Migration simulation and pollution assessment of Cr (III) and ammonia from tannery wastewater in typical vadose zone in North China Plain
-
摘要:研究目的
为探明制革废水中的特征污染物铬(Cr(III))和氨氮(NH4+–N)在华北平原典型包气带中的迁移规律,评价其可能产生的土壤与地下水污染风险。
研究方法采用土柱淋滤实验研究Cr(III)和NH4+–N在典型粉土中的吸附和迁移转化特征,结合Hydrus–1D建立的包气带水流和溶质运移模型,模拟预测深0.5 m渗坑中NH4+–N连续入渗状态下通过包气带到达地下水面所需时间及不同深度浓度值的变化规律。
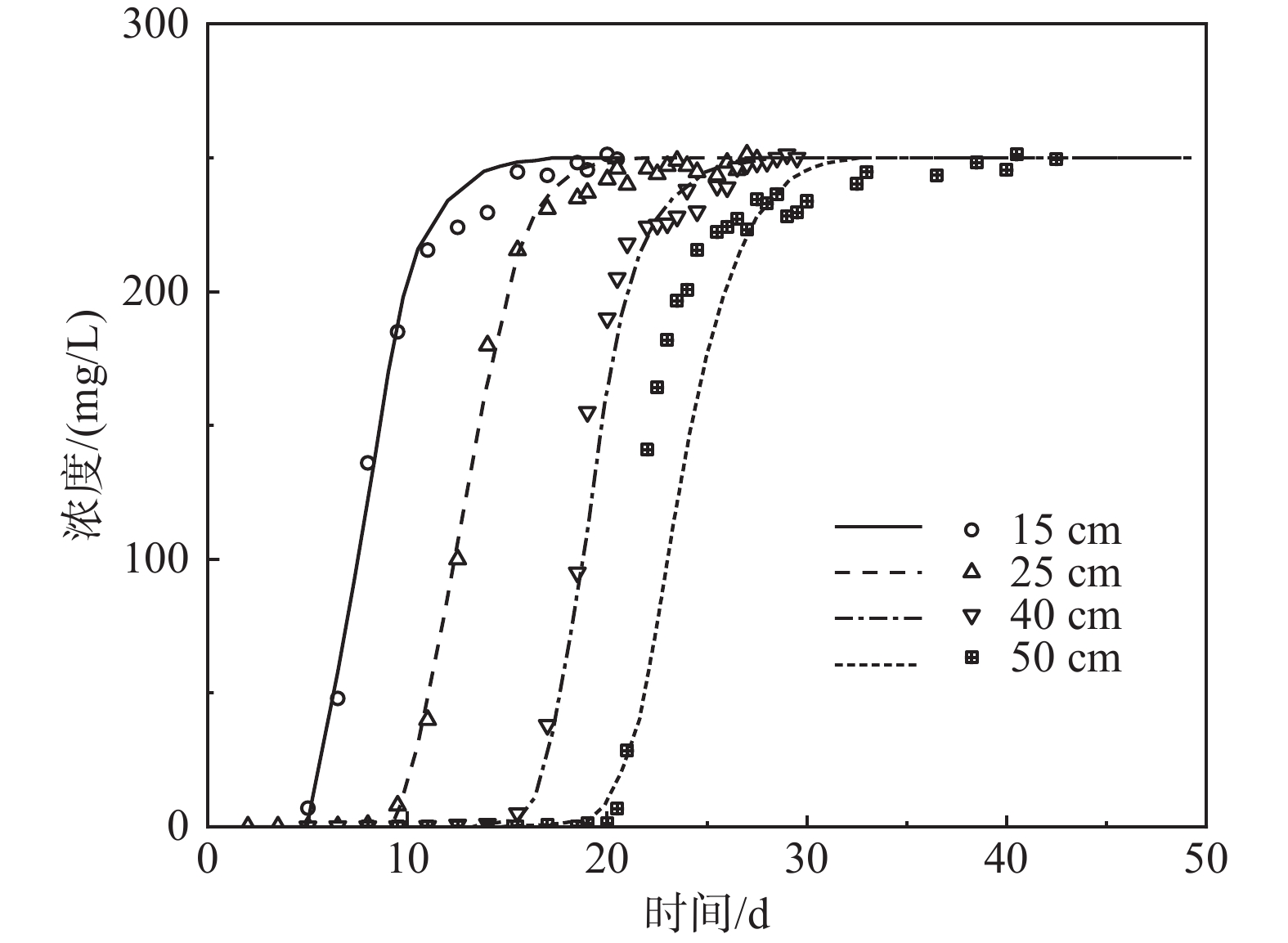
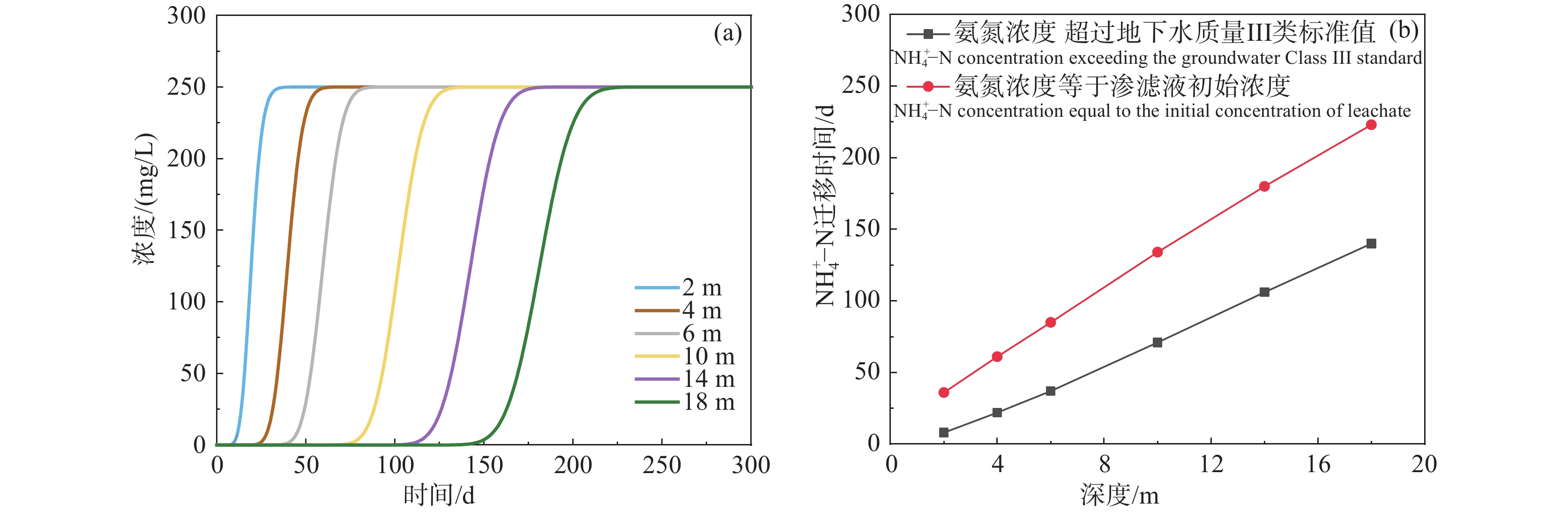
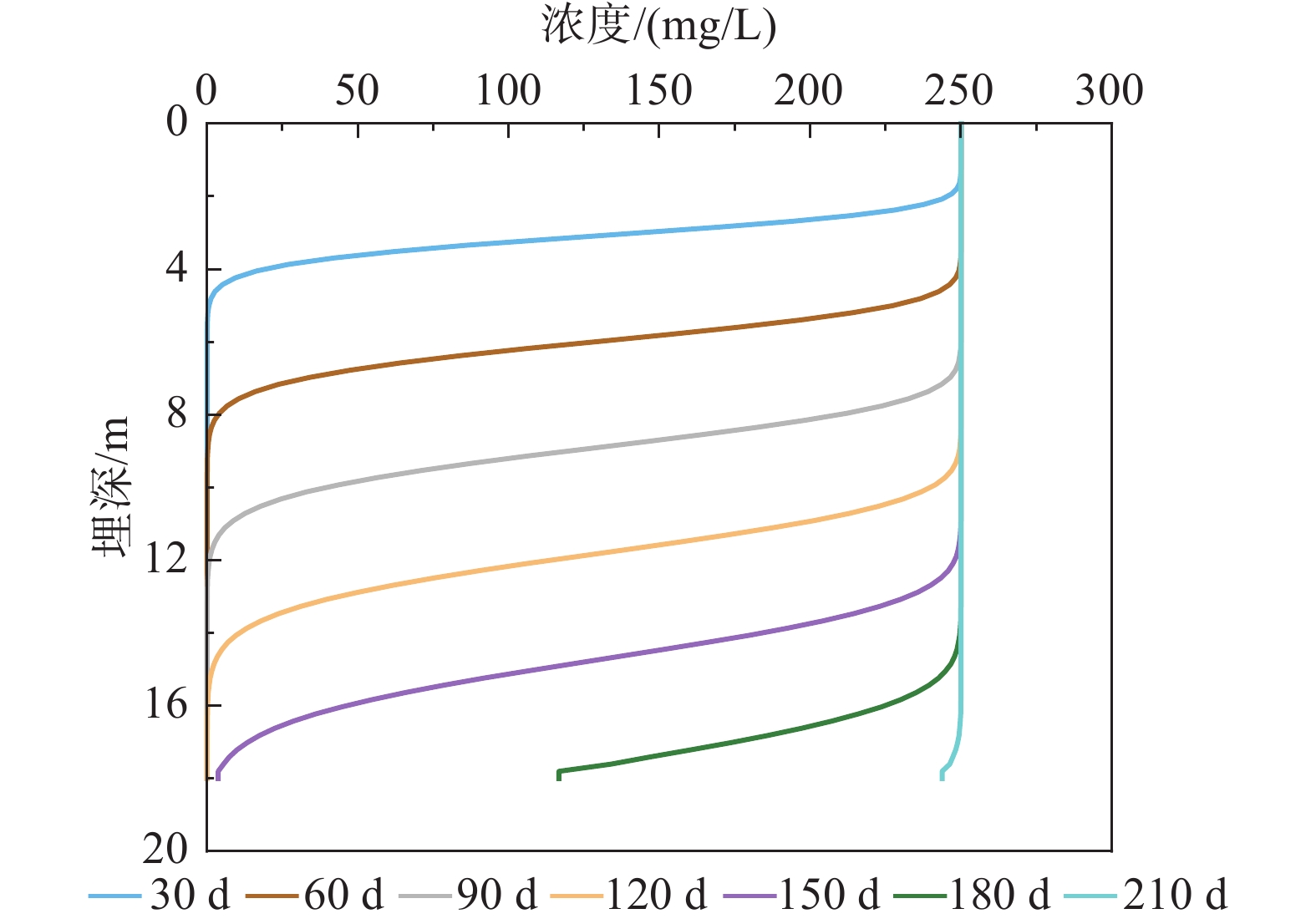
研究结果在3 cm定水头,污染液(Cr(III) 20 mg/L,NH4+–N 250 mg/L)定浓度持续淋滤120 d的情况下,Cr(III)在土柱中垂向迁移距离小于10 cm,且以残渣态(73%)为主,未检出Cr(VI)。NH4+–N则迁移能力较强,淋滤40 d后即穿透50 cm厚粉土柱。在高含盐量(电导率为10.08 ms/cm)条件下,NH4+–N在粉土中的迁移主要受吸附作用控制,土−水分配系数为25.87 L/kg,未发生硝化作用。持续淋滤150 d时NH4+–N迁移至地下水面(18 m埋深)且浓度超过III类地下水质量标准(0.5 mg/L, GB/T 14848–2017),在223 d完全穿透包气带,严重污染地下水。
结论高含盐量制革废水中Cr(III)在粉土中迁移能力较弱,且难以被氧化为Cr(VI),对地下水威胁较小。NH4+–N则随水流快速迁移至地下水面,严重威胁地下水安全。
创新点:(1) 模拟了制革废水非正规排放NH4+–N和Cr(III)在包气带中的迁移转化规律;(2) 结合Hydrus–1D建立数值模型,预测了制革废液NH4+–N对地下水污染风险。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveThis study aims to elucidate the migration patterns of characteristic pollutants, i.e., chromium (Cr(III)) and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+–N), from tannery wastewater in the vadose zone of the North China Plain and to assess the potential risks of soil and groundwater contamination.
MethodsThe adsorption and transport characteristics of Cr(III) and NH4+–N in typical silts were examined using soil column leaching experiments. Additionally, the vadose zone water flow and solute transport model established by Hydrus−1D was utilized to simulate and predict the time required for NH4+–N to reach the groundwater table at a depth of 0.5 m under continuous infiltration conditions, along with changes in concentrations at various depths.
ResultsUnder a constant head of 3 cm and a pollutant solution concentration (Cr(III) 20 mg/L and NH4+–N 250 mg/L) maintained for 120 d, the vertical migration distance of Cr(III) in the soil column was less than 10 cm, predominantly in the residual form (73%), with no detection of Cr(VI). By contrast, NH4+–N exhibited a stronger migration capability, penetrating a 50 cm thick silt column within 40 d. Under high salinity conditions (EC: 10.08 ms/cm), the migration of NH4+–N was controlled by adsorption, with a Kd of 25.87 L/kg, and no nitrification occurred. After 150 d of continuous leaching, NH4+–N migrated to the groundwater table (18 m depth) with concentrations exceeding the Class III Groundwater Quality Standard (0.5 mg/L, GB/T 14848–2017). By 223 d, it completely penetrated the vadose zone, severely contaminating the groundwater.
ConclusionsIn high–salinity tannery wastewater, Cr (III) exhibits limited migration capacity in silt and is difficult to oxidize to Cr (VI), posing a lesser threat to groundwater. Conversely, NH4+–N rapidly migrates to the groundwater surface with water flow, posing a serious threat to groundwater safety.
Highlights:(1) Simulated the migration and transport pattern of NH4+–N and Cr (III) from irregular discharges of tanning wastewater in the vadose zone. (2) Integrated a numerical model using Hydrus–1D to predict the groundwater contamination risk from tannery effluent NH4+–N.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
湘中坳陷作为南方复杂构造区页岩气勘探的热点地区之一,也是中国油气勘探久攻未克的地区。前期在湘中地区北部的涟源凹陷泥盆系和石炭系获得了页岩气突破和发现,证实了湘中地区上古生界页岩气资源丰富。但对湘中地区南部的邵阳凹陷调查程度较为薄弱,针对邵阳凹陷二叠系仅开展了少量基础地质调查工作,页岩气资源潜力评价方面的工作尤为欠缺。本次研究依托邵阳湘邵地1井(XSD1井)钻探工程建立了邵阳凹陷二叠系地层层序序列,揭示了主要含气页岩层系的分布特征,获取了含气性评价参数,对湘中地区二叠系页岩气勘探开发和重新评价湘中坳陷页岩气资源潜力具有重要的现实意义。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
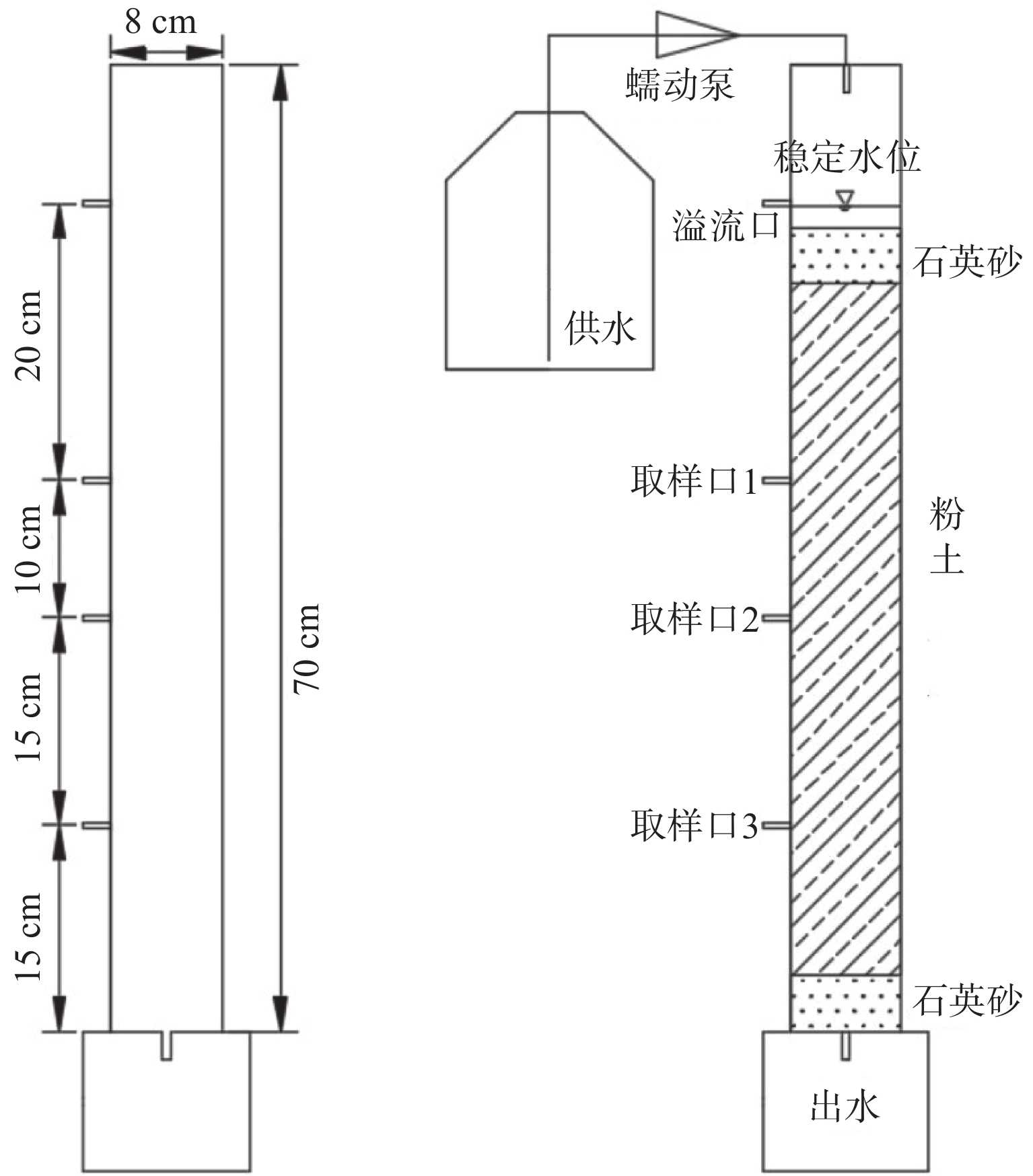
中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心在收集分析区域地质相关资料的基础上,结合邵阳凹陷短陂桥向斜的煤田浅钻、非震物探等资料开展页岩气地质综合评价,采用页岩埋深500~4500 m,页岩有机碳含量≥1.0%,页岩厚度≥15 m,页岩有机质热演化程度1.0%~3.5%的评价参数在短陂桥向斜区优选页岩气远景区,论证部署了1口小口径页岩气地质调查井—XSD1井,湖南煤田地质勘查有限公司组织实施钻探(图 1a)。该井采样全井段取心钻井工艺,测井选取PSJ-2数字测井系统,录井采用SK-2000G气测录井,钻获二叠系大隆组156.05 m(暗色硅质页岩、钙质泥岩94.48 m),龙潭组349.95 m(暗色泥岩216.93 m,粉砂质泥岩36.9 m),对这两套层系共采集暗色泥岩样品33件,进行解析气含量测定分析,落实了含气性评价参数。
3. 结果(Results)
本次样品分析工作由武汉地质调查中心古生物与生命-环境协同演化重点实验室完成,采用YSQ-IIIA岩石解析气测定仪(燃烧法)对含气段岩心共计33件样品进行分析。该井钻获二叠系大隆组厚度156.05 m,为一套硅质岩、硅质页岩、炭质钙质泥岩地层。其中在井深842~930.2 m硅质页岩、钙质泥岩段,气测全烃值从1.06%上升至16.54%,甲烷值从1.01%上升至14.04%,13件大隆组硅质页岩现场解析总含气量为1.29~9.97 m3/t,平均4.85 m3/t。实现了湘中坳陷二叠系页岩气新发现,有效拓展了华南地区大隆组勘探范围。
钻获龙潭组厚度349.95 m,上段为一套细砂岩、粉砂岩夹泥岩潮坪相沉积地层,下段为一套炭质泥岩、粉砂质泥岩夹薄层细砂岩泻湖相沉积地层。在井深1013.4~1048 m泥岩与粉砂岩互层段气测全烃值最高可达19.87%,甲烷值最高为16.94%,7件泥岩与粉砂岩样品现场解析总含气量0.57~3.42 m3/t,平均1.78 m3/t;井深1088.10~1199.75 m泥岩夹泥质粉砂岩含气层111.6 m,气测全烃值最高可达28.2%,甲烷值最高为23.6%,13件泥岩、粉砂质泥岩样品现场解析总含气量0.90~4.55 m3/t,平均2.01 m3/t(图 1b),首次查明了湘中坳陷二叠系龙潭组非常规油气分布特点。
通过区域地质背景分析,并结合煤田区域地质资料,本研究认为滑脱断裂(F9)上下盘具有不同的页岩气聚集条件。滑脱断裂之上由一系列的同向逆断层形成的逆冲推覆体,地层变形强烈,且裂缝发育,导致页岩气保存条件变差。滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,地层平缓,不发育次级通天断裂,与下盘地层形成反向遮挡,易形成封闭,保存条件良好(图 1c)。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)二叠系大隆组岩性以硅质岩、硅质页岩为主,夹少量灰岩。主要含气段存在于上段硅质页岩段,厚88.2 m,含气量平均为4.85 m3/t,含气性优越,资源潜力大。
(2)二叠系龙潭组上段以致密砂岩气为主,含气量平均为1.78 m3/t;下段以页岩气为主,泥岩厚达177.47 m,含气量平均为2.01 m3/t,具有泥岩厚度大,含气性好等特征。
(3)保存条件是页岩气富集关键,构造改造弱的封闭演化环境有利于页岩气保存,研究区滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,易形成封闭,保存条件良好。
(4)湘邵地1井在二叠系大隆组和龙潭组获得良好的页岩气显示,证实了湘中地区二叠系具有良好的页岩气资源潜力,对湘中地区页岩气资源潜力评价具有重要意义。
5. 基金项目(Fund support)
本文为中国地质调查局项目“中扬子地区油气页岩气调查评价”(DD20221659)资助的成果。
-
表 1 制革污泥中各种组分含量与比例
Table 1 Contents and proportions of various components in the tanning sludge
组分 含量/(mg/kg) 比例/% N
形态总N 30900 100.00 NH4+–N 14400 46.60 NO3−–N 420 1.36 NO2−–N <1 0.00 Cr
价态总Cr 28822 100.00 Cr(VI) 170 0.59 Cr(III) 28652 99.41 Cr形态 水溶态 153 0.53 弱酸提取态 229 0.79 铁锰氧化物
结合态21700 75.29 有机质结合态 3860 13.39 残渣态 2880 9.99 pH值 7.94 总盐量/(mg/kg) 99000 表 2 污染场地周边表层(0~10 cm)洁净土壤的基本特征
Table 2 Characteristics of clean soil (0−10 cm) surrounding the contaminated sites
容重/(g/cm3) CEC/(mol/kg) pH 黏粒/% 粉粒/% 砂粒/% 有机碳/% Fe2O3total/% Cr(III)/(mg/kg) (NH4+–N)/(mg/kg) 1.64 13.6 7.61 10.52 74.39 15.09 1.7 6.13 69.9 20.2 表 3 包气带水分运动参数
Table 3 Parameters of water movement in the vadose zone
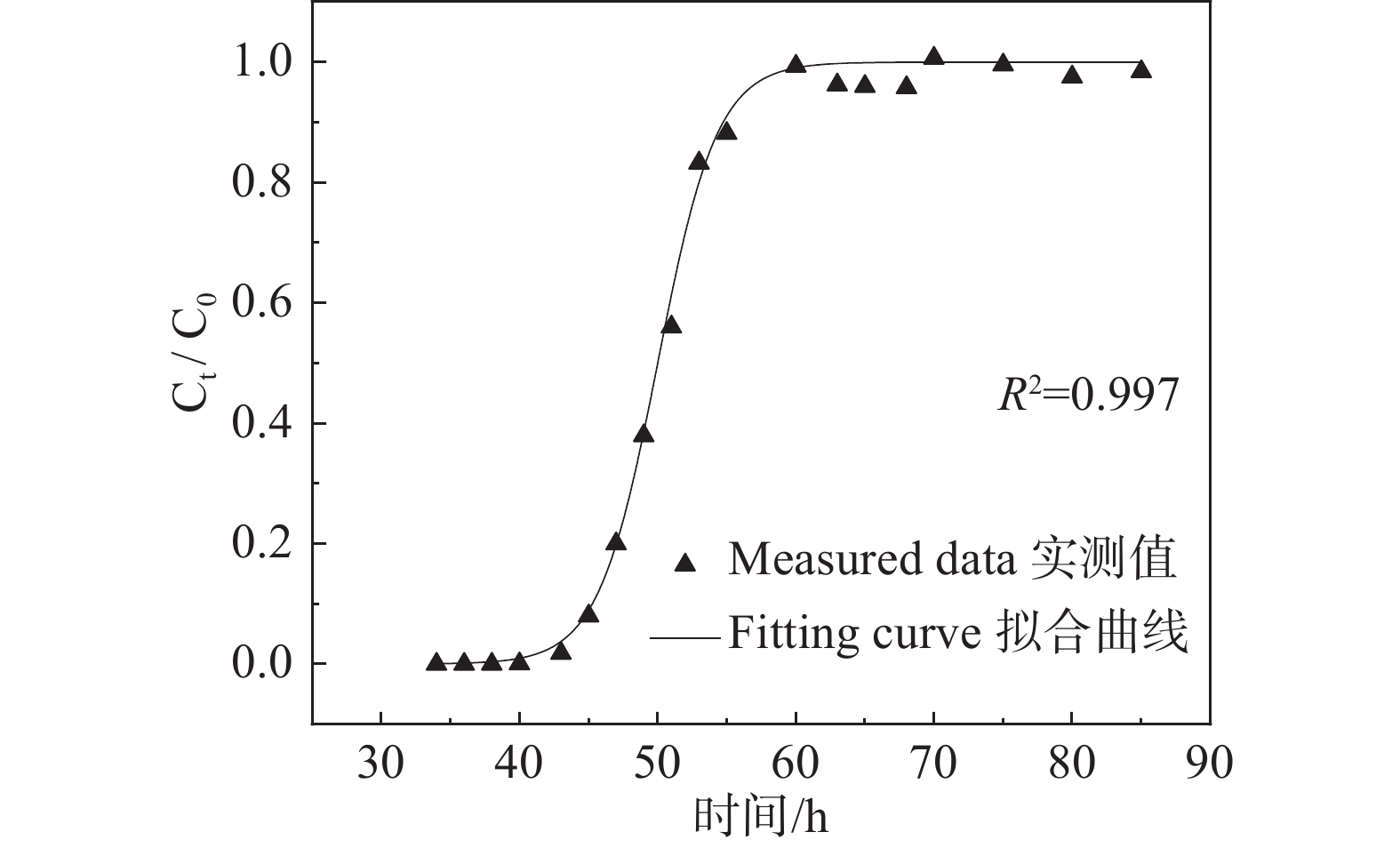
参数 θr/% θs/% α/cm−1 n Ks/(cm/d) l 粉土 5.7 45.64 0.0049 1.6979 31.59 0.5 注:θr为土壤的残余含水率,θs为土壤的饱和含水率,α、n为土壤水力特性经验参数,Ks为渗透系数。 表 4 渗流速度及弥散系数求解结果
Table 4 Results of percolation velocity and dispersion coefficients
参数 t0.16/h t0.50/h t0.84/h v/(cm/h) D/(cm2/h) Disp/cm 粉土 46.4 50.2 53.8 0.997 0.134 0.134 表 5 土柱表层粉土(0~2 cm)中不同形态的Cr(III)含量
Table 5 Contents of different forms of chromium(III) in topsoil of silt column (0~2 cm)
形态 水溶态 弱酸
提取态铁锰氧化物
结合态有机质
结合态残渣态 含量/
(mg/kg)8.6 142.02 1127.38 771 5420 占比/% 0.12 1.90 15.09 10.32 72.57 -
[1] Alibardi L, Cossu R. 2016. Pre–treatment of tannery sludge for sustainable landfilling[J]. Waste Management, 52: 202−211. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.04.008
[2] Barajas–Aceves M, Rios–Berber J, Oropeza–Mota J, Rodríguez–Vázquez R. 2014. Assessment of tannery waste in semi–arid soils under a simulated rainfall system[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 23: 954−964. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2014.896861
[3] Chen Pei, Zhang Yongbo, Zheng Xiuqing, Zhao Xuehua. 2016. Prediction of the migration of ammonia nitrogen in vadose zone by using HYDRUS–1D model[J]. Water Power, 42(4): 10−12,30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chidambaram S, Karmegam U, Prasanna M, Sasidhar P. 2012. A study on evaluation of probable sources of heavy metal pollution in groundwater of Kalpakkam region, South India[J]. The Environmentalist, 32: 371−382. doi: 10.1007/s10669-012-9398-1
[5] China C R, Maguta M M, Nyandoro S S, Hilonga A, Kanth S V, Njau K N. 2020. Alternative tanning technologies and their suitability in curbing environmental pollution from the leather industry: A comprehensive review[J]. Chemosphere, 254: 1−18.
[6] Cyrus J S, Reddy G. 2011. Sorption and desorption of ammonium by zeolite: Batch and column studies[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 46: 408−414. doi: 10.1080/02773813.2010.542398
[7] Ding Shaolan, Li Ling, Zhao Mengjun. 2009. Investigation on the characteristic of COD and nitrogen in waste water from making cattle leather[J]. Leather Science and Engineering, 19(2): 19−21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Du Hangtao, Xu Rui, Xu Hui, Shi Wenqing, Deng Haoyuan, He Junlong, Zhu Lin. 2022. Ammonia nitrogen removal by nitrifying bacteria from different habitats[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 12(1): 81−91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Evanylo G, Sukkariyah B, Anderson Eborall M, Zelazny L. 2006. Bioavailability of heavy metals in biosolids−amended soil[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 37: 2157−2170. doi: 10.1080/00103620600817309
[10] Fu Xuezhong. 2012. Progress in resource utilization of tannery solid wastes[J]. Leather and Chemicals, 29(1): 19−22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Guo Huaming, Gao Zhipeng, Xiu Wei. 2022. Research status and trend of coupling between nitrogen cycle and arsenic migration and transformation in groundwater systems[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 49(3): 153−163 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] He Z, Hu Y, Yin Z, Hu Y, Zhong H. 2016. Microbial diversity of chromium–contaminated soils and characterization of six chromium–removing bacteria[J]. Environmental Management, 57: 1319−1328.
[13] Hu Shuyan. 2008. Adsorption and Competitive Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Humic Acid and Fulvic Acid [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 1−63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Huang Xuefen, Meng Min, Xie Gang, Luo Yuchen, Li Lei, Wang Weisheng. 2017. Study on speciation distribution of Cr and reduction of Cr (VI) in tannery sludge[J]. Journal of Guangxi University(Natural Science Edition), 42(5): 1930−1936 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Jellali S, Diamantopoulos E, Kallali H, Bennaceur S, Anane M, Jedidi N. 2010. Dynamic sorption of ammonium by sandy soil in fixed bed columns: Evaluation of equilibrium and non–equilibrium transport processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 91: 897−905.
[16] Kong Xiangke, Huang Guanxing, Han Zhantao, Li Zhitao, Wand Pping, Xu Youming. 2017. Vertical distribution characteristics of pollutants in a typical soil profile in the tannery sludge landfill site[J]. South–to–North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 15(6): 96−100 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Kong X, Li C, Wang P, Huang G, Li Z, Han Z. 2019. Soil pollution characteristics and microbial responses in a vertical profile with long–term tannery sludge contamination in Hebei, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16: 563. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16040563
[18] Kong X, Wang Y, Ma L, Li H, Han Z. 2022. Impact of δ–MnO2 on the chemical speciation and fractionation of Cr (III) in contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29: 45328–45337.
[19] Kotaś J, Stasicka Z. 2000. Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 107: 263−283. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00168-2
[20] Li Wei, He Jiangtao, Liu Liya, Gao Peng, Ji Yaping. 2013. Application of Hydrus–1D software in groundwater contamination risk assessment[J]. China Environmental Science, 33(4): 639−647 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Liu Gang, Gao Zhipeng, Qu Jihong. 2017. Effects of hydraulic parameters in the unsaturated zones on pressure head and solute transport under the influence of river[J]. North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power, 38(2): 72−76 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Ma Hongrui, Xi Yinyin, Chen Zhanguang. 2010. Emision Factor of Ammonia Nitrogen and Total Nitrogen from Leather Process[J]. China Leather, 39(1): 6−10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Mao Jiajun, Liu Qing. 2019. Study on the migration of chromiun (Ⅵ) in the vadose zone of coal ash stacking yard based on Hydrus–1D[J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 33(1): 13−18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Pang Yajie, Liu Changli, Wang Cuiling, Zhang Yun, Pei Lixin, Hou Hongbing, Wang Zhiliang. 2013. A study of the migration of factory pollutants COD_Cr in the vasose zone using numerical simulation methods[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 40(3): 115−120 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Pantazopoulou E, Zouboulis A. 2018. Chemical toxicity and ecotoxicity evaluation of tannery sludge stabilized with ladle furnace slag[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 216: 257−262. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.077
[26] Reijonen I, Hartikainen H. 2016. Oxidation mechanisms and chemical bioavailability of chromium in agricultural soil–pH as the master variable[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 74: 84−93. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.08.017
[27] Sungur A, Soylak M, Yilmaz S, Özcan H. 2014. Determination of heavy metals in sediments of the Ergene River by BCR sequential extraction method[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72: 3293−3305. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3233-6
[28] Wang C, Liu C, Pei L, Pang Y, Zhang Y, Hou H. 2015. Experimental and modeling study of pure terephthalic acid (PTA) wastewater transport in the vadose zone[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 17: 389–397.
[29] Wang D, He S, Shan C, Ye Y, Ma H, Zhang X, Zhang W, Pan B. 2016. Chromium speciation in tannery effluent after alkaline precipitation: Isolation and characterization[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 316: 169−177. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.021
[30] Wu Yanqing. 2007. Dynamics of Fluid Folw and Contaminant Transport in Porous Media [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Xia Xing, Yang Jianjun. 2019. Molecular sequestration mechanisms of heavy metals by iron oxides in soils using synchrotron–based techniques: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(1): 348−358 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Xiao Wendan. 2014. Migration and Transformation Characteristics of Chromium in Typical Soil and Pollution Diagnosis Index [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 1−141 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Xu Chengbin, Meng Xuelian, Ma Xiping, Zhang Lihong, Li Yaoyao, Bao Kun. 2012. Research on influence of Cr pollution on index for biological characteristics of soil quality[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 37(8): 1−3 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Zhang Dazheng, Li Haiming, Zhan Xiaoyan, Xia Yuezhen. 2014. Characteristics of groundwater salt pollution in a typical leather–contaminated site[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 41(2): 18−23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Zhou Jianjun, Ma Hongrui, Dong Hexiang, Du Kai, Li Ka. 2018. Research progress on resourceful treatment and disposal of tannery sludge[J]. China Leather, 47(4): 44−49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] 陈佩, 张永波, 郑秀清, 赵雪花. 2016. 氨氮在包气带中迁移的HYDRUS–1D预测模型[J]. 水力发电, 42(4): 10−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2016.04.003 [37] 丁绍兰, 李玲, 赵梦君. 2009. 牛皮制革废水COD和氮素排放特征研究[J]. 皮革科学与工程, 19(2): 19−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7964.2009.02.003 [38] 杜杭涛, 徐睿, 徐慧等, 施文卿, 邓皓元, 何俊龙, 朱琳. 2022. 不同生境来源硝化细菌群对氨氮的去除性能[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 12(1): 81−91. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210380 [39] 傅学忠. 2012. 制革固体废弃物的资源化利用进展[J]. 皮革与化工, 29(1): 19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0939.2012.01.006 [40] 郭华明, 高志鹏, 修伟. 2022. 地下水氮循环与砷迁移转化耦合的研究现状和趋势[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 49(3): 153−163. [41] 胡书燕. 2008. 腐殖酸对重金属的吸附作用及金属竞争吸附特征[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 1−63. [42] 黄雪芬, 蒙敏, 谢刚, 罗宇晨, 李磊, 王维生. 2017. 制革污泥中Cr形态分布及Cr(Ⅵ)还原性研究[J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 1930−1936. [43] 孔祥科, 黄国鑫, 韩占涛, 李志涛, 王平, 许有明. 2017. 制革污泥堆存场地典型土壤剖面中污染物的垂向分布特征[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 15(6): 96−100. [44] 李玮, 何江涛, 刘丽雅, 高鹏, 纪亚萍. 2013. Hydrus–1D软件在地下水污染风险评价中的应用[J]. 中国环境科学, 33(4): 639−647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.04.009 [45] 刘钢, 高志鹏, 屈吉鸿. 2017. 河流影响下包气带水力参数对压力水头及溶质运移的影响[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 38(2): 72−76. [46] 马宏瑞, 郗引引, 陈占光. 2010. 制革过程中氨氮和总氮产污系数的试验模拟核算[J]. 中国皮革, 39(1): 6−10. [47] 茅佳俊, 刘清. 2019. 基于Hydrus–1D的粉煤灰堆场Cr(Ⅵ)在包气带中迁移规律的研究[J]. 能源环境保护, 33(1): 13−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2019.01.003 [48] 庞雅婕, 刘长礼, 王翠玲, 张云, 裴丽欣, 侯宏冰, 王志良. 2013. 某化工厂废液COD_(Cr)在包气带中的迁移规律及数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 40(3): 115−120. [49] 仵彦卿. 2007. 多孔介质污染物迁移动力学[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社. [50] 夏星, 杨建军. 2019. 基于同步辐射技术研究土壤铁氧化物固定重金属分子机制的进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(1): 348−358. [51] 肖文丹. 2014. 典型土壤中铬迁移转化规律和污染诊断指标[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 1−141. [52] 徐成斌, 孟雪莲, 马溪平, 张利红, 李瑶瑶, 包坤. 2012. 铬污染对土壤环境质量生物特征指标的影响研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 37(8): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2012.08.001 [53] 张达政, 李海明, 詹晓燕, 夏跃珍. 2014. 典型制革污染场地地下水盐污染特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 41(2): 18−23. [54] 周建军, 马宏瑞, 董贺翔, 杜凯, 李卡. 2018. 制革污泥资源化处理与处置研究进展[J]. 中国皮革, 47(4): 44−49.




 下载:
下载: