Research progress of stable isotopic geochemistry of cadmium and zinc and its harm and control in soil and other geological bodies
-
摘要:研究目的
镉、锌既是重要的矿产资源,也是有害的重金属元素。随着多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(MC–ICP–MS)的发展,镉、锌等非传统稳定同位素体系的建立与应用使镉、锌地球化学研究水平迈上新的高度,镉、锌同位素体系建立与应用成为国际研究热点。
研究方法本文通过查阅大量镉、锌同位素的相关文献,从镉、锌同位素的分析方法、分馏机制、自然界储库组成及应用领域进行了综述。
研究结果(1)随着镉、锌同位素分析技术的不断改进,其同位素体系正在逐步建立;(2)地球各储库中的锌同位素组成已基本查明,镉同位素组成正处于数据积累阶段;(3)镉、锌同位素分馏机制主要包括吸附沉淀、生物作用、化学作用等,目前已逐渐被应用到指示行星分异、探明成矿机制、重建古环境、示踪污染源等多种领域中;(4)在解析重金属污染源时,多种同位素的联用有助于减小不确定性。
结论在新型同位素分析仪器和技术的开发下,镉、锌同位素的研究拥有更大的发展空间。未来的研究重点主要包括对镉、锌同位素分馏机制、部分储库含量、应用领域进行完善。
创新点:(1)本文将具有相似地球化学性质的镉元素和锌元素放在一起进行论述,有利于该领域学者对其进行对比分析;(2)本文较全面地总结了近年来镉、锌同位素的分析方法、研究成果、污染现状及修复技术,并提出了未来的主要研究方向,旨在推动镉、锌同位素的研究进程。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveCadmium(Cd) and zinc(Zn) are both important mineral resources and harmful heavy metal elements. The recent development of multi–collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC–ICP–MS) has improved the precision of Zn isotope composition analysis in different environments. The establishment and application of non–traditional stable isotope systems such as cadmium and zinc have raised the geochemical research of cadmium and zinc to a new level, which also have become hot topics in isotope geochemistry.
MethodsThis paper reviews recent research progress on the analytical methods, fractionation mechanisms, isotopic compositions in different reservoirs, and application fields of Zn and Cd isotopes investigated in many studies.
Results(1) The improvement of Zn and Cd isotope analysis technology has promoted the establishment of their isotope systems. (2) The compositions of Zn isotopes in various reservoirs have been basically identified. The data for Cd isotope compositions in reservoirs and anthropogenic sources is in the period of accumulation. (3) The isotopic fractionation mechanisms of Cd and Zn mainly include mineral adsorption, biological processes, and chemical reactions, which have been applied in the indication of planetary evolution, the exploration of metallogenic mechanisms, paleoenvironmental reconstruction, and pollution source tracer. (4) The combination of multiple isotopes helps to reduce uncertainty in the analysis of heavy metal pollution sources.
ConclusionsThe development of new isotope analysis instruments and technologies has made the research of Zn and Cd isotopes more promising. It is expected that more work should be carried out in the near future to improve the fractionation mechanisms, compositions in partial reservoirs, and application fields.
Highlights:(1) This paper reviews Cd and Zn with similar geochemical properties together, which is conducive to similar research; (2) This paper summarizes the analysis methods, research results, pollution status, and remediation technology of Cd and Zn isotopes. The authors propose the main research directions for the future with the aim of promoting the research process for Cd and Zn isotopes.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
湘中坳陷作为南方复杂构造区页岩气勘探的热点地区之一,也是中国油气勘探久攻未克的地区。前期在湘中地区北部的涟源凹陷泥盆系和石炭系获得了页岩气突破和发现,证实了湘中地区上古生界页岩气资源丰富。但对湘中地区南部的邵阳凹陷调查程度较为薄弱,针对邵阳凹陷二叠系仅开展了少量基础地质调查工作,页岩气资源潜力评价方面的工作尤为欠缺。本次研究依托邵阳湘邵地1井(XSD1井)钻探工程建立了邵阳凹陷二叠系地层层序序列,揭示了主要含气页岩层系的分布特征,获取了含气性评价参数,对湘中地区二叠系页岩气勘探开发和重新评价湘中坳陷页岩气资源潜力具有重要的现实意义。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心在收集分析区域地质相关资料的基础上,结合邵阳凹陷短陂桥向斜的煤田浅钻、非震物探等资料开展页岩气地质综合评价,采用页岩埋深500~4500 m,页岩有机碳含量≥1.0%,页岩厚度≥15 m,页岩有机质热演化程度1.0%~3.5%的评价参数在短陂桥向斜区优选页岩气远景区,论证部署了1口小口径页岩气地质调查井—XSD1井,湖南煤田地质勘查有限公司组织实施钻探(图 1a)。该井采样全井段取心钻井工艺,测井选取PSJ-2数字测井系统,录井采用SK-2000G气测录井,钻获二叠系大隆组156.05 m(暗色硅质页岩、钙质泥岩94.48 m),龙潭组349.95 m(暗色泥岩216.93 m,粉砂质泥岩36.9 m),对这两套层系共采集暗色泥岩样品33件,进行解析气含量测定分析,落实了含气性评价参数。
3. 结果(Results)
本次样品分析工作由武汉地质调查中心古生物与生命-环境协同演化重点实验室完成,采用YSQ-IIIA岩石解析气测定仪(燃烧法)对含气段岩心共计33件样品进行分析。该井钻获二叠系大隆组厚度156.05 m,为一套硅质岩、硅质页岩、炭质钙质泥岩地层。其中在井深842~930.2 m硅质页岩、钙质泥岩段,气测全烃值从1.06%上升至16.54%,甲烷值从1.01%上升至14.04%,13件大隆组硅质页岩现场解析总含气量为1.29~9.97 m3/t,平均4.85 m3/t。实现了湘中坳陷二叠系页岩气新发现,有效拓展了华南地区大隆组勘探范围。
钻获龙潭组厚度349.95 m,上段为一套细砂岩、粉砂岩夹泥岩潮坪相沉积地层,下段为一套炭质泥岩、粉砂质泥岩夹薄层细砂岩泻湖相沉积地层。在井深1013.4~1048 m泥岩与粉砂岩互层段气测全烃值最高可达19.87%,甲烷值最高为16.94%,7件泥岩与粉砂岩样品现场解析总含气量0.57~3.42 m3/t,平均1.78 m3/t;井深1088.10~1199.75 m泥岩夹泥质粉砂岩含气层111.6 m,气测全烃值最高可达28.2%,甲烷值最高为23.6%,13件泥岩、粉砂质泥岩样品现场解析总含气量0.90~4.55 m3/t,平均2.01 m3/t(图 1b),首次查明了湘中坳陷二叠系龙潭组非常规油气分布特点。
通过区域地质背景分析,并结合煤田区域地质资料,本研究认为滑脱断裂(F9)上下盘具有不同的页岩气聚集条件。滑脱断裂之上由一系列的同向逆断层形成的逆冲推覆体,地层变形强烈,且裂缝发育,导致页岩气保存条件变差。滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,地层平缓,不发育次级通天断裂,与下盘地层形成反向遮挡,易形成封闭,保存条件良好(图 1c)。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)二叠系大隆组岩性以硅质岩、硅质页岩为主,夹少量灰岩。主要含气段存在于上段硅质页岩段,厚88.2 m,含气量平均为4.85 m3/t,含气性优越,资源潜力大。
(2)二叠系龙潭组上段以致密砂岩气为主,含气量平均为1.78 m3/t;下段以页岩气为主,泥岩厚达177.47 m,含气量平均为2.01 m3/t,具有泥岩厚度大,含气性好等特征。
(3)保存条件是页岩气富集关键,构造改造弱的封闭演化环境有利于页岩气保存,研究区滑脱断裂下盘是页岩气主要富集区,易形成封闭,保存条件良好。
(4)湘邵地1井在二叠系大隆组和龙潭组获得良好的页岩气显示,证实了湘中地区二叠系具有良好的页岩气资源潜力,对湘中地区页岩气资源潜力评价具有重要意义。
5. 基金项目(Fund support)
本文为中国地质调查局项目“中扬子地区油气页岩气调查评价”(DD20221659)资助的成果。
-
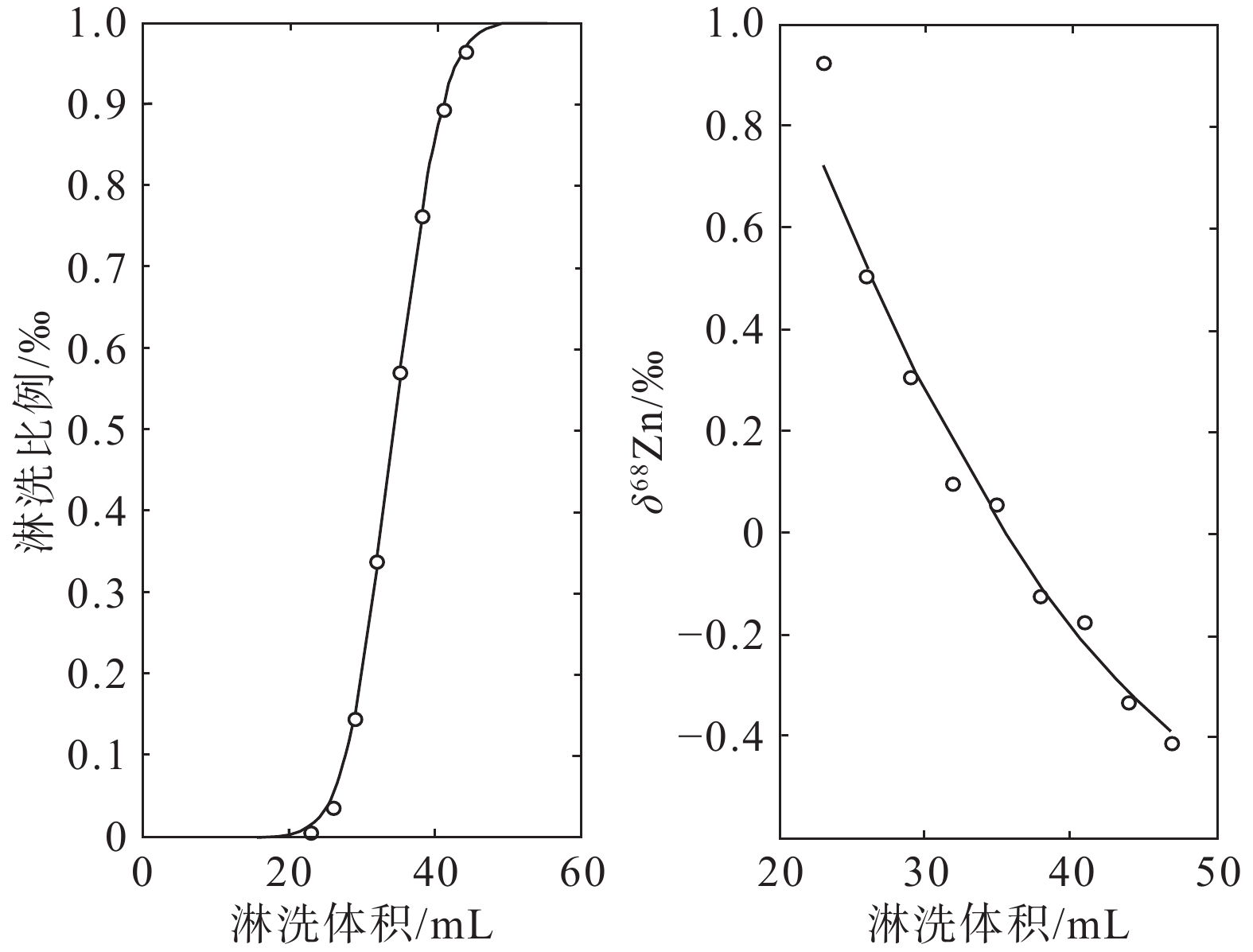
图 1 阴离子交换树脂法洗脱过程中的Zn同位素分馏(据Maréchal and Albaréde, 2002)
Figure 1. Zn isotope fractionation during anionexchange chromatography (after Maréchal and Albaréde, 2002)
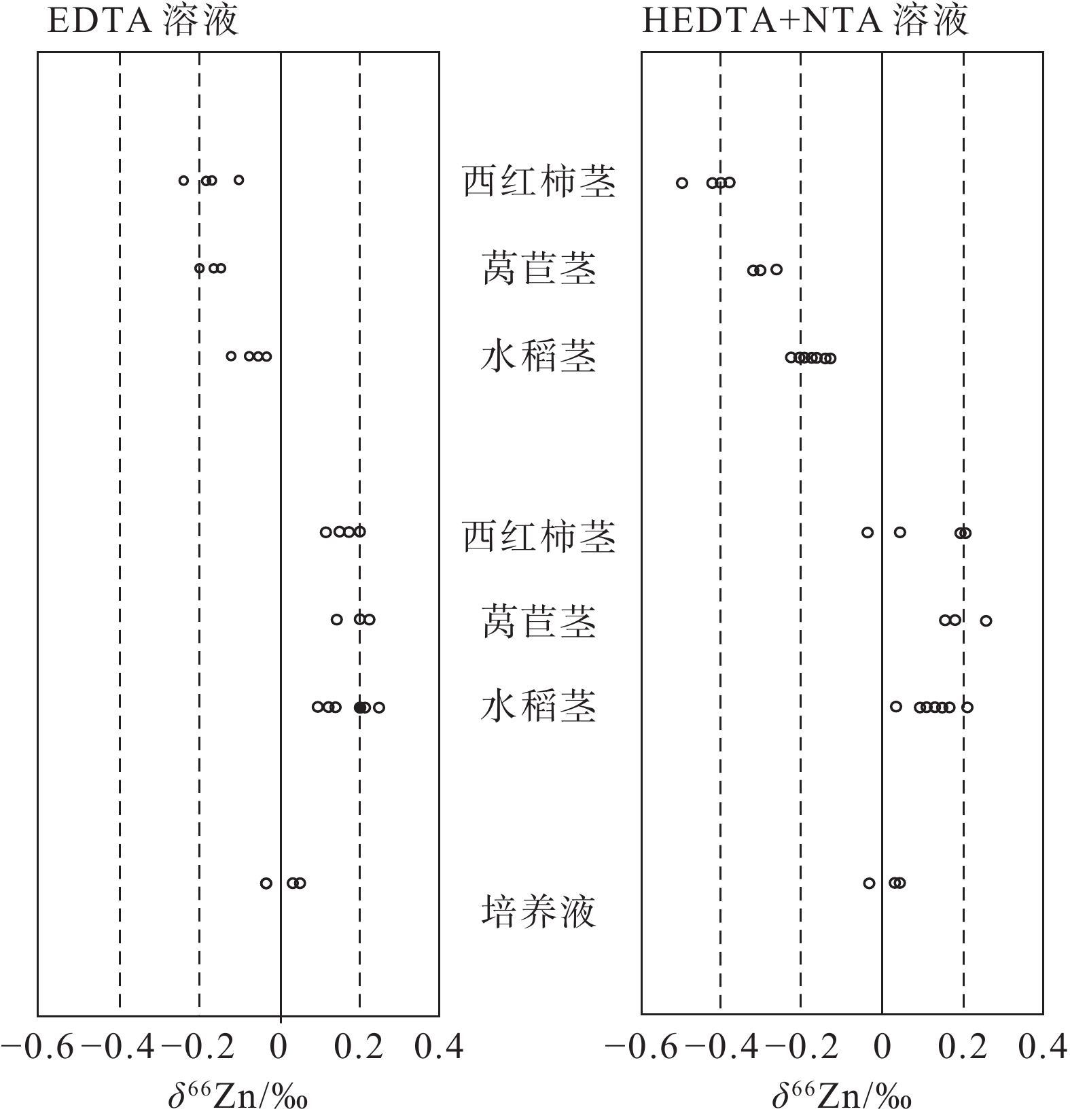
图 2 不同高等植物在培养液中的Zn同位素分馏(据Weiss et al., 2005)
Figure 2. Zn isotope fractionation of different higher plantsin nutrient solutions (after Weiss et al., 2005)
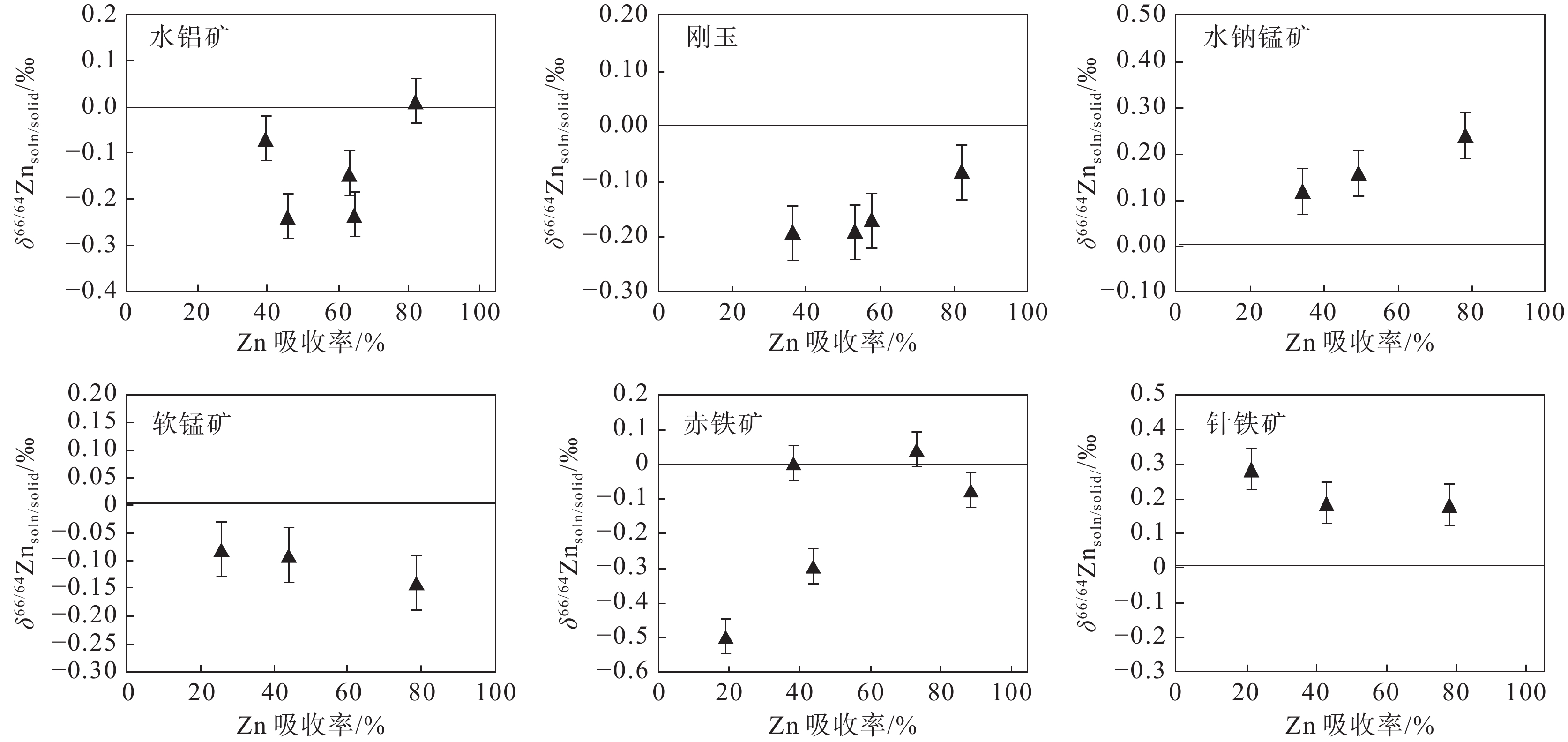
图 3 不同矿物吸附过程中的Zn同位素分馏(据Pokrovsky et al., 2005)
Figure 3. Zn isotope fractionation during adsorption on different minerals (after Pokrovsky et al., 2005)
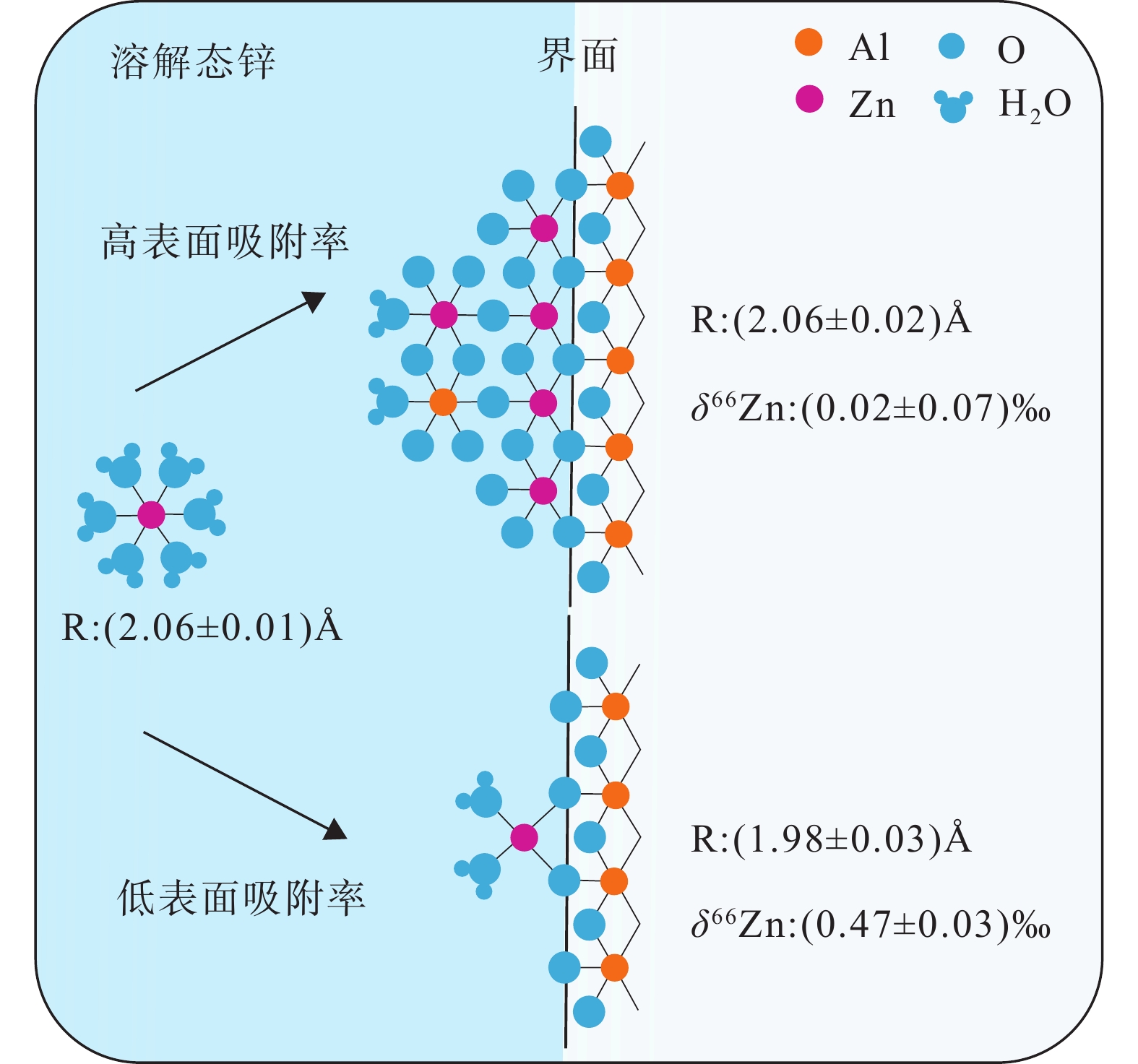
图 4 氧化铝吸附过程中的Zn同位素分馏(据Gou et al., 2018修改)
Figure 4. Zn isotope fractionation during adsorption on aluminum oxide (modified from Gou et al., 2018)
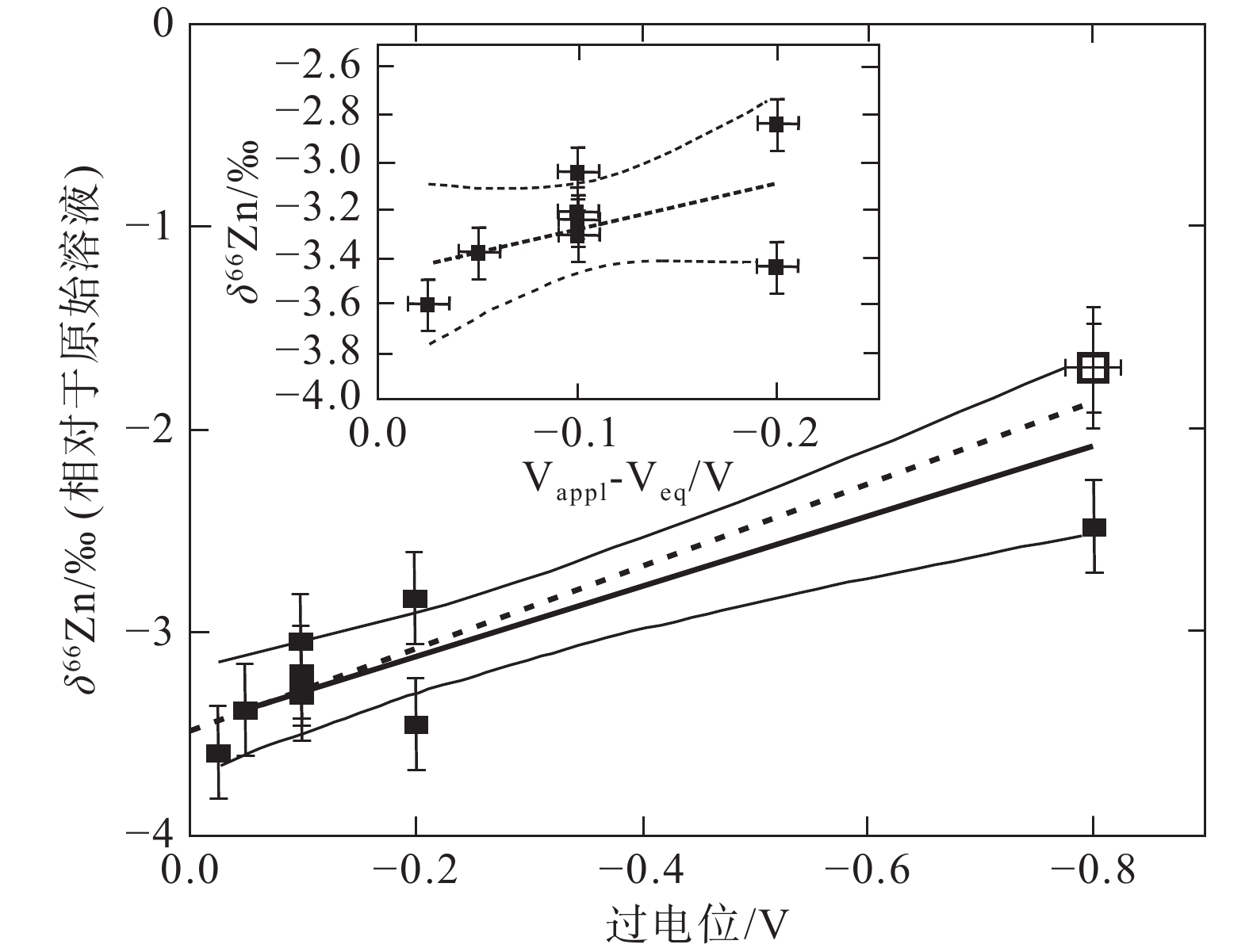
图 5 氧化还原反应电位变化过程中的Zn同位素分馏(据Kavner et al., 2008)
Figure 5. Zn isotope fractionation duringthe potential change process of redox reaction (after Kavner et al., 2008)
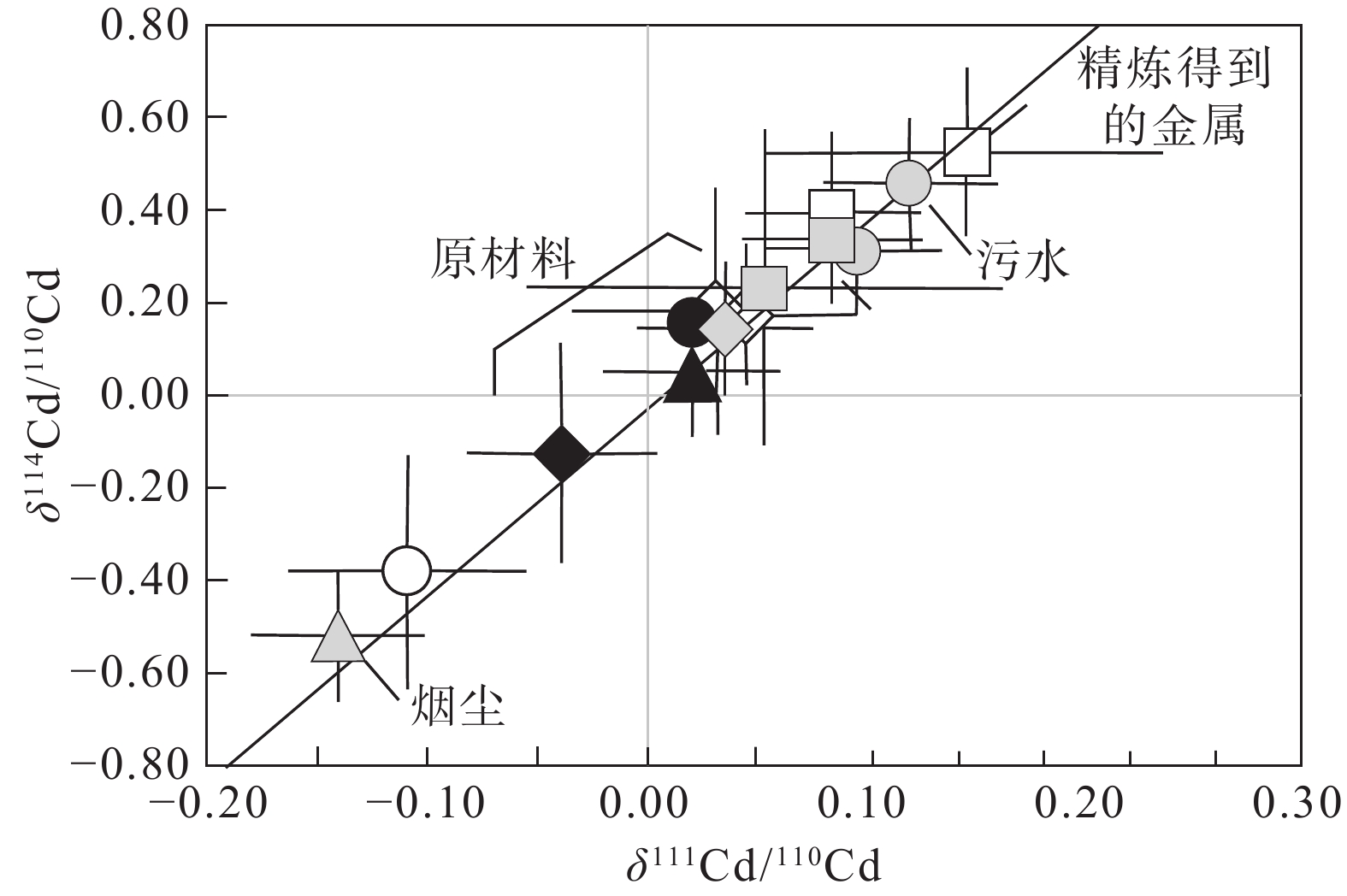
图 6 加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚省一冶炼厂样品中的Cd同位素分馏(据Shiel et al., 2010)
Figure 6. Cd isotope fractionation in samples from a smelter in British Columbia, Canada (after Shiel et al., 2010)
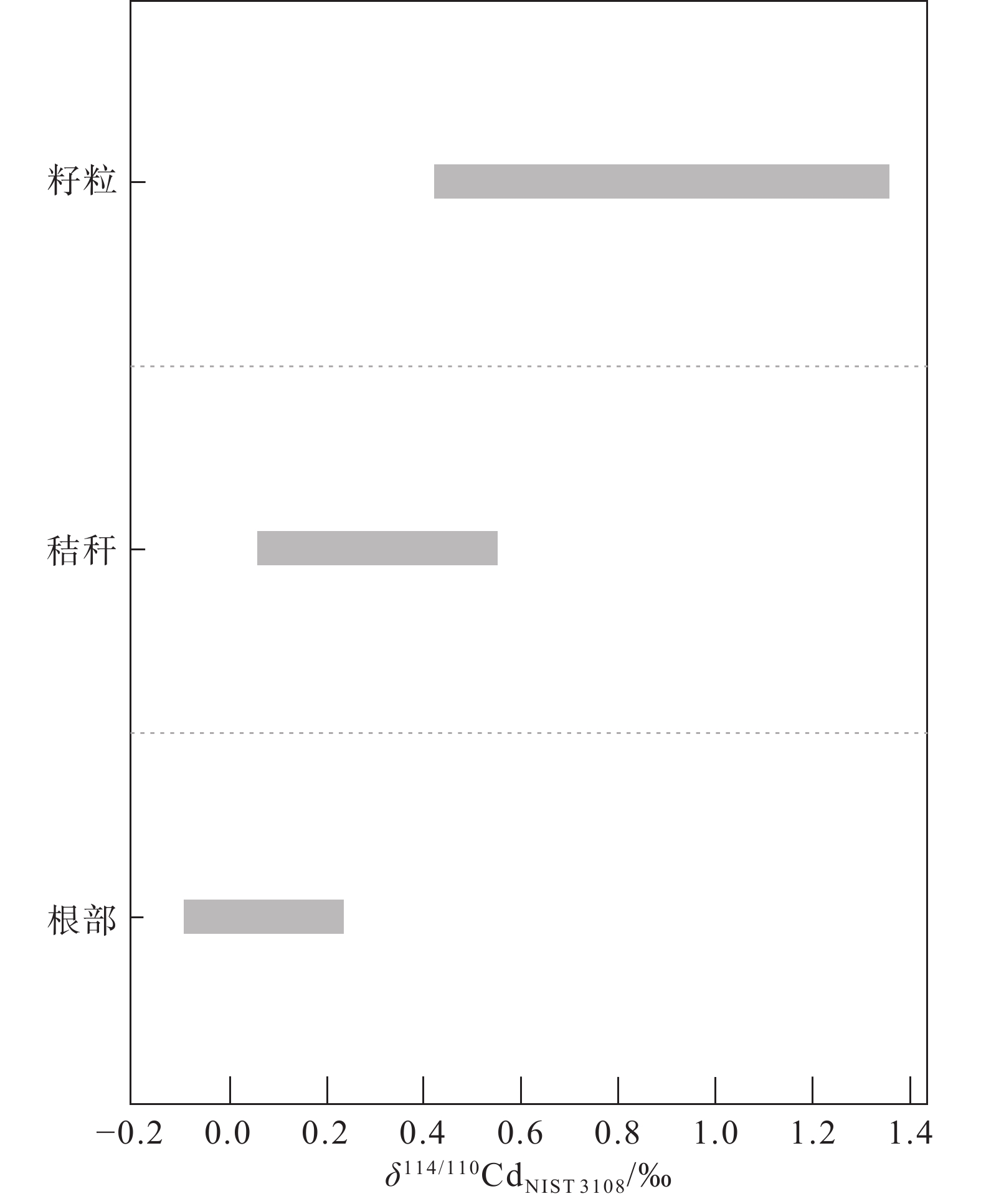
图 7 小麦不同部位的Cd同位素组成(据钟松雄等, 2021)
Figure 7. Isotope composition of the cadmium in the root, straw and grain of wheat (after Zhong Songxiong et al., 2021)
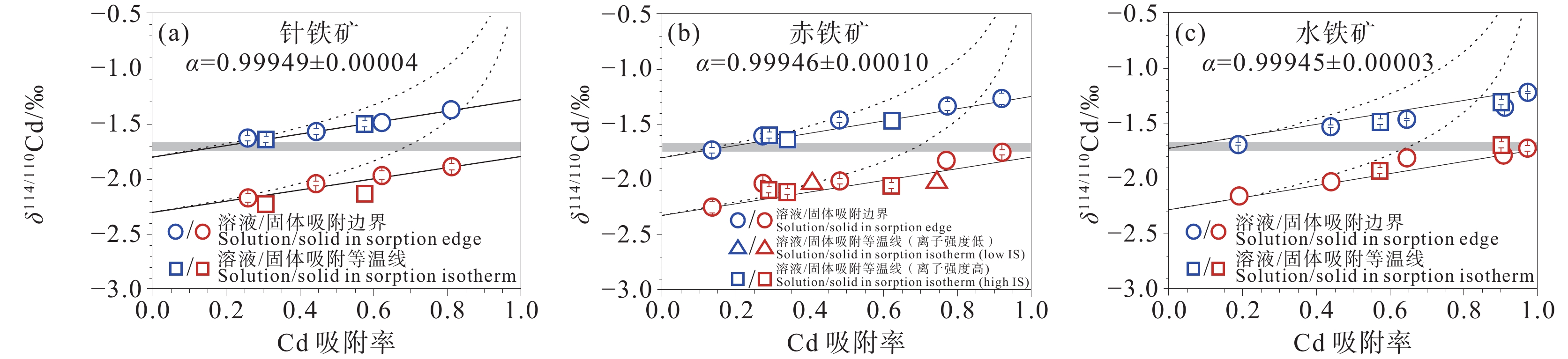
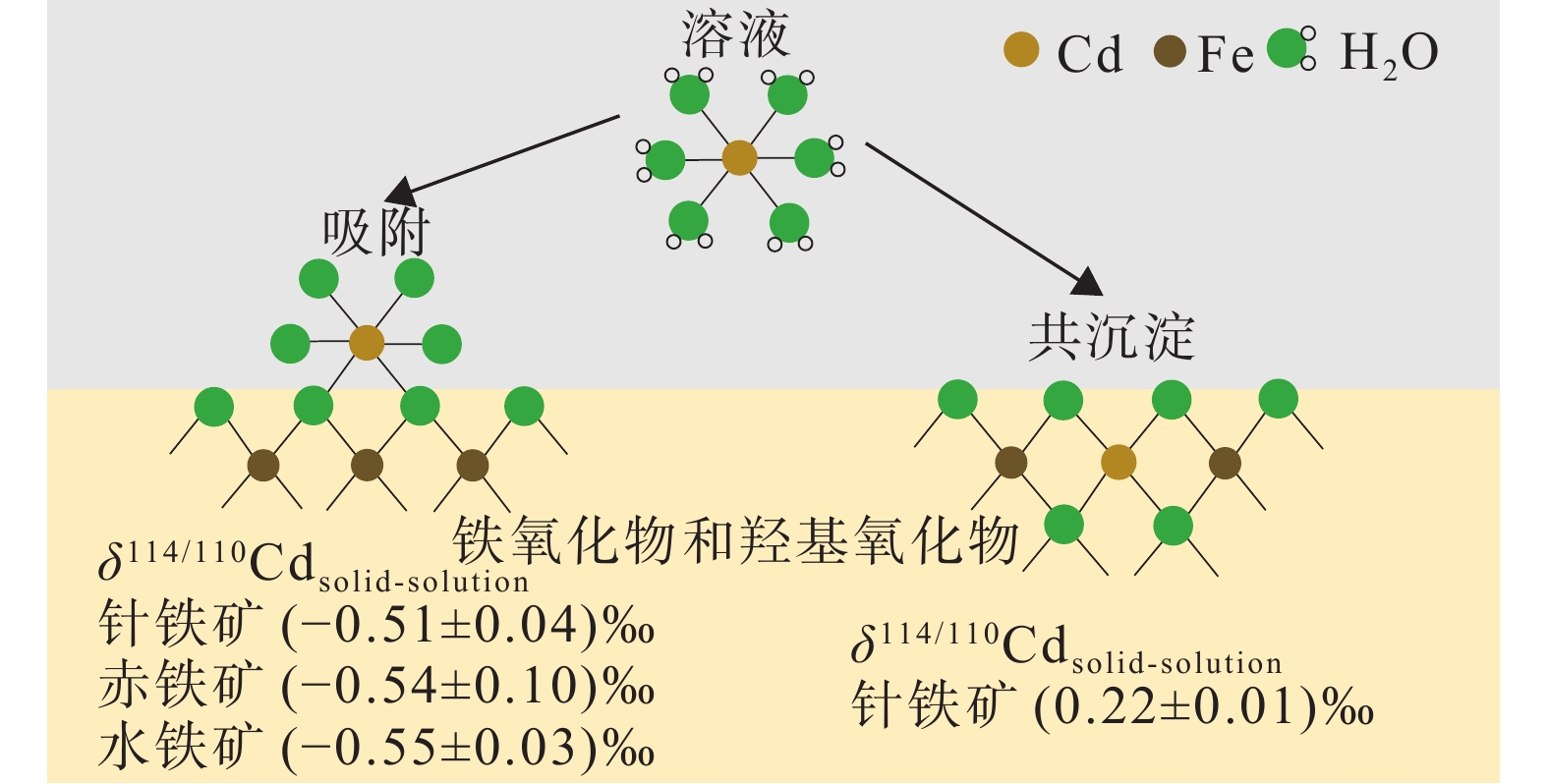
图 8 δ114/110Cdsolid–solution值与针铁矿(a)、赤铁矿(b)和水铁矿(c)表面Cd吸附率的函数关系(图形内部线条代表误差棒;据Yan et al., 2021)
Figure 8. Cd isotope compositions between solution and solid phases as the function of Cd–adsorbed fraction during adsorption onto goethite (a), hematite (b), and 2L ferrihydrite (c) (the lines inside the graphs represent error bars; after Yan et al., 2021)
图 9 铁氧化物和羟基氧化物吸附和共沉淀过程中的Cd同位素分馏(据Yan et al., 2021)
Figure 9. Cd isotope fractionation during adsorption and coprecipitation of iron (oxyhydr) oxides (after Yan et al., 2021)
图 10 陨石中的Zn同位素组成(据Brugier et al., 2019)
Figure 10. Zn isotopic composition of meteorites (after Brugier et al., 2019)
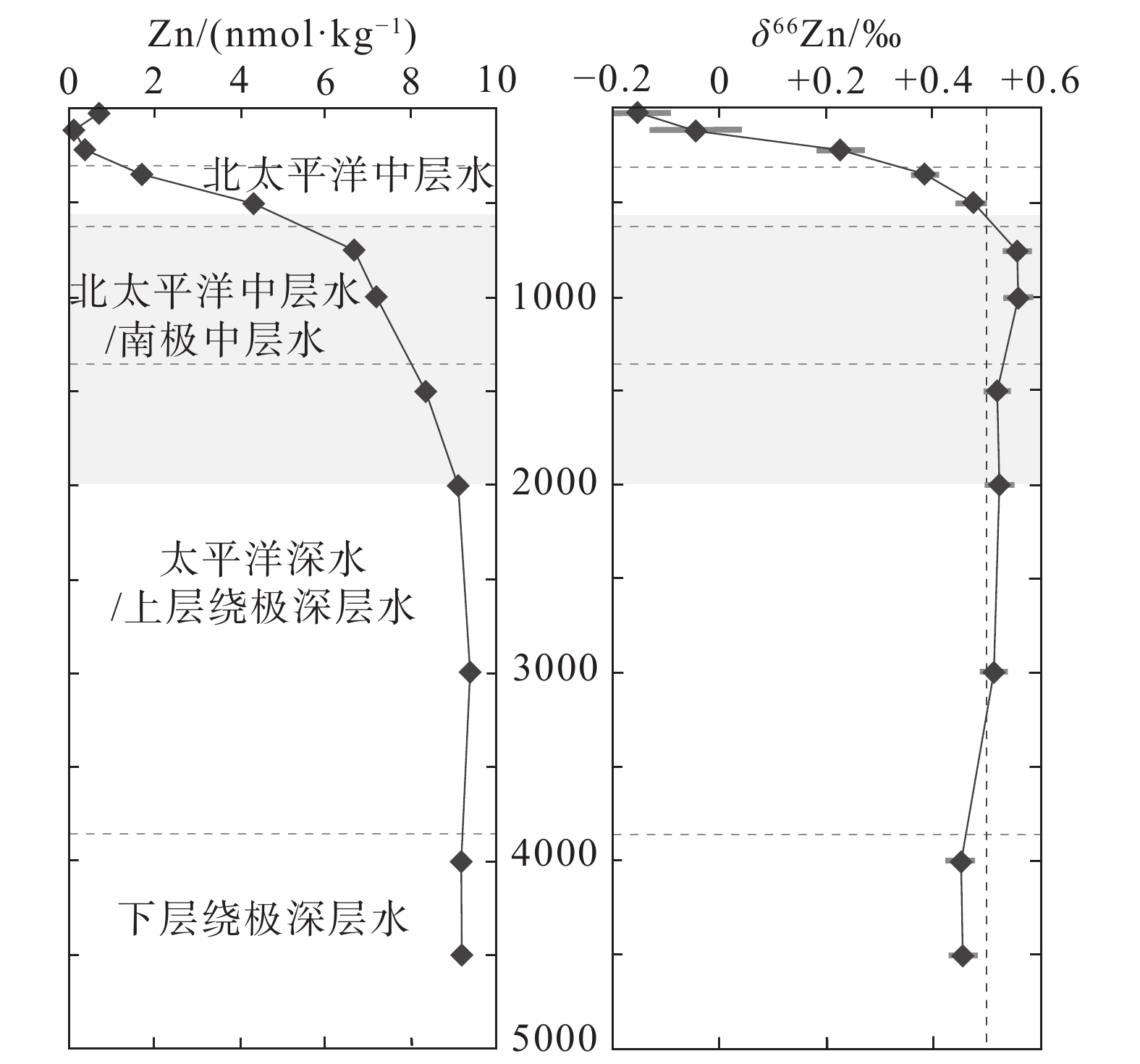
图 11 东北太平洋SAFe站(30°N 140°W)海水中的Zn浓度和δ66Zn值(据Conway and John, 2015)
Figure 11. Dissolved Zn concentrations and stable isotope ratio (δ66Zn) profiles from the SAFe station in the Northeast Pacific (30°N 140°W) (after Conway and John, 2015)
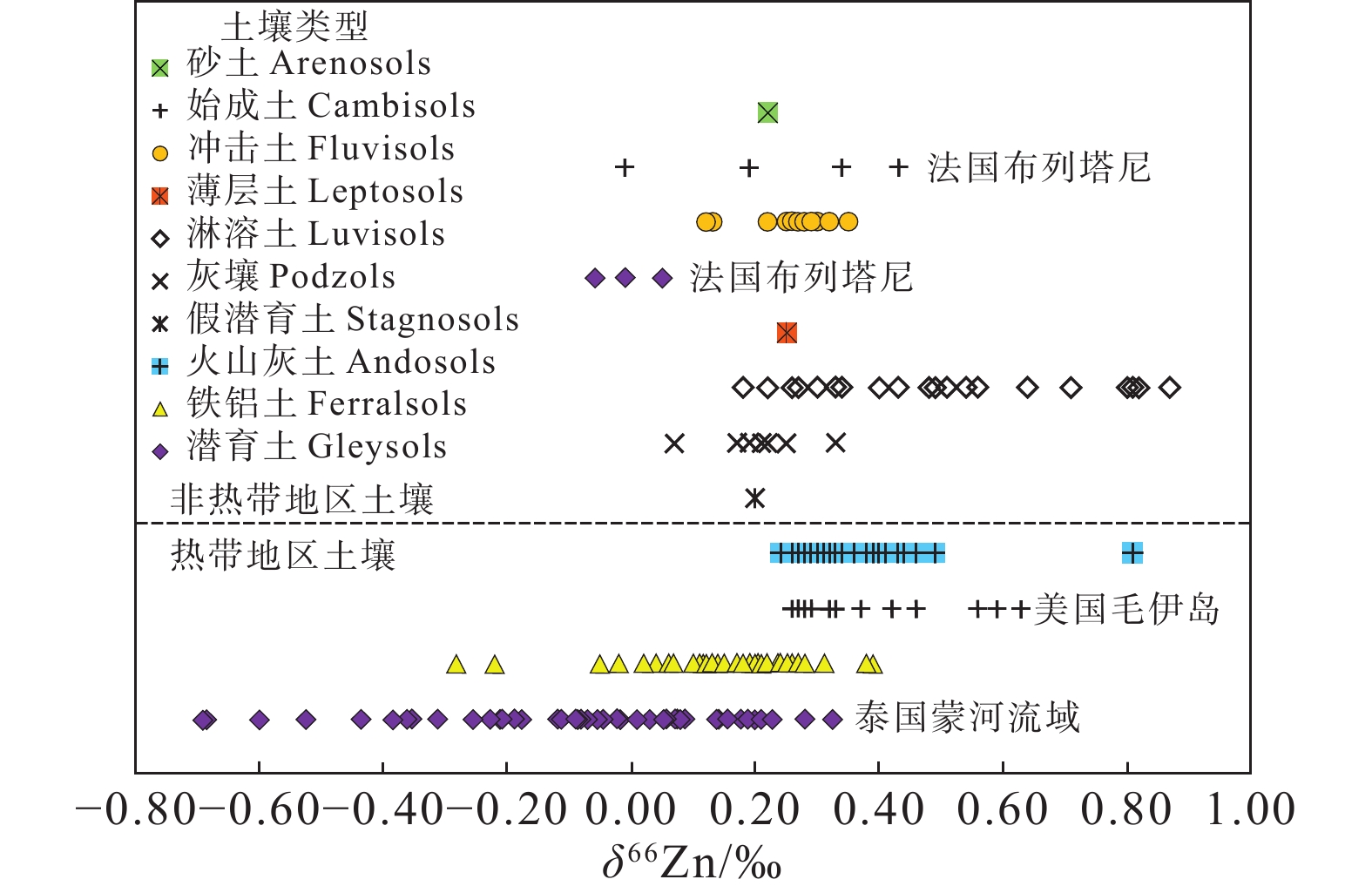
图 12 不同类型土壤的Zn同位素组成(据Liang et al., 2022)
Figure 12. δ66Zn variations in the different types of soils (after Liang et al., 2022)
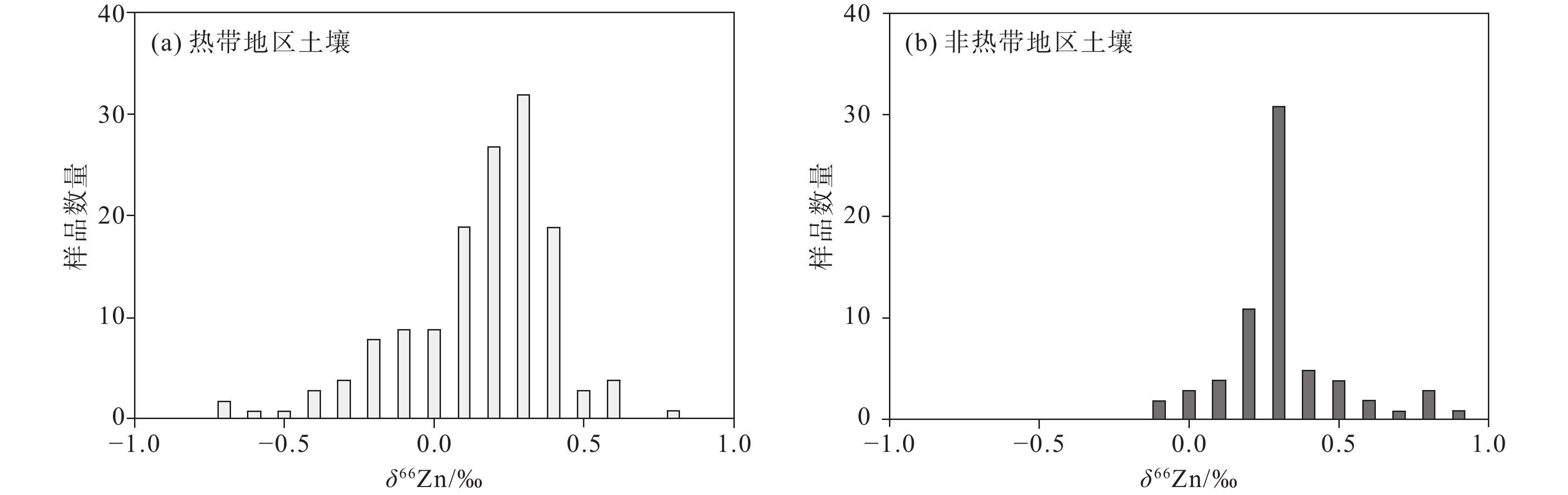
图 13 热带地区土壤(a)和非热带地区土壤(b)中的δ66Zn值频率分布(据Liang et al., 2022)
Figure 13. Frequency distribution of δ66Zn in the tropical soils (a) and non–tropical soils (b) (after Liang et al., 2022)
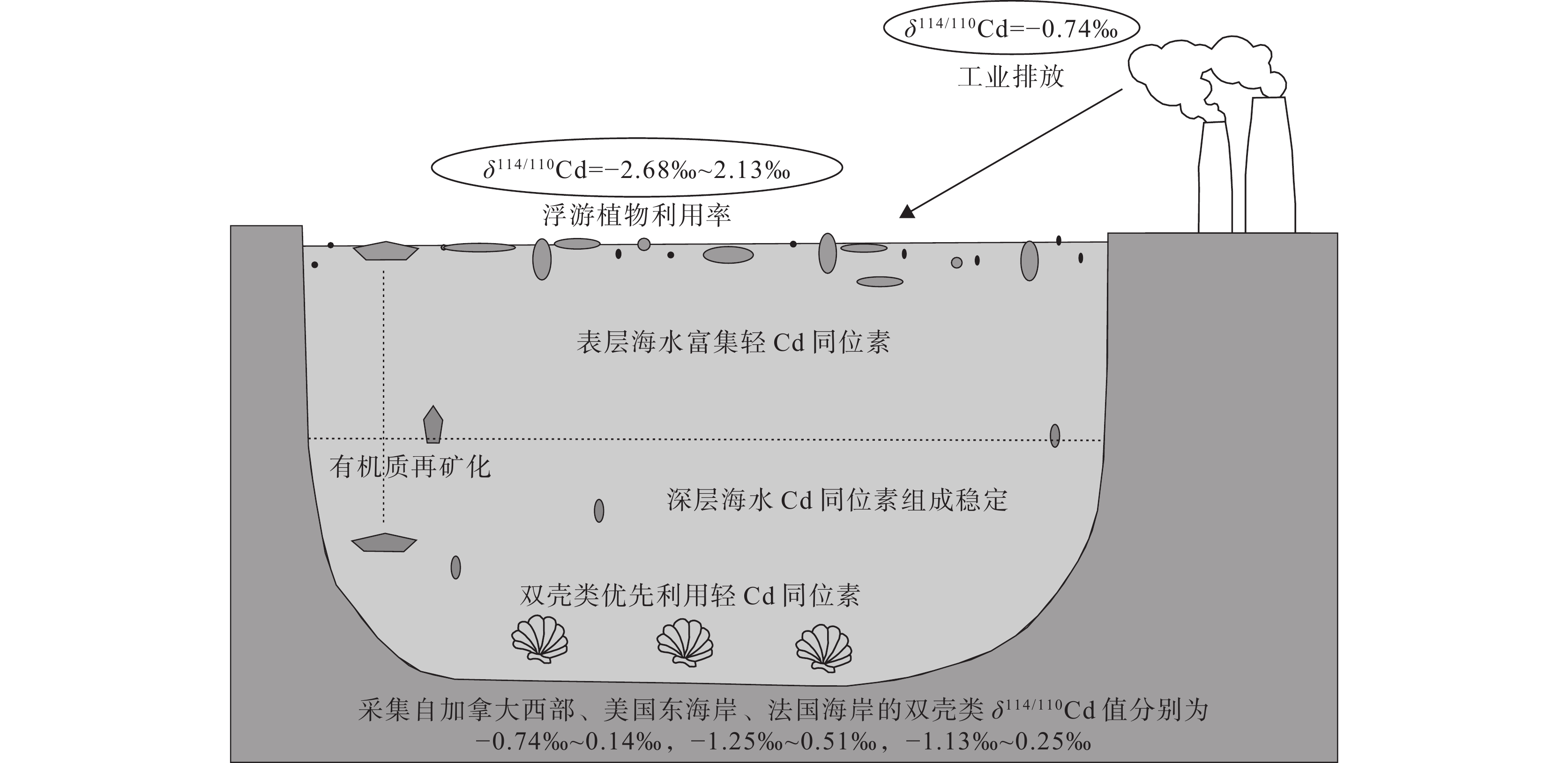
图 14 不同地区双壳类的Cd同位素组成(据Zhong et al., 2020)
Figure 14. Cadmium isotopic compositions of bivalves in the different areas (after Zhong et al., 2020)
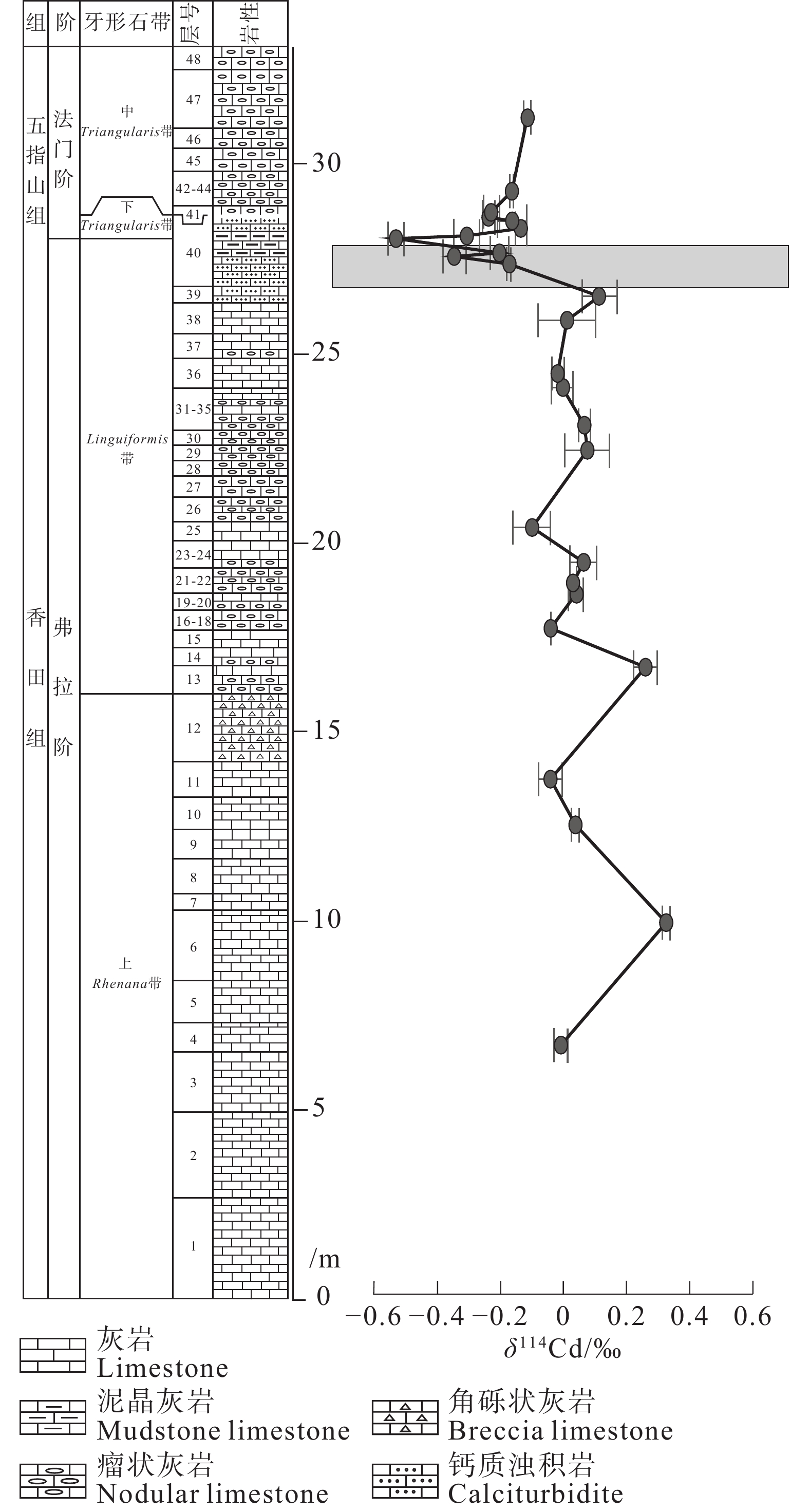
图 15 杨堤剖面F–F 之交δ114Cd演化图(据王伟中等, 2020)
Figure 15. Variations of δ114Cd of carbonates in the Yangdi profile across the FFB (after Wang Weizhong et al., 2020)
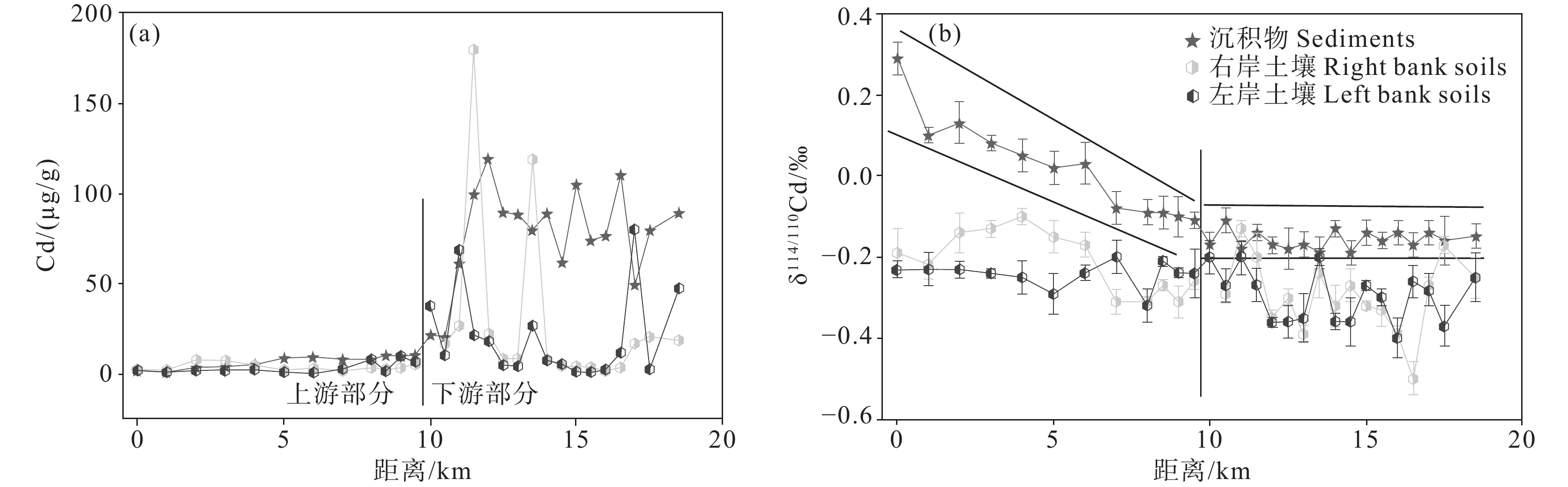
图 16 中国沘江河流沉积物和河岸土壤Cd浓度及同位素组成(据Zhang et al., 2016)
Figure 16. Cd concentrations and Cd isotopic compositions in the soil and stream sediment samples of the Bijiang River, China (after Zhang et al., 2016)
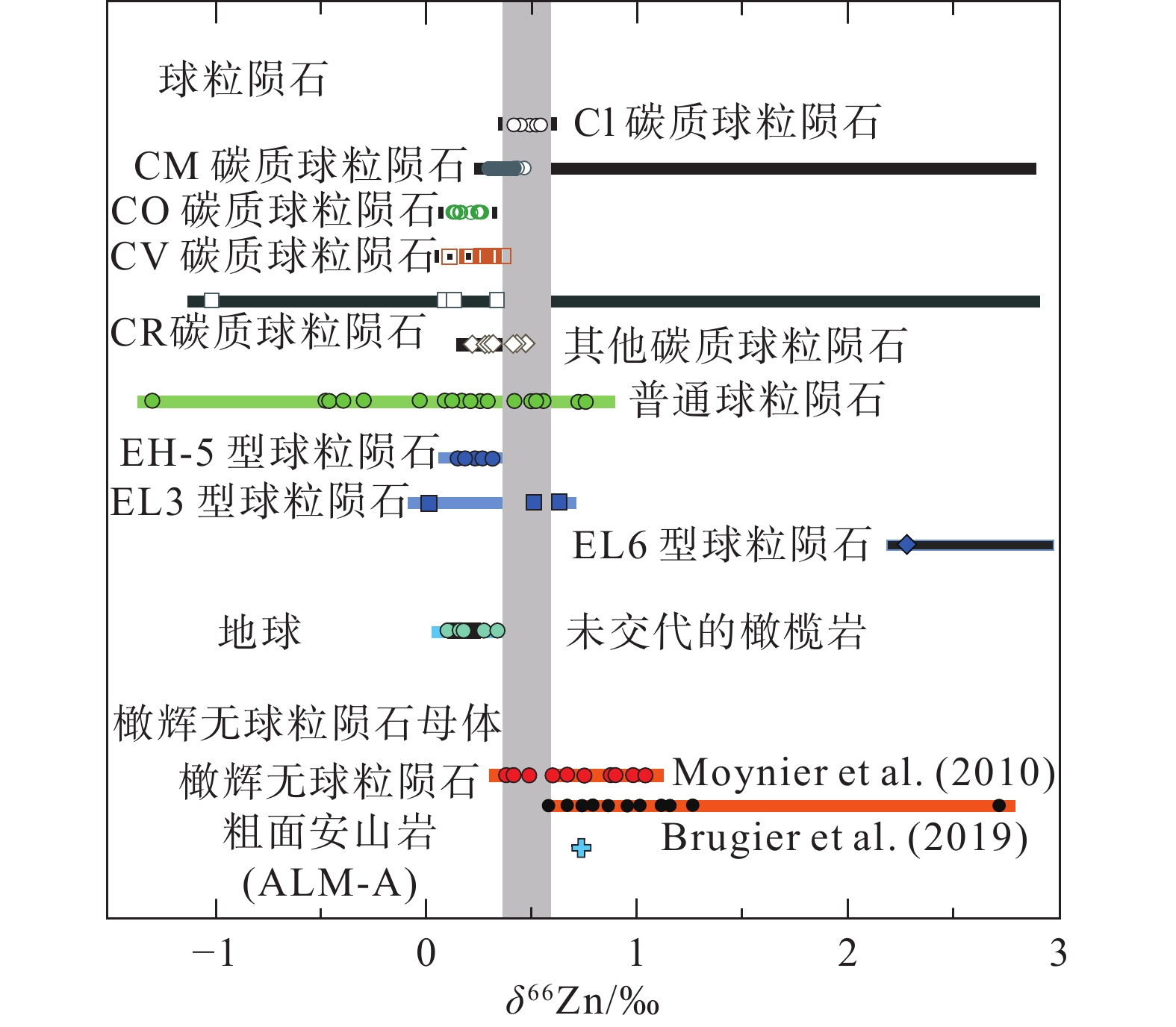
图 17 橄辉无球粒陨石中δ66Zn与锌同位素丰度的关系(据Moynier et al., 2010)
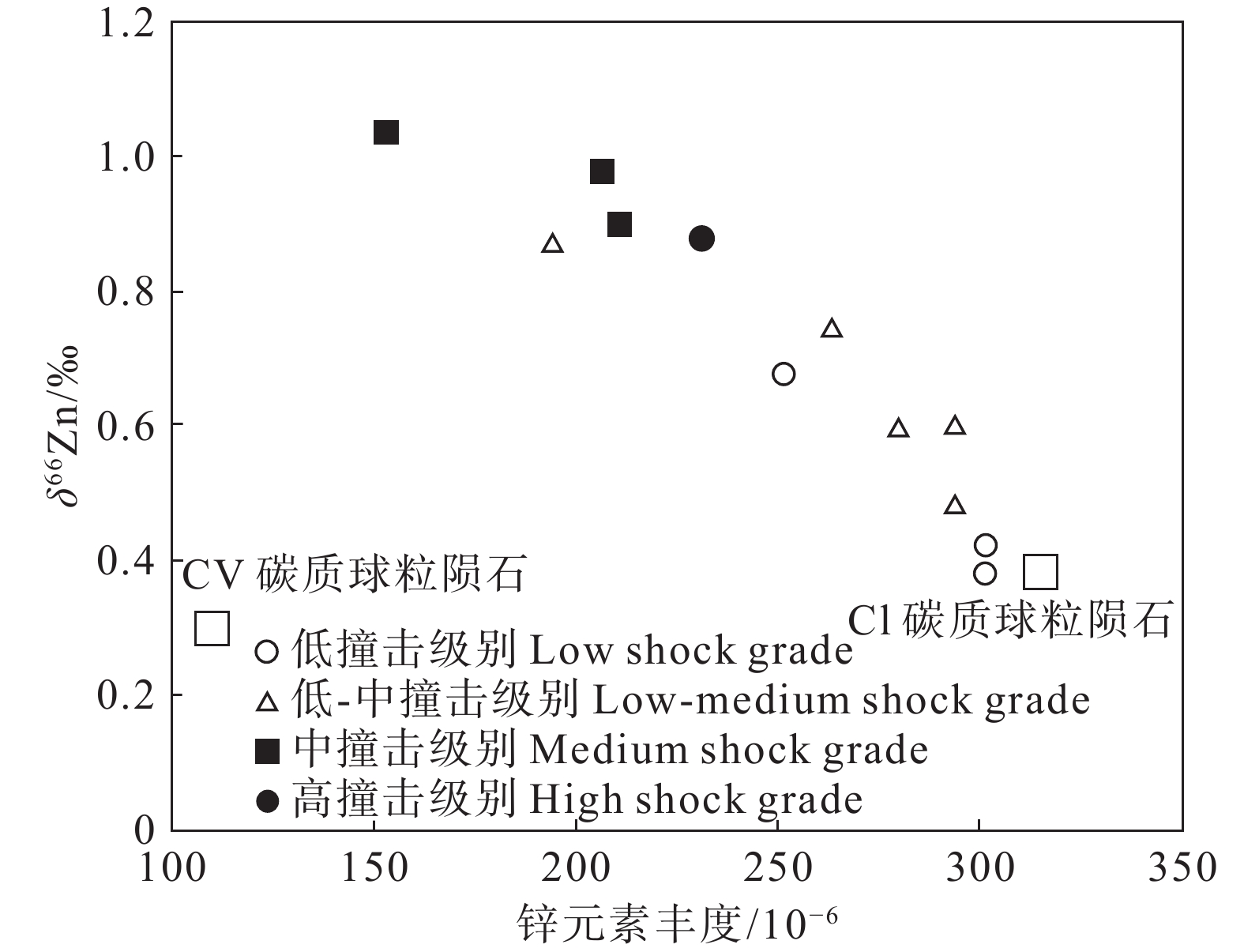
Figure 17. δ66Zn vs. abundance of Zn in ureilites. The ureilite samples are designatedwith their degree of shock (after Moynier et al., 2010)
图 18 月海玄武岩中δ66Zn与锌元素丰度的数据(据Dhaliwal et al., 2018)
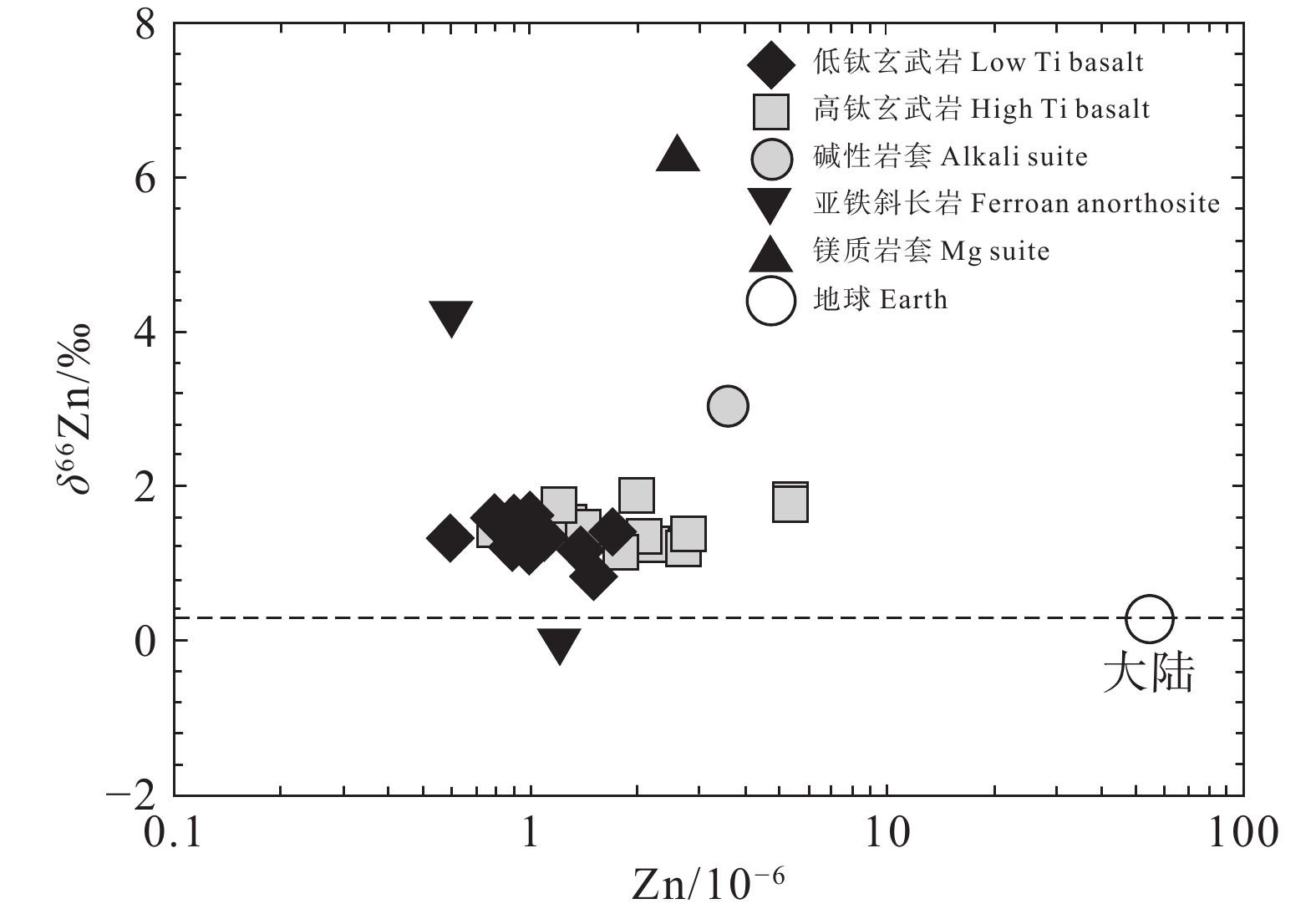
Figure 18. Zinc isotope vs. abundance data in the lunar samples (after Dhaliwal et al., 2018)
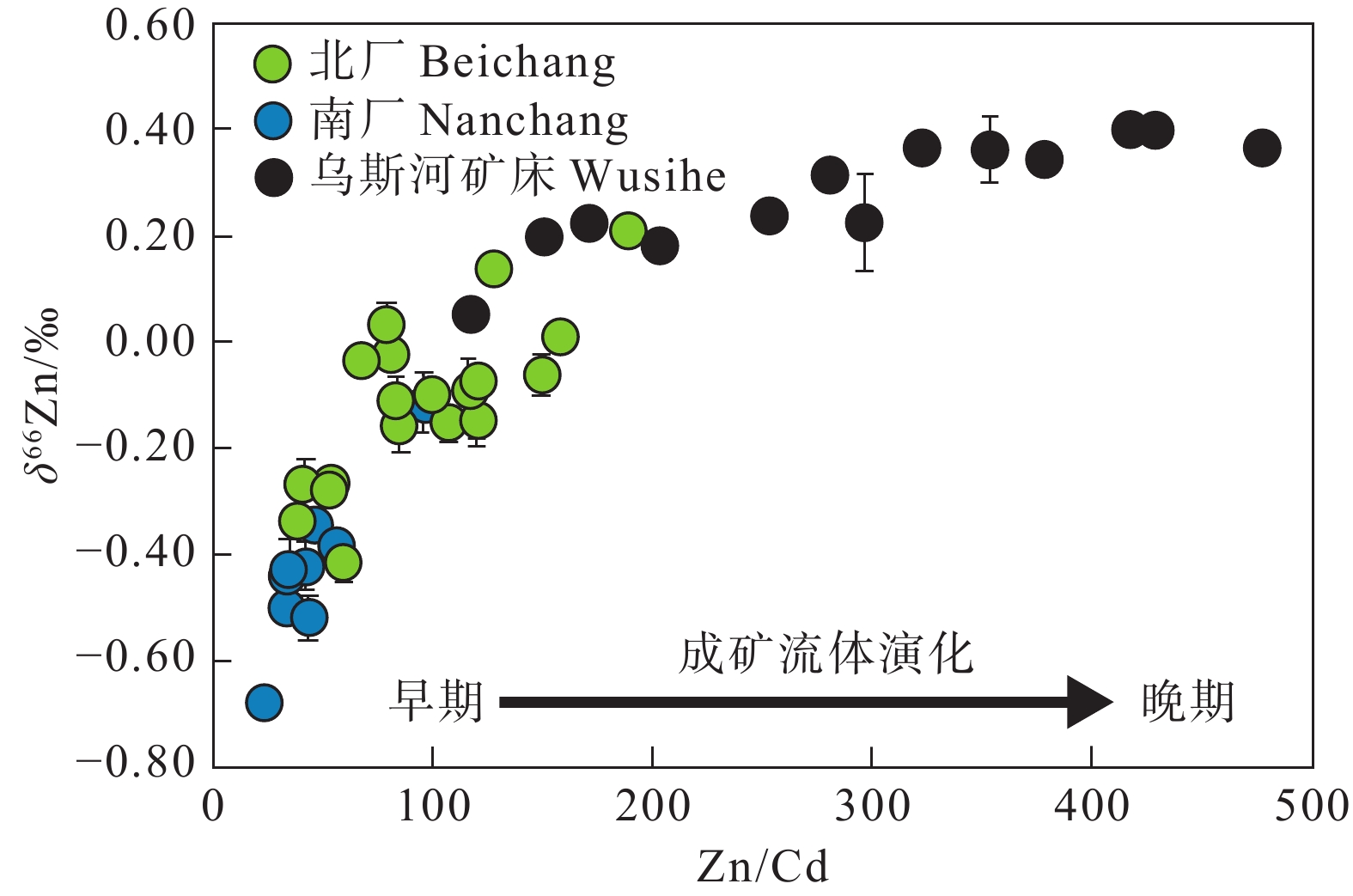
图 19 金顶矿床和乌斯河矿床中δ66Zn值与Zn/Cd值的关系(据Li et al., 2019)
Figure 19. Correlation between Zn/Cd ratios and δ66Zn of sphalerites in the Jinding and Wusihe Zn–Pb deposits (after Li et al., 2019)
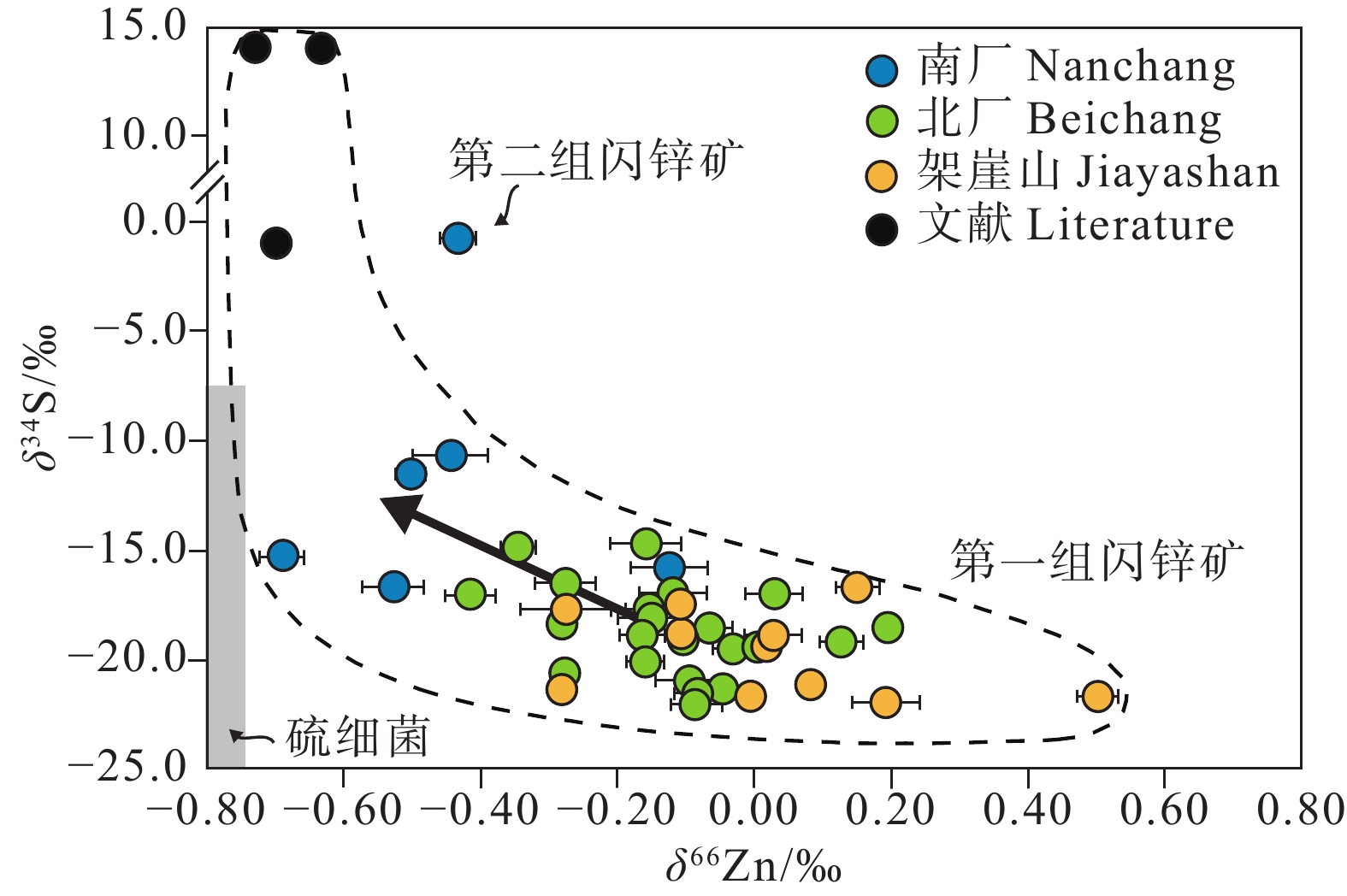
图 20 金顶矿床中δ66Zn值与δ34S值的关系(据Li et al., 2019)
注:除第2组闪锌矿外,第1组闪锌矿的δ66Zn值与δ34S值呈负相关。灰色框代表硫细菌的δ34S值范围,灰色箭头指向细菌代谢更强的方向。文献数据来源于Pašava et al. (2014)
Figure 20. Variation of zinc isotope ratios of sphalerites as a function of sulfur isotopic compositions (after Li et al., 2019)
The gray box represents δ34S ranges of bacteriogenic sulfur and the gray arrow points to the larger degree of bacterial metabolism (Li et al., 2019). Literature data in the figure are from Pašava et al. (2014)
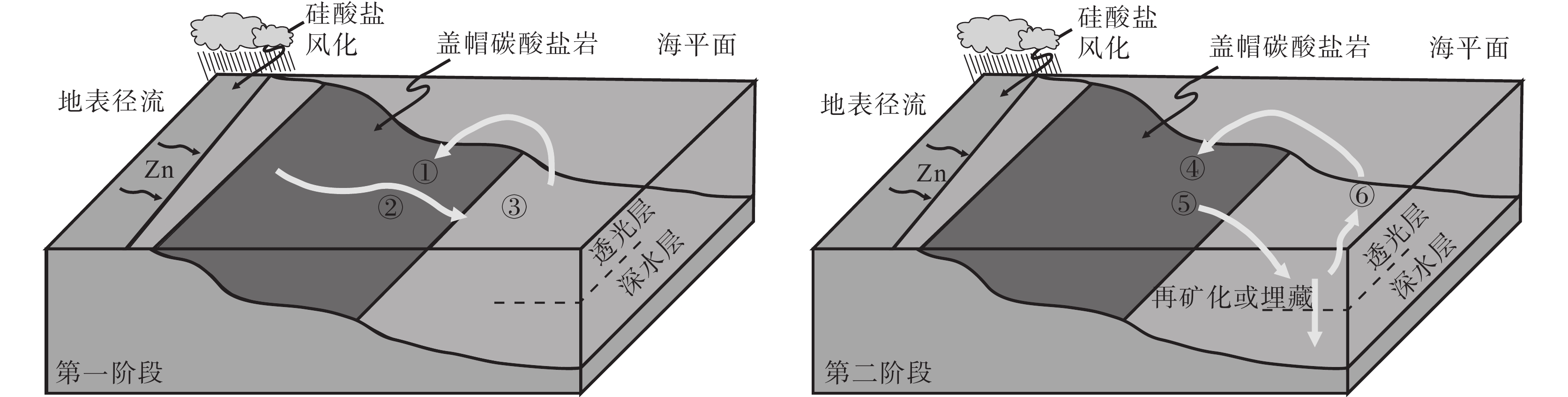
图 21 雪球事件后海洋和盖层白云岩的Zn同位素演化示意图(据Kunzmann et al., 2013)
①—66Zn亏损;②—运输66Zn贫化的锌同位素;③—66Zn贫化的表层海水;④—66Zn富集;⑤—初级生产者优先摄取64Zn;⑥—66Zn富集的表层海水
Figure 21. Schematic portrayal of the Zn isotope evolution of the post–snowball ocean and cap dolostones (after Kunzmann et al., 2013)
①−66Zn depleted caps; ②−Delivering of 66Zn–depleted zinc; ③−Surface ocean depleted in 66Zn; ④−66Zn enriched caps; ⑤−Preferential 64Zn−uptake by primary producers; ⑥−Surface ocean enriched in 66Zn
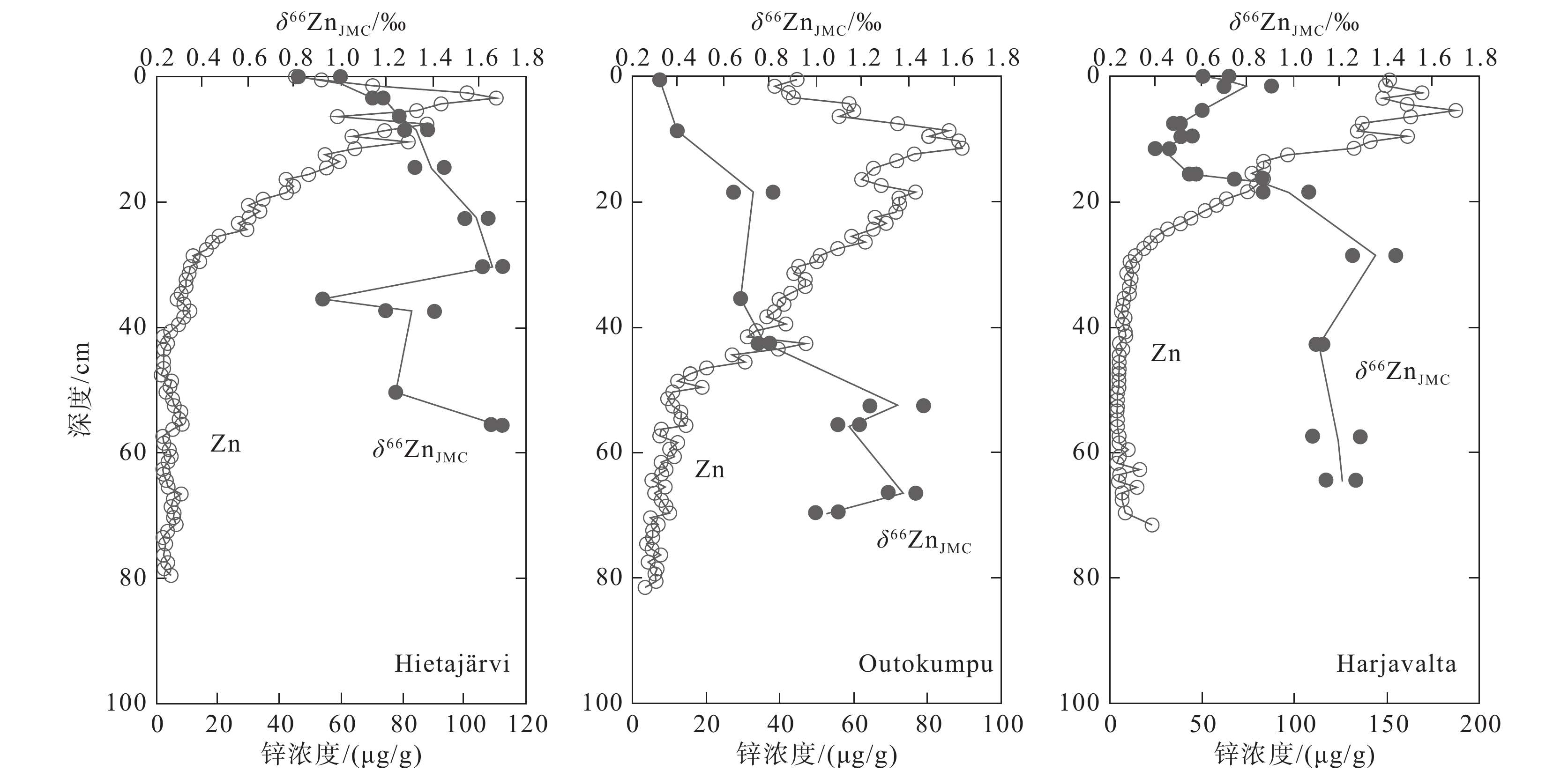
图 22 Hietajärvi、Outokumpu和Harjavalta三地泥炭样品的锌浓度和δ66ZnJMC值(据Weiss et al., 2007)
Figure 22. δ66ZnJMC and zinc concentrations measured in the peat samples at Hietajärvi Outokumpu and Harjavalta (after Weiss et al., 2007)
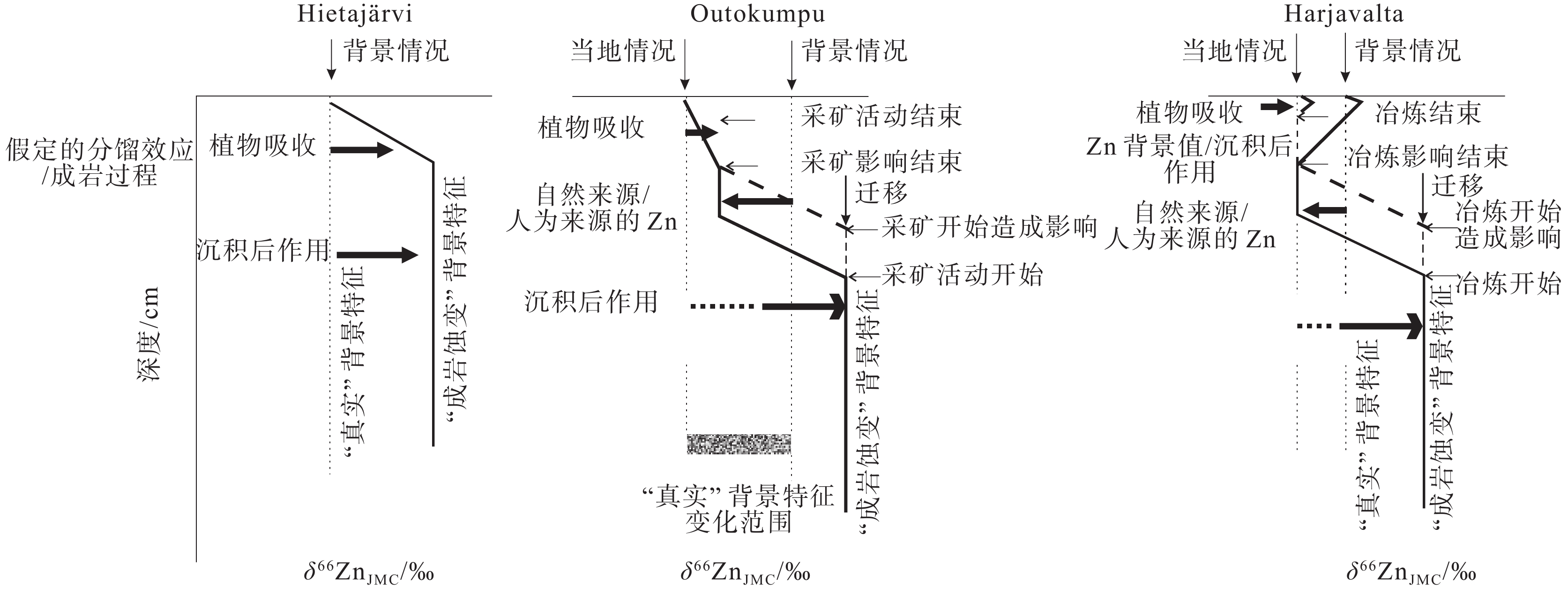
图 23 Hietajärvi、Outokumpu和Harjavalta三地泥炭样品δ66ZnJMC值变化过程及机制(据Weiss et al., 2007)
Figure 23. Processes and mechanisms of the observed isotopic variability of zinc in the peat samples at Hietajärvi Outokumpu and Harjavalta (after Weiss et al., 2007)
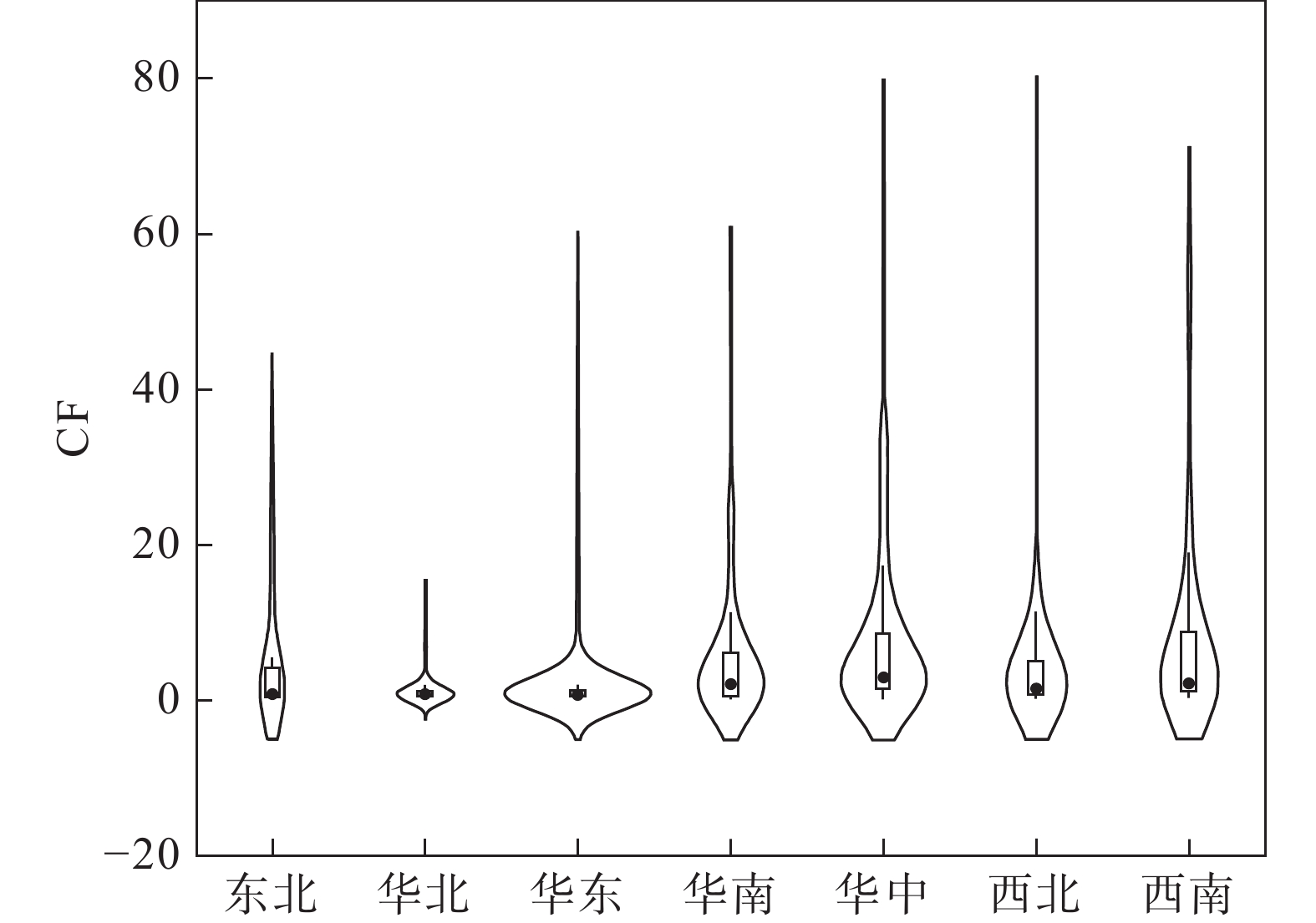
图 24 全国不同地区土壤Cd污染指数(据王静等, 2023)
Figure 24. Soil Cd pollution index in different regions of China (after Wang Jing et al., 2023)
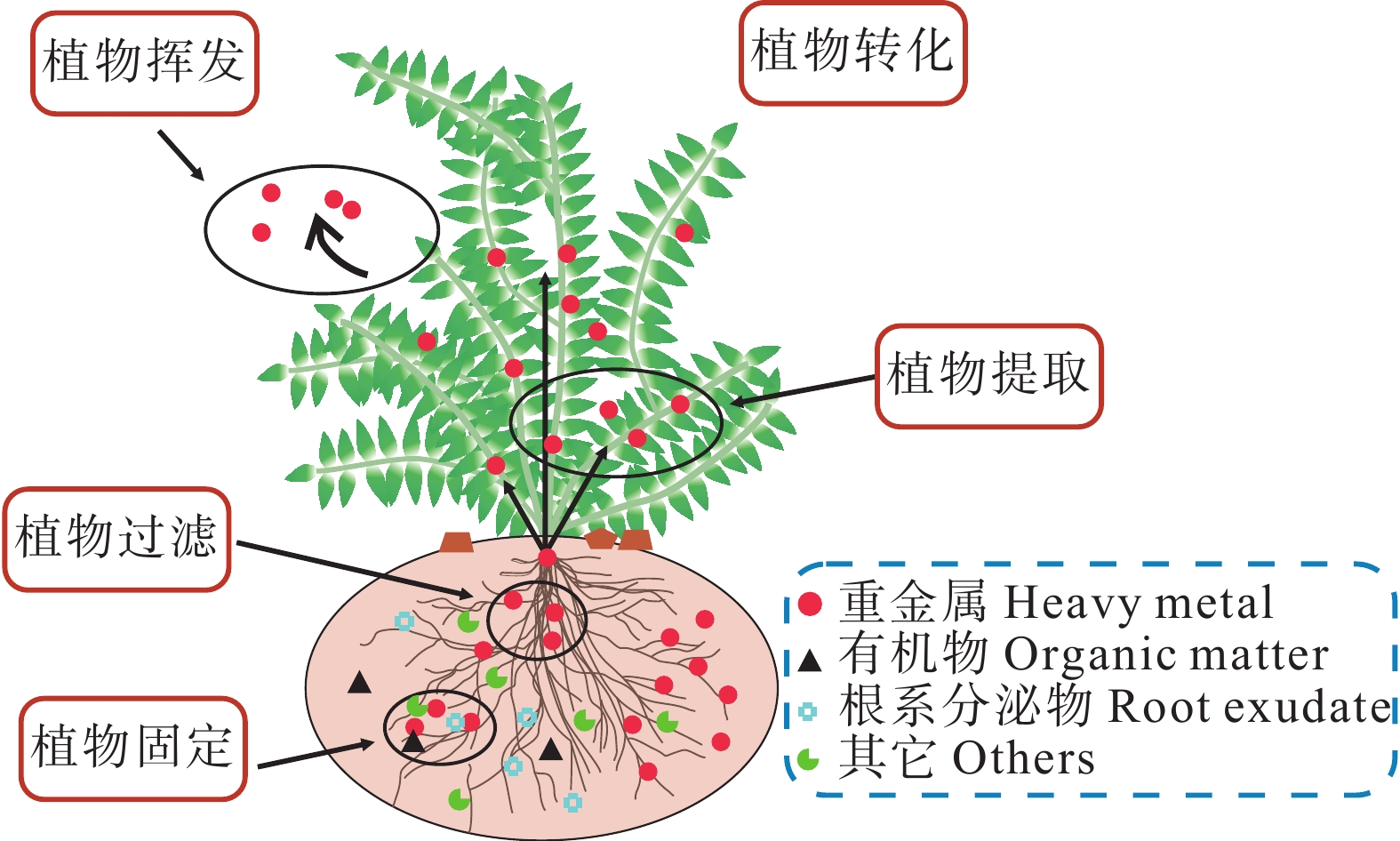
图 25 植物修复原理(据Shen et al., 2021)
Figure 25. Principles of phytoremediation (after Shen et al., 2021)
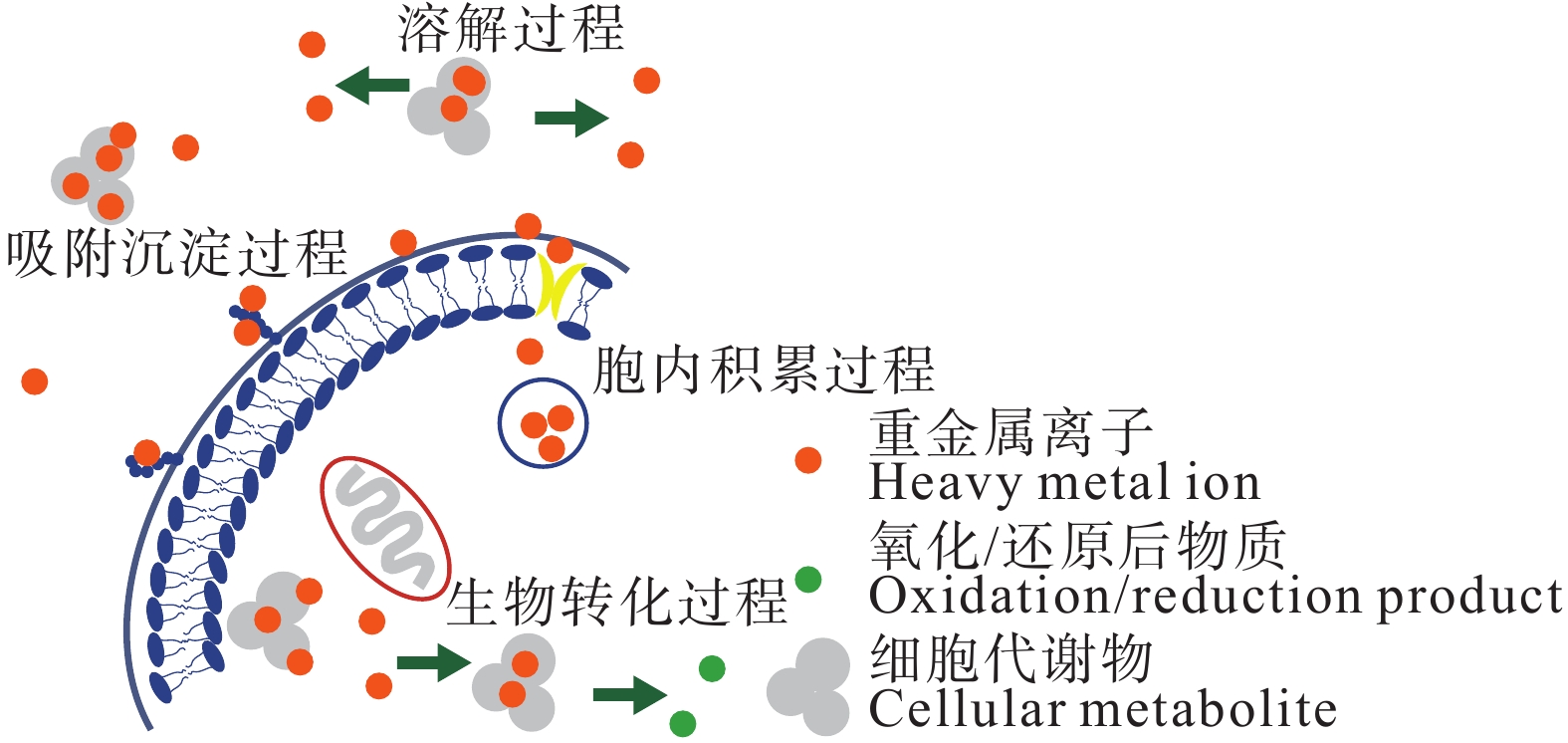
图 26 微生物修复原理(据常海伟等, 2018)
Figure 26. Principles of microbial remediation (after Chang Haiwei et al., 2018)
表 1 固体样品中Zn的消解方法
Table 1 Digestion methods of zinc in the solid samples
表 2 不同样品中Zn的分离纯化方法
Table 2 Separation and purification methods of zinc in the different samples
样品类型 树脂类型 淋洗酸种类 Zn回收率 文献来源 黄铜矿和闪锌矿 AG MP–1 HCl 100%±6% Maréchal et al. (1999) 玄武岩 AG MP–1
EichromTRUSpecHCl 100% Archer and Vance (2004) 硅酸盐、金属硫化物等 AG MP–1 HCl+HNO3 100%±5% Zhu et al. (2015) 海水 Chelex100 HNO3 100.8%±0.7% Bermin et al. (2006) 溪水 AG MP–1 HCl 100% Borrok et al. (2007) 雨水和河水 Chelex100
AG1–X4HNO3 100%±1% Chen et al. (2009b) 表 3 固体样品中Cd的消解方法
Table 3 Digestion method of cadmium in the solid samples
样品类型 消解方法 酸的种类 Cd回收率 文献来源 土壤、污泥和沉积物 微波消解法 HCl+ HNO3+HF 94%~102% Pallavicini et al. (2014) 富含有机物的基质 高温高压密闭消解法 HNO3 高温灰化法 HCl 植物 酸提取法 HF+HNO3+HClO4 >95% Wei et al. (2015) 煤灰、受污染的土壤、生活污泥、工业污泥 酸提取法 HNO3、HClO4、HCl和HF的不同组合 2.6%~89.1% Park et al. (2019) 全消解法 21.6%~88.7% 沉积物、大米 干法灰化法 HNO3 72.8%~97.0% 苗鑫等(2021) 酸提取法 HNO3+HCl 90.2%~98.0% 微波消解法 HNO3+HF 96.6%~99.8% 高温高压密闭消解法 HNO3+HF 97.6%~102% 表 4 不同样品中Cd的分离纯化方法
Table 4 Separation and purification methods of cadmium in the different samples
样品类型 分离方法 树脂类型 淋洗酸种类 Cd回收率 文献来源 陆源矿物 两步阴离子树脂分离 DowexAGI–X8 HCl 50% Rosman and De Laeter (1975) 岩石
陨石离子交换树脂双柱法 Biorad AG 1–X8
Eichrom TRU SpecHNO3+HCl+HBr 98% Wombacher et al. (2003) 土壤、
铁锰结核等离子交换树脂单柱法 AG MP–1 HCl >95% Cloquet et al. (2005) 河流沉积物 离子交换树脂单柱法 AG MP–1 HCl >90% Gao et al. (2008) 铅锌矿床矿物 离子交换树脂单柱法 AGMP–1M HCl 99.82% 朱传威等(2013, 2015) 海水 离子交换树脂双柱法 Chelex+AG MP–1 HCl+ HNO3+HBr 93% Lacan et al. (2006) 海水 离子交换树脂三柱法 Biorad AG 1–X8
Eichrom TRU SpecHCl >90% Ripperger and Rehkämper (2007) 海水 离子交换树脂三柱法 Biorad AG 1–X8+TRU HCl+H2O2+HNO3 >99% Gault–Ringold et al. (2012) 海水 离子交换树脂三柱法 Biorad AG 1–X8+TRU HCl+ HNO3+HBr >90% Yang et al. (2012) 低Cd含量
海水离子交换树脂三柱法 Biorad AG 1–X8
Eichrom TRU SpecHCl >85% Xue et al. (2012) 表 5 Zn、Cd同位素的质量歧视校正及测试精度
Table 5 Precision of Zn and Cd isotopic determination and instrument mass fractionation correction in literatures
目标元素 校正方法 ±2SD 资料来源 Zn Cu 0.04 Maréchal et al. (1999) SSB 0.07 Mason et al. (2005) 0.09 Archer and Vance(2004) DS 0.04~0.08 Bermin et al. (2006) Cd Ag、Sb 0.2~0.8 Wombacher et al. (2003) Ag 0.8 Lacan et al. (2006) 0.2~1 Pallavicini et al. (2014) SSB 1.0~1.5 Wombacher et al. (2004) 0.1~0.5 Cloquet et al. (2005) Cd106–Cd108DS 0.04 Abouchami et al. (2011) Cd111–Cd113 DS 0.13~0.2 Xue et al. (2012) 0.15 Martinková et al. (2016) 注:Ag、Sb分别表示Ag、Sb外标法;SSB表示标样–样品交叉法;DS表示双稀释剂法;2SD表示多次测定标准溶液所得数值的重现性(魏荣菲等, 2014),对于Zn和Cd分别代表δZn/amu和εCd/amu。 表 6 沘江河流沉积物和河岸土壤Cd同位素组成(据Zhang et al., 2016修改)
Table 6 Cd concentrations and Cd isotopic compositions of stream sediment and soil samples in the Bijiang River (modified from Zhang et al., 2016)
河流沉积物 左岸土壤 右岸土壤 距离/km 样品编号 δ114/110Cd/‰ 样品编号 δ114/110Cd/‰ 样品编号 δ114/110Cd/‰ SSD–1 0.29±0.04 LS–1 –0.23±0.02 RS–1 –0.19±0.06 0 SSD–2 0.10±0.02 LS–2 –0.23±0.04 RS–2 –0.22±0.01 1 SSD–3 0.13±0.05 LS–3 –0.23±0.02 RS–3 –0.14±0.05 2 SSD–4 0.08±0.02 LS–4 –0.24±0.01 RS–4 –0.13±0.02 3 SSD–5 0.05±0.04 LS–5 –0.25±0.04 RS–5 –0.10±0.02 4 SSD–6 0.02±0.04 LS–6 –0.29±0.05 RS–6 –0.15±0.04 5 SSD–7 0.03±0.05 LS–7 –0.24±0.02 RS–7 –0.17±0.03 6 SSD–8 –0.08±0.04 LS–8 –0.20±0.04 RS–8 –0.31±0.03 7 SSD–9 –0.09±0.03 LS–9 –0.32±0.04 RS–9 –0.31±0.01 8 SSD–10 –0.09±0.04 LS–10 –0.21±0.01 RS–10 –0.27±0.01 8.8 SSD–11 –0.10±0.05 LS–11 –0.24±0.01 RS–11 –0.31±0.04 9 SSD–12 –0.11±0.02 LS–12 –0.24±0.06 RS–12 –0.26±0.02 9.5 SSD–13 –0.17±0.02 LS–13 –0.20±0.04 10 SSD–14 –0.11±0.03 LS–14 –0.27±0.04 RS–14 –0.29±0.02 10.5 SSD–15 –0.18±0.02 LS–15 –0.20±0.04 RS–15 –0.13±0.02 11 SSD–16 –0.14±0.02 LS–16 –0.27±0.04 RS–16 –0.20±0.06 11.5 表 7 自然界不同储库中的Zn同位素的组成
Table 7 Isotopic compositions of Zn in the different reservoirs
地质体 δ66Zn值 资料来源 变化范围 均值 天体
陨石碳质球粒陨石 +0.16‰~+0.52‰ +0.37‰ Luck et al. (2006) 普通球粒陨石 –1.30‰~+0.76‰ +0.10‰ 铁陨石 –0.59‰~+3.68‰ +1.34‰ 顽火辉石球粒陨石 +0.01‰~+7.35‰ — Moynier et al. (2017) 橄辉无球粒陨石 +0.40‰~+2.71‰ +0.85‰ Brugier et al. (2019) 月壤 +2.18‰~+6.39‰ +0.46‰ Moynier et al. (2006) 月海玄武岩 +0.17‰~+0.75‰ +3.89‰ 地幔 火山岩 +0.28‰±0.05‰ +0.28‰ Chen et al. (2013) 橄榄岩 +0.18‰±0.06‰ +0.18‰ Wang et al. (2016) 橄榄岩、科马提岩 +0.16‰±0.06‰ +0.16‰ Sossi et al. (2017) 苦橄岩 +0.20‰±0.03‰ +0.20‰ Mccoy–West et al. (2018) 上地壳 黑山页岩 +0.20‰~+0.32‰ +0.26‰ Maréchal et al. (2000) 地中海腐泥 +0.26‰~+0.29‰ +0.28‰ 海相碳酸盐岩 +0.32‰~+1.34‰ +0.91‰ Pichat et al. (2003) 黄土 +0.17‰±0.30‰ +0.24‰ Zhang et al. (2022a) 下地壳 麻粒岩、下地壳捕虏体 +0.28‰±0.04‰ +0.28‰ Zhang et al. (2020) 水圈 巴黎市区雨水 — +0.17‰ Chen et al. (2008, 2009a) 巴黎市区屋顶径流 –0.07‰~–0.02‰ –0.04‰ 巴黎市区污水 –0.03‰~+0.28‰ +0.11‰ 塞纳河流域 +0.07‰~+0.58‰ — 河流 –0.12‰~+0.88‰ +0.38‰ Little et al. (2014) 中欧雪样 –0.60‰~+0.68‰ — Voldrichova et al. (2014) 中欧冰样 –0.67‰~+0.14‰ — 生物圈 喀麦隆南部植物、枯枝落叶 –0.91‰~+0.75‰ +0.31‰ Viers et al. (2007) 绵羊骨骼 +0.36‰~+0.53‰ +0.45‰ Balter et al. (2010) 绵羊红细胞 –0.13‰~–0.01‰ –0.06‰ 绵羊血清 +0.41‰~+0.57‰ +0.49‰ 绵羊肝脏 –0.67‰~–0.34‰ –0.45‰ 绵羊肾脏 –0.36‰~+0.03‰ –0.11‰ 绵羊肌肉 +0.26‰~+0.59‰ +0.46‰ 绵羊粪便 +0.15‰~+0.19‰ +0.17‰ 绵羊尿液 +0.17‰~+0.47‰ +0.37‰ 杂食者血液 +0.12‰±0.07‰ +0.12‰ Costas–Rodriguez et al. (2013) 素食者血液 +0.26‰±0.04‰ +0.26‰ 表 8 自然界不同储库中的Cd同位素的组成
Table 8 Isotopic compositions of Cd in the different reservoirs
地质体 δ114/110Cd值 资料来源 变化范围 均值 天体
陨石普通球粒陨石 –9.2‰~+15.0‰ +3.1‰ Wombacher et al. (2008) 碳质球粒陨石 –3.9‰~+4.5‰ –0.1‰ 顽火辉石球粒陨石 –0.7‰~+16.0‰ +3.3‰ 辉石无球粒陨石 –0.8‰~–0.3‰ –0.6‰ 月球样品 +1.1‰~+11.3‰ +7.6‰ 海水 南海北部深水层 +0.34‰±0.05‰ +0.34‰ Yang et al. (2012) 双壳类 英吉利海峡 –0.88‰~–0.20‰ –0.54‰ Shiel et al. (2013) 大西洋 –1.08‰~–0.62‰ –0.88‰ 地中海 –0.51‰~–0.27‰ –0.43‰ 表 9 部分陨石及月球样品中的Cd同位素组成(据Wombacher et al., 2008修改)
Table 9 Cd isotope composition of some meteorites and lunar samples (modified from Wombacher et al., 2008)
陨石类型 δ114/110Cd值/‰ 碳质球粒陨石 Orgueil C1 regolith breccia –0.1 –0.3 Murchison CM2 breccia 0.4 Acfer 209 CR2 breccia 0.3 0.5 Acfer 094 C2 ungrouped breccia –0.3 –0.4 Leoville CV3 reduced 1.8 Dar al Gani 005 CO3 4.5 Watson 002 CK3–anomalous 0.4 Dar al Gani 275 CK4/5 –1.0 Dar al Gani 412 CK5 –0.3 辉石球粒陨石 Sahara 97166 EH3 3.4 Qingzhen EH3 16.0 Indarch EH 4 0.0 –0.4 Abee EH4 impact melt breccia –0.1 –0.7 Hvittis EL6 breccia 7.6 Ilafegh 009 EL7 with impact melt 4.3 月球样品 Dar al Gani 400 anorthositic breccia 1.1 Dar al Gani 262 polym anorth breccia 10.0 Pristine ferroan anorthosite (60025,771) 7.8 Soil (14163,910) 11.3 表 10 不同铅锌矿床样品的Cd含量和同位素组成(据Zhu et al., 2013)
Table 10 Cadmium concentrations and isotopic compositions of samples in the different lead−zinc deposits (modified from Zhu et al., 2013)
名称 样品编号 样品类型 颜色 Cd/ (µg/g) δ114/110Cd /‰ 会泽 HZP5–11–2 闪锌矿 黑色 913 0.12 ± 0.08 会泽 HZP5–11–2 闪锌矿 黑色 923 0.07 ± 0.04 会泽 HZP9–2–1–① 闪锌矿 红棕色 770 0.16 ± 0.23 会泽 HZP9–2–1–② 闪锌矿 红棕色 1410 0.31 ± 0.28 会泽 HZP9–6–1 闪锌矿 黑色 623 0.24 ± 0.21 会泽 HZP9–7–1 闪锌矿 黑色 673 0.15 ± 0.11 会泽 HZP10–7 闪锌矿 黑色 725 −0.08 ± 0.20 会泽 HZP5–11–2 方铅矿 8 −1.53 ± 0.18 会泽 HZP9–2–2 方铅矿 24 −0.60 ± 0.10 会泽 HZP9–8–2 方铅矿 21 −0.63 ± 0.12 会泽 HZP9–8–2 方铅矿 15 −0.58±0.08 杉树林 SS01 闪锌矿 黑色 590 −0.13 ± 0.24 杉树林 SS13 闪锌矿 黑色 571 0.12 ± 0.03 杉树林 SS14–1 闪锌矿 黑色 930 −0.07 ± 0.21 杉树林 SS14–3 闪锌矿 红棕色 884 0.02 ± 0.34 杉树林 SS16 闪锌矿 黑色 608 −0.34 ± 0.24 杉树林 SS16 闪锌矿 黑色 510 −0.28 ± 0.28 富乐 FL128–① 闪锌矿 黑色 5430 0.32 ± 0.16 富乐 FL128–② 闪锌矿 浅黄褐色 11477 0.32 ± 0.13 富乐 FL43–① 闪锌矿 红棕色 9263 0.34 ± 0.21 富乐 FL43–② 闪锌矿 黑色 19714 0.03 ± 0.07 富乐 FL48 闪锌矿 黑色 6953 −0.20 ± 0.13 富乐 FL46 闪锌矿 黑色 10799 −0.30 ± 0.11 富乐 FL86 闪锌矿 红棕色 7116 0.02 ± 0.03 牛角塘 LJP3–3 闪锌矿 浅黄褐色 5330 −0.48 ± 0.01 牛角塘 LJP4–3 闪锌矿 浅黄褐色 7128 −0.34 ± 0.16 牛角塘 LJP2–2 闪锌矿 浅黄褐色 2177 0.18 ± 0.07 牛角塘 LJP2–8 闪锌矿 浅黄褐色 5207 −0.59 ± 0.01 牛角塘 LJP 3–1 闪锌矿 浅黄褐色 2075 −0.41 ± 0.07 金顶 Z–3 氧化物 −0.58 ± 0.09 金顶 Z–4 氧化物 −0.74 ± 0.09 金顶 Z–5 原生矿物 −0.35 ± 0.13 金顶 Z–6 原生矿物 −0.39 ± 0.07 金顶 Z–7 原生矿物 −0.50 ± 0.10 表 11 巴西中元古代晚期Paranoá群穹隆状叠层石和共生型叠层石的部分元素含量及Cd同位素组成(据Viehmann et al., 2018修改)
Table 11 Partial element concentrations and Cd isotopic compositions of the Paranoá Group stromatolites (modified from Viehmann et al., 2018)
样品类型 样品编号 ε112/ 110Cd Cd/(µg/g) U/(µg/g) Ce/(µg/g) MnO/% 穹隆状叠层石 BR_SG_10a –0.58 0.1201 0.0721 1.48 20.2 BR_SG_10c –0.17 0.0383 0.0846 1.43 21.0 共生型叠层石 BR_FF_20b 1.72 0.0195 0.24 3.04 0.05 BR_FF_30b –0.74 0.0177 0.357 2.14 0.05 BR_FF_30cI 0.32 0.0121 0.483 2.60 0.05 BR_FF_30cII (duplicate) 0.67 0.0149 BR_FF_STR40aI –3.06 0.024 0.639 2.77 0.04 BR_FF_STR40aII (duplicate) –3.52 0.0203 BR_FF_STR40b –2.78 0.0249 0.565 2.61 0.04 BR_FF_STR40c –1.00 0.0160 0.456 2.59 0.05 BR_FF_STR40d –1.19 0.0145 0.537 2.55 0.04 BR_FF_STR50b 3.46 0.0057 0.28 1.85 0.06 表 12 锌镉污染环境的修复技术
Table 12 Remediation technology of cadmium and zinc contaminated environment
修复技术 修复方法 优点 缺点 资料来源 物理修复 客土法 在受污染的土壤之上覆盖非当地原生的、由其他地区移来的非污染优质土壤 修复效果好,能隔离污染土壤、提高土壤的养分含量 施行代价高,对大面积污染的土壤治理难以推广,容易降低土壤肥力 侯李云等, 2015; Aoshima, 2016 换土法 将部分或全部受污染的土壤替换成非污染土壤 黄益宗等, 2013 深耕翻土 通过机械方式翻出深层的非污染土壤,从而置换表层的污染土壤 提高土壤肥力,改善土壤的理化性质 未从根源上解决污染问题,存在二次污染 黄益宗等, 2013 电动力学修复法 在污染环境的两侧施加直流电压,驱动重金属活化,并通过电泳、电渗流、电迁移使环境中重金属离子迁移到电极两端 设备简单、不易发生二次污染、去除效
率高具有局限性,适用于小范围的污染,修复成本高 Acar et al., 1995; 魏树和等, 2019 化学修复 化学淋洗法 使用淋洗液淋洗,使得吸附在土壤颗粒上的重金属离子发生溶解从而被清除 效率高、操作简单、修复范围广、时间短 成本高,容易造成二次污染和降低土壤肥力或水体质量 Poclecha and Lestan, 2010; 姚振楠等, 2021 化学固定法 加入固化剂,降低重金属的有效性 操作简单、成本低 只改变了元素的存在形式 徐慧婷等, 2019 生物修复 植物修复 通过植物稳定与吸收进行转运、修复重金属污染 环保性能高、成本低 修复周期长,不适用于多种重金属元素污染的环境;微生物活性易受温度等其他条件的影响 Rubin and Ramaswami, 1998; 俞文钰等, 2023 微生物修复 通过吸附、矿化、沉淀、溶解等方式来改变元素的生物有效性 Singh et al., 2004 动物修复 通过动物直接吸收或通过动物活动降低元素含量 田伟莉等,2013 -
[1] Abouchami W, Galer S J G, de Baar H J W, Alderkamp A C, Middag R, Laan P, Feldmann H, Andreae M O. 2011. Modulation of the Southern Ocean Cd isotope signature by ocean circulation and primary productivity[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 305(1/2): 83−91. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.02.044
[2] Abouchami W, Galer S J G, Horner T J, Rehkamper M, Wombacher F, Xue Z, Lambelet M, Gault–Ringold M, Stirling C H, Schonbachler M. 2013. A common reference material for cadmium isotope studies–NIST SRM 3108[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 37(1): 5−17. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2012.00175.x
[3] Acar Y B, Gale R J, Alshawabkeh A N, Marks R E, Puppala S, Bricka M, Parker R. 1995. Electrokinetic remediation: Basics and technology status[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 40(2): 117−137. doi: 10.1016/0304-3894(94)00066-P
[4] Aoshima K. 2016. Itai–itai disease: Renal tubular osteomalacia induced by environmental exposure to cadmium–historical review and perspectives[J]. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 62(4): 1−8.
[5] Archer C, Andersen M B, Cloquet C, Conway T M, Dong S F, Ellwood M, Moore R, Nelson J, Rehkämper M, Rouxel O, Samanta M, Shin K–C, Sohrin Y, Takano S, Wasylenki L. 2017. Inter–calibration of a proposed new primary reference standard AA–ETH Zn for zinc isotopic analysis[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 32(2): 415−419. doi: 10.1039/C6JA00282J
[6] Archer C, Vance D. 2004. Mass discrimination correction in multiple–collector plasma source mass spectrometry: An example using Cu and Zn isotopes[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 19(5): 656−665. doi: 10.1039/b315853e
[7] Arnold T, Markovic T, Kirk G, Schonbachler M, Rehkamper M, Zhao F J, Weiss D J. 2015. Iron and zinc isotope fractionation during uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa) grown in oxic and anoxic soils[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 347(7/8): 397−404. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2015.05.005
[8] Balter V, Zazzo A, Moloney A P, Moynier F, Schmidt O, Monahan F J, Albarède F. 2010. Bodily variability of zinc natural isotope abundances in sheep[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 24(5): 605−612. doi: 10.1002/rcm.4425
[9] Barrat J A, Zanda B, Moynier F, Bollinger C, Liorzou C, Bayon G. 2012. Geochemistry of CI chondrites: Major and trace elements, and Cu and Zn isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 83(1): 79−92.
[10] Bermin J, Vance D, Archer C, Statham P J. 2006. The determination of the isotopic composition of Cu and Zn in seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 226(3): 280−297.
[11] Bewers J M, Yeats P A. 1977. Oceanic residence times of trace metals[J]. Nature, 268(5621): 595−598. doi: 10.1038/268595a0
[12] Blix R, Ubisch H V, Wickman F E. 1957. A search for variations in the relative abundance of the zinc isotopes in nature[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 11(3): 162−164. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(57)90078-9
[13] Borrok D M, Wanty R, Ridley W I, Wolf R E, Lamothe P J, Adams M. 2007. Separation of copper, iron, and zinc from complex aqueous solutions for isotopic measurement[J]. Chemical Geology, 242(3): 400−414.
[14] Brugier Y A, Barrat J A, Gueguen B, Agranier A, Yamaguchi A, Bischoff A. 2019. Zinc isotopic variations in ureilites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 246: 450−460. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.12.009
[15] Callagon E, Lee S S, Eng P J, Laanait N, Sturchio N C, Nagy K L, Fenter P. 2016. Heteroepitaxial growth of cadmium carbonate at dolomite and calcite surfaces: Mechanisms and rates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 205(1): 360−380.
[16] Chang Haiwei, Liu Daihuan, He Qianfeng. 2018. Advances in microbial redemption mechanism of heavy metal polluted farmland[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 38(2): 114−121 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Chen H, Savage P S, Teng F Z, Helz R T, Moynier F. 2013. Zinc isotope fractionation during magmatic differentiation and the isotopic composition of the bulk Earth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 369–370(1): 34–42.
[18] Chen J B, Gaillardet J, Louvat P, Huon S. 2009a. Zn isotopes in the suspended load of the Seine River, France: Isotopic variations and source determination[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(14): 4060−4076. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.04.017
[19] Chen J B, Gaillardet J, Louvat P. 2008. Zinc isotopes in the Seine River Waters, France: A probe of anthropogenic contamination[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(12): 6494−6501.
[20] Chen J B, Louvat P, Gaillardet J, Birck J L. 2009b. Direct separation of Zn from dilute aqueous solutions for isotope composition determination using multi–collector ICP–MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 259(3/4): 120−130. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.040
[21] Cheng Y L, Wang K Q, Tu B Y, Xia Y, Zhang J Q, Xue S, Tao H S. 2019. High–temperature reduction of calcium alginate to carbon sphere for efficient removal of bivalent cadmium[J]. Chemistry Select, 4(31): 9058−9064. doi: 10.1002/slct.201902329
[22] Cloquet C, Carignan J, Lehmann M F, Vanhaecke F. 2008. Variation in the isotopic composition of zinc in the natural environment and the use of zinc isotopes in biogeosciences: A review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 390(2): 451−463. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1635-y
[23] Cloquet C, Rouxel O, Carignan J, Libourel G. 2005. Natural cadmium isotopic variations in eight geological reference materials (NIST SRM 2711, BCR 176, GSS–1, GXR–1, GXR–2, GSD–12, Nod–P–1, Nod–A–1) and anthropogenic samples, measured by MC–ICP–MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 29(1): 95−106. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00658.x
[24] Conway T M, John S G. 2015. The cycling of iron, zinc and cadmium in the North East Pacific Ocean–Insights from stable isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 164: 262−283. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.023
[25] Costas–Rodriguez M, VanHeghe L, Vanbaecke F. 2013. Evidence for a possible dietary effect on the isotopic composition of Zn in blood via isotopic analysis of food products by multi–collector ICP–mass spectrometry[J]. Metallomics, 6(1): 139−146.
[26] Dhaliwal J K, Day J M D, Moynier F. 2018. Volatile element loss during planetary magma ocean phases[J]. Icarus, 300: 249−260. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2017.09.002
[27] Fedyunina N N, Seregina I F, Bolshov M A, Okina O I, Lyapunov S M. 2012. Investigation of the efficiency of the sample pretreatment stage for the determination of the rare earth elements in rock samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 713(3): 97−102.
[28] Fekiacova Z, Cornu S, Pichat S. 2015. Tracing contamination sources in soils with Cu and Zn isotopic ratios[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 517: 96−105. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.046
[29] Fu Zhiyou, Feng Chenglian, Zhao Xiaoli, Guo Wenjing, Sun Siyang, Liu Xinmei, Wang Yu, Li Xiaofeng, Wu Fengchang. 2019. Ecological risks and management countermeasures of copper and zinc in water environment of China[J]. Environmental Engineering, 37(11): 70−74 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Gao B, Liu Y, Sun K, Liang X R, Peng P A, Sheng G Y, Fu J M. 2008. Precise determination of cadmium and lead isotopic compositions in river sediments[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 612(1): 114−120. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.02.020
[31] Gao B, Zhou H D, Liang X, Liang X R, Tu X L. 2013. Cd isotopes as a potential source tracer of metal pollution in river sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 181(13): 340−343.
[32] Gao Z F, Zhu X K, Sun J, Luo ZH, Bao C, Tang C, Ma J K. 2018. Spatial evolution of Zn–Fe–Pb isotopes of sphalerite within a single ore body: A case study from the Dongshengmiao ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 53(1): 55−65. doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0724-x
[33] Gault–Ringold M, Adu T, Stirling C H, Frew R D, Hunter K A. 2012. Anomalous biogeochemical behavior of cadmium in subantarctic surface waters: Mechanistic constraints from cadmium isotopes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 341–344(1): 94–103.
[34] Georgiev S V, Horner T J, Stein H J, Hannah J L, Bingen B, Rehkämper M. 2015. Cadmium–isotopic evidence for increasing primary productivity during the Late Permian anoxic event[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 410(1): 84−96.
[35] Ghidan O Y, Loss R D. 2012. Zinc isotope fractionation analyses by thermal ionization mass spectrometry and a double spiking technique[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 309: 79−87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2011.09.001
[36] Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse–Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg D A. 2006. The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health[J]. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology, 1(1): 22. doi: 10.1186/1745-6673-1-22
[37] Gou W X, Li W, Ji J F, Li W Q. 2018. Zinc isotope fractionation during sorption onto Al oxide: Atomic level understanding from EXAFS[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(16): 9087−9096.
[38] He Tianrong. 1995. Harm and prevention of zinc oxide smelting by local method in rural enterprises on human health[J]. Safety & Health at Work, 3: 30 (in Chinese).
[39] Horner T J, Rickaby R, Henderson G M. 2011. Isotopic fractionation of cadmium into calcite[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 312(1): 243−253.
[40] Hou Liyun, Zeng Xibai, Zhang Yangzhu. 2015. Application and outlook of alien earth soil–improving technology in arsenic contaminated soil remediation[J]. Chinese Journal of EcoAgriculture, 23(1): 20−26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Hu Hongtao, Cheng Jinping. 2009. Experimental study on electrokinetic remediation of zinc contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(10): 53−56,102 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Huang Shiqi, Gong Yingli, Tian Shihong, Liang Zhengwei, Zhu Chunhui. 2023. Recent advances on zinc isotopes in Earth science[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(4): 1002−1029 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Huang Yizong, Hao Xiaowei, Lei Ming, Tie Baiqing. 2013. The remediation technology and remediation practice of heavy metals–contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Agro–Environment Science, 32(3): 409−417 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Juillot F, Maréchal C, Morin G, Jouvin D, Cacaly S, Telouk P, Benedetti M F, Ildefonse P, Sutton S, Guyot F, Brown G E. 2012. Contrasting isotopic signatures between anthropogenic and geogenic Zn and evidence for post–depositional fractionation processes in smelter–impacted soils from Northern France[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(9): 2295−2308.
[45] Kavner A, John S G, Sass S, Boyle E A. 2008. Redox–driven stable isotope fractionation in transition metals: Application to Zn electroplating[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(7): 1731−1741. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.01.023
[46] Kingston H M, Barnes I L, Brady T J, Rains T C, Champ M A. 1978. Separation of eight transition elements from alkali and alkaline earth elements in estuarine and seawater with chelating resin and their determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 50(14): 21−27.
[47] Kong Jing, Guo Qingjun, Wei Rongfei, Zhu Guangxu, Hu Jian. 2017. Measurement and application of zinc stable isotope in environmental science[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(6): 1718−1726 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Kunzmann M, Halverson G P, Sossi P A, Raub T D, Payne J L, Kirby J. 2013. Zn isotope evidence for immediate resumption of primary productivity after snowball Earth[J]. Geology, 41(1): 27−30. doi: 10.1130/G33422.1
[49] Lacan F, Francois R, Ji Y, Sherrell R M. 2006. Cadmium isotopic composition in the ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(20): 5104−5118. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.07.036
[50] Li Fuyan, Zhang Liming, Li Xuming, Guo Bin, Chen Liuyan, Qi Zhiping. 2006. Research advances on zincum pollution and remediation of soil–plant system[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 22: 5920−5921, 5979 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] Li Haitao, Yang Xin, Lei Huaji, Yang Yan, Jin Lanlan, Hu Shenghong. 2021. Research Progress of Cadmium Stable Isotopes[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 40(1): 1−15 (in Chinese).
[52] Li Jin, Zhu Xiangkun, Tang Suohan. 2008. Some important processes of Zn isotope fractionation in low temperature environments[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 27(5): 465−471 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[53] Li M L, Liu S A, Xue C J, Li D D. 2019. Zinc, cadmium and sulfur isotope fractionation in a supergiant MVT deposit with bacteria[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 265: 1−18. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.08.018
[54] Li X F, Wang Y X, M. Crabbe M J C, Wang L, Ma W L, Ren Z M. 2022. Genetically modified metallothionein/cellulose composite material as an efficient and environmentally friendly biosorbent for Cd2+ removal[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 218: 543−555. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.144
[55] Li Yi, Chen Xi, Xiao Pixian, Ma Qiong, Wu Guo. 2020. Study on the species composition, geographical distribution and flora characteristics of Cd hyperaccumulators in China[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 39(6): 11−16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[56] Li Zhengxian, Li Wei, Lei Jiajun, Li Qianyu, Liu Lintao, Zhou Lian. 2020. Effect and hazard of common metal elements on human body[J]. Materials China, 39(12): 934−944 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[57] Li Zhi, Xu Yingkui, Zhu Dan, Li Shijie, Li Xiongyao, Liu Jianzhong. 2023. Advances in zinc isotope in planetary science[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 43(3): 273−283 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[58] Liang B, Han G L, Zhao Y. 2022. Zinc isotopic signature in tropical soils: A review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 820: 153303. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153303
[59] Liang Lili, Liu Congqiang, Wang Zhongliang, Zhu Xiangkun, Song Liuting, Li Jin. 2008. Zinc isotope characteristics in the biogeochemical process of karst plateau lakes[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 7(4): 326−334 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[60] Little S H, Vance D, Walker–Brown C, Landing W M. 2014. The oceanic mass balance of copper and zinc isotopes, investigated by analysis of their inputs, and outputs to ferromanganese oxide sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 125(1): 673−693.
[61] Liu M S, Zhang Q, Zhang Y N, Zhang Z F, Huang F, Yu H M. 2020. High–precision Cd isotope measurements of soil and rock reference materials by MC–ICP–MS with double spike correction[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 44(1): 169−182. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12291
[62] Liu Mengshu, Zhang Qun, Zhang Yingnan, Zhang Zhaofeng, Huang Fang, Yu Huimin. 2019. Cadmium isotope analysis method and cadmium isotope composition of international standard sample[C]//Proceedings of the 17th Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Society of Mineral and Petrology Geochemistry, 989 (in Chinese).
[63] Liu S A, Wu H C, Shen S Z, Jiang G Q, Zhang S H, Lü Y W, Zhang H, Li S G. 2017. Zinc isotope evidence for intensive magmatism immediately before the end–Permian mass extinction[J]. Geology, 45(4): 343−346. doi: 10.1130/G38644.1
[64] Liu Yizhang, Xiao Tangfu, Zhu Jianming. 2015. Cadmium isotopes and environmental tracing[J]. Earth and Environment, 43(6): 687−696 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[65] Luck J M, Othman D B, Albarède F. 2006. Zn and Cu isotopic variations in chondrites and iron meteorites: Early solar nebula reservoirs and parent–body processes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(22): 5351−5363.
[66] Ma Guiyun, Zhang Zhenhua, Yan Shaohua, Tang Wanying. 2003. Study progress of fish pollution by heavy metals[J]. Jiangsu Environmental Science and Technology, 16(2): 38−40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[67] Ma Lei, Li Dandan, Lü Yiwen, Wang Xun, Wang Zezhou, Li Menglun, Yang Chun, Qu Yuanru, Shu Zitan, Liu Sheng’ao. 2022. Zinc isotope geochemistry and its applications: A critical review[J]. Geochimica, 51(2): 161−175 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[68] Maréchal C N, Albaréde F. 2002. Ion–exchange fractionation of copper and zinc isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66(9): 1499−1509. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00815-8
[69] Maréchal C N, Douchet C, Nicolas E, Albarède F. 2000. Abundance of zinc isotopes as a marine biogeochemica tracer[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 1(5): 1015.
[70] Maréchal C N, Télouk P, Albarède F. 1999. Precise analysis of copper and zinc isotopic compositions by plasma–source mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Geology, 156(1/4): 251−273. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00191-0
[71] Marques A, Oliveira R, Samardjieva K, Pissarra J, Rangel A, Castro P. 2008. EDDS and EDTA– enhanced zinc accumulation by solanum nigrum inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi grown in contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 70(6): 1002−1014. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.045
[72] Martinková E, Chrastný E, Francová M, Šípková A, Čuřík Jan, Myška O, Mižič L. 2016. Cadmium isotope fractionation of materials derived from various industrial processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 302: 114−119. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.039
[73] Mason T, Weiss D J, Chapman J B, Wilkinson J, Tessalina S G, Baruch S, Horstwood M S A, Spratt J, Coles B J. 2005. Zn and Cu isotopic variability in the Alexandrinka volcanic–hosted massive sulphide (VHMS) ore deposit, Urals, Russia[J]. Chemical Geology, 221(3): 170−187.
[74] Matthies R, Sinclair S A, Blowes D W. 2014. The zinc stable isotope signature of waste rock drainage in the Canadian permafrost region[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 48(1): 53−57.
[75] Mccoy–West A J, Godfrey F J, Marie–Laure P, Inglis E C, Williams H M. 2018. The Fe and Zn isotope composition of deep mantle source regions: Insights from Baffin Island picrites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 238: 542−562. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.07.021
[76] Miao Xin, Chen Linjie, Zhou Feiyang, Liu Xing, He Dong, Zheng Hongtao, Zhu Zhenli. 2021. Comparison of sample digestion methods for high precision cadmium isotope analysis[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 40(6): 947−953 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[77] Moynier F, Albarède F, Herzog G. 2006. Isotopic composition of zinc, copper, and iron in lunar samples[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(24): 6103−6117. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.02.030
[78] Moynier F, Beck P, Yin Q Z, Ferroir T, Barrat J A, Paniello R, Telouk P, Gillet P. 2010. Volatilization induced by impacts recorded in Zn isotope composition of ureilites[J]. Chemical Geology, 276(3−4): 374−379. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.07.005
[79] Moynier F, Vance D, Fujii T, Savage P. 2017. The isotope geochemistry of Zinc and Copper[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 82(1): 543−600. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2017.82.13
[80] Nordberg G F. 2009. Historical perspectives on cadmium toxicology[J]. Toxicology & Applied Pharmacology, 238(3): 192−200.
[81] Pallavicini N, Engstroem E, Baxter D C, Öhlander B, Ingria J, Rodushkin I. 2014. Cadmium isotope ratio measurements in environmental matrices by MC–ICP–MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 29(9): 1570−1584. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00125G
[82] Paniello R C, Day J M, Moynier F. 2012. Zinc isotopic evidence for the origin of the Moon[J]. Nature, 490(7420): 376−379. doi: 10.1038/nature11507
[83] Park J, Kim J Y, Lee K, Kim M S, Kim M J, Choi J W. 2019. Comparison of acid extraction and total digestion methods for measuring Cd isotope ratios of environmental samples[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(1): 1−10.
[84] Pašava J, Tornos F, Chrastny V. 2014. Zinc and sulfur isotope variation in sphalerite from carbonate–hosted zinc deposits, Cantabria, Spain[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 49(7): 797−807. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0535-2
[85] Peng Mao, Liu Bo, Xing Xiaomiao, Zhou Yefeng, Wang Zhuoran, Li Cheng, Wei Jianlin. 2022. Investigation on the treatment effect of heavy metal cadmium (Cd) pollution in paddy fields[J]. Food Science and Technology And Economy, 47(5): 4 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[86] Pichat S, Douchet C, AlbarèdeF. 2003. Zinc isotope variations in deep–sea carbonates from the eastern equatorial Pacific over the last 175 ka[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 210(1/2): 167−178.
[87] Poclecha M, Lestan D. 2010. Using electrocoagulation for metal and chelant separation from washing solution after EDTA leaching of Pb, Zn and Cd contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1/3): 670−678.
[88] Pokrovsky O S, Viers J, Freydier R. 2005. Zinc stable isotope fractionation during its adsorption on oxides and hydroxides[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 291(1): 192−200. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2005.04.079
[89] Poynton H C, Varshavsky J R, Chang B, Cavigiolio G, Chan S, Holman P S, Loguinov A V, Bauer D J, Komachi K, Theil E C, Perkins E J, Hughes O, Vulpe C D. 2007. Daphnia magna ecotoxicogenomics provides mechanistic insights into metal toxicity[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(3): 1044−1050.
[90] Rahmi, Lelifajri, Julinawati, Shabrina. 2017. Preparation of chitosan composite film reinforced with cellulose isolated from oil palm empty fruit bunch and application in cadmium ions removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 170: 226−233. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.084
[91] Ren Bangfang, Ling Wenli, Zhang Junbo, Zhang Yongqing, Duan Ruichun. 2007. Analysis methods of zinc isotope and their applications in geology[J]. Geological Science and Techology Information, 26(6): 30−35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[92] Ripperger S, RehkäMper M. 2007. Precise determination of cadmium isotope fractionation in seawater by double spike MC–ICPMS[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(3): 631−642. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.10.005
[93] Rosman K J R, De Laeter J R. 1975. The isotopic composition of cadmium in terrestrial minerals[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Physics, 16(4): 385−394. doi: 10.1016/0020-7381(75)85027-3
[94] Rosman K, De Laeter J. 1988. Cadmium mass fractionation in unequilibrated ordinary chondrites[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 89(2): 163−169.
[95] Rubin E, Ramaswami A. 1998. The potential for phytoremediation of MTBE[J]. Water Research, 35(5): 1348−1353.
[96] Rudnick R, Gao S. 2014. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 4: 1–51.
[97] Sands D G, Rosman K, De Laeter J. 2001. A preliminary study of cadmium mass fractionation in lunar soils[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 186(1): 103−111.
[98] Schmitt A D, Galer S, Abouchami W. 2009. Mass–dependent cadmium isotopic variations in nature with emphasis on the marine environment[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 277(1/2): 262−272.
[99] Shao Minghao, Zuo Shengpeng, Hong Wenxiu. 2020. Environmental monitoring and ecological restoration effects on limnodrilus hoffmeisteri[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 39(2): 1−9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[100] Shen X, Dai M, Yang J W, Sun L, Tan X, Peng C S, Ali I, Naz I. 2021. A critical review on the phytoremediation of heavy metals from environment: Performance and challenges[J]. Chemosphere, 291(3): 132979.
[101] Shiel A E, Weis D, Cossa D, Orians K. 2013. Determining provenance of marine metal pollution in French bivalves using Cd, Zn and Pb isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 121(1): 155−167.
[102] Shiel A E, Weis D, Orians K J. 2010. Evaluation of zinc, cadmium and lead isotope fractionation during smelting and refining[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 408(11): 2357−2368. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.02.016
[103] Singh N, Megharaj M, Kookana R S, Naidu R, Sethunathan N. 2004. Atrazine and simazine degradation in Pennisetum rhizosphere[J]. Chemosphere, 56(3): 257−263. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.03.010
[104] Song Wenrui, Zhu Chuanwei, Yang Zhen, Wu Yunzhu, Li Qiankun, Gao Lisheng, Zhang Jiawei, Zhang Yuxu, Fan Haifeng, Wen Hanjie. 2023. Genesis of the Nayongzhi lead–zinc deposit in Guizhou Province: Constraints from Cd isotopes and trace elements[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 42(1): 206–214 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[105] Sonke J E, Sivry Y, Viers J, Freydier R, Dejonghe L, André L, Aggarwal J K, Fontan F, Dupré B. 2008. Historical variations in the isotopic composition of atmospheric zinc deposition from a zinc smelter[J]. Chemical Geology, 252(3/4): 145−157. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.02.006
[106] Sossi P A, Nebel O, O’Neill H S C, Moynier F. 2017. Zinc isotope composition of the Earth and its behaviour during planetary accretion[J]. Chemical Geology, 477: 73−84.
[107] Sun Y C, Chi P H, Shiue M Y. 2001. Comparison of different digestion methods for total decomposition of siliceous and organic environmental samples[J]. Analytical Sciences the International Journal of the Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry, 17(12): 1395. doi: 10.2116/analsci.17.1395
[108] Tan Decan, Zhu Jianming, Li Shehong, Ren Kun, Zhao Bo, Wang Jing, Zeng Li. 2017. The principle and application of isotopic double spike technique: The application[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(6): 948–954 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[109] Tan Decan, Zhu Jianming, Wang Jing, Tao Faxiang, Zeng Li. 2016. The principle and application of isotopic double spike technique Ⅰ: Principle[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 35(1): 138–145 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[110] Tian Weili, Liu Dan, Wu Jiasen, Wang Lijiang, Chen Kunbai. 2013. Application of animal and plant combination remediation technology in complex heavy metalscontaminated soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(5): 188−192.
[111] Tu Guangchi, Gao Zhenmin, Hu Ruizhong, Zhang Qian, Li Chaoyang, Zhao Zhenhua, Zhang Bao. 2004. Dispersed Element Geochemistry and Metallogenic Mechanism[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1–400 (in Chinese).
[112] Viehmann S, Hohl S V, Kraemer D, Bau M, Walde D H G, Galer S J G, Jiang S Y, Meister P. 2018. Metal cycling in Mesoproterozoic microbial habitats: Insights from trace elements and stable Cd isotopes in stromatolites[J]. Gondwana Research, 67(1): 101−114.
[113] Viers J, Oliva P, Nonell A, Gélabert A, Sonke J E, Freydier R, Gainville R, Dupré B. 2007. Evidence of Zn isotopic fractionation in a soil–plant system of a pristine tropical watershed (Nsimi, Cameroon)[J]. Chemical Geology, 239(1/2): 124−137. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.01.005
[114] Vogelmeier C, König G, Bencze K, Fruhmann G. 1987. Pulmonary involvement in zinc fume fever[J]. Chest, 92(5): 946–948.
[115] Voldrichova P, Chrastny V, Sipkova A, Farkas J, Novak M, Stepanova M, Krachler M, Veselovsky F, Blaha V, Prechova E, Komarek A, Bohdalkova L, Curik J, Mikova J, Erbanova L, Pacherova P. 2014. Zinc isotope systematics in snow and ice accretions in Central European mountains[J]. Chemical Geology, 388(1): 130−141.
[116] Wan Dan, Chen Jiubin, Zhang Ting, An Yuchen, Shuai Wangcai. 2022. Cadmium isotope fractionation and its applications in tracing the source and fate of cadmium in the soil: A review[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 41(3): 341−352 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[117] Wang Jing, Wei Heng, Pan Bo. 2023. Accumulation characteristics and probabilistic risk assessment of Cd in agricultural soils across China[J]. Environmental Science, 44(7): 4006−4016 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[118] Wang Shuguang, Liu Shetang, Namkha Norbu, Xu Yan. 2016. Application of zinc isotopic tracing technology in soil pollution traceability[J]. Western Development (Land Development and Engineering Research), (2): 61−65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[119] Wang Weizhong, Zhang Zhaohui, Wen Hanjie, Zhu Chuanwei, Zhang Yuxu. 2020. The application of Cd isotopes in the paleo–environment reconstruction: A case study of the Frasnian–Famennian mass extinction event in the Late Devonian[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 39(1): 80–88 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[120] Wang Yinquan, Zhou Taofa, Li Xiangling. 2013. Progress in the application of cadmium isotope tracing technology in the source analysis of cadmium pollution in soil and sediments[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(2): 713−714 (in Chinese).
[121] Wang Z Z, Liu S A, Liu J G, Huang J, Xiao Y, Chu Z Y, Zhao X M, Tang L M. 2016. Zinc isotope fractionation during mantle melting and constraints on the Zn isotope composition of Earth’s upper mantle[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 198(1): 151−167.
[122] Wang Zhongwei, Yuan Wei, Chen Jiubin. 2015. Zn stable isotope geochemistry: A review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(5): 84−93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[123] Weber T, John S, Tagliabue A, DeVries T. 2018. Biological uptake and reversible scavenging of zinc in the global ocean[J]. Science, 361(6397): 72−76. doi: 10.1126/science.aap8532
[124] Wei R F, Guo Q J, Wen H J, Yang J X, Peters M, Zhu C W, Ma J, Zhu G X, Zhang H Z, Tian L Y. 2015. An analytical method for precise determination of the cadmium isotopic composition in plant samples using multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Methods, 7(6): 264−272.
[125] Wei Rongfei, Guo Qingjun, Yang Junxing, Zhu Guangxu, Zhang Hanzhi, Marc Peters, Wang Chunyu, Wan Yingxin. 2021. Application and progress of Cd isotope technology in environmental science[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(2): 525−536 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[126] Wei Shuhe, Xu Lei, Han Ran, Dou Xuekai, Yang Wei. 2019. Review on combined electrokinetic and phytoremediation technology for soil contaminated byheavy metal[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 43(1): 154−160 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[127] Wei Shuhe, Zhou Qixing, Wang Xin, Zhang Kaisong, Guo Guanlin. 2004. A newly discovered cadmium hyperaccumulating plant (Solanum nigrum L)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 24: 2568−2573 (in Chinese).
[128] Weiss D J, Mason T F D, Zhao F J, Kirk G J, Coles B J, Horstwood M S. 2005. Isotopic discrimination of zinc in higher plants[J]. New Phytologist, 165(3): 703−710. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01307.x
[129] Weiss D J, Rausch N, Mason T, Coles B J, Wilkinson J J, Ukonmaanaho L, Arnold T, Nieminen T M. 2007. Atmospheric deposition and isotope biogeochemistry of zinc in ombrotrophic peat[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(14): 3498−3517. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.026
[130] Wen H J, Zhu C W, Zhang Y X, Cloquet C, Fu S H. 2016. Zn/Cd ratios and cadmium isotope evidence for the classification of lead–zinc deposits[J]. Scientific Reports, 6: 25273. doi: 10.1038/srep25273
[131] Wiggenhauser M, Bigalke M, Imseng M, Keller A, Rehkämper M, Wilcke W, Frossard E. 2018. Using isotopes to trace freshly applied cadmium through mineral phosphorus fertilization in soil–fertilizer–plant systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 648(1): 779−786.
[132] Wiggenhauser M, Bigalke M, Imseng M, Müller M, Keller A, Murphy K, Kreissig K, Rehkämper M, Wilcke W, Frossard E. 2016. Cadmium isotope fractionation in soil–wheat systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(17): 9223−9231.
[133] Wolf R E, Todd A S, Brinkman S, Lamothe P J, Smith K S, Ranville J F. 2009. Measurement of total Zn and Zn isotope ratios by quadrupole ICP–MS for evaluation of Zn uptake in gills of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J]. Talanta, 80(2): 676−684. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2009.07.048
[134] Wombacher F, RehkäMper M, Mezger K, Bischoff A, Münker C. 2008. Cadmium stable isotope cosmochemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(2): 646−667. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.10.024
[135] Wombacher F, RehkäMper M, Mezger K. 2004. Determination of the mass–dependence of cadmium isotope fractionation during evaporation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(10): 2349−2357. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.12.013
[136] Wombacher F, Rehkmper M, Mezger K, Belshaw N, Gall L, Halliday A N. 2003. Stable isotope compositions of cadmium in geological materials and meteorites determined by multiple−collector ICPMS[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(23): 4639−4654. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00389-2
[137] Wu J F, Boyle E A. 1997. Low blank preconcentration technique for the determination of lead, copper, and cadmium in small–volume seawater samples by isotope dilution ICPMS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 69(13): 2464−2470. doi: 10.1021/ac961204u
[138] Wu Wei, Zhang Zhixin, Niu Honghong, Wang Weiwei, Cai Yuhong. 2014. Analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and remediation measures[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 8: 249−251 (in Chinese).
[139] Wu Xiaomei, Ye Meifeng, Wu Feilong, Lin Daiyan. 2018. Cu and Zn accumulations in myriophyllum spicatum for purification of pig farm biogas slurry[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 33(11): 1195−1200 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[140] Xiang Zhonglan. 2001. The harm of excessive zinc supplementation to the human body[J]. Modern Medicine Health, 9: 727 (in Chinese).
[141] Xiang Zuopeng, Li Bo, Wang Xinfu, Tang Guo. 2020. Characteristics of Zn isotopic composition of sphalerite in different lead–zinc deposits[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 45(1): 32–41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[142] Xie R C, Galer S J G, Abouchami W, Rijkenberg M J A, de Baar H J W, De Jong, J, Andreae M O. 2017. Non–Rayleigh control of upper–ocean Cd isotope fractionation in the western South Atlantic[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 471: 94–103.
[143] Xiong Jieqian, Gong Xiaofeng, Jiang Liang, Li Haoling, Yuan Shaofen, Lin Yuan, Wu Li. 2021. Toxic effects of zinc and cadium on the benthic organisms in sediments of Lake Poyang and verification of quality guideline[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 33(6): 1687−1700 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/2021.0607
[144] Xu Huiting, Zhang Weiwen, Shen Xuyang, Fu Juyang, Chen Feifei, Wang Yan, Yang Meng, Zhao Tonghe, Zhu Weiqin. 2019. Advances in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by in situ chemical fixation[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 58(1): 10−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[145] Xue Z C, M Rehkämper M, Schönbächler M, Statham P J, Coles B J. 2012. A new methodology for precise cadmium isotope analyses of seawater[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 402(2): 883−893. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5487-0
[146] Xue Z, Rehkämper M, Horner T J, Abouchami W, Middag R, van de Flierd T, de Baar H J W. 2013. Cadmium isotope variations in the Southern Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 382: 161−172. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.09.014
[147] Yan B, Zhu X K, He X X, Tang S H. 2019. Zn isotopic evolution in early Ediacaran ocean: A global signature[J]. Precambrian Research, 320: 472−483. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.11.021
[148] Yan Jialei, Li Yanbin. 2023. Research progress on the biogeochemical cycling of cadmium in the ocean[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 42(3): 720−732 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[149] Yan X R, Zhu M Q, Li W, Peacock C L, Ma J Y, Wen H J, Liu F, Zhou Z B, Zhu C W, Yin H. 2021. Cadmium isotope fractionation during adsorption and substitution with iron (Oxyhydr) oxides[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(17): 11601−11611.
[150] Yang Hongfei, Yan Mi, Yao Jing, Wang Youbao, Liu Dengyi. 2007. Impact of Cu and Zn pollution on rape growth and soil enzyme activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 7: 1484−1490 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[151] Yang J L, Li Y B, Liu S Q, Tian H Q, Chen C Y, Liu J M, Shi Y L. 2015. Theoretical calculations of Cd isotope fractionation in hydrothermal fluids[J]. Chemical Geology, 391: 74−82. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.10.029
[152] Yang S C, Lee D C, Ho T Y. 2012. The isotopic composition of Cadmium in the water column of the South China Sea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 98(1): 66−77.
[153] Yang W J, Ding K B, Zhang P, Qiu H, Cloquet C, Wen H J, Morel J L, Qiu R L, Tang Y T. 2019. Cadmium stable isotope variation in a mountain area impacted by acid mine drainage[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 646: 696−703. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.210
[154] Yang Yong, He Yanming, Luan Jingli, Liu Jingyang, Guo Yuwen. 2012. Comprehensive analysis on soil remediation technologies of international contaminated sites[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(10): 92−98 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[155] Yao Zhennan, Niu Kaizhi, Li Ming, Xu Ziqian. 2021. Engineering investigation of chemical washing removing Cd, Pb and As in soil[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 48(12): 154−156 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[156] Yin X Z, Wei R F, Chen H D, Zhu C W, Liu Y Z, Wen H J, Guo Q J, Ma J. 2021. Cadmium isotope constraints on heavy metal sources in a riverine system impacted by multiple anthropogenic activities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 750: 141233. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141233
[157] Yu Wenyu, Hao Tongfeng, Nanhai Lin, Zhang Shulin, Zhang Qingjing. 2023. Research progress of Aquatic plant in the treatment of heavy metal pollution in water[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 841(11): 156−158, 164 (in Chinese).
[158] Zhang G L, Liu Y S, Moynier F, Zhu Y T, Wang Z C, Hu Z C, Zhang L, Li M, Chen H H. 2020. Zinc isotopic composition of the lower continental crust estimated from lower crustal xenoliths and granulite terrains[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 276: 92−108. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.02.030
[159] Zhang J P, Zhuang Z X, Chen C X, Huang H B, Qi S L, Wang X R. 2008. Study on the distributions of lead and cadmium in rats by ICP–MS with stable isotope tracer[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 27(8): 835−838 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[160] Zhang Lihao, Bai Jiaojie, Tian Ruiyun, Wang Guochang, You Laiyong, Liang Jiani, Ci Kaidong, Liu Mengli, Kou Leyong, Zhou Lingli, Zhou Jun, Wu Dafu, Sun Bin, Zhou Jing. 2023. Cadmium remediation strategies in alkaline arable soils in Northern China: Current status and challenges[J/OL]. Acta Pedologica Sinica: 1–13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1119.P.20230612.1349.002.html (in Chinese with English abstract).
[161] Zhang X C, Huang J, Gong Y Z, Zhang L L, Huang F. 2022a. Climate influence on zinc isotope variations in a loess–paleosol sequence of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 321: 115−132. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.01.023
[162] Zhang X Y, Chen L H, Wang X J, Hanyu T, Hofmann A W, Komiya T, Nakamura K, Kato Y, Zeng G, Gou W X, Li W Q. 2022b. Zinc isotopic evidence for recycled carbonate in the deep mantle[J]. Nature Communications, 13(1): 6085. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33789-6
[163] Zhang Y X, Wen H J, Zhu C W, Fan H F, Luo C G, Liu J, Cloquet C. 2016. Cd isotope fractionation during simulated and natural weathering[J]. Environmental Pollution, 216(16): 9−17.
[164] Zhang Ying. 2018. The impact of zinc pollution on soil and plants[J]. Vacation Tour, 8: 86−87 (in Chinese).
[165] Zhang Yuxu, Wen Hanjie, Fan Haifeng, Wang Jiasheng, Zhang Jinrang. 2010. Chemical pretreatment methods for measurement of Cd isotopic ratio on geological samples[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 29(6): 633−637 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[166] Zhao Yu. 2020. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy meatal Cd pollution of shallow groundwater and surface water in main stream of Weihe River, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 42(2): 267−277 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[167] Zheng Guihong, Tang Lingling, Sun Jianmei, Liu Zhanmin, Cheng Chao, Feng Zhaojun. 2014. The effect of zinc on oxidative damage of koi tissues[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 42(3): 187−189 (in Chinese).
[168] Zhong Q H, Zhou Y C, Tsang D C W, Liu J, Yang X, Yin M L, Wu S J, Wang J, Xiao T F, Zhang Z F. 2020. Cadmium isotopes as tracers in environmental studies: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 736: 139585. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139585
[169] Zhong Songxiong, Li Xiaomin, Li Fangbai. 2021. Cadmium isotopes fractionation in soil–plant systems: A review[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 58(4): 825−836 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[170] Zhou Jiadong, Ma Dandan, Liu Min, Hong Xiaohui, Fu Jiahui, Jiang Luman, Lü Dandan, Fang Jiaqi, Cao Yong, Li Weidong. 2020. On the accumulation and purification of three kinds of aquatic plants to heavy metals[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 19(1): 57−63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[171] Zhou Zhen, Huang Li, Huang Guodi, Ma Customs, Peng Gang. 2023. Passivation and remediation of cadmium and zinc contaminated soil by biochar and sepiolite[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 42(2): 158−166 (in Chinese).
[172] Zhu C W, Liao S L, Wang W, Zhang Y X, Yang T, Fan H F, Wen H J. 2018. Variations in Zn and S isotope chemistry of sedimentary sphalerite, Wusihe Zn–Pb deposit, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews: Journal for Comprehensive Studies of Ore Genesis and Ore Exploration, 95: 639−648.
[173] Zhu C W, Wen H J, Zhang Y X, Fan H F, Fu S H, Xu J, Qin T R. 2013. Characteristics of Cd isotopic compositions and their genetic significance in the lead–zinc deposits of SW China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(12): 2056−2065. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4668-4
[174] Zhu C W, Wen H J, Zhang Y X, Fu S H, Fan H F, Cloquet C. 2017. Cadmium isotope fractionation in the Fule Mississippi Valley–type deposit, Southwest China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 52(5): 675−686. doi: 10.1007/s00126-016-0691-7
[175] Zhu Chuanwei, Wen Hanjie, Zhang Yuxu, Fan Haifeng, Liu Jie, Zhou Zhengbing. 2015. Analytical technique for cadmium stable isotopes and its applications[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(5): 115−123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[176] Zhu Chuanwei, Wen Hanjie, ZhangYuxu, Fan Haifeng, Fu Shaohong, Xu Juan, Qin Tingrong. 2013. Characteristics of Cd isotopic compositions and their genetic significance in the lead–zinc deposits of SW China[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 43(11): 1847−1856 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/zd-2013-43-11-1847
[177] Zhu Minge, Wang Shuzhi, Zhang Cheng’e. 1990. The effect of zinc on soil bioactivity[J]. Journal of Agro–environmental Science, 2: 6–9, 13–48 (in Chinese).
[178] Zhu X K, O’Nions R K, Guo Y, Belshaw N S, Rickard D. 2000. Determination of natural Cu–isotope variation by plasma–source mass spectrometry: Implications for use as geochemical tracers[J]. Chemical Geology, 163(1): 139−149.
[179] Zhu Z Y, Jiang S Y, Yang T, Wei, H Z. 2015. Improvements in Cu–Zn isotope analysis with MC–ICP–MS: A revisit of chemical purification, mass spectrometry measurement and mechanism of Cu/Zn mass bias decoupling effect[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 393: 34−40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2015.10.009
[180] Zhu Zhiyong, Zhu Xiangkun, Yanh Tao. 2020. A fully automated chemical separation and purification system and its application to isotope analysis[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 39(3): 384−390 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[181] 常海伟, 刘代欢, 贺前锋. 2018. 重金属污染农田微生物修复机理研究进展[J]. 微生物学杂志, 38(2): 114−121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2018.02.017 [182] 符志友, 冯承莲, 赵晓丽, 郭文景, 孙思杨, 刘新妹, 王宇, 李晓峰, 吴丰昌. 2019. 我国流域水环境中铜、锌的生态风险及管理对策[J]. 环境工程, 37(11): 70−74. [183] 何天荣. 1995. 乡村企业土法冶炼氧化锌对人体的危害与预防[J]. 劳动安全与健康, 3: 30. [184] 侯李云, 曾希柏, 张杨珠. 2015. 客土改良技术及其在砷污染土壤修复中的应用展望[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 23(1): 20−26. [185] 胡宏韬, 程金平. 2009. 土壤锌污染修复实验研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 32(10): 53−56,102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2009.10.013 [186] 黄施棋, 龚迎莉, 田世洪, 梁正伟, 朱春会. 2023. 锌同位素在地球科学研究中的新进展[J]. 地质学报, 97(4): 1002−1029. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.04.003 [187] 黄益宗, 郝晓伟, 雷鸣, 铁柏清. 2013. 重金属污染土壤修复技术及其修复实践[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 32(3): 409−417. [188] 孔静, 郭庆军, 魏荣菲, 朱光旭, 胡健. 2017. 锌稳定同位素分析方法及其在环境科学研究中的应用[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(6): 1718−1726. [189] 李福燕, 张黎明, 李许明, 郭彬, 陈柳燕, 漆智平. 2006. 土壤–植物系统锌污染与修复技术研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 22: 5920−5921, 5979. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2006.22.079 [190] 李海涛, 杨鑫, 雷华基, 杨艳, 靳兰兰, 胡圣虹. 2021. 镉稳定同位素研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 40(1): 1−15. [191] 李津, 朱祥坤, 唐索寒. 2008. 低温环境下Zn同位素分馏的若干重要过程[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 27(5): 465−471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2008.05.012 [192] 李熠, 陈熹, 肖丕显, 马琼, 吴国. 2020. 中国镉超富集植物种类组成及分布特征研究[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 39(6): 11−16. [193] 李争显, 李伟, Lei Jiajun, Li Qianyu, 刘林涛, 周廉. 2020. 常见金属元素对人体的作用及危害[J]. 中国材料进展, 39(12): 934−944. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.202003018 [194] 李智, 许英奎, 朱丹, 李世杰, 李雄耀, 刘建忠. 2023. 锌同位素在行星科学中的研究进展[J]. 矿物学报, 43(3): 273−283. [195] 梁莉莉, 刘丛强, 王中良, 朱祥坤, 宋柳霆, 李津. 2008. 喀斯特高原湖泊生物地球化学过程中的锌同位素特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 27(4): 326−334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2008.04.009 [196] 刘梦蜀, 张群, 张英男, 张兆峰, 黄方, 于慧敏. 2019. 镉同位素分析方法及国际标样的镉同位素组成[C] //中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第17届学术年会论文集, 989. [197] 刘意章, 肖唐付, 朱建明. 2015. 镉同位素及其环境示踪[J]. 地球与环境, 43(6): 687−696. [198] 马桂云, 张振华, 严少华, 唐婉莹. 2003. 重金属对鱼类污染的研究进展[J]. 江苏环境科技, 16(2): 38−40. [199] 马蕾, 李丹丹, 吕逸文, 王勋, 王泽洲, 李孟伦, 杨春, 瞿瑗汝, 舒梓坦, 刘盛遨. 2022. 锌同位素地球化学及应用研究进展[J]. 地球化学, 51(2): 161−175. [200] 苗鑫, 陈林捷, 周飞杨, 刘星, 何栋, 郑洪涛, 朱振利. 2021. 高精度镉同位素分析样品消解方法对比研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 40(6): 947−953. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2021.06.022 [201] 彭毛, 刘波, 邢小苗, 周业丰, 王卓然, 李成, 魏建林. 2022. 稻田重金属镉污染治理效果研究[J]. 粮食科技与经济, 47(5): 4. [202] 任邦方, 凌文黎, 张军波, 张永清, 段瑞春. 2007. Zn同位素分析方法及其地质应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 26(6): 30−35. [203] 邵明昊, 左胜鹏, 洪文秀. 2020. 霍甫水丝蚓(Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri)环境监测与生态修复效应研究进展[J]. 环境科学导刊, 39(2): 1−9. [204] 宋文睿, 朱传威, 杨振, 吴云柱, 李乾坤, 高立生, 张嘉玮, 张羽旭, 樊海峰, 温汉捷. 2023. 贵州纳雍枝铅锌矿床成因研究: 来自镉同位素和微量元素的约束[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 42(1): 206−214. [205] 谭德灿, 朱建明, 李社红, 任堃, 赵博, 王静, 曾理. 2017. 同位素双稀释剂法的原理与应用Ⅱ: 应用部分[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(6): 948−954. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.06.010 [206] 谭德灿, 朱建明, 王静, 陶发祥, 曾理. 2016. 同位素双稀释剂法的原理与应用Ⅰ: 原理部分[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(1): 138−145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.01.016 [207] 田伟莉, 柳丹, 吴家森, 王立江, 陈昆柏. 2013. 动植物联合修复技术在重金属复合污染土壤修复中的应用[J]. 水土保持学报, 27(5): 188−192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2242.2013.05.037 [208] 涂光炽, 高振敏, 胡瑞忠, 张乾, 李朝阳, 赵振华, 张宝. 2004. 分散元素地球化学及成矿机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1–400. [209] 万丹, 陈玖斌, 张婷, 安宇宸, 帅旺财. 2022. 镉同位素分馏及其在示踪土壤镉来源和迁移转化过程中的应用进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 41(3): 341−352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.3.ykcs202203001 [210] 王静, 魏恒, 潘波. 2023. 中国农田土壤Cd累积分布特征及概率风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 44(7): 4406−4416. [211] 王曙光, 刘社堂, 南卡俄吾, 徐艳. 2016. 锌同位素示踪技术在土壤污染溯源中的应用[J]. 西部大开发(土地开发工程研究), (2): 61−65. [212] 王伟中, 张朝晖, 温汉捷, 朱传威, 张羽旭. 2020. 镉同位素在古环境重建中的应用: 以晚泥盆世弗拉期—法门期生物灭绝事件为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 39(1): 80−88. [213] 王银泉, 周涛发, 李湘凌. 2013. 镉同位素示踪技术在土壤和沉积物镉污染来源解析中的应用进展[J]. 矿物学报, 33(2): 713−714. [214] 王中伟, 袁玮, 陈玖斌. 2015. 锌稳定同位素地球化学综述[J]. 地学前缘, 22(5): 84−93. [215] 魏荣菲, 郭庆军, 杨俊兴, 朱光旭, 张晗芝, Marc Peters, 王春雨, 万鹰昕. 2014. 镉同位素技术在环境科学研究中的应用进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(2): 525−536. [216] 魏树和, 徐雷, 韩冉, 窦薛楷, 杨微. 2019. 重金属污染土壤的电动–植物联合修复技术研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 43(1): 154−160. [217] 魏树和, 周启星, 王新, 张凯松, 郭观林. 2004. 一种新发现的镉超积累植物龙葵(Solanum nigrum L)[J]. 科学通报, 24: 2568−2573. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.24.013 [218] 吴晓梅, 叶美锋, 吴飞龙, 林代炎. 2018. 狐尾藻对生猪养殖场沼Cu、Zn的富集与净化效果[J]. 福建农业学报, 33(11): 1195−1200. [219] 武巍, 张之鑫, 牛红红, 王巍巍, 蔡玉红. 2014. 浅析土壤重金属污染及修复措施[J]. 农业与技术, 8: 249−251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-962X.2014.01.193 [220] 向中兰. 2001. 补锌过量对人体的危害[J]. 现代医药卫生, 9: 727. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2001.09.050 [221] 向佐朋, 李波, 王新富, 唐果. 2020. 不同类型铅锌矿床中闪锌矿的Zn同位素组成特征[J]. 昆明理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 45(1): 32−41. [222] 熊捷迁, 弓晓峰, 江良, 李昊霖, 袁少芬, 林媛, 吴莉. 2021. 鄱阳湖水体沉积物中Zn、Cd对底栖生物的毒性效应及基准验证[J]. 湖泊科学, 33(6): 1687−1700. doi: 10.18307/2021.0607 [223] 徐慧婷, 张炜文, 沈旭阳, 傅巨阳, 陈菲菲, 王艳, 杨梦, 赵桐鹤, 朱维琴. 2019. 重金属污染土壤原位化学固定修复研究进展[J]. 湖北农业科学, 58(1): 10−14. [224] 闫家蕾, 李雁宾. 2023. 海洋镉生物地球化学循环研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 42(3): 720−732. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022041906 [225] 杨红飞, 严密, 姚婧, 王友保, 刘登义. 2007. 铜、锌污染对油菜生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 7: 1484−1490. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2007.07.013 [226] 杨勇, 何艳明, 栾景丽, 刘景洋, 郭玉文. 2012. 国际污染场地土壤修复技术综合分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 35(10): 92−98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2012.10.020 [227] 姚振楠, 钮恺之, 李明, 徐子茜. 2021. 化学淋洗法修复土壤中Cd、Pb、As的工程研究[J]. 广东化工, 48(12): 154−156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2021.12.063 [228] 俞文钰, 郝桐锋, 南海林, 张树林, 张清靖. 2023. 水生植物治理水体重金属污染的研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 841(11): 156−158,164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2023.11.040 [229] 张建平, 庄峙厦, 陈成祥, 黄华斌, 齐士林, 王小如. 2008. 大鼠体内铅镉分布的稳定同位素示踪ICP–MS研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 27(8): 835−838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2008.08.010 [230] 张力浩, 白姣杰, 田瑞云, 王国昌, 游来勇, 梁家妮, 慈凯东, 刘梦丽, 寇乐勇, 周伶俐, 周俊, 吴大付, 孙斌, 周静. 2023. 中国北方碱性农田土壤镉污染修复: 现状与挑战[J/OL]. 土壤学报: 1–13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1119.P.20230612.1349.002.html. [231] 张莹. 2018. 锌污染对土壤和植物的影响[J]. 度假旅游, 8: 86−87. [232] 张羽旭, 温汉捷, 樊海峰, 王加昇, 张锦让. 2010. Cd同位素地质样品的预处理方法研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 29(6): 633−637. [233] 赵玉. 2020. 渭河干流浅层地下水与地表水中重金属Cd污染特征及风险评价[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 42(2): 267−277. [234] 郑桂红, 唐玲玲, 孙建梅, 刘缠民, 程超, 冯照军. 2014. 重金属锌对锦鲤组织氧化损伤的作用[J]. 江苏农业科学, 42(3): 187−189. [235] 钟松雄, 李晓敏, 李芳柏. 2021. 镉同位素分馏在土壤–植物体系中的研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 58(4): 825−836. [236] 周佳栋, 马丹丹, 刘敏, 洪小慧, 傅嘉辉, 蒋璐蔓, 吕丹丹, 方佳琪, 曹勇, 李伟东. 2020. 三种水生植物对重金属的富集及净化能力研究[J]. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 19(1): 57−63. [237] 周振, 黄丽, 黄国棣, 马海关, 彭岗. 2023. 生物炭和海泡石复配对镉和锌复合污染土壤的钝化修复[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 42(2): 158−166. [238] 朱传威, 温汉捷, 张羽旭, 樊海峰, 付绍洪, 徐娟, 覃廷荣. 2013. 铅锌矿床中的Cd同位素组成特征及其成因意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 43(11): 1847−1856. [239] 朱传威, 温汉捷, 张羽旭, 樊海峰, 刘洁, 周正兵. 2015. Cd稳定同位素测试技术进展及其应用[J]. 地学前缘, 22(5): 115−123. [240] 朱铭莪, 王淑芝, 张成娥. 1990. 锌对土壤生物活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2: 6–9, 13–48. [241] 朱志勇, 朱祥坤, 杨涛. 2020. 自动分离提纯系统的研制及其在同位素分析测试中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 39(3): 384−390.




 下载:
下载: