Development stage of Jurassic Che-Mo Paleouplift in the Junggar Basin and its constraints on sedimentary system
-
摘要:研究目的
准噶尔盆地车—莫同沉积古隆起是影响侏罗系结构样式和储层分布特征的重要地貌单元,研究其发育过程有利于认识准噶尔盆地盆山耦合关系和油气藏的聚集规律。
研究方法本文基于盆地腹部41口井的测井数据和地震资料,对侏罗系砂体和地层结构进行了详细分析和等时性对比,重点阐述车—莫古隆起阶段性发育与准噶尔盆地周缘造山带,尤其是博格达山的协同演化及这种协同演化对盆地边界和沉积格局等的影响。
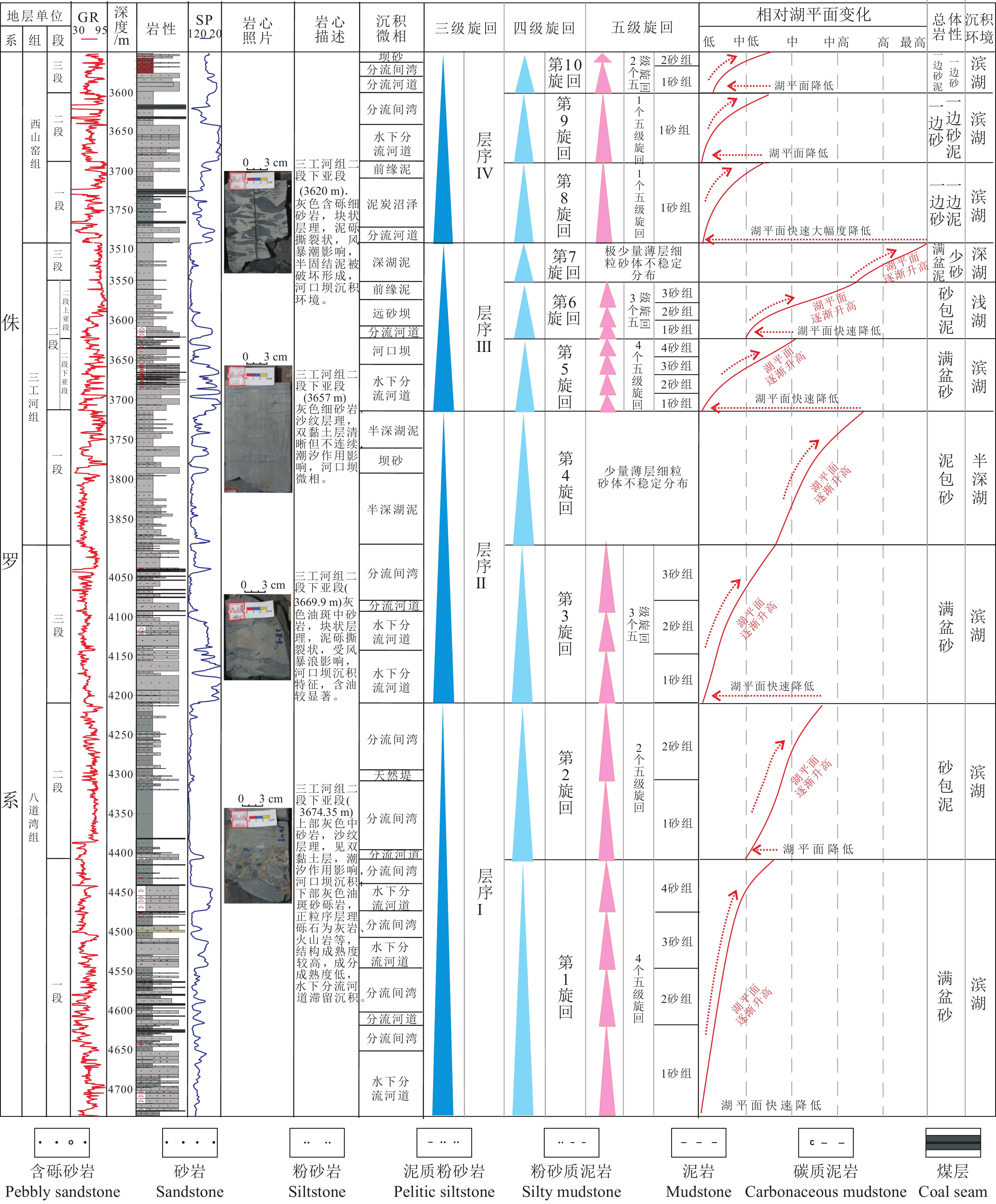
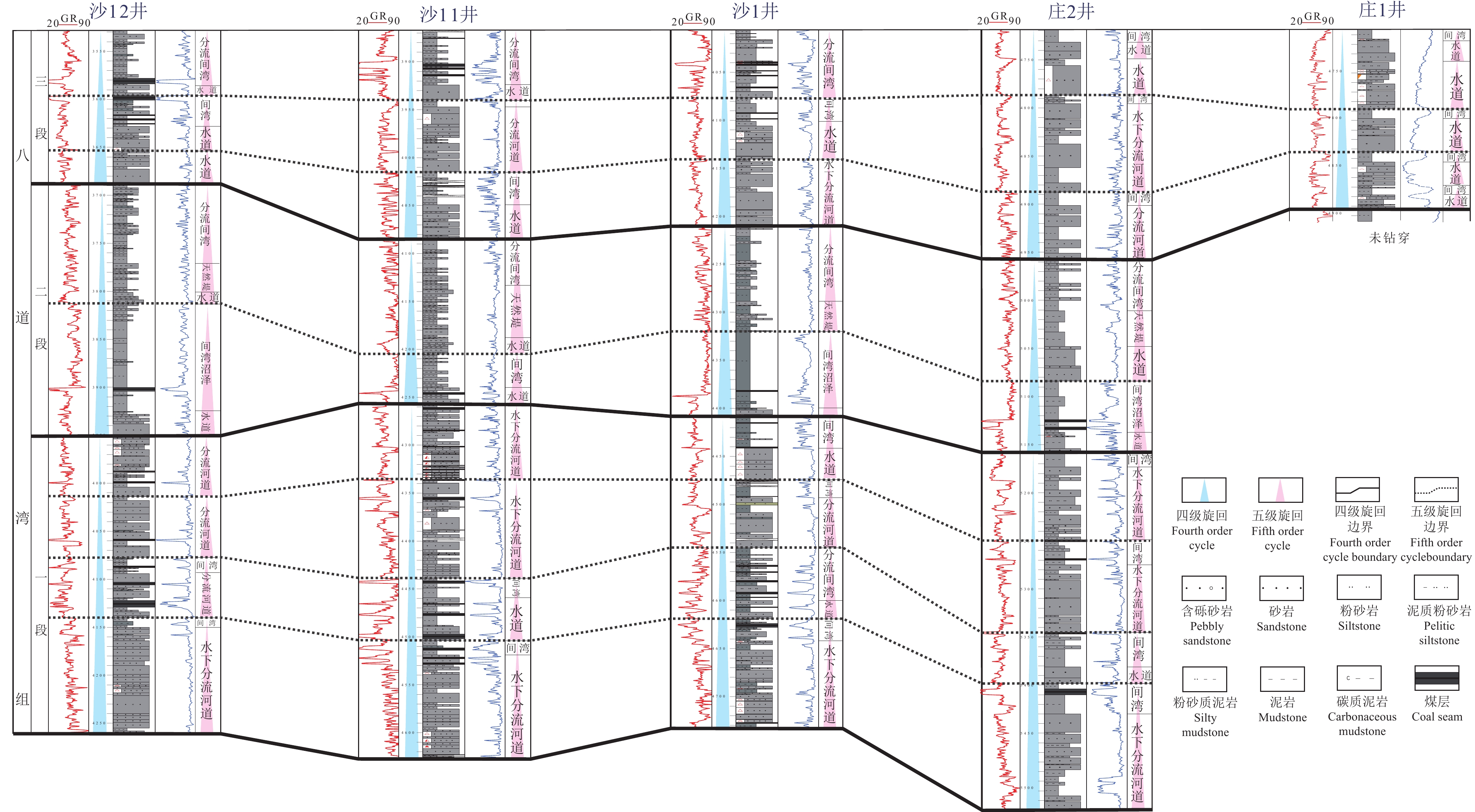
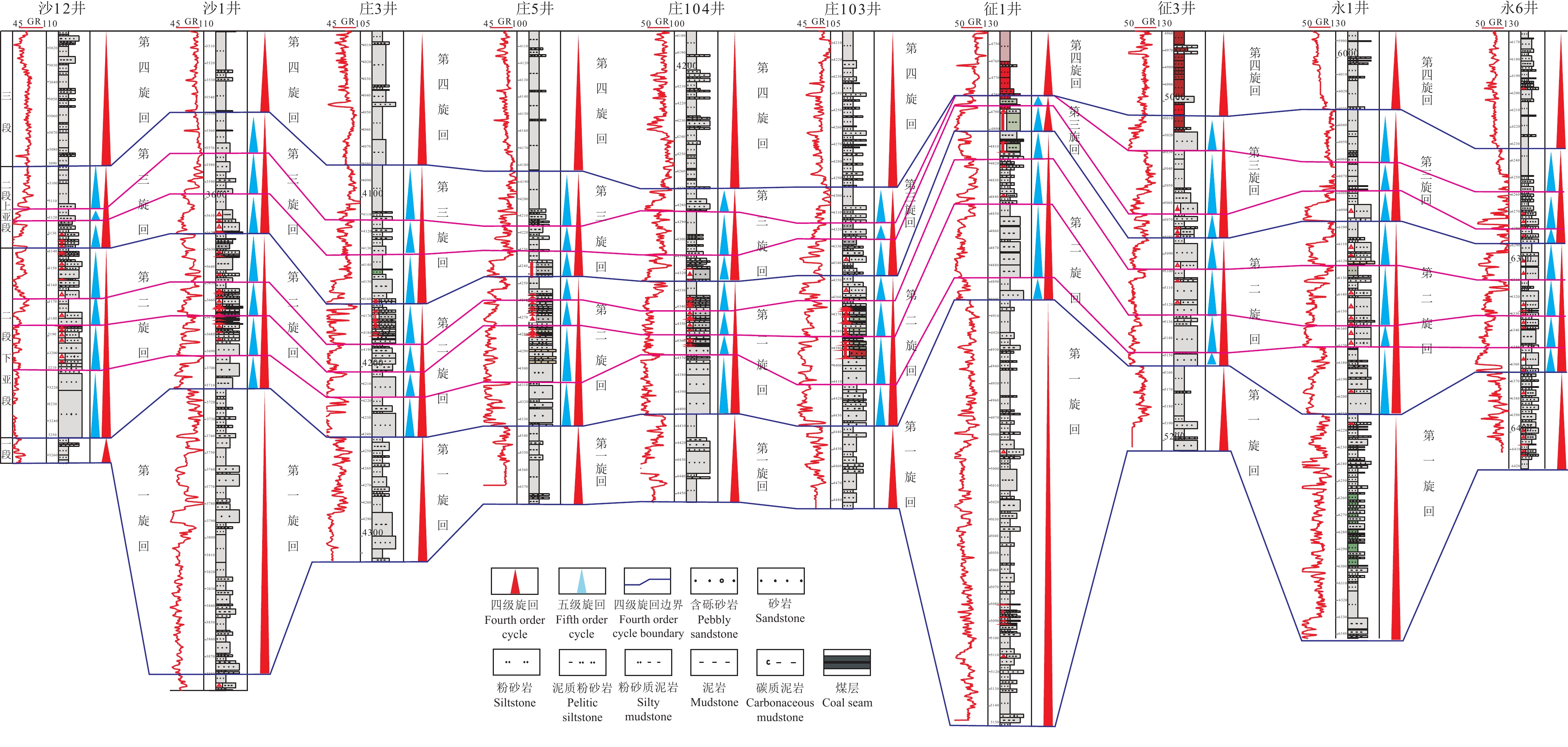
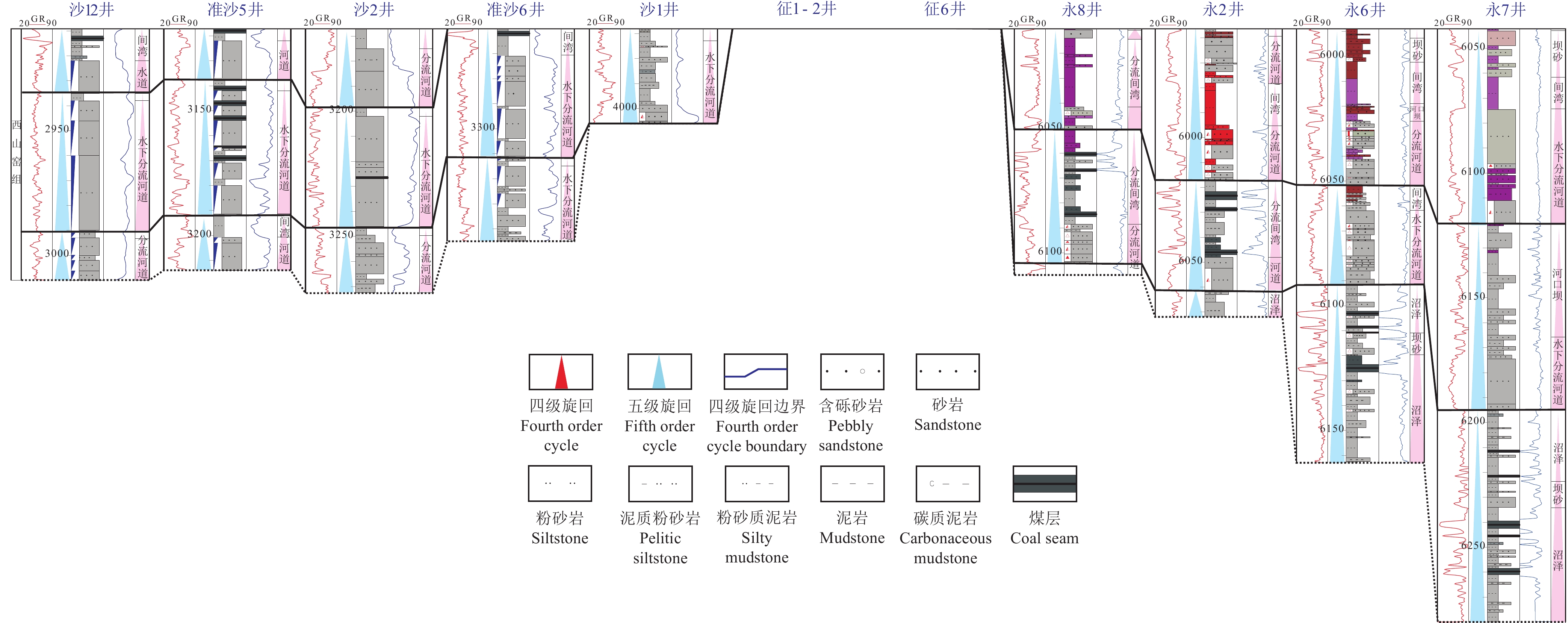
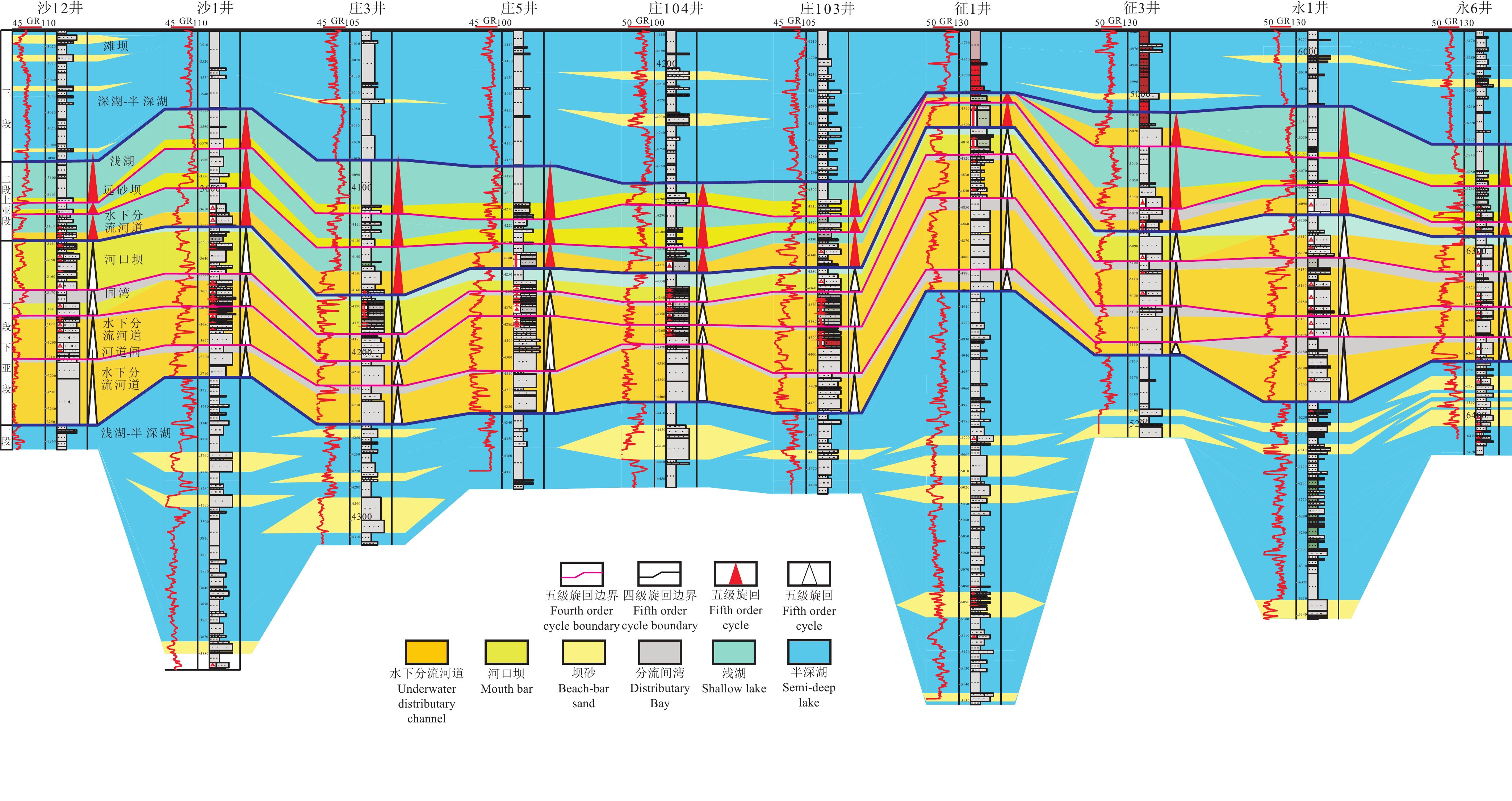
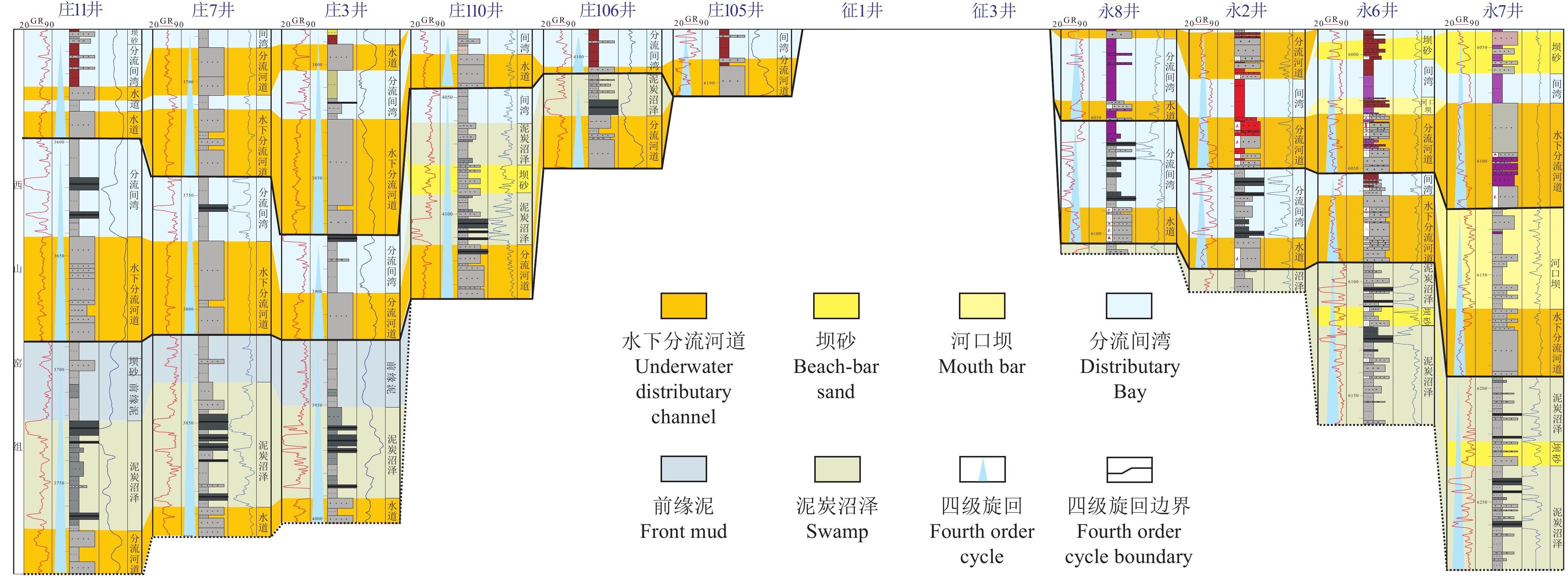
研究结果车—莫古隆起在侏罗纪的演化可划分为初始发育、快速隆升和隆升后剥蚀等三个阶段。早侏罗世车—莫古隆起的初始发育对八道湾组和三工河组展布和结构样式没有影响或影响很小,研究区由西北部扎伊尔山和东北部克拉美丽山供源,主要形成辫状河三角洲沉积体系;中侏罗世为车—莫古隆起的快速隆升阶段,除了西北部扎伊尔山和东北部克拉美丽山供源之外,博格达山也同步隆出水面开始供源,导致盆地边界、地层分布及结构样式的重大转变,使得西山窑组一段、二段大面积超覆、西山窑组三段沉积缺失或遭受剥蚀,沉积体系也随之发生转变,形成辫状河三角洲和滩坝共存的沉积体系组合;中侏罗世晚期和晚侏罗世车—莫古隆起隆升出水面则导致头屯河组和齐古组的剥蚀缺失,形成了与白垩系的区域不整合面。
结论车—莫古隆起在侏罗纪的形成和演化不仅影响到盆地的沉积地貌,也使盆地边界、物源格局发生重大改变,并导致沉积体系、地层结构样式和分布规律等的显著变化。
创新点:探讨了车—莫古隆起阶段性发育与准噶尔盆地周缘造山带,尤其是博格达山的协同演化及这种协同演化对盆地边界和沉积格局等的影响。
Abstract:This paper is the result of oil and gas exploration engineering.
ObjectiveChe−Mo synsedimentary paleouplift in Junggar basin is an important geomorphic unit that affects the structural style and reservoir distribution characteristics of Jurassic. The study of its development process is helpful to understand the basin mountain coupling relationship and the accumulation law of oil and gas reservoirs in Junggar basin.
MethodsBased on the logging data and seismic data of 41 wells in the abdomen of the basin, this paper makes a detailed analysis and isochronous comparison of Jurassic sand body and stratigraphic structure, and focuses on the synergistic evolution between the phased development of Che−Mo paleouplift and the orogenic belt around Junggar basin, especially Bogda mountain, and its influence on the basin boundary and sedimentary pattern.
ResultsThe evolution of Che−Mo paleouplift can be divided into three stages: initial development stage, rapid uplift stage and post uplift denudation stage. The initial development stage of Early Jurassic Che−Mo paleouplift has no or little influence on the distribution and structural style of Badaowan Formation and Sangonghe Formation. The study area is supplied by Zhayier mountain in the northwest and Kelameili mountain in the northeast, mainly forming braided river delta sedimentary system; The Middle Jurassic was the rapid uplift stage of Che−Mo paleouplift. In addition to the source supply of Zhayier mountain in the northwest and Kelameili mountain in the northeast, Bogda mountain also rose out of the water at the same time and began to supply the source, resulting in significant changes in basin boundary, stratigraphic distribution and structural style, resulting in large−area overlap of the first and second members of Xishanyao Formation, loss or denudation of the third members of Xishanyao Formation, The sedimentary system combination of Braided River Delta and beach bar is formed; The uplift of Che−Mo paleouplift in late Middle Jurassic and late Jurassic resulted in the denudation loss of Toutunhe Formation and Qigu Formation, forming a regional unconformity with Cretaceous.
ConclusionsThe formation and evolution of Che−Mo paleouplift in Jurassic not only affected the sedimentary landform of the basin, but also significantly changed the basin boundary and provenance pattern, and led to significant changes in sedimentary system, stratigraphic structure style and distribution law.
-
Keywords:
- Che−Mo paleouplift /
- Jurassic /
- sedimentary system /
- tectonic evolution /
- Junggar Basin
Highlights:The co-evolution of the staged development of the Che−Mo paleouplift and the orogenic belt around the Junggar Basin, especially the Bogda Mountains, and the impact of this co-evolution on the basin boundary and sedimentary pattern are discussed.
-
-
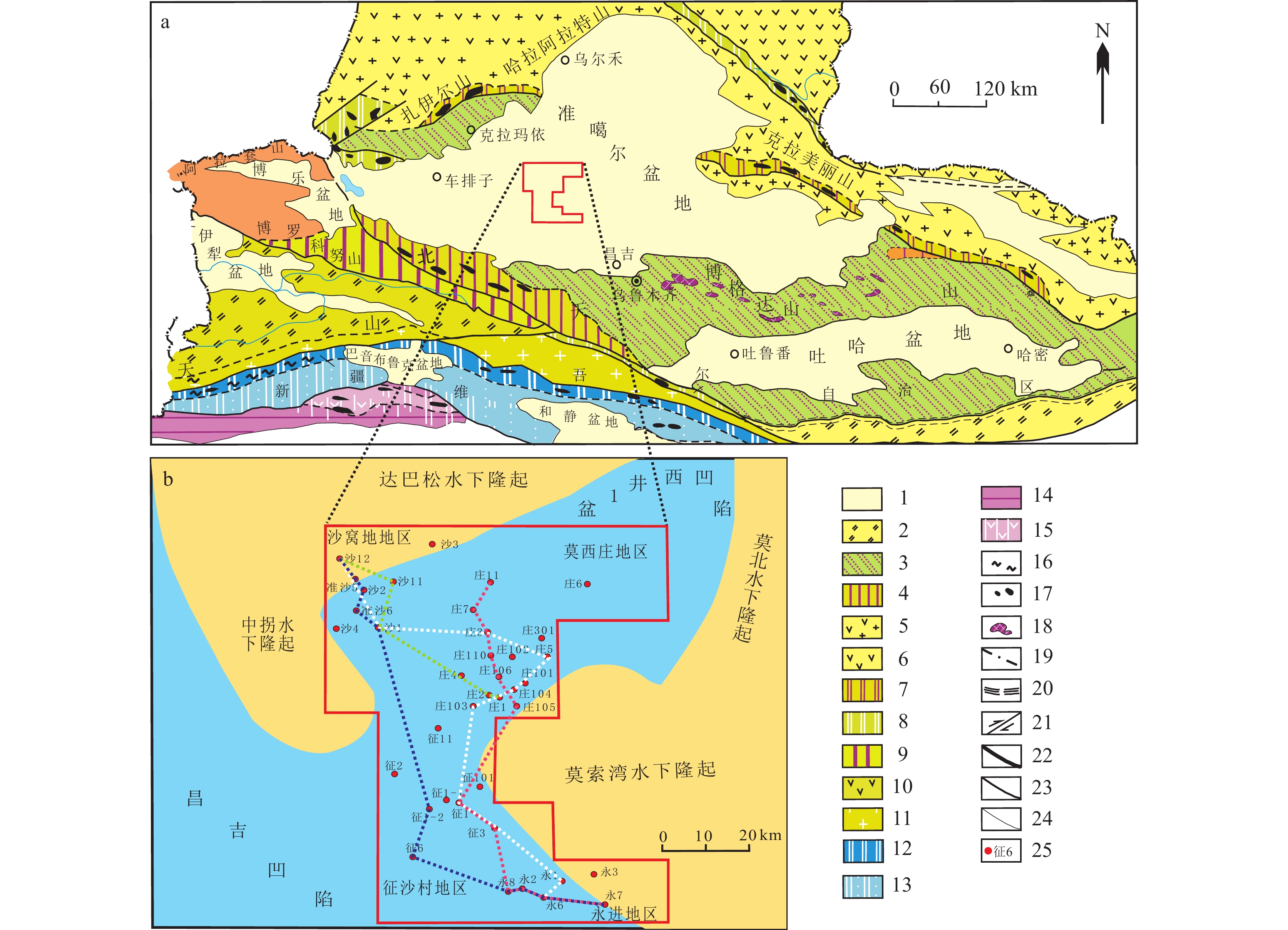
图 1 准噶尔盆地的位置及区域地质背景(a据徐学义等,2016修改)
1—中新生代盆地;2—前南华系基底上板内裂谷;3—古生代褶皱基底上板内裂谷;4—红海式裂谷;5—火山弧+岩浆弧;6—火山岛弧;7—早中泥盆世洋壳残片带;8—早古生代弧盆系及蛇绿混杂岩带;9—外陆棚沉积盆地;10—火山岛弧;11—岩浆弧;12—缝合带(蛇绿混杂岩带);13—弧前增生楔;14—上叠盆地;15—陆缘裂谷;16—高压及超高压变质岩;17—超镁铁质岩;18—辉长岩及辉长-辉绿岩;19—地球物理探测的断裂带;20—韧性断裂带;21—走滑断裂;22—缝合带边界断裂及一级构造单元边界断裂;23—二级构造单元边界断裂;24—三级构造单元边界断裂及区域性大型断裂;25—井位及井号
Figure 1. The location and regional geological background of the Junggar Basin(Fig.a modified from Xu Xueyi et al., 2016)
1−Meso−Cenozoicbasin; 2−Intraplate rift on the Prenanhua basement system; 3−Intraplate rift onPaleozoic foldedbasement; 4−Red Sea type rift; 5−Volcanic arc+Magmatic arc; 6−Volcanic island−arc; 7−Early−Middle Devonian oceanic crustal debris belt; 8−Early Paleozoic arc basin system and ophiolitic mélange belt; 9−Outer shelf sedimentary basin; 10−Volcanic island−arc; 11−Magmatic arc; 12−Suture zone (ophiolite mélange belt); 13−Forearc accretive wedge; 14−Superimposed basin; 15−Marginal rift; 16−High pressure and ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks; 17−Ultramafic rocks; 18−Gabbro and gabbro−diabase; 19−Geophysically detected fault zone; 20−Ductile fault zone; 21−Strike−slip fault; 22−Boundary fault of primary tectonic unit; 23−Boundary fault of secondary tectonic unit; 24−Boundary fault of tertiary tectonic unit; 25−Well location and well number
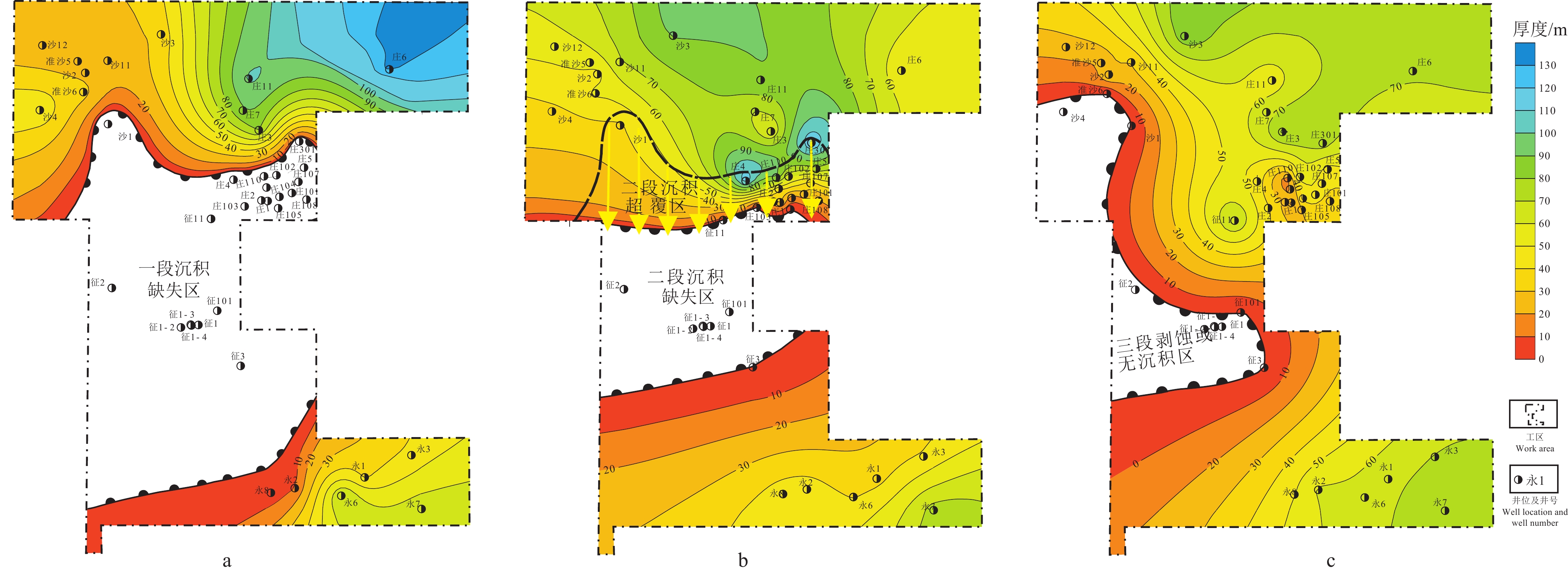
图 6 车—莫古隆起区周缘地区西山窑组各段地层厚度反映的地层缺失和超覆特征
a—西山窑组一段等厚图;b—西山窑组二段等厚图;c—西山窑组三段等厚图
Figure 6. Stratum loss and overlap characteristics reflected by the stratum thickness of each section of Xishanyao Formation in the peripheral area of Chepaizi−Mosuowan paleouplift area
a–Isopach map of the first member of Xishanyao Formation; b–Isopach map of the second member of of Xishanyao Formation; c–Isopach map of the third member of ofXishanyao Formation
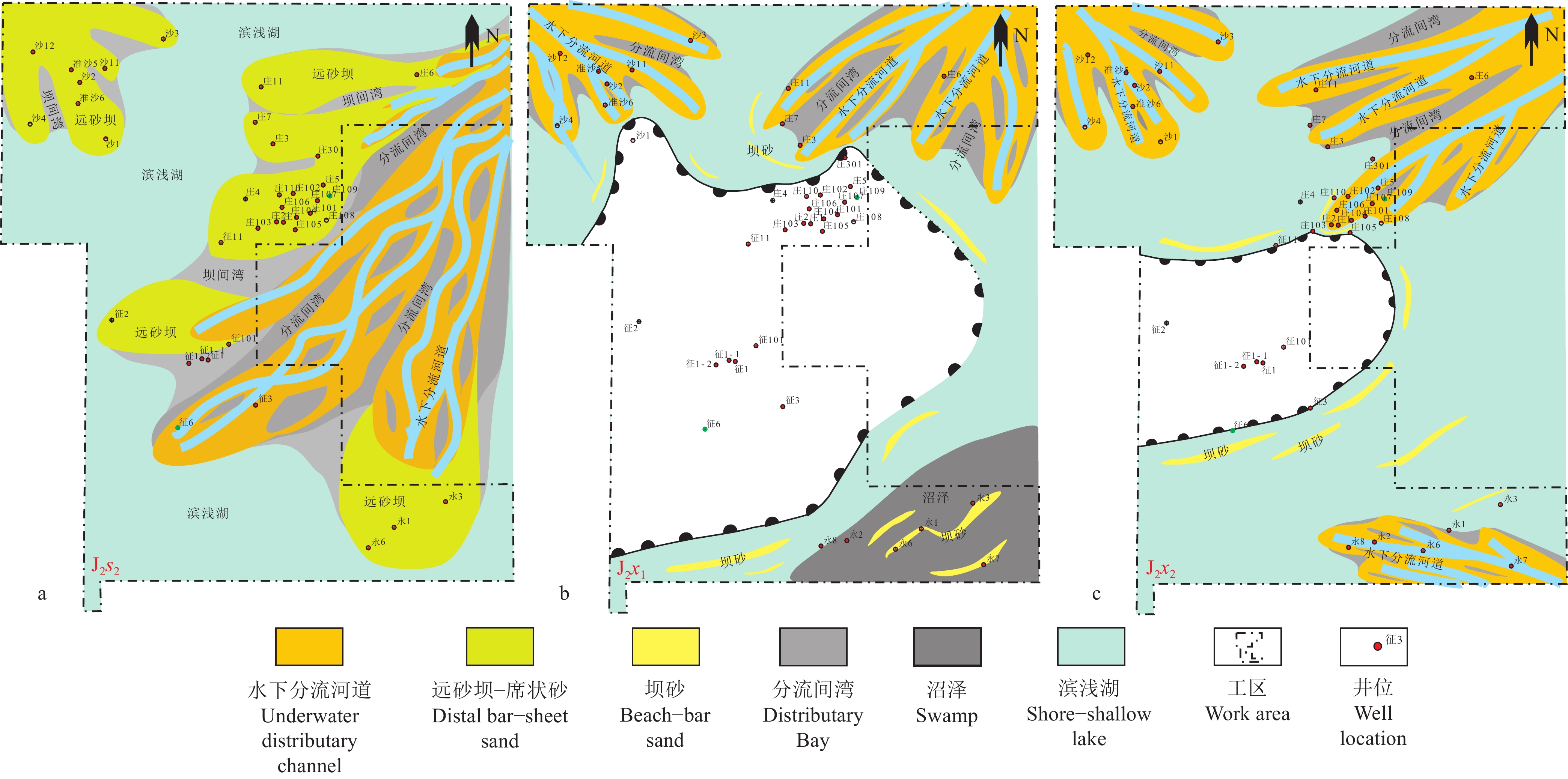
图 7 研究区物源格局平面展布
a—三工河组二段沉积体系;b—西山窑组一段沉积体系;c—西山窑组二段沉积体系
Figure 7. Plane distribution of provenance pattern in the study area
a–Sedimentary system of the second member of Sangonghe Formation; b–Sedimentary system of the first member of Xishanyao Formation; c–Sedimentary system of the second member of Xishanyao Formation
-
[1] Eberth J, Pascovici G, Thomas H G, Warr N, Weißhaar D, Miniball C. 2001. From euroball to gamma−ray tracking arrays − new developments in ge detector technologies [C]//Nuclear Structure Physics − Celebrating the Career of Peter von Brentano − The International Symposium. Gottingen, Germany.
[2] Fang Shihu, Guo Zhaojie, Jia Chengzao, Zhang Zhicheng, Wang Xulong, Wang Meina. 2006. Meso−cenozoicheavy minerals’assemblages in the southern Junggar Basin and its im plications for Basin−orogen pattern[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 41(4): 648−662 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Fang Y, Wu C, Guo Z, Kejun H, Lin D, Wang L, Li L. 2015. Provenance of the Southern Junggar Basin in the Jurassic: Evidence from detrital zircon geochronology and depositional environments[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 315: 47−63. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2014.10.014
[4] Guo Zhaojie, Zhang Zhicheng, Wu Chaodong, Fang Shihu, Zhang Rui. 2006. Mesozoic Cenozoic Tianshan uplift process and its comparative study with Junggar and Altai Mountains[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(1): 1−15 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2006.tb00788.x
[5] He Dengfa, Chen Xinfa, Kuang Jun, Zhou Lu, Tang Yong, Liu Deguang. 2008. Formation, evolution and genetic mechanism of Chepaizi Mosuo Bay paleouplift in Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(4): 42−55 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60038-X
[6] He Guoqi, Lu Shuning, Li Maosong. 1995. Significance of large fault systems in paleo−plate studies: A case study of Central Asia[J]. Geological Journal of Universities, 1(1): 1−10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Ji Youliang, Zhou Yong, Kuang Jun, Wan Lu, Zhang Rui, Lu Chunhong. 2010. Formation and evolution of Che Mo ancient uplift in Junggar Basin and its control over sedimentary facies[J]. Science China Earth Science, 40(10): 1342−1355 (in Chinese).
[8] Kuang Jun, Hou Lianhua, Zhang Yueqian, Shi Xinpiao, Wang Jinghong. 2009. Shallow reservoir forming factors and exploration direction of chemogu uplift in Junggar Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 30(4): 445–449 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Kuang Lichun, Lei Dewen, Tang Yong. 2013. Jurassic Cretaceous Sedimentary Characteristics and Lithostratigraphic Reservoirs in Junggar Basin [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1–156 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Li Zhong, Peng Shoutao. 2013. Mesozoic Cenozoic detrital zircon U−Pb chronology, provenance system analysis and intracontinental basin mountain evolution at the north and south foothills of Tianshan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(3): 739−755 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Liu Chuanpeng. 2013. Microscopic characteristics and effective reservoir control factors of the second member of Sangonghe Formation in Moxizhuang area, Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 40(5): 1515−1522 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Liu Zhaorong. 2008. There is no Mesozoic paleouplift in the central Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 29(2): 256−259 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Lu Cheng. 2016. Study on Secondary Logging Interpretation of Old Wells in Blocks 1 and 3 in the Central Junggar Basin [D]. Xinjiang: Xinjiang University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Ma Baojun, Qi Jiafu, Yu Fusheng, Zhang Kexin. 2008, Structural characteristics and physical simulation of Che Mo ancient uplift in Junggar Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 32(1): 36–41(in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Peng B, Jin Z J, Wang H, Jia X. 2018. Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of a retrogradational fan−delta system within Lower Triassic in the Mabei area, Junggar Basin (northwestern China)[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 59: 606−619. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2018.05.002
[16] Shang Xiaofei, Hou Jiagen, Cheng Yuanzhong, An Zhenyue, Yao Ruixiang, Li Yan. 2014. Discussion on the genetic mechanism of thick lake beach bar sand body and Its geological significance—Taking the second member of Shahejie Formation in Banqiao sag of Huanghua depression as an example[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(9): 1705−1718 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Song Yan, Chen Shi, Zhang yilou, Liang Xinxin, Liang Yuanyuan, Hou Wen. 2020. Calibration of basin mountain differentiation time limit in the Middle and Late Jurassic in Bogda area, southeast margin of Junggar Basin[J]. ScienceTechnology and Engineering, 20(3): 924−934 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Wang Jufeng, Deng Hongwen, Cai Xiyuan. 2005. Sedimentary system of Sangonghe Formation of Lower Jurassic in the hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 26(2): 137−141 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Wang Xuying, Jiang Zaixing. 2020. Sedimentary system characteristics and model of Paleogene Fusan member in Subei Basin[J]. Geoscience, 34(6): 1132−1143 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Wei Hongxing. 2007. Structural Characteristics and Formation and Evolution of the Southern Margin of Bogda Mountain [D]. Shaanxi: Northwest University, 1–75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Xu Shumei, Li Meng, Wang Jinduo, Ren Xincheng, Zeng Zhiping, Wu Xiangfeng, Xu Pengcheng, Feng Huaiwei. 2020. Cycle style and sand body superposition law of Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation in the abdomen ofJunggar Basin[J]. Journal ofPalaeogeography, 22(2): 221−234 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Xu Xueyi, Wang Hongliang, Chen Junlu. 2016. Geology of Tianshan and Its Adjacent Areas in China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1–175 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Peng Xiling. 2007. Query on chemo ancient uplift in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, (6): 63−71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Yang Y T, Song C C, He S. 2015. Jurassic tectonostratigraphic evolution of the Junggar basin, NW China: A record of Mesozoic intraplate deformation in Central Asia[J]. Tectonics, 34(1): 86−115. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003640
[25] Yue Yong, Jiang Shu, Tian Jingchun, Lin Xin. 2024. Late Cretaceous to Early Paleocene sedimentary environment evolution: Geochemical evidences of Well PBX1 in the southwestern Tarim Basin[J]. Geology in China, 51(2): 592−605 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Yu Fusheng, Amuguleng, Yang Guangda, Ma Baojun. 2008. Structural evolution characteristics and genetic simulation of Che Mo ancient uplift in Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(1): 39−44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Zhang Fushun, Yu Yingfan, Zhu Yunhui, Xia Mouzhong. 2007. Formation and evolution of Che Mo ancient uplift and oil and gas distribution[J]. Oil and Gas Geology of Western China, 3(1): 13−20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Zhang Zhihuan, Qin liming, Li Wei, Wang Chunjiang, Qiu Nansheng, Meng Xianlong, Zhang Zhenying, Yuan Dongshan. 2009. Oil source and hydrocarbon source focus transfer of oil−bearing structures on the north and south sides of chemogu uplift in the abdomen of Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 36(4): 826−836 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Zhao Shujuan, Li Sanzhong, Liu Xin, Lou Da, Suo Yanhui , Dai Liming, Sun Wenjun, Li Tao, Wang Xuebin, Yang Chao. 2014. The structure of the eastern margin of Junggar Basin: The intracontinental process of the transition between Altay and North Tianshan orogenic belt[J]. Science China Earth Science, 44(10): 2130–2141 (in Chinese).
[30] Zhao Wenzhi, Jin Jiuqiang. 2000. Formation and Evolution of Jurassic Prototype Basins in Northwest China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Zhu Wen, Wang Ren, Lu Xinchuan, Shi Wanzhong, Ren Mengyi, Liu Kai. 2021. Yanshanian tectonic activity and sedimentary response in the northwest hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science, 46(5): 1692−1709 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Zhu X M, Li S L, Wu D, Zhu S F, Dong Y L, Zhao D N, Wang X L, Zhang Q. 2017. Sedimentary characteristics of shallow−water braided delta of the Jurassic, Junggar basin, Western China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 149: 591−602. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.10.054
[33] Zhu Yunhui, Meng Xianlong. 2005. Formation and evolution of chemo ancient uplift in Junggar Basin and its influence on oil and gas accumulation in the abdomen[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 1(1): 55−57 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Zheng Youwei, Wang Yadong, Guo Jianming, Liu Xingwang, Zhao Guangliang, Su Long, Zheng Jianjing. 2016. Evolution characteristics of Jurassic heavy minerals in the southeast margin of Junggar Basin and its response to the uplift of Bogda mountain[J]. Acta Sedimentation Sinica, 34(6): 1147−1154 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Zhao Hongliang. 2006. Evolution and reservoir control law of Che Mo paleouplift in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 27(2): 160−162.
[36] Zhou T Q, Wu C D, Yuan B, Shi Z K, Wang J L, Zhu W, Zhou Y X, Jiang X, Zhao J Y, Wang J, Ma J. 2019. New insights into multiple provenances evolution of the Jurassic from heavy minerals characteristics in Southern Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(1): 67−81.
[37] 方世虎, 郭召杰, 贾承造, 张志诚, 王绪龙, 王美娜. 2006. 准噶尔盆地南缘中−新生界沉积物重矿物分析与盆山格局演化[J]. 地质科学, 41(4): 648−662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.04.008 [38] 郭召杰, 张志诚, 吴朝东, 方世虎, 张锐. 2006. 中、新生代天山隆升过程及其与准噶尔、阿尔泰山比较研究[J]. 地质学报, 80(1): 1−15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.01.001 [39] 何登发, 陈新发, 况军, 周路, 唐勇, 刘德光. 2008. 准噶尔盆地车排子–莫索湾古隆起的形成演化与成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 15(4): 42−55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.04.006 [40] 何国琦, 陆书宁, 李茂松. 1995. 大型断裂系统在古板块研究中的意义—以中亚地区为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 1(1): 1–10. [41] 纪友亮, 周勇, 况军, 万璐, 张锐, 卢春红. 2010. 准噶尔盆地车–莫古隆起形成演化及对沉积相的控制作用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 40(10): 1342−1355. [42] 况军, 侯连华, 张越迁, 石新朴, 王京红. 2009. 准噶尔盆地车莫古隆起浅层成藏因素及勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 30(4): 445−449. [43] 匡立春, 雷德文, 唐勇. 2013. 准噶尔盆地侏罗–白垩系沉积特征和岩性地层油气藏[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1–156. [44] 李忠, 彭守涛. 2013. 天山南北麓中–新生界碎屑锆石U–Pb年代学记录、物源体系分析与陆内盆山演化[J]. 岩石学报, 29(3): 739−755. [45] 刘传鹏. 2013. 准噶尔盆地莫西庄地区三工河组二段储层微观特征及有效储层控制因素[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1515−1522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.016 [46] 刘朝荣. 2008. 准噶尔盆地中部不存在中生代古隆起[J]. 新疆石油地质, 29(2): 256−259. [47] 路成. 2016. 准噶尔盆地中部1、3区块老井测井二次解释研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. [48] 马宝军, 漆家福, 于福生, 张克鑫. 2008. 准噶尔盆地车–莫古隆起构造特征及物理模拟[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 32(1): 36−41. [49] 商晓飞, 侯加根, 程远忠, 安振月, 姚瑞香, 李燕. 2014. 厚层湖泊滩坝砂体成因机制探讨及地质意义—以黄骅坳陷板桥凹陷沙河街组二段为例[J]. 地质学报, 88(9): 1705−1718. [50] 宋燕, 陈石, 张艺楼, 梁鑫鑫, 梁媛媛, 侯文. 2020. 关于准噶尔盆地东南缘博格达地区中晚侏罗世盆山分异时限的标定[J]. 科学技术与工程, 20(3): 924−934. [51] 王居峰, 邓宏文, 蔡希源. 2005. 准噶尔盆地腹部下侏罗统三工河组沉积体系[J]. 新疆石油地质, 26(2): 137−141. [52] 王旭影, 姜在兴. 2020. 苏北盆地古近系阜三段沉积体系特征与模式[J]. 现代地质, 34(6): 1132−1143. [53] 魏红兴. 2007. 博格达山南缘构造特征及其形成演化[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 1–75. [54] 许淑梅, 李萌, 王金铎, 任新成, 曾治平, 武向峰, 舒鹏程, 冯怀伟. 2020. 准噶尔盆地腹部下侏罗统三工河组旋回样式及砂体叠置规律[J]. 古地理学报, 22(2): 221−234. [55] 徐学义, 王洪亮, 陈隽璐. 2016. 中国天山及邻区地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1–175. [56] 彭希龄. 2007. 准噶尔盆地车莫古隆起质疑[J]. 中国石油勘探, (6): 63–71. [57] 岳勇, 蒋恕, 田景春, 林新. 2024. 塔里木盆地西南部晚白垩世—早古新世沉积环境演化: 来自皮山PBX1井的地化证据[J]. 中国地质, 51(2): 592−605. [58] 于福生, 阿木古冷, 杨光达, 马保军. 2008. 准噶尔盆地车–莫古隆起的构造演化特征及其成因模拟[J]. 地球学报, 29(1): 39−44. [59] 张福顺, 余滢帆, 朱允辉, 夏忠谋. 2007. 车—莫古隆起形成演化与油气分布[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 3(1): 13−20. [60] 张枝焕, 秦黎明, 李伟, 王春江, 邱楠生, 孟闲龙, 张振英, 袁东山. 2009. 准噶尔盆地腹部车莫古隆起南北两侧含油构造油源及烃源灶转移[J]. 中国地质, 36(4): 826−836. [61] 赵淑娟, 李三忠, 刘鑫, 楼达, 索艳慧, 戴黎明, 孙文军, 李涛, 王学斌, 杨朝. 2014. 准噶尔盆地东缘构造: 阿尔泰与北天山造山带交接转换的陆内过程[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 44(10): 2130–2141. [62] 赵文智, 靳久强. 2000. 中国西北地区侏罗纪原型盆地形成与演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [63] 朱文, 王任, 鲁新川, 石万忠, 任梦怡, 刘凯. 2021. 准噶尔盆地西北腹部燕山期构造活动与沉积响应[J]. 地球科学, 46(5): 1692−1709. [64] 朱允辉, 孟闲龙. 2005. 准噶尔盆地车莫古隆起的形成演化及其对腹部油气成藏的影响[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 1(1): 55−57,108. [65] 郑有伟, 王亚东, 郭建明, 刘兴旺, 赵光亮, 苏龙, 郑建京. 2016. 准噶尔盆地东南缘侏罗系重矿物演化特征及对博格达山隆升的响应[J]. 沉积学报, 34(6): 1147−1154. [66] 赵宏亮. 2006. 准噶尔盆地车莫古隆起演化及其控藏规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 27(2): 160−162.



 下载:
下载: