Depositional process and model of debrite dominated deep-water system in the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
-
摘要:研究目的
碎屑流是深水环境沉积物搬运和分散的重要机制,其相关的砂岩储层是含油气盆地重要的勘探目标,然而,与经典浊流及浊积系统相比,对碎屑流主控型深水体系的发育规律目前仍知之甚少。
研究方法本文基于岩心、测井及全三维地震资料,通过系统的岩心观察描述、测井及地震资料解释,对渤海湾盆地东营凹陷始新统沙三中亚段深水体系沉积过程及模式开展研究。
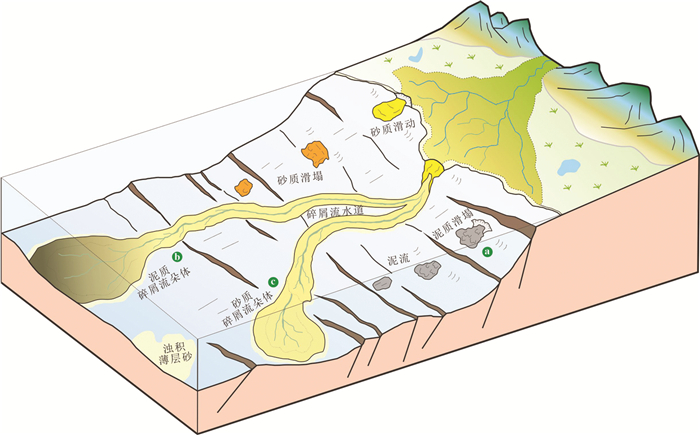
研究结果结果表明,沙三中深水体系发育九种异地搬运岩相,可概括为四大成因类型,反映了块体及流体两种搬运过程。岩相定量统计表明,该深水体系主要由碎屑流沉积构成,浊流沉积很少,碎屑流中又以砂质碎屑流为主。重力流在搬运过程中经历了滑动、滑塌、砂质碎屑流、泥质碎屑流及浊流等5个阶段演变,发育5类主要的深水沉积单元,包括滑动体、滑塌体、碎屑流水道、碎屑流朵体及浊积薄层砂。从发育规模及储层物性上,砂质碎屑流水道、朵体及砂质滑动体构成了本区最重要的深水储层类型。
结论认为沙三中时期充足的物源供给、三角洲前缘高沉积速率、断陷期频繁的断层活动以及较短的搬运距离是碎屑流主控型深水体系形成及演化的主控因素,最终基于沉积过程、沉积样式及盆地地貌特征综合建立了碎屑流主控型深水体系沉积模式。本研究将进一步丰富深水沉积理论,为陆相深水储层预测提供借鉴。
创新点:(1)明确了陆相断陷湖盆碎屑流主控型深水体系的存在,对其成因流体类型进行了定量研究;(2)揭示了碎屑流主控型深水体系的沉积动力过程、沉积结构单元特征及发育控制机理。
Abstract:This paper is the result of oil and gas exploration engineering.
ObjectiveDebris flow represents an important mechanism of sediment transport and dispersal in deep-water environment, the related sandstone reservoir constitute one of the important targets for petroleum exploration in petroliferous basins, while deep-water systems dominated by debris flows are still poorly understand compared to well-studied turbidity currents and turbidite systems.
MethodsThe depositional process and model of gravity flows which developed in the Middle Sub-member of the 3rd Member of the Eocene Shahejie Formation, Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin have been studied through the integration of core data examination, well logging data and 3D seismic data interpretation.
ResultsIt is suggested that nine base types of lithofacies can be recognized in slump-derived gravity flow deposits, which can be summarized into four main origin types, which indicate mass transport and flow transport processes, respectively. Quantitative lithofacies analysis suggests that the slump-derived gravity flow depositional system is dominated by debris flows, while turbidity currents are less important, and sandy debris flows represent the most important debris flow type. The slump-derived gravity flows undergo five evolution stages including slide, slump, sandy debris flow, muddy debris flow and turbidity currents, which correspondingly develop five types of deep-water depositional elements during transportation and evolution, including slide, slump, debrite channel, debrite lobe and turbidite sheet. Sandy debrite channels, lobes and sandy slides constitute the most important deep-water reservoirs in the study area according to their wide distribution and reservoir property.
ConclusionsIt is proposed that adequate sediment supply, high depositional rate on delta-front, frequent tectonic activities and short transport distance are the main controlling factors. Accordingly, a depositional model is proposed to depict slump-derived gravity flow systems based on depositional processes, sedimentary patterns and basin morphology. This study seeks to improve deep-water sedimentary theories and provide guidance for petroleum exploration of deep-water sands in deep-lacustrine basins.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
甘肃省高台县大青山地区地处阿拉善地块龙首山基底杂岩带,位于酒东盆地马营凹陷东段山前沉积盆地北缘(图 1a)。区内主要出露有古元古界—新太古界龙首山岩群、中元古界蓟县系墩子沟群、海西期侵入岩、侏罗系龙凤山组和白垩系庙沟组(图 1b)。
为实现研究区金属资源和油气资源的综合调查,中国地质调查局发展研究中心联合甘肃省地调院、探矿工程所、吉林大学在前期“甘肃省高台县臭泥墩—西小口子地区三幅1∶5万矿产远景调查”项目基础上,通过开展专题地质填图、矿产综合信息预测、智能找矿预测等工作,部署实施钻孔ZK1201,以期实现找矿突破。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
利用研究区地质调查、磁法、激电测深、化探数据和无人机影像等资料,开展综合信息解译。采用卷积和孪生网络神经网络模型对区内典型金属矿床成矿作用特征标志、油气赋矿层位进行深度学习,提出工程验证建议。钻探验证所采用钻机为汽车钻,整机包括车底盘、动力系统、液压系统、操控系统等。
3. 结果(Results)
在综合研究和智能预测的基础上,布设的ZK1201孔在钻穿早二叠世花岗闪长岩(图 1c)后,钻遇地层,续钻至393.8 m后终孔(图 1c)。此次工作共钻遇中侏罗统龙凤山组地层220 m,共发现14层油层(总厚145 m,单层最大厚度28 m,最小厚度1.4 m)。钻孔含油性由上部砾岩(油斑级以下)向下部砂岩(富含油或饱含油)逐渐增多,其中高角度裂缝普遍见可流动原油(图 1d~g)。经国家地质实验测试中心分析,原油中饱和烃、芳烃含量分别占32.4%和34.6%,为高品质轻质原油。原油中正构烷烃分布完整,主峰碳数、奇偶优势及甾烷和藿烷分布都指示其陆相烃源岩来源。
野外地质调查发现,白垩系庙沟组近水平发育,与下伏侏罗系龙凤山组呈角度不整合接触。庙沟组主要由厚层暗色泥岩组成,并发育薄层暗色粉砂质泥岩,可能为区域烃源岩层。初步判断成熟的烃源岩排出的油气沿角度不整合运移至侏罗系砂砾岩和砂岩储层后,被逆冲推覆花岗岩体封闭,形成构造-岩性油气藏(图 1h)。
研究发现区域内沉积盆地最南缘边界处在祁连山北缘断裂之下,最北缘处在龙首山断裂的下盘,南北跨度约80 km。区域内沉积地层较厚,其中侏罗系龙凤山组厚约2100 m,白垩系庙沟组厚约900 m,说明研究区具有较大的成藏潜力。此次油气藏的发现,预示着大青山地区具有完整的油气成藏系统,显示出良好油气勘探前景。建议进一步加强油气基础地质调查研究工作。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)在大青山地区花岗岩逆冲推覆体之下的中生代沉积地层中发现原油,所发现的高品质轻质原油,具陆相烃源岩来源特征。
(2)研究区具有良好的油气勘探前景,建议进一步加强油气地质调查研究工作。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
感谢甘肃省地质调查院董国强,北京探矿工程研究所渠洪杰、谭春亮以及国家实验测试中心沈斌在野外工作和样品测试过程中的协助。
-
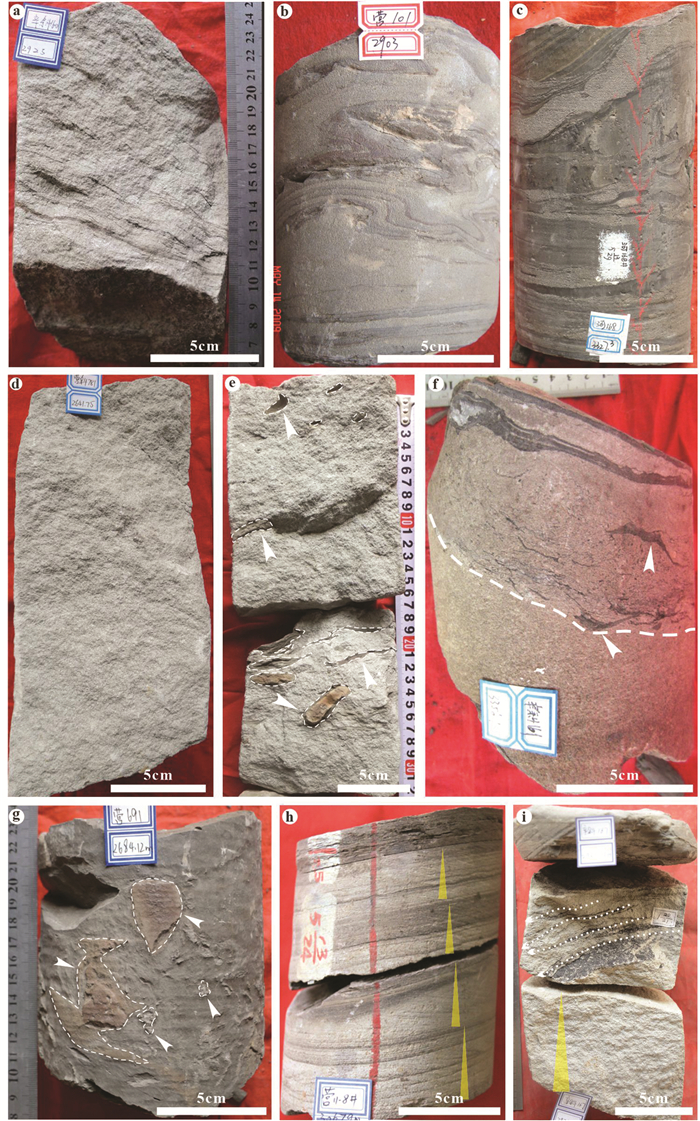
图 2 东营凹陷沙三中亚段重力流沉积岩相特征
a—交错层理;b—砂岩中的变形层理,见泥质纹层扭曲;c—泥岩中的变形构造,见砂质条带扭曲;d—洁净块状砂岩;e—块状砂岩中的漂浮泥砾;f—洁净块状砂岩与上覆含漂砾块状砂岩直接接触;g—块状泥岩中漂浮砾石;h—砂岩中的垂向多期正韵律;i—波纹交错层理
Figure 2. Sedimentary facies of gravity flow deposits in the Es3m in the Dongying Depression
a-Cross bedding; b-Deformed bedding and contorted mud layers in sandstones; c-Deformed structure and contorted sand layers in mudstones; d-Clean massive sandstones; e-Floating mud clasts in massive sandstones; f-Clean massive sandstones immediately contacted with overlying massive sandstones with floating clasts; g-Floating clasts in massive mudstones; h-Multiple fining-upwards rhythm in sandstones; i-Sand ripples
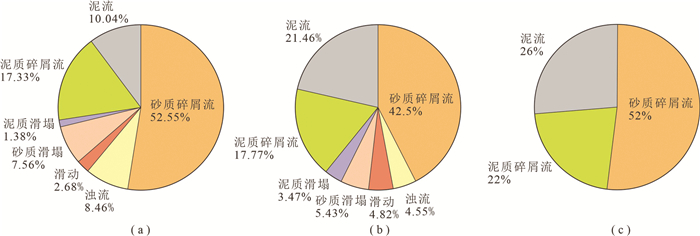
图 3 沙三中亚段重力流沉积岩相定量分析
a—不同成因类型的重力流沉积钻遇频次饼状图;b—不同成因类型的重力流沉积钻遇厚度饼状图;c—碎屑流沉积钻遇厚度饼状图
Figure 3. Quantification of lithofacies in gravity flow deposits in the Es3m
a-Pie chart of frequency distribution of different gravity flow deposits; b- Pie chart of thickness distribution of different gravity flow deposits; c- Pie chart of thickness distribution of different debris flow deposits
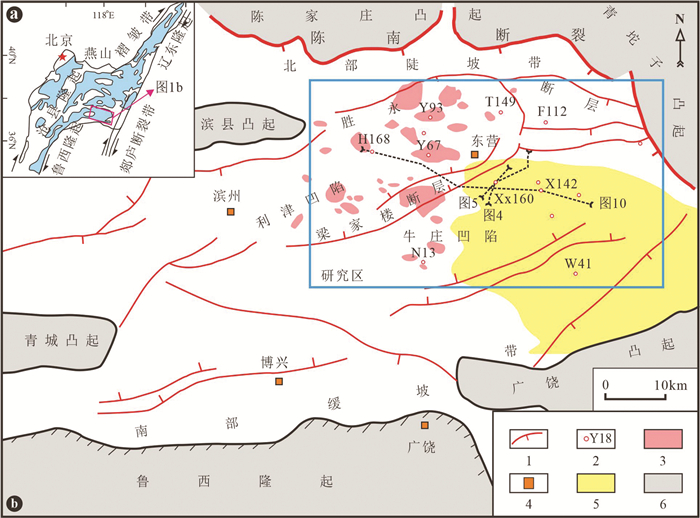
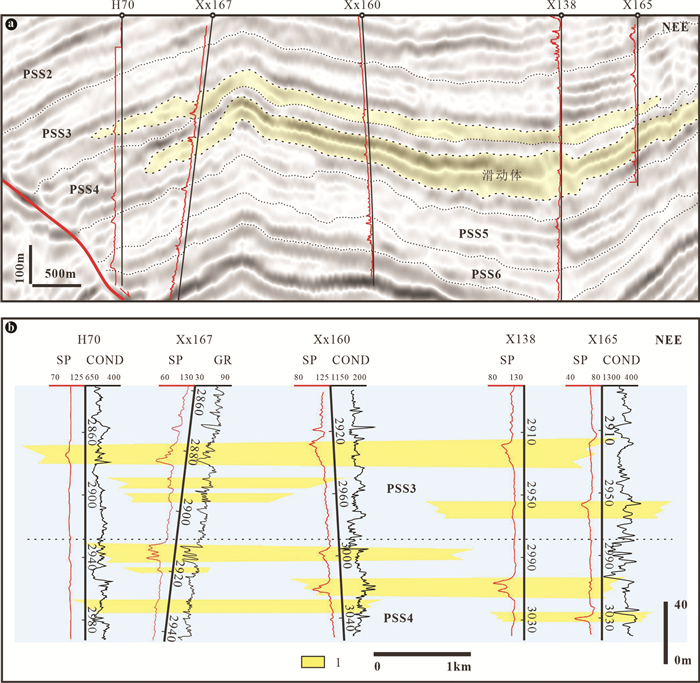
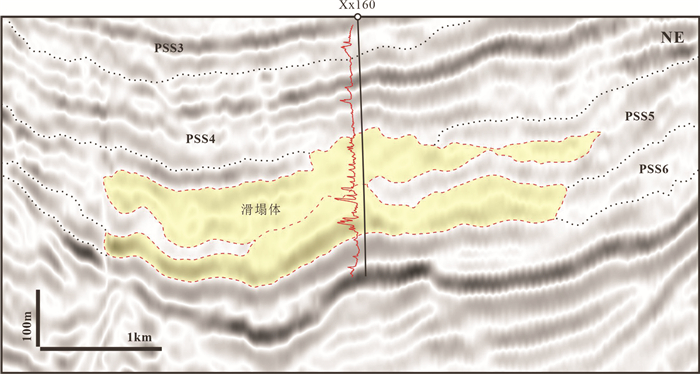
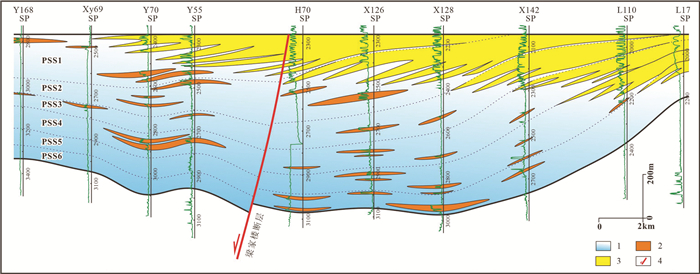
图 4 东营凹陷沙三中亚段滑动体垂直物源地震剖面解释及砂岩分布(剖面位置见图 1)
图a中钻井旁红色曲线为自然电位测井曲线;SP—自然电位测井;GR—伽马测井;COND—感应测井;PSS—准层序组;1—砂质滑动体
Figure 4. Seismic facies of slide in the vertical direction of source and sand distribution in the Es3m in the Dongying Depression (see location in Fig. 1)
Logging curves (red) in Fig. 4a indicate spontaneous potential well-logs; SP- spontaneous potential logging; GR-Gamma ray logging; COND- Induction-conductivity logging; PSS-Parasequence set; 1-Sand slides
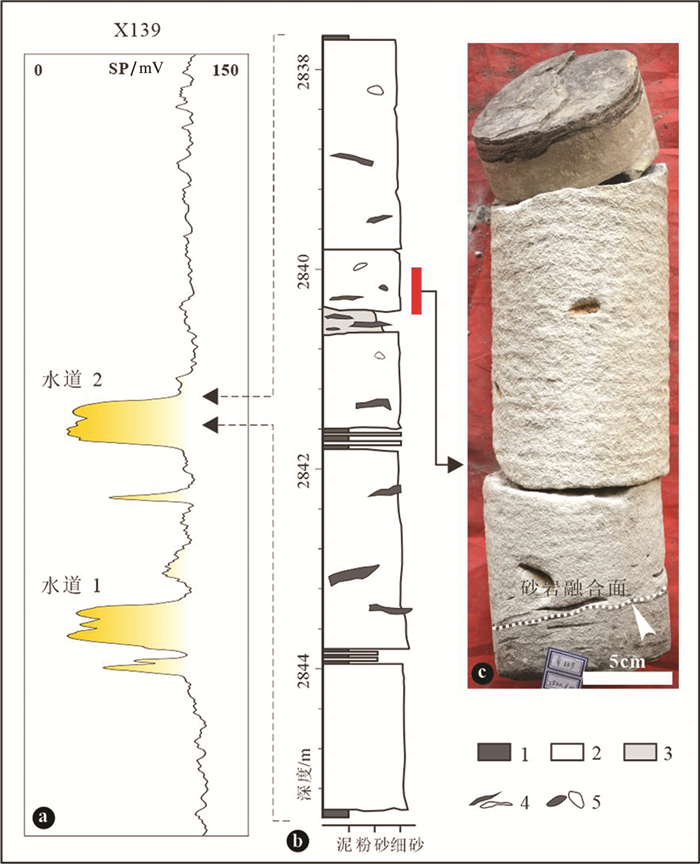
图 6 X139井沙三中亚段砂质碎屑流水道沉积特征
a—X139井碎屑流水道自然电位测井曲线特征,SP—自然电位测井;b—水道岩心柱状图;c—水道中块状砂岩沉积1—泥岩;2—砂岩;3—泥质砂岩;4—泥/砂撕裂屑;5—泥/砂砾石
Figure 6. Depositional charactristics of sandy debris flow channel in Well X139 in the Es3m
a-Spontaneous potential well-log of debris flow channel in Well X139, SP-Spontaneous potential logging; b-Core description of debris flow channel; c-Massive sandstones in debris flow channel; 1-Mudstone; 2-Sandstone; 3-Muddy sandstone; 4-Mud/sand rip ups; 5-Mud/sand pebbles
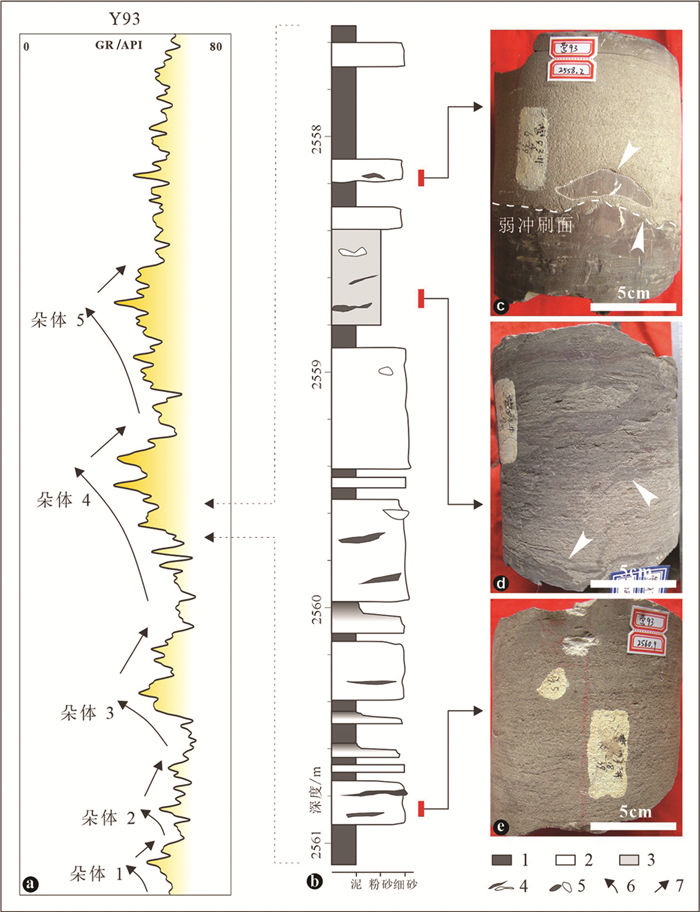
图 7 Y93井沙三中亚段碎屑流朵体沉积特征
a—Y93井碎屑流朵体伽马测井曲线特征,GR—伽马测井;b—朵体岩心柱状图;c—朵体中冲刷面及含漂砾块状砂岩沉积;d—朵体中含漂砾块状泥质砂岩沉积;e—朵体中洁净块状砂岩沉积;1—泥岩;2—砂岩;3—泥质砂岩;4—泥/砂撕裂屑;5—泥/砂砾石;6—朵体前积;7—朵体退积
Figure 7. Depositional characteristics of sandy debris flow lobe in Well Y93 in the Es3m
a-GR logging responses of debris flow lobe in Well Y93, GR-Gamma ray logging; b-Core description of debris flow lobe; c-Erosive surface and sandstones with floating clasts in debris flow lobe; d- Massive muddy sandstones with floating clasts in debris flow lobe; e- Clean massive sandstones in debris flow lobe; 1-Mudstone; 2-Sandstone; 3-Muddy sandstone; 4-Mud/sand rip ups; 5-Mud/sand pebbles; 6-Lobe progradation; 7-Lobe retrogradation
图 8 沙三中亚段碎屑流朵体沉积特征
a—朵体地震反射剖面;b—碎屑流朵体地震均方根振幅属性切片;c—沉积解释;1—碎屑流朵体;2—碎屑流水道;3—浊积薄层砂;4—深湖;5—井位;6—断层;PSS—准层序组
Figure 8. Depositional characteristics of sandy debris flow lobe in the Es3m
a-Seismic profile of debris flow lobe; b-RMS seismic amplitude slice of debris flow lobe; c-Sedimentary interpretation; 1-Debrite lobe; 2-Debrite channel; 3-Turbidite sheet; 4-Deep lake; 5-Well location; 6-Fault; PSS-Parasequence set
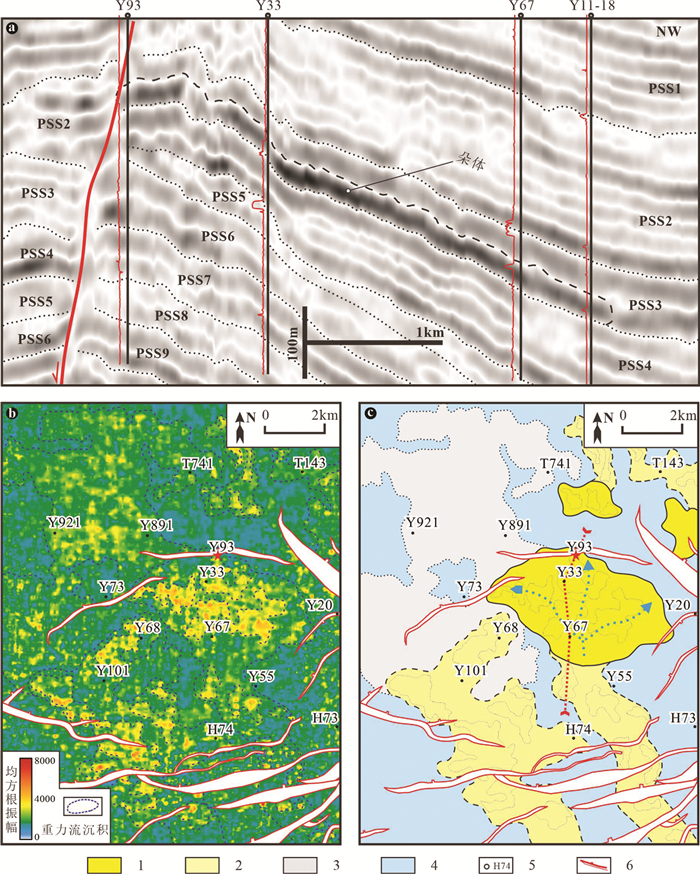
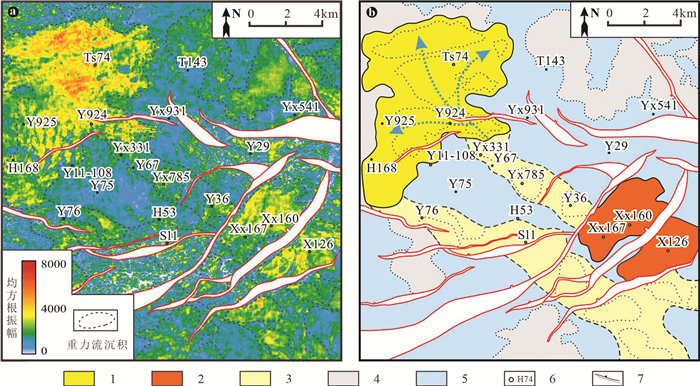
图 9 东营凹陷沙三中亚段重力流沉积地震切片及相解释
a—地震均方根振幅属性切片;b—沉积解释;1—碎屑流朵体;2—滑动体;3—碎屑流水道;4—浊积薄层砂;5—深湖;6—井位;7—断层
Figure 9. Seismic slicing and facies interpretation of gravity flow deposits in in the Es3m in the Dongying Depression
a-RMS amplitude seismic slice; b-Sedimentary interpretation; 1-Debrite lobe; 2-Slides; 3-Debrite channel; 4-Turbidite sheet; 5-Deep lake; 6-Well location; 7-Fault
图 10 东营凹陷沙三中亚段连井对比及重力流沉积分布特征
井旁为自然电位测井曲线,SP-自然电位测井;1—湖相;2—重力流沉积;3—三角洲;4—断层
Figure 10. Correlation section along the supply direction and gravity flow deposits distribution in the Es3m in the Dongying Depression
Logging curves in Fig. 10 indicate spontaneous potential well-logs, SP-Spontaneous potential logging; 1-Lake; 2-Gravity flow deposits; 3-Delta; 4-Fault
表 1 东营凹陷始新统沙三中亚段重力流岩相类型划分
Table 1 Lithofacies classification of gravity flow deposits of the Es3m in the Eocene Dongying Depression

-
Cao Yingchang, Jin Jiehua, Liu Haining, Yang Tian, Liu Keyu, Wang Yanzhong, Wang Jian, Liang Chao. 2021. Deep-water gravity flow deposits in a lacustrine rift basin and their oil and gas geological significance in eastern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(2): 247-257(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cao Yingchang, Zhang Qingqing, Wang Yanzhong, Yang Tian, Wang Xinyi, Xue Xiujie. 2017. Delta front gravity flow deposits in the middle submember of the third member of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying depression: Lithofacies and lithofacies association types and their distribution[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 37(1): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2017.01.002
Clare M A, Talling P J, Challenor P, Malgesini G, Hunt J. 2014. Distal turbidites reveal a common distribution for large (>0.1 km3) submarine landslide recurrence[J]. Geology, 42(3): 263-266. doi: 10.1130/G35160.1
Dott Jr R H. 1963. Dynamics of subaqueous gravity depositional processes[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 47(1): 104-128.
Enos P. 1977. Flow regimes in debris flow[J]. Sedimentology, 24(1): 133-142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1977.tb00123.x
Fan Daidu, Qiu Guiqiang, Li Congxian, Cong Youzi, Yang Jizeng. 2000. Paleocurrent properties of Dongying Delta in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 21(1): 29-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.01.005
Felix M, Leszczynski S, Slaczka A, Uchman A, Amy L, Peakall J. 2009. Field expressions of the transformation of debris flows into turbidity currents, with examples from the Polish Carpathians and the French Maritime Alps[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 26(10): 2011-2020. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.02.014
Feng Youliang, Li Sitian, Lu Yongchao. 2013. Sequence stratigraphy and architectural variability in late Eocene lacustrine strata of the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 295: 1-26. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.07.004
Gao Hongfang, Zhong Hexian, Sun Meijing, Nie Xin, Jiang Tao, Huang Wenkai, Du Wenbo, Chen Jiale. 2020. The large deep-water turbidity fan system in southeastern South China Sea Basin: Formation and tectonic constraint[J]. Geology in China, 47(5): 1395-1406(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gawthorpe R L, Leeder M R. 2000. Tectono-sedimentary evolution of active extensional basins[J]. Basin Research, 12(3/4): 195-218.
Haughton P, Davis C, Mccaffrey W, Barker, S. 2009. Hybrid sediment gravity flow deposits-Classification, origin and significance[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 26(10): 1900-1918. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.02.012
Ilstad T, Elverhøi A, Issler D. 2004. Subaqueous debris flow behaviour and its dependence on the sand/clay ratio: a laboratory study using particle tracking[J]. Marine Geology, 213(1/4): 415-438.
Iverson R M. 1997. The physics of debris flows[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 35(3): 245-296. doi: 10.1029/97RG00426
Kane I A, Ponten A S. 2012. Submarine transitional flow deposits in the Paleogene Gulf of Mexico[J]. Geology, 40(12): 1119-1122. doi: 10.1130/G33410.1
Koo W M, Olariu C, Steel R J, Olariu M I, Carvajal C R, Kim W. 2016. Coupling between shelf-edge architecture and submarine-fan growth style in a supply dominated margin[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 86(6): 613-628. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2016.42
Kuenen P H, Migliorini C I. 1950. Turbidity currents as a cause of graded bedding[J]. Journal of Geology, 58(2): 91-127. doi: 10.1086/625710
Lei Zhenyu, Zhang Li, Su Ming, Luo Shuaibing, Qian Xing, Shuai Qingwei, Zhang Boda. 2017. Middle Miocene deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin, Southern South China Sea: Types, characteristics and implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 37(6): 110-118(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Chenyi. 2005. Study on the Forming Mechanism of the Slumped Turbidite and the Controlling Sandbody Model of High Frequency Base-Level Cycle of Dongying Deltas[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscience (Beijing), 1-126.
Li Hua, He Mingwei, Qiu ChunGuang, Wang Yingmin, He Youbin, Xu Yanxia, He Ruiwu. 2022. Research processes on deep-water interaction between contour current and gravity flow deposits, 2000 to 2022[J/OL]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica. DOI: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.027.
Li Xiangbo, Liu Huaqing, Wanyan Rong, Wei Lihua, Liao Jianbo, Ma Yuhu. 2009. First discovery of the sandy debris flow from the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 21(4): 19-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2009.04.003
Lin Changsong, Pan Yuanlin, Xiao Jianxin, Kong Fanxian, Liu Jingyan, Zhen Herong. 2000. Structural slope_break zone: Key concept for stratigraphic sequence analysis and petroleum forecasting in fault subsidence basins[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 25(3): 42-48(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jianping, Xian Benzhong, Wang Lu, Lu Zhiyong, Li Yuzhi, Liu Saijun, Jiang Jian. 2016. Seismic sedimentology of delta-fed turbidites of the Eocene in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 18(6): 961-975(in Chinese with English abstract).
Middleton G V, Hampton M A. 1976. Subaqueous sediment transport and deposition by sediment gravity flows[C]//Stanley DJ, Swift D J P(eds.). Marine Sediment Transport and Environmental Management. New York: Wiley, 197-218.
Middleton G V, Hampton M A. 1977. Sediment gravity flows: Mechanics of flow and deposition[C]//Middleton G V, Bouma A H. Turbidites and Deep-Water Sedimentation. Anaheim: SEPM, California Short Course Notes, 1973: 38.
Mohrig D, Ellis C, Parker G, Whipple K X, Hondzo M. 1998. Hydroplaning of subaqueous debris flows[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 110(3): 387-394. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1998)110<0387:HOSDF>2.3.CO;2
Mulder T, Alexander A. 2001. The physical character of subaqueous sedimentary density flows and their deposits[J]. Sedimentology, 48(2): 269-299. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2001.00360.x
Mulder T, Syvitski J P, Migeon S, Faugères J C, Savoye B. 2003. Marine hyperpycnal flows: Initiation, behavior and related deposits. A review[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 20(6/8): 861-882.
Mutti E, Bernoulli D, Lucchi F R, Tinterri R. 2009. Turbidites and turbidity currents from Alpine 'flysch' to the exploration of continental margins[J]. Sedimentology, 56(1): 267-318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2008.01019.x
Normark W R. 1970. Growth patterns of deep-sea fans[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 54(11): 2170-2195.
Piper D J W, Cochonat P, Morrison M L. 1999. The sequence of events around the epicentre of the 1929 Grand Banks earthquake: Initiation of debris flows and turbidity current inferred from sidescan sonar[J]. Sedimentology, 46(1): 79-97. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00204.x
Piper D J W, Normark W R. 2001. Sandy fans-from Amazon to Hueneme and beyond[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 85(8): 1407-1438.
Postma G, Cartigny M J. 2014. Supercritical and subcritical turbidity currents and their deposits-A synthesis[J]. Geology, 42(11): 987-990. doi: 10.1130/G35957.1
Prelat A, Covault J A, Hodgson D M, Fildani A, Flint S S. 2010. Intrinsic controls on the range of volumes, morphologies, and dimensions of submarine lobes[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 232(1/2): 66-76.
Qiu Guiqiang, Wang Jufeng, Zhang Xin, Li Congxian. 2001. Preliminary study on stratigraphic architecture of middle-Shasan Dongying Delta and its significance to hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 19(4): 569-574(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.04.015
Shanmugam G. 1996. High-density turbidity currents: Are they sandy debris flows?[J] Journal of Sedimentary Research, 66(1): 2-10. doi: 10.1306/D426828E-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Shanmugam G. 2000. 50 years of the turbidite paradigm (1950s-1990s): Deep-water processes and facies models-a critical perspective[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2
Shanmugam G. 2013. New perspectives on deep-water sandstones: Implications[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(3): 294-301.
Shanmugam G, Lehtonen L R, Straume T, Syvertsen S E, Hodgkinson R J, Skibeli M. 1994. Slump and debris-flow dominated upper slope facies in the Cretaceous of the Norwegian and northern North Seas (61-67 N): Implications for sand distribution[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 78(6): 910-937.
Sohn Y K, Choe M Y, Jo H R. 2002. Transition from debris flow to hyperconcentrated flow in a submarine channel (the Cretaceous Cerro Toro Formation, southern Chile)[J]. Terra Nova, 14(5): 405-415. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00440.x
Song Mingshui, Xiang Kui, Zhang Yu, Cai Pan, Liu Jianlei, Yang Renchao. 2017. Research progresses on muddy gravity flow deposits and their significances on shale oil and gas: A case study from the 3rd oil-member of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 35(4): 740-751.
Steel R J, Milliken K L. 2013. Major advances in siliciclastic sedimentary geology, 1960-2012[J]. The Web of Geological Sciences: Advances, Impacts, and Interactions. Geological Society of America, Special Papers 500: 121-166.
Stow D A V, Johansson M. 2000. Deep-water massive sands: Nature, origin and hydrocarbon implications[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 145-174. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00051-3
Talling P J, Masson D G, Sumner E J, Malgesini G. 2012. Subaqueous sediment density flows: Depositional processes and deposit types[J]. Sedimentology, 59(7): 1937-2003. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2012.01353.x
Talling P J, Wynn R B, Masson D G, Frenz M, Cronin B T, Schiebel R, Akhmetzhanov A M, Dallmeier-Tiessen S, Benetti S, Weaver P P E, Georgiopoulou A, Zühlsdorff C, Amy L A. 2007. Onset of submarine debris flow deposition far from original giant landslide[J]. Nature, 450(7169): 541-544. doi: 10.1038/nature06313
Talling P J. 2014. On the triggers, resulting flow types and frequencies of subaqueous sediment density flows in different settings[J]. Marine Geology, 352: 155-182. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.02.006
Tan Mingxuan, Zhu Xiaomin, Liu Wei, Shi Ruisheng. 2017. The morphodynamics of cyclic steps and sedimentary characteristics of associated deposits[J]. Geological Review, 63(06): 1512-1522(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jiahao, Wang Hua, Xiao Dunqing, Pu Xiugang, Han Wenzhong, Zhang Wei. 2020. Differentiation between hyperpycnal flow deposition and slump-induced gravity flow deposition in terrestrial rifted lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 41(04): 392-402, 411(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xingxing, Wang Yingmin, Gao Shengmei, Mao Peixiao, Zhuo Haiteng, Wang Minghan, Zhou Jiawei. 2018. Advancements of the deep-water gravity flow simulations and their implications for exploitation of marine petroleum[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 47(3): 588-602(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Wei, Jiang Youlu, Li Ruilei, Zhu Jianfeng, Zhao Honghao. 2018. Genetic types and characteristic research on deep-water gravity flows of Yingcheng Formation in Longfengshan subsag, Changling Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 42(5): 23-34(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2018.05.003
Xian Benzhong, An Siqi, Shi Wenhua. 2014. Subaqueous debris flow: Hotspots and sdvances of deep-water sedimentation[J]. Geological Review, 60(1): 39-51(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xian Benzhong, Wan Jinfeng, Dong Yanlei, Ma Qian, Zhang Jianguo. 2013. Sedimentary characteristics, origin and model of lacustrine deep-water massive sandstone: An example from Dongying Formation in Nanpu depression[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9): 3287-3299(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xian Benzhong, Wang Lu, Liu Jianping, Lu Zhiyong, Li Yuzhi, Niu Shuanwen, Zhu Yongfei, Hong Fanghao. 2016. Sedimentary characteristics and model of delta-fed turbidites in Eocene eastern Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 40(5): 10-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2016.05.002
Xing Zuochang, Zhang Zhongtao, Lin Changsong, Zhang Bo, Hong Fanghao, Zhang Zhengtao. 2020. Provenance feature of Upper Oligocene to Early Miocene in Liwan Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin and its influence on depositional filling[J]. Geology in China, 47(5): 1577-1588(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Renchao, He Zhiliang, Qiu Guiqiang, Jin Zhijun, Sun Dongsheng, Jin Xiaohui. 2014. Late Triassic gravity flow depositional systems in the southern Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(6): 661-670(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Tian, Cao Yingchang, Liu Keyu, Wang Yanzhong, Carlos Zavala, Henrik Friis, Song Mingshui, Yuan Guanghui, Liang Chao, Xi Kelai, Wang Jian. 2019. Genesis and depositional model of subaqueous sediment gravity-flow deposits in a lacustrine rift basin as exemplified by the Eocene Shahejie Formation in the Jiyang Depression, Eastern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 102: 231-257. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.033
Yang Tian, Cao Yingchang, Wang Yanzhong, Zhang Shaomin. 2015. Types, sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanisms of deep-water gravity flows: a case study of the middle submember in Member 3 of Shahejie Formation in Jiyang depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(9): 1048-1059(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan Jing, Liang Huiyuan, Liang Bing, Dong Daotao, Min Wei, Song Pan, Li Heyong. 2016. Sedimentary characteristics and development model of lacustrine gravity flow: A case study of Dainan Formation in deep sag belt of Gaoyou depression, Northern Jiangsu Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(3): 348-359(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zavala C, Arcuri M. 2016. Intrabasinal and extrabasinal turbidites: Origin and distinctive characteristics[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 337: 36-54. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.03.008
Zhang Jianguo, Jiang Zaixing, Liang Chao, Wu Jing, Xian Benzhong, Li Qing. 2016. Lacustrine massive mudrock in the Eocene Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Nature, origin and significance[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 77: 1042-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.008
Zou Caineng, Wang Lan, Li Ying, Tao Shizhen, Hou Lianhua. 2012. Deep-lacustrine transformation of sandy debrites into turbidites, Upper Triassic, Central China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 265: 143-155.
Zou Caineng, Zhao Zhengzhang, Yang Hua, Fu Jinhua, Zhu Rukai, Yuan Xuanjun, Wang Lan. 2009. Genetic mechanism and distribution of sandy debris flows in terrestrial lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 27(6): 1065-1075(in Chinese with English abstract).
操应长, 金杰华, 刘海宁, 杨田, 刘可禹, 王艳忠, 王健, 梁超. 2021. 中国东部断陷湖盆深水重力流沉积及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 48(2): 247-257. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202102003.htm 范代读, 邱桂强, 李丛先, 丛友滋, 杨积增. 2000. 东营三角洲的古流向研究[J]. 石油学报, 21(1): 29-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200001004.htm 高红芳, 钟和贤, 孙美静, 聂鑫, 姜涛, 黄文凯, 杜文波, 陈家乐. 2020. 南海海盆东南部大型深水浊积扇体系及其成因的构造控制[J]. 中国地质, 47(5): 1395-1406. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20200508?st=search 雷振宇, 张莉, 苏明, 骆帅兵, 钱星, 帅庆伟, 张伯达. 2017. 南海南部北康盆地中中新世深水沉积体类型、特征及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 37(6): 110-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201706013.htm 李趁义. 2005. 东营三角洲滑塌浊积岩形成机制与高频基准面旋回控砂模式研究[D]. 博士学位论文, 中国地质大学(北京), 1-126. 李相博, 刘化清, 完颜容, 魏立花, 廖建波, 马玉虎. 2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组砂质碎屑流储集体的首次发现[J]. 岩性油气藏, 21(4): 19-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200904004.htm 林畅松, 潘元林, 肖建新, 孔凡仙, 刘景彦, 郑和荣. 2000. "构造坡折带"——断陷盆地层序分析和油气预测的重要概念[J]. 地球科学, 25(3): 42-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200003008.htm 刘建平, 鲜本忠, 王璐, 路智勇, 李宇志, 刘赛君, 蒋健. 2016. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷始新世三角洲供给型重力流地震沉积学研究[J]. 古地理学报, 18(6): 961-975. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201606006.htm 李华, 何明薇, 邱春光, 王英民, 何幼斌, 徐艳霞, 何瑞武. 2022. 深水等深流与重力流交互作用沉积(2000-2022年)研究进展[J/OL]. 沉积学报. DOI: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.027. 邱桂强, 王居峰, 张昕, 李从先. 2001. 东营三角洲沙河街组三段中亚段地层格架初步研究及油气勘探意义[J]. 沉积学报, 19(4): 569-574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200104015.htm 谈明轩, 朱筱敏, 刘伟, 施瑞生. 2017. 旋回阶梯底形的动力地貌及其相关沉积物发育特征[J]. 地质论评, 63(6): 1512-1522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201706008.htm 王尉, 蒋有录, 李瑞磊, 朱建峰, 赵鸿皓. 2018. 长岭断陷龙凤山次凹营城组重力流成因类型及沉积特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 23-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201805003.htm 王家豪, 王华, 肖敦清, 蒲秀刚, 韩文忠, 张伟. 2020. 陆相断陷湖盆异重流与滑塌型重力流沉积辨别[J]. 石油学报, 41(4): 392-402, 411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202004004.htm 王星星, 王英民, 高胜美, 毛佩筱, 卓海腾, 王明晗, 周家伟. 2018. 深水重力流模拟研究进展及对海洋油气开发的启示[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 47(3): 588-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201803014.htm 鲜本忠, 万锦峰, 董艳蕾, 马乾, 张建国. 2013. 湖相深水块状砂岩特征、成因及发育模式——以南堡凹陷东营组为例[J]. 岩石学报, 29(9): 3287-3299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201309026.htm 鲜本忠, 安思奇, 施文华. 2014. 水下碎屑流沉积: 深水沉积研究热点与进展[J]. 地质论评, 60(1): 39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401005.htm 鲜本忠, 王璐, 刘建平, 路智勇, 李宇志, 牛栓文, 朱永飞, 洪方浩. 2016. 东营凹陷东部始新世三角洲供给型重力流沉积特征与模式[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5): 10-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201605003.htm 邢作昌, 张忠涛, 林畅松, 张博, 洪方浩, 张正涛. 2020. 珠江口盆地荔湾凹陷上渐新统-早中新统物源特征及其对沉积充填的影响[J]. 中国地质, 47(5): 1577-1588. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20200522?st=search 杨仁超, 何治亮, 邱桂强, 金之钧, 孙冬胜, 金晓辉. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部晚三叠世重力流沉积体系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 41(6): 661-670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201406003.htm 杨田, 操应长, 王艳忠, 张少敏. 2015. 深水重力流类型、沉积特征及成因机制——以济阳坳陷沙河街组三段中亚段为例[J]. 石油学报, 36(9): 1048-1059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509003.htm 袁静, 梁绘媛, 梁兵, 董道涛, 闵伟, 宋璠, 李鹤永. 2016. 湖相重力流沉积特征及发育模式——以苏北盆地高邮凹陷深凹带戴南组为例[J]. 石油学报, 37(3): 348-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201603007.htm 邹才能, 赵政璋, 杨华, 付金华, 朱如凯, 袁选俊, 王岚. 2009. 陆相湖盆深水砂质碎屑流成因机制与分布特征——以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报, 27(6): 1065-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htm




 下载:
下载: