Tectono-geochemistry and deep prospecting prediction in the Lekai lead-zinc deposit, Northwestern Guizhou Province, China
-
摘要:研究目的
乐开铅锌矿床是近些年黔西北铅锌矿集区内新发现的矿床之一,与该矿集区内铅锌矿床主要受NW向断裂控制有所不同,乐开铅锌矿床严格受NE向断褶构造控制,与滇东北矿集区铅锌矿床具有一致的成矿地质条件。该研究对黔西北乐开地区乃至川滇黔接壤区铅锌矿深部找矿具有重要的指示意义。
研究方法主要包括构造精细解析和构造地球化学等方法。
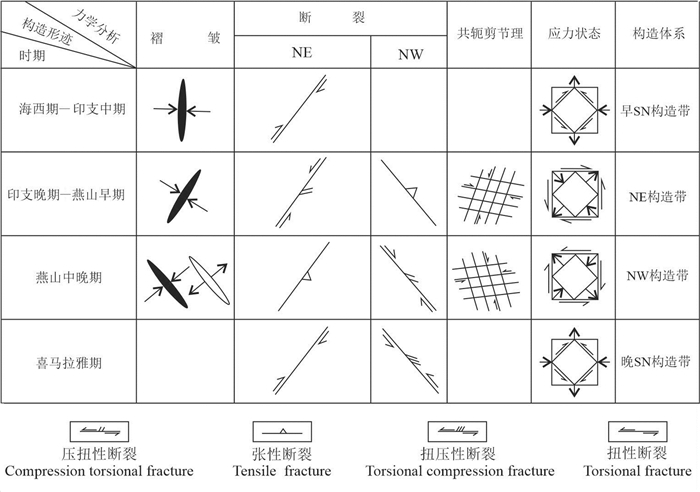
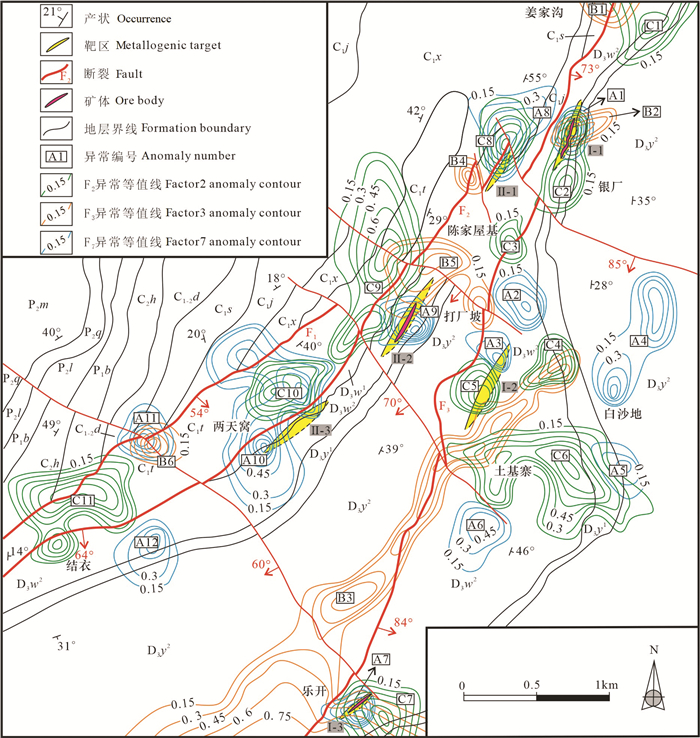
研究结果该区控矿构造型式为典型的“多字型”和“入字型”,并划分出3种构造组合,分别代表 4种不同的构造体系:海西期—印支中期(早SN构造带)、印支晚期—燕山早期(NE构造带)、燕山中晚期(NW构造带)及喜马拉雅期(晚SN构造带)。断裂构造岩主要表现为低温成矿阶段的前缘晕元素组合(Sb-As-Hg)、中温成矿阶段的近矿晕元素组合(Zn-Pb-Cd)与中高温成矿阶段的尾晕元素组合(In-Sn-Ni-Cu)。
结论NE构造带为该矿床的成矿构造体系,推断成矿流体在平面上自SW向NE向运移,提出矿区深部6个定位找矿靶区。
创新点:厘定了矿区4种不同的构造体系和主要成矿构造体系;提出了矿区深部找矿的新方向并提供了6个找矿靶区。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe Lekai lead-zinc deposit, located in the Pb-Zn deposit concentration of northwestern Guizhou, is one of the small-scale lead-zinc deposits newly discovered in recent years. Different from most lead-zinc deposits in the Pb-Zn deposit concentration of northwestern Guizhou, the Lekai lead-zinc deposit is controlled strictly by NE trending fault-fold structure, which is similar to most lead-zinc deposits in the Pb-Zn deposit concentration of northeastern Yunnan. The current research provided significant implications for the deep exploration in the Lekai lead-zinc deposit and the Sichuan–Yunnan–Guizhou Triangle area (SYGT).
MethodsThis study applied a large deal of detailed structural analysis on mechanical properties for faults and folds in the mining area and tectono-geochemistry method.
ResultsThe results showed that duo-type and λ-type are the main ore-controlling structural styles in this area. Moreover, three tectonic associations have been divided, which are correspond to four tectonic systems, namely Hercynian to Mid Indosinian, Late Indosinian to Early Yanshanian, Mid-Late Yanshanian, and Himalayan epochs. The trace elements concentrations of tectonites represented three element associations of principal factors, including frontal halo elements (Sb-As-Hg) in low temperature ore-forming stage, mineralization-halo elements (Zn-Pb-Cd) in medium-low temperature ore-forming stage, and tail-halo elements (In-Sn-Ni-Cu) in medium temperature ore-forming stage.
ConclusionsIn four tectonic systems, ore-forming tectonic system corresponded with Late Indosinian to Early Yanshanian. According to anomaly features and their distribution regularities, the possible migration direction of ore-forming fluid is from southwest to northeast, and six target prospecting areas have been put forward in the depth of mining.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
松科二井,获取了从基底—火石岭组—沙河子组—营城组—登娄库组下部连续完整的原位岩心。本文对松科二井沙河子组上部的孢粉化石进行研究,为研究白垩纪地球温室气候和环境变化,建立服务“百年大庆”目标和基础地质研究的“金柱子”提供基础资料。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
孢粉样品采自松科二井3395.46~3901.35 m,岩性为黑色、灰黑色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩,层位为沙河子组上部。孢粉分析鉴定在吉林大学古生物学与地层学研究中心完成,具体过程为:每个样品取过筛的干样50 g,进行盐酸→氢氟酸→氢氧化钾→盐酸→硝酸→氢氧化钾→盐酸等分析处理,用筛选法将样品中的孢粉化石集中在试管中,制2个固定片在生物显微镜下鉴定。
3. 研究结果(Results)
依据松科二井3395.46~3901.35 m井段的孢粉化石演化特征,划分出两个孢粉组合。
(1)Leiotriletes sp.- Cyathidites australis - Chasmatosporites sp.组合(简称LCC组合),分布在3832.94~3901.35m井段。蕨类孢子占绝对优势,裸子类花粉较低,未见被子类花粉。蕨类孢子含量最高的是Cyathidites australis,其次是Leiotriletes sp.和Cyclogranisporites sp.,有时代意义的还有Cicatricosisporites exilis、C. minutaestriatus、C. splendidus、C.australiensis、Klukisporites sp.、Maculatisporites sp.、Triporoletes singularis、Trilobosporites tribotrys、Aequitriradites sp.和Polycingulatisporites reduncus等;裸子类花粉含量最高的是Chasmatosporites sp.,其次是Psophosphaera sp.,有时代意义的类型有Parvisaccites sp.、Erlianpollis minisculus、Paleoconifersp.、Pseudowalchia sp.和Classopollis sp.等。
(2)Klukisporites triangulus- Aequitriradites sp.- Pristinuspollenites sp.组合(简称KAP组合),分布在3395.46~3613.62 m井段。裸子类花粉百分含量(53.03%~72.13%)较高,其次为蕨类孢子(27.87% ~46.97%),未见到被子类花粉。裸子类花粉中含量最高的是Alisporites parvus,其次是Piceaepollenites sp.,含量较高的类型还有Chasmatosporites sp.、Pinuspollenites divulgatus和P. sp.等,有时代意义的还有Parvisaccites otagoensis、Erlianpollis minisculus、E. mediocris、Jiaohepollis sp.和Classopollis classoides等。蕨类孢子含量最高的是Klukisporites sp.,其次是Leiotriletes sp.和Cyathidites australis,含量较高的类型还有Cyclogranisporites sp.等,有时代意义的有Cicatricosisporites exilis、C.apiteretus、C. australiensis、Klukisporites triangulus、K.variegatus、Pilosisporites scitulus、Impardecispora sp.、Levisporites wulinensis、Triporoletes singularis、Trilobosporites humilis、Aequitriradites sp.和Schizaeoisporites sp.等。
含有早白垩世特有或在早白垩世繁盛的分子:Cicatricosisporites、Klukisporites、Pilosisporites、Maculatisporites、Impardecispora、Levisporites、Triporoletes、Trilobosporites、Aequitriradites、Schizaeoisporites、Polycingulatisporites、Parvisaccites、Paleoconiferus、Erlianpollis、Foveotriletes.和Classopollis等(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 松科二井沙河子组部分孢粉化石(1-Cicatricosisporites exilis,样品号:SK2-375;2. -Cicatricosisporites minutaestriatus,标品号:SK2-385;3-Cicatricosisporites splendidus,标品号:SK2-385;4-Cicatricosisporites australiensis,样品号(sample number):SK2-375;5-Levisporites wulinensis,样品号(sample number):SK2-205;6. Aequitriradites sp.,样品号(sample number):SK2-389; 7-Trilobosporites tribotrys,样品号(sample number):SK2-389;8- Classopollis classoides,标品号:SK2-97;9-Erlianpollis minisculus,样品号(number):SK2-395; 10. Parvisaccites sp.,样品号:SK2-395;11. Pilosisporites scitulus,标品号:SK2-201;12-Triporoletes asper,标品号(specimen number):SK2-219;13. Foveotriletes subtriangulularis,样品号:SK2-219;14-Klukisporites triangulus,样品号(sample number):SK2-205;15-Impardecispora sp.,样品号:SK2-201; 16-Schizaeoisporites polaris,样品号:SK2-173;17-Polycingulatisporites reduncus,标品号:SK2-395;18-Maculatisporites sp.,样品号:SK2-391。19-Chasmatosporites sp.,样品号:SK2-389; 20-Paleoconiferae sp.,样品号(sample number):SK2-391;线段比例尺为10 μm, the scale of the line segment is 10 μm)Figure 1. Spores and pollen from the Lower Cretaceous Shahezi Formation in Well SK2
图 1 松科二井沙河子组部分孢粉化石(1-Cicatricosisporites exilis,样品号:SK2-375;2. -Cicatricosisporites minutaestriatus,标品号:SK2-385;3-Cicatricosisporites splendidus,标品号:SK2-385;4-Cicatricosisporites australiensis,样品号(sample number):SK2-375;5-Levisporites wulinensis,样品号(sample number):SK2-205;6. Aequitriradites sp.,样品号(sample number):SK2-389; 7-Trilobosporites tribotrys,样品号(sample number):SK2-389;8- Classopollis classoides,标品号:SK2-97;9-Erlianpollis minisculus,样品号(number):SK2-395; 10. Parvisaccites sp.,样品号:SK2-395;11. Pilosisporites scitulus,标品号:SK2-201;12-Triporoletes asper,标品号(specimen number):SK2-219;13. Foveotriletes subtriangulularis,样品号:SK2-219;14-Klukisporites triangulus,样品号(sample number):SK2-205;15-Impardecispora sp.,样品号:SK2-201; 16-Schizaeoisporites polaris,样品号:SK2-173;17-Polycingulatisporites reduncus,标品号:SK2-395;18-Maculatisporites sp.,样品号:SK2-391。19-Chasmatosporites sp.,样品号:SK2-389; 20-Paleoconiferae sp.,样品号(sample number):SK2-391;线段比例尺为10 μm, the scale of the line segment is 10 μm)Figure 1. Spores and pollen from the Lower Cretaceous Shahezi Formation in Well SK2上述2个孢粉组合分布在,属沙河子组上部,LCC组合蕨类孢子百分含量占绝对优势,裸子类花粉较少,从组合特点来看,可以与高瑞琪等人建立的沙河子组上部Granulatisporites-Lophotriletes-Cicatricosisporites组合大致对比,但上部的KAP组合层位显然高于高瑞琪等人建立的孢粉组合。与高瑞琪等人建立的孢粉组合相比,当前孢粉组合出现的有时代意义的孢粉类型更多且时代更新。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
两个孢粉组合海金砂科孢子繁盛,类型多样化,没有发现早期被子植物花粉;虽在蕨类孢子与裸子类花粉的百分含量及属种构成上明显不同,但出现的有时代意义的化石类型基本相同,其时代均为早白垩世早期。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
本文为国家自然科学基金项目(41790451)和中国地质调查局项目(DD20190097)共同资助。孢粉化石由张淑琴研究员鉴定。
致谢: 在野外工作和撰稿过程中得到了西南能矿有限公司技术人员和昆明理工大学刘飞博士、王明志博士的无私帮助,论文审稿过程中审稿人提出了宝贵的修改意见,谨致谢忱! -
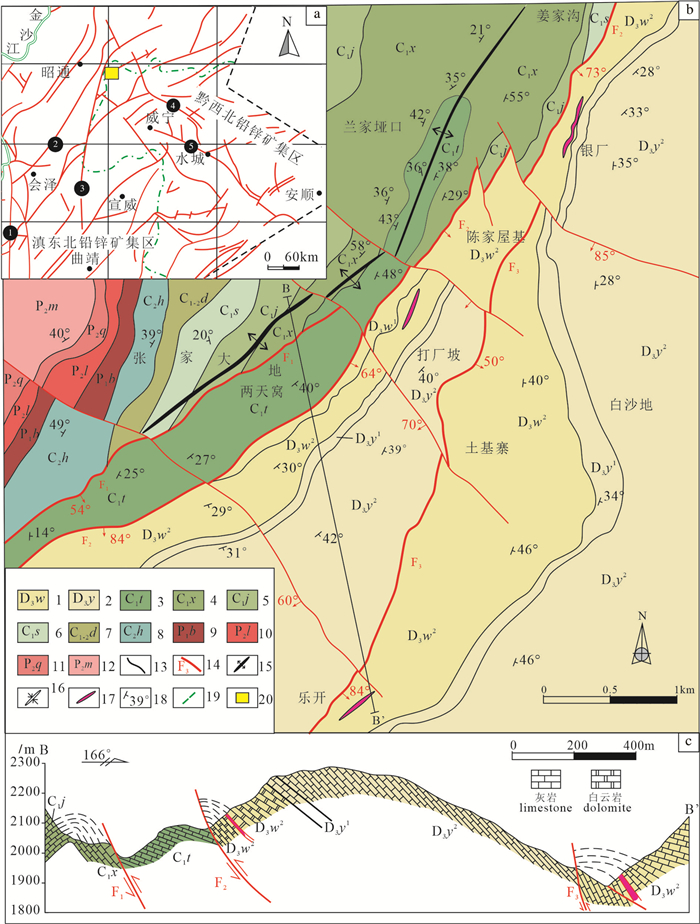
图 1 a—乐开铅锌矿床地质简图;b—川滇黔区域地质图(据柳贺昌, 1995修改);c—矿区BB’实测地质剖面图
1—泥盆系望城坡组; 2—泥盆系尧梭组; 3—石炭系汤粑沟组; 4—石炭系祥摆组; 5—石炭系旧司组; 6—石炭系上司组; 7—石炭系大浦组; 8—石炭系黄龙组; 9—二叠系包磨山组; 10—二叠系梁山组; 11—二叠系栖霞组; 12—二叠系茅口组; 13—地层界线; 14—断裂及编号; 15—背斜; 16—向斜; 17—矿体; 18—产状; 19—省界; 20—研究区; ❶—小江断裂带; ❷—会泽—牛街断裂带; ❸—昭通—曲靖隐伏断裂带; ❹—垭都—蟒硐断裂带; ❺—威宁—水城断裂带
Figure 1. a-simplified geological map of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit; b-distribution of the main fold-belts in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou district (modified from Liu Hechang, 1995); c-BB'measured geological profile of the mine
1- Wangchengpo Formation; 2- Yaosuo Formation; 3- Tangbagou Formation; 4- Xiangbai Formation; 5- Jiusi Formation; 6- Shangsi Formation; 7-Dapu Formation; 8-Huanglong Formation; 9-Baomoshan Formation; 10-Liangshan Formation; 11-Qixia Formation; 12-Maokou Formation; 13-Stratigraphic boundary; 14-Fault and number; 15-Anticline; 16-Syncline; 17-Ore body; 18-Attitude; 19-Provincial boundaries; 20-Research area; ❶ - Xiaojiang fault zone; ❷ - Huize—Niujie fault zone; ❸ - Zhaotong—Qujing buried fault zone; ❹ - Yadu—Mangdong fault zone; ❺-Weining—Shuicheng fault zone
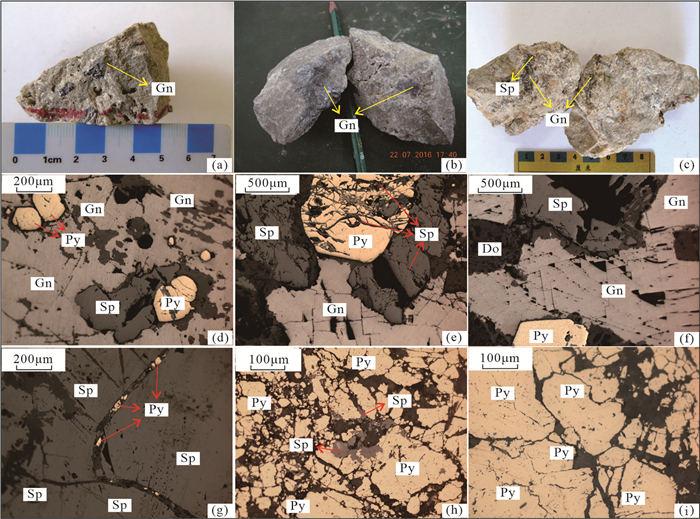
图 2 乐开铅锌矿床主要类型矿石结构构造照片
a—角砾状铅锌矿石; b—浸染状铅锌矿石; c—脉状铅锌矿石; d—包含结构; e—交代结构; f—共边结构; g, h—填隙结构; i—压碎结构; Gn—方铅矿; Sp—闪锌矿; Py—黄铁矿; Do—白云石
Figure 2. Photographs showing main ore textures and structures of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
a-Brecciated lead-zinc ore; b-Disseminated lead-zinc ore; c-Vein lead-zinc ore; d-Inclusion structure; e-Metasomatic structure; f-Coplanar structure; g, h-Interstitial structure; i-Crushed structure; Gn-Gelenite; Sp-Sphalerite; Py-Pyrite; Do-Dolomite
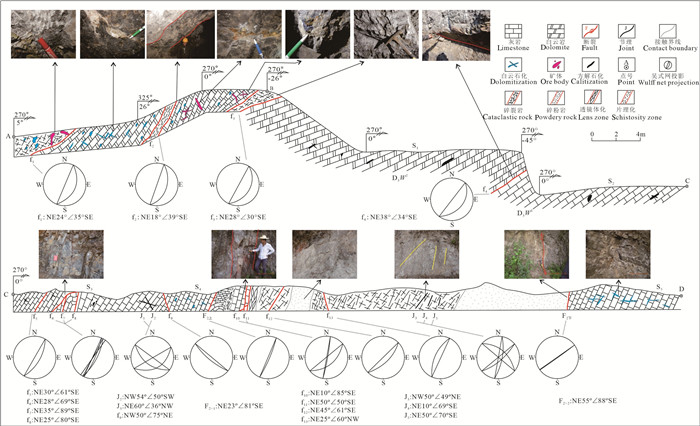
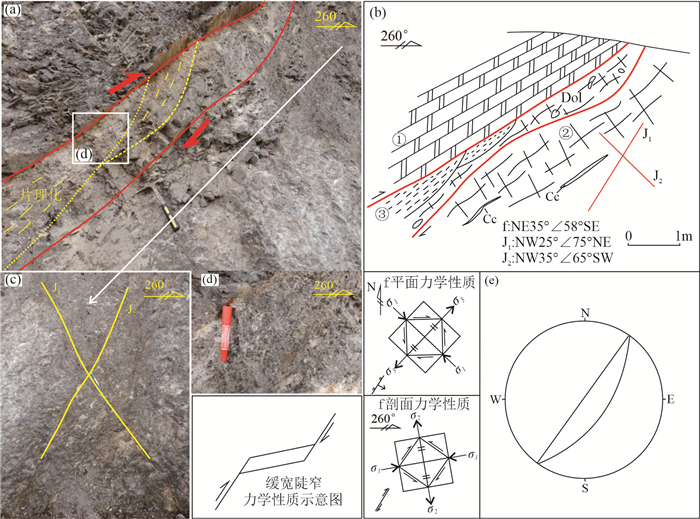
图 4 乐开铅锌矿床LK11点断裂剖面素描图与照片
a、b—NE向断裂野外照片及素描图; c—断裂f吴式网下半球投影图; 图b中:①—深灰色白云岩角砾; ②—片理化断层泥; ③—浅灰色白云质碎裂岩; Cc—方解石
Figure 4. Profiles and photographs of fractures at point LK11 of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
a, b-Picture and sketch map of NE trending fault; c-Projection map of the Wulff net about the fault; Fig. 4b: ①-Dark-gray dolomite breccia; ②-Schistose fault gouge; ③-Pale gray dolomitic cataclasite; Cc-Calcite
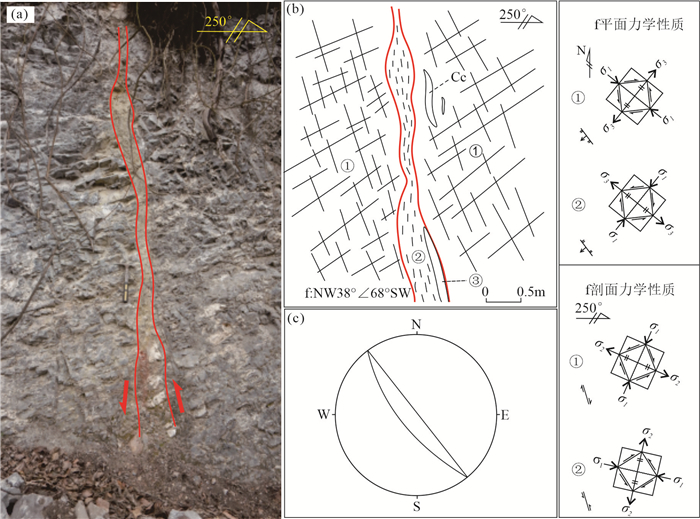
图 5 乐开铅锌矿床LK917点断裂剖面素描图和照片
a、b—NE向断裂野外照片及素描图; c—共轭节理野外照片; d—断裂带内片理化照片; e—断裂f吴式网下半球投影图; ①—灰色中细晶白云岩; ②—灰色白云质碎裂岩; ③—片理化、透镜体化破碎带,发育少量白云石脉; Dol—白云石
Figure 5. Profiles and photographs of fractures at point LK917 of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
a, b-Photographs and sketches of NE trending faults; c-Photographs of conjugated joints; d-Physical and chemical photographs within the fault zone; e-Projection map of the Wulff net about the fault; ①-Grey medium-fine dolomite; ②-Grey dolomitic cataclasite rock; ③-Foliated lenticular broken zone, the development of a small amount of dolomite veins; Dol-Dolomite
图 6 乐开铅锌矿床LK90点断裂剖面素描图和照片
a、b—断裂面上擦痕,分别代表了两期构造活动; c—断裂吴式网下半球投影图; d, e—NNE向断裂野外照片及素描图
图e中:①—灰—灰白色白云质碎粉岩; ②—灰—灰黄色白云质碎裂岩; ③—第四系坡积物Figure 6. Profiles and photographs of fractures at point LK90 of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
a, b-Scratches on the fault surface, representing two stages of tectonic activity respectively; c-Projection map of the Wulff net about the fault; d, e-Photographs and sketches of NNE trending faults
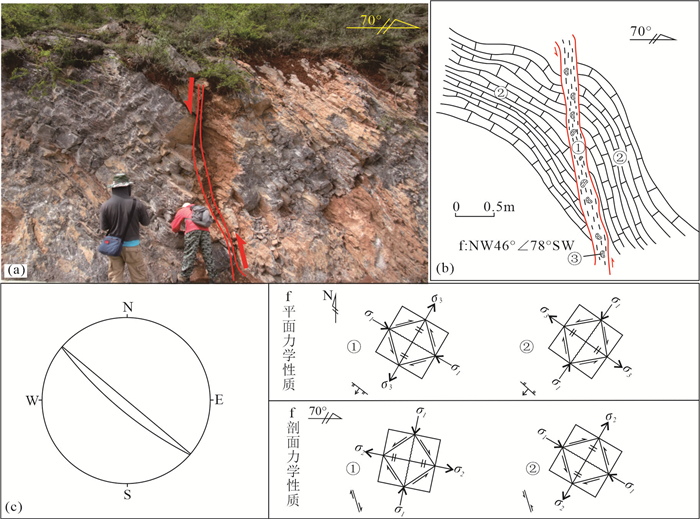
Fig. 6e: ①-Gray-white dolomitic pulverized rock; ②-Gray-yellow dolomitic cataclastic rock; ③-Quaternary sediment图 7 乐开铅锌矿床LK918点断裂剖面照片和素描图
a、b—NW向断裂野外照片及素描图; c—断裂吴式网下半球投影图
图b:①—灰色细晶碎裂白云岩,发育脉状、团块状方解石; ②—片理化断层泥; ③—梳状方解石Figure 7. Profiles and photographs of fractures at point LK90 of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
a, b-Photographs and sketches of NW trending faults; c-Projection map of the Wulff net about the fault
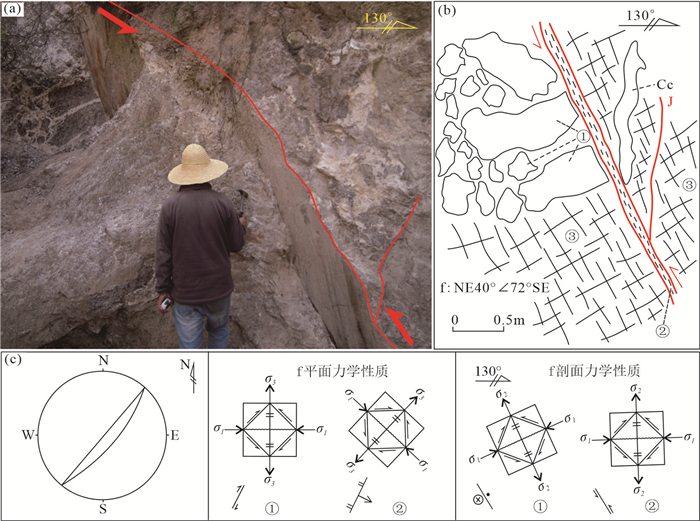
Fig. 7b: ①-Gray fine grain cataclastic dolomite, with veins and clumpy calcite; ②-Schistose fault gouge; ③-Comb-shape calcite图 8 乐开铅锌矿床LK133点断裂剖面素描图
a、b—NW向断裂野外照片及素描图; c—断裂吴式网下半球投影图
图b:①—红褐色断层泥; ②—灰色细晶灰岩,见脉状方解石; ③—灰色灰岩角砾,具有一定磨圆度Figure 8. Profiles and photographs of fractures at point LK133 of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
a, b-Photographs and sketches of NW-trending faults; c-Projection map of the Wulff net about the fault
Fig. 8b: ①-Reddish brown fault gouge; ②-Grey fine limestone with vein calcite; ③-Grey limestone breccia, with a certain degree of roundness图 9 乐开铅锌矿床所在的区域构造地质简图
1—第四系至古近系; 2—侏罗系; 3—三叠系; 4—石炭系至二叠系; 5—泥盆系; 6—志留系至奥陶系; 7—河流; 8—城镇; 9—乐开矿区(床); 10—地层界线; 11—断裂; 12—向斜; 13—背斜
Figure 9. Structure outline map in the Lekai area of the Lekai lead-zinc deposit
1-Quaternary to Paleogene strata; 2-Jurassic strata; 3-Triassic strata; 4-Carboniferous to Permian strata; 5-Devonian strata; 6-Silurian to Ordovician strata; 7-River; 8-Cities and towns; 9-Lekai deposit; 10-Stratigraphic boundary; 11-Fault; 12-Syncline; 13-Anticline
表 1 乐开铅锌矿床构造岩因子分析方差极大旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 1 Varimax rotation factor load matrix for tectonites in Lekai lead-zinc deposit

-
Cheng Chen, Han Runsheng, Wang Lei, Xiao Xianguo, He Zhiwei, Li Bo, Zhou Xuanling. 2019. The generation, development and ore-controlling of structures of the Fulaichang lead-zinc deposit, northeastern Guizhou[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1): 90-104(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng Penglin, Xiong Wei, Zhou Gao, He Zhiwei. 2015. A preliminary study on the origins of ore-forming fluids and their migration directions for Pb-Zn Deposits in NW Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 35(4): 509-514(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Runsheng, Liu Congqiang, Ma Deyun, Ma Gensheng, Hu Bin. 2001. Fault tectono-geochemical features and ore-forming prognosis of orientation in Tongchang ore-field, Tongchang, Shaanxi[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 29(3): 158-163(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2001.03.028
Han Runsheng. 2003. Preliminary discussion on research contents and methods of tectono-metallogenic dynamics and concealed ore orientation prognosis[J]. Geology and Exploration, 39(1): 5-9(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Runsheng. 2005. Orefield/deposit tectono-geochemical method for the localization and prognosis of concealed orebodies[J]. Geology and Exploration, 24(10/11): 978-984(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Runsheng, Liu Congqiang, Huang Zhilong, Chen Jin, Ma Deyun, Lei Li, Ma Gengsheng. 2007. Geological features and origin of the Huize carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb-(Ag) district, Yunnan, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 31: 360-383. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.03.003
Han Runsheng, Hu Yuzhao, Wang Xuekun, Hou Baohong, Huang Zhilong, Chen Jin, Wang Feng, Wu Peng, Li Bo, Wang Hongjiang, Dong Ying, Lei Li. 2012. Mineralization model of rich Ge-Ag-bearing Zn-Pb polymetallic deposit concentrated district in Northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(2): 280-294(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.02.007
Han Runsheng. 2013. Main study progress for ten years of tectono-geochemistry[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(2): 198-203(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.02.005
Han Runsheng, Wang Feng, Hu Yuzhao, Wang Xuekun, Ren Tao, Qiu Wenlong, Zhong Kanghui. 2014. Metallogenic tectonic dynamics and chronology constrains on the Huize-type (HZT) germanium-rich silver-zinc-lead deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(4): 758-771(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.003
Han Runsheng, Chen Jin, Wang Feng, Wang Xuekun, Li Yuan. 2015. Analysis of metal-element association halos within fault zones for the exploration of concealed ore-bodies——A case study of the Qilinchang Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposit in the Huize mine district, northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 159(11): 62-78.
Han Runsheng, Zhang Yan, Wang Feng, Wu Peng, Qiu Wenlong, Li Wenyao. 2017. Metallogenic Mechanism and Concealed Ore Orientation Prognosis of Rich Ge-Ag-bearing Zn-Pb Polymetallic Deposit Concentrated District in Northeastern Yunnan[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 125-196(in Chinese).
Han Runsheng, Wu Peng, Wang Feng, Zhou Gaoming, Li Wenyao, Qiu Wenlong. 2019. "Four Steps Type" ore-prospecting method for deeply concealed hydrothermal ore deposits——A case study of the Maoping Zn-Pb (Ag-Ge) deposit in southwestern China. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(2): 246-257(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Runsheng, Wang Mingzhi, Jin Zhongguo, Li Bo, Wang Ziyong. 2020. Ore-controlling mechanism of NE-trending ore-forming structural system at Zn-Pb polymetallic ore concentration area in northwestern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(3): 850-868(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.013
Hu Bin, Han Runsheng. 2003. The ore-controlling structure and ore-prospecting direction of Maoping lead-zinc deposit[J]. Yunnan Geology, 22(3): 295-303(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2003.03.008
Jin Zhongguo. 2008. Research on the Ore-controlling Factors, Metallogenic Regularity an Prediction of Lead-Zinc Ore District in Northwest, Guizhou[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1-109(in Chinese).
Liu Hechang. 1995. Tectonic ore-control in Yunnan-Sichuan-Guizhou lead-zinc mining areas[J]. Yunnan Geology, 14(3): 173-189(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Yingjun, Cao Liming, Li Zhaolin, Wang Henian, Chu Tongqing, Zhang Jinrong. 1984. Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1-548(in Chinese).
Lü Guxian, Sun Yan, Liu Deliang, Wu Xueyi, Liu Ruixun. 2011. Tectono-geochemistry: A review[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(4): 479-494(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.04.002
Pan Guitang, Xiao Qinghui, Lu Songnian, Den Jinfu, Feng Yimin, Zhang Kexin, Zhang Zhiyong, Wang Fangguo, Xing Guangfu, Hao Guojie, Feng Yanfang. 2009. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 36(1): 1-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.01.001
Qin Shourong, Liu Aimin. 1998. A discussion on the Himalayan tectonic movement in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 15(2): 105-114(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qin Shourong, Zhang Mingfa, Gong Mei, Kuang Zhong. 2009. Indosinian movement in Guizhou[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 29(2): 100-103(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2009.02.016
Shao Yue. 1997. Rock Measurements (Primary Halo Method) in the Hydrothermal Deposits Prospecting[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-62(in Chinese).
Song Danhui, Han Runsheng, Wang Feng, Wang Mingzhi, Zhou Wei, Luo Da. 2021. Structural ore-controlling mechanism and its implications for deep prospecting of Qingshan lead-zinc deposit in northwest Guizhou, China[J]. Geology in China. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20210104.1853.006.html (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Jiacong, Han Runsheng. 2016. Theory and Method of Ore-field Geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1-356(in Chinese).
Tu Guangchi. 1984. Tectonics and geochemistry[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 8(1): 1-5(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Mingzhi, Han Runsheng, Zhou Wei, Song Danhui, Luo Da, Zhou Jianfei, Wu Ruilin. 2019. Ore-forming structure analysis of the Liangyan Lead-zinc mining area in northwestern Guizhou deposit concentration district, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2): 187-197(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Kaibin, Jiang Kaiyuan, Huang Wenjun, Yue Lianhong, Zhang Deming. 2019. Tectonic formation features and its evolution in Nayong-Shuicheng area of northwest Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 36(2): 165-172(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2019.02.009
Xiao Xianguo, Huang Zhilong, Zhou Jiaxi, Jin Zhongguo, Li Xiaobiao, Zhang Lunwei. 2011. Several problems involved in genetic studies on the Pb-Zn deposits, northwest Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 31(3): 419-424.
Xu Yaming, Liao Guixinag, Liao Liping. 2009. Geological and geochemical characteristics of multi-elements and prospecting criteria in northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 39(5): 818-823(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Zhengbang, Lou Yuanren. 1994. Foundation of Mathematical Geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-62(in Chinese).
Yu Weilai, Fan Liangwu. 2007. Geological charcteristics of typical lead-zinc deposits and pondering on ore prospecting in northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 27(3/4): 461-465.
成晨, 韩润生, 王雷, 肖宪国, 何志威, 李波, 周暄翎. 2019. 黔西北福来厂铅锌矿床构造成生发展及其控矿作用[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(1): 90-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201901038.htm 程鹏林, 熊伟, 周高, 何志威. 2015. 黔西北地区铅锌矿床成矿流体起源与运移方向初探[J]. 矿物学报, 35(4): 509-514. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201504015.htm 韩润生, 刘丛强, 马德云, 马更生, 胡彬. 2001. 陕西铜厂地区断裂构造地球化学及定位成矿预测[J]. 地质地球化学, 29(3): 158-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200103027.htm 韩润生. 2003. 初论构造成矿动力学及其隐伏矿定位预测研究内容和方法[J]. 地质与勘探, 39(1): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200301002.htm 韩润生. 2005. 隐伏矿定位预测的矿田(床)构造地球化学方法[J]. 地质通报, 24(10/11): 978-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2005Z1018.htm 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, Hou Baohong, 黄智龙, 陈进, 王峰, 吴鹏, 李波, 王洪江, 董英, 雷丽. 2012. 滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J]. 地质学报, 86(2): 280-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201202008.htm 韩润生. 2013. 构造地球化学十年主要进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(2): 198-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201302005.htm 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 任涛, 邱文龙, 钟康惠. 2014. 会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 38(4): 758-771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201404003.htm 韩润生, 张艳, 王峰, 吴鹏, 邱文龙, 李文尧. 2017. 滇东北矿集区富锗铅锌矿床成矿机制与隐伏矿定位预测[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 125-197. 韩润生, 吴鹏, 王峰, 周高明, 李文尧, 邱文龙. 2019. 论热液矿床深部大比例尺"四步式"找矿方法——以川滇黔接壤区毛坪富锗铅锌矿为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(2): 246-257. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201902005.htm 韩润生, 王明志, 金中国, 李波, 王子勇. 2020. 黔西北铅锌多金属矿集区成矿构造体系及其控矿机制[J]. 地质学报, 94(3): 850-868. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003013.htm 胡彬, 韩润生. 2003. 毛坪铅锌矿构造控矿及找矿方向[J]. 云南地质, 22(3): 295-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200303007.htm 金中国. 2008. 黔西北地区铅锌矿控矿因素、成矿规律与找矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1-109. 柳贺昌. 1995. 滇、川、黔铅锌成矿区的构造控矿[J]. 云南地质, 14(3): 173-189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD503.000.htm 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 王鹤年, 储同庆, 张景荣. 1984. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-548. 吕古贤, 孙岩, 刘德良, 吴学益, 刘瑞珣. 2011. 构造地球化学的回顾与展望[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 35(4): 479-494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201104004.htm 秦守荣, 刘爱民. 1998. 论贵州喜山期的构造运动[J]. 贵州地质, 15(2): 105-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ199802000.htm 秦守荣, 张明发, 龚梅, 况忠. 2009. 贵州的印支运动[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 29(2): 100-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200902015.htm 邵跃. 1997. 热液矿床岩石测量(原生晕法)找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-62. 宋丹辉, 韩润生, 王峰, 王明志, 周威, 罗达. 2021. 黔西北青山铅锌矿床构造控矿机理及其对深部找矿的启示[J]. 中国地质. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20210104.1853.006.html. 孙家骢, 韩润生. 2016. 矿田地质力学理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-356. 涂光炽. 1984. 构造与地球化学[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 8(1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK198401001.htm 王明志, 韩润生, 周威, 宋丹辉, 罗达, 周剑飞, 吴睿林. 2019. 黔西北矿集区亮岩铅锌矿区成矿构造解析[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(2): 187-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201902059.htm 吴开彬, 蒋开源, 黄文俊, 跃连红, 张德明. 2019. 黔西北纳雍-水城一带构造变形特征及其演化[J]. 贵州地质, 36(2): 165-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201902009.htm 肖宪国, 黄智龙, 周家喜, 金中国, 李晓彪, 张伦尉. 2011. 黔西北铅锌矿床成因研究中的几个问题[J]. 矿物学报, 31(3): 419-424. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201103016.htm 许亚明, 廖桂香, 廖莉萍. 2009. 黔西北地区多元素地球化学特征与找矿标志[J]. 吉利大学学报(地球科学版), 39(5): 818-823. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200905009.htm 徐振邦, 娄元仁. 1994, 数学地质基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-226. 余未来, 范良伍. 2007. 黔西北地区典型铅锌矿床地质特征分析及找矿思路[J]. 矿物学报, 27(3/4): 461-465. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2007Z1035.htm -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 吴怀春,李山,王成善,褚润健,王璞珺,高远,万晓樵,贺怀宇,邓成龙,杨光,黄永建,高有峰,席党鹏,王天天,房强,杨天水,张世红. 松辽盆地白垩纪综合年代地层格架. 地学前缘. 2024(01): 431-445 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张德军,郑月娟,张淑芹,张健,黄欣,陈树旺,孙雷. 松科2井早白垩世沙河子组孢粉组合及其古气候意义. 地质通报. 2024(Z1): 429-442 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: