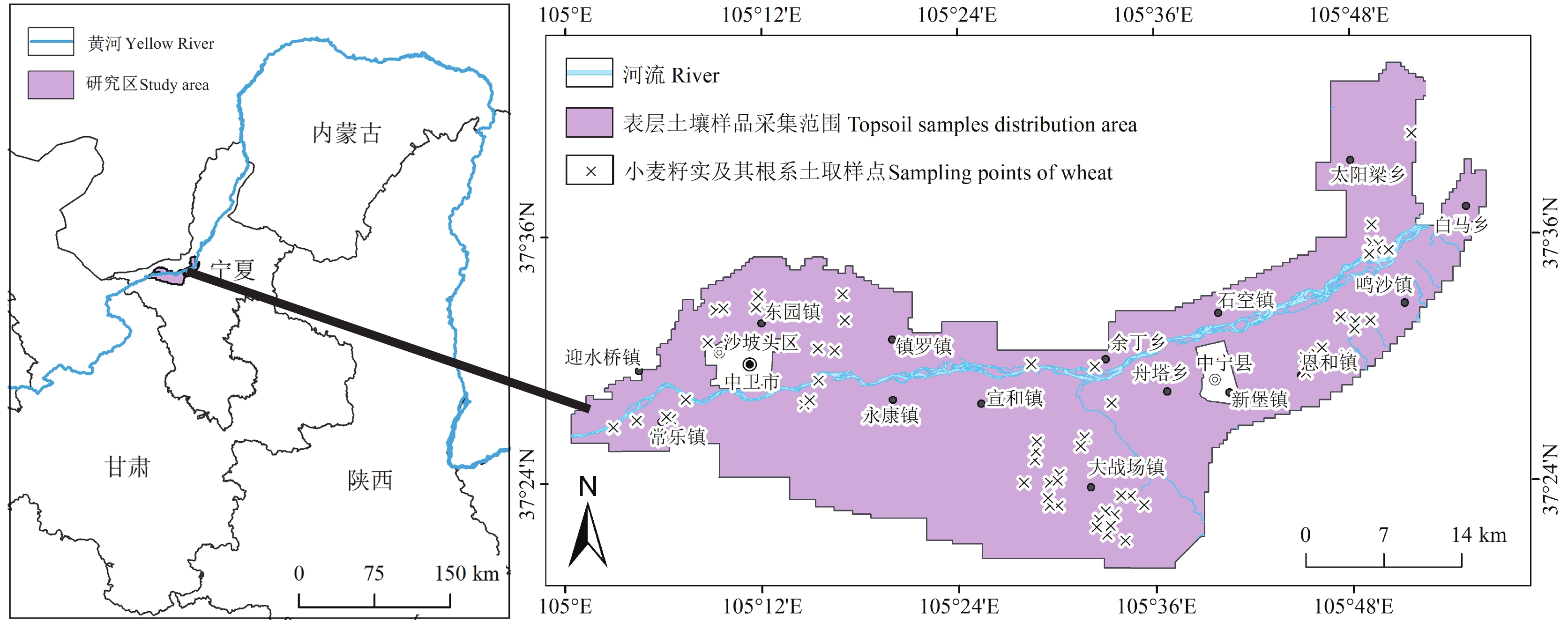
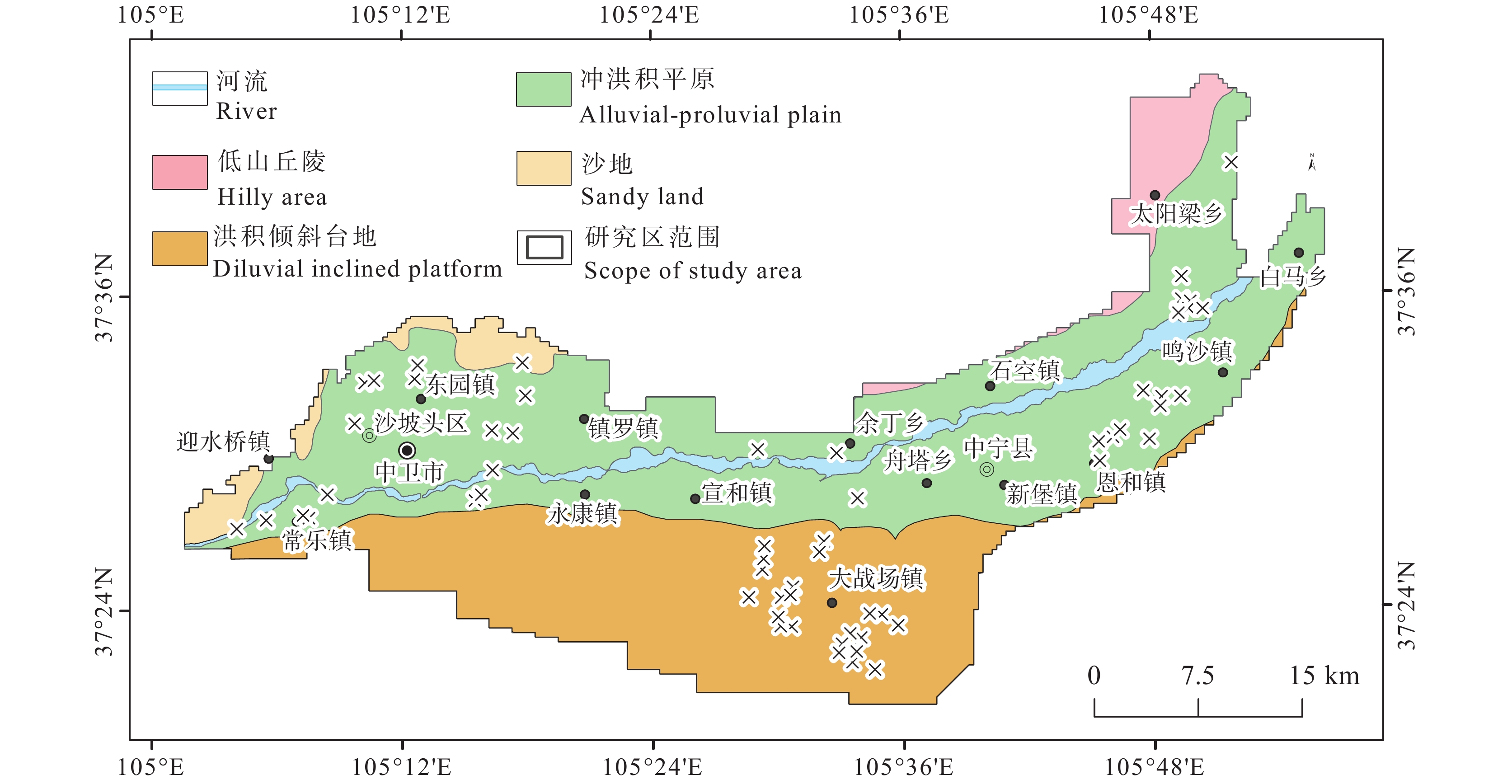
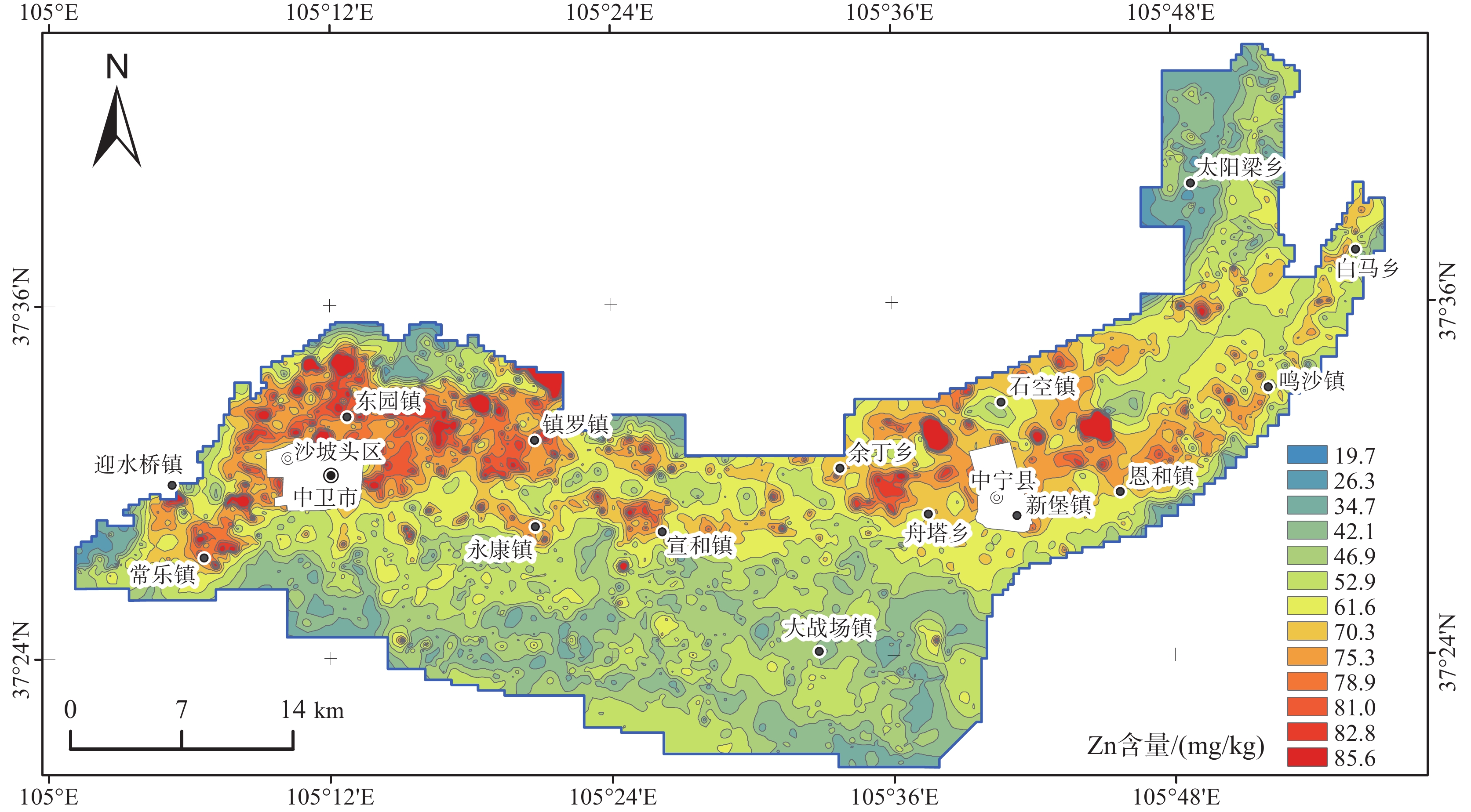
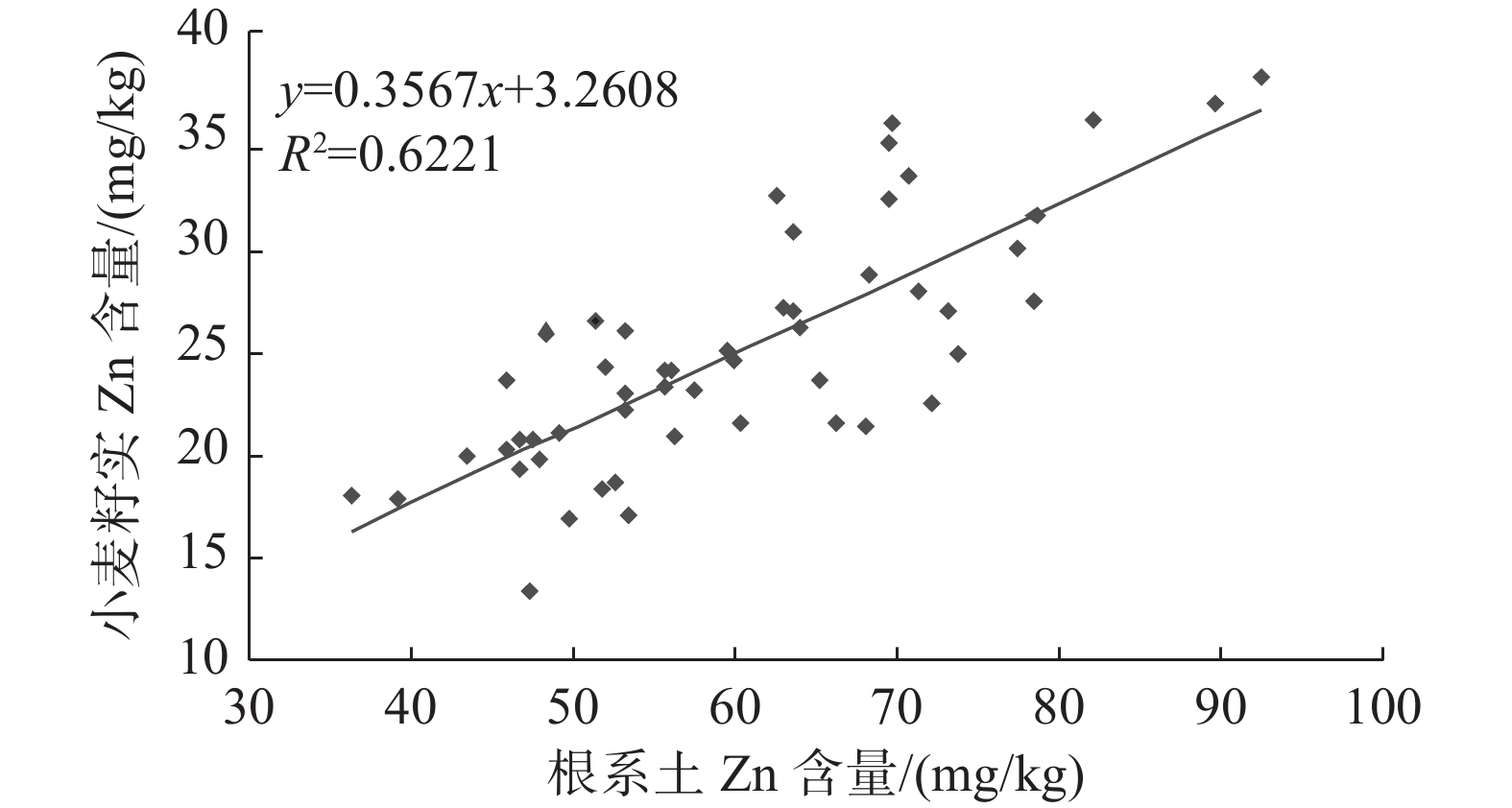
Geochemical characteristics of zinc in soil and prediction of Zn−rich wheat cultivating areas in Weining Plain, Northwest China
-
摘要:研究目的
大部分粮食作物锌含量较低,人体难以从正常的膳食结构中获取足够的锌元素。通过开展土地质量地球化学调查,探寻种植富锌作物的适宜区域,是基于自然途径使作物达到富锌标准的最优方案。
研究方法本研究以宁夏卫宁平原农业用地为研究区,基于土地质量地球化学调查所获取的农用地表层土壤、小麦籽实及其根系土中元素地球化学数据,研究了表层土壤、小麦籽实Zn地球化学特征,探究了小麦籽实富集Zn的影响因素;以中国健康膳食营养结构与居民膳食营养素参考摄入量为基准,推算出富锌小麦锌含量区间值。
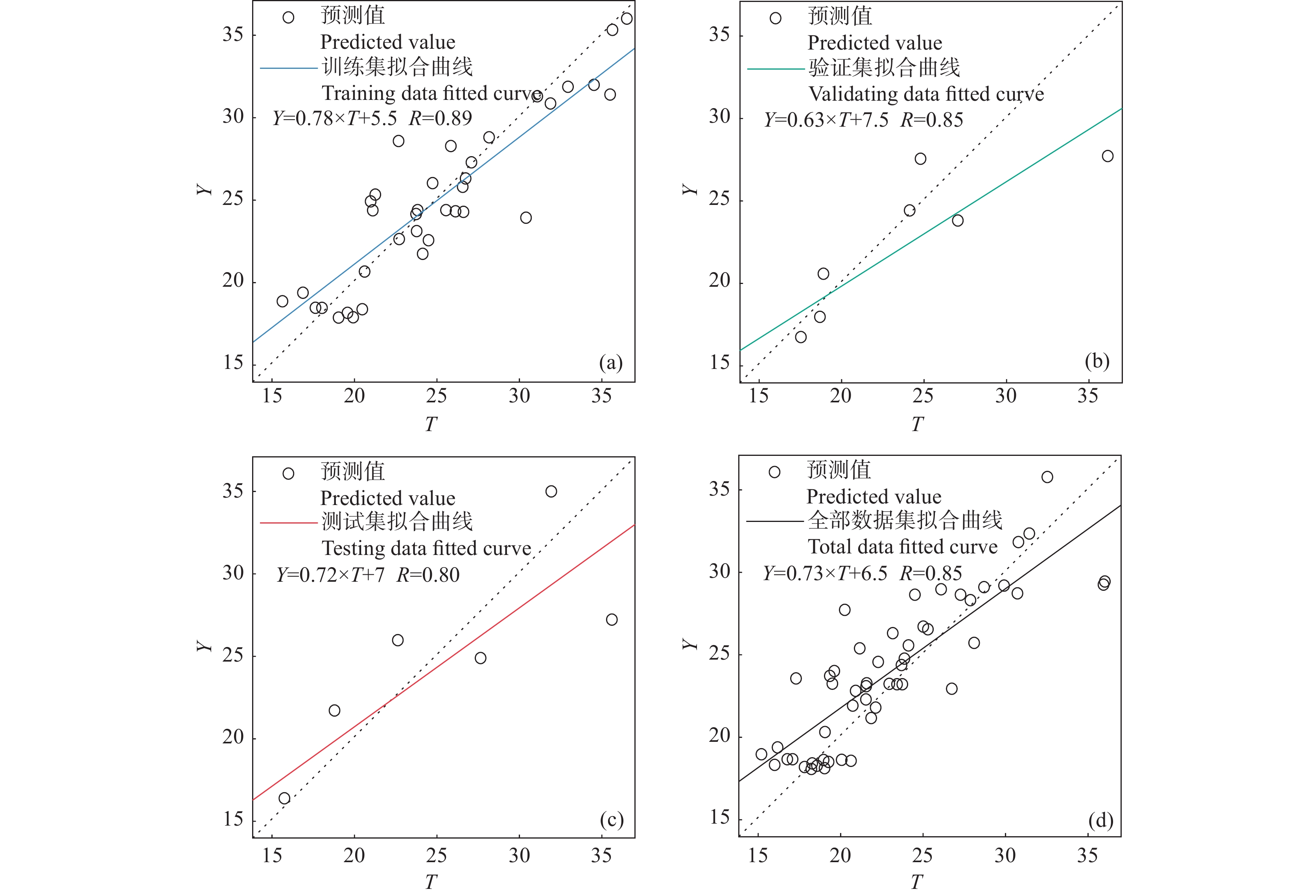
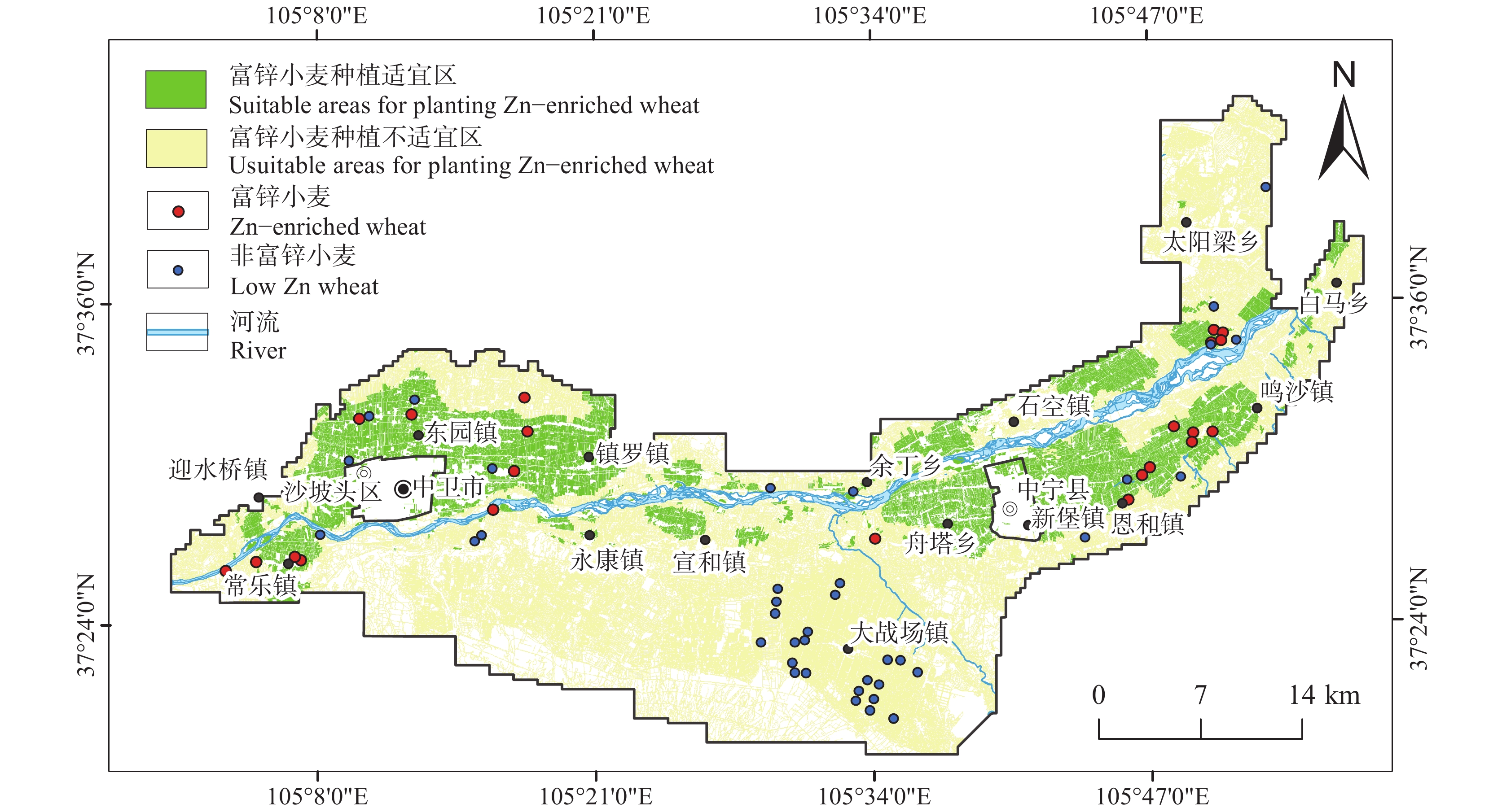
研究结果研究区表层土壤Zn含量范围25.1~102.0 mg/kg,背景值61.4 mg/kg;研究区小麦籽实Zn含量范围13.34~37.78 mg/kg,平均值24.72 mg/kg,生物富集系数(BCF)平均值0.41;富锌小麦Zn含量取值范围为26.5~50.0 mg/kg,研究区小麦籽实的富锌比例为36.7%;基于神经网络模型预测出卫宁平原适宜种植富锌小麦的农用地面积为242.86 km2。
结论研究区表层土壤Zn空间分布较为均匀且主要受到成土母质控制;小麦籽实富集Zn的能力为中等,土壤Zn、Fe2O3、K2O、SiO2/Al2O3与小麦籽实Zn具有显著相关关系;神经网络模型能构建出可靠的预测模型,可以作为基于地球化学调查数据探寻有益微量元素富集作物种植适宜区的方法。
创新点:基于中国健康膳食营养结构与居民膳食营养素参考摄入量,推算出富锌小麦Zn含量区间值;运用神经网络模型构建了小麦籽实Zn含量预测模型,通过预测小麦籽实Zn含量,划分出适宜种植富锌小麦的区域。
Abstract:This paper is the result of agricultural geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveMost of the food crops are low in zinc and it is difficult for humans to obtain sufficient zinc through the normal diet. Land quality geochemical survey, as nature−based solutions, is the best scheme to find the suitable region for cultivating zinc−rich crops.
MethodsThis study takes agricultural land in Weining Plain of Ningxia as the research region, geochemical data of surface soils, wheat seeds and rhizosphere soils of agricultural lands were obtained through land quality geochemical survey, the geochemical characteristics of zinc in surface soil and wheat seed were studied, and the influencing factors of zinc enrichment in wheat seed were explored. The interval value of zinc content in zinc−rich wheat was calculated based on the nutritional structure of healthy diet in China and the reference intake of dietary nutrients in residents.
ResultsIn the research region, the range of zinc content in surface soils was 25.1 mg/kg to 102.0 mg/kg, and the background value of surface soil was 61.4 mg/kg. The range of zinc content in wheat seeds was 13.34 mg/kg to 37.78 mg/kg, the average content was mg/kg, and the averagebio−enrichment coefficient was 0.41. The range of zinc content in Zn−enriched wheat was 26.5 to 50.0 mg/kg, and the proportion of zinc enriched wheat seeds in the research region was 36.7%.Based on the neural network model, we predicted that the region of agricultural lands, which were suitable for cultivating zinc enriched wheat in Wei Ning Plain, was 242.86 km2.
ConclusionsThe spatial distribution of zinc in the surface soil of the research region was relatively uniform and was mainly controlled by soil parent materials. The zinc enrichment ability of wheat seeds was medium. The zinc enrichment ability of wheat seeds is significantly correlated with Zn, Fe2O3, K2O, SiO2/Al2O3 in rhizosphere soils. Neural network model can construct a reliable prediction model, which can be used as a method to explore suitable cultivating regions for beneficial micronutrient enrichment crops through geochemical survey data.
Highlights:Based on the healthy nutrition structure of Chinese diet and the reference intake of dietary nutrients, the interval value of zinc content in zinc enrichment wheat seeds was calculated. A prediction model of zinc content in wheat seeds was established through neural network model.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
湘中坳陷作为南方复杂构造区页岩气勘探的热点地区之一,也是中国油气勘探久攻未克的地区。前期在湘中地区北部的涟源凹陷泥盆系和石炭系获得了页岩气突破和发现,证实了湘中地区上古生界页岩气资源丰富。但对湘中地区南部的邵阳凹陷调查程度较为薄弱,针对邵阳凹陷二叠系仅开展了少量基础地质调查工作,页岩气资源潜力评价方面的工作尤为欠缺。本次研究依托邵阳湘邵地1井(XSD1井)钻探工程建立了邵阳凹陷二叠系地层层序序列,揭示了主要含气页岩层系的分布特征,获取了含气性评价参数,对湘中地区二叠系页岩气勘探开发和重新评价湘中坳陷页岩气资源潜力具有重要的现实意义。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心在收集分析区域地质相关资料的基础上,结合邵阳凹陷短陂桥向斜的煤田浅钻、非震物探等资料开展页岩气地质综合评价,采用页岩埋深500~4500 m,页岩有机碳含量≥1.0%,页岩厚度≥15 m,页岩有机质热演化程度1.0%~3.5%的评价参数在短陂桥向斜区优选页岩气远景区,论证部署了1口小口径页岩气地质调查井—XSD1井,湖南煤田地质勘查有限公司组织实施钻探(图 1a)。该井采样全井段取心钻井工艺,测井选取PSJ-2数字测井系统,录井采用SK-2000G气测录井,钻获二叠系大隆组156.05 m(暗色硅质页岩、钙质泥岩94.48 m),龙潭组349.95 m(暗色泥岩216.93 m,粉砂质泥岩36.9 m),对这两套层系共采集暗色泥岩样品33件,进行解析气含量测定分析,落实了含气性评价参数。
3. 结果(Results)
本次样品分析工作由武汉地质调查中心古生物与生命-环境协同演化重点实验室完成,采用YSQ-IIIA岩石解析气测定仪(燃烧法)对含气段岩心共计33件样品进行分析。该井钻获二叠系大隆组厚度156.05 m,为一套硅质岩、硅质页岩、炭质钙质泥岩地层。其中在井深842~930.2 m硅质页岩、钙质泥岩段,气测全烃值从1.06%上升至16.54%,甲烷值从1.01%上升至14.04%,13件大隆组硅质页岩现场解析总含气量为1.29~9.97 m3/t,平均4.85 m3/t。实现了湘中坳陷二叠系页岩气新发现,有效拓展了华南地区大隆组勘探范围。
钻获龙潭组厚度349.95 m,上段为一套细砂岩、粉砂岩夹泥岩潮坪相沉积地层,下段为一套炭质泥岩、粉砂质泥岩夹薄层细砂岩泻湖相沉积地层。在井深1013.4~1048 m泥岩与粉砂岩互层段气测全烃值最高可达19.87%,甲烷值最高为16.94%,7件泥岩与粉砂岩样品现场解析总含气量0.57~3.42 m3/t,平均1.78 m3/t;井深1088.10~1199.75 m泥岩夹泥质粉砂岩含气层111.6 m,气测全烃值最高可达28.2%,甲烷值最高为23.6%,13件泥岩、粉砂质泥岩样品现场解析总含气量0.90~4.55 m3/t,平均2.01 m3/t(图 1b),首次查明了湘中坳陷二叠系龙潭组非常规油气分布特点。
通过区域地质背景分析,并结合煤田区域地质资料,本研究认为滑脱断裂(F9)上下盘具有不同的页岩气聚集条件。滑脱断裂之上由一系列的同向逆断层形成的逆冲推覆体,地层变形强烈,且裂缝发育,导致页岩气保存条件变差。滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,地层平缓,不发育次级通天断裂,与下盘地层形成反向遮挡,易形成封闭,保存条件良好(图 1c)。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)二叠系大隆组岩性以硅质岩、硅质页岩为主,夹少量灰岩。主要含气段存在于上段硅质页岩段,厚88.2 m,含气量平均为4.85 m3/t,含气性优越,资源潜力大。
(2)二叠系龙潭组上段以致密砂岩气为主,含气量平均为1.78 m3/t;下段以页岩气为主,泥岩厚达177.47 m,含气量平均为2.01 m3/t,具有泥岩厚度大,含气性好等特征。
(3)保存条件是页岩气富集关键,构造改造弱的封闭演化环境有利于页岩气保存,研究区滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,易形成封闭,保存条件良好。
(4)湘邵地1井在二叠系大隆组和龙潭组获得良好的页岩气显示,证实了湘中地区二叠系具有良好的页岩气资源潜力,对湘中地区页岩气资源潜力评价具有重要意义。
5. 基金项目(Fund support)
本文为中国地质调查局项目“中扬子地区油气页岩气调查评价”(DD20221659)资助的成果。
-
表 1 土壤样品分析项目及其测试方法和检出限
Table 1 Analysis items and its testing method and detection limits of samples
样品类型 元素或指标 分析方法 分析方法检出限 准确度 精密度/% 土壤 Al2O3/% XRF 0.05 0.01 3.82 CaO/% 0.02 0.02 3.97 Fe2O3/% 0.02 0.01 3.55 K2O/% 0.03 0.01 3.17 SiO2/% 0.05 <0.01 2.86 有机质/% VOL 0.034 <0.01 6.19 Zn/% ICP−MS 1 <0.01 3.29 pH ISE 0.1 0.01 3.51 小麦籽实 Zn/(mg/kg) ICP−MS 1 0.01 10.53 表 2 研究区小麦籽实及其根系土Zn含量
Table 2 Zn content of wheat seeds and their rhizosphere soils
样品分布区域 样品量 类别 含量范围 平均值 标准偏差 变异系数/% 黄河
冲洪积平原38(件) 小麦籽实/(mg/kg) 13.34~37.78 27.15 6.04 22.26 根系土/(mg/kg) 43.38~92.43 67.80 10.74 15.84 富集系数(BCF) 0.28~0.51 0.40 0.06 15.56 洪积倾斜台地 22(件) 小麦籽实/(mg/kg) 16.77~26.25 21.41 2.81 13.11 根系土/(mg/kg) 36.34~56.31 49.76 5.15 10.34 富集系数(BCF) 0.34~0.53 0.43 0.05 12.08 研究区 60(件) 小麦籽实/(mg/kg) 13.34~37.78 24.72 5.68 22.98 根系土/(mg/kg) 36.34~92.43 60.17 12.55 20.86 富集系数(BCF) 0.28~0.53 0.41 0.06 14.63 表 3 Zn生物富集系数与土壤理化指标相关系数
Table 3 Correlation analysis of BCF with soil physicochemical properties
SiO2/Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O 有机质 根系土Zn pH 小麦籽实 Zn −0.77** 0.41* 0.73** 0.67** 0.38 0.79** −0.25 注:*代表在0.05水平显著;**代表在0.01水平显著。 表 4 居民平衡膳食结构Zn供应量及富锌谷类锌含量下限值
Table 4 The supply of Zn in residents balanced dietary and the lower limit of zinc content in zinc-rich crops
食物 推荐食用量/(g/d) Zn含量
/(mg/kg)Zn摄入量
/(mg/d)推荐范围 本文取值 奶 300~500 400 4.50 1.80 动物性食物 120~200 160 25.80 4.13 蔬菜 300~500 400 2.21 0.88 水果 200~350 225 1.68 0.38 谷类 200~300 250 X Y 除富锌谷类外其他普通食物(奶、动物性食品、蔬菜、水果)每日Zn供应量 7.19 成年人每日Zn推荐摄入量(RNI) 12.5 富锌谷类每日Zn最低供应量(Y) 5.31 X = (5.31 mg/d)/(250 g/d)= 21.24 mg/kg -
[1] Bao Chenglong, Xu Xiaoyan, Liu Bowen. 2014. The nutrition and comprehensive utilization of wheat bran[J]. Grains and Oils, 27(8): 58−60 (in Chinese).
[2] Cakmak I, Kutman U B. 2018. Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: A review[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 69: 172−180.
[3] Chen Nengwang, Yu Yiqi, Chen Jixin, Chen Longbiao, Zhang Dongzhan. 2021. Artificial neural network models for water quality early warning: A review[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(12): 4771−4782 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Qingxia, Tu Chenglong, Lu Xiaohui, Li Longbo. 2021. Spatial heterogeneity of Zn and organic matter in dryland yellow soil of Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(10): 4179−4187 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Cheng X X, Wei L X, Huang X D, Zheng J, Shao M M, Feng T, Li J, Han Y L, Tan W L, Tan W, Lin D X, Wu C. 2017. Solute carrier family 39 member 6 gene promotes aggressiveness of esophageal carcinoma cells by increasing intracellular levels of zinc, activating phosphatidylinositol 3–kinase signaling, and up–regulating genes that regulate metastasis–science direct[J]. Gastroenterology, 152(8): 1985−1997.
[6] Dou Weiqiang, An Yi, Qin Li, Dong Mingming, Lin Dasong. 2021. Quantitative relationship between the bioconcentration factor of rice cadmium and its influencing factors[J]. Soils, 53(4): 788−793 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Frangos T, Maret W. 2020. Zinc and Cadmium in the aetiology and pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nutrients, 13(1): 53.
[8] Gao Yu, Liu Zhijian. 2017. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in selenium–rich area in Changshantou, Ningxia Province, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 45(6): 628−633 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Hou Qingye, Yang Zhongfang, Yu Tao, Xia Xueqi, Cheng Hangxin. 2020. Soil Geochemical Dataset of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 3–53 (in Chinese).
[10] Li Ning, Zhao Huijuan. 2011. Investigation of copper, manganese, zinc and selenium contents in vegetables, fruits, grains and fresh meat in Jinan, Shandong[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 28(7): 613−615 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Liu Jingyun, Zuo Qun. 2019. Trace elements copper, zinc, selenium, iron, the change of oxidative stress and inflammation in body condition and the mechanism research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Sports Medicine, 38(2): 159−164 (in Chinese).
[12] Liu Yingjun, Cao Liming, Li Zhaolin Wang Henian, Chu Tongqing, Zhang Jingrong. 1984. Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 309–310 (in Chinese).
[13] Makabe S, Kakuda K, Sasaki Y, Ando T, Fujiihrs, Ando H. 2009. Relationship between mineral composition or soil texture and available silicon in alluvial paddy soils on the Shounai Plain, Japan[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 55(2): 300−308. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0765.2008.00352.x
[14] Ma Honghong, Peng Min, Liu Fei, Guo Fei, Tang Shiqi, Liu Xiuquan, Zhou Yalong, Yang Ke, Li Kuo, Yang Zheng, Cheng Hangxin. 2020. Bioavailability, translocation, and accumulation characteristic of heavy metals in a soil–crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi, China[J]. Environmental Science, 41(1): 449−459 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Ma Xudong, Yu Tao, Yang Zhongfang, Zhang Shenghu, Wu Zhiliang, Wang Jue, Li Minghui, Lei Fenghua. 2022. Geochemical characteristics of zinc in soil and prediction of zinc content inmaize and rice grains in Linshui County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 324−335 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Mezzaroba L, Alfieri D F, Colado Simão A N, Vissoci Reiche E M. 2019. The role of zinc, copper, manganese and iron in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Neuro Toxicology, 74: 230−241.
[17] Ning Yunwang, Zhang Yongchun, Wang Jidong, Xu Xianju, Hu Yonghong. 2009. Research of zinc in soil–plant–human system and development of zinc enrichment agricultural products[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, (3): 1−4 (in Chinese).
[18] Sanna A, Firinu D, Zavattari P, Valera P. 2018. Zinc status and autoimmunity: A systematic review and meta–analysis[J]. Nutrients, 10(1): 68. doi: 10.3390/nu10010068
[19] Shang Heping, Li Yang, Zhang Tao, Su Dechun. 2015. Form tendency and bio–availability dynamics of Cu and Zn in different farm soils after application of organic fertilizer of livestock and poultry manures[J]. Environmental Science, 36(1): 314−324 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Shi Jianfang, Hu Mingli. 2012. Nutrient components and utilization status of wheat bran[J]. Modern Flour Milling Industry, 26(2): 25−28 (in Chinese).
[21] Song Yinxian. 2011. Ecogeochemistry of Heavy Metals in Sediment and Soil of Changjiang River Delta[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 1–206 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Su Da, Wu Liangquan, Søren K Rasmussen, Zhou Lujian, Pan Gang, Cheng Fangmin. 2020. Influence of phosphorus on ricegrain zinc bioavailability and its relation to inositol phosphate profiles concentration[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 46(2): 228−237 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.92032
[23] Sun Houyun, Wei Xiaofeng, Sun Xiaoming, Jia Fengchao, Li Duojie, Li Jian. 2021. Bioaccumulation and translocation characteristics of heavy metals in a soil–maize system in reclaimed land and surrounding areas of typical vanadium titanium magnetite tailings[J]. Environmental Science, 42(3): 1166−1176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Tang Molan, Fan Bolun, Yao Lingyang, An Ziyi, Bao Zhengyu. 2020. Geochemical characteristics and impact factors of seleniumin soil−crop systems[J]. Guizhou Geology, 37(4): 417−424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Wang Cheng, Cheng Jianhua, Meng Fang, Li Tianbin. 2017. Regional Geology of China–Ningxia[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 770–839 (in Chinese).
[26] Wang Rui, Deng Hai, Jia Zhongmin, Yan Mingshu, Zhou Jiao, He Zhongxiang, Liang Shaobiao, Dong Jinxiu, Su Liming. 2020. Distribution characteristics of selenium in a soil–crop system and thethreshold of selenium–rich soils[J]. Environmental Science, 41(12): 5571−5578 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Wang Yizheng, Yang Zhongfang, Liu Xu, Li Cheng, Ji Wenbin, Zhang Qizuan, Zhuo Xiaoxiong, Wang Lei. 2023. Geochemical characteristics of copper in soil and ecological health research in Qintang district of Guigang City in Guangxi[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 237−248 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Wu Zhiliang, Li Zhikun, Hou Qingye, Yang Zhongfang, Yu Tao, Wang Jue, Wang Chen, Ma Xudong. 2021. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soils and crops and its research significance in Linshui County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience, 35(6): 1752−1761 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Xi Xiaohuan. 2021. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soils background value versus reference value: A paper written on the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China's publication[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 28(1): 308−317 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Xiao Gaoqiang, Zong Qingxia, Xiang Longzhou, Dao Yan, Xu Yongqiang. 2020. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of Selenium insoils and agricultural products in the Jiucheng–Jiemao area, Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 44(2): 412−418 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Yan Yaping, Wang Gang, Jiang Shengji, Xu Min. 2022. Research progress of artificial neural networks in the field of environment[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 51(1): 170−176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Yang Qiong, Yang Zhongfang, Zhang Qizuan, Liu Xu, Zhuo Xiaoxiong, Wu Tiansheng, Wang Lei, Wei Xueji, Ji Junfeng. 2021. Ecological risk assessment of Cd and other heavy metals in soil–rice system in the karst areas with high geochemical background of Guangxi, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(8): 1317−1331.
[33] Yang X E, Chen W R, Ying F. 2007. Improving human micronutrient nutrition through biofortification in the soil–plant system: China as a case study [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29: 413–428.
[34] Zhang Hanqing, Zhang Zhengying, Zhao Weizhang. 2020. Fresh milk quality security investigation and assay for cows in large scale farm, Qinghai Province[J]. Shandong Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, 41(6): 57−58 (in Chinese ).
[35] Zhang Jiguo, Zhang Bin, Wang Huijun, Du Wenwen, Su Chang, Zhai Fengying. 2012. Nutrients intake trend of chinese population in nine provinces from 1989 to 2009 (Ⅶ) zinc intake trend of Chinese adults aged 18–49 years[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 28(9): 111−113 (in Chinese).
[36] Zhang Ye, Li Mingchao, Han Shuai. 2018. Automatic identification and classification in lithology based on deep learning in rockimages[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(2): 333−342 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Zhao Duoyong, Wei Yimin, Wei Shuai, Guo Boli, Cai Xianfeng, Wu Xiaosheng. 2012. Isotope analysis of lead pollution sources in wheat kernel[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28(8): 258−262 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Zhao Huixian, Zhao Yang, Qin Shouxian, Zhao Yuxin, Huang Kehe. 2008. Effect of Se–enriched yeast in hen diets on the selenium content and distribution in eggs[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, (4): 31−35 (in Chinese).
[39] Zhao Xiaohon, He Hui, Jia Lei, Hou Tao. 2022. Plant fortified with selenium and zinc: A new exploration on dietary supplements[J]. Food Science and Technology, 47(5): 95−101 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Zhao Xiaoyuan, Yang Zhongfang, Cheng Huiyi, Ma Xudong, Wang Jue, Li Zhikun, Wang Chen, Li Minghui, Lei Fenghua. 2022. Geochemical characteristics and ecological health–related ranges of Copper in soil in Huaying Mountain–Xicao in Linshui County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 46(1): 238−249 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] 包成龙, 许晓燕, 刘博文. 2014. 小麦麸皮营养成分和综合利用[J]. 粮食与油脂, 27(8): 58−60. [42] 陈能汪, 余镒琦, 陈纪新, 陈龙彪, 张东站. 2021. 人工神经网络模型在水质预警中的应用研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(12): 4771−4782. [43] 陈清霞, 涂成龙, 陆晓辉, 李龙波. 2021. 贵州省旱地黄壤Zn和有机质的空间异质性特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(10): 4179−4187. [44] 窦韦强, 安毅, 秦莉, 董明明, 林大松. 2021. 稻米镉的生物富集系数与其影响因素的量化关系[J]. 土壤, 53(4): 788−793. [45] 高宇, 刘志坚. 2017. 宁夏长山头富硒区土壤硒地球化学特征研究[J]. 地球与环境, 45(6): 628−633. [46] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 夏学齐, 成杭新. 2020. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 3–53. [47] 李宁, 赵慧娟. 2011. 济南市区蔬菜、水果、粮食和鲜肉中铜、锰、锌、硒含量调查[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 28(7): 613−615. [48] 刘婧昀, 左群. 2019. 微量元素铜、锌、硒、铁在机体氧化应激与炎症状态下的变化及机制研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 38(2): 159−164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2019.02.012 [49] 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 王鹤年, 储同庆, 张景荣. 1984. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 309–310. [50] 马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 郭飞, 唐世琪, 刘秀金, 周亚龙, 杨柯, 李括, 杨峥, 成杭新. 2020. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤–作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 41(1): 449−459. [51] 马旭东, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 张虎生, 武芝亮, 王珏, 李明辉, 雷风华. 2022. 四川省邻水县土壤锌地球化学特征及玉米水稻籽实锌含量预测[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 324−335. [52] 宁运旺, 张永春, 汪吉东, 许仙菊, 胡永红. 2009. 土壤–植物–人类系统中锌与富锌农产品的开发[J]. 江苏农业科学, (3): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2009.03.001 [53] 史建芳, 胡明丽. 2012. 小麦麸皮营养组分及利用现状[J]. 现代面粉工业, 26(2): 25−28. [54] 商和平, 李洋, 张涛, 苏德纯. 2015. 畜禽粪便有机肥中Cu、Zn在不同农田土壤中的形态归趋和有效性动态变化[J]. 环境科学, 36(1): 314−324. [55] 宋垠先. 2011. 长江三角洲沉积物和土壤重金属生态地球化学研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 1−206. [56] 苏达, 吴良泉, Søren K Rasmussen, 周庐建, 潘刚, 程方民. 2020. 磷营养对水稻籽粒锌生物有效性的影响及其与植酸等磷酸肌醇谱含量的关系[J]. 作物学报, 46(2): 228−237. [57] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 孙晓明, 贾凤超, 李多杰, 李健. 2021. 钒钛磁铁矿尾矿库复垦土地及周边土壤–玉米重金属迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 42(3): 1166−1176. [58] 唐沫岚, 范博伦, 姚凌阳, 安子怡, 鲍征宇. 2020. 土壤—作物系统中硒的地球化学特征及影响因素研究(代序2)[J]. 贵州地质, 37(4): 417−424. [59] 王成, 程建华, 孟方, 李天斌. 2017. 中国区域地质志—宁夏志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 770–839. [60] 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 严明书, 周皎, 何忠庠, 梁绍标, 董金秀, 苏黎明. 2020. 硒在土壤–农作物系统中的分布特征及富硒土壤阈值[J]. 环境科学, 41(12): 5571−5578. [61] 王懿铮, 杨忠芳, 刘旭, 李程, 季文兵, 张起钻, 卓小雄, 王磊. 2023. 广西贵港市覃塘区土壤Cu地球化学特征与生态健康研究[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 237−248. [62] 武芝亮, 李致坤, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 王珏, 王琛, 马旭东. 2021. 四川省邻水县土壤及作物硒地球化学特征及其研究意义[J]. 现代地质, 35(6): 1752−1761. [63] 奚小环. 2021. 大数据科学从信息化、模式化到智能化: 现代地球化学应用研究的新范式[J]. 地学前缘, 28(1): 308−317. [64] 肖高强, 宗庆霞, 向龙洲, 刀艳, 徐永强. 2020. 云南省盈江县旧城—姐冒地区土壤和农产品硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 44(2): 412−418. [65] 严亚萍, 王刚, 姜盛基, 徐敏. 2022. 人工神经网络在环境领域中的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 51(1): 170−176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2022.01.036 [66] 杨琼, 杨忠芳, 张起钻, 刘旭, 卓小雄, 吴天生, 王磊, 韦雪姬, 季峻峰. 2021. 中国广西岩溶地质高背景区土壤–水稻系统Cd等重金属生态风险评价[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 51(8): 1317−1331. [67] 张汉青, 张正英, 赵维章. 2020. 青海奶牛规模养殖场鲜奶质量安全抽样调查与分析[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 41(6): 57−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1733.2020.06.031 [68] 张继国, 张兵, 王惠君, 杜文雯, 苏畅, 翟凤英. 2012. 1991–2009年中国9省(自治区)中老年人膳食锌的摄入状况及变化趋势[J]. 营养学报, 28(9): 707−709,718. [69] 张野, 李明超, 韩帅. 2018. 基于岩石图像深度学习的岩性自动识别与分类方法[J]. 岩石学报, 34(2): 333−342. [70] 赵多勇, 魏益民, 魏帅, 郭波莉, 蔡先峰, 吴小胜. 2012. 小麦籽粒铅污染来源的同位素解析研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 28(8): 258−262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.08.041 [71] 赵慧贤, 赵洋, 秦守贤, 赵玉鑫, 黄克和. 2008. 蛋鸡日粮中添加富硒酵母对鸡蛋中硒含量及分布的影响[J]. 畜牧与兽医, (4): 31−35. [72] 赵小红, 何慧, 贾蕾, 侯焘. 2022. 植物生物强化硒与锌: 膳食补充剂的新探索[J]. 食品科技, 47(5): 95−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.5.spkj202205015 [73] 赵筱媛, 杨忠芳, 程惠怡, 马旭东, 王珏, 李志坤, 王琛, 李明辉, 雷风华. 2022. 四川邻水县华蓥山—西槽土壤Cu地球化学特征与生态健康[J]. 物探与化探, 46(1): 238−249.




 下载:
下载: