Geothermal geological characteristics, genetic model and resource potential of hot dry rocks in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province
-
摘要:研究目的
位于青藏高原东北缘的共和盆地干热岩体是近年来我国内陆地区深层高温地热探测的重要发现之一,其成因机制一直备受争议,是研究的热点内容。现今热状态是盆地地热地质研究的重要内容,对深入理解高温地热分布规律及成藏机理具有重要的意义。
研究方法本文基于地球物理探测和钻井测温资料,分析了共和盆地基底结构特征与高温地热分布规律。采用数值模拟方法,初步获取了盆地近东西向二维温度场剖面,在此基础上,评估了干热岩资源潜力并对干热岩成藏要素进行了讨论。
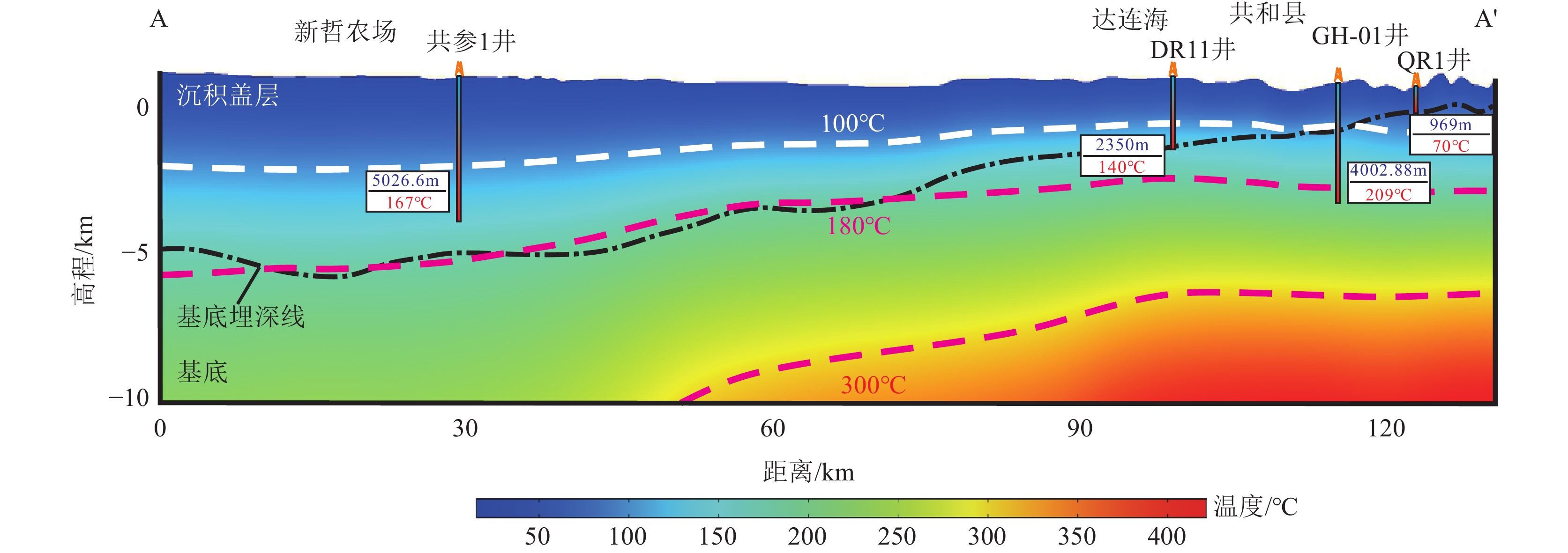
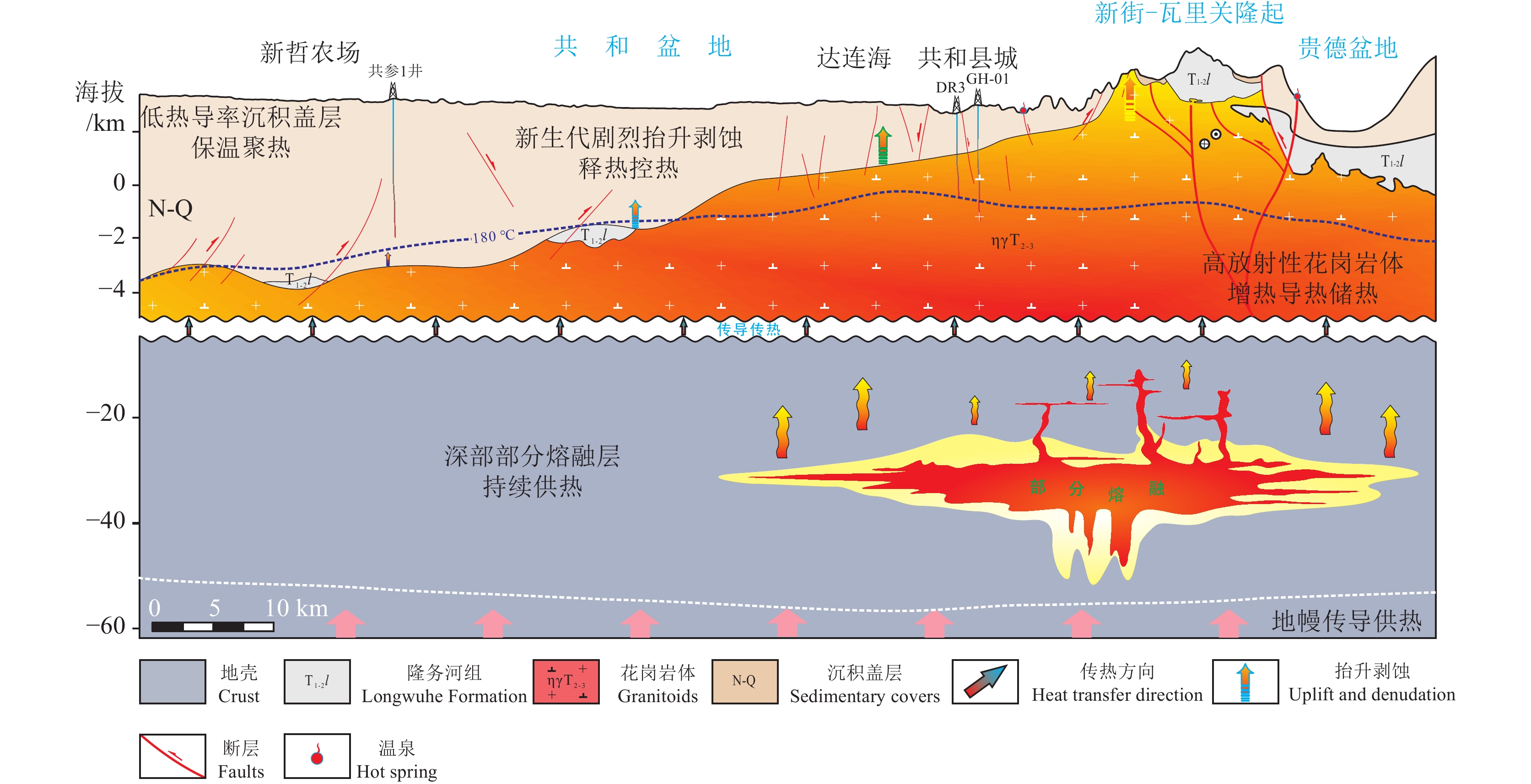
研究结果共和盆地干热岩地热资源丰富,5 km以浅资源量估算为2.48×1021 J。盆地温度场东西向存在显著差异,变化规律与盆地基底埋深起伏特征相类似,盆地东北部新街—瓦里关隆起带周缘地区具有较好的地热地质条件。
结论在综合前人研究基础上,我们认为,共和盆地深部部分熔融持续供热,放射性花岗岩体增温导热,新构造抬升剥蚀释热控热,沉积盖层保温聚热多种因素的影响,共同导致了盆地现今东西向差异明显的温度场特征和干热岩体的成藏就位。
创新点:(1)结合二维地震勘探、钻井等资料,厘定了共和盆地基底埋深特征,采用数值模拟方法,获取了盆地近东西向浅部地壳二维温度场分布;(2)在系统研究共和盆地地热地质特征基础上,探讨了共和盆地高温地热成因机制,为共和盆地干热岩勘探提供了地质依据。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geothermal geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveThe Gonghe Basin, situated on the northeastern margin of the Qinghai−Tibet Plateau, is a significant experimental area for the exploration and development of hot dry rock (HDR) in China. The formation mechanisms of HDR within the Gonghe Basin remain controversial and have attracted considerable research attention. The current thermal state is of great significance for a deeper understanding the distribution patterns and formation mechanisms of high−temperature geothermal reservoirs.
MethodsIn this study, extensive geophysical exploration and drilling data are integrated to describe the geological and geothermal architecture of the Gonghe Basin. A two−dimensional temperature field profile across the east−west axis is established through numerical simulation. Based on these results, the resource potential of HDR is assessed, and the key factors controlling HDR formation are analyzed.
ResultsThe Gonghe Basin hosts abundant HDR resources, with an estimated 2.48×1021 J within the depth of 5 km. The two−dimensional numerical simulation reveals significant temperature field variations between the eastern and western parts of the basin. The temperature field variations are consistent with the distribution of the basin's basement depth, which decreases from west to east. High−temperature anomalies are observed in the northeastern region, particularly around the Xinjie−Waliguan uplift belt.
ConclusionsOn the basis of understanding the knowledge of predecessors, this paper proposes a comprehensive HDR formation mechanism from the perspectives of geological, geothermal, and geophysical backgrounds. The formation of HDR within the Gonghe Basin is controlled by multiple factors, including continuous heating by partial melting, heating and conducting heat by granite, heat controlling by neotectonic uplift and denudation, and heat preservation and accumulation by sedimentary covers.
Highlights:(1) The stratigraphic distribution within the Gonghe Basin was determined through the integration of 2D seismic, drilling and other exploration datasets , and the two−dimensional temperature field distribution of the shallow crust in the basin was established for the first time by numerical simulation; (2) Based on the systematic study of geothermal geological characteristics of the Gonghe Basin, a genetic mechanism for the high−temperature geothermal resources within the basin was proposed. This mechanism provides a fundamental geological basis for the exploration of hot dry rock (HDR) resources in the Gonghe Basin.
-
1 ❶中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心. 2023. 青海共和盆地干热岩调查评价与勘查示范成果报告[R]. -
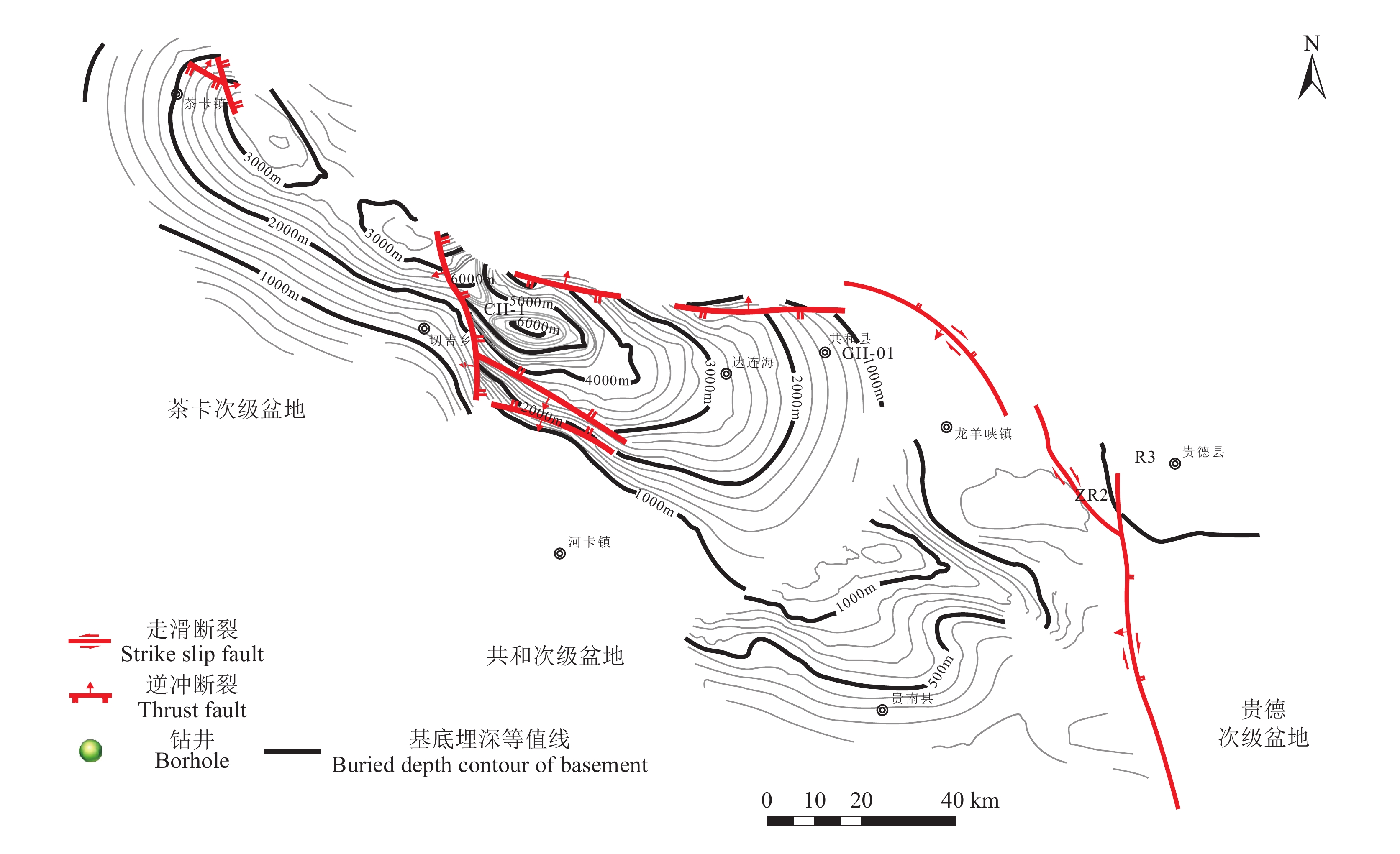
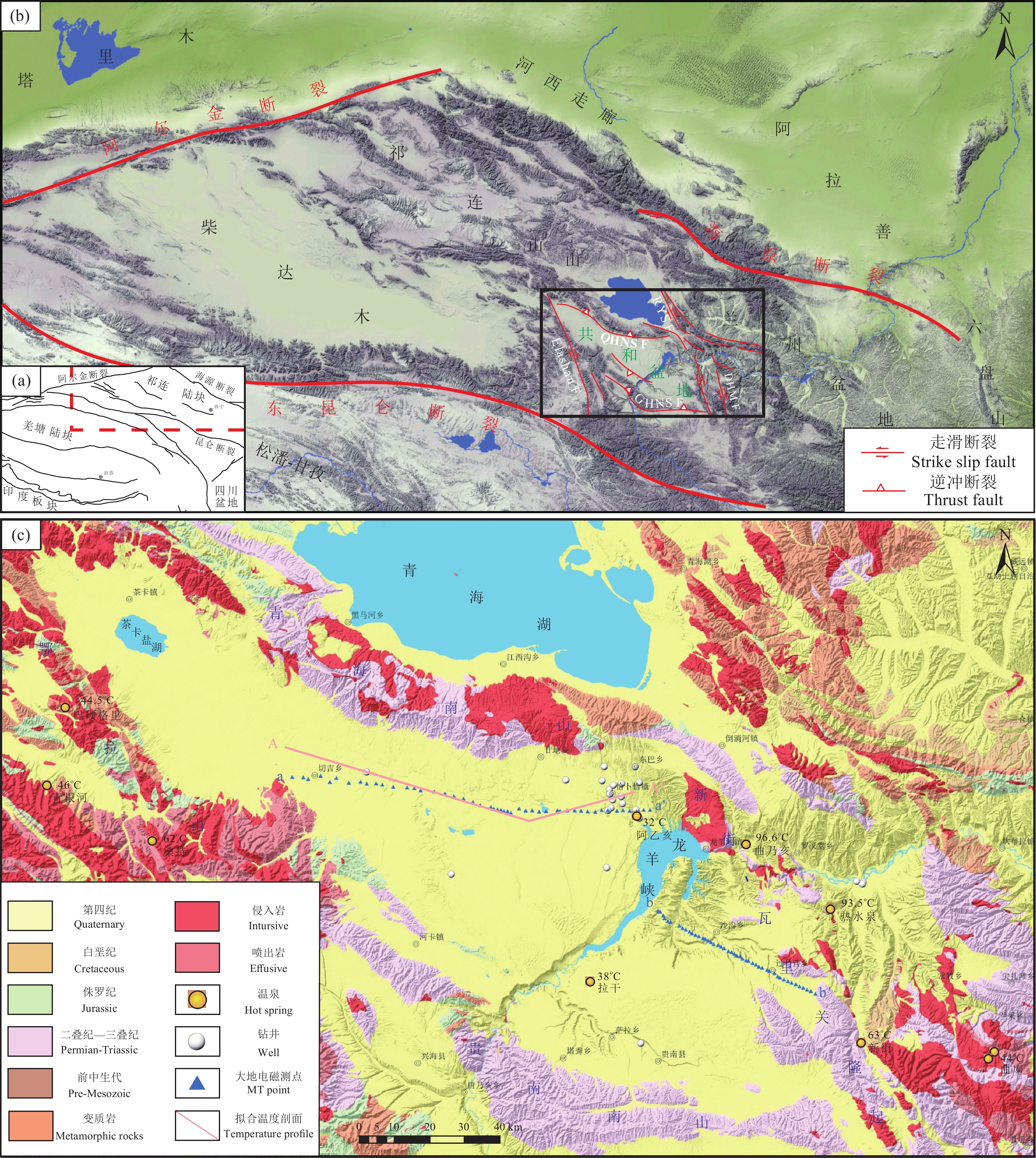
图 1 共和盆地区域构造位置图(a)、共和盆地及周缘地貌图(b)、共和盆地及周缘地质简图(c)
WQ—WHS F:温泉—哇洪山断裂;RYS F:日月山断裂;QHNS F:青海南山南缘断裂;GHNS F:共和南山断裂;DHM F:多禾茂断裂
Figure 1. The regional tectonic location map of the Gonghe basin (a), geomorphological map of Gonghe Basin and its surrounding margins (b), the geological map of the Gonghe Basin and its surrounding margins (c)
WQ−WHS F: Wenquan−Wahongshan fault; RYS F: Riyueshan fault; QHNS F: South margin of Qinghai Nan Shan fault; GHNS F: Gonghe Nan Shan fault; DHM F: Duohemao fault
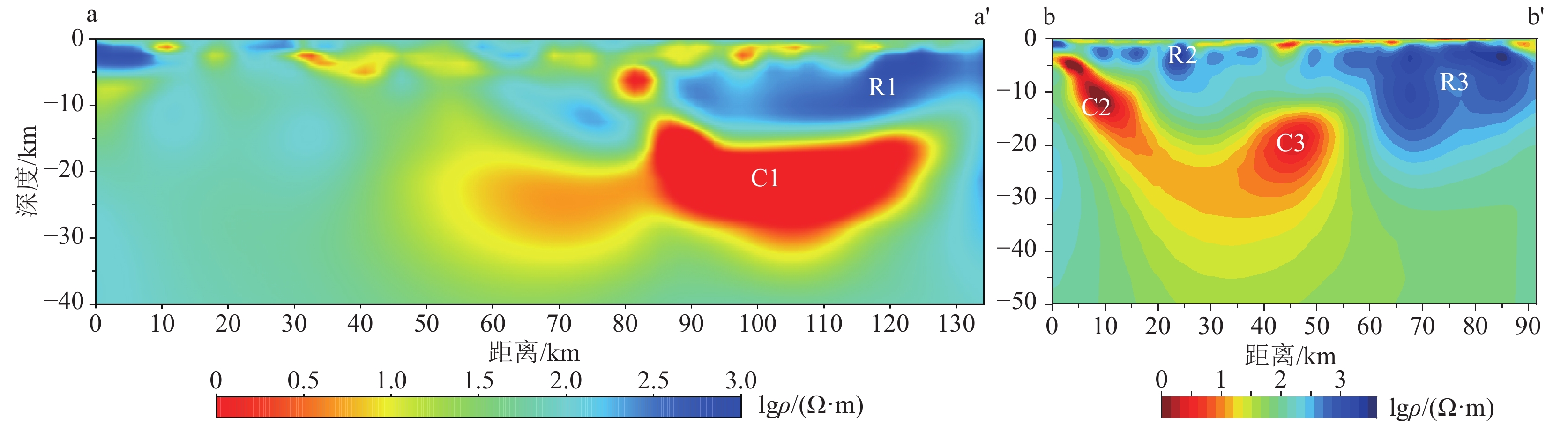
图 2 共和盆地主要断裂构造及基底埋深等值线图(据中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心,2023
1 )Figure 2. The buried depth contour of basement and the distribution of main faults in the Gonghe Basin
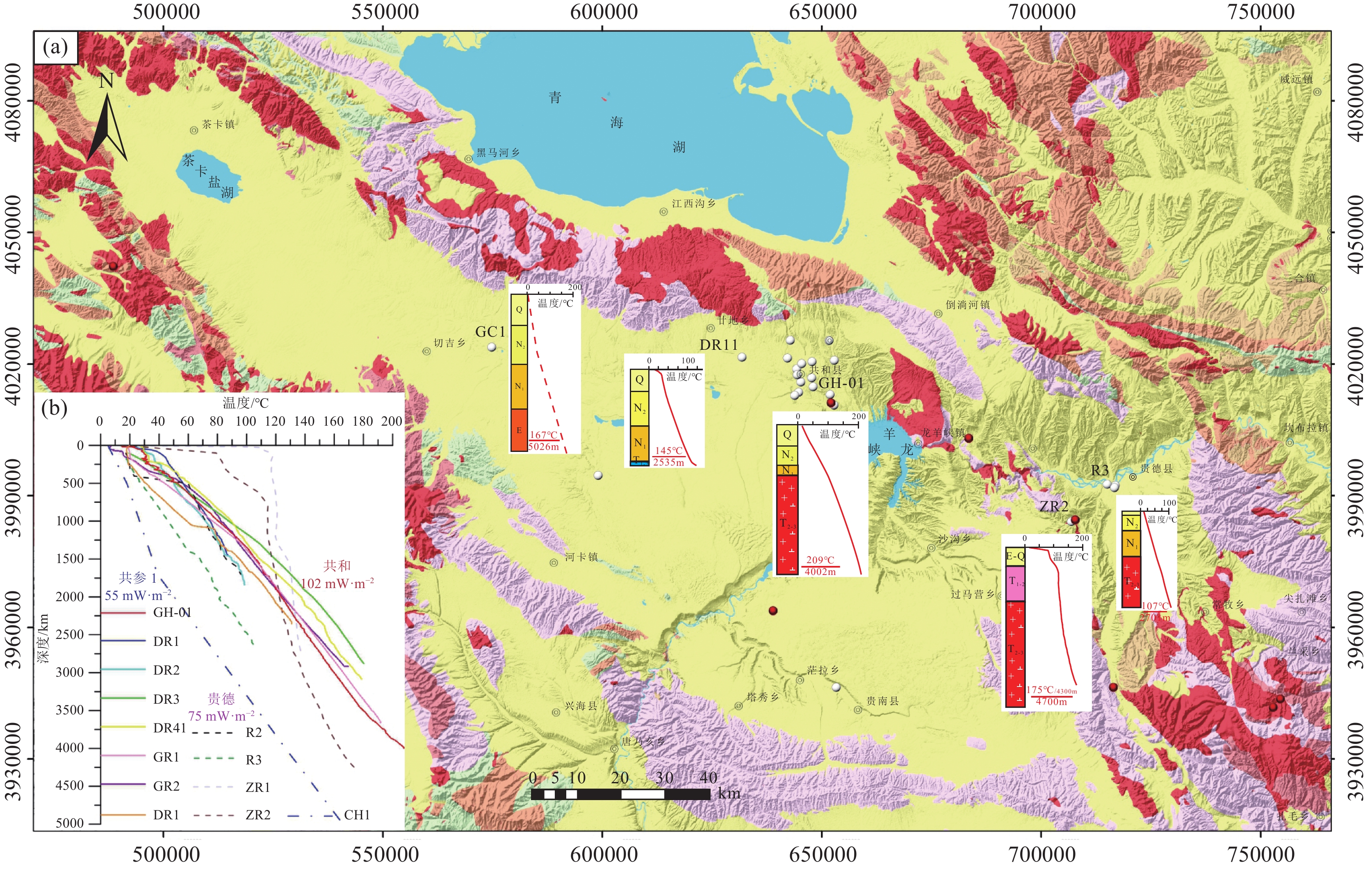
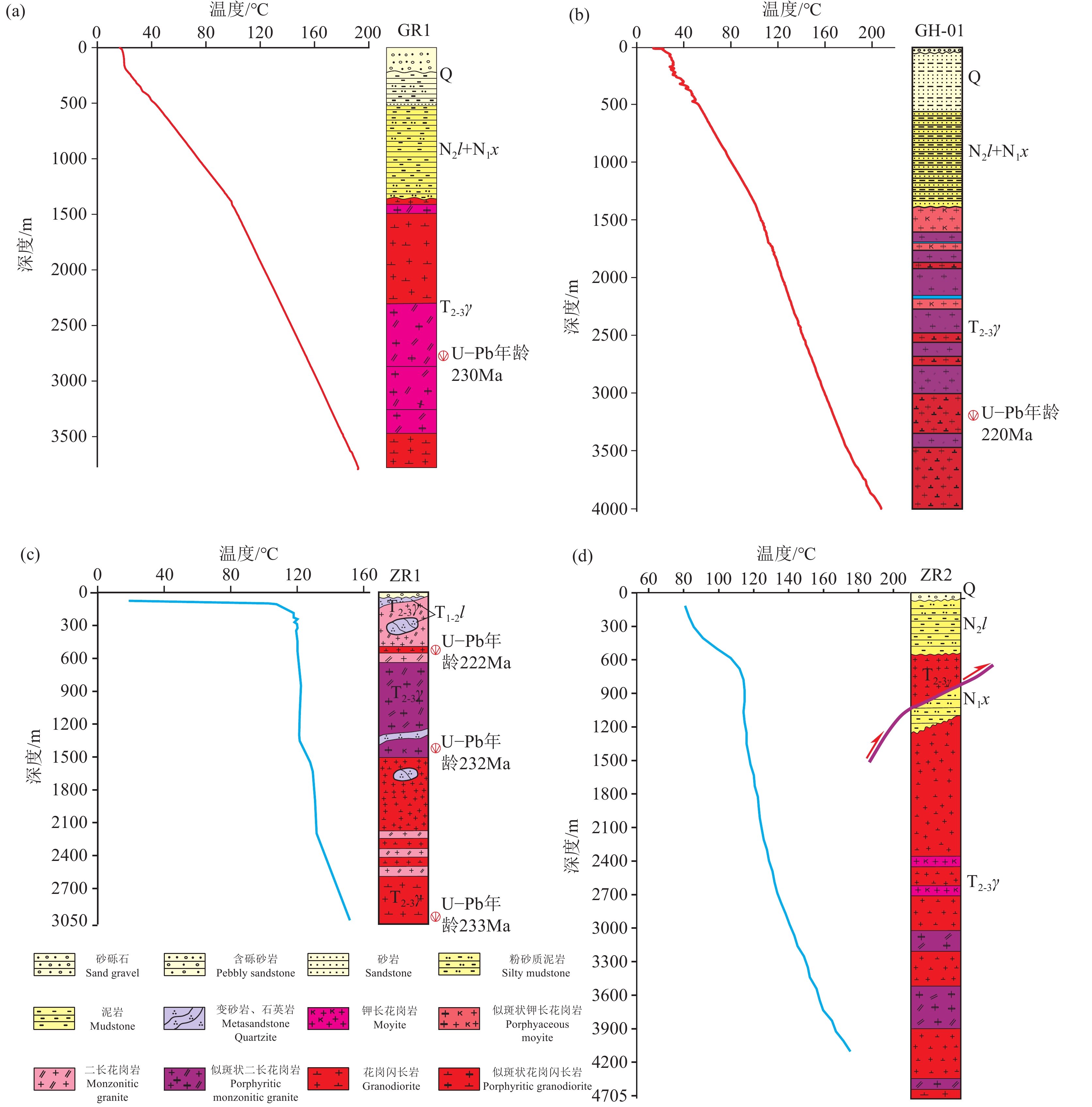
图 4 共和—贵德地区已有钻井地层结构及测温曲线
Q—第四纪;N2l—新近系中—上新统临夏组;N1x—新近系中新统咸水河组;T1-2l—早—中三叠统隆务河组;T2-3γ—中—晚三叠世花岗岩
Figure 4. Existing drilling formation structure and temperature measurement curve in Gonghe−Guide area
Q−Quaternary; N2l−Middle to Upper Pliocene Linxia Formation (Neogene); N1x−Middle Miocene Xianshuihe Formation (Neogene); T1-2l−Lower to Middle Triassic Longwuhe Formation; T2-3γ− Middle to Late Triassic Granite
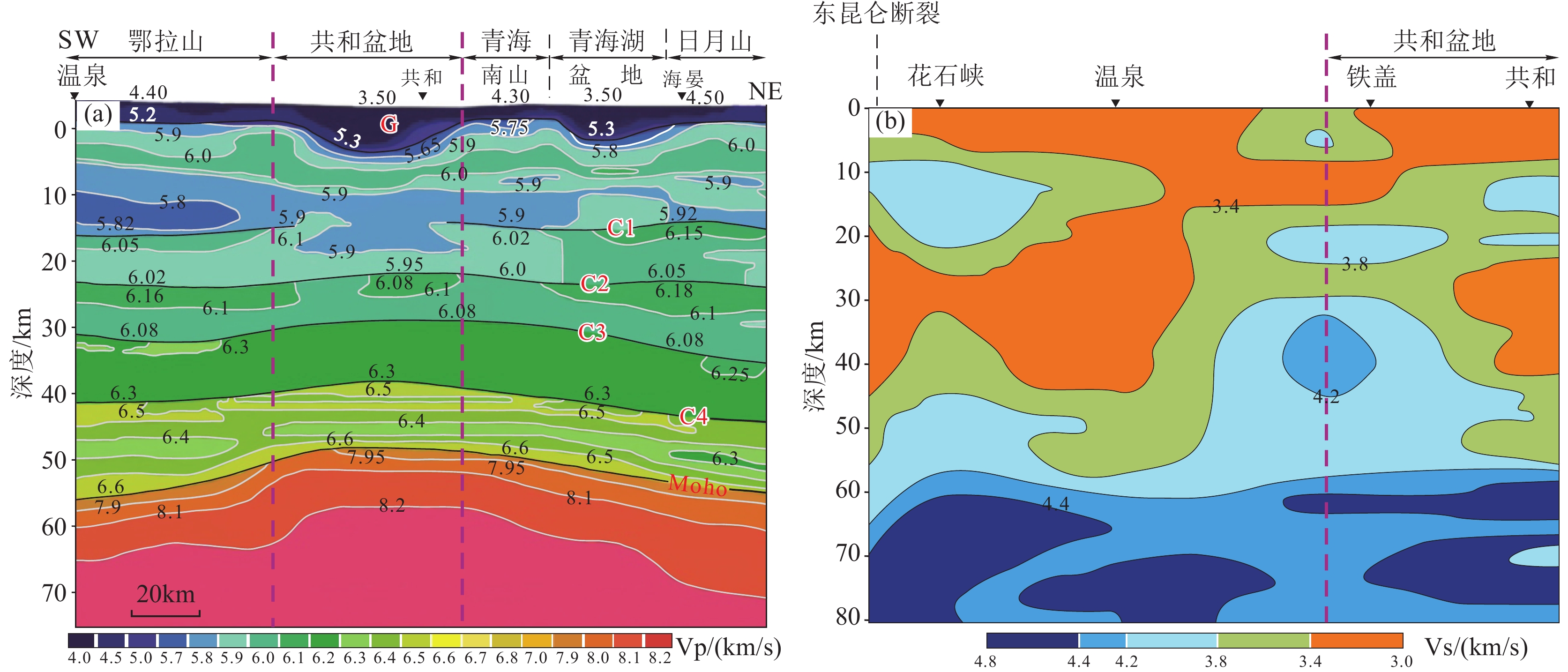
图 6 共和盆地地震波速度结构(据Jia et al., 2019, 钱辉等, 2001修改)
Figure 6. The seismic wave velocity structure in the Gonghe Basin (modified from Jia et al., 2019, Qian Hui et al., 2001)
表 1 共和主要钻井信息
Table 1 Drilling information within the Gonghe Basin
孔号 经纬度 成井时间
/年孔深
/m基底埋深/m 井底温度
/℃测温类型 东经 北纬 DR1 100°36′45″ 36°14′31″ 2011 1453.58 1354 88 连续测温 DR2 100°36′08″ 36°14′08″ 2012 1852.38 1440.9 99 连续测温 DR3 100°37′06″ 36°15′48″ 2014 2927.26 1340.25 181 连续测温 DR4 100°37′15″ 36°18′02″ 2015 3102 1402 182 连续测温 DR11 100°29′15″ 36°18′45″ 2021 2356 2220 131 连续测温 GH-01 100°38′44″ 36°16′17″ 2019 4002.88 1360 209 连续测温 GR1 100°38'55" 36°15'09" 2017 3705 1350 180/3325 连续测温 GR2 100°41'30" 36°14'09" 2017 3003 940 186 连续测温 GC1 99°50'11" 36°20'32" 1995 5026 - 167 地层随压测试温度 R2 101°24′32″ 36°2′14″ 2010 1709.56 1490.55 97 连续测温 R3 101°23′18″ 36°2′23″ 2012 2701.2 1400 104 连续测温 ZR1 101°18′06″ 36°58′05″ 2014 3050.68 12 151 连续测温 ZR2 101°17′41″ 35°57′54″ 2017 4700 550 205 连续测温 表 2 共和盆地不同区域钻井大地热流值
Table 2 Thermal current values of drilling in different areas of Gonghe Basin
钻井编号 地温梯度/(℃/100 m) 热导率/(W·m−1·k−1) 大地热流 数据来源 数据质量 GC1 34.4 1.59 54.7 本文 C GH-01 40.5 2.51 101.6 本文 A ZR1 2.91 2.93 79.5 郎旭娟等,2016 B 注:GC1采用地层随压测试温度计算地温梯度,采用邻区地层热导率计算大地热流值,因此归为C类数据;GH-01井大地热流基于为完井1个月后准稳态测温,及钻井岩心热导率数据,因此归为A类。分类依据参考(汪集旸和黄少鹏, 1990)。 表 3 模型热物性参数及取值
Table 3 Model thermal property parameters and values
地质体结构 热导率/(W·m−1·k−1) 生热率/(μW·m−3) 沉积盖层 1.59 1.67 结晶基底 2.51 3.20 注:热导率和生热率据(Zhang et al., 2020),模型上边界地形起伏数据来自30 m高程DEM数据。 -
[1] Aghahosseini A, Breyer C. 2020. From hot rock to useful energy: A global estimate of enhanced geothermal systems potential[J]. Applied Energy, 279: 115769. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115769
[2] Allen P A, Allen J R. 2013. Basin analysis: Principles and application to petroleum play assessment[M]. UK: John Wiley & Sons, 479−480.
[3] Artemieva I M, Thybo H, Jakobsen K, Sørensen N K, Nielsen L S K. 2017. Heat production in granitic rocks: Global analysis based on a new data compilation GRANITE 2017[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 172: 1−26. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.003
[4] Axelsson G. 2024. Chapter 20−The future of geothermal energy, in: Living with Climate Change[M]. Netherlands: Elsevier, 397−422.
[5] Ayling B F, Hogarth R A, Rose P E. 2016. Tracer testing at the Habanero EGS site, central Australia[J]. Geothermics, 63: 15−26.
[6] Beardsmore G. 2004. The influence of basement on surface heat flow in the Cooper Basin[J]. Exploration Geophysics. 35(4): 223−235.
[7] Benato S. 2016. Conceptual model and numerical analysis of the Desert Peak EGS project: Reservoir response to the shallow medium flow−rate hydraulic stimulation phase[J]. Geothermics, 63: 139−156. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2015.06.008
[8] Bertani R. 2016. Geothermal power generation in the world 2010−2014 update report[J]. Geothermics, 60: 31−43.
[9] Breede K, Dzebisashvili K, Liu X, Falcone G. 2013. Systematic review of enhanced (or engineered) geothermal systems: past, present and future[J]. Geothermal Energy, 1(1): 4. doi: 10.1186/2195-9706-1-4
[10] Brown M, Rushmer T. 2008. Evolution and Differentiation of the Continental Crust[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press.
[11] Callonnec L L, Renard M, Rafélis M D, Minoletti F, Beltran C, Chêne R J D. 2014. Evolution of the trace element contents (Sr and Mn) of hemipelagic carbonates from the Zumaia Paleocene section (Gipuzkoa, Spain): Implications for the knowledge of seawater chemistry during the Selandian[J]. Bulletin De La Societe Geologique De France, 185(6): 413−435.
[12] Chen Xijie, Yun Xiaorui, Lei Min, Cai Zhihui, Zhang Shengsheng, Liu Ruohan, Li Yibing, He Bizhu. 2020. Petrogenesis of Middle Triassic granite association in the Gonghe basin, Qinghai: Constraints from geochemistry, U−Pb ages and Hf isotopic[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica 36(10): 3152−3170 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Craddock W H. 2011. Structural and geomorphic evolution of the Gonghe basin complex, northeastern Tibet: Implications for the timing of plateau growth[D]. State College: Pennsylvania State University.
[14] Craddock W H, Kirby E, Zhang H, Clark M K, Champagnac J D, and Yuan D. 2014. Rates and style of Cenozoic deformation around the Gonghe Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geosphere, 10(6): 1255−1282. doi: 10.1130/GES01024.1
[15] Davies J H, Davies D R. 2010. Earth's surface heat flux[J]. Solid Earth, 1(1): 5−24. doi: 10.5194/se-1-5-2010
[16] Davies J H. 2013. Global map of solid Earth surface heat flow[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 14(10): 4608−4622.
[17] England P C, Thompson A B. 1984. Pressure−temperature−time paths of regional metamorphism I. Heat transfer during the evolution of regions of thickened continental crust[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25: 894−928.
[18] Fang X, Yan M, Voo R V D, Rea D K, Song C, Parés J M, Gao J, Nie J, Shuang D. 2005. Late Cenozoic deformation and uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from high−resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Guide Basin, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 117(9−10): 1208−1225.
[19] Feng Y F, Zhang X X, Zhang B, Liu J T, Wang Y G, Jia D L, Hao L R, Kong Z Y. 2018. The geothermal formation mechanism in the Gonghe Basin: Discussion and analysis from the geological background[J]. China Geology, 1(3): 331−345. doi: 10.31035/cg2018043
[20] Gao J, Zhang H J, Zhang H P, Zhang S Q, Cheng Z P. 2020. Three−dimensional magnetotelluric imaging of the SE Gonghe Basin: Implication for the orogenic uplift in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 789: 228525.
[21] Gao J, Zhang H J, Zhang S Q, Chen X B, Cheng Z P, Jia X F, Li S T, Fu L, Gao L, Xin H L. 2018. Three−dimensional Magnetotelluric Imaging of the Geothermal System beneath the Gonghe Basin, Northeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geothermics, 76: 15−25.
[22] Garcia J. 2016. The Northwest Geysers EGS Demonstration Project, California: Part 1: Characterization and reservoir response to injection[J]. Geothermics, 63: 97−119.
[23] Genter A, Guillou−Frottier L, Feybesse J L, Nicol N, Dezayes C, Schwartz S. 2003. Typology of potential hot fractured rock resources in europe[J]. Geothermics, 32(4/6): 701−710.
[24] He Bizhu, Zheng Menglin, Yun Xiaorui, Cai Zhihui, Jiao Cunli, Chen Xijie, Zheng Yong, Ma Xuxuan, Liu Ruohan, Chen Huiming, Zhang Shengsheng, Lei Min, Fu Guoqiang, Li Zhenyu. 2023. Structural architecture and energy resource potential of Gonghe Basin, NE Qinghai−Tibet Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 30(1): 81−105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] He L J, Zhang L Y. 2018. Thermal evolution of cratons in China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 164(15): 237−247.
[26] Hu S B, He L J, Wang J Y. 2000. Heat flow in the continental area of China: a new data set[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 179(2): 407−419. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00126-6
[27] Jia L Y, Hu D G, Wu H H, Zhao X T, Chang P Y, You B J, Zhang M, Wang C Q, Ye M N, Wu Z Q, Liang X Z. 2017. Yellow River terrace sequences of the Gonghe–Guide section in the northeastern Qinghai–Tibet: Implications for plateau uplift[J]. Geomorphology, 295: 323−336. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.06.007
[28] Jia S X, Guo W B, Mooney W D, Wang F Y, Duan Y H, Zhao J M, Lin J Y, Liu Z. 2019. Crustal structure of the middle segment of the Qilian fold belt and the coupling mechanism of its associated basin and range system[J]. Tectonophysics, 770: 128154. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.06.024
[29] Jiang F M, Chen J L, Huang W B, Luo L. 2014. A three−dimensional transient model for EGS subsurface thermo−hydraulic process[J]. Energy, 72: 300−310. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.05.038
[30] Jiang G Z, Hu S B, Shi Y Z, Zhang C, Wang Z T, Hu D. 2019. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: Updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 753: 36−48. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.01.006
[31] Kong Y L, Pan S, Ren Y Q, Zhang W Z, Wang K, Jiang G Z, Cheng Y Z, Sun W J, Zhang C, Hu S B, He L J. 2021. Catalog of Enhanced Geothermal Systems based on Heat Sources[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 95(6): 1882−1891. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14876
[32] Lang Xujuan, Liu Feng, Liu Zhiming, Lin Wenjing, Xing Linxiao, Wang Guiling. 2016. Terrestrial heat flow in Guide Basin, Qinghai[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 35(3): 227 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Lei Yude, Yuan Youjing, Qin Guangxiong, Ba Ruishou, Zhao Zhen, Li Tongbang. 2023. Analysis of thermal storage characteristics of the Guide Zhacang geothermal field in Gonghe Basin based on logging data[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 44(1): 145−157 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Li Linguo, Li Baixiang. 2017. A discussion on the heat source mechanism and geothermal system of Gonghe−Guide basin and mountain geothermal field in Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 41(1): 29−34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Lin Wenjing, Gan Haonan, Zhao Zhen, Zhang Shengsheng. 2022. Lithospheric Thermal−rheological Structure and Geothermal Significance in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 44: 45−56 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Lin Wenjing, Wang Guilin, Zhang Shengsheng, Zhao Zhen, Xing Linxiao, Gan Haonan. 2022. Heat Source Mechanism of Hot Dry Rock in the Gonghe Basin on the Northeastern Qinghai−Tibet Plateau[J]. Geothermal Energy, 3: 14−24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Lu S Y M. 2018. A global review of enhanced geothermal system (EGS)(Review)[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 81: 2902−2921. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.097
[38] Olasolo P, Juárez M C, Morales M P, D´Amico S, Liarte I A. 2016. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS): A review[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 56: 133−144.
[39] Pan S , Kong Y L, Wang K, Ren Y Q, Pang Z H, Zhang C, Wen D G, Zhang L Y, Feng, Q D, Zhu G L, Wang J Y. 2021. Magmatic origin of geothermal fluids constrained by geochemical evidence: Implications for the heat source in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 603: 126985.
[40] Pollack A, Horne R N, Mukerji T. 2020. What are the challenges in developing enhanced geothermal systems (EGS)? Observations from 64 EGS Sites[C]// Reykjavik, Iceland: Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2020+1.
[41] Qian Hui, Jiang Mei, Xue Guangqi, Su Heping, Wittlinger G, Vergne J. 2001. Crustal structure of northeastern Tibet inferred from receiver function analysis[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 23(1): 103−108 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Qiu Nansheng. 2002. Characters of thermal conductivity and radiogenic heat production rate in basins of Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 37(2): 196−206 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Shen Xianjie, Zhang Wenren, Guan Hua, Jin Xu. 1989. The Yadong−Qaidam heat flow great section spanning the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 17: 1329−1329 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Siégel C, Bryan S E, Purdy D, Allen C M, Schrank C, Uysal T, Gust D, Beardsmore G. 2012. Evaluating the role of deep granitic rocks in generating anomalous temperatures in south−west Queensland, in Geological Survey of Queensland: Digging Deeper 10 Seminar Extended Abstracts [Queensland Geological Record 2012/14][R]. Brisbane, Australia: Geological Survey of Queensland, Department of Natural Resource and Mines, 95–102.
[45] Sun Yangui, Fang Hongbin, Zhang Kun, Zhao Fuyue, Liu Shiying. 2007. Step−like landform system of the Gonghe basin and the uplift of the Qinghai−Tibet Plateau and development of the Yellow River[J]. Geology in China, 34(6): 1141−1147 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Sun Yangui. 2004. Gonghe Aulacogen and Conjugate and Transfer Between the West Qinling and East Kunlun Orogens[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Tang X C, Liu S S, Zhang D L, Wang G L, Luo Y F, Hu S B, Xu Q. 2022. Geothermal accumulation constrained by the tectonic transformation in the Gonghe Basin, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithosphere, 2021 (Special 5): 3936881.
[48] Tang Xianchun, Wang Guiling, Ma Yan, Zhang Dailei, Liu Zhong, Zhao Xu, Cheng Tianjun. 2020. Geological model of heat source and accumulation for geothermal anomalies in the Gonghe basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(7): 2052−2065 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Tang Xianchun, Wang Guiling, Zhang Dailei, Ma Yan. 2023. Coupling mechanism of geothermal accumulation and the cenozoic active tectonics evolution in Gonghe Basin, Northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 44(1): 7−20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] Wang Changgui, Lü Yousheng. 2004. Gonghe Basin: A new and worth−researching Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 25(5): 471−473 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] Wang Jiyang, Huang Shaopeng. 1990. Compilation of heat flow data in the China continental area (2nd Edition)[J]. Seismology and Geology, 12(4): 351−366 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[52] Wang Jiyang, Pang Zhonghe, Cheng Yuanzhi, Huang Yonghui, Jiang Guangzheng, Lu Zhenneng, Kong Yanlong. 2023. Current state, utilization and prospective of global geothermal energy[J]. Science & Technology Review, 41(12): 5−11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[53] Wang Q, Hawkesworth C J, Wyman D, Chung S L, Wu F Y, Li X H, Li Z X, Gou G N, Zhang X Z, Tang G J, Dan W, Ma L, Dong Y H. 2015. Pliocene−Quaternary crustal melting in central and northern Tibet and insights into crustal flow[J]. Nature Communications, 7: 11888.
[54] Weinert S, Br K, Scheuvens D, Sass I. 2021. Radiogenic heat production of crystalline rocks in the Gonghe Basin Complex (northeastern Qinghai–Tibet plateau, China)[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80: 270. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09558-x
[55] Woodhouse J H, Birch F. 1980. Comment on 'Erosion, uplift, exponential heat source distribution, and transient heat flux' by T. −C. Lee[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 85(B5): 2691−2693.
[56] Wu D L, Ge W P, Liu S Z, Yuan D Y, Zhang B, Wei C M. 2024. Present−day 3D Crustal Deformation of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau from Space Geodesy[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 51(4): e2023GL106143. doi: 10.1029/2023GL106143
[57] Wu Huanhuan, Wu Xuewen, Li Yue, Hu Daogong, Jia Liyun, Yan Jiandong, Wang Chaoqun, Xia Mengmeng. 2019. River terraces in the Gonghe−Guide section of the Yellow River: Implications for the late uplift of the northeastern margin of the Qinghai− Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(12): 3239−3248 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[58] Xu Ming, Zhu Chuanqing, Tian Yuntao, Rao Song, Hu Shengbiao. 2011. Borehole temperature logging and characteristics of subsurface temperature in Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(4): 1052−1060 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[59] Xu Shuying, Xu Defu, Shi Shengren. 1984. Discussion on geomorphic development and environmental evolution of Gonghe Basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 20(1): 146−157 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[60] Xu T, Wu Z B, Zhang Z J, Tian X B, Deng Y F, Wu C L, Teng J W. 2014. Crustal structure across the Kunlun fault from passive source seismic profiling in East Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 627: 98−107. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.11.010
[61] Yan Weide, Wang Yanxin, Gao Xuezhong, Zhang Shuheng, Ma Yuehua, Shang Xiaogang, Guo Shouyun. 2013. Distribution and aggregation mechanism of geothermal energy in Gonghe Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 46(4): 223−230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[62] Yun Xiaorui, Chen Xijie, Cai Zhihui, He Bizhu, Zhang Shengsheng, Lei Min, Xiang Hua. 2020. Preliminary study on magmatic emplacement and crystallization conditions and deep structure of hot dry rock in the northeastern Gonghe basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(10): 3171−3191 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[63] Zhang C, Hu S B, Zhang S S, Li S T, Zhang L Y, Kong Y L, Zuo Y H, Song R C, Jiang G Z, Wang Z T. 2020. Radiogenic heat production variations in the Gonghe basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the origin of high−temperature geothermal resources[J]. Renewable Energy, 148: 284−297. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.11.156
[64] Zhang C, Huang R H, Qin S, Hu S B, Zhang S S, Li S T, Zhang L Y, Wang Z T. 2021. The high−temperature geothermal resources in the Gonghe−Guide area, northeast Tibetan plateau: A comprehensive review[J]. Geothermics, 97: 102264. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102264
[65] Zhang C, Jiang G Z, Shi Y Z, Wang Z T, Wang Y, Li S T, Jia X F, Hu S B. 2018. Terrestrial heat flow and crustal thermal structure of the Gonghe−Guide area, northeastern Qinghai−Tibetan plateau[J]. Geothermics, 72: 182−192. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2017.11.011
[66] Zhang Chao, Hu Shengbiao, Song Rongcai, Zuo Yinhui, Jiang Guangzheng, Lei Yude, Zhang Shengsheng, Wang Zhuting. 2020. Genesis of the hot dry rock geothermal resources in the Gonghe basin: Constraints from the radiogenic heat production rate of rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(7): 2697−2709 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[67] Zhang Chao, Zhang Shengsheng, Li Shengtao, Jia Xiaofeng, Jiang Guangzheng, Gao Peng, Wang Yibo, Hu Shengbiao. 2018. Geothermal characteristics of the Qiabuqia geothermal area in the Gonghe basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(11): 4545−4557 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[68] Zhang E Y, Wen D G, Wang G L, Yan W De, Wang W S, Ye C M, Li X F, Wang H, Tang X C, Weng W, Li K, Zhang C Y, Liang M X, Luo H B, Hu H Y, Zhang W, Zhang S Q, Jin X P, Wu H D, Zhang L Y, Feng Q D, Xie J Y, Wang D, He Y C, Wang Y W, Chen Z B, Cheng Z P, Luo W F, Yang Y, Zhang H, Zha E L, Gong Y L, Zheng Y, Jiang C S, Zhang S S, Niu X, Zhang H, Hu L S, Zhu G L, Xu W H, Niu Z X, Yang L. 2022. The first power generation test of hot dry rock resources exploration and production demonstration project in the Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province, China[J]. China Geology, 5: 372−382. doi: 10.31035/cg2022038
[69] Zhang Huiping, Liu Shaofeng. 2009. Pleistocene deposition and subsequent erosion distribution around Xunhua−Guide Basin, North Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 29(4): 806−815 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[70] Zhang Peizhen, Zheng Dewen, Yin Gongming, Yuan Daoyang, Zhang Guangliang, Li Chuanyou, Wang Zhicai. 2006. Discussion on Late Cenozoic growth and rise of northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 26(1): 5−13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[71] Zhang Senqi, Fu Lei, Zhang Yang, Song Jian, Wang Fuchun, Huang Jinhui, Jia Xiaofeng, Li Shengtao, Zhang Linyou, Feng Qingda. 2020b. Delineation of hot dry rock exploration target area in the Gonghe Basin based on high−precision aeromagnetic data[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 40(9): 156−169 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[72] Zhang Senqi, Li Xufeng, Song Jian, Wen Dongguang, Li Zhiwei, Li Dunpeng, Cheng Zhengpu, Fu Lei, Zhang Linyou, Feng Qingda, Yang Tao, Niu Zhaoxuan. 2021. Analysis on geophysical evidence for existence of partial melting layer in crust and regional heat source mechanism for hot dry rock resources of Gonghe Basin[J]. Earth Science, 46(4): 1416−1436 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[73] Zhang Senqi, Wu Haidong, Zhang Yang, Song Jian, Zhang Linyou, Xu Weilin, Li Dunpeng, Li Shengtao, Jia Xiaofeng, Fu Lei, Li Xufeng, Feng Qingda. 2020a. Characteristics of regional and geothermal geology of the Reshuiquan HDR in Guide County, Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(5): 1591−1605 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14324
[74] Zhang Senqi, Yan Weide, Li Dunpeng, Jia Xiaofeng, Zhang Shengsheng, Li Shengtao, Fu Lei, Wu Haidong, Zeng Zhaofa, Li Zhiwei, Mu Jianqiang, Cheng Zhengpu, Hu Lisha. 2018. Characteristics of geothermal geology of the Qiabuqia HDR in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1087−1102 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[75] Zhang Yongming. 2017. Indosinian Tectonic−Magmatism and Regional Tectonic Evolution in the Qinghainanshan Tectonic Belt[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[76] Zhao X Y, Zeng Z F, Huai N, Wang K. 2020. Geophysical responses and possible geothermal mechanism in the Gonghe Basin, China[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo−Energy and Geo−Resources, 6(1): 1−12. doi: 10.1007/s40948-019-00123-2
[77] 陈希节, 贠晓瑞, 雷敏, 蔡志慧, 张盛生, 刘若涵, 李毅兵, 何碧竹. 2020. 青海共和盆地中三叠世花岗岩组合岩石成因: 地球化学、锆石U−Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 36(10): 3152−3170. [78] 何碧竹, 郑孟林, 贠晓瑞, 蔡志慧, 焦存礼, 陈希节, 郑勇, 马绪宣, 刘若涵, 陈辉明. 2023. 青海共和盆地结构构造与能源资源潜力[J]. 地学前缘, 30(1): 81−105. [79] 郎旭娟, 刘峰, 刘志明, 蔺文静, 邢林啸, 王贵玲. 2016. 青海省贵德盆地大地热流研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 35(3): 227−232. [80] 雷玉德, 袁有靖, 秦光雄, 巴瑞寿, 赵振, 李铜邦. 2023. 基于测井资料的共和盆地贵德扎仓地热田热储特征分析[J]. 地球学报, 44(1): 145−157. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2022.100903 [81] 李林果, 李百祥. 2017. 从青海共和—贵德盆地与山地地温场特征探讨热源机制和地热系统[J]. 物探与化探, 41(1): 29−34. [82] 蔺文静, 甘浩男, 赵振, 张盛生. 2023. 青海共和盆地岩石圈热−流变结构及地热意义[J]. 地球学报, 44(1): 45−56. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2022.092001 [83] 蔺文静, 王贵玲, 张盛生, 赵振, 邢林啸, 甘浩男. 2022. 青藏高原东北缘共和盆地干热岩热源机制[J]. 地热能, 3: 14−24. [84] 钱辉, 姜枚, 薛光琦, 宿和平, Wittlinger G, Vergne J. 2001. 天然地震接收函数揭示的青藏高原东部地壳结构[J]. 地震学报, 23(1): 103−108. [85] 邱楠生. 2002. 中国西北部盆地岩石热导率和生热率特征[J]. 地质科学, 37(2): 196−206. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.02.007 [86] 沈显杰, 张文仁, 管烨, 金旭. 1989. 纵贯青藏高原的亚东−柴达木热流大断面[J]. 科学通报, 17: 1329−1329. [87] 孙延贵, 方洪宾, 张琨, 赵福岳, 刘世英. 2007. 共和盆地层状地貌系统与青藏高原隆升及黄河发育[J]. 中国地质, 34(6): 1141−1147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.06.021 [88] 孙延贵. 2004. 西秦岭—东昆仑造山带的衔接转换与共和坳拉谷[D]. 西安: 西北大学. [89] 唐显春, 王贵玲, 马岩, 张代磊, 刘忠, 赵旭, 程天君. 2020. 青海共和盆地地热资源热源机制与聚热模式[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 2052−2065. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.013 [90] 唐显春, 王贵玲, 张代磊, 马岩. 2023. 青藏高原东北缘活动构造与共和盆地高温热异常形成机制[J]. 地球学报, 44(1): 7−20. [91] 王昌桂, 吕友生. 2004. 共和盆地—一个值得研究的新盆地[J]. 新疆石油地质, 25(5): 471−473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2004.05.003 [92] 汪集旸, 黄少鹏. 1990. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第二版)[J]. 地震地质, 12(4): 351−366. [93] 汪集暘, 庞忠和, 程远志, 黄永辉, 姜光政, 陆振能, 孔彦龙. 2023. 全球地热能的开发利用现状与展望[J]. 科技导报, 41(12): 5−11. [94] 吴环环, 吴学文, 李玥, 胡道功, 贾丽云, 颜建东, 王超群, 夏蒙蒙. 2019. 黄河共和−贵德段河流阶地对青藏高原东北缘晚期隆升的指示[J]. 地质学报, 93(12): 3239−3248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.12.015 [95] 徐明, 朱传庆, 田云涛, 饶松, 胡圣标. 2011. 四川盆地钻孔温度测量及现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(4): 1052−1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.04.020 [96] 徐叔鹰, 徐德馥, 石生仁. 1984. 共和盆地地貌发育与环境演化探讨[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 20(1): 146−157. [97] 严维德, 王焰新, 高学忠, 张树恒, 马月花, 尚小刚, 郭守鋆. 2013. 共和盆地地热能分布特征与聚集机制分析[J]. 西北地质, 46(4): 223−230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.04.022 [98] 贠晓瑞, 陈希节, 蔡志慧, 何碧竹, 张盛生, 雷敏, 向华. 2020. 青海共和盆地东北部干热岩岩浆侵位结晶条件及深部结构初探[J]. 岩石学报, 36(10): 3171−319. [99] 张超, 胡圣标, 宋荣彩, 左银辉, 姜光政, 雷玉德, 张盛生, 王朱亭. 2020. 共和盆地干热岩地热资源的成因机制: 来自岩石放射性生热率的约束[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(7): 2697−2709. doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0381 [100] 张超, 张盛生, 李胜涛, 贾小丰, 姜光政, 高堋, 王一波, 胡圣标. 2018. 共和盆地恰卜恰地热区现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(11): 4545−4557. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0747 [101] 张会平, 刘少峰. 2009. 青藏高原东北缘循化一贵德盆地及邻区更新世时期沉积与后期侵蚀样式研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 29(4): 806−816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.04.17 [102] 张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 袁道阳, 张广良, 李传友, 王志才. 2006. 有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(1): 5−13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.01.002 [103] 张森琦, 付雷, 张杨, 宋健, 王富春, 黄金辉, 贾小丰, 李胜涛, 张林友, 冯庆达. 2020b. 基于高精度航磁数据的共和盆地干热岩勘查目标靶区圈定[J]. 天然气工业, 40(9): 156−169. [104] 张森琦, 李旭峰, 宋健, 文冬光, 李志伟, 黎敦朋, 程正璞, 付雷, 张林友, 冯庆达. 2021. 共和盆地壳内部分熔融层存在的地球物理证据与干热岩资源区域性热源分析[J]. 地球科学, 46(4): 1416−1436. [105] 张森琦, 吴海东, 张杨, 宋健, 张林友, 许伟林, 黎敦朋, 李胜涛, 贾小丰, 付雷. 2020a. 青海省贵德县热水泉干热岩体地质—地热地质特征[J]. 地质学报, 94(5): 1591−1605. [106] 张森琦, 严维德, 黎敦朋, 贾小丰, 张盛生, 李胜涛, 付雷, 吴海东, 曾昭发, 李志伟, 穆建强, 程正璞, 胡丽莎. 2018. 青海省共和县恰卜恰干热岩体地热地质特征[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1087−1102. doi: 10.12029/gc20180601 [107] 张永明. 2017. 青海南山构造带印支期构造岩浆作用与区域构造演化[D]. 西安: 长安大学. [108] 张永明. 2017. 青海南山构造带印支期构造岩浆作用与区域构造演化[D]. 西安: 长安大学.



 下载:
下载: