Distribution characteristics and ecological environment assessment of potassium in topsoil of cultivated land in Tongzi County, Guizhou Province
-
摘要:研究目的
钾是植物必需的三大营养元素之一,也是土壤肥力的重要影响因子。开展桐梓县耕地表层土壤钾分布特征研究,为县域农业发展、生态环境评价提供环境地质本底参考。
研究方法本文以桐梓县为研究区,依据耕地质量地球化学调查所获得的表层土壤样品中钾、速效钾等指标数据,系统地探讨了耕地表层土壤钾和速效钾的含量、空间分布特征、等级状况及影响因素。
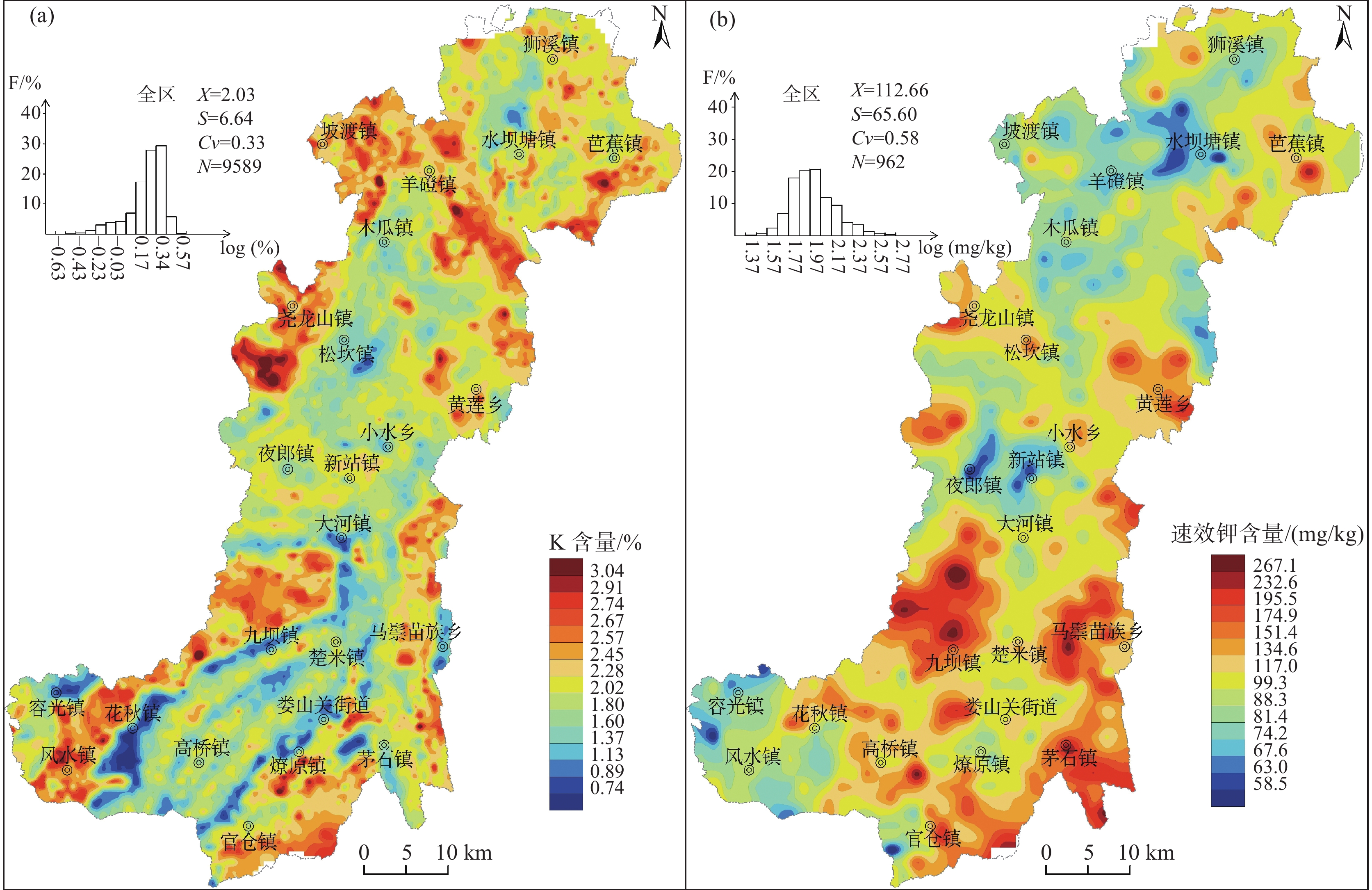
研究结果研究区耕地表层土壤钾含量范围为2.50~49.60 g/kg,平均值为20.30 g/kg;钾含量整体以中等、较丰富、丰富等级为主。速效钾含量范围为22.40~684.00 mg/kg,平均值为112.66 mg/kg;速效钾含量整体为中等至较缺乏等级。耕地表层土壤钾、阳离子交换量与速效钾呈正相关关系,pH与速效钾呈负相关关系。
结论研究区耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾分布不均衡。耕地表层土壤钾受地质背景影响显著,高值区、低值区的分布与区内地层、构造套合较好。耕地表层土壤钾含量主受控于成土母岩,钾在灰岩及其形成的土壤中含量较低,其在南部乡镇集中大面积缺乏与广泛分布的二叠系茅口组灰岩母岩区有关。
创新点:首次对桐梓县全域进行耕地表层土壤钾地球化学调查;系统地探讨了耕地表层土壤钾与速效钾的含量、空间分布特征、等级状况及影响因素。
Abstract:This paper is the result of Agricultural geological survey engineering.
ObjectivePotassium is one of the three essential nutrients for plants and an important factor influencing soil fertility. Distribution characteristics of potassium in topsoil of cultivated land in Tongzi County was carried out to provide environmental geological background reference for county agricultural development and ecological environment evaluation.
MethodsTaking Tongzi County as the research area, this paper systematically discussed the content, spatial distribution, grade status and influencing factors of potassium and available potassium in surface soil samples obtained from cultivated land quality geochemical survey.
ResultsThe content of potassium in topsoil of cultivated land in the study area ranged from 2.50 to 49.60 g/kg, with an average of 20.30 g/kg, and the overall potassium content is mainly in medium, relatively rich and rich grade. The content of available potassium ranging from 22.40 to 684.00 mg/kg, with an average of 112.66 mg/kg, and the content of available potassium was in moderate to relatively deficient grade. Potassium and cation exchange capacity are positively correlated with available potassium, while the pH is negatively correlated with available potassium in topsoil of cultivated land.
ConclusionsThe distribution of potassium and available potassium in topsoil of cultivated land in the study area is uneven. The geological factor plays an essential role in the content of potassium in topsoil of cultivated land, and the distribution of high−value and low−value of potassium is well integrated with the stratigraphic and tectonics of the study area. The content of potassium in topsoil of cultivated land is mainly controlled by the parent rock, which is relatively low in the limestone and forming soil. Large−scale potassium depletion in the southern part of the study area is related to the widely distributed of the Permian Maokou Formation limestone.
Highlights:This study is the first time to report the potassium geochemical survey in topsoil of cultivated land in Tongzi County. This paper systematically discusses the content, spatial distribution characteristics, grade status, and influencing factors of potassium and available potassium in topsoil of cultivated land.
-
1. 引 言
钾是主要造岩元素之一,在上地壳的丰度值为2.32%(Rudnick and Gao,2003)。钾在土壤中含量为1.36%,我国多数土壤含量为0.5%~2.0%(黄昌勇和徐建明,2010)。钾作为土壤酶的良好活化剂,也是土壤养分及土壤肥力重要影响因子,对农作物的生长、代谢和产量及品质有直接影响(Ismail,2010;钟来元和郭良珍,2012;刘晓伟等,2021)。土壤矿物质的风化,特别是通过释放钾素,为世界各地的植物提供了营养(Portela et al.,2019)。而随着人口的增长及生活水平的提高,对农产品需求的量、质都有急剧增加,土壤养分消耗巨大;土壤钾供应不足将会严重制约作物质量与产量(张苏江等,2015;Li et al.,2015;王栋等,2017)。因此,全面了解与研究耕地土壤钾丰缺及分布状况对农业发展、粮食安全十分必要。国内外学者对土壤钾的含量(Gurav et al.,2019;汪实等,2021)、形态(Sharpley and Smith,1988;欧阳志标等,2016)和有效性(Dessougi et al.,2002;Li et al.,2020)等方面进行了大量研究,并探讨了在农业集约栽培条件下土壤供钾能力(Das et al.,2019;Zhu et al.,2020)以及施用钾肥(Greenwood and Karpinets,1997a,b;黄振瑞等,2020)、不同耕作方式(张珊珊等,2012)和不同有机物料还田(湛玉曼等,2021)对农作物生长及土壤钾含量的影响。
我国土壤钾分布不均衡,呈南低、北高,缺钾土壤主要分布在南方地区(黄昌勇和徐建明,2010)。桐梓县位于贵州省北部的乌蒙山集中连片特殊困难区,生态脆弱,耕地土壤瘠薄,供钾潜力较低(黄昌勇和徐建明,2010)。贵州区域性土壤钾研究主要在20世纪80至90年代及21世纪初。研究发现:贵州耕地土壤钾含量也不均衡,约1/3的耕地缺钾或极缺钾(曹文藻,1989,1993);土壤钾贮备日渐减少,土壤钾与速效钾含量逐年降低,平均含量分别从1985年的1.51%、121.60 mg/kg降到1998年的1.42%、88.90 mg/kg(陈旭晖,2001;陈旭辉和陈湘燕,2003);到2007年速效钾缺乏等级仍占29.30%,缓效钾极缺乏等级占26.86%(高雪等,2013)。前人在桐梓县仅仅开展了小范围地域及特定作物对象的表层土壤钾研究。如桐梓县高桥镇龙爪沟小流域土壤、林场中竹笋林地土壤、燎原镇花园村水稻土、木瓜镇中山村马铃薯种植地土壤、花秋镇油菜主产区土壤、方竹笋基地土壤的钾含量研究(罗平源等,2006;王良波和杨彩霞,2010;杨彩霞等,2013;刘均霞和陆引罡,2016;钱旭等,2018;何雨茹等,2021),并开展了少量测土配方施肥实验(王良波和杨彩霞,2010;杨彩霞等,2013;刘均霞和陆引罡,2016)。而全县域的耕地表层土壤钾研究处于空白状态。
因此,本文以贵州省桐梓县耕地质量地球化学调查评价为基础,通过系统地调查取样分析,首次从全域尺度对研究区耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾的含量及特征进行分析,全面掌握桐梓县耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾分布状况,研究不同地质背景、土壤类型、利用方式下耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾的含量水平,评价耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾丰缺及等级状况,初步探讨影响钾含量的因素,为桐梓县耕地资源管护、动态监测、污染防治等提供基础成果支撑,对桐梓县乡村振兴、山地特色高效农业发展、生态地球化学研究提供理论参考。
2. 研究区地质背景
桐梓县,隶属于贵州省遵义市管辖,位于贵州省北部,北接重庆市。地理位置:27°57′N~28°54′N,106°26′E~107°17′E,总面积3207 km2。桐梓县位于黔北山地与四川盆地的衔接地带,属黔北中山峡谷区;地势呈东北高、西南低,地貌主要由山地、丘陵、盆地、山原4类构成。
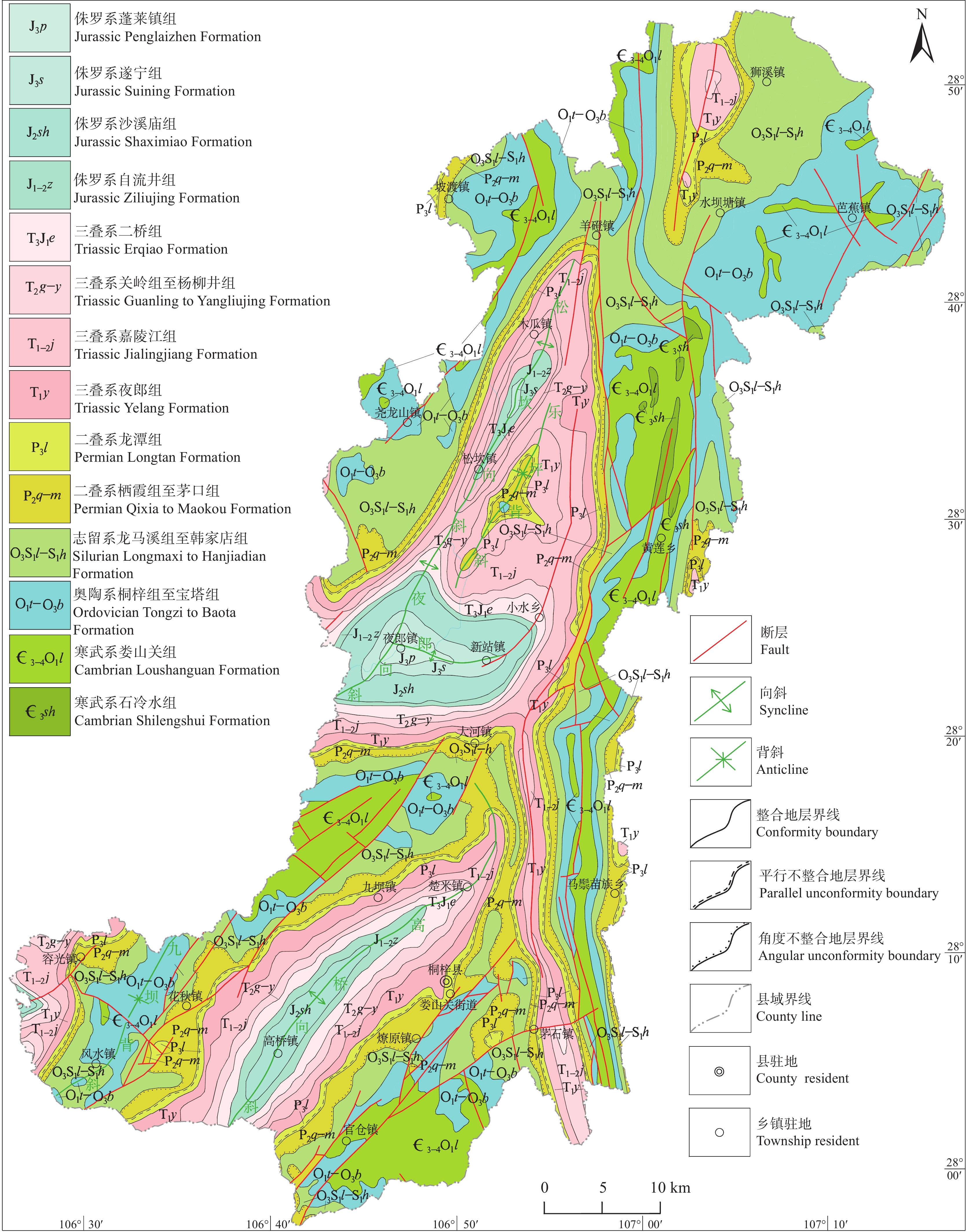
研究区大地构造单元横跨上扬子陆块黔北隆起区毕节北东向弧形褶皱带(Ⅳ−4−1−3(2))和凤冈南北向隔槽式褶皱变形区(Ⅳ−4−1−3(3))(戴传固等,2017)。研究区出露地层由老到新有古生界的寒武系(Є)、奥陶系(O)、志留系(S)、二叠系(P),中生界的三叠系(T)、侏罗系(J),新生界的第四系(Q)。出露岩性有碳酸盐岩,包括白云岩、灰岩、白云岩−灰岩等;陆源碎屑岩,包括砂岩−黏土岩、砂岩、紫红色砂岩−黏土岩等(图1)。矿产主要有煤矿、黄铁矿、菱铁矿等。根据《土地利用现状分类》(GB/T 21010—2017)划分,研究区土地利用现状主要有耕地、园地、林地、草地、城镇村及工矿用地、交通运输用地、水域及水利设施用地、其他土地。根据《中国土壤系统分类检索》(2001),研究区土壤类型主要有6大类:黄壤(约60.53%)、石灰土(约23.62%)、紫色土(约10.30%)、水稻土(约3.91%)、黄棕壤(约1.33%)和粗骨土(约0.30%)。研究区耕地土壤的水分状况为湿润型(陆晓辉等,2018),主要种植玉米、水稻、马铃薯、高粱等。
![]() 图 1 桐梓县区域地质简图(据张钟华等,2019修改)Figure 1. Sketch regional geological map of Tongzi County (modified from Zhang Zhonghua et al., 2019)
图 1 桐梓县区域地质简图(据张钟华等,2019修改)Figure 1. Sketch regional geological map of Tongzi County (modified from Zhang Zhonghua et al., 2019)3. 样品采集与分析方法
3.1 样品采集
研究对象:以耕地(水田、旱地、水浇地)为主,兼顾园地(果园、茶园及其他园地)、林地(有林地、灌木林地、其他林地)、裸地及可以复垦的工矿用地。
样品布设:以《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)为依据、1 km2为单元,采用“九宫网格+全国第二次土地调查(简称:“二调”)地类图斑”结合地形图及卫星影像图的方法,均匀布设基本样(点密度约9.40件/km2),同时在耕地分布区均匀布设10%采样点作为有效态样品,按2%随机布设重复样点。
样品采集:采取多点组合形式,以主样点为中心,按“S”、“X”或“棋盘”形向四周辐射20~50 m布设3~5个子样点,每个样点采集表层0~20 cm的原始新鲜土壤(去除地表腐殖质、杂草根、砾石等杂质,避开施肥、粪堆及其他污染)等份组合成一件混合样,样重≥2 kg。研究区共采集表层土壤基本样9589件,有效态样962件;并对元素异常区采集了土壤剖面样80件、成土母岩样20件、成因检查样160件。野外采样时间从2017年11月至2019年5月。
样品加工:野外采集的样品在室内自然风干后,按照规范要求进行粗加工,用10目尼龙筛过筛截取2 mm粒级的全部自然泥粒后,用缩分法取样≥200 g送实验室测试分析。
3.2 分析测试及质量
研究区耕地表层土壤各指标分析方法、检测依据、检出限等,具体见表1。采集的样品交由贵州省地质矿产中心实验室分析测试。各指标分析数据报出率均为100%,经国家一级标准物质验证准确度和精密度合格率为100%,并通过了贵州省地质环境监测院组织的专家验收,质量可靠。
表 1 样品分析方法Table 1. Sample analysis methods序号 指标 分析方法 检测依据 主检仪器 实验室检出限 1 钾 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法
(ICP−OES)区域地球化学样品分析方法
(DZ/T 0279.2—2016)电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪 0.01% 2 速效钾 等离子体发射光谱法(ICP−OES) 森林土壤 钾的测定
(LY/T 1234—2015)等离子体
发射光谱仪1.00 μg/g 3 有机质 容量法(VOL) 区域地球化学样品分析方法
(DZ/T 0279.27—2016)滴定管 0.02% 4 pH 电位法(ISE) 区域地球化学样品分析方法
(DZ/T 0279.34—2016)pH计 0.01
(无量纲)5 阳离子交换量(CEC) 容量法(VOL) 森林土壤
阳离子交换量的测定
(LY/T 1243—1999)凯氏定氮仪 1.00 mmol/L 3.3 评价方法及标准
本次评价方法参照《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)。评价单元是耕地质量地球化学等级划分的最小空间单位,以1∶50000或更高精度的土地利用现状调查图斑(“二调”成果)为基础。
3.4 数据处理
采用SPSS 18.0与Excel 2019软件统计地球化学特征参数等。地球化学图及等值线图由MapGIS6.7及Geo Chem Studio软件联合制作;地球化学等级图以“二调”图斑为底图,由中国地质调查局发展研究中心开发的“土地质量地球化学评价管理与维护(应用)子系统”和MapGIS6.7软件共同完成。
取得耕地表层土壤样品分析数据后,检验各元素(指标)数据的频数分布形态,并对异常值进行剔除。对于(近似)符合正态分布的元素经剔除异常值后,取算术平均值;对于(近似)符合对数正态分布的元素经剔除异常值后,取几何平均值;对于偏态分布的元素,取中位值,作为研究区耕地表层土壤该元素地球化学背景值。
4. 分析结果
4.1 钾地球化学分布特征
研究区耕地表层土壤钾含量范围为2.50~49.60 g/kg,分布不均衡(表2)。从表2可以得到,钾剔除异常值后平均值为20.30 g/kg,高于贵州耕地表层土壤背景值16.59 g/kg(蔡大为等,2020),富集系数K1=1.22,属于弱富集类元素;也高于第二次土壤普查贵州省土壤表层平均含量16.03 g/kg(贵州省土壤普查办公室,1994);略低于全国土壤表层背景值(鄢明才等,1997),富集系数K2=0.98,属于背景类元素;变异系数为0.33,为弱离散类。结合图1和图2a可知,研究区耕地表层土壤钾受地质背景影响显著,分带性明显,高值区、低值区的分布与区内地层、构造套合较好。高值区主要分布在寒武系、三叠系地层母岩区,低值区主要分布于二叠系、侏罗系地层母岩区。从图2a和表3得到,南部乡镇部分地区耕地表层土壤钾含量较低,呈带状分布,特别是在花秋镇附近,其区域平均值最低,为16.97 g/kg;而北部地区,钾含量相对较高,平均值以尧龙山镇区域最高,为25.43 g/kg,其次为坡渡镇。
表 2 耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾地球化学参数Table 2. Geochemical parameters of topsoil potassium and available potassium in cultivated land元素 样本数
(N)最小值 最大值 均值
(X)标准差
(S)变异系数
(Cv)剔除异常值后 贵州耕地表层 全国表层土壤 样本数 均值 背景值 K1 背景值 K2 钾 9589 2.50 49.60 20.30 6.64 0.33 9578 20.30 16.59① 1.22 20.70③ 0.98 速效钾 962 22.40 684.00 112.66 65.60 0.58 945 98.00 139.65② 0.70 — — pH 9589 4.01 8.78 6.33 1.58 0.17 — — — — — — 注:钾含量单位为g/kg,速效钾含量单位为mg/kg,pH为无量纲;①引自蔡大为等(2020),②引自高雪等(2013),③引自鄢明才等(1997)。 表 3 桐梓县各乡镇表层土壤钾、速效钾含量统计Table 3. Statistics of topsoil potassium and available potassium contents in each town of Tongzi County乡镇名 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 乡镇名 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 平均值 样本数 平均值 样本数 平均值 样本数 平均值 娄山关街道 437 20.16 41 115.82 木瓜镇 456 19.91 47 88.17 楚米镇 310 18.95 35 131.81 坡渡镇 388 25.11 40 88.58 新站镇 406 19.51 39 98.63 燎原镇 279 18.29 27 117.69 松坎镇 316 17.88 34 92.44 狮溪镇 593 21.95 56 103.12 高桥镇 401 17.42 40 132.44 茅石镇 387 20.16 37 173.61 水坝塘镇 539 20.79 52 92.40 尧龙山镇 416 25.43 41 118.24 官仓镇 522 20.03 54 124.43 风水镇 300 23.93 29 89.13 花秋镇 697 16.97 71 109.21 容光镇 276 18.31 32 76.33 羊磴镇 409 23.57 42 83.57 芭蕉镇 346 23.38 38 113.87 九坝镇 564 18.12 52 158.70 小水乡 314 18.88 37 105.87 大河镇 324 18.73 31 129.68 黄莲乡 227 22.58 20 119.58 夜郎镇 441 19.56 39 99.07 马鬃乡 241 20.79 28 151.13 4.2 速效钾地球化学分布特征
研究区耕地表层土壤中速效钾含量范围为22.40~684.00 mg/kg,平均值为112.66 mg/kg,分布较不均衡(表2)。从表2得到,速效钾剔除异常值后平均值为98.00 mg/kg,低于贵州耕地土壤背景值139.65 mg/kg(高雪等,2013),富集系数K1=0.70,属于贫化类;相比也低于第二次土壤普查贵州省土壤平均含量123.90 mg/kg(贵州省土壤普查办公室,1994);变异系数为0.58,属于弱离散类。从图2b及表3可知,速效钾高值区主要分布在南部的茅石镇、九坝镇、马鬃乡附近区域,平均含量分别为173.61 mg/kg、158.70 mg/kg、151.13 mg/kg;低值区分布在中部的新站镇、夜郎镇及北部的水坝塘镇、西南部的容光镇附近,以容光镇区域平均值最低,为76.33 mg/kg。
4.3 不同地质背景下土壤钾含量特征
依据不同地质单元及岩性,对研究区耕地表层土壤钾和速效钾含量水平统计(表4)。由表4可知,耕地表层土壤中钾含量平均值,以奥陶系碎屑岩母岩区最高,为25.50 g/kg,二叠系碳酸盐岩母岩区最低,为11.84 g/kg。耕地表层土壤中速效钾含量平均值,以寒武系碳酸盐岩母岩区最高,为151.03 mg/kg,侏罗系碳酸盐岩母岩区最低,为72.06 mg/kg。耕地表层土壤中钾含量平均值,以碎屑岩母岩区最高,其次为碳酸盐岩母岩区,最低为第四系冲洪积物母岩区。耕地表层土壤中速效钾含量平均值,以第四系冲洪积物母岩区最高,其次为碳酸盐岩母岩区,最低为碎屑岩母岩区。碳酸盐岩母岩区速效钾含量(119.39 mg/kg)略高于贵州省第二次土壤普查结果(116.40 mg/kg)(贵州省土壤普查办公室,1994)。
表 4 不同地质背景下耕地土壤钾及速效钾含量特征Table 4. Characteristics of topsoil potassium and available potassium content in cultivated land under different geological backgrounds地层 岩性 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 Є 碳酸盐岩 398 10.80 42.20 22.98 39 46.30 492.00 151.03 碎屑岩 50 9.80 35.70 20.84 7 63.00 298.00 137.51 O 碳酸盐岩 1498 5.20 43.70 23.50 146 33.60 529.00 115.55 碎屑岩 804 7.20 49.60 25.50 78 50.00 394.00 118.01 S 碳酸盐岩 1034 3.50 39.30 22.70 107 42.00 244.00 101.18 碎屑岩 929 5.60 43.30 25.10 96 33.10 684.00 101.87 P 碳酸盐岩 1295 2.50 40.70 11.84 117 26.30 318.00 110.17 碎屑岩 177 6.50 32.50 17.13 30 45.10 329.00 94.84 T 碳酸盐岩 1667 5.00 36.60 19.13 186 29.10 484.00 133.32 碎屑岩 588 2.90 39.10 19.02 48 30.30 204.00 85.57 J 碳酸盐岩 47 4.20 25.90 17.24 5 45.80 106.00 72.06 碎屑岩 1072 3.00 32.30 18.16 98 22.40 239.00 94.19 Q 冲洪积物 30 4.50 33.90 18.02 5 40.00 226.00 122.98 碳酸盐岩 5939 2.50 43.70 19.51 600 26.30 529.00 119.39 碎屑岩 3620 2.90 49.60 21.70 357 22.40 684.00 101.21 4.4 不同土壤类型下土壤钾含量特征
对研究区不同土壤类型的耕地表层土壤钾和速效钾含量水平进行统计(表5)。由表5可知,钾含量平均值以粗骨土最高,为23.78 g/kg,石灰土最低,为18.73 g/kg,高低顺序为粗骨土>黄棕壤>水稻土>黄壤>紫色土>石灰土。石灰土中速效钾含量平均值最高,为123.61 mg/kg;紫色土中速效钾含量平均值最低,为79.69 mg/kg;高低顺序为石灰土>黄壤>黄棕壤>水稻土>粗骨土>紫色土。从变化范围来看,粗骨土中钾含量变化最大,为4.00~49.60 g/kg;黄壤中速效钾含量变化最大,为26.30~684.00 mg/kg。与贵州省耕地质量地球化学调查评价结果(蔡大为等,2020)相比,研究区不同土壤类型的耕地表层土壤钾含量平均值均高于贵州省背景值,黄棕壤中钾含量约为全省背景值2倍;也高于贵州省第二次土壤普查结果(贵州省土壤普查办公室,1994),说明研究区钾相对富集。
表 5 不同土壤类型下耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾含量特征Table 5. Characteristics of topsoil potassium and available potassium contents in cultivated land under different soil types类型 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 全省表
层均值全省耕层
背景值样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 黄壤 3412 2.90 47.80 21.42 14.40 19.01 351 26.30 684.00 113.95 黄棕壤 149 5.30 43.30 22.42 12.73 11.73 12 45.80 244.00 110.28 石灰土 3277 2.50 41.80 18.73 16.84 17.48 336 29.10 492.00 123.61 紫色土 1059 4.70 39.10 19.25 19.13 18.84 93 22.40 186.00 79.69 粗骨土 157 4.00 49.60 23.78 15.34 13.89 12 49.30 189.00 93.87 水稻土 1535 4.60 41.90 21.52 17.40 16.85 158 42.00 394.00 107.54 注:全省表层均值引自贵州省土壤普查办公室(1994);全省耕层背景值引自蔡大为等(2020)。 4.5 不同利用方式下土壤钾含量特征
表6以不同土地利用方式对研究区耕地表层土壤钾和速效钾含量水平进行统计。由表6可知,钾含量平均值以草地发育的土壤最高,为23.60 g/kg;园地发育的土壤最低,为17.45 g/kg;高低顺序为草地>水田>旱地>林地>裸地>园地。速效钾平均含量以裸地发育的土壤最高,为129.00 mg/kg;草地发育的土壤最低,为79.20 mg/kg;高低顺序为裸地>旱地>水田>园地>林地>草地。旱地发育的土壤中钾及速效钾含量变化范围最大,分别为2.90~49.60 g/kg、22.40~684.00 mg/kg。研究区旱地、水田、林地、草地表层土壤钾含量平均值整体高于贵州省第二次土壤普查结果(贵州省土壤普查办公室,1994),但速效钾含量却相反。在不同利用方式下,研究区耕地表层土壤钾相对富集,而速效钾低于全省平均值。
表 6 不同利用方式下耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾含量特征Table 6. Characteristics of potassium and available potassium content in topsoil of different cultivated land−use types类型 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 全省表层均值 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 全省表层均值 水田 1609 4.60 41.90 21.55 16.80 160 42.00 394.00 112.25 131.20 旱地 7561 2.90 49.60 20.15 15.00 765 22.40 684.00 113.48 129.50 园地 160 2.50 31.10 17.45 - 18 36.40 157.00 97.44 - 林地 201 4.00 36.90 20.00 11.90 12 29.10 145.00 87.38 139.80 草地 12 16.40 33.40 23.60 2 77.40 81.00 79.20 裸地 46 7.10 30.20 19.36 - 5 65.00 235.00 129.00 - 注:全省表层均值引自贵州省土壤普查办公室(1994)。 5. 评价与讨论
5.1 钾地球化学等级评价
研究区耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾的分级标准参照全国第二次土壤养分地球化学分级标准(表7)。
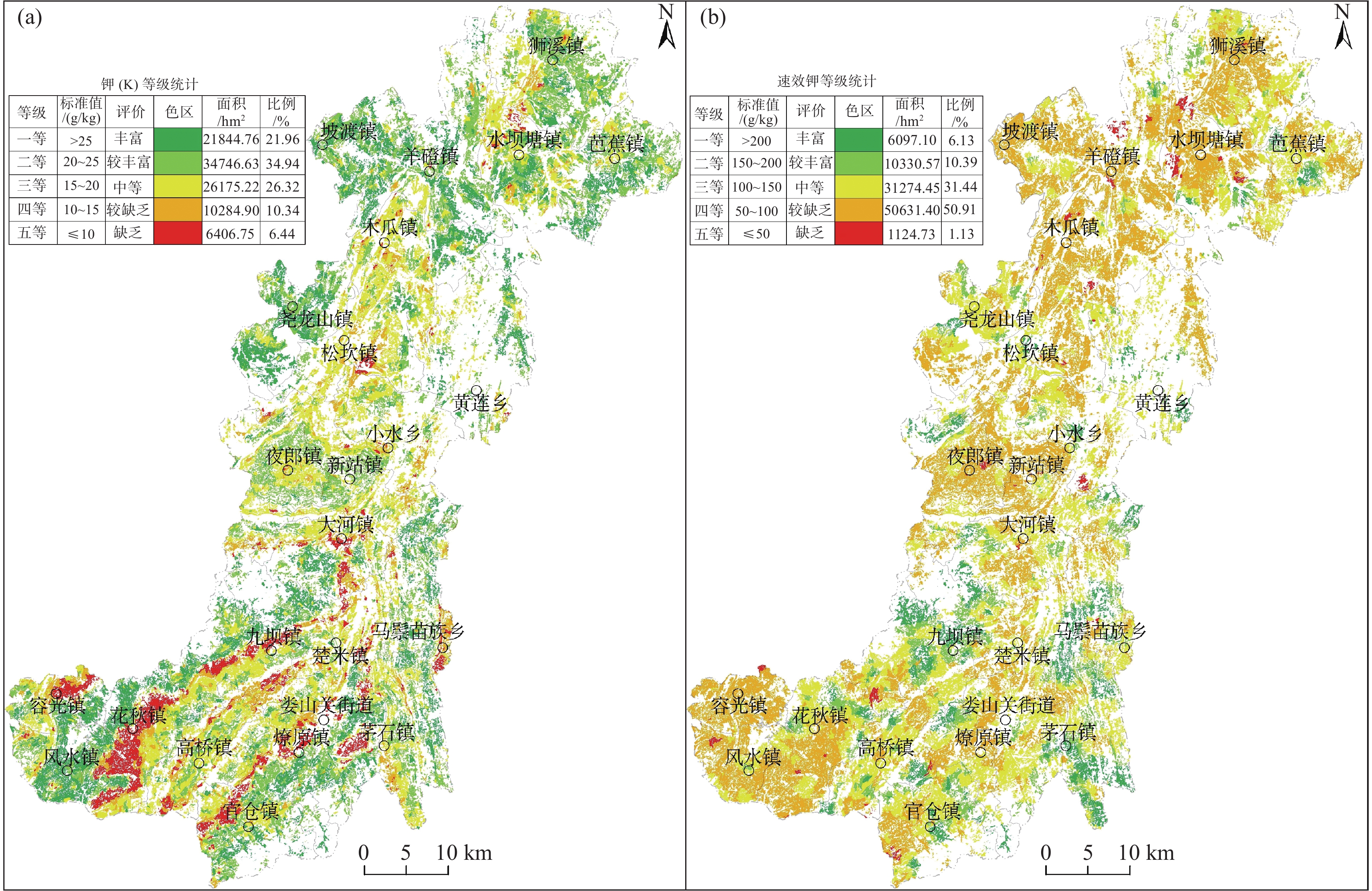
表 7 土壤中钾、速效钾等级划分标准Table 7. Classification standards of potassium and available potassium in topsoil指标 一级 二级 三级 四级 五级 丰富 较丰富 中等 较缺乏 缺乏 钾/(g/kg) >25 20~25 15~20 10~15 ≤10 速效钾/(mg/kg) >200 150~200 100~150 50~100 ≤50 通过对研究区耕地表层土壤钾含量等级评价,结果显示钾含量整体以中等、较丰富、丰富为主(图3a)。其中,一等(丰富)等级耕地面积21844.76 hm2,占总评价面积的21.96%;二等(较丰富)等级耕地面积34746.63 hm2,占总评价面积的34.94%;三等(中等)等级耕地面积26175.22 hm2,占总评价面积的26.32%;四等(较缺乏)等级耕地面积10284.90 hm2,占总评价面积的10.34%;五等(缺乏)等级耕地面积6406.75 hm2,占总评价面积的6.44%。从图3a可知,在容光镇、花秋镇、九坝镇、官仓镇、燎原镇、大河镇与娄山关街道办附近有连片缺乏等级耕地分布,其余等级耕地在各乡镇均有分布。
5.2 速效钾地球化学等级评价
根据地球化学等级划分结果显示,研究区耕地表层土壤速效钾含量整体为中等至较缺乏(图3b)。其中,一等(丰富)等级面积为6097.10 hm2,占总评价面积的6.13%;二等(较丰富)等级面积为10330.57 hm2,占总评价面积的10.39%;三等(中等)等级面积为31274.45 hm2,占总评价面积的31.44%;四等(较缺乏)等级面积为50631.40 hm2,占总评价面积的50.91%;五等(缺乏)等级面积为1124.73 hm2,占总评价面积的1.13%。从图3b可知,研究区各乡镇基本以中等至较缺乏为主,丰富至较丰富主要集中分布在茅石镇、九坝镇、马鬃乡,缺乏等级耕地零星分布在部分乡镇。以速效钾中等等级以下数据与高雪等(2013)报道的结果(遵义地区:73.02%;全省:66.01%;)相比,研究区整体优于遵义地区及全省;与贵州省土壤普查办公室(1994)报道的贵州省第二次土壤普查结果(遵义地区、全省同为42.30%)相比,本次研究结果整体略低。耕地表层土壤速效钾含量在不同时期是变化的,这种变化应与相应时间内耕地的不同利用方式、耕作及施肥习惯、耕种作物种类有关。
5.3 土壤理化性质与速效钾相关性分析
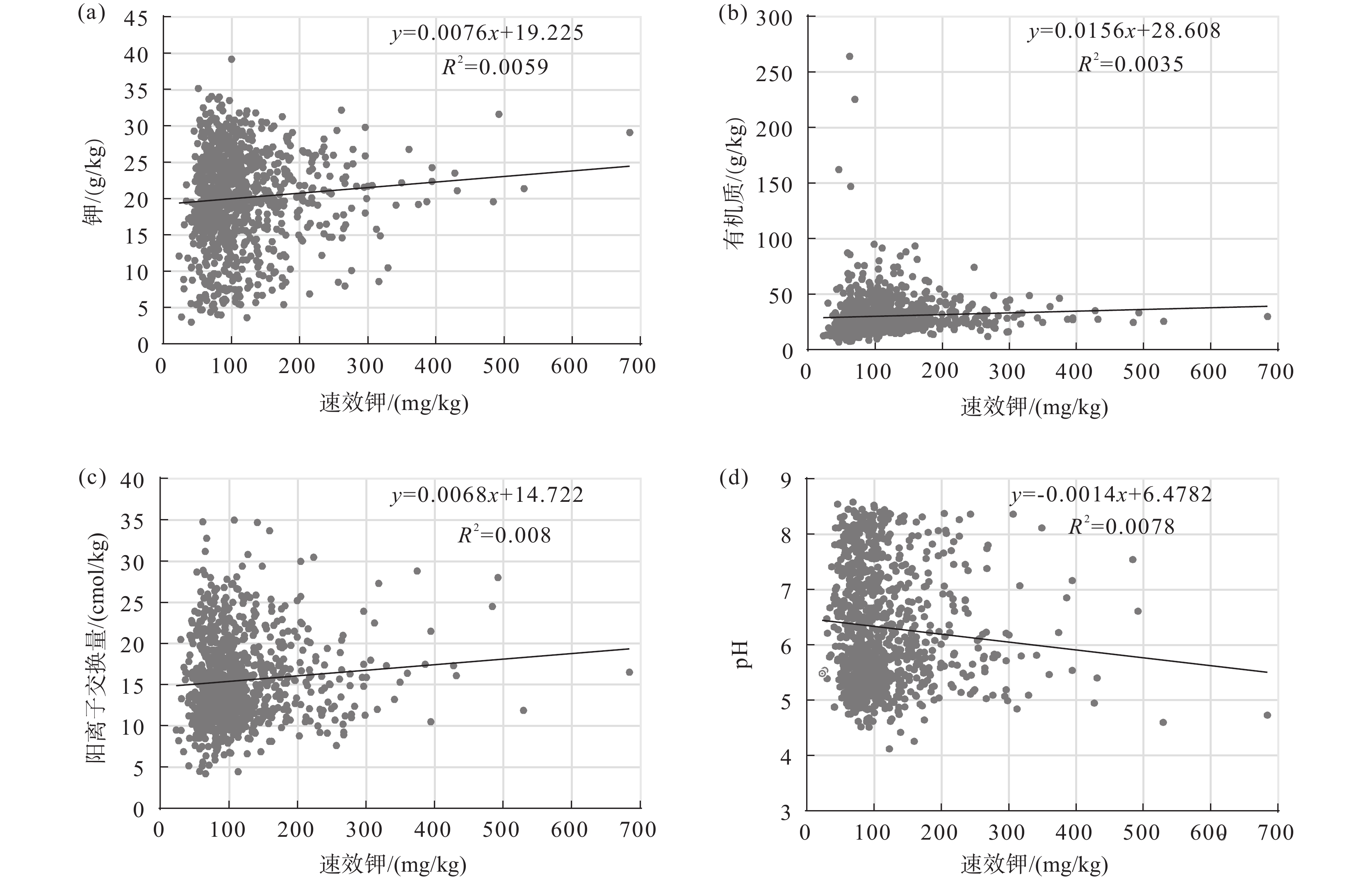
土壤中的钾从植物营养角度可分为矿物钾(约90%)、缓效钾(2%~8%)和速效钾(0.1%~0.2%)(蒋梅茵,1982)。速效钾虽然占土壤钾含量少,但其作为当季作物吸收钾的主要来源,是评价土壤供钾能力的容量和强度因子(杨振明等,1998)。土壤中速效钾的含量除受钾的制约外,一般还与土壤pH值、有机质含量及阳离子交换量(CEC)有密切联系(全思懋等,2019)。对研究区耕地表层土壤速效钾与土壤理化性质进行相关性及散点图分析(表8,图4),结果显示:pH值与速效钾呈在0.01水平(双侧)上显著负相关,阳离子交换量、有机质与钾呈在0.01水平(双侧)上显著负相关;阳离子交换量与速效钾呈在0.01水平(双侧)上显著正相关,钾与速效钾呈在0.05水平(双侧)上显著正相关(表8)。由图4可知,速效钾、有机质与阳离子交换量呈弱正相关关系,与pH值呈弱负相关关系。结合表8和图4得到,钾与速效钾呈一定的正相关关系,pH与速效钾呈负相关关系,但pH与钾呈不显著正相关关系,可能是缓效钾和矿物钾与pH的相关性为正相关关系,当二者的正相关关系影响程度略大于速效钾的负相关关系时,pH与钾会表现出为不显著正相关关系。综上,研究区耕地表层土壤钾、阳离子交换量与速效钾呈正相关关系,pH与速效钾呈负相关关系。
表 8 土壤理化性质与速效钾的相关系数Table 8. Correlation coefficient between soil physicochemical properties and available potassium元素(指标) 钾 有机质 pH 阳离子交换量 速效钾 钾 1 有机质 −0.265** 1 pH 0.057 0.002 1 阳离子交换量 −0.116** 0.360** 0.257** 1 速效钾 0.077* 0.060 −0.088** 0.089** 1 注:**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关,*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;n=962。 5.4 影响耕地表层土壤钾含量的因素
影响耕地表层土壤钾含量的因素,主要有成土母岩、土壤类型、利用方式、质地等。不同土壤类型,其风化淋溶、生物种群、元素等循环强度也会不一样,因此钾的积累量也会不同;不同耕地利用方式,土壤内部物质的交换及作物、植被对元素的利用都会有差距,从而导致土壤中钾水平有差异;不同质地的耕地土壤,作物、植被生长吸收及返还的钾量不一样;因而土壤钾在不同土壤类型及利用方式中含量有差异。
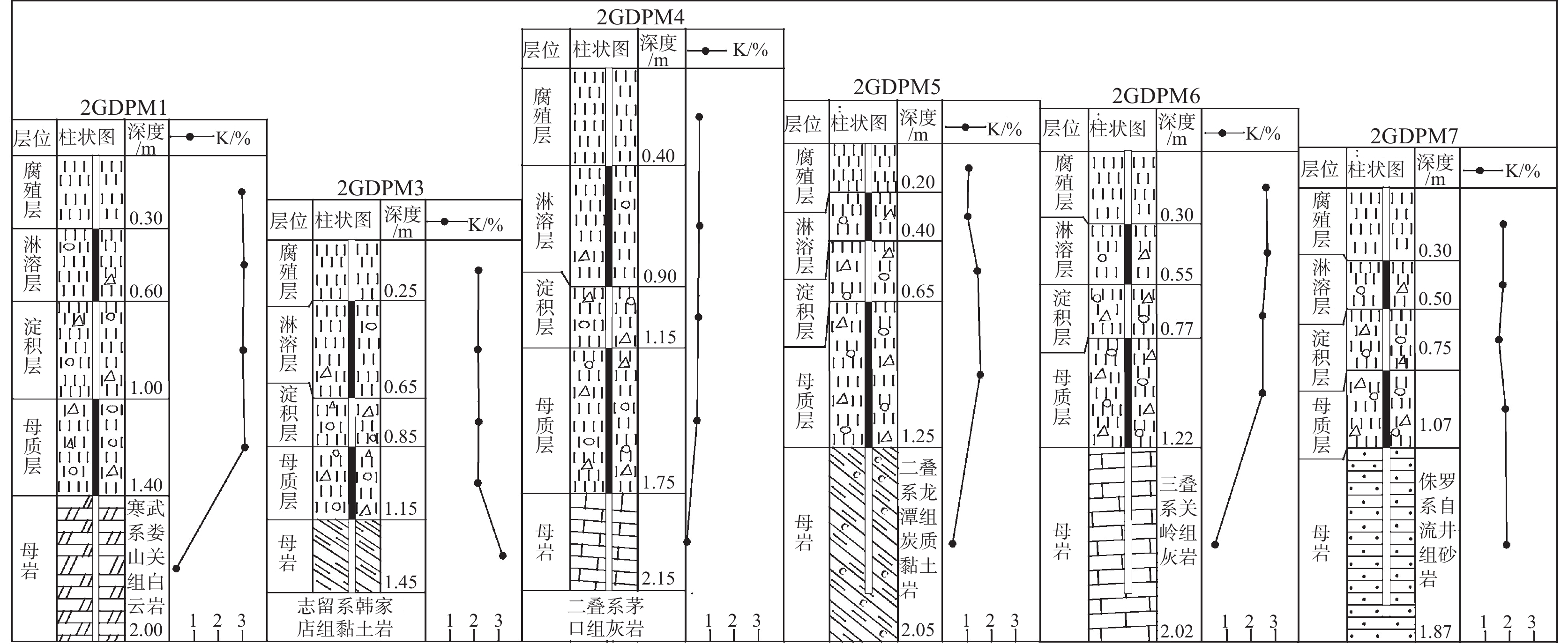
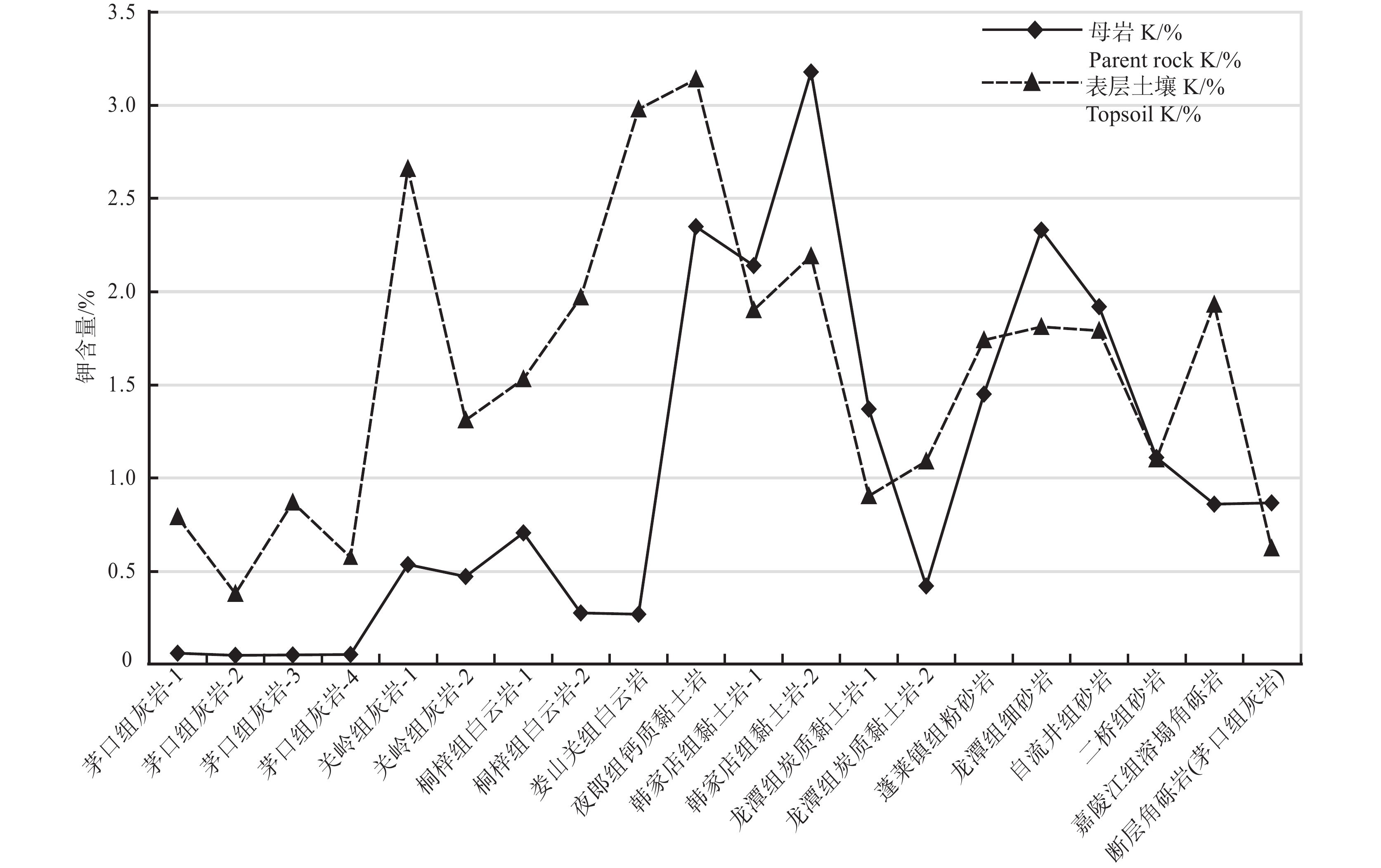
研究区耕地表层土壤钾虽然整体含量以中等至丰富为主,但在花秋、容光、燎原等南部乡镇较缺乏。按照2%、8%、15%的累频值圈定钾负异常内、中、外带,其内、中、外带的异常值分别为0.93%、1.36%与1.59%。研究区钾负异常整体呈北东向、北北东向与近南北向展布,异常面积447.39 km2。对此,本次研究根据钾异常空间分布情况及其组合关系,对异常区进行了异常查证及土壤剖面取样。通过钾在不同土壤层位、成土母岩及表层土壤地球化学参数对比研究,得到钾在二叠系茅口组灰岩及其形成的土壤中含量普遍偏低(图5,图6)。依据不同地质单元及岩性,对研究区耕地表层土壤钾含量水平统计得到,二叠系碳酸盐岩母岩区耕地表层土壤中钾平均含量最低(表4),这与曹文藻(1993)报道一致;对研究区不同土壤类型的耕地表层土壤钾含量水平进行统计,以石灰土的平均值最低(表5)。元素在土壤中富集受成土母质、表生地球化学环境等综合影响(陈怀满等,2018),而母质是成土的物质基础(唐志敏等,2023),成土母质的组成和性质对土壤中元素的含量起决定性作用(严洪泽等,2018;张哲寰等,2020)。成土母质与土壤的主要成分来源于其下伏母岩(刘洪等,2020;陈兴等,2022),灰岩形成的土壤中碳酸钙、砂粒含量相对较高,从而各形态钾的含量也相对较低(Irshad et al.,2020);而含钾矿物较高的岩石多形成细粒结构土,其土壤钾含量较高(Misal et al.,2020)。因此,研究区耕地表层土壤钾含量主受控于成土母岩,钾在灰岩及其形成的土壤中含量较低,其在南部乡镇集中大面积缺乏与广泛分布的二叠系茅口组灰岩母岩区有关。
5.5 生态环境评价
耕地表层土壤钾的来源主要有矿物质的风化和钾肥的施用,在连续耕作及现代集约式农业发展下,耕地土壤本底钾逐渐耗竭。本次调查研究发现,研究区耕地表层土壤钾失去生态平衡,花秋、高桥、松坎、九坝等乡镇钾含量较低,容光镇、羊磴镇、坡渡镇等区域速效钾含量整体较缺乏(表3);花秋镇速效钾含量平均值从132 mg/kg(刘均霞和陆引罡,2016)下降到109.21 mg/kg;木瓜镇速效钾含量平均值(88.17 mg/kg)较前人研究数据(59 mg/kg;杨彩霞等,2013)有一定提高,但其速效钾整体较缺乏。因而,这些地区外源钾肥的补充十分必要。若连年大量施用化学钾肥,钾肥中部分重金属进入土壤和水体,易被作物吸收,危害生态环境(王起超和麻壮伟,2004)。因此,为保持研究区耕地土壤钾素生态环境平衡,提出以下建议。首先,在研究区耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾缺乏的地区加强测土配方施肥研究,科学利用有机物料还田和矿物钾肥替代化学钾肥,促进土壤钾库生态系统的良性循环及资源的有效利用;其次,合理调整种植结构,在速效钾含量较高的区域(如茅石镇、九坝镇、马鬃乡,速效钾等级丰富、平均含量高)选择种植一些嗜钾经济作物(马铃薯、烤烟等),既可降低钾肥施用及其带来的风险,又可节约钾肥资源,改善耕地土壤生态环境。
6. 结 论
(1)研究区耕地表层土壤中钾、速效钾分布不均衡。钾受地质背景影响显著,高值区、低值区的分布与区内地层、构造套合较好;钾含量整体以中等、较丰富、丰富为主。速效钾含量整体为中等至较缺乏为主,丰富至较丰富主要集中分布在茅石镇、九坝镇、马鬃乡附近,缺乏等级耕地零星分布。
(2)通过土壤理化性质与速效钾相关性分析,耕地表层土壤钾、阳离子交换量与速效钾呈正相关关系,pH与速效钾呈负相关关系。
(3)研究区耕地表层土壤钾含量主受控于成土母岩,钾在灰岩及其形成的土壤中含量较低,其在南部乡镇集中大面积缺乏与广泛分布的二叠系茅口组灰岩母岩区有关。
(4)在耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾较缺乏及缺乏地区加强测土配方施肥研究,科学施用钾肥;根据耕地质量,调整农业种植结构及耕作方式,发展特色优质农产品。
致谢: 感谢唐亮、赵银兵老师在论文撰写过程中提供有益的建议,同时感谢项目组成员的辛勤付出,以及参加该项目的安泉、陈富斌、杨友、田永红、王华斌等同仁。由衷感谢编辑和审稿人对论文提出的宝贵意见和建议。
-
图 1 桐梓县区域地质简图(据张钟华等,2019修改)
Figure 1. Sketch regional geological map of Tongzi County (modified from Zhang Zhonghua et al., 2019)
表 1 样品分析方法
Table 1 Sample analysis methods
序号 指标 分析方法 检测依据 主检仪器 实验室检出限 1 钾 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法
(ICP−OES)区域地球化学样品分析方法
(DZ/T 0279.2—2016)电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪 0.01% 2 速效钾 等离子体发射光谱法(ICP−OES) 森林土壤 钾的测定
(LY/T 1234—2015)等离子体
发射光谱仪1.00 μg/g 3 有机质 容量法(VOL) 区域地球化学样品分析方法
(DZ/T 0279.27—2016)滴定管 0.02% 4 pH 电位法(ISE) 区域地球化学样品分析方法
(DZ/T 0279.34—2016)pH计 0.01
(无量纲)5 阳离子交换量(CEC) 容量法(VOL) 森林土壤
阳离子交换量的测定
(LY/T 1243—1999)凯氏定氮仪 1.00 mmol/L 表 2 耕地表层土壤钾、速效钾地球化学参数
Table 2 Geochemical parameters of topsoil potassium and available potassium in cultivated land
元素 样本数
(N)最小值 最大值 均值
(X)标准差
(S)变异系数
(Cv)剔除异常值后 贵州耕地表层 全国表层土壤 样本数 均值 背景值 K1 背景值 K2 钾 9589 2.50 49.60 20.30 6.64 0.33 9578 20.30 16.59① 1.22 20.70③ 0.98 速效钾 962 22.40 684.00 112.66 65.60 0.58 945 98.00 139.65② 0.70 — — pH 9589 4.01 8.78 6.33 1.58 0.17 — — — — — — 注:钾含量单位为g/kg,速效钾含量单位为mg/kg,pH为无量纲;①引自蔡大为等(2020),②引自高雪等(2013),③引自鄢明才等(1997)。 表 3 桐梓县各乡镇表层土壤钾、速效钾含量统计
Table 3 Statistics of topsoil potassium and available potassium contents in each town of Tongzi County
乡镇名 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 乡镇名 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 平均值 样本数 平均值 样本数 平均值 样本数 平均值 娄山关街道 437 20.16 41 115.82 木瓜镇 456 19.91 47 88.17 楚米镇 310 18.95 35 131.81 坡渡镇 388 25.11 40 88.58 新站镇 406 19.51 39 98.63 燎原镇 279 18.29 27 117.69 松坎镇 316 17.88 34 92.44 狮溪镇 593 21.95 56 103.12 高桥镇 401 17.42 40 132.44 茅石镇 387 20.16 37 173.61 水坝塘镇 539 20.79 52 92.40 尧龙山镇 416 25.43 41 118.24 官仓镇 522 20.03 54 124.43 风水镇 300 23.93 29 89.13 花秋镇 697 16.97 71 109.21 容光镇 276 18.31 32 76.33 羊磴镇 409 23.57 42 83.57 芭蕉镇 346 23.38 38 113.87 九坝镇 564 18.12 52 158.70 小水乡 314 18.88 37 105.87 大河镇 324 18.73 31 129.68 黄莲乡 227 22.58 20 119.58 夜郎镇 441 19.56 39 99.07 马鬃乡 241 20.79 28 151.13 表 4 不同地质背景下耕地土壤钾及速效钾含量特征
Table 4 Characteristics of topsoil potassium and available potassium content in cultivated land under different geological backgrounds
地层 岩性 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 Є 碳酸盐岩 398 10.80 42.20 22.98 39 46.30 492.00 151.03 碎屑岩 50 9.80 35.70 20.84 7 63.00 298.00 137.51 O 碳酸盐岩 1498 5.20 43.70 23.50 146 33.60 529.00 115.55 碎屑岩 804 7.20 49.60 25.50 78 50.00 394.00 118.01 S 碳酸盐岩 1034 3.50 39.30 22.70 107 42.00 244.00 101.18 碎屑岩 929 5.60 43.30 25.10 96 33.10 684.00 101.87 P 碳酸盐岩 1295 2.50 40.70 11.84 117 26.30 318.00 110.17 碎屑岩 177 6.50 32.50 17.13 30 45.10 329.00 94.84 T 碳酸盐岩 1667 5.00 36.60 19.13 186 29.10 484.00 133.32 碎屑岩 588 2.90 39.10 19.02 48 30.30 204.00 85.57 J 碳酸盐岩 47 4.20 25.90 17.24 5 45.80 106.00 72.06 碎屑岩 1072 3.00 32.30 18.16 98 22.40 239.00 94.19 Q 冲洪积物 30 4.50 33.90 18.02 5 40.00 226.00 122.98 碳酸盐岩 5939 2.50 43.70 19.51 600 26.30 529.00 119.39 碎屑岩 3620 2.90 49.60 21.70 357 22.40 684.00 101.21 表 5 不同土壤类型下耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾含量特征
Table 5 Characteristics of topsoil potassium and available potassium contents in cultivated land under different soil types
类型 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 全省表
层均值全省耕层
背景值样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 黄壤 3412 2.90 47.80 21.42 14.40 19.01 351 26.30 684.00 113.95 黄棕壤 149 5.30 43.30 22.42 12.73 11.73 12 45.80 244.00 110.28 石灰土 3277 2.50 41.80 18.73 16.84 17.48 336 29.10 492.00 123.61 紫色土 1059 4.70 39.10 19.25 19.13 18.84 93 22.40 186.00 79.69 粗骨土 157 4.00 49.60 23.78 15.34 13.89 12 49.30 189.00 93.87 水稻土 1535 4.60 41.90 21.52 17.40 16.85 158 42.00 394.00 107.54 注:全省表层均值引自贵州省土壤普查办公室(1994);全省耕层背景值引自蔡大为等(2020)。 表 6 不同利用方式下耕地表层土壤钾及速效钾含量特征
Table 6 Characteristics of potassium and available potassium content in topsoil of different cultivated land−use types
类型 钾/(g/kg) 速效钾/(mg/kg) 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 全省表层均值 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 全省表层均值 水田 1609 4.60 41.90 21.55 16.80 160 42.00 394.00 112.25 131.20 旱地 7561 2.90 49.60 20.15 15.00 765 22.40 684.00 113.48 129.50 园地 160 2.50 31.10 17.45 - 18 36.40 157.00 97.44 - 林地 201 4.00 36.90 20.00 11.90 12 29.10 145.00 87.38 139.80 草地 12 16.40 33.40 23.60 2 77.40 81.00 79.20 裸地 46 7.10 30.20 19.36 - 5 65.00 235.00 129.00 - 注:全省表层均值引自贵州省土壤普查办公室(1994)。 表 7 土壤中钾、速效钾等级划分标准
Table 7 Classification standards of potassium and available potassium in topsoil
指标 一级 二级 三级 四级 五级 丰富 较丰富 中等 较缺乏 缺乏 钾/(g/kg) >25 20~25 15~20 10~15 ≤10 速效钾/(mg/kg) >200 150~200 100~150 50~100 ≤50 表 8 土壤理化性质与速效钾的相关系数
Table 8 Correlation coefficient between soil physicochemical properties and available potassium
元素(指标) 钾 有机质 pH 阳离子交换量 速效钾 钾 1 有机质 −0.265** 1 pH 0.057 0.002 1 阳离子交换量 −0.116** 0.360** 0.257** 1 速效钾 0.077* 0.060 −0.088** 0.089** 1 注:**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关,*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;n=962。 -
[1] Cai Dawei, Li Longbo, Jiang Guocai, Yan Qi, Ren Mingqiang. 2020. Statistics and analysis of geochemical backgrounds of main elements of cultivated land in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 37(3): 233−239 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Cao Wenzao. 1989. Critical and supplying level of available potassium in paddy soil Guizhou and its application in the potassium fertilizer recommendation[J]. Journal of Guizhou Agricultural Science, 17(6): 35−38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Cao Wenzao. 1993. Study on potassium suppling power of soil in Guizhou Province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 6(3): 69−75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Huaiman, Zhu Yongguan, Dong Yuanhua, Zhou Dongmei. 2018. Environmental Soil Science (Third Edition)[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[5] Chen Xing, Wu Kaibin, Wang Jun, Huang Jianguo, Chen Jun, Yang Zhen, Deng Guibiao, Liao Zhumin, Bai Peirong. 2022. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil nutrients in cultivated land in Renhuai, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(3): 860−879 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Chen Xuhui. 2001. Variations of soil nutrient content and fertilization in Guizhou[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 7(2): 121−128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Chen Xuhui, Chen Xiangyan. 2003. The Content of soil potassium in Guizhou and the application of potassic fertilizer[J]. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 25(2): 157−160,163 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Dai Chuangu, Chen Jianshu, Wang Min, Lu Dingbiao, Wang Xuehua, Qin Shourong, Zhang Minghua, Lin Shuji, Jiao Huiliang, Wang Liting, Ye Nianzeng, Zheng Qilin, Liu Aimin, Zhu Dayou, Liu Yingzhong, Qiao Wenlang, Xiao Jiafei, Ma Huizhen. 2017. The Regional Geology of China, Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 128–1015(in Chinese).
[9] Das D, Dwivedi B S, Datta S P, Datta S C, Meena M C, Agarwal B K, Shahi D K, Singh M, Chakraborty D, Jaggi S. 2019. Potassium supplying capacity of a red soil from eastern India after forty–two years of continuous cropping and fertilization[J]. Geoderma, 341: 76−92. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.01.041
[10] Dessougi H E, Claassen N, Steingrobe B. 2002. Potassium efficiency mechanisms of wheat, barley, and sugar beet grown on a K fixing soil under controlled conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 165(6): 732−737. doi: 10.1002/jpln.200290011
[11] Gao Xue, Chen Haiyan, Tong Qianqian. 2013. Nutrient status of surface soil of cultivated land in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 41(12): 87−91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Greenwood D J, Karpinets T V. 1997a. Dynamic model for the effects of K fertilizer on crop growth, K–uptake and soil–K in arable cropping. 1. Description of the model[J]. Soil Use and Management, 13: 178−183. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-2743.1997.tb00582.x
[13] Greenwood D J, Karpinets T V. 1997b. Dynamic model for the effects of K fertilizer on crop growth, K–uptake and the soil–K in arable cropping. 2. Field test of the model[J]. Soil Use and Management, 13: 184−189. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-2743.1997.tb00583.x
[14] Gurav P P, Ray S K, Choudhari P L, Shirale A O, Meena B P, Biswas A K, Patra A K. 2019. Potassium in shrink–swell soils of India[J]. Current Science, 117(4): 587−597. doi: 10.18520/cs/v117/i4/587-596
[15] He Yuru, Yan Xiong, Fan Leilei. Li Wenzhao, Liu Yehong, Ouyang Shengnan. 2021. Quality evaluation of soil fertility in Fang Bamboo shoots in Tongzi County[J]. South China Agriculture, 15(25): 65−67,71 (in Chinese).
[16] Huang Changyong, Xu Jianming. 2010. Soil (Third Edition) [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 18–19, 162–163(in Chinese).
[17] Huang Zhenrui, Zhou Wenling, Ao Junhua, Chen Diwen, Huang Ying, Jiang Yong, Li Qiwei. 2020. Sugarcane yield and soil potassium balance in potassium application of four consecutive years[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 41(7): 1347−1353 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Irshad I, Chesti M H, Mir S, Mansoor M, Kirmani N A, Sofi J A, Sofi K A, Qadri T N. 2020. Distribution of different forms of potassium in soils of district Ganderbal of Kashmir Region[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 68(2): 194−200. doi: 10.5958/0974-0228.2020.00022.5
[19] Ismail C. 2010. Potassium for better crop production and quality[J]. Plant Soil, 335: 1−2. doi: 10.1007/s11104-010-0534-8
[20] Jiang Meiyin. 1982. Fixation and release of potassium from potassium–bearing minerals in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, (5): 44−49 (in Chinese).
[21] Li S, Duan Y, Guo T, Zhang P, He P, Johnston A, Shcherbakov A. 2015. Potassium management in potato production in Northwest region of China[J]. Field Crops Research, 174: 48−54. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.01.010
[22] Li X S, Li Y F, Wu T Q, Qu C Y, Ning P, Shi J L, Tian X H. 2020. Potassium fertilization combined with crop straw incorporation alters soil potassium fractions and availability in northwest China: An incubation study[J]. PLoS One, 15(7): e0236634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236634
[23] Liu Hong, Huang Hanxiao, OuYang Yuan, Zhang Jinghua, Zhang Tengjiao, Li Fu, Xiao Qiliang, Zeng Jian, Hou Qian, Wen Dengkui, Duan Shengyi. 2020. Soil’s geologic investigation in Daliangshan, Xichang, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(1): 91−105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Liu Xiaowei, Zhang Haoyue, Li Wenxuan, Liu Haodong, Zhao Sihang, Yang Xueju, Zhao Yong, Wang Dianwu. 2021. Effect of potassium deficiency on soil potassium and quality of different winter wheat varieties[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 58(2): 332−341 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Liu Junxia, Lu Yingang. 2016. Soil nutrient survey and formula fertilization in main rape producing area of Huaqiu Town, Tongzi County[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 36(13): 91−93 (in Chinese).
[26] Lu Xiaohui, Dong Yubo, Tu Chenglong, Wang Ji. 2018. Estimation of soil moisture regime of Guizhou Province, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 46(1): 89−96 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Luo Pingyuan, Jiang Yan, Zhang Wanping, Zhang Cuiping. 2006. Physicochemical properties of different bamboo shoot forests in Guizhou[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 26(3): 20−22 (in Chinese).
[28] Misal N B, Sukul P, Polara K B. 2020. Dynamics of potassium fractions in the calcareous soils of Gujarat[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 68(1): 62−69. doi: 10.5958/0974-0228.2020.00007.9
[29] Portela E, Monteiro F, Fonseca M, Abreu M M. 2019. Effect of soil mineralogy on potassium fixation in soils developed on different parent material[J]. Geoderma, 343: 226−234. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.02.040
[30] Ouyang Zhibiao, Luo Jianxin, Wang Juan. 2016. Potassium form of soils from different parent materials in Hunan[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, (1): 13−17,52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Qian Xu, Liao Xiaofeng, Xie Yuangui. 2018. Response of soil physicochemical properties to different land use types in typical small watershed in Karst area of Guizhou Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 46(11): 247−251 (in Chinese).
[32] Quan Simao, Guan Xiaojin, Wang Xukui, Hu feng. 2019. Changes of soil available potassium content in farmland in Jiangsu Province and its influential factors[J]. Soils, 51(2): 257−262 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Rudnick R L, Gao S. 2003. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Rudnick R L(ed.). The Crust, Treatise on Geochemistry. Oxford: Elsevier–Pergamon, 3: 1–64.
[34] Sharpley A N, Smith S J. 1988. Distribution of potassium forms in virgin and cultivated soils of the U.S.A[J]. Geoderma, 42: 317−329. doi: 10.1016/0016-7061(88)90008-0
[35] Soil Census Office of Guizhou Province. 1994. Soil of Guizhou Province[M]. Guiyang: Guizhou Science and Technology Press, 585−592 (in Chinese).
[36] Tang Zhimin, Zhang Xiaodong, Zhang Ming, Zhou Mo, Tian Fujin, Wang Shangxiao, Ma Qinshan, Wang Chong, Zhang Jie, Niu Xiaonan, Zong Leli, Huang Dinglin. 2023. Geochemical characteristics of soil elements in Xin'an River Basin: constraints from rock formation types[J]. East China Geology, 44(2): 172−185 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Wang Dong, Feng Mingwei, Li Huiying. 2017. The current status of China’s potash resources development[J]. China Mining Magazine, 26(S2): 5−9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Wang Liangbo, Yang Caixia. 2010. Effects of formula fertilization by soil testing on rice[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 14(5): 50−52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Wang Qichao, Ma Zhuangwei. 2004. Heavy metals in chemical fertilizer and environmental risks[J]. Rural Eco–Environment, 20(2): 62−64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Wang Shi, Zhu Xin, Li Xurong, Luo Siliang. 2021. Geochemical characteristics of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and soil fertility evaluation in Leizhou Peninsula, Guangdong Province[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1177−1187 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Yan Hongze, Zhou Guohua, Sun Binbin, He Ling, Liu Yinfei, Hou Shujun. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of the bayberry producing area in Longhai, Fujian[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1155−1166 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Yan Mingcai, Gu Tiexin, Chi Qinghua, Wang Chunshu. 2021. Abundance of chemical elements of soils in China and supergenesis geochemistry characteristics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 21(3): 161−167 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Yang Caixia, Wang Liangbo, LingHu Dandan. 2013. Test of soil testing and formula fertilization of potato in Tongzi County[J]. Agricultural Technology Service, 30(4): 376−377 (in Chinese).
[44] Yang Zhengming, Yan Fei, Han Limei. 1998. Advances in the research of soil potassium[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 20(3): 99−106 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhan Yuman, Hao Xiaoyu, Xiao Yang. 2021. Research progress on the effect of different organic materials returning on soil potassium[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, (11): 106−112 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Zhang Shanshan, Cai Liqun, Zhang Renzhi. 2012. Effects of tillage measures on the soil potassium contents and yields in the double sequence rotation system[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 47(3): 32−38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Zhang Sujiang, Cui Liwei, Gao Pengxin, Jiang Ailin, Li Jianbo. 2015. Analysis on development situation of potash ore resources and recommended management strategies in China[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 47(11): 1−6 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Zhang Zhehuan, Zhao Jun, Dai Huimin, He Pengfei, Wei Minghui. 2020. Geochemistry of selenium in soil–crop system of Nehe City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 29(1): 38−43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Zhang Zhonghua, Wang Xiaohong, An Quan, Liu Hao, Pan Youliang, Xiao Bo, Wu Peng, Tang Daixue, Wang Ting, Wang Ping, Chen Fubin, Luo Jianjun, Tian Yonghong, Yang You, Liu Jiao, Wu Zhijun, Huang Chuan, Yang Shaoxue, Dong Xinyuan, Shi Ruiwu. 2019. Geochemical investigation and evaluation of cultivated land quality in Tongzi County, Guizhou Province[R]. Guiyang: 117 Geological Party, Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration & Development(in Chinese).
[50] Zhong Laiyuan, Guo Liangzhen. 2012. Comprehensive evaluation and analysis on spatial variation of agricultural soils fertility in the Southern Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 32(3): 76−81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] Zhu D D, Zhang J L, Lu J W, Cong R H, Ren T Li X K. 2020. Optimal potassium management strategy to enhance crop yield and soil potassium fertility under paddy–upland rotation[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 101(8): 3404−3412.
[52] 蔡大为, 李龙波, 蒋国才, 严琦, 任明强. 2020. 贵州耕地主要元素地球化学背景值统计与分析[J]. 贵州地质, 37(3): 233−239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2020.03.003 [53] 曹文藻. 1989. 贵州水稻土速效钾的临界水平和丰缺指标及在水稻钾肥施用中的应用[J]. 贵州农业科学, 17(6): 35−38. [54] 曹文藻. 1993. 贵州土壤供钾能力与钾肥的有效施用[J]. 西南农业学报, 6(3): 69−75. [55] 陈怀满, 朱永官, 董元华, 周东美. 2018. 环境土壤学 (第三版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [56] 陈兴, 吴开彬, 王军, 黄建国, 陈军, 杨镇, 邓贵标, 廖铸敏, 白培荣. 2022. 贵州省仁怀市耕地土壤养分地球化学特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国地质, 49(3): 860−879. doi: 10.12029/gc20220313 [57] 陈旭晖. 2001. 贵州土壤养分含量的变化与施肥管理[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 7(2): 121−128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2001.02.001 [58] 陈旭晖, 陈湘燕. 2003. 贵州土壤钾素状况与钾肥施用问题[J]. 西南农业大学学报, 25(2): 157−160,163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9868.2003.02.019 [59] 戴传固, 陈建书, 王敏, 卢定彪, 王雪华, 秦守荣, 张明发, 林树基, 焦惠亮, 王立亭, 叶念曾, 郑启钤, 刘爱民, 朱大友, 刘应忠, 谯文浪, 肖加飞, 马会珍. 2017. 中国区域地质志·贵州志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 128–1015. [60] 高雪, 陈海燕, 童倩倩. 2013. 贵州耕地耕层土壤养分状况评价[J]. 贵州农业科学, 41(12): 87−91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2013.12.022 [61] 贵州省土壤普查办公室. 1994. 贵州省土壤[M]. 贵阳: 贵州科技出版社, 585–592. [62] 何雨茹, 颜雄, 樊磊磊, 李文昭, 柳叶红, 欧阳胜男. 2021. 桐梓县方竹笋基地土壤肥力质量评价[J]. 南方农业, 15(25): 65−67,71. [63] 黄昌勇, 徐建明. 2010. 土壤学 (第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 18–19, 162–163. [64] 黄振瑞, 周文灵, 敖俊华, 陈迪文, 黄莹, 江永, 李奇伟. 2020. 连续4年施钾的甘蔗产量及土壤钾素平衡[J]. 热带作物学报, 41(7): 1347−1353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.07.009 [65] 蒋梅茵. 1982. 土壤含钾矿物中钾的固定与释放[J]. 土壤通报, (3): 44−49. [66] 刘洪, 黄瀚霄, 欧阳渊, 张景华, 张腾蛟, 李富, 肖启亮, 曾建, 侯谦, 文登奎, 段声义. 2020. 基于地质建造的土壤地质调查及应用前景分析——以大凉山区西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(1): 91−105. [67] 刘晓伟, 张浩月, 李文瑄, 刘昊东, 赵思航, 杨学举, 赵勇, 王殿武. 2021. 缺钾对不同品种冬小麦土壤钾素和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 58(2): 332−341. [68] 刘均霞, 陆引罡. 2016. 桐梓县花秋镇油菜主产区土壤养分调查和配方施肥[J]. 农业与技术, 36(13): 91−93. [69] 陆晓辉, 董宇博, 涂成龙, 王济. 2018. 贵州省土壤水分状况估算及分析[J]. 地球与环境, 46(1): 89−96. [70] 罗平源, 江燕, 张万萍, 张翠萍. 2006. 贵州不同竹笋林地土壤理化性状分析[J]. 耕作与栽培, 26(3): 20−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2239.2006.03.007 [71] 欧阳志标, 罗建新, 王娟. 2016. 湖南不同母质植烟土壤钾的形态与特征[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, (1): 13−17,52. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20160103 [72] 钱旭, 廖小锋, 谢元贵. 2018. 贵州喀斯特地区典型小流域土壤理化性质对不同土地利用类型的响应[J]. 江苏农业科学, 46(11): 247−251. [73] 全思懋, 管晓进, 王绪奎, 胡锋. 2019. 江苏省域农田土壤速效钾含量变化及其影响因子研究[J]. 土壤, 51(2): 257−262. [74] 唐志敏, 张晓东, 张明, 周墨, 田福金, 王尚晓, 马青山, 王冲, 张洁, 牛晓楠, 宗乐丽, 黄丁伶. 2023. 新安江流域土壤元素地球化学特征: 来自岩石建造类型的约束[J]. 华东地质, 44(2): 172−185. [75] 王栋, 冯明伟, 李慧英. 2017. 中国钾盐资源发展现状及建议[J]. 中国矿业, 26(S2): 5−9. [76] 王良波, 杨彩霞. 2010. 水稻测土配方施肥效果研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 14(5): 50−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1088-1631.2010.05.022 [77] 王起超, 麻壮伟. 2004. 某些市售化肥的重金属含量水平及环境风险[J]. 农村生态环境, 20(2): 62−64. [78] 汪实, 朱鑫, 黎旭荣, 罗思亮. 2021. 广东雷州半岛土壤氮、磷、钾元素地球化学特征及其土壤肥力评价[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1177−1187. doi: 10.12029/gc20210414 [79] 严洪泽, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 刘银飞, 候树军. 2018. 福建龙海杨梅产地元素地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1155−1166. doi: 10.12029/gc20180606 [80] 鄢明才, 顾铁新, 迟清华, 王春书. 1997. 中国土壤化学元素丰度与表生地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 21(3): 161−167. [81] 杨彩霞, 王良波, 令胡丹丹. 2013. 桐梓县马铃薯测土配方施肥试验[J]. 农技服务, 30(4): 376−377. [82] 杨振明, 阎飞, 韩丽梅. 1998. 土壤钾素研究的新进展[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 20(3): 99−106. [83] 湛玉曼, 郝小雨, 肖洋. 2021. 不同有机物料还田对土壤钾素影响研究进展[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, (11): 106−112. doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2021.11.0106 [84] 张珊珊, 蔡立群, 张仁陟. 2012. 不同耕作方式对双序列轮作系统土壤钾素含量及产量的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 47(3): 32−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4315.2012.03.006 [85] 张苏江, 崔立伟, 高鹏鑫, 姜爱玲, 李建波. 2015. 中国钾盐资源形势分析及管理对策建议[J]. 无机盐工业, 47(11): 1−6. [86] 张哲寰, 赵君, 戴慧敏, 贺鹏飞, 魏明辉. 2020. 黑龙江省讷河市土壤–作物系统Se元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 29(1): 38−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.01.005 [87] 张钟华, 王小洪, 安泉. 刘浩, 潘有良, 肖波, 吴鹏, 唐代学, 王艇, 王平, 陈富斌, 罗建均, 田永红, 杨友, 刘娇, 吴治君, 黄川, 杨绍学, 董新元, 石瑞武. 2019. 贵州省桐梓县耕地质量地球化学调查评价报告[R]. 贵阳: 贵州省地质矿产勘查开发局117地质大队. [88] 钟来元, 郭良珍. 2012. 雷州半岛南部土壤肥力综合评价及空间变异[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 32(3): 76−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2012.03.015



 下载:
下载: