zhu Dingwei, Liu Zhujiang. 2014. The gas content of continental Yanchang shale and its main controlling factors: A case study of Liuping-171 well in Ordos basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(2): 291-301 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhai Gangyi, Wang Yufang, Bao Shujing, Guo Tianxu, Zhou Zhi, Chen Xianglin, Wang Jinzhu. 2017. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity of marine shale gas and prospect forecast in Southern China[J]. Earth Science, 42(7): 1057-1068(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jian, Wang Lansheng, Yang Yueming, Wan Maoxia, Zhou Chunyan, Deng Hongbin, Kong Lingming. 2016. The development and application of the evaluation method of marine shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 27(3): 433-441(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jinchuan, Liu Shugen, Wei Xiaoliang, Tang Xuan, Liu Yang. 2021. Evaluation of gas content in shale[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 42(1): 28-40(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Wenzheng, Yang Hua, Yang Weiwei, Wu Kai, Liu Fei. 2015. Assessment of geological characteristics of lacustrine shale oil reservoir in Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Geochimica, 44(5): 505-515(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Xiangyuan, Zeng Lianbo, Zu Kewei, Hu Xiangyang, Jiao Jun, Zhu Lifeng, Shi Jinxiong. 2016. Brittleness characteristics and its control on natural fractures in tight reservoirs: A case study from Chang 7 tight reservoir in Longdong area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 37(1): 62-71(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Tong, Wang Feng, Yu lingjie, Sun Runxuan. 2016. Controlling factors and types of shale gas enrichment in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 37(3): 399-407(in Chinese with English abstract).
程明, 罗晓容, 雷裕红, 王香增, 俞雨溪, 张丽霞, 姜呈馥, 孙兵华, 张立宽. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地张家滩页岩粉砂质夹层/纹层分布、分形特征和估算方法研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 26(5): 845-854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201505008.htm 范柏江, 王香增, 吴小斌. 2017. 页岩的气体解析特征及地球化学认识——以鄂尔多斯盆地中南部长7段页岩为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 46(3): 554-562, 577. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201703015.htm 郭彤楼, 张汉荣. 2014. 四川盆地焦石坝页岩气田形成与富集高产模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 41(1): 28-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201401003.htm 郭旭升, 胡东风, 文治东, 刘若冰. 2014. 四川盆地及周缘下古生界海相页岩气富集高产主控因素: 以焦石坝地区五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 中国地质, 41(3): 893-901. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20140316?st=search 何治亮, 聂海宽, 张钰莹. 2016. 四川盆地及其周缘奥陶系五峰组-志留系龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素分析[J]. 地学前缘, 23(2): 8-17 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602004.htm 姜呈馥, 程玉群, 范柏江, 高胜利. 2014. 陆相页岩气的地质研究进展及亟待解决的问题——以延长探区上三叠统延长组长7段页岩为例[J]. 天然气工业, 34(2): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201402004.htm 金之钧, 胡宗全, 高波, 赵建华. 2016. 川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气富集与高产控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 23(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601002.htm 李延钧, 刘欢, 刘家霞, 曹利春, 贾学成. 2011. 页岩气地质选区及资源潜力评价方法[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 33(2): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201102003.htm 卢龙飞, 秦建中, 申宝剑, 腾格尔, 刘伟新, 张庆珍. 2018. 中上扬子地区五峰组-龙马溪组硅质页岩的生物成因证据及其与页岩气富集的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 25(4): 226-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201804022.htm 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 2018. 国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 45(4): 561-574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804004.htm 潘仁芳, 龚琴, 鄢杰, 金吉能. 2016. 页岩气藏"甜点" 构成要素及富气特征分析——以四川盆地长宁地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 36(2): 7-13 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201603003.htm 王朋飞, 吕鹏, 姜振学, 金璨, 李鑫, 张昆, 黄璞, 王毅. 2018. 中国海陆相页岩有机质孔隙发育特征对比——基于聚焦离子束氦离子显微镜(FIB-HIM)技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 40(5): 739-748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201805019.htm 王社教, 杨涛, 张国生, 李登华, 陈晓明. 2012. 页岩气主要富集因素与核心区选择及评价[J]. 中国工程科学, 14(6): 94-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX201206012.htm 王香增. 2016. 延长石油集团非常规天然气勘探开发进展[J]. 石油学报, 37(1): 137-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201601016.htm 王香增, 高潮. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部长7陆相泥页岩生烃过程研究[J]. 非常规油气, 1(1): 2-10. 王香增, 高胜利, 高潮. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部中生界陆相页岩气地质特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 41(3): 294-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403007.htm 王香增, 郝进, 姜振学, 郭超, 邢金艳, 李卓, 唐相路. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地下寺湾地区长7段油溶相页岩气量影响因素及其分布特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 26(4): 744-753. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201504021.htm 王香增, 任来义. 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区油气勘探理论与实践进展[J]. 石油学报, 37(增刊1): 79-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2016S1008.htm 王永炜, 高胜利, 高潮. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区陆相页岩气勘探[J]. 地质科技情报, 33(6): 88-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201406013.htm 吴松涛, 朱如凯, 崔京钢, 崔景伟, 白斌, 张响响, 金旭, 朱德升, 游建昌. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7湖相泥页岩孔隙演化特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 42(2): 167-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201502006.htm 谢军, 赵圣贤, 石学文, 张鉴. 2017. 四川盆地页岩气水平井高产的地质主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 37(7): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201707004.htm 袁伟, 柳广弟, 徐黎明, 牛小兵. 2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段有机质富集主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 40(2): 326-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201902012.htm 曾维特, 张金川, 丁文龙, 王香增, 朱定伟, 刘珠江. 2014. 延长组陆相页岩含气量及其主控因素——以鄂尔多斯盆地柳坪171井为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 25(2): 291-301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201402021.htm 翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 包书景, 郭天旭, 周志, 陈相霖, 王劲铸. 2017. 我国南方海相页岩气富集高产主控因素及前景预测[J]. 地球科学, 42(7): 1057-1068 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707002.htm 张鉴, 王兰生, 杨跃明, 万茂霞, 邹春艳, 邓鸿斌, 孔令明. 2016. 四川盆地海相页岩气选区评价方法建立及应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 27(3): 433-441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603007.htm 张金川, 刘树根, 魏晓亮, 唐玄, 刘飏. 2021. 页岩含气量评价方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 42(1): 28-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101004.htm 张文正, 杨华, 杨伟伟, 吴凯, 刘飞. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7湖相页岩油地质特征评价[J]. 地球化学, 44(5): 505-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201505010.htm 赵向原, 曾联波, 祖克威, 胡向阳, 焦军, 朱利锋, 史今雄. 2016. 致密储层脆性特征及对天然裂缝的控制作用——以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7致密储层为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 37(1): 62-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201601010.htm 朱彤, 王烽, 俞凌杰, 孙润轩. 2016. 四川盆地页岩气富集控制因素及类型[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 37(3): 399-407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201603014.htm -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴凯,高娟琴,解古巍,杨伟伟,罗丽荣,李善鹏. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段页岩气储层特征及其勘探开发前景. 石油实验地质. 2024(06): 1298-1311 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: