Sedimentary rare earth in the eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou: A new genetic type and potential of development and utilization
-
摘要:研究目的
稀土是重要的自然资源,更是宝贵且关键的战略资源。本文通过对滇东—黔西地区沉积型稀土资源野外地质调查及室内综合研究,揭示了该稀土资源的优势及开发利用潜力,既丰富了全球稀土资源工业类型,又支撑了国家关键稀土资源战略储备。
研究方法本文基于对含矿地层特征、典型矿石特征、稀土元素配分特征以及稀土资源潜力等方面的研究,探讨该稀土资源的成因类型、稀土元素赋存状态以及开发利用潜力。
研究结果查明含矿地层为二叠系上统宣威组(P3x);富稀土矿石的岩性为灰白色铝土质黏土岩和粉砂质黏土岩;其成因属沉积型;在威宁县黑石头—麻乍—哲觉地区,矿体厚度2~18m不等,矿体延伸较连续,稀土氧化物(TREO)含量最高达1.6%,矿体块段稀土(TREO)加权平均品位为0.18%~0.46%,推断资源量超30万t;该稀土资源中“关键稀土元素(CREE)”占比高达22.6%(以∑CREO计),高于国内外大多数正在开发利用的稀土矿;针对该稀土资源研发了“选择性浸出”新工艺,使稀土回收率达90%以上,该稀土资源有望实现规模化工业利用。
结论该沉积型稀土资源具有矿体厚度大、矿石品位高、资源潜力大、开采成本低、矿石中关键稀土元素(CREO)占比高、开发利用前景好等优点。
创新点:估算出威宁县黑石头—麻乍—哲觉地区稀土矿推断资源量超30万t;对比研究该稀土资源中“关键稀土元素(CREE)”含量,突显其潜在价值大;通过综合研究,认为该沉积型稀土资源开发利用潜力巨大,同时丰富了全球稀土资源工业类型。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveRare earth is not only important natural non-renewable resources, but also a key strategic resource. Based on the field geological survey and indoor comprehensive study of sedimentary rare earth resources in the eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou area, this paper reveals the advantages and development and utilization potential of the rare earth resources, which not only enriches the industrial types of the global rare earth resources, but also supports the national strategic reserve of key rare earth resources.
MethodsBased on the research on the characteristics of ore-bearing strata, typical ore characteristics, the partition characteristics of rare earth elements and the potential of rare earth resources, this paper discusses the genetic types of the rare earth resources, the occurrence state of rare earth elements and the potential of development and utilization.
ResultsThe ore-bearing stratum is identified as Xuanwei Formation of Upper Permian (P3x); the lithology of rare-earth rich ore is gray- white aluminite claystone and silty claystone; the origin of rare earth ore belongs to sedimentary type; in Weining County Heishitou—Mazha—Zhejue area, the thickness of ore body varies from 2m to 18m, the ore body extension is relatively continuous, the content of rare earth oxide (TREO) is up to 1.6%, the weighted average grade of ore body block (TREO) is 0.18% to 0.46%, and the inferred resource is over 300, 000 tons; the proportion of "Critical rare earth elements (CREE)" in the rare earth resources is up to 22.6% (∑CREO), which is higher than most of the rare earth deposits under development and utilization at domestic and overseas. In addition, the new selective leaching technology is used in the dressing and metallurgy test, and the results indicate that the recovery of rare earth can reach more than 90%. This new type of rare earth mine is expected to realize large-scale industrial utilization.
ConclusionsThe sedimentary rare earth resource has the advantages of large ore thickness, high ore grade, large resource potential, low mining cost, high proportion of critical rare earth elements (CREO) in ore, and good development and utilization prospect.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
莱阳是我国著名的恐龙之乡,晚白垩世鸭嘴龙类的骨骼化石十分丰富,但早白垩世恐龙则发现不多,仅有少量鹦鹉嘴龙类。2000年,曾在莱阳早白垩世龙旺庄组发现过兽脚类足迹化石。最近,我们在海阳凤城镇凤翔路附近(36°43'17"N,121°14'40"E)发现了一个新的小型兽脚类恐龙足迹化石点。本项研究的目的,是确定造迹恐龙的类型,并探讨其足迹分类意义,为早白垩世胶莱盆地恐龙群面貌恢复提供重要化石依据。
2. 研究方法(Methords)
采用传统的地层学、古生态学研究方法。首先,野外测制含化石层位的地层剖面,分层并进行岩性描述,标注足迹化石的产出层位,测量足迹大小等参数、绘制足迹产出状态图、采集有关的足迹标本等;其次,根据区域地质资料确定足迹的产出层位,室内绘制地层剖面图和足迹平面分布图等;最后,开展恐龙足迹的古生态学研究,查明造迹恐龙的种类,探讨其行为习性及生活环境等。
3. 研究结果(Results)
恐龙足迹产于中层灰绿色、灰紫色粉砂岩、细砂岩中。根据岩性组合、沉积特征及与区域地层对比,确认其产出层位为早白垩世莱阳群杨家庄组,为一套河湖湘沉积。该组与以往报道的莱阳地区产兽脚类足迹拟跷脚龙足迹Paragrallator的龙旺庄组及下伏的水南组时代相当。
此次共发现较清晰的恐龙足迹化石26个。其中,15个产于层面上,为正常凹型足迹,未能采集(图 1);7个位于岩层底面,为凸型足迹,分布于2块标本上,已被采集(图 2)。足迹均为小的三趾型,最大的长10.0 cm,宽5.3 cm;最小的长5.0 cm,宽4.0 cm。因为足长大于宽,足迹较窄且爪迹明显,应为小型兽脚类恐龙的足迹。根据足迹大小、长宽比值以及Ⅱ、Ⅳ趾间角的大小,可将这些足迹分为a、b、c 3个形态类群(表 1)。类型a:长略大于宽,足长和宽均值分别为6.0 cm和4.7 cm;类型b:长远大于宽,长和宽均值为7.3 cm和3.6 cm(图 2b);类型c:只有一个足迹,长10.0 cm,宽5.3 cm。研究认为,类型a类似于山东诸城黄龙沟同时期的兽脚类足迹强壮足迹Corpulentapus,但后者个体要大得多,几乎是其2倍;类型b与山东莒南后左山早白垩世田家楼组的甄朔南小龙足迹Minisauripus zhenshuonani大小相似,但后者的长宽比值较小,特别是类型b的Ⅲ趾更长直、粗壮,这点又与后左山的跷脚龙足迹Grallator isp.相似,因此,其应为二者之间的过渡类型;类型c根据形态、大小等则可归入Grallator isp.。Grallator是最早被命名的恐龙足迹属之一,足迹长一般不超过15 cm,三趾型,两侧趾间夹角较小,中趾较两侧趾前伸明显(大于Eubrontes或Anchisauripus),足迹狭窄,长宽比值大于或等于2。以往足长小于15 cm的三趾型兽脚类足迹往往归于该足迹属。需要指出的是,恐龙足迹的分类主要是根据形态,受底质等环境因素影响很大,往往同一个恐龙个体可以形成不同的足迹属。因此,研究者对于对于足迹的分类比较谨慎,本文也对类型a和b进行进一步的分类归并。需要指出,这些小型足迹的层面分布相对密集、方向性较为杂乱,可能意味着它们的造迹恐龙具有群居特征,起码足迹的产地是一个小型恐龙经常聚会的地区。此外,根据有关的经验公式,可以推测造迹恐龙的大小,一般身高是足长的4倍,而身长是身高的3倍。据此推测这批足迹的造迹恐龙体长约为80~90 cm,高近30 cm。但由于这些足迹杂乱,加之出露局限,难以识别出完整的行迹(trackway),因此,步长及运动速度等参数暂时无法获取。
表 1 海阳恐龙足迹主要特征Table 1. Main characteristics of dinosaur footprints in Haiyang
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1) 凤城镇的足迹三趾型,由小型兽脚类恐龙形成,它们是海阳地区恐龙足迹的首次发现,时代为早白垩世中晚期,产出地层层位是下白垩统莱阳群杨家庄组。
(2) 可以识别出26个恐龙足迹,采集的两块标本含8个足迹,另外18个足迹仍然保持在野外。这些足迹可分为3个形态类型。类型a类似于Corpulentapus,但个体偏小;类型b应为足迹属Minisauripus与Grallator之间的过渡类型,将在小型兽脚类恐龙足迹的分类中占据重要位置;类型c则可归入Grallator isp。
(3) 尽管该地没有发现兽脚类骨骼化石,但此次恐龙足迹的发现表明,在早白垩世,胶莱盆地东南部的海阳为河湖相环境,生活着体长80~90 cm群居的小型肉食性兽脚类恐龙群。因此,恐龙足迹是恐龙研究的重要内容,特别在缺乏恐龙骨骼化石的情况下,足迹化石是研究恐龙的绝佳材料。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
本文为国家自然科学基金项目(41741008)和中国地质调查局项目“1:100万天津幅海洋区域地质调查”(1212011220113)资助的成果。
致谢: 感谢谭洪旗博士在本文成稿过程中提供帮助;感谢孙勇、梅亚军、田康志参与了本文图件的绘制;感谢两位匿名审稿专家及编辑部老师给本文提出了宝贵的意见、建议。 -
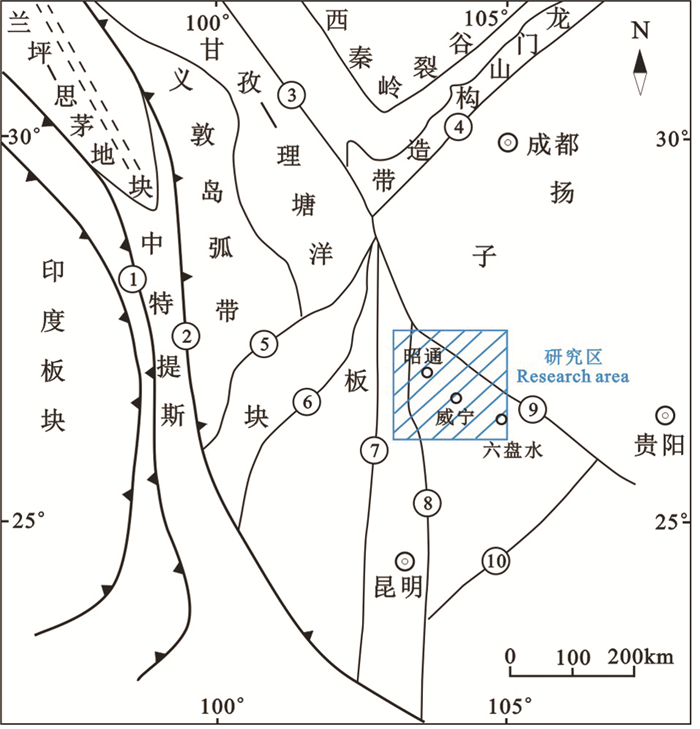
图 1 研究区大地构造位置图(据骆耀南, 1985; 张志斌等, 2006)
①—怒江断裂;②—金沙江—红河断裂;③—鲜水河断裂;④—龙门山山前断裂;⑤—小金河断裂;⑥—箐河—程海断裂;⑦—安宁河—绿汁江断裂;⑧—小江断裂;⑨—康定—水城断裂;⑩—弥勒—师宗断裂
Figure 1. Sketch map showing geotectonic position of the research area (after Luo Yaonan, 1985; Zhang Zhibin et al., 2006)
①-Nujiang fault; ②-Jinsha River—Red River fault; ③-Xian Shui River fault; ④-Longmen Mountain piedmont fault; ⑤-Xiao Jian River fault; ⑥-Jing River—Chenghai fault; ⑦-Anning River—Lü zhi River fault; ⑧-Xiao River fault; ⑨-Kang ding—Shui cheng fault; ⑩-Mile—Shizong fault
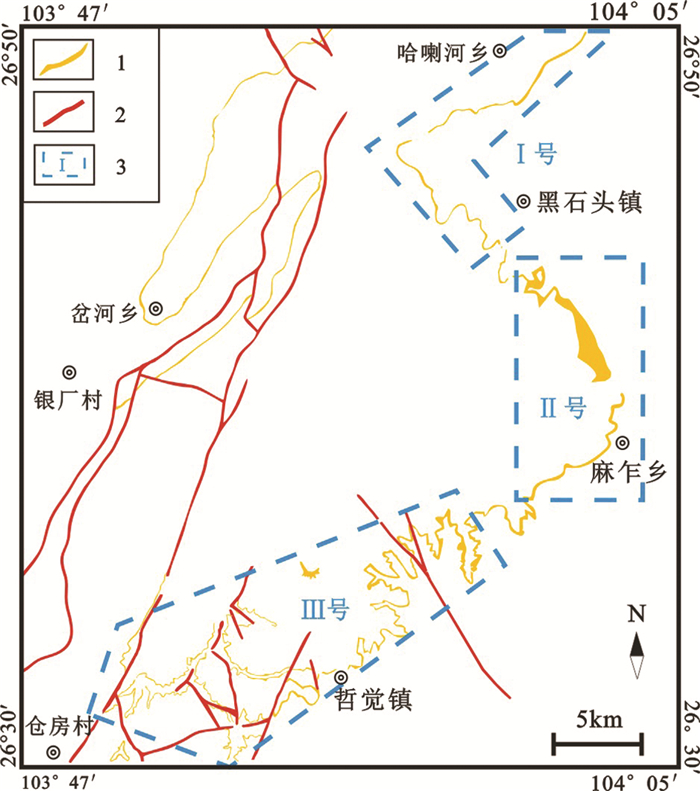
图 3 贵州威宁哲觉镇宣威组一段(P3x1)剖面-柱状图
a—宣威组一段典型剖面;b—宣威组一段柱状图;c、d、e—铝土质黏土岩;f—砾屑砂岩
Figure 3. Typical profile and histogram of the first part of Xuanwei Group (P3x1) in the Zhejue town of Weining area, Guizhou Province
a-Typical section of the first part of Xuanwei Group; b-Histogram of the first passage of Xuanwei Group; c, d, e-Bauxitic clay rock; f-Gravel sandstone
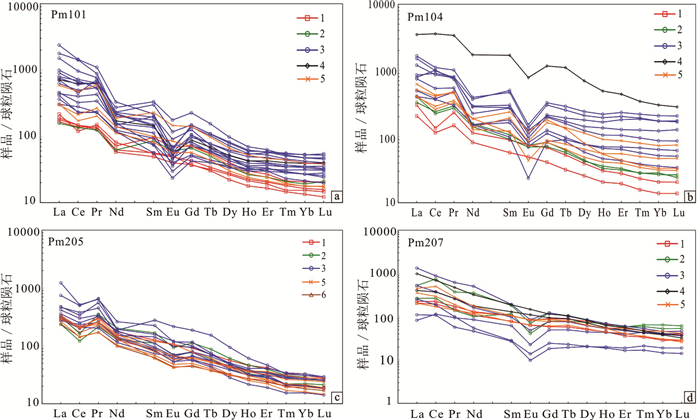
图 6 全岩球粒陨石稀土配分图(据田恩源等, 2020修改;标准化数值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
1—玄武岩;2—铁质粉砂质黏土岩;3—铝土质黏土岩;4—炭质粘土岩;5—黏土质粉砂岩;6—砂质砾岩
Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the samples (modifiled from Tian Enyuan et al., 2020; standardized values modifiled from Sun and McDonough, 1989)
1-Basalt; 2-Fe-Silty clay rock; 3-Bauxitic clay rock; 4-Carbonaceous clay rock; 5-Clayey siltstone; 6-Sandy conglomerate
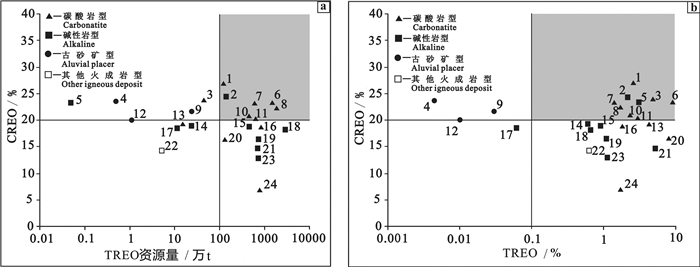
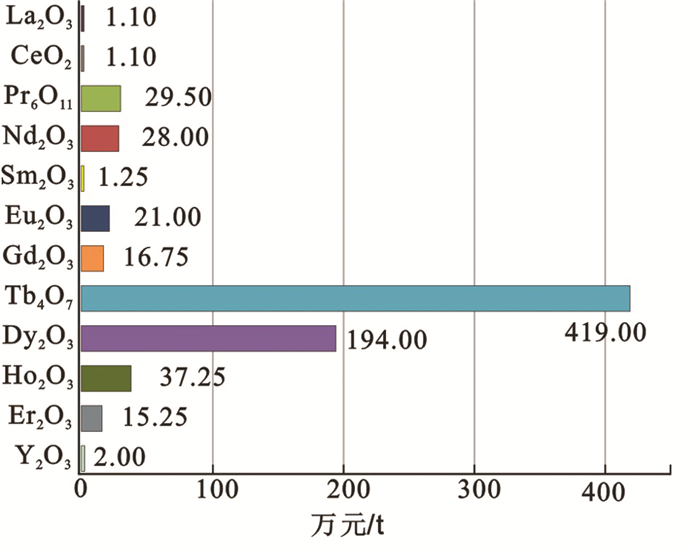
表 1 世界典型稀土矿床对比表
Table 1 Comparison table of typical rare earth deposits in the world

-
Dai Chuangu. 2017. Regional Geology of Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dai S F, Zhou Y P, Zhang M Q, Wang X B, Wang J M, Song X L, Jiang Y F, Luo Y B, Song Z T, Yang Z, Ren D Y. 2010. A new type of Nb(Ta)-Zr(Hf)-REE-Ga polymetallic deposit in the late Permian coal-bearing strata, eastern Yunnan, southwestern China: Possible economic significance and genetic implications[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 83(1): 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.04.002
Friedrichs P. 2017. Development of a Rare Earth Element Resource Database Management System[D]. Aachen: Rheinisch-Westfalisch Technische Hochschule Aachen, 165-169.
Ge Zhihua. 2018. Study on the mechanism of rare earth migration in the weathering crust of basaltic rocks in Weining region, Guizhou[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 1-71(in Chinese with English abstract).
He P N, He M Y, Zhang H. 2018. State of rare earth elements in the rare earth deposits of Northwest Guizhou, China[J]. Acta Geochimica, 37(6): 867-874. doi: 10.1007/s11631-018-0278-3
Huang Xunhua. 1997. The Lufang rare earth deposit in Weining, Western Guizhou and its mineralization[J]. Guizhou Geology, (4): 328-333(in Chinese with English abstract).
Information Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. 2012. China's Rare Earth Situation and Policy: June 2012[M]. Beijing: People's Publishing House(in Chinese with English abstract).
Long X, Xu Y G, Mei H J, Zheng Y F, He B, Pirajno F. 2004. Distinct mantle sources of low-Ti and high-Ti basalts from the western Emeishan large igneous province, SW China: Implications for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 228: 525-546. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.10.002
Luo Yaonan. 1985. Understanding and progress in the study of Panxi Paleorift[J]. Geology in China, (1): 29-35(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mclennan S M. 1993. Weathering and global denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 101(2): 295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
Pan Guitang, Xiao Qinghui, Lu Songnian, Deng Jinfu, Feng Yimin, Zhang Kexin, Zhang Zhiyong, Wang Fangguo, Xing Guangfu, Hao Guojie, Feng Yanfang. 2009. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 36(1): 1-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.01.001
Schnwandt H K, Barnes G B, Ulrich T. 2016. A description of the world-class rare earth element deposit, Ranbreez, South Greenland[J]. Rare Earths Industry, 73-85.
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Tian Enyuan, Gong Daxing, Lai Yang, Qiu Xiaolong, Xie Hua, Tian Kangzhi. 2020. Genesis and enrichment of sedimentary rare earth in Weining area, Guizhou Province[J]. Earth Science. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Denghong, Zhao Zhi, Yu Yang, Dai Jingjing, Deng Maochun, Zhao Ting, Liu Lijun. 2018. Exploration and research progress on ion-adsorption type REE deposit in South China[J]. China Geology, 1: 415-424.
Wang Wei. 2008. Study on Permian Basalt Weathering Crust and Enrichment of Rare-earth element in Western Guizhou Province China[D]. Guizhou: Guizhou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wen Jun, Zhu Helin, Zhang Jinyuan, Zhang Hangfei, Guo Wenyan, You Xuejun, Zhao Wei, Li Pengcheng, Chen Dongfang. 2021. The first discovery of the paleo-weathering crust-sedimentary Nb and rare earth deposits at the bottom of Xuanwei Formation in the Muchuan area of southern Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 48(3): 970-971(in Chinese with English abstract).
Weng Z H, Simon J, Gavin M, Nawshad H. 2015. A detailed assessment of global rare earth element resources: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 110: 1925-1952. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.8.1925
Wu Chengquan, Zhang Zhengwei, Qing Haibo, Yoshio Takahashi, Zhou Lingjie, Xu Jinghong, Li Xiyao, Jin Ziru. 2019. Occurrence and enrichment of rare earth elements in clay rocks of Xuanwei formation in western Guizhou[C]//Abstracts of the 9th National Symposium on metallogenic theory and prospecting methods(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Guangxiang. 1995. Rare Earth[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1-699(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Lu, Li Yuankun, Hui Bo, Qing Jianhua, Dai Zongmin, Gong Daxing. 2020. A selective leaching method of sedimentary rare earth ore[P]. China, 2020-04-24(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Y G, Chung S L, Jahn B M, Wu G Y. 2001. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China[J]. Lithos, 58(3-4): 145-168. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00055-X
Xu Ying, Dai Zongming, Gong Daxing, Hui Bo. 2018. Study on the occurrence state of rare earth elements of rare earth-enriched rocks in the Permian Xuanwei Group in Guizhou Province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 214(6): 95-99, 106(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Ruidong, Wang Wei, Bao Miao, Wang Qiang, Wei Huairui. 2006. Geochemical character of rare earth mineral from the top of Permin basalt, Hezhang County, Guizhou province[C]//National Conference on mineral deposits(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang R D, Wang W, Zhang X D, Liu L, Wei H R, Bao M, Wang J X. 2008. A new type of rare earth elements deposit in weathering crust of Permian basalt in western Guizhou, NW China[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 26(5): 753-759. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60177-5
Zhang Hai. 2014. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Metallogenic Mechanism of REE Deposits, Northwestern Guizhou[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1-130(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zheng, Dai Chaohui. 2010. Rare earth ore and metallogenic geological characteristics in Guizhou[J]. Mineral resources and geology, (5): 433-439(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2010.05.010
Zhang Zhibin, Li Chaoyang, Tu Guangchi, Xia Bing, Wei Zhenquan. 2006. Geotectonic evolution background and ore-forming process of Pb-Zn deposits in Chuan-Dian-Qian area of Southwest China[J]. Geotectonica et Mettallogenia, 30(3): 343-354(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Z W, Yang X Y, Li S, Zhang Z S. 2010. Geochemical characteristics of the Xuanwei Formation in West Guizhou: Significance of sedimentary environment and mineralization[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 29(4): 355-364. doi: 10.1007/s11631-010-0467-1
Zhang Z W, Zheng G D, Takahashi Y, Wu C Q, Zheng C F, Yao J H, Xiao C Y. 2016. Extreme enrichment of rare earth elements in hard clay rocks and its potential as a resource[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 191-212. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.018
Zhao L X, Dai S F, Graham I T, Li X, Zhang B B. 2016. New insights into the lowest Xuanwei Formation in eastern Yunnan Province, SW China: Implications for Emeishan large igneous province felsic tuff deposition and the cause of the end-Guadalupian mass extinction[J]. Lithos, 264: 375-391. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.08.037
Zhao L X, Dai S F, Graham I T, Li X, Liu H D, Song X L, Hower J C, Zhou Y P. 2017. Cryptic sediment-hosted critical metal mineralization from eastern Yunnan Province, southwestern China: mineralogy, geochemistry, relationship to Emeishan alkaline magmatism and possible origin[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 80: 116-140. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.06.014
Zhou L J, Zhang Z W, Li Y J, You F H, Wu C Q, Zheng C F. 2013. Geological and geochemical characteristics in the paleo-weathering crust sedimentary type REE deposits, western Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 73: 184-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.011
Zhou Lingjie. 2012. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics of Sedimentary Kaolinite Clay Rare Earth Deposits in Western Guizhou[D]. Guizhou: Institute of geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1-81(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou M F, Malpas J, Song X Y, Robinson P T, Sun M, Kennedy A, Lesher M, Keays R R. 2002. A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China) and the end-Guadalupian mass extinction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196: 113-122. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00608-2
《Mineral resources industry requirements Manual》 Editorial Committee. 2014. Mineral Resources Industry Requirements Manual[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House(in Chinese with English abstract). 戴传固. 2017. 贵州省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-1153. 葛枝华. 2018. 威宁地区玄武岩风化壳中稀土迁移富集机制研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 1-71. 黄训华. 1997. 威宁鹿房稀土矿地质特征及成矿作用初步分析[J]. 贵州地质, (4): 328-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ199704007.htm 骆耀南. 1985. 攀西古裂谷研究中的认识和进展[J]. 中国地质, (1): 29-35. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/DIZI198501009?st=search 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 邓晋福, 冯益民, 张克信, 张智勇, 王方国, 邢光福, 郝国杰, 冯艳芳. 2009. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 36(1): 1-28. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20090101?st=search 田恩源, 龚大兴, 赖杨, 邱小龙, 谢华, 田康志. 2020. 贵州威宁地区沉积型稀土含矿岩系成因与富集规律[J]. 地球科学(网络首发). 王伟. 2008. 贵州西部二叠系玄武岩风化壳及其中稀土富集规律研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 1-67. 文俊, 竹合林, 张金元, 张航飞, 郭文彦, 游学军, 赵伟, 李鹏程, 陈东方. 2021. 川南沐川地区首次发现宣威组底部古风化壳-沉积型铌、稀土矿[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 970-971. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210327?st=search 吴承泉, 张正伟, 秦海波, Yoshio, Takahashi, 周灵洁, 徐进鸿, 李溪遥, 靳子茹. 2019. 贵州西部宣威组黏土岩稀土元素赋存状态和富集规律[C]//第九届全国成矿理论与找矿方法学术讨论会论文摘要集. 徐光宪. 1995. 稀土[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1-699. 徐璐, 李元坤, 惠博, 秦建华, 戴宗明, 龚大兴. 2020. 一种选择性浸出沉积型稀土矿的方法[P]. 中国, CN 109266839 B. 2020-04-24. 徐莺, 戴宗明, 龚大兴, 惠博. 2018. 贵州某地二叠系宣威组富稀土岩系稀土元素赋存状态研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 214(6): 95-99, 106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL201806018.htm 杨瑞东, 王伟, 鲍淼, 王强, 魏怀瑞. 2006. 贵州赫章二叠系玄武岩顶部稀土矿床地球化学特征[C]. 全国矿床会议. 张海. 2014. 黔西北地区稀土矿床地质地球化学特征及其成矿机制研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大, 1-130. 张震, 戴朝辉. 2010. 贵州稀土矿及成矿地质特征[J]. 矿产与地质, (5): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201005010.htm 张志斌, 李朝阳, 涂光帜, 夏斌, 韦振权. 2006. 川、滇、黔接壤地区铅锌矿床产出的大地构造演化背景及成矿作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 30(3): 343-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200603009.htm 中华人民共和国国务院新闻办公室. 2012. 中国的稀土状况与政策: 2012年6月[M]. 北京: 人民出版社, 2012年6月. 周灵洁. 2012. 贵州西部沉积型高岭石质黏土岩稀土矿床的地质和地球化学特征[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所, 1-81. 《矿产资源工业要求手册》编委会. 2014. 矿产资源工业要求手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李炎桂,姚华舟,William J.Foster,邢立达,王传尚,Asma Tahir,Junaid Khan,安志辉,赵赫,王建雄. 藏东昌都地区首次发现中侏罗世兽脚类恐龙行迹. 地球科学. 2022(11): 4222-4244 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: