Distribution characteristics of fluorine in deep geothermal water in Jizhong Depression and its risk assessment and development utilization suggestions
-
摘要:研究目的
冀中坳陷地区地热资源丰富,地下热水中氟分布特征及其风险评估对地热资源开发利用具有重要意义。
研究手段本文以冀中坳陷地区地下热水为研究对象,通过分析砂岩热储层和碳酸盐岩热储层地热流体水化学数据,研究地热流体中氟的分布特征和富集规律,评价地热流体质量,提出地热流体开发利用相关建议。
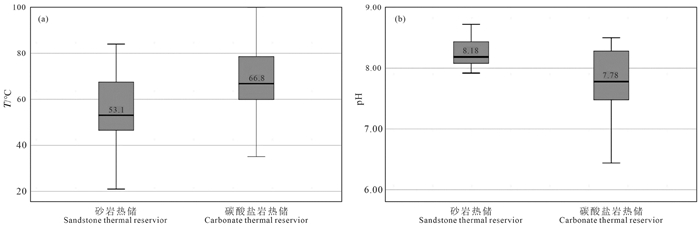
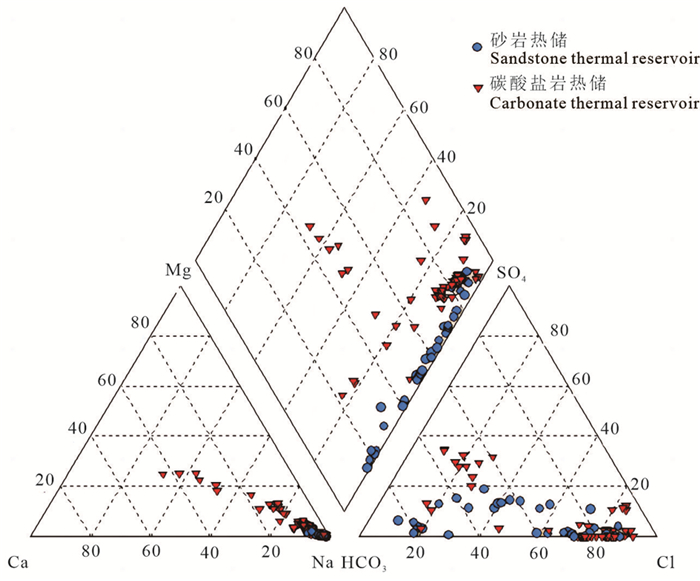
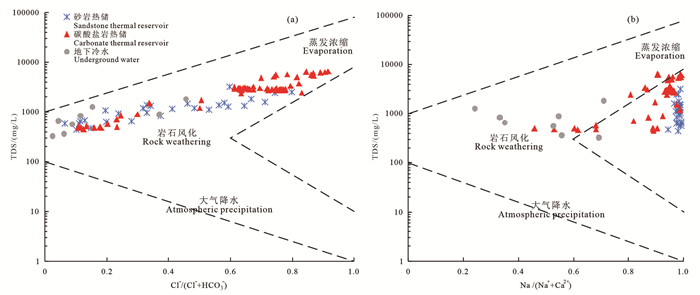
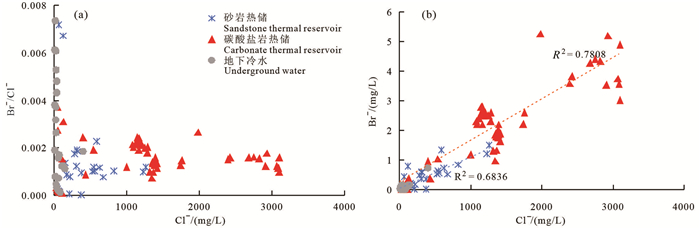
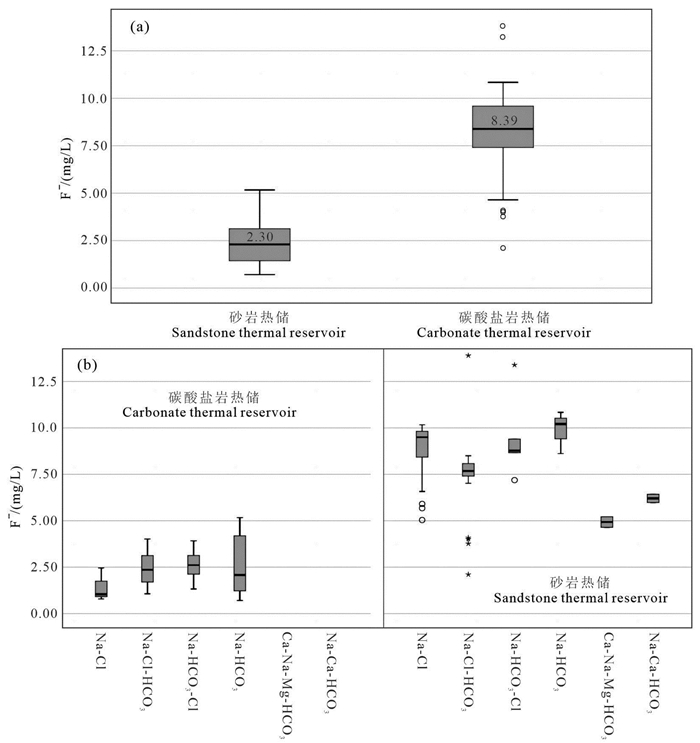
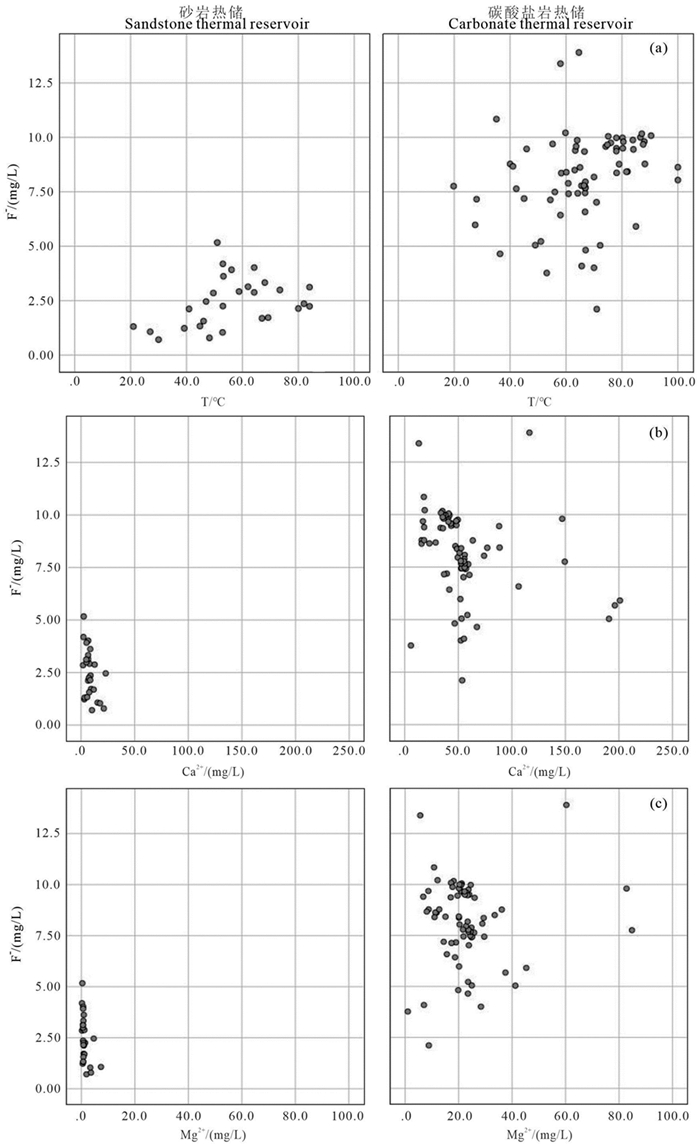
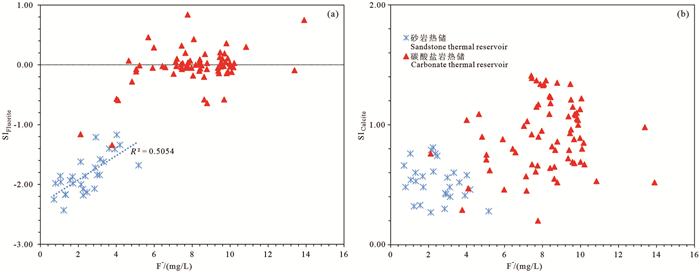
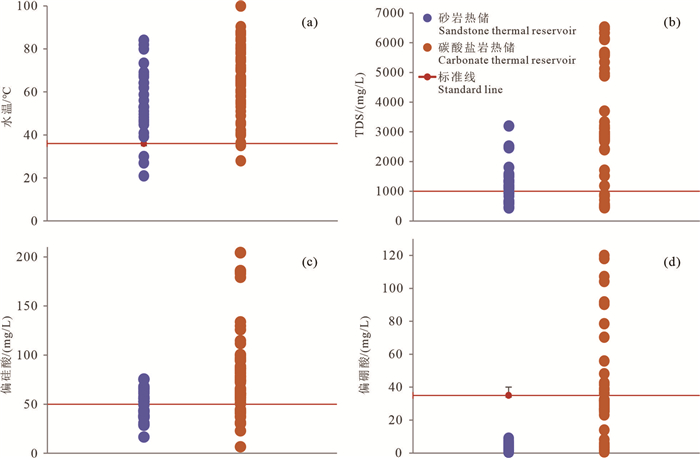
研究结果研究区地热流体以Na-Cl和Na-Cl-HCO3型水为主,基本为碱性水,优势阳离子为钠离子,氟含量较高,尤其碳酸盐岩热储地热流体氟离子含量集中分布在7.5~9.5 mg/L,最高达13.9 mg/L;弱碱性环境、水温和水岩作用是影响研究区氟离子富集的主要因素,砂岩热储中氟离子浓度与Ca2+、Mg2+浓度呈显著负相关,而碳酸盐岩热储中其相关性并不显著。氟的富集受到萤石等含氟矿物的控制,砂岩热储地热流体萤石饱和指数全部小于零,而氟离子浓度较高的碳酸盐岩储层地热流体萤石饱和指数普遍分布在零附近。
结论研究区高氟地热流体不能直接用于生活饮用水、农田灌溉和渔业用水,在进行地热资源综合梯级利用时解决地热尾水除氟问题至关重要。
创新点: 揭示了冀中坳陷地区不同热储层地热流体氟分布特征和富集规律,评价了地热流体质量,提出了地热流体合理开发利用建议。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survey engineering.
ObjectiveThe geothermal resources of Jizhong Depression are rich. The distribution characteristics and risk assessment of fluorine in geothermal waiter are of great significance to the development and utilization of geothermal resources.
MethodsThis study takes the geothermal water in Jizhong Depression as the research object. The distribution characteristics and enrichment regularity of fluorine in geothermal fluid were studied by analyzing the hydrochemical data of geothermal fluid in sandstone and carbonate reservoirs, and the quality of geothermal fluid was evaluated, and furthermore some suggestions on the development and utilization of geothermal fluid were put forward.
ResultsThe results show that the geothermal fluids in the study area are mainly Na-Cl and Na-Cl-HCO3 type water, basically alkaline water, with high fluorine content. In particular, the concentration trend of fluorine ion content in the geothermal fluids of carbonate reservoir is 7.5-9.5 mg/L, and the highest is 13.9 mg/L. Weakly alkaline environment, water temperature and water-rock interaction are the main factors affecting fluoride ion enrichment in the study area. The F-concentration in sandstone geothermal reservoir has a significant negative correlation with Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations, while the correlation is not significant in carbonate geothermal reservoir. Fluorine enrichment is controlled by fluorite and other fluorine-bearing minerals. Fluorite saturation index of the geothermal fluids in sandstone reservoirs is all less than 0, while fluorite saturation index of the geothermal fluids in carbonate reservoirs with higher fluoride ion concentration is generally distributed around 0.
ConclusionsThe high fluorine geothermal fluid in the study area cannot be directly used for drinking water, farmland irrigation and fisheries. It is of great importance to solve the problem of fluoride removal in geothermal tail water at the situation of conducting gradient utilization of geothermal resources in the study area.
-
1. 引言
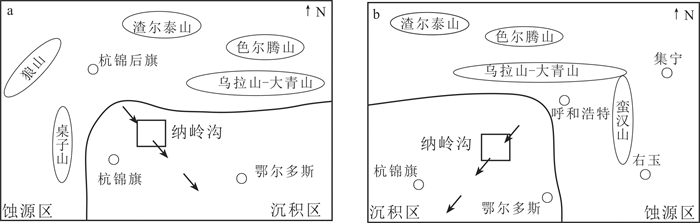
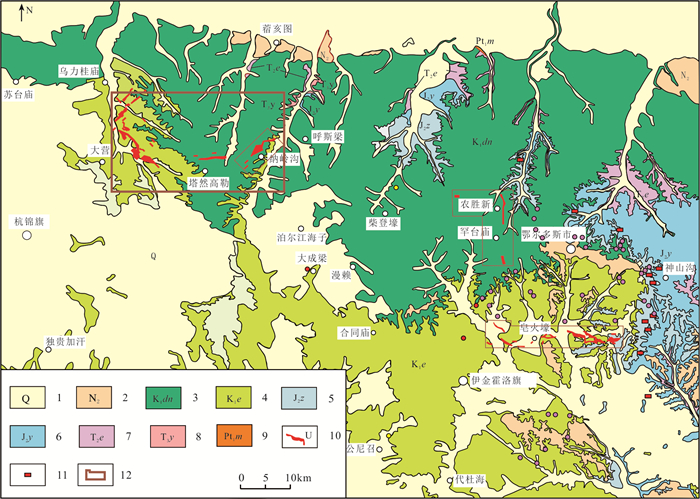
砂岩型铀矿以资源储量规模大、可地浸、开采成本低等特点已经成为当今世界上经济价值最大的铀矿类型,它也被列入了保障我国铀资源储量持续增长的主要类型。由于成功实现可地浸采铀实验,纳岭沟铀矿成为鄂尔多斯盆地北部最具经济价值的铀矿床(图 1),为研究砂岩型铀提供了理想对象和目标。作为砂岩型铀矿重要的成矿要素,蚀源区直接关联铀源的规模大小、含铀流体迁移、铀富集方式和铀成矿机制等,对于成矿作用研究和找矿预测工作至关重要。无论中亚的楚·萨雷苏和锡尔河铀矿田(Jaireth et al., 2008)和中央克兹尔库姆铀矿田(陈祖伊等,2010),还是我国伊犁盆地南缘铀矿田(侯明才等,2016),均将蚀源区作为一个重要的科学问题。
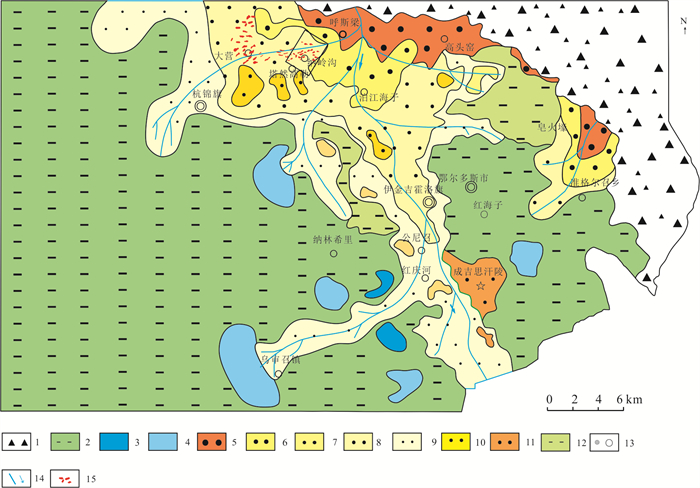
![]() 图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿区域地质简图1—第四系;2—新近系;3—下白垩统东胜组;4—下白垩统伊金霍洛组;5—中侏罗统直罗组;6—中侏罗延安组;7—中三叠统二马营组;8—中三叠统二马营组;9—古元古代美岱召岩群;10—铀矿体地表投影范围;11—地表放射性异常点;12—研究区范围Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Dongsheng uranium orefield1-Quaternary; 2-Neogene; 3-Lower Cretaceous Dongsheng Formation; 4-Lower Cretaceous Yijinhuoluo Formation; 5-Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 6-Middle Jurassic Yan'an Formation; 7-Middle Triassic Ermaying Formation; 8-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 9-Paleoproterozoic Meidaizhao Group; 10-Uranium ore bodies; 11-Surface radioactive anomaly; 12-Study area
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿区域地质简图1—第四系;2—新近系;3—下白垩统东胜组;4—下白垩统伊金霍洛组;5—中侏罗统直罗组;6—中侏罗延安组;7—中三叠统二马营组;8—中三叠统二马营组;9—古元古代美岱召岩群;10—铀矿体地表投影范围;11—地表放射性异常点;12—研究区范围Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Dongsheng uranium orefield1-Quaternary; 2-Neogene; 3-Lower Cretaceous Dongsheng Formation; 4-Lower Cretaceous Yijinhuoluo Formation; 5-Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 6-Middle Jurassic Yan'an Formation; 7-Middle Triassic Ermaying Formation; 8-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 9-Paleoproterozoic Meidaizhao Group; 10-Uranium ore bodies; 11-Surface radioactive anomaly; 12-Study area对于纳岭沟地区直罗组含铀岩系的蚀源区示踪,前人从岩石学、地球化学、碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年等方面开展了大量研究工作,根据直罗组碎屑锆石测年结果将阴山、乌拉山、大青山、狼山、集宁地区太古宙、元古宙变质岩和不同时代岩浆岩认定为蚀源区(李子颖等,2009;张龙等,2016;刘晓雪等,2016;陈印等,2017;雷开宇等,2017;刘璐等,2018;王思力等,2018;Jin et al., 2020;司庆红等,2021;张媛媛等,2021)。赵俊峰等(2008)依据鄂尔多斯盆地东部直罗组露头和盆地内146个钻孔建立了全盆地沉积相展布图,认为纳岭沟地区直罗组上、下段辫状河相沉积体系的古流向为北西向。焦养泉等(2015)则基于纳岭沟地区部分钻孔资料和神山沟地区自然露头剖面建立了东胜地区大型直罗组沉积垛体,也将蚀源区也指向阴山地区。而冯晓曦等(2019)认为盆地北部出露的含新元古代美岱召群的孔兹岩带可能为直罗组的主要蚀源区。
针对纳岭沟地区直罗组含铀岩系的蚀源区的分歧,笔者认为主要有三个原因:(1)鄂尔多斯盆地北部中侏罗世古地貌格局对直罗组含铀岩系物源区制约的研究不充分。早中侏罗世,阴山地区的沉积物最大可能汇聚于河套盆地、包头地区石拐盆地河湖相沉积环境。同时,中侏罗世,鄂尔多斯盆地北部中元古代大规模孔兹岩带最大程度屏蔽了阴山地区剥蚀物到达纳岭沟地区。(2)鄂尔多斯盆地中生代旋转和古地磁研究成果对直罗组物源的影响重视不足。(3)不少学者放大了碎屑锆石定年在蚀源区识别中的权重。虽然碎屑锆石定年结果是一种重要的示踪蚀源区方法,但蚀源区与碎屑锆石定年结果属于充分非必要关系。纳岭沟地区直罗组碎屑锆石的中生代锆石(157 Ma、165 Ma)(陈印等,2017;俞礽安等,2020)难以在阴山地区找到理想物源区。
河套地区中生代古地理研究表明,内蒙古狼山地区的炭窑口—东升庙北东向早中侏罗世凹陷(付星辉等,2016),包头地区的早中侏罗世河湖相石拐盆地(葛玉辉等,2010)最可能容纳了阴山地区的陆源碎屑物,可能进一步汇入鄂尔多斯盆地西缘的吉兰泰凹陷。1∶25万乌拉特前旗幅(K49C004001)的钻孔揭露,纳岭沟铀矿区北部直罗组(J2z)直接覆盖于三叠系、二叠系等前中生代地层之上,表明中侏罗世,矿区北侧近缘的前直罗组则可直接提供物源。笔者在2015—2019年野外地质调查中,发现纳岭沟铀矿区北侧达拉旗高头窑至响沙湾一带出露小面积的古元古代美岱召岩群(Pt2m)变质岩,具有近缘直接供给直罗组物源的能力。张云等(2022)建立的东胜地区直罗期古地貌三维模型、大营—纳岭沟一带直罗组下段砂体等厚图指示沉积体系北东向展布,也指示纳岭沟地区直罗组物源来自于矿区北侧的近缘前侏罗纪隆起区。
古地磁结果表明鄂尔多斯盆地中生代发生了逆时针旋转(马醒华等,1993),据此推断中侏罗世,纳岭沟铀矿区可能正对内蒙古与山西交界一带。内蒙古南部和山西北部地区太古代、元古代、古生代变质岩、岩浆岩和山西宁武—静乐盆地中下侏罗统火山碎屑岩,具有提供纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组各时代碎屑锆石能力。
因此,笔者以纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组含铀岩系碎屑矿物学、重矿物特征、岩石化学、沉积相等为基础,结合前人碎屑锆石定年、1∶25区调、古地磁和河套地区古地理研究进展,多角度论证纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组物源主要来源于,包括矿区东北缘前侏罗纪隆起区在内的内蒙古与山西交界地区太古宙、元古宙、古生代、中生代变质岩、岩浆岩和火山岩,有别于一些学者认为的阴山隆起区。
将晋蒙交界地带厘定为纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组含铀岩系的蚀源区,可为鄂尔多斯盆地北部中侏罗世地质构造演化研究提供借鉴,可能对深化纳岭沟铀矿成矿作用研究产生影响,也可为鄂尔多斯等北方其他盆地砂岩铀成矿作用研究提供参考,以及为“十四五”新一轮地质找矿工作部署提供理论支持。
2. 地质背景
鄂尔多斯盆地是晚三叠世华北克拉通西部前陆盆地演化而成的侏罗纪大型坳陷盆地,南北缘分别受秦岭造山带、阴山隆起带控制,东西囿于吕梁及贺兰山,盆山耦合作用强烈。早—中侏罗世,鄂尔多斯盆地处于弱伸张环境下和构造稳定演化阶段,印支期碰撞挤压造成的高低不平古地貌被河湖相、沼泽相填平。中—晚侏罗世受到多向挤压作用,形成了伊盟隆起、伊陕斜坡、天环坳陷等大地构造单元。盆地不同地区隆升、剥蚀程度差异较大,盆地呈不均衡演化,形成北高西低,西高东低的地貌形态。纳岭沟铀矿床大地构造位置处于鄂尔多斯北部东西向展布的伊盟隆起带中部。伊盟隆起带基底为新太古界中高级变质岩(包洪平等,2019),上覆下二叠统太原组海陆交互相含煤岩层、下三叠统刘家沟组和和尚沟组、中三叠统二马营组、上三叠统延长组、中侏罗统延安组河流相含煤碎屑岩、直罗组和安定组河湖相砂岩和泥岩建造,下白垩统东胜组红色河流相碎屑岩。其中,直罗组角度不整合覆盖基底变质岩、古生界、三叠系和延安组之上(图 1)。
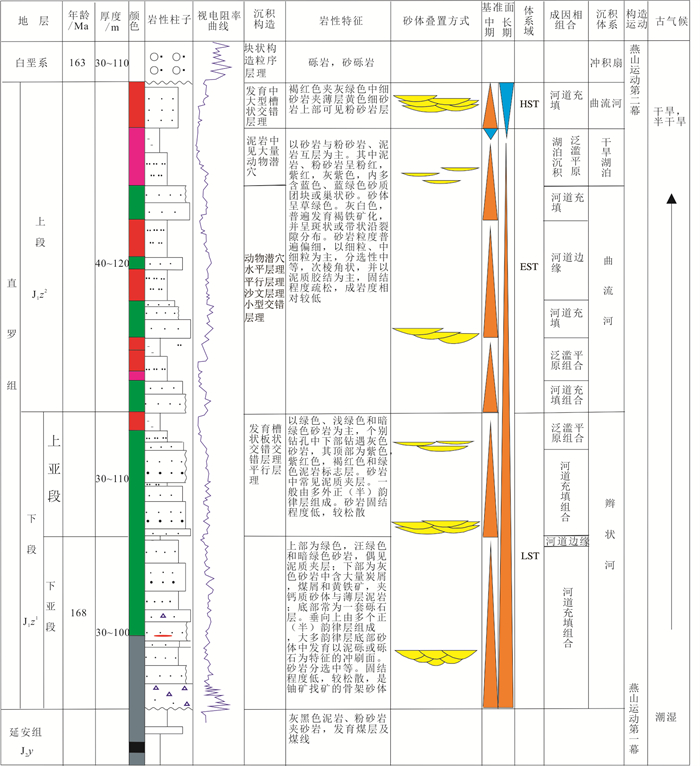
纳岭沟铀矿床主要含铀地层为中侏罗统直罗组潮湿—干旱、半干旱河流相碎屑岩建造(程先钰等,2021),厚度一般在100~200 m。铀矿体赋存于直罗组下段(J2z1)辫状河沉积体系中。根据直罗组沉积时期古气候的变化、岩性发育特点和物性参数特征,将直罗组划分为下段(J2z1)和上段(J2z2)(焦养泉等,2005)。下段(J2z1)为低位域(LST)沉积。低位域(LST)划分为上亚段、下亚段。下亚段(J2z1)为潮湿气候环境下沉积的以砂岩为主的粗碎屑岩建造。上亚段以灰绿色中粒和中细粒砂岩为主,下亚段为灰色、灰白色中细粒-中粗粒砂岩与灰色、灰绿色粉砂质泥岩。上段(J2z2)为湖扩体系域(EST)和高位域(HST)沉积,主要为紫红色、褐红色泥岩、粉砂岩及砂岩,夹灰绿色泥岩。铀矿体主要赋存于下段下亚段分布稳定、固结程度低的砂体中,与大营铀矿的矿体一并沿乌力桂庙—大营—塔然高勒—纳岭沟一线呈“半弧”状展布(图 2),圆心指向三叠纪地层出露的宿亥图一带,暗示成矿流体或赋矿层物源来源于宿亥图方向。
3. 样品采集与测试
3.1 样品采集
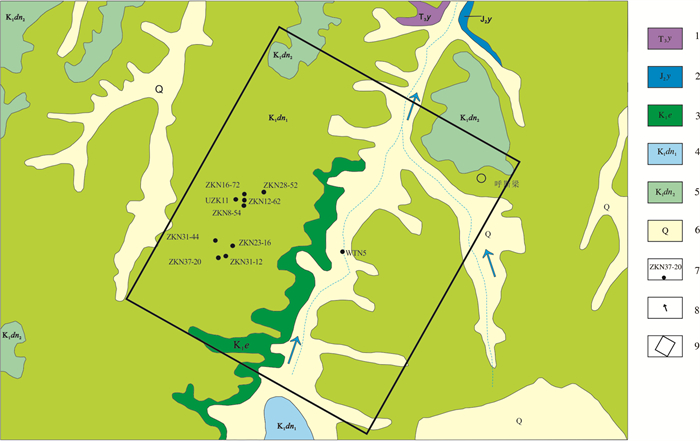
岩石化学样品采集对象为纳岭沟铀矿钻孔ZK23-16样品(图 3)。岩矿鉴定、粒度分析、常量元素、微量和稀土元素样品采集于钻孔ZK23-16、UZK11。重矿物样品采集于ZKN16-72等10个钻孔(图 3)。
![]() 图 3 纳岭沟铀矿地质简图1—上三叠统延长组;2—中侏罗统延安组;3—下白垩统伊金霍洛组;4—下白垩统东胜组一段;5—下白垩统东胜组二段;6—第四系;7—钻孔;8—水流方向;9—矿区范围Figure 3. Simplified geological map of the Nalinggou uranium deposit1-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 2-Middle Jurassic Yanan Formation; 3-Lower Cretaceous Yijinhuoluo Formation; 4-The first member of Dongsheng Formation of Lower Cretaceous; 5-The second member of Dongsheng Formation of Lower Cretaceous; 6-Quaternary system; 7-Drill; 8-Current Direction; 9-Mining area
图 3 纳岭沟铀矿地质简图1—上三叠统延长组;2—中侏罗统延安组;3—下白垩统伊金霍洛组;4—下白垩统东胜组一段;5—下白垩统东胜组二段;6—第四系;7—钻孔;8—水流方向;9—矿区范围Figure 3. Simplified geological map of the Nalinggou uranium deposit1-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 2-Middle Jurassic Yanan Formation; 3-Lower Cretaceous Yijinhuoluo Formation; 4-The first member of Dongsheng Formation of Lower Cretaceous; 5-The second member of Dongsheng Formation of Lower Cretaceous; 6-Quaternary system; 7-Drill; 8-Current Direction; 9-Mining area3.2 样品测试
样品前处理、重矿物鉴定、岩矿鉴定由河北廊坊宇能地质勘查技术服务有限公司完成。岩石主量、微量、稀土元素分析测试单位为核工业北京地质研究院。粒度分析、碎屑成分鉴定由河南省岩石矿物实验测试中心承担。
常量元素测试仪器为PW4400/40 X射线荧光光谱仪,FeO由氢氟酸、硫酸溶样,采用重铬酸钾滴定容量法进行测试,分析精度优于2%,微量和稀土元素测试设备为X SeriesII等离子体质谱仪,检测依据为《硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法》(GB/T14506-2010),检测环境温度24℃,湿度28%,分析精度优于5%。
3.3 沉积相图编制
纳岭沟地区中侏罗统直罗组下段下亚段沉积相图数据来源于中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心建立的鄂尔多斯盆地北部钻孔数据库,利用石文软件编制而成。
4. 测试分析结果
4.1 岩石学特征
几乎所有学者均认为纳岭沟地区直罗组岩石类型相对简单(易超等,2014;王思力等,2018),铀矿层主要有灰绿色、灰白色中粒、中粗粒长石砂岩,夹少量泥岩和含砾砂岩。弱成岩作用致岩石胶结程度低,呈疏松、较疏松状,细粒、中粒、粗粒砂状结构,分选性中等至差,磨圆度差,多为棱角状、次棱角状、次滚圆状,总体呈现较低的结构成熟度,具有以近源为主,伴有远源沉积的特点。胶结方式主要为孔隙式胶结,其次是基底式胶结。多泥颗粒支撑。碎屑粒径0.06~2.8 mm,其中,以钻孔ZK23-16为例(表 1),铀矿层顶板粗粒占比13%,中粒占比39%,细粒占比42%,铀矿层粗粒占比18%,中粒占比45%,细粒占比31%,底板粗粒占比10%,中粒占比43%,细粒占比33%,高占比的粗粒碎屑物具近源沉积特点。碎屑含量85%~90%,其中长石35%~55%,石英20%~35%,云母2%~9%。其中,单晶石英含量39.95%~61.02%,多晶石英0.94%~8.82%,斜长石6.33%~21.13%,钾长石12.68%~28.47%,云母1.41%~15.53%,沉积岩/变质岩值0.45~9.84。岩屑4%~12%,成分有火成岩岩屑(花岗岩岩屑、流纹岩岩屑)、沉积岩岩屑(泥岩岩屑、燧石、细粒砂岩岩屑)、变质岩岩屑(石英岩岩屑、绢云千枚岩岩屑、云母石英片岩岩屑),表明物源区岩石类型复杂,且具近源沉积特点(彭胜龙等,2023)。
表 1 钻孔ZK23-16直罗组下亚段含铀岩系粒度分析Table 1. Grain size analysis of uraniferous rocks in lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16
佩蒂庄的成分成熟度指数Q/(F+R)(Q为石英、F为长石、R为岩屑),长石/岩屑比值可以反映物源区的不同。以钻孔ZK23-16为例(表 2),石英(Q)含量25%~35%,长石(F)含量40%~55%,岩屑(R)含量6%~12.5%,成分成熟度指数Q/(F+R)=0.41~0.71,平均值0.60,长石(F)/岩屑(R)比值3.20~9.17,平均值5.51,表明含铀岩系砂岩成熟度低,具近源沉积特点。
表 2 钻孔ZK23-16直罗组下亚段含铀岩系成分成熟度指数Table 2. Compositional maturity index of uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16
4.2 重矿物特征
选取矿区西部11个钻孔的铀矿层、顶板、底板绿色、灰色砂岩分析重矿物(表 3)。极稳定重矿物有锆石、电气石、石榴子石、金红石、白钛石、赤褐铁矿,稳定重矿物有榍石、钛铁矿、锐钛矿,不稳定重矿物绿帘石、磷灰石、黄铁矿、辉石等,与鄂尔多斯盆地山西组、下石盒子组锆石、电气石、金红石、磁铁矿、锐钛矿等重矿物特征相似(汪正江等,2001;张道锋等,2009)。
表 3 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系重矿物含量(%)统计Table 3. Statistics of heavy mineral content (%) of uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16 in the Nalinggou uranium deposit
4.2.1 重矿物组合特征
重矿物组合有锆石、石榴子石组合和榍石、钛铁矿组合。重矿物含量与物源区存在必然联系(David et al.,2020;Wang et al.,2022)。前者含量12%~49%,后者含量2%~23%,变化幅度大,分选差,符合近源沉积特征。
ZTR(锆石%+电气石%+金红石%)指数= 4~13。UM/SM(不稳定矿物/(稳定矿物+极稳定矿物))值= 0.37~3.20,GZi(100×石榴子石%)/(石榴子石%+锆石%)指数=16.67~91.67,三项指数变化幅度大,ZTR指数较低,电气石含量较低,0~2%,说明蚀源区发育变质岩、岩浆岩,且剥蚀、较短距离迁移沉积于直罗组地层中。
4.2.2 单矿物特征
重矿物成分复杂,含量变化大。锆石含量4%~12%,石榴子石含量2%~41%,钛铁矿含量2%~30%,电气石、金红石、白钛石、赤褐铁矿、锐钛矿分布极不均匀,多见集合体状,含量小于2%。锆石呈次滚圆状,次棱角状,其中磨圆度相对高的次滚圆状锆石表明碎屑物经历了再循环(Pawan et al., 2022)。重矿物绿帘石含量1%~57%,磷灰石含量1%~9%,黄铁矿含量1%~44%,其他黄铜矿、辉石、方铅矿、碳硅石等均呈集合体状产出,表明蚀源区发育变质岩、岩浆岩、火山岩(David et al.,2020),且碎屑沉积物成分变化大,沉积环境多变,具近源沉积特点。
重矿物磨圆度低,电气石呈茶褐色,粒状,短柱状;石榴子石呈不规则粒状,块状,粒状,个别圆形五角十二面体(表 4)。以样号17nzk026为例,锆石呈深、浅玫瑰色,锆石均呈次棱角状,次浑圆粒状,透明,粒径主要0.05~0.15 mm,0.16~0.25 mm次之;个别0.26~0.30 mm;延长系数主要1.5~2.5,次要2.6~3.5,个别4~6,系较短距离搬运的结果(Zeh and Czbral et al.,2021)。
表 4 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系稳定重矿物磨圆度和延长系数Table 4. Roundness and elongation coefficient of stable heavy minerals of uraniferous series from the lower segment of Zhiluo Formation
4.3 岩石化学特征
陆源碎屑岩地球化学特征是对蚀源区岩石类型、古地理、古气候、物理化学风化、水动力条件等因素的地球化学综合响应,对有效示踪蚀源区具有重要参考意义(周科,2014)。以钻孔ZKN23-16为例(表 5),含铀岩系(354~504.4 m)中粗粒砂岩SiO2含量48.79%~75.14%,平均63.27%。Al2O3含量9.24%~19.04%,平均13.89%。SiO2/Al2O3值3.05~6.01。相较砂岩,泥岩中Si含量偏低,而泥岩中Al含量高于砂岩,明显负相关,应与长石碎屑有关,并非后生流体的改造(王金平等,2005;易超等,2015)。Fe2O3含量介于1.12%~9.10%,平均4.50%,FeO含量0.11%~4.95%,平均2.52%,MgO含量0.58%~4.26%,平均2.18%,TiO2含量0.18%~0.80%,平均0.50%,具有低铁、镁、钛特征,说明蚀源区出露基性、超基性岩浆岩。CaO含量0.62%~18.50%,平均2.70%,说明沉积环境属干旱—半干旱古气候。K2O含量2.21%~3.65%,平均3.07%。Na2O含量0.71%~2.34%,平均1.51%。K2O/Na2O值1.41~4.41,大于1,碎屑物具有来自被动陆缘的特点。Al2O3/TiO2值19.25~44.68,多介于19~28,表明蚀源区岩石主要为长英质岩石。
表 5 纳岭沟铀矿直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZKN23-16)主量元素分析结果(%)Table 5. Major element data (%) of uraniferous rocks (drill ZKN23-16) from the lower member of theZhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit
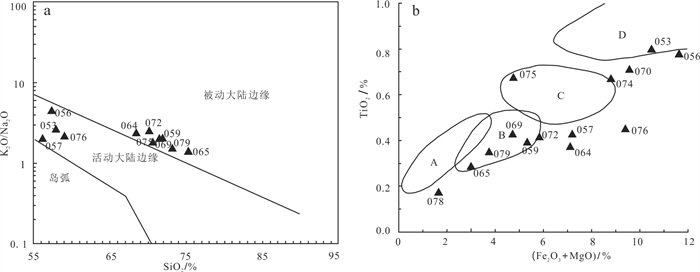
利用SiO2 -K2O/Na2O构造环境判别图(Roser and Korsch, 1986),除绿色泥砾(15nzk070、15nzk074)、钙质粗砂岩(15nzk078)外,部分样品(15nzk053、15nzk056、15nzk057、15nzk078)落入活动大陆边缘,其他落入被动大陆边缘。在Bhatia(1985)TiO2-Fe2O3+MgO中有4个样品(15nzk059、15nzk065、15nzk069、15nzk079)落入大陆壳内裂谷或弧后盆地,1个样品(15nzk075)落入大陆边缘弧,1个样品(15nzk053)落入大洋弧。判别图反映蚀源区剥蚀物原岩大地构造环境相对复杂,兼具岛弧特点的活动大陆边缘和被动大陆边缘环境(图 4)。
![]() 图 4 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZK23-16)SiO2-K2O/Na2O(a)、Fe2O3+MgO-TiO2(b)构造环境判别图A—克拉通盆地;B—大陆壳内裂谷或弧后盆地;C—大陆边缘弧;D—大洋弧Figure 4. Discriminant diagrams of tectonic environment on SiO2-K2O/Na2O(a)、Fe2O3+MgO-TiO2(b)for uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16A-Craton basin; B-Intracontinental rift or back-arc basin; C-Continental margin arc; D-Oceanic arc
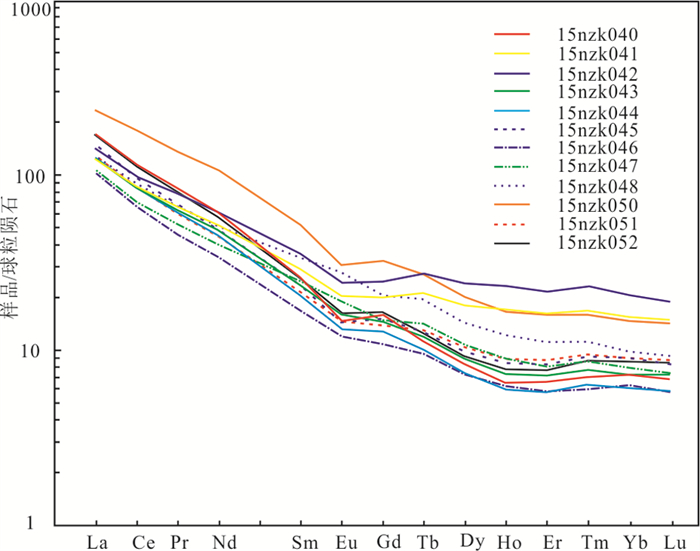
图 4 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZK23-16)SiO2-K2O/Na2O(a)、Fe2O3+MgO-TiO2(b)构造环境判别图A—克拉通盆地;B—大陆壳内裂谷或弧后盆地;C—大陆边缘弧;D—大洋弧Figure 4. Discriminant diagrams of tectonic environment on SiO2-K2O/Na2O(a)、Fe2O3+MgO-TiO2(b)for uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16A-Craton basin; B-Intracontinental rift or back-arc basin; C-Continental margin arc; D-Oceanic arcREE具有在成岩过程中受改造程度很小的稳定地球化学性质,可用来指示原始母岩性质及特点。以钻孔ZK23-16(418~450 m)为例(表 6),岩石REE配分曲线总体右倾,总体趋势相似,部分重稀土曲线扬起(图 5),或与富HREE重矿物非均匀分布有关,或受盆地深部热流体影响。样品15nzk47、15nzk48曲线具有大陆岛弧球粒陨石标准化曲线,15nzk40、15nzk 41、15nzk42属安第斯型曲线,其余属被动边缘曲线特征,表明蚀源区母岩构造环境具有被动边缘、大陆岛弧和安第斯型俯冲带特征。
表 6 纳岭沟铀矿直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZKN23-16)稀土元素分析结果(10-6)Table 6. REE(10-6) element data of uraniferous rocks (drill ZKN23-16) from the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposi
ΣREE含量104.75×10-6~283.86×10-6,La含量24.3×10-6~55.5×10-6,La/Yb值11.11~32.66,表明蚀源区具有大陆岛弧、活动边缘、被动边缘特点,岩石类型复杂,与前人结果一致(张宾等,2020b)。
4.4 砂体分布特征
4.4.1 砂体厚度及含砂率特征
直罗组下段砂体总体呈北东-南西向展布,砂体厚度变化较小,多在120~140 m。其中直罗组下段下亚段砂体厚度一般为60~100 m(图 6)。其中,厚度≥60 m的砂体在纳岭沟铀矿区分布广、面积大,呈片状,小于60 m的区域分布较局限,反映了北东-南西向古流向小幅摆动。
![]() 图 6 纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段下亚段砂体厚度等值图(据核工业208大队❶,略改)1—钻孔及编号;2—勘探线及编号;3—砂体厚度等值线;4—古流向Figure 6. The sand body thickness contour map of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit(modified from CNNC No.208 Geological Party❶)1-Drill and number; 2-Survey line and number; 3-Sand body thickness isoline; 4-Ancient flow direction
图 6 纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段下亚段砂体厚度等值图(据核工业208大队❶,略改)1—钻孔及编号;2—勘探线及编号;3—砂体厚度等值线;4—古流向Figure 6. The sand body thickness contour map of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit(modified from CNNC No.208 Geological Party❶)1-Drill and number; 2-Survey line and number; 3-Sand body thickness isoline; 4-Ancient flow direction纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段赋矿砂体含砂率69.5%~100%,平均值96.5%,分布规律与砂体厚度相似(图 7),含砂率等值线图显示砂体整体呈北东-南西向展布趋势。高值含砂率砂体与高厚度砂体吻合度较高,反映了沉积物搬运方向。
![]() 图 7 纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段下亚段含砂率等值线图(据核工业208大队❶,略改)1—钻孔及编号;2-勘探线及编号;3—含砂率等值线;4—古流向Figure 7. The sand percentage isogram of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit (Modified from CNNC No.208 Geological Party❶)1-Drill and number; 2-Survey line and number; 3-Sand isoline; 4-Ancient flow direction
图 7 纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段下亚段含砂率等值线图(据核工业208大队❶,略改)1—钻孔及编号;2-勘探线及编号;3—含砂率等值线;4—古流向Figure 7. The sand percentage isogram of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit (Modified from CNNC No.208 Geological Party❶)1-Drill and number; 2-Survey line and number; 3-Sand isoline; 4-Ancient flow direction4.4.2 沉积相特征
纳岭沟铀矿地区中侏罗统直罗组下段下亚段沉积相图(图 8)显示,蚀源区、辫状河、三角洲、泛滥平原总体由北东部的呼斯梁—高头窑一带,向南西向的杭锦旗—伊金吉霍洛旗水平展布,空间分布趋势明显,而不是来源于北西向的辫状河相(赵俊峰等,2008),指示了一种由北东至南西方向的古地貌构造环境(Himadri et al., 2021; Beverly et al., 2022)。盆地东北部呼斯梁—高头窑—皂火壕蚀源区,规律性向纳岭沟—泊江海子—准格尔召乡砾质辫状河、杭锦旗砂质辫状河、伊金吉霍洛旗三角洲延展,系一完整的风化、搬运、沉积的源-汇系统。纳岭沟铀矿正处于毗邻砾质辫状河相的砂质辫状河相。张天福等(2020)、张云等(2022)根据3200口钻孔数据库编制的鄂尔多斯盆地北部直罗期古地貌图和三维地质模型也显示,纳岭沟地区直罗组下段沉积相变明显,冲积扇—辫状河—三角洲沉积由北部的呼斯梁地区向西南方向展布。张泓等(2008)认为的中侏罗世达拉特旗高头窑地区发育砾岩和砂砾岩质冲积扇体系,向盆地发育直罗组下段辫状河沉积相,直罗组上段和安定组下部带相变为曲流河沉积相一致。本次研究与两者一致,表明纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组主要物源来自于北东部的蚀源区,且迁移距离较近。
![]() 图 8 纳岭沟地区直罗组下段下亚段沉积相图1—蚀源区;2—泛滥平原;3—河间洼地;4—湖泊;5—砾质辫状河道;6—砂质辫状河道;7—辫状河道;8—三角洲平原;9—心滩;10—边滩;11—沙坝;12—分流间湾;13—地理位置;14—河流及流向;15—铀矿体地表投影Figure 8. The sedimentary facies map of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou area1-Erosion source; 2-Flood plain; 3-Gamma herculis depression; 4-Lake; 5-Gravel braided channel; 6-Sandy braided channel; 7-Braided channel; 8-Delta plain; 9-Heart beach; 10-Side beach; 11-Sand bar; 12-Distributary bay; 13-Geographic location; 14-River and flow direction; 15-Projection of Uranium ore body
图 8 纳岭沟地区直罗组下段下亚段沉积相图1—蚀源区;2—泛滥平原;3—河间洼地;4—湖泊;5—砾质辫状河道;6—砂质辫状河道;7—辫状河道;8—三角洲平原;9—心滩;10—边滩;11—沙坝;12—分流间湾;13—地理位置;14—河流及流向;15—铀矿体地表投影Figure 8. The sedimentary facies map of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou area1-Erosion source; 2-Flood plain; 3-Gamma herculis depression; 4-Lake; 5-Gravel braided channel; 6-Sandy braided channel; 7-Braided channel; 8-Delta plain; 9-Heart beach; 10-Side beach; 11-Sand bar; 12-Distributary bay; 13-Geographic location; 14-River and flow direction; 15-Projection of Uranium ore body5. 讨论
一般认为,盆地沉积物主要来自于盆地边缘蚀源区,蚀源区的岩石组合很大程度上制约了盆地沉积建造的成分、结构、构造和矿化特征。同时,盆地沉积建造也可有效示踪盆地沉积物的蚀源区方向、距离和岩石类型。虽然物源区分析方法很多,很多学者将碎屑锆石LA-ICPMS定年作为一项重要手段(Zeh and Cabral, 2021)。但就纳岭沟铀矿区而言,沉积相稳定,分布面积不足100 km2,厚度n×10 m的直罗组下段含铀岩系应是鄂尔多斯盆地边缘某一区段剥蚀的产物。
5.1 物源方向
对于盆地沉积物的物源分析,学者多采目标层位的碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MSU-Pb年龄示踪蚀源区的方法(张龙等,2016;陈印等,2017;雷开宇等,2017;俞礽安等,2020;Zeh and Cabral et al., 2021;Yu et al.,2021),取得了许多进展。就纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组的物源示踪,焦养泉等(2015)、谢惠丽等(2016)根据纳岭沟地区前期钻孔和自然露头信息,建造了包括纳岭沟铀矿在内的大型沉积朵体,认为源于阴山—古河套的物源以北西-南东方向搬运至盆地。张龙等(2016)发现大营—纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组砂岩LA-ICP-MS碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄主要集中在251~308 Ma、322~354 Ma、1529~2182 Ma、2200~2632 Ma;陈印等(2017)根据纳岭沟铀矿直罗组下段LA-ICP-MS碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄(2479±11)~(2460±19) Ma、2300~1950 Ma、(1896±21)~(1820±32) Ma、316~266 Ma及165 Ma,俞礽安等(2020)依据纳岭沟铀矿毗邻的塔然高勒铀矿区直罗组下段LA-ICP-MS碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄2200~2600 Ma、1500~2000 Ma、280~248 Ma、157 Ma,均认为纳岭沟地区直罗组物源主要来自盆地北部的大青山—乌拉山地区的高级变质岩和岩浆岩等。
鄂尔多斯盆地东北部上石炭统本溪组(C2b)(309~440 Ma、1687~2669 Ma)、下二叠统太原组(P3t)(310~390 Ma、781~901 Ma、1803~2669 M)、下石盒子8段(2200~1800 Ma、2600~2320 Ma和390~310 Ma)、上二叠统石千峰组(P3s)(276~421 Ma、803~839 Ma和1718~2583 Ma)(韩会平等,2014;屈红军等,2020),内蒙古凉城蛮汗山古元古代二长花岗岩(1933.3±9.8)Ma(张玉清等,2016)、内蒙古和林—凉城一带花岗岩(1923~1958)Ma(陈海东等,2016)、前寒武纪岩浆岩,集宁地区岩浆岩(267.2~272.1)Ma(蒋孝君等,2016),以及山西宁武—静乐盆地太原组(N-8)碎屑锆石(303~320 Ma)(李洪颜等,2009)、火山碎屑岩((179.2±0.79)Ma)和凝灰质碳酸盐岩年龄((160.6±0.55)Ma))(李振宏等,2015)等,均表明鄂尔多斯盆地东北部至内蒙古与山西交界处完全具备向直罗组提供各时代碎屑锆石的能力。
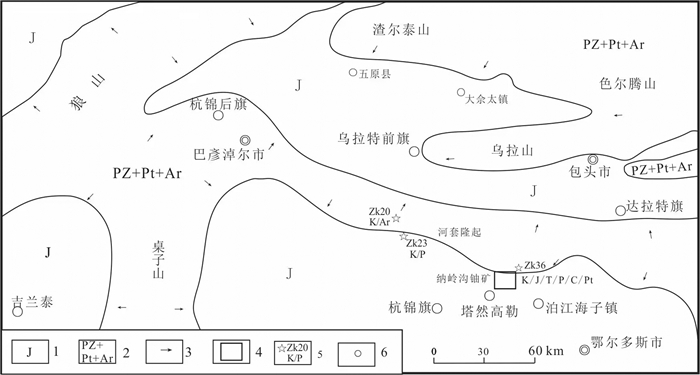
笔者依据鄂尔多斯盆地北部河套盆地和石拐盆地发育的与中侏罗统直罗组同期的五当沟组(J1-2w)含煤碎屑岩建造,侏罗世长汉沟组(J2c)杂砂岩建造(Bradley et al.,2001;葛玉辉等,2010;梁子若等,2020;陆鹿等,2022),狼山东升庙和义和久地区中下侏罗统碎屑岩(付星辉等,2016),盆地北部直罗组由东向西的沉积古流向(赵俊峰等,2010),以及河套盆地南部吉兰泰凹陷下侏罗系地层(杨德相等,2020),初步编制了鄂尔多斯盆地北部早侏罗世蚀源区分布示意图(图 9),表明早侏罗世开始沉积的河套盆地屏蔽了狼山、阴山和乌拉山地区的剥蚀物对纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组的贡献,也表明矿区北侧的早中侏罗世隆起区最有可能承担了重要物源区,其中的孔兹岩带、变质岩可与前人碎屑锆石定年结果相对应。
![]() 图 9 鄂尔多斯盆地北部早中侏罗世蚀源区分布示意图1—早中侏罗世沉积区;2—前侏罗纪剥蚀区;3—物源方向;4—纳岭沟矿区;5—钻孔、编号及揭露地层;6—城镇Figure 9. The distribution diagram of the Early-Middle Jurrassic provenance in the north Ordos Basin1-Early-middle Jurassic sediment; 2-Pre-Jurassic strata; 3-Source direction; 4-Nalinggou mining area; 5-Drill, number and strata; 6-Cities and towns
图 9 鄂尔多斯盆地北部早中侏罗世蚀源区分布示意图1—早中侏罗世沉积区;2—前侏罗纪剥蚀区;3—物源方向;4—纳岭沟矿区;5—钻孔、编号及揭露地层;6—城镇Figure 9. The distribution diagram of the Early-Middle Jurrassic provenance in the north Ordos Basin1-Early-middle Jurassic sediment; 2-Pre-Jurassic strata; 3-Source direction; 4-Nalinggou mining area; 5-Drill, number and strata; 6-Cities and towns包括达拉特旗地区出露的古元古代美岱召群变质岩的孔兹岩带最大可能成为阴山物源南迁纳岭沟地区的屏障(图 1)(钟炎等,2016;冯晓曦等,2019)。虽然杭锦后旗至达拉特旗一带的河套盆地缺少深部地球物理和岩心资料,依据包头石拐盆地的下侏罗统推测乌拉特前旗的河套地区隐伏中侏罗统河湖相沉积,与纳岭沟地区直罗组河流相沉积分居孔兹岩两侧。
纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组含铀岩系剖面图和沉积相显示,直罗组含铀岩系物源来源于矿区的东北方向。直罗组赋矿砂体厚度等值线图(图 6)和含砂率等值线图(图 7)则比较明显指出直罗组下段物源方向来自于纳岭沟矿区的北东向。直罗组下段下亚段沉积相图(图 8)表明纳岭沟地区直罗组下段蚀源区、冲积扇相、辫状河相、三角洲相由东北向—西南方向展布,纳岭沟铀矿区正处于砂质辫状河相。矿区东北缘出露和古元古代变质岩和三叠系沉积岩(图 1),据此判断,矿区东北缘的蚀源区提供了物源,与张云等(2022)编制的鄂尔多斯盆地北部三维地质模型一致。
古地磁研究表明,晚三叠世—中侏罗世,鄂尔多斯地块曾发生了45°以上的大角度构造旋转(马醒华等,1993)。中国大陆高精度GPS网表明,晚新生代以来,鄂尔多斯盆地的北边界以走滑速率1.1~1.2 mm/a逆时针旋转(李延兴等,2005)。据此,笔者推断早中侏罗世,鄂尔多斯盆地北部可能指向晋北、内蒙南部交界地带。当然,对于鄂尔多斯地块的旋转,尚不确定鄂尔多斯盆地与周缘的阴山造山带和山西断隆是否同步旋转,但晚三叠世至中侏罗世,鄂尔多斯原型盆地东部的宁武—静乐盆地发现的下侏罗统永定庄组火山碎屑岩((179.2±0.79)Ma)和中侏罗统云岗组顶部凝灰质碳酸盐岩((160.6±0.55)Ma),具备提供165 Ma、157 Ma的碎屑锆石(赵俊峰等,2010;李相博等,2012;李振宏等,2015),以及样品15ZKN28-52-K3和17nzk026中发现的碳硅石,说明内蒙古南部与山西北部的办罗界处具有为纳岭沟直罗组提供物源的充分条件。如果山西宁武—静乐地区的中侏罗统火山岩参与了纳岭沟地区直罗组砂体建造,那么纳岭沟等铀矿床的成矿作用研究将成为新的研究方向。
就重矿物而言,直罗组的重矿物与鄂尔多斯盆地山西组、下石盒子组可对照(汪正江等,2001;张道锋等,2009),表明鄂尔多斯盆地东北方向的晚古生界地层具有向纳岭沟地区直罗组提供物源的能力。
据此,笔者认为纳岭沟铀矿区直罗组含铀岩系物源来自于包括呼斯梁—高头窑—皂火壕蚀源区在内的晋蒙交界处太古代、元古代、古生代变质岩、岩浆岩和中生代的沉积岩、火山岩。
5.2 物源距离
物源距离影响盆地沉积物的胶结程度、成分、结构、构造和地球化学等重要指标。通常情况下,长距离搬运的碎屑物具有较好的分选性和磨圆度,较高的成分成熟度,而短距离迁移的碎屑物具有较差的分选性、磨圆性、成分成熟度。纳岭沟铀矿直罗组具有较低的结构成熟度和成分成熟度,这在学者的研究成果已形成了共识(易超等,2014;王思力等,2018;张宾等,2020a)。直罗组含铀岩系主要岩石类型为疏松、较疏松状中粗粒长石砂岩,碎屑多呈棱角状、次棱角状,碎屑成分复杂的长石砂岩,而滚圆状碎屑则表明部分碎屑物系远距离搬运来的,未引起学者的足够重视。较低的结构成熟度(粗粒、中粒碎屑占比63%),较低的成分成熟度指数(Q/(F+R)=0.41~0.71),表明物源区剥蚀期处于寒冷、干旱的古气候和相对高差大的地形地貌,剥蚀物经历了较短的搬运、沉积时间和距离。重矿物中棱角状的锆石,集合体状产出的棱角状、次棱角状电气石,低值ZTR(4~13)、UM/SM(0.37~3.20),GZi(16.67~91.67),均说明碎屑剥蚀、迁移距离较短。
对于直罗组含铀岩系的迁移距离,许多学者认为纳岭沟地区直罗组属近源沉积。例如:冯晓曦等(2017)认为直罗组的岩石学、碎屑锆石年龄图谱指示阴山造山带前寒武纪高级变质岩、古生代花岗岩及中生代火山岩等为纳岭沟铀矿提供了物源;张宾等(2020b)根据纳岭沟含铀长石岩屑砂岩、岩屑长石砂岩和岩屑砂岩较低的成分成熟度,认为直罗组下段下亚段属近源沉积。但是,冯晓曦等(2019)根据鄂尔多斯盆地北部包括美岱召岩群(Pt1m)的孔兹岩带与东胜铀矿田相依的空间关系,推测其是直罗组的重要物源区之一。同时,1∶25万乌拉特前旗幅(K49C004001)钻孔ZK20(地层K、Ar)、ZK23(地层K、P)、ZK24(地层K、Ar)、ZK33(地层T、P)、ZK36(地层K、J、T、P、C、Pt)等揭露的地层埋深情况,表明中侏罗统直罗组沉积时,盆地边缘出露了T、P、C、Pt地层,这与张云等(2022)编制的鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区直罗组“北高南低、东高西低”古地貌特点一致。
虽然如此,盆地北部的孔兹岩带未发现与316~266 Ma、165~157 Ma锆石年龄相对照的岩石类型,这也暗示直罗组含铀岩系的物源可能更复杂。直罗组含铀岩系较低的结构成熟度和成分成熟度属于近源沉积,而许多次棱角状、次滚圆状的锆石、粒状金红石、不规则状榍石等碎屑物的搬运距离或者来自较远距离,或者近处蚀源区沉积物的再循环。对比晋蒙交界处出露的各时代的岩石类型可满足碎屑物的结构和成分特征,山西宁武—静乐盆地的中下侏罗统火山碎屑岩(李振宏等,2015)可提供含铀岩系中165 Ma、157 Ma的碎屑锆石。
同时,晋蒙交界处是五台地块、阴山陆块和鄂尔多斯地块长期相互作用的结果,具有岩石地球化学特征显示的活动边缘、被动边缘、大陆岛弧和安第斯型俯冲带构造环境。
由于缺少侏罗纪晋蒙交界处和鄂尔多斯盆地北部古地貌、古气候、古沉积体系的对比,本文还无法准确判断纳岭沟直罗组含铀岩系搬运轨迹。因此,根据分选、磨圆和碎屑锆石年龄,初步判断纳岭沟直罗组含铀岩系具有近源沉积和远距离沉积的特点,但以近源沉积为主。
5.3 物源类型
盆地沉积物的岩石类型、碎屑成分和地球化学特征是蚀源区岩石类型的综合响应。虽然风化、搬运过程中,蚀源区岩石经历了复杂的物理、化学、生物等表生营力作用,但碎屑物仍保留了丰富的蚀源区信息,可有效反演物源区岩石类型,进而构建盆地古地质构造格架(Vanesa et al., 2019)。直罗组含铀岩系中大量具有波状消光石英表明其来自于变质岩。岩屑成分指示蚀源区存在火成岩岩屑(花岗岩岩屑、流纹岩岩屑)、沉积岩岩屑(泥岩岩屑、燧石、细粒砂岩岩屑)、变质岩岩屑(石英岩岩屑、绢云千枚岩岩屑、云母石英片岩岩屑)。
重矿物中次滚圆状石榴子石、电气石、金红石、绿帘石等可由横贯鄂尔多斯地块北部的孔兹岩带、山西天镇一带太古代片麻岩提供,其中达拉特旗一带古元古代美岱召岩群(Pt1m)(图 1)硅质岩、含石墨片岩可能提供重要物源。次棱角锆石、磷灰石、金红石、榍石的重矿物组合为酸性花岗岩,角闪石、辉石、钛铁矿指示基性、超基性岩浆岩,可对应内蒙凉城一带的大面积古元古代二长花岗岩和脉状辉长岩。次滚圆粒状锆石可能来自于鄂尔多斯东胜至准格尔旗一带二叠系、三叠系砂岩。单晶石英和样品17026、15UZK11-K36的碳硅石指示物源区或分布火山岩,或沉积过程受到同期火山岩的污染,山西宁武—静乐盆地中侏罗世火山碎屑岩提供了印证。
张宾等(2020a)根据岩石学和重矿物特征,认为直罗组下段下亚段物源区为阴山—大青山—乌拉山地区的前寒武纪孔兹岩、片麻岩、闪长岩以及海西—印支期辉长岩和花岗闪长岩;俞礽安等(2020)根据碎屑锆石U-Pb认为大青山—乌拉山地区的孔兹岩、TTG片麻岩、麻粒岩和酸性、基性岩浆岩为直罗组提供了物源,而本文认为括呼斯梁—高头窑—皂火壕蚀源区在内的,纳岭沟铀矿以东的内蒙古呼和浩特—山西右玉、集宁—山西大同交界地带太古宙、元古宙孔兹岩、片麻岩、花岗岩、辉绿岩、正长岩和古生代和中生代砂岩、灰岩,晋北早中侏罗世火山碎屑岩为含铀岩系提供了物源,其中,横亘于伊盟隆起北缘的孔兹岩(冯晓曦等,2019)和鄂尔多斯准格尔旗一带的石炭纪、二叠纪、三叠纪沉积岩主要物源区。究其原因,本文示踪了直罗组含铀岩系中的沉积岩、火山岩岩屑和重矿物碳硅石来源,并简要恢复了鄂尔多斯盆地北部乌拉山地区侏罗纪地貌,参考了古地磁研究(马醒华等,1993)和大地测量GPS成果(李延兴等,2005)。
综上所述,直罗组含铀岩系物源区为包括呼斯梁—高头窑—皂火壕近源在内的,内蒙古准格尔旗—山西右玉交界地带为太古宙、元古宙、古生代、中生代变质岩、岩浆岩、沉积岩和火山岩。碎屑物具有以近源为主,伴有远源沉积的特征。由于岩石矿物学、重矿物学示踪母岩的多解性和晋北、内蒙古南部蚀源区岩相古地理研究的薄弱,物源区岩石类型仍处于定性认识推测阶段。
虽然如此,本文将纳岭沟铀矿直罗组含铀岩系物源区厘定为,包括达拉特旗孔兹岩带在内的鄂尔多斯盆地东北方向的晋北—内蒙古南部交界处前侏罗世基岩出露区,有别于前人认为的阴山、乌拉山地区(图 10)。
加强晋北—内蒙古集宁地区南部交界处蚀源区的研究或许有助于深化纳岭沟、大营、塔然高勒等其他铀矿床含矿砂体物源、铀源、含铀流体来源研究,也可为鄂尔多斯盆地中生代构造演化提供一定的科学信息。
6. 结论
(1)纳岭沟铀矿直罗组含铀岩系主要为长石砂岩,碎屑分选中等至差,主要为棱角状、次棱角状,少量为次滚圆状;棱角状、次棱角状尖晶石、锐钛矿、角闪石、碳硅石等重矿物非均匀分布,ZTR指数2%~10%,具低的结构成熟度和成分成熟度,呈现以近距离沉积为主,伴有远源沉积的特点。
(2)稀土元素配分曲线相似,元素含量变化幅度大;岩层产状、赋矿砂体、高含砂率砂体由北东方向至南西方向规律性同步展布,呈现整套含铀岩系沉积体系稳定,且碎屑物由矿区北东端迁入,向南西端布局的趋势,表明矿区北东方向的前中侏罗世晋蒙交界处的剥蚀区为直罗组含铀岩系的蚀源区。
(3)种类繁多的石英岩、云母石英片岩、花岗岩、流纹岩、砂岩、硅质岩岩屑和角闪石、辉石、碳硅石等特殊标型重矿物表明,处于纳岭沟矿区北东向蚀源区的太古代片麻岩,元古代孔兹岩、花岗岩、辉长岩,古生代岩浆岩、沉积岩和中生代火山岩为蚀源区,其中矿区北邻的东西向含早元古代美岱召群的孔兹岩带提供了重要物源。
注释
❶核工业208大队. 2014.内蒙古达拉特旗纳岭沟铀矿床N12~N28线详查地质报告[R].
致谢: 感谢冀中坳陷深部碳酸盐岩热储调查评价项目组在样品采集方面提供的帮助。 -
表 1 地热水F-浓度和pH描述统计
Table 1 Description statistics of F- concentration and pH in geothermal water

表 2 F-与其他离子相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between F- and other ions

表 3 地热流体开发利用水质评价统计
Table 3 Statistics of water quality of geothermal exploitation and utilization

表 4 可命名矿水样本统计
Table 4 Statistics of namable mineral water samples

-
Chen Moxiang. 1988. Geothermics of North China[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Deng J, Lin W, Xing L, Chen L. 2022. The estimation of geothermal reservoir temperature based on integrated multicomponent geothermometry: A case study in the Jizhong depression, North China Plain[J]. Water, 14: 2489. doi: 10.3390/w14162489
Gao Z J, Zhu Z H, Liu X D. 2014. The formation and model of high fluoride groundwater and in-situ dispelling fluoride assumption in Gaomi City of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2(2): 34-39. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2014.9280016
Guo Q, Wang Y, Liu W. 2007. Major hydrogeochemical processes in the two reservoirs of the Yangbajing geothermal field, Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 166: 255-268. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2007.08.004
He Jin, Zhang Fucun, Han Shuangbao, Li Xufeng, Yao Xiujü, Zhang Wei. 2010. The distribution and genetic types of high-fluoride groundwater in northern China[J]. Geology in China, 37(3): 621-626 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Chunhua, Wang Wei, Yang Lizhi, Zhu Henghua, Guo Yan, Ma Yuhong, Guo Jing, Liu Bohan. 2021. Driving mechanisms of fluorine enrichment characteristics in groundwater, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1962-1972 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu Mengsheng, Han Baoping, Wu Fan, Sun Dequ, Zhang Zhaomin. 2014. Characteristics and genesis of high-fluorine groundwater in southwestern Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 41(1): 294-302 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Feng, Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Zhu Xi, Zhang Hanxiong, Yue Gaofan. 2020. Structure of geothermal reservoirs and resource potential in the Rongcheng geothermal field in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(7): 1981-1990 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ou Hao, Lu Guoping, Hu Xiaonong, Wang Beibei. 2019. Fluoride enrichment in geothermal waters in Xinyi-Lianjiang region, Guangdong[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 38(5): 1128-1138 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren Fuhong, Ceng Jianghui, Liu Wensheng, Zhang Cuiyun. 1996. Hydrogeochemical environment of high fluorine groundwater and the relation between the speciation of fluorine and the diseased ratio of endemic fluorosis: A case study of the North China Plain[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, (1): 85-97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi Weidong, Guo Jianqiang, Zhang Senqi, Ye Chengming, Li Jian, Ma Xinhua. 2010. The distribution and geochemistry of geothermal groundwater bearing F and as in the guide basin[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 37(2): 36-41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Hongli, Ma Feng; Liu Zhao, Liu Zhiming, Wang Guiling, Nan Dawa. 2015. The distribution and enrichment characteristics of fluoride in geothermal active area in Tibet[J]. China Environmental Science, 35(1): 251-259 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin W J, Wang G L, Gan H N, Zhang S S, Zhao Z, Yue G F, Long X T. 2023. Heat source model for Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) under different geological conditions in China[J]. Gondwana Research, 122: 243-259. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.08.007
Wang Guiling, Lin Wenjing. 2020. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(7): 1923-1937 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Liang Jiyun, Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli. 2017a. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(4): 448-459 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Lin Wenjing, Liu Feng, Zhu Xi, Liu Yanguang, Li Jun. 2017b. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1074-1085 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Ruizhi, Liu Jian, Wu Jinhui, Xia Lu, Cui Xiao, Zhang Qiangying. 2019. Preparation of magnetic nanocomposite and their removal properties of F and As in geothermal water[J]. The Journal of New Industrialization, 9(6): 82-85 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xinwei, Guo Shiyan, Gao Nan'an, Liu Huiying, Wang Tinghao, Wei Guangren, Lei Haifei. 2023. Detection of carbonate geothermal reservoir in Niudong fault zone of Xiong'an New Area and its geothermal exploration significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 42(1): 14-26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei Xiaoyang, Guo Qinghai, Yuan Jianfei, Ye Lu, Chang Juntan. 2009. Environmental migration and transformation of fluoride from high-temperature geothermal fluid: A case study at Yangbajing, Tibet, China[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 32(1): 38-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Lihan. 2015. Characteristics and Genesis of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Hengshui City, the North China Plain China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xing Lina, Guo Huaming, Wei Liang, Zhan Yanhong, Hou Chuntang, Li Ruimin, Wang Yi. 2012. Evolution feature and gensis of fluoride groundwater in shallow aquifer from North China Plain[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 34(4): 57-67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Dongyi. 1986. Distribution of fluorine and geothermal fields[J]. Geotechnical Investigation Surveying, (6): 56 (in Chinese).
Yu Bo, Ren Tong, Du Xinghong, Chu Zhiqing, Guo Meiyi. 2020. Study on the treatment process of fluorine-containing waste water[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 38(11): 192-195 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Lan. 2007. A Study of the Occurrence and Origin of Fluoride in Thermal Groundwater in Some Areas of China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan Ruoxi, Wang Guiling, Liu Feng, Zhang Wei, Cao Shengwei. 2021. Study on the indication of fluorine of the low-medium temperature convective geothermal system in Northeastern Hebei Province[J]. Geological Review, 67(1): 218-230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Jianhui. 1995. Numerical modelling of geochemical behavious of fluorine in the shallow groundwater system[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, (3): 267-277 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Dezhong, Liu Zhigang, Lu Hongliu. 2013. Geothermal of Hebei[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Zhang Lin, Sun Yongmei, Lin Chunzhu, Xie Zhenyuan, Wang Jun, Gao Weiqin. 1996. Utilization of geothermal water and environmental pollution of fluoride[J]. Agro-Enyironment and Development, 13(3): 40-42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Wei, Wang Guiling, Liu Feng, Xing Linxiao, Li Man. 2019. Characteristics of geothermal resources in sedimentary basins[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 255-268 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Guisen, Li Liangjing, Lü Jinbo. 2019. Research on method of processing tail water in geothermal exploration in Beijing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(2): 397-403 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈墨香. 1988. 华北地热[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 何锦, 张福存, 韩双宝, 李旭峰, 姚秀菊, 张徽. 2010. 中国北方高氟地下水分布特征和成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 37(3): 621-626. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/cn/article/id/20100311 刘春华, 王威, 杨丽芝, 朱恒华, 郭艳, 马瑜宏, 郭晶, 刘柏含. 2021. 山东省地下水氟富集规律及其驱动机制[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1962-1972. 鲁孟胜, 韩宝平, 武凡, 孙德全, 张兆民. 2014. 鲁西南地区高氟地下水特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 41(1): 294-302. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/cn/article/id/20140124 马峰, 王贵玲, 张薇, 朱喜, 张汉雄, 岳高凡. 2020. 雄安新区容城地热田热储空间结构及资源潜力[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 1981-1990. 欧浩, 卢国平, 胡晓农, 王贝贝. 2019. 广东省信宜-廉江地区地热水中氟的富集过程[J]. 环境化学, 38(5): 1128-1138. 任福弘, 曾溅辉, 刘文生, 张翠云. 1996. 高氟地下水的水文地球化学环境及氟的赋存形式与地氟病患病率的关系——以华北平原为例[J]. 地球学报, (1): 85-97. 石维栋, 郭建强, 张森琦, 叶成明, 李健, 马新华. 2010. 贵德盆地高氟、高砷地下热水分布及水化学特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 37(2): 36-41. 孙红丽, 马峰, 刘昭, 刘志明, 王贵玲, 男达瓦. 2015. 西藏高温地热显示区氟分布及富集特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 35(1): 251-259. 王贵玲, 蔺文静. 2020. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 1923-1937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽. 2017a. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 38(4): 448-459. 王贵玲, 张薇, 蔺文静, 刘峰, 朱喜, 刘彦广, 李郡. 2017b. 京津冀地区地热资源成藏模式与潜力研究[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1074-1085. doi: 10.12029/gc20170603 王睿智, 刘建, 吴金辉, 夏露, 崔骁, 张强英. 2019. 磁性纳米复合物的制备及其在地热水中F和As的去除性能研究[J]. 新型工业化, 9(6): 82-85. 汪新伟, 郭世炎, 高楠安, 刘慧盈, 王婷灏, 魏广仁, 雷海飞. 2023. 雄安新区牛东断裂带碳酸盐岩热储探测及其对地热勘探的启示[J]. 地质通报, 42(1): 14-26. 魏晓阳, 郭清海, 袁建飞, 叶露, 常军坦. 2009. 高温地热流体来源氟在环境中的分布特征——以西藏羊八井热田为例[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(1): 38-44. 乌丽罕. 2015. 衡水地区高氟地下水化学特征及其成因[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 邢丽娜, 郭华明, 魏亮, 詹燕红, 侯春堂, 李瑞敏, 王轶. 2012. 华北平原浅层含氟地下水演化特点及成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 34(4): 57-67. 杨东义. 1986. 氟与地热田的分布[J]. 工程勘察, (6): 56. 杨明金, 杨帆, 王谋凤, 陈建明, 张少安. 2005. 地热水水质及其对农田和农作物影响研究[J]. 福建农业科技, (6): 65-67. 于波, 任桐, 都兴红, 褚志强, 郭美祎. 2020. 含氟废水处理工艺研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 38(11): 192-195. 虞岚. 2007. 我国部分地下热水中氟的分布与成因探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 原若溪, 王贵玲, 刘峰, 张薇, 曹胜伟. 2021. 冀东北地区中低温对流型地热系统的氟指示意义研究[J]. 地质论评, 67(1): 218-230. 曾溅辉. 1995. 浅层地下水系统氟地球化学行为的数值模拟[J]. 地质学报, (3): 267-277. 张德忠, 刘志刚, 卢红柳. 2013. 河北地热[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 张林, 孙咏梅, 林春竹, 谢镇远, 王军, 高维勤. 1996. 地热水的开发利用与环境氟污染[J]. 农业环境与发展, 13(3): 40-42. 张薇, 王贵玲, 刘峰, 邢林啸, 李曼. 2019. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 255-268. doi: 10.12029/gc20190204 郑桂森, 李良景, 吕金波. 2019. 北京地热开采中的尾水氟处理方法[J]. 地质通报, 38(2): 397-403. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 段明,张博,汤超,谢瑜,滕雪明,张祺,徐增连,魏安军,蒋职权. 内蒙古额仁淖尔凹陷赛汉组砂(泥)岩地球化学特征及其对铀成矿作用的制约. 中国地质. 2024(03): 932-950 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 郑余修,罗跃,阳奕汉,周义朋,李光辉,刘志锋,张传飞,崔博. 鄂尔多斯某砂岩铀矿试验开采过程中地下水流场时空特征. 有色金属(冶炼部分). 2024(08): 94-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李焕纪,孙永刚,郑近龙,董峻麟,张徐平. 青海沱沱河地区夏里组砂岩形成时代及物源区构造环境判别. 世界核地质科学. 2024(05): 875-887 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: