Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the intermediate-acid plutons in Shatanjiao ore-field, Tongling, Anhui
-
摘要:
安徽省铜陵地区是中国著名的以矽卡岩和斑岩型矿床为主的铜-金多金属矿集区, 区内广泛产出的中酸性侵入岩与成矿关系十分密切。沙滩脚矿田位于该矿集区的东部, 出露沙滩脚、桂花冲和姚家岭岩体及其不同规模、不同矿化类型的铜、金、锌等矿床, 岩体对成矿起了重要的控制作用。本文在前人研究的基础上, 对该矿田内的沙滩脚、姚家岭、桂花冲3个岩体进行了详细的岩石学、地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学研究, 以期查明沙滩脚矿田中酸性侵入岩的成因及成岩构造环境。岩石地球化学分析表明, 3个岩体具有准铝质特征, 均属于高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩类, 轻稀土富集, 重稀土亏损, 具有弱的负Eu异常, 富集Rb、Th等元素, 亏损Nb、Ta等高场强元素。姚家岭岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄为140.4~140.9 Ma, 沙滩脚岩体形成时代相对较早(141.4~144.1 Ma), 桂花冲岩体形成相对较晚(138.3Ma)。结合区域地质背景, 笔者认为沙滩脚矿田的这些岩体形成于早白垩世伸展环境, 是由来自于富集地幔的分异的碱性玄武质岩浆与地壳易熔组分部分熔融形成的花岗质岩浆混合后分期侵位形成的。
Abstract:The Tongling area of Anhui Province is a famous copper-gold polymetallic ore concentration area dominated by skarn and porphyry type deposits in China. The widely exposed intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in the area are closely related to mineralization. The Shatanjiao ore-field is located in the eastern part of the ore concentration area. The Shatanjiao, Guihuachong and Yaojialing rock bodies and their copper, gold and zinc deposits of different scales and mineralization types are exposed. Rock bodies play an important role in controlling mineralization. On the basis of previous studies, a detailed studies on petrography, geochemistry and zircon U-Pb chronology for Shatanjiao, Yaojialing and Guihuachong plutons in the ore-field were carried out in order to find out the petrogenesis of these plutons and their forming tectonic setting. Geochemically, the three plutons have a metaluminous characteristics, all of which belong to high-potassium calc-alkline series Ⅰ-type granites with depletion in HREE, Nb, Ta, and enrichment in LREE, Rb, Th, and slightly negative Eu anomaly. The zircon U-Pb age of the Yaojialing pluton is 140.4-140.9Ma, while the Shatanjiao pluton formed relatively earlier (141.4-144.1 Ma), and the Guihuachong pluton formed later (138.3Ma). Combined with the regional geology, we infer that these plutons in the ore-field were emplaced in the early Cretaceous extended environment, which is crystallized from a mixed magma between a differentiated basaltic magma derived from the enriched mantle and a felsic magma from the partial melting of crustal fusible component.
-
1. 引言
地壳中天然含有一定量的重金属,其中一些元素(如Cu、Zn、Cr)是人体代谢必需的;在自然条件下,它们很少累积到对环境和生态系统造成有害影响的水平(Sun et al., 2018)。然而,随着工业发展对矿产资源需求的增加,在金属矿山开采过程中,矿体中的重金属元素容易产生流失并进入土壤中,导致后者重金属含量升高;最终,它们可能通过各种介质进入人体,对矿区附近的居民构成潜在的健康风险(Lu et al., 2019;张进德等,2021;Chen et al., 2023)。Singh and Kalamdhad(2011)在重金属对土壤、植物、人类健康和水生生物的影响研究中,发现重金属在过度累积下,Cu的长期接触会导致肝肾损伤和中枢神经损伤,Zn的长期接触会导致系统功能失调、生长和繁殖受损,Cr的长期接触将导致肝、肾脏循环和神经组织受损等健康问题。Duruibe et al.(2007)对重金属污染和人类的生物毒性效应研究中,发现Cd、Pb、Hg在人类生物化学或生理学中没有任何已知的功能,在生物体中也不是天然存在的;因此,即使在较低暴露下,也会在生物中累积并造成影响。Cd对肾脏和骨骼具有高度毒性,较高水平的吸入会对肺部产生损伤,可能会引起呕吐和腹泻;长时间接触会累积在肾脏中,最终导致肾脏疾病和肺损伤(Bernard,2008)。Pb对人体具有生理和神经毒性,可能导致肾脏、生殖系统、肝脏和大脑功能障碍,严重可导致死亡(Zahra and Kalim, 2017);已观察到Pb对神经系统有着最为敏感的影响,尤其是对儿童和婴儿,长期的接触会导致儿童发育不良、智商低下(Reuben et al., 2017)。Hg则被认为是环境中毒性较大的重金属,可以与其他元素结合形成无机汞和有机汞;会损害大脑,肾脏和发育中的胎儿(Al Osman et al., 2019)。Jaishankar et al.(2014)研究发现As具有显著的毒性和致癌性,以氧化物或硫化物的形式广泛存在;低剂量摄入会导致恶心和呕吐、心率异常、血管损伤等症状,长期接触可导致皮肤癌、肺癌、肝癌和膀胱癌。
湖南省矿产资源丰富,矿种较多,享有“有色金属之乡”的美誉。在采、选、冶等矿业活动过程中产生的“三废”会对周边土壤生态环境产生破坏。研究表明,湖南省因有色金属矿产开采导致的重金属污染土地面积达2.8×104 km2,占全省总面积的13%(郭朝晖和朱永官,2004)。虽然有部分学者对湖南省矿区土壤污染开展研究(余旋等,2016;江诚毅,2020;余嘉衍等,2020),但针对锡矿区污染资料仍非常有限,需要进一步开展针对性的调查与评价。研究区位于湘南地区,区内有成规模的锡矿区、工业区以及农业区;在生活与生产过程中对周边土壤具有潜在的威胁,而其土壤重金属污染和健康风险研究几近空白。因此,基于对生态环境和当地居民人体健康的保护,本文对研究区土壤重金属展开研究,采用多元评价评估锡矿区重金属含量与分布特征,探讨重金属污染程度与生态风险,为当地土壤环境安全及受同样问题影响的地区提供参考与科学依据。
2. 区域地质与研究方法
2.1 研究区概况
研究区区域地层以南华系、泥盆系,石炭系为主(图 1a),前者为浅变质碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩,主要分布于泗洲山背斜;后者为浅海相碳酸盐岩夹滨海相碎屑岩,分布于大义山岩体周围;此外,河流周围发育少量第四系,为洪积、冲积及残坡积层。区域基底褶皱总体呈NNE走向,控制着区域整体构造格架;盖层褶皱多呈近SN—NNW向分布于岩体周边,背斜多具紧密线型特征,向斜则较开阔;区域断裂构造总体走向325°,倾向北东、倾角大于65°;按走向划分为NE、NW—NNW、NW、NNW—近SN向四组(张遵遵等, 2022)。区域岩浆岩主要为大义山岩体,研究区主要发育中细粒斑状角闪黑云二长花岗岩(ηγJ3a)、中细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγJ3c)、细粒少斑状黑云母二长花岗岩(ηγJ3b)、细粒斑状(含电气石)二云母二(正)长花岗岩(ηγJ3e),中细粒斑状角闪黑云二长花岗岩为本文所采集样品的母岩。
大义山是南岭地区重要的成锡岩体,自2000年以来,该区已查明万金窝、猫仔山、藤山坳、白沙子岭、大顺窿、台子上、狮形岭等大中型矿山7处,小型矿床(点)40余处;累计提交锡资源量10余万t。本文研究对象为该岩体东南部某大型锡矿区,地处南岭北麓,舂陵江中上游。研究区地形地貌复杂,山地丘陵约占总面积的3/4,属于典型丘岗山地地带;地势由东南向西北倾斜,东南地势高峻多山地,西北山势低矮,以丘陵为主。研究区土类主要分为红壤、黄壤与水稻土3类,以林地、荒草地、耕地与园地为主,种植作物以烤烟、蔬菜、水稻为主。本区属亚热带湿润性季风气候,气候温暖,光照充足,雨热同期,1月平均气温2.5℃,7月平均气温28℃。区内年降雨量1460 mm,年内降雨变化较大,多集中于3—7月。
2.2 样品采集与分析
调查与研究表明,多数矿区土壤存在显著的重金属异常或污染,本文结合已有分析先例和研究区成矿元素的组成特点,选取Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Cd、As、Hg元素为分析内容。在矿区以及周边地区采集114个表层土壤样品(图 1b),其中南北向土壤样本89个,东西向土壤样本25个,采样深度为0~20 cm,并在区内工程揭露的天然土壤边坡取3个垂向剖面,深度140~220 cm。土壤样品采用多点采样法,去除植物根系、碎石等杂质,留取1 kg装入样品袋。干燥后研磨过100目尼龙筛,取筛下粒级样品150 g备用。样品测试在中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心完成,Cu、Pb、Zn和Cr含量采用原子吸收分光光度计AAS nos300-ZEEnit600测定,Cd、As和Hg含量使用全自动原子荧光分光光度计AFS-230E测定;采用国家一级标准物质对准确度和精密度进行验证,所有样本测试分析均在允许值范围内;Cu、Pb、Cr、As元素检出限为0.01 mg/kg,Cd、Hg元素检出限0.001 mg/kg,分析精度优于0.8%。
2.3 评价方法
2.3.1 地累积指数
地累积指数法是综合考虑人为污染因素、地球化学背景值和自然成岩作用的共同影响,判别土壤重金属污染程度的一种评价方法(Xia et al., 2020)。计算公式为:

式中,Ci为第i种重金属的实测值,Bi为土壤中第i种元素的地球化学背景值,K为成岩作用引起的背景值的变动系数(通常取值K=1.5)。根据Forstner et al.(1993)提出的划分标准,可将重金属分为7个等级(表 1)。
表 1 地累积指数污染程度分级Table 1. Classifications of geo-accumulation index pollution level
2.3.2 潜在生态风险评估
采用Hakanson潜在生态风险指数法评价土壤重金属的生态风险(表 2),该指数法是将生态效应、毒理效应和环境效应联系在一起,可系统、全面地评估土壤重金属污染状况(何东明等,2014;高瑞忠等,2019)。计算公式为:
 表 2 潜在生态风险评价等级划分Table 2. Classifications potential ecological risk evaluation level
表 2 潜在生态风险评价等级划分Table 2. Classifications potential ecological risk evaluation level
式中,RI为综合潜在生态风险指数;Eri为第i种重金属单项潜在生态风险指数;Tri为第i种重金属的毒性相应系数;各毒性响应系数为:Cu=5、Pb=5、Zn=1、Cr=2、Cd=30、As=10、Hg=40(Hakanson, 1980; 徐争启等, 2008);Pi为重金属i污染指数;Ci为重金属i的实测值;Cni为土壤重金属i元素背景值。
2.3.3 人体健康风险评价
根据USEPA风险评估方法,土壤重金属往往通过3种途径被人体摄入并危害人体健康,即经口摄入、皮肤接触、吸入土壤颗粒物。计算公式为:

式中,ADDing、ADDderm和ADDinh分别代表经口摄入、皮肤接触和呼吸吸入的日均暴露剂量;Ci为土壤中重金属i的含量。暴露皮肤表面积参照(刘同等, 2022),其他参数值(表 3)参照《建设用地土壤污染风险评估技术导则》(HJ 25.3-2019)推荐值以及EPA暴露因子手册。
表 3 健康风险评估模型暴露参数Table 3. Exposure parameters of health risk assessment model exposure parameters
健康风险效应分析分为致癌效应和非致癌效应,其中非致癌效应通过非致癌风险指数(HQ)和总非致癌风险指数(HI)表示。致癌效应通过致癌风险指数(CR)和总致癌风险指数(TCR)表示。

式中,ADD表示摄入、皮肤或呼吸暴露途径的日均暴露含量,RfD表示参考剂量,SF为斜率因子,具体参考值见表 4(王昌宇等,2021;刘同等,2022)。当HI≤1时,非致癌风险属于可接受范围,当HI>1时,意味将因接触特定的有毒元素而具有潜在的非致癌风险。TCR < 1.0×10-6不会对人体产生致癌风险;1.0× 10-6≤TCR≤1.0×10-4时,致癌风险属于可接受范围;TCR>1.0×10-4时,则认为致癌风险不可接受,会对人体产生致癌风险(Rehmana et al., 2018)。
表 4 不同暴露途径的参考剂量(RfD)和斜率因子(SF)Table 4. Reference dose (RfD) and slope factor (SF) of different exposure routes
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 表层土壤重金属含量与分布特征
结果显示研究区土壤中重金属含量均值均超出湖南省土壤环境背景值(表 5),其中,Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Cd、As和Hg含量均值分别为湖南土壤背景值的12.26、35.27、11.84、1.66、218.52、115.31和2.11倍,样本超标率分别为94.74%、100%、100%、67.54%、100%、100%和82.46%。参考《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618-2018)筛选值,重金属元素存在部分点位超过筛选值的情况,其中,Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Cd、As和Hg超出筛选值样本分别占总样本的45.61%、79.82%、63.16%、4.39%、84.21%和100%,Hg样本均未超标。变异系数可以反映重金属元素在空间上的离散和变异程度,变异系数越大意味着受到人为影响越大(Li et al., 2017)。研究区表层土壤变异系数由大到小依次为:Cd>As>Cu>Zn>Pb>Cr>Hg,Cd、As、Cu、Zn和Pb变异系数分别为2.24、2.08、1.66、1.59和1.40,表明这些重金属分布具有明显空间差异,存在人为污染的可能。
表 5 研究区土壤重金属含量特征分析(mg/kg)Table 5. Characterization of soil heavy metal content in the study area (mg/kg)
研究区土壤环境地球化学表层剖面显示,土壤中Cd、As、Pb、Zn和Cu元素含量在空间分布上具有明显的相似性(图 2)。富集区均位于矿区附近,尾矿库与冶炼区为矿山主要污染区域,可见冶炼区以及尾矿库具有集中分布和复合污染的特点(Hu et al., 2018);Cr元素含量较低,富集区呈岛状分布,集中于居民区;Hg元素浓度分布较均匀,高值区位于矿区北侧。综上所述,研究区土壤重金属在不同程度上受到外源物质的影响。根据土壤重金属的来源可知,土壤重金属来源主要分为自然源以及人为活动,自然来源与成土母质有关,而人为来源主要受到人为活动和强度的影响(王昌宇等, 2021)。结合变异系数等已有分析初步判断,Cd、As、Pb、Zn和Cu异常富集主要是由于矿业活动中重金属流失进入土壤中造成的,Cr主要受到生活污染的影响,Hg可能受到部分人为活动的影响,但主要受到花岗岩母岩风化作用的影响。此外,重金属污染程度还取决于重金属的迁移,雨水淋滤作用的强度是影响迁移的主要因素(Meite et al., 2018),研究区年降水量约1460 mm,区内较强的淋滤作用可能是造成研究区污染范围较广的主要因素之一。
综上所述,研究区内土壤中重金属浓度偏高,并伴随向外扩散的趋势;矿业活动被视为研究区重金属的主要来源,通过风、水等其他可能运输的方式向周边输出重金属。由于矿区内以及居民区表层土壤中重金属的累积可能会增加当地居民的健康风险,因此,可以进行更多的调查,以评估其风险和潜在的不利影响。
3.2 剖面土壤重金属含量与分布特征
为探究矿区土壤重金属垂向分布规律,选取矿区内HTZ1、HTZ2、HTZ3剖面为研究对象(图 3)。Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、As含量随深度增加而降低,在表层土壤中含量较高,且在0~60 cm深度内含量下降较明显,60 cm之下深度含量趋于稳定;这种表层土壤中重金属累积的现象,可能受到矿业活动的影响。在不同剖面中,剖面土壤重金属含量排序为HTZ3>HTZ2>HTZ1;根据剖面所在功能区可知,HTZ1、HTZ2剖面均位于采矿区,而HTZ2则更靠近冶炼区,HTZ3剖面靠近尾矿坝和冶炼区。尾矿的堆积以及冶炼中产生的废气、废渣、废液对土壤重金属具有活化作用,加速重金属的富集,从而导致区域内重金属在环境中不断累积并高于周边地区(邬光海等,2020)。这与郭世鸿等(2015)通过对矿区土壤重金属污染特征的研究中发现在不同功能区中污染排序呈尾矿库区>冶炼区>废弃冶炼区>采矿区的结果基本一致,说明研究区矿业活动中冶炼以及尾矿的堆积是造成土壤重金属累积的主要原因,而采矿导致的重金属累积则较小。Cr剖面含量分布在HTZ1、HTZ2、THZ3变化趋势相同,含量增加与减少所在的深度单位略有不同:HTZ1在0~60 cm重金属含量随深度增加而增加,60~100 cm重金属含量急剧下降,随后逐渐上升,至160 cm达到高峰,160~220 cm持续下降;HTZ2、HTZ3在20cm处含量达到最大值,随后波动变化分别在80 cm、120 cm和100 cm、180 cm处出现小高峰。Hg剖面含量分布具有如下规律:HTZ1在0~60 cm含量增加并达到最大值,随后波动变化在100 cm、140 cm、200 cm出现小高峰;HTZ2在20 cm含量达到最大值,随后波动变化在120 cm、180 cm出现小高峰;HTZ3在0~60 cm含量波动变化并在60 cm达到最大值,随后持续下降;Cr与Hg元素在不同土层深度含量变化略有不同的状况,可能是由于不同土壤剖面中土壤理化性质相似层的厚度不同,从而影响重金属垂向迁移和富集(Bi et al., 2006)。
3.3 土壤重金属污染程度分析
采用地累积指数法对研究区表层土壤中7种重金属进行评价,Igeo平均值从大到小依次为Cd (4.80)>As(4.14)>Pb(3.55)>Zn(1.90)>Cu(1.68)>Hg(0.20)>Cr(-0.44)。不同等级污染样本占比结果表明(图 4):研究区表层土壤中Cd污染最为严重,极重污染样本占比42%,中度及以上污染样本占比达97%;As和Pb元素极重污染样本分别占比28%和18%,中度及以上污染样本分别占比98%和97%;Zn和Cu极度污染样本分别占比8%和11%,中度及以上污染样本分别占比66%和72%;Hg和Cr不存在重度以上污染的样品,中度及以上污染样本占比不超过20%。研究结果表明锡矿最为突出的污染元素为Cd和As,其次为Pb、Zn和Cu,Hg和Cr污染相对较小,与前人得出的研究结果基本一致(莫佳等,2015;陈希清等,2021;张浙等,2022),因此在锡矿区周边土壤重金属污染治理中应重视Cd、As、Pb、Zn和Cu污染的治理。
3.4 土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价
研究区表层土壤Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Cd、As和Hg的潜在生态风险因子(Eri)平均值分别为15.94、28.01、3.71、0.91、874.07、645.71和2.20(图 5),生态风险样本占比结果表明:Cr、Hg、Zn全部样本的生态风险指数均小于40,为轻微生态风险;Cu和Pb样本大部分为轻微污染,中风险以上样本占比不足20%;As生态风险处于中—极重风险区间,中度及以上风险样本占比75%;研究区Cd生态风险最高,中度及以上风险样本占比高达80%,是研究区土壤最主要的潜在生态风险因子。土壤的RI值范围为31.84~17392.10,平均值为1570.55;生态风险处于轻微—极重风险区间,其中,中度及以上风险样本占比67%,极重风险样本占比31%。整体而言,研究区生态风险较高,As和Cd元素为生态风险的主要贡献因子。
3.5 人体健康风险评价
3.5.1 暴露风险评估
基于健康风险评估模型暴露参数计算研究区土壤重金属的日暴露量,结果如表 6和表 7所示:成人致癌与非致癌平均日摄入量顺序为ADDing>ADDinh>ADDderm,儿童致癌与非致癌平均日摄入量顺序为ADDing>ADDderm>ADDinh。经口摄入是致癌与非致癌风险的主要摄入途径,根据不同途径暴露量可知非致癌风险暴露途径中儿童的暴露量均高于成人,致癌风险暴露途径中儿童经口摄入以及皮肤接触途径暴露量均高于成人,呼吸吸入途径低于成人。根据不同元素暴露量可知,在致癌与非致癌风险中儿童暴露量均高于成人;这可能是受到儿童的生理和行为特征(吸吮行为,以及较差的解毒和排毒能力)的影响,使得儿童的健康更易受到威胁。
表 6 土壤重金属非致癌平均日暴露量(mg/(kg·d))Table 6. Average daily exposure of non-carcinogenic heavy metals in soils (mg/(kg·d)) 表 7 土壤重金属致癌平均日暴露量(mg/(kg·d))Table 7. Average daily exposure of soil heavy metals causing cancer (mg/(kg·d))
表 7 土壤重金属致癌平均日暴露量(mg/(kg·d))Table 7. Average daily exposure of soil heavy metals causing cancer (mg/(kg·d))
3.5.2 健康风险评价
根据日暴露量和参考剂量计算研究区7种重金属的非致癌与致癌健康风险指数,结果如表 8、表 9所示。
表 8 土壤重金属非致癌健康风险指数Table 8. Non-carcinogenic health risk index of soil heavy metal 表 9 土壤重金属致癌健康风险指数Table 9. Cancer health risk index of soil heavy metal
表 9 土壤重金属致癌健康风险指数Table 9. Cancer health risk index of soil heavy metal
非致癌健康风险指数显示:成人非致癌风险不同暴露途径顺序为HQing>HQinh>HQderm,儿童为HQing>HQderm>HQinh,表明经口摄入是非致癌风险的主要途径。从重金属元素来看,成人的非致癌风险排序依次为As>Pb>Cd>Cr>Cu>Zn>Hg,儿童排序为为As>Pb>Cr>Cd>Cu>Zn>Hg。其中,As和Pb元素为高风险元素,As元素成人和儿童经口摄入途径均值大于1,Pb元素儿童经口摄入途径均值大于1;意味着这些重金属将通过经口摄入途径对人体尤其是儿童健康造成不良影响。此外,研究区土壤中Cd与Cr元素儿童经口摄入途径最大值大于1,Cd元素成人和儿童呼吸吸入途径最大值大于1,暗示二者会对人体产生非致癌风险;其余重金属元素在不同暴露途径中均小于1,对人体健康影响较弱。因此,需要着重管理和控制研究区内As、Pb以及部分区域Cd和Cr的污染状况,以免对当地居民尤其是儿童产生不利影响。
致癌健康风险指数显示,成人与儿童不同暴露途径致癌风险顺序均为CRing>CRinh>CRderm;表明经口摄入途径为成人和儿童致癌风险的主要途径,呼吸吸入途径为成人和儿童致癌风险的次要途径。研究区重金属元素对成人和儿童致癌风险贡献顺序依次为As>Cd>Cr>Pb。As元素成人和儿童的CRing的均值分别为1.19×10-3和1.91×10-3,CRinh的均值分别为9.74×10-5和4.05×10-5,CRderm的均值分别为1.03×10-5和1.14×10-5;即As经口摄入途径对人体健康构成了致癌风险,呼吸吸入和皮肤接触途径则属于可接受范围;Cd经口摄入途径的均值位于10-6~10-4,呼吸吸入以及皮肤接触均值小于10-6。表明经口摄入属于可接受范围,呼吸吸入以及皮肤接触途径不会对人体产生致癌风险;此外,Cd元素成人和儿童经口摄入的最大值分别为5.56×10-4和8.95×10-4,这表明研究区内部分采样点中Cd元素存在致癌风险;Cr所有接触途径均位于10-6~10-4,属于可接受范围;Pb经口摄入属于可接受范围,呼吸吸入与皮肤接触途径不会对人体产生致癌风险。根据TCR以及上述分析可知,研究区土壤As元素对人体健康构成了潜在的致癌风险,Cd部分采样点同样存在致癌风险,Cr和Pb元素则属于可接受范围,对人体致癌风险较小。
3.6 讨论
土壤中重金属污染是当前环境、土壤等领域的主要研究问题之一,城市、工业区以及矿区是重金属污染的高危地带。本文通过对研究区土壤重金属含量,变异系数和空间分布分析可知:研究区土壤中Cd、As、Pb、Zn、Cu含量明显高于土壤环境背景值,呈现出富集于矿业区的特点;它们在空间分布上亦较为一致,重金属含量呈现尾矿库>冶炼区>采矿区的规律;研究区Cr富集区主要分布在生活区,可能与矿业无关;Hg分布较均匀,无明显富集区。
目前,土壤重金属评价主要基于生态风险和健康风险,本文结合已有研究发现,研究区土壤重金属生态风险与邻近区域研究结果趋于一致。沈红艳(2021)评价了湖南省某典型流域农田土壤重金属的生态风险,发现Cd、As、Pb受到工业、交通运输等影响污染最为突出,Cr和Hg受自然活动影响污染较轻;余璇等(2016)对湖南某铅锌矿生态风险评价,发现Cd、Pb、As、Cu、Zn属于中等及以上风险状态,Cr属于相对安全水平;雷鸣等(2008)对湖南9个县市采矿区和冶炼区附近水稻土5种重金属风险进行评价,发现土壤重金属Cd、As、Zn、Cu、Pb都在中等潜在风险之上。通过上述研究发现该片区土壤重金属均存在严重的生态危害,需要对该地区土壤生态环境的治理采取综合且有效的措施。
研究区土壤重金属致癌与非致癌的主要暴露途径为经口摄入,儿童受到的致癌与非致癌风险总体要大于成人,表明儿童更易受到重金属的威胁。这与杨敏等(2016)、鲍丽然等(2020)等研究结果相近,可能是由于儿童的生理和行为特征(吸吮行为等)更易接触到土壤以及儿童较差的免疫所导致。该区As和Pb对人体构成了潜在的威胁,其中As为主要的风险元素,这可能是由于As较大的毒性和较高的含量所致。周楠(2016)、王昌宇等(2021)指出重金属健康风险除了与含量有关之外,还与重金属毒性有关,As具有较大的毒性,更易对人体产生潜在的健康威胁。考虑到重金属无法被人体全部吸收消化,李华等(2015)、刘同等(2022)引入生物可给性,发现基于总量的评价与生物体内含量相关性较差,往往夸大了危害程度。本次研究评价基于土壤中重金属总量,缺乏一些间接因素(如作物对重金属的转归、人体对重金属的拮抗作用),因此本次研究有一定程度的不确定性,真实情况还需进一步研究。但从土壤环境与健康角度出发,土壤环境治理依然不容懈怠,对潜在的健康风险应保持警惕。
4. 结论
(1)地统计分析表明研究区土壤重金属含量高于土壤背景值,其中As和Cd最为突出;变异系数表明,Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As元素受到矿业活动影响较大,Cr和Hg元素受矿业活动影响较小;空间分布结果表明Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As含量富集区位于矿区附近,具有集中分布和复合污染的趋势。
(2)地累积指数评价结果显示,研究区Cd和As元素污染现象最为突出,Cu、Pb和Zn元素污染次之,Cr和Hg总体呈无污染—轻度污染状态。潜在生态风险指数表明,研究区土壤中重金属潜在生态风险主要以中—极重风险为主,As和Cd生态风险较高,是生态风险的主要贡献元素,Pb和Cu元素次之,Zn、Cr和Hg为轻微风险。
(3)人体健康风险评估结果表明,儿童更容易受到重金属威胁,经口摄入是重金属非致癌和致癌风险的主要暴露途径。土壤中Cd和Cr部分样本对人体具有潜在的非致癌风险,Cd部分样品对人体具有潜在的致癌风险。As和Pb总非致癌风险指数大于1,为主要非致癌因子,具有潜在的非致癌风险;As总致癌风险指数大于10-4,为主要致癌因子。
-
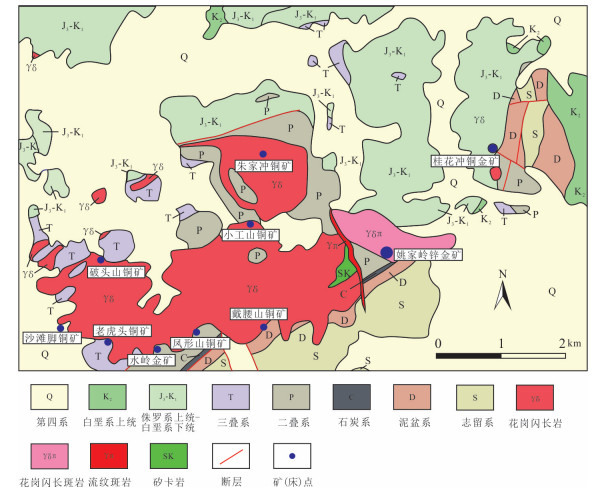
图 1 长江中下游成矿带位置及构造单元简图(a、b)及铜陵矿集区地质简图(c, 据Wu et al., 2014)
Figure 1. Location and structural map of the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt (a, b) and geological sketch map of the Tongling ore district (c, after Wu et al., 2014)
图 3 沙滩脚矿田3个岩体镜下照片
a—沙滩脚岩体, 不等粒-似斑状结构; b—姚家岭岩体, 似斑状结构; c—桂花冲岩体, 似斑状结构, 斜长石强烈的绢云母化; Pl—斜长石; Kfs—钾长石; Q—石英
Figure 3. Microphotographs of the three plutons in Shtanjiao ore-field
a- Shatanjiao pluton, inequigranular and porphyritic-like texture; b-Yaojialing pluton, porphyritic-like texture; c-Guihuachong pluton, porphyritic-like texture, strong sericitization for plagioclase; Pl-Plagioclase; Kfs-Potash feldspar; Q-Quartz
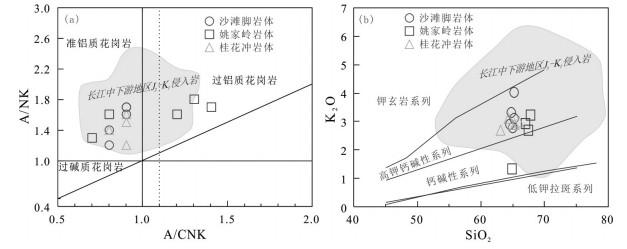
图 5 A/NK-A/CNK图解(a)(据Maniar et al., 1989)和K2O-SiO2图解(b)(据Rickwood, 1989)
(图中浅灰色区域代表长江中下游地区J3-K1侵入岩, 据Wu et al., 2018))
Figure 5. Diagrams of A/NK-A/CNK (a) (after Maniar et al., 1989) and K2O-SiO2 (b)(after Rickwood, 1989)
(The gray area in the Figure represents the J3-K1 granitoicl rocks in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, after Wu et al., 2018)
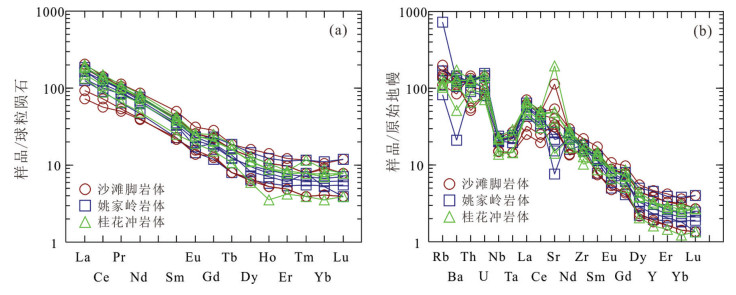
图 6 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and trace elements spider diagram (b) (after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
图 7 沙滩脚、姚家岭与桂花冲岩体构造环境判别图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)
Figure 7. Nb VS. Y、Rb VS.(Y+Nb)、Ta VS. Y discrimination diagrams (after Pearce et al., 1984)
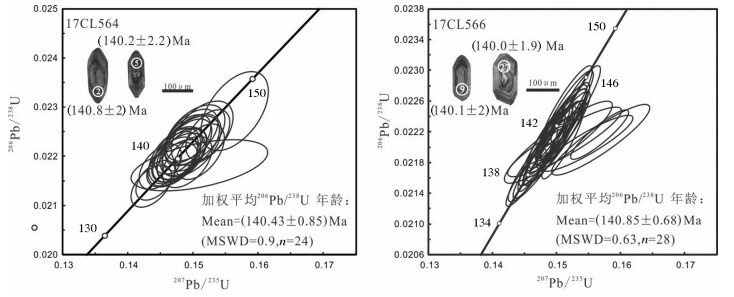
表 1 姚家岭岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic data of the Yaojialing pluton

表 2 沙滩脚矿田3个岩体岩石化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of three plutons in Shatanjiao ore-field

-
Ames Leslie, Zhou Gaozhi, Xiong Baocheng. 1996. Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism with implications for collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtze Cratons, central China[J]. Tectonics, 15(2):472-489. doi: 10.1029/95TC02552
Chang Yinfo, Liu Xuegui.1983. On strata-bound skarn deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, (1):13-22 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198301001.htm
Chang Yinfo, Pei Rongfu, Hou Zengqian, Yang Zhusen. 2017.Geochemical dataset of the Shizishan magmatic fluid system in the Tongling ore concentration area, Anhui Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(S1):49-55(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chu Guozheng, Cao Fenyang. 2000. A discussion on the major control factors of the metallogenic belt around the Yangtze River in Anhui[J]. Geology of Anhui, 10(1):35-43 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=06c62b8064564aabf7bfbefde1af47df&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chu Guozheng. 1999. The copper, gold and polymetallic mineralization series and their mutual relationship around the river in Anhui[J]. Geology of Anhui, 9(1):45-53 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-AHDZ199901007.htm
Corfu F.2003.Atlas of zircon textures[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1):469-500. doi: 10.2113/0530469
Di Yongjun, Wu Ganguo, Zhang Da, Song Biaozang, Wen Shuan, Zhang Zhongyi, Li jinwen.2005. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of Xiaotongguanshan and Shatanjiao intrusive rocks from Tongling and their petrological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(6):804 (in Chinese).
Dou Zhijuan, Yang Zhuliang, Chen zhihong, Zhang Baosong.2015.Geochronology and significance of Lishui Basin (SUB) volcanic rocks of the Yangtze River metallogenic belt[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 35(2):25-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201502004
Gao Shan, Ling Wenli, Qiu Yumin, Lian Zhou, Hartmann G, Simon K.1999.Contrasting geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of Archean metasediments from the Kongling high-grade terrain of the Yangtze craton:Evidence for Cratonic evolution and redistribution of REE during crustal anataxis[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63:2071-2088. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00153-2
Han Changsheng, Zhong Guoxiong. 2013. Geological characteristics and genesis of Shatanjiao ore field in Tongling ore district, Anhui[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology, 36(12):1504-1510(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hfgydxxb201312021
He Liuchang.2018. Analysis of buried rock masses and deep prospecting potential in the southwestern Shatanjiao area in the Tongling ore deposit cluster[J]. Geology of Anhui, 28(2):114-118(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ahdz201802008
Huang Huiqing, Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Li Wuxian.2013.Intraplate crustal remelting as the genesis of Jurassic high-K granites in the coastal region of the Guangdong Province, SE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 74:280-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.09.009
Huang Wenming.2016. Analysis of geological characteristics and ore controlling factors of the copper polymetallic deposit in Hanling County, Anhui Province[J].Geology of Anhui, 26(3):182-188(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-AHDZ201603009.htm
Lei Min, Wu Cailai, Gao Qianming, Guo Heping, Liu Lianggen, Guo Xiangyan, Gao Yuanhong, Chen Qilong, Qin Haipeng.2010.Petrogenesis of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and enclaves, and application of mineral thermobarometry[J]. Acta Petrol.Mineral., 29(3):271-288 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201003005
Li Jianhua, Zhang Yueqiao, Dong Shuwen, Johnston S T.2014.Cretaceous tectonic evolution of South China:A preliminary synthesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 134:98-136. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.03.008
Li Jianwei, Zhao Xinfu, Zhou Meifu, Vasconcelos P, Ma Changqian, Deng Xiaodong, Souza Z S, Zhao Yongxin, Wu Gang. 2008.Origin of the Tongshankou porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze craton, Eastern China:Geochronological, geochemical, and SrNd-Hf isotopic constraints[J].Mineralium Deposita, 43(3):315-336. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0161-3
Li Mingze, Wu Cailai, Lei Min, Gao Yuanhong, Wang Nan.2016.Zircon U-Pb geochronology of intermediate-acid intrusions in the Shujiadian ore district of the Tongling ore concentration Area[J]. Geology in China, 43(5):1514-1544(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201605004
Li Xianhua, Li Zhengxiang, Li Wuxian, Wang Xuance, Gao Yuya.2013. Revisiting the "C-type adakites" of the lower Yangtze River Belt, central eastern China:In-situ zircon Hf-O isotope and geochemical constraints[J]. Chemical Geology, 345:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.02.024
Li Xiaohui, Yuan Feng, Zhang Mingming, Jiang Qisheng, Han Changsheng, Huang Jianman, Zhang Shuhong, Zhong Guoxiong.2016.3D spatial quantitative analysis of alteration in Yaojialing zinc-gold polymetallic deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(2):390-398(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201602009
Ling M X, Wang F Y, Ding X, Hu Y H, Zhou J B, Zartman R E, Yang X Y, Sun W D.2009. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the lower Yangtze River belt, eastern China[J]. Economic Geology, 104:303-321. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.303
Ling Mingxing, Wang Fangyue, Ding Xing, Zhou Jibin, Sun Weidong.2011. Different origins of adakites from the Dabie Mountains and the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China:Geochemical constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 53(5/6):727-740. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d8641ea25bcd388e5b6e349e43cdfafe&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Jianmin, Yanjun, Li Quanzhong, Liu Xiaoqiang, Xie Jiancheng.2014. Zircon dating and petrogenesis of the Yaojialing intrusionin Tongling area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 49(2):494-512(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKX201402012.htm
Liu Shaofeng, Du Yangsong, Fu Shuixing, Zhong Hong, Cao Yi.2013.U-Pb age and Hf isotopic characteristics of zircons from granodiorite porphyry in the Yaojialing Zn-Au-polymetallic mine, Anhui Province and their geological significance[J]. Earth ScienceJournal of China University of Gcosciences, (S1):91-102(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4a755c58e6c64a28e5d9edc58aea0bfb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Yongsheng, Gao Shan, Hu Zhaochun, Gao Changgui, Zong Keqing, Wang Dongbing.2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-north China orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle venoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1/2):537-571. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6e670e94216d07dcd3c8ccc5b2989818&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Lou Jinwei.2012. Intermediate-Acid Intrusive Rocks of Tongling Ore District and Copper-Polymetallic Deposits of Shizishan OreField, Anhui Province[D]. Hefei University of Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lü Qingtian, Dong Shuwen, Tang Jingtian, Shi Danian, Chang Yinfo.2015. Multi-scale and integrated geophysical data revealing mineral systems and exploring for mineral deposits at depth:A synthesisi from SinoProbe-03[J].Chineses Journal of Geophysics, 58(12):4319-4343 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201512002.htm
Lu Qingtian, Hou Zengqian, Zhao Jinhua, Shi Danian, Wu Xuanzhi, Chang Yinfo, Pei Rongfu, Huang Dongding, Ni Zhaoyang.2003.Deep seismic reflection profiles to reveal the complex crustal structure of the Tongling ore cluter region[J]. China Science Series D:Earth Sciences, 33(5):442-449 (in Chinese).
Ludwig K R.2003.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M.1989.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Mao Jingwen, Xie Guiqing, Zhang Zuoheng, Li Xiaofeng, Zhang Tianqing, LiYongfeng. 2005.Mesozoic largescale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings[J]. Acta Perologica Sinica, 21(1):169-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1472321
Meng Xiangjin, Lu Qingtian, Yang Zhusen, Xu Wenyi.2011.Geochemical characteristics of Mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in Tongling and adjacent area of the middle and lower Reaches of the Yangtze River and its indication to the deepseated magmatism[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5):757-777 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201105013.htm
Pearce J A, Harris N BW, Tindle A G.1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Jour. Petrol., 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Qu Hongying, Pei Rongfu, Li Jin wen, Wang Yonglei.2010. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Zircon from the Fenghuangshan quartz monzodiorite and granodiorite in Tongling Area, Anhui Province and its geological implication[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 40(3):581-590 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201003014
Rickwood P C.1989.Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Roberts M P, Clemens J D. 1993. Orgin of high-potassium, tackalkaline, Ι -type granitoids[J]. Geology, 21:825-828. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0825:OOHPTA>2.3.CO;2
Song Yang, Du Yangsong, Zhang Zhiyu, Ma hong, Zhu Xiaoqiang.2017. Petrography and U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Jitou pluton in the Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe deposit, Tongling Area, Anhui Province, and its geological significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 36(1):33-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201701005
Sun S S, McDonough W F.1989.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and Processes[C]/Saunders A D, Norry M J(eds.).Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231575101_Chemical_and_isotopic_systematics_of_oceanic_basalts_Implications_for_mantle_composition_and_processes
Sun Weidong, Ling Mingxing, Yang Xiaoyong, Fan Weiming, Ding Xing, Liang Huaying.2010. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization:An overview[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 53(4):475-484. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=64e6a27e3a30424c29d801ce590a526d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Sylvester P J.1998.Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 45:29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3
Tian Shihong, DuYangsong, Qin Xinlong, Li Xuanju, Jin Shang Zhong, Yin Jinwu, Li Zanxi.2001. Mineral inclusion studies of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and their rock enclaves in Tongling Area, Anhui Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 8(4):422-428(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200104024
Wang Chunyong, Zeng Rongsheng, Mooney W D, Hacker B R.2000.A crustal model of the ultrahigh-pressure Dabie Shan orogenic belt, China, derived from deep seismic refraction profiling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(B5):10857-10869. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900415
Wang Guochang, Jiang Yaohui, Liu Zheng, Ni Chunyu, Qing Long, Zhang Qiao, Zhu Shuqi.2016. Multiple origins for the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous high-K calc-alkaline Ⅰ-type granites in northwestern Fujian Province, SE China and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 246:197-211. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=092b6808dcb32d196f923183887a82a0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Qiang, Wyman D A, Xu Jifeng, Jian Ping, Zhao Zhenhua, Li Chaofeng, Xu Wei, Ma Jinlong, He Bin.2007. Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China:Implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(10):2609-2636. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.008
Wang Qiang, Wyman D A, Xu Jifeng, Zhao Zhenhua, Jian Ping, Xiong Xiaolin, Bao Zhiwei, Li Chaofeng F, Bai Zhenghua.2006.Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China):Implications for geodynamics and Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Lithos, 89(3/4):424-446. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3590d80924b5785495955e268146f0b3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wang Qiang, Xu jifeng, Zhao zhenhua, Zifeng, Tang gongjian, Jia Xiaohui, Jiang Ziqi.2008. Tectonic Setting and Associated Rock Suites of Adakitic Rocks[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 27(4):344-350. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb200804003
Wang Yanbin, Liu Dunyi, Meng Yifeng, Zeng Pusheng, Yang Zhusen, Tian Shihong.2004c. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe-Au deposit in the Tongling ore district, Anhui[J].Geology in China, 31(2):169-173(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200402008
Wang Yanbin, Liu Dunyi, Zeng Pusheng, Yang Zhusen, Meng Yifeng, Tian Shihong. 2004a. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of Xiaotongguanshan quartz-dioritic intrusions in Tongling district and its petrogenetic implications[J].Acta Petrol. Mineral., 23(4):298-304 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200404002
Wang Yanbin, Liu Dunyi, Zeng Pusheng, Yang Zhusen, Tian Shihong.2004b.SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of gabbro-diorite in the Chaoshan gold deposit and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 25(4):423-427 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yuanlong, Wang Yan, Zhang Qi, Jia Xiuqin, Han Song.2004.The geochemical characteristics of mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusives of the Tongling area and its metallogenesis-geodynamic implications[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2):325-338(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200402013
Wu Cailai, Chen Songyong, Shi Rendeng, Hao Meiying.2003. Origin and features of the Mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusive in the Tongling Area, Anhui, China[J].Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 24(1):41-48(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4f0d4b2991913e1769f0c60986c9f16d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Guo Heping, Guo Xiangyan, Gao Qianming, Liu Lianggen, Chen Qilong, Lei min.2008.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Intermediate-acid intrusive rocks from Shizishan, Tongling and the Deep processes magmatism[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1801-1812 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200808012
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Robinson P T, Frost B R, Gao Yuanhong, Lei Min, Chen Qilong, Qin Haipeng.2014. Petrogenesis of high-K, calc-alkaline and shoshonitic intrusive rocks in the Tongling area, Anhui Province (eastern China), and their tectonic implications[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 126(1/2):78-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=421f07b8ad63715633436d9a17c0a81d
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Wang Lutai, Lei Min, Wu Di.2016. The discovery of the syenogranite with an age of 126 Ma in the depth of Tongling:Evidence from 3000 meters scientific drilling[J]. Geology in China, 43(5):1495-1513(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=db5ed73454ef85eba89b1283445ecf3c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wu Cailai, Dong Shuwen, Wu Di, Zhang Xin, Ernst W G.2017.Late Mesozoic High-K calc-alkaline magmatism in Southeast China:The Tongling example[J]. International Geology Review, 60(11/14):1326-1360. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4c68f4d9ed956bbe6311db69c3ddc1ec&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wu Cailai, Gao Qianming, Guo Heping, Guo Xiangyan, Liu Lianggen, Gao Yuanhong, Lei min, Qin Haipeng.2010a. Petrogenesis of the intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and zircon SHRIMP dating in Tongling, Anhui, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9):2630-2652(in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201009011
Wu Cailai, Gao Qianming, Guo Heping, Liu Lianggen, Guo Yuanhong, Lei Min, Qin Haipeng, Liu Chunhua, Li Mingze, Chen Qilong. 2010b. Zircon SHRIMP Dating of Intrusive Rocks from the Tongguashan Ore-Field in Tongling, Anhui, China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(12):1746-1758(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201012004
Wu Cailai, Guo Xiangyan, Wang Cisong, Wu Xiuping, Gao Yuanhong, Lei Min, Qin Haipeng, Liu Chunhua, Li Mingze, Chen Qilong. 2013. Age of high-K calc-alkaline intrusions from Tongling and tectonic setting[J]. Geochimica, 42(1):11-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Cailai, Wang Zhihong, Qiao Dewu, Li Haibing, Hao Meiying, Shi Rengdeng.2000. Types of enclaves and their features and origins in intermediate-acid intrusive rocks from the Tongling Distract, Anhui, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 74(1):54-67. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2803c671b001db670729ab11cfb85109&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wu Cailai, Zhou Xunruo, Huang Xuchen, Zhang Chenghuo, Xu Sheng, Guo Heping, Chen Siyou.1997. Enclave petrology of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in Tongling District, Anhui[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 18(2):71-80 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dqxb702.008.htm
Wu Ganguo, Zhang Da, Di Yongjun, Zang Wenshuan, Song Biao, Zhang Zhongyi. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP dating and their tectonic settings of intrusive rocks in Tongling ore concentration area[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, (5):630-645.
Wu Xingxing, Yan Jun, Tang Yulun, Chu Xiaoqiang, Peng Ge.2011.Geochronology and geochemistry of Shatanjiao granodiorite from Tongling, Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 31(1):75-82(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys201101012
Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei.2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15):1554-1569. doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
Xie Jiancheng, Yang Xiaoyong, Du Jianguo, Sun Weidong.2008.Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Tongling region:Implications for copper-gold Mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinca, 24(8):1782-1800(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=88263568f6b4da9f1266527a1d00fc13&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Xu Jifeng, Shinjo R, Defant M J, Wang Qiang, Rapp P T.2002.Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China:Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?[J]. Geology, 30(12):1111-1114. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2
Xu Xiaochun, Lu Sanming, Xie Qiaozhen, Bo Lin, Chu Guozheng.2008. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating for the magmatic rocks in Shizishan ore-field of Tongling, Anhui Province, and its geological implications[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(4):500-509(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200804007
Xu Xisheng, Fan Qincheng, O'Reilly S Y, Jiang Shaoyong, Griffin W L, Wang Rucheng, QiuJiansheng.2014. Zircon U-Pb dating of the quartz diorite and its enclaves in Tongguanshan, Anhui province:Discussion on the petrologic genesis[J]. Chinese Science Bullatin, 49(18):1883-1891 (in Chinese). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225654808_U-Pb_dating_of_zircons_from_quartz_diorite_and_its_enclaves_at_Tongguanshan_in_Anhui_and_its_petrogenetic_implication
Yan Dairong, Deng Xiaodong, Hu Hao, Li Jianwei.2012. U-Pb age and petrogenesis of the Ruanjiawan granodiorite pluton and Xiniushan granodiorite porphyry, southeast Hubei Province:Implications for Cu-Mo mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28:3373-3388 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201210023
Yin Yanduan, Hong Tianqiu, Jia Zhihai, Zhao Huan, Li Chao, Luo Lei, Huang Jianman.2016.The Re-Os age of molybdenite and oreforming material source from the Yaojialing Zn-Au polymetallic deposit, Tongling[J].Geological Reviews, 62(1):248-256.
Yue Yuanzhen, Shi Hongqi, Wang Xiaoping, Liu Zongquan, Shi Jiuming.1986. Mineralogical characteristics of neutral-acidic intrusive rock in Tongling, and some suggestions on their Orgin[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, (2):134-150(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KWYS198602019.htm
Yue Zilong, Du Yangsong, Cao Yi, Cao Yi, Zuo Xiaomin, Zhang Aiping, Huang Wenming.2015. Geochemical features and U-Pb age of the Guihuachong granodiorite porphyry in Tongling and their geological implications[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 35(1):82-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201501011
Yue Zilong, Du Yangsong, Caoyi, Zuo Xiaomin, Zhang Aiping.2016.Alteration and mineralization of the Guihuachong porphyry copper deposit, Tongling Area, Anhui Province[J]. Geoscience, 30(1):50-58(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201601005
Zhai Yusheng, Yao Shuzhen, Lin Xinduo, Jin Fuquan, Zhou Xunruo, Wan Tianfeng, Zhou Zonggui.1992. Metallogenic regularity of iron and copper deposits in the middle and lower valley of the Yangtze River[J]. Mineral Deposits, (1):1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199201000.htm
Zhang Qi, Wang Yan, Qian Qing, Yang Jinhui.2012. The characteristics and tectonic-metallogenic significances of the adakites in Yanshan period from eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4):236-244 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200102008
Zhang Zhongjie, Wang Guangjie, Teng Jiwei, Klemperer S.2000b.CDP mapping to obtain the fine structure of the crust and upper mantle from seismic sounding data:An example for the southeastern China[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 122(1/2):133-146. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c4a1da79527431ba40621781f8aac5bc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang Zhongjie, Li Yingkang, Lu Deyuan, Teng Jiwen, Wang Guangjie.2000a. Velocity and anisotropystructure of the crust in the Dabieshan orogenic belt from wideangle seismic data[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 122(1-2):115-131. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(00)00190-4
Zhao Zifu, Gao Peng, Zheng Yongfei.2015. The source of Mesozoic granitoids in South China:Integrated geochemical constraints from the Taoshan batholith in the Nanling Range[J]. Chemical Geology, 395:11-26. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.11.028
Zhao Zifu, Zheng Yongfei, Wei Chunsheng, Wu Yuanbao.2007. Post collisional granitoids from the Dabie orogenin China:Zircon U-Pb age, element and O isotope evidence for recycling of subducted continental crust[J]. Lithos, 93(3/4):248-272. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ef0bf499525f32f76fa19c33f95596b1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhong Guoxiong, Zhou Taofa, Yuan Feng, Jiang Qisheng, Fan Yu, Zhang Dayu, Huang Jianman.2014.LA-ICPMS U-Pb zircon age and molybdenite Re-Os dating of Yaojialing large zinc-gold polymetallic deposit, Tongling, Anhui Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(4):1075-1086(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201404014
Zhou Xunruo, Wu Cailai, Huang Xuchen, Zhang Chenghuo.1993.Characteristics of congnate inclusions in intermediate-acid intrusive rocks of Tongling Area and their magmatic Dynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, (1):20-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199301003.htm
常印佛, 刘学圭. 1983.关于层控式矽卡岩型矿床——以安徽省内下扬子坳陷中一些矿床为例[J].矿床地质, (1):13-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KCDZ198301001.htm 常印佛, 裴荣富, 侯增谦, 杨竹森. 2017.安徽省铜陵矿集区狮子山岩浆流体系统地球化学测试数据集[J].中国地质, 44(S1):49-55. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2017S106&flag=1 储国正, 曹奋扬. 2000.安徽沿江成矿带主要控制因素的探讨[J].安徽地质, 10(1):35-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHDZ200001007.htm 储国正. 1999.安徽沿江地区铜金多金属矿化系列及相互关系[J].安徽地质, (1):45-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHDZ199901007.htm 狄永军, 吴淦国, 张达, 宋彪臧, 文拴, 张忠义, 李进文. 2005.铜陵地区小铜官山和沙滩脚岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究及其岩石学意义[J].地质学报, 79(6):660-660. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200506023 窦志娟, 杨祝良, 陈志洪, 张宝松. 2015.长江中下游成矿带溧水盆地(次)火山岩的年代学及其意义[J].矿物岩石, 35(2):25-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys201502004 韩长生, 钟国雄. 2013.铜陵矿集区沙滩脚矿田矿床地质特征及成因[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 36(12):1504-1510. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2013.12.021 何柳昌.2018.铜陵矿集区沙滩脚西南地区隐伏岩体及深部找矿潜力分析[J].安徽地质, 28(2):114-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2018.02.008 黄文明. 2016.安徽省南陵县桂花冲铜多金属矿矿床地质特征及控矿因素分析[J].安徽地质, 26(3):182-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2016.03.007 雷敏, 吴才来, 高前明, 国和平, 刘良根, 郭祥炎, 郜源红, 陈其龙, 秦海鹏.2010.铜陵地区中酸性侵入岩及其包体的成因和矿物温压计的应用[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 29(3):271-288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.03.005 李名则, 吴才来, 雷敏, 郜源红, 王楠. 2016.铜陵矿集区舒家店矿区中酸性侵入岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J].中国地质, 43(5):1514-1544. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160504&flag=1 李晓晖, 袁峰, 张明明, 蒋其胜, 韩长生, 黄建满, 张淑虹, 钟国雄.2016.姚家岭锌金多金属矿床围岩蚀变三维空间定量分析研究[J].岩石学报, 32(2):390-398. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201602009 刘建敏, 闫峻, 李全忠, 宋传中, 刘晓强, 谢建成.2014.铜陵姚家岭岩体的锆石定年和岩石成因[J].地质科学, 49(2):494-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2014.02.011 刘绍锋, 杜杨松, 付水兴, 钟宏, 曹毅. 2013.安徽姚家岭锌金多金属矿区花岗闪长斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 38(1):91-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX2013S1012.htm 楼金伟. 2012.安徽铜陵矿集区中酸性侵入岩及狮子山矿田铜多金属矿床[D].合肥: 合肥工业大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10359-1013260199.htm 吕庆田, 董树文, 汤井田, 史大年, 常印佛. 2015.多尺度综合地球物理探测:揭示成矿系统、助力深部找矿——长江中下游深部探测(SinoProbe-03)进展[J].地球物理学报, 58(12):4319-4343. doi: 10.6038/cjg20151201 吕庆田, 侯增谦, 赵金花, 史大年, 吴宣志, 常印佛, 裴荣富, 黄东定, 匡朝阳. 2003.深地震反射剖面揭示的铜陵矿集区复杂地壳结构形态[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 33(5):442-449. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200305006 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 李晓峰, 王义天, 张长青, 李永峰.中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报, 2005(1):171-190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200501017 孟祥金, 吕庆田, 杨竹森, 徐文艺. 2011.长江中下游铜陵及邻区中生代中酸性侵入岩地球化学特征及其深部岩浆作用探讨[J].地质学报, 85(5):757-777. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201105011 瞿泓滢, 裴荣富, 李进文, 王永磊. 2010.安徽铜陵凤凰山石英二长闪长岩和花岗闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 40(3):581-590. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201003014 宋扬, 杜杨松, 张智宇, 马宏, 朱晓强. 2017.安徽铜陵新桥铜-硫-铁矿床矶头岩体的矿物学和锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 36(1):33-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201701005 田世洪, 杜杨松, 秦新龙, 李铉具, 金尚中, 尹京武, 李赞熙. 2001.安徽铜陵地区中酸性侵入岩及其岩石包体中的矿物包裹体研究[J].地学前缘, 8(4):422-428. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.04.024 王强, 许继峰, 赵振华, 资锋, 唐功建, 贾小辉, 姜子琦. 2008.埃达克质岩的构造背景与岩石组合[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 27(4):344-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.04.003 王彦斌, 刘敦一, 曾普胜, 杨竹森, 蒙义峰, 田世洪. 2004a.铜陵地区小铜官山石英闪长岩锆石SHRIMP的年龄及其成因指示[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 23(4):298-304. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200404002 王彦斌, 刘敦一, 曾普胜, 杨竹森, 田世洪. 2004b.安徽铜陵地区幔源岩浆底侵作用的时代——朝山辉石闪长岩锆石SHRIMP定年[J].地球学报, 25(4):423-427. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200404006 王彦斌, 刘敦一, 蒙义峰, 曾普胜, 杨竹森, 田世洪. 2004c.安徽铜陵新桥铜-硫-铁-金矿床中石英闪长岩和辉绿岩锆石SHRIMP年代学及其意义[J].中国地质, 32(2):169-173. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040208&flag=1 王元龙, 王焰, 张旗, 贾秀琴, 韩松. 2004.铜陵地区中生代中酸性侵入岩的地球化学特征及其成矿——地球动力学意义[J].岩石学报, 20(2):325-338. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200402013 吴才来, 陈松永, 史仁灯, 郝美英. 2003.铜陵中生代中酸性侵入岩特征及成因[J].地球学报, 24(1):41-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.01.007 吴才来, 董树文, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 高前明, 刘良根, 陈其龙, 雷敏, Wooden J L, Mazadab F K, Mattinson C. 2008.铜陵狮子山地区中酸性侵入岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及岩浆作用的深部过程[J].岩石学报, 24(8):1801-1812. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200808012 吴才来, 董树文, 王陆太, 王次松, 雷敏, 吴迪. 2016.铜陵矿集区深部发现126 Ma的正长花岗岩:来自3000m科学钻探的证据[J].中国地质, 43(5):1495-1513. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160503&flag=1 吴才来, 高前明, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 刘良根, 郜源红, 雷敏, 秦海鹏, 陈其龙. 2010b.铜陵地区铜官山矿田侵入岩锆石SHRIMP定年[J].地质学报, 84(12):1746-1758. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201012004 吴才来, 高前明, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 刘良根, 郜源红, 雷敏, 秦海鹏. 2010a.铜陵中酸性侵入岩成因及锆石SHRIMP定年[J].岩石学报, 26(9):2630-2652. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201009011 吴才来, 郭祥焱, 王次松, 武秀平, 郜源红, 雷敏, 秦海鹏, 刘春花, 李名则, 陈其龙. 2013.铜陵地区高钾钙碱性系列侵入岩锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J].地球化学, 42(1):11-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.01.004 吴才来, 周询若, 黄许陈, 张成火, 许胜, 国和平, 陈思友. 1997.铜陵地区中酸性侵入岩的包体岩石学研究[J].地球学报, 18(2):71-80. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2007066893.htm 吴淦国, 张达, 狄永军, 臧文拴, 张祥信, 宋彪, 张忠义. 2008.铜陵矿集区侵入岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其深部动力学背景[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 38(5):630-645. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200805010 吴星星, 闫峻, 唐裕禄, 初晓强, 彭戈. 2011.安徽铜陵沙滩脚岩体年代学及地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石, 31(1):75-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.01.012 谢建成, 杨晓勇, 杜建国, 孙卫东. 2008.铜陵地区中生代侵入岩LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学及Cu-Au成矿指示意义[J].岩石学报, 24(8):1782-1800. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200808011 徐夕生, 范钦成, O'Reilly S Y, 蒋少涌, Griffin W L, 王汝成, 邱检生. 2004.安徽铜官山石英闪长岩及其包体锆石U-Pb定年与成因探讨[J].科学通报, 49(18):1883-1891. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.18.012 徐晓春, 陆三明, 谢巧勤, 柏林, 储国正. 2008.安徽铜陵狮子山矿田岩浆岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其成因意义[J].地质学报, 82 (4):500-509. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.04.007 颜代蓉, 邓晓东, 胡浩, 李建威. 2012.鄂东南地区阮家湾和犀牛山花岗闪长岩的时代、成因及成矿和找矿意义[J].岩石学报, 28(10):3373-3388. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201210023 殷延端, 洪天求, 贾志海, 赵欢, 李超, 罗雷, 黄建满. 2016.铜陵姚家岭锌金多金属矿的辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及成矿物质来源[J].地质论评, 62(1):248-256. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201601021 岳元珍, 史鸿歧, 王小平, 刘宗权, 史久明. 1986.铜陵地区中酸性侵入岩的矿物特征及成岩条件初析[J].矿物岩石, 6(2):132-148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWYS198602019.htm 岳紫龙, 杜杨松, 曹毅, 左晓敏, 张爱萍, 黄文明. 2015.铜陵桂花冲花岗闪长斑岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].矿物岩石, 35(1):82-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys201501011 岳紫龙, 杜杨松, 曹毅, 左晓敏, 张爱萍. 2016.安徽铜陵桂花冲斑岩铜矿围岩蚀变与矿化作用[J].现代地质, 30(1):50-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.01.005 翟裕生, 姚书振, 林新多, 金福全, 周珣若, 万天丰, 周宗桂. 1992.长江中下游地区铁、铜等成矿规律研究[J].矿床地质, (1):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KCDZ199201000.htm 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 杨进辉, 王元龙, 赵太平, 郭光军. 2001.中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 17(2):236-244. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200102008 钟国雄, 周涛发, 袁峰, 蒋其胜, 范裕, 张达玉, 黄建满. 2014.安徽铜陵姚家岭锌金多金属矿床成岩成矿年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 30(4):1075-1086. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201404014 周珣若, 吴才来, 黄许陈, 张成火. 1993.铜陵中酸性侵入岩同源包体特征及岩浆动力学[J].岩石矿物学杂志, (1):20-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSKW199301003.htm -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 张昌民,张祥辉,王庆,冯文杰,李少华,易雪斐,Adrian J.HARTLEY. 分支河流体系沉积学工作框架与流程. 岩性油气藏. 2024(01): 1-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张倩,王永诗,王学军,杨怀宇,王天福. 东营凹陷缓坡带陆相红层砂岩粒度特征及沉积环境意义. 地质科技通报. 2024(05): 81-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈春峰,陈忠云,万延周,陈建文,徐东浩,冯桢鸣,俞伟哲,姜雪. 东海盆地西湖凹陷南部花港组上段浅水曲流河三角洲发育特征. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(06): 175-185 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. Xianghui Zhang,Changmin Zhang,Adrian Hartley,Qinghai Xu,Wenjie Feng,Taiju Yin,Rui Zhu. Analysis of the Sedimentary Characteristics of a Modern Distributive Fluvial System:A Case Study of the Great Halten River in the Sugan Lake Basin, Qinghai, China. Journal of Earth Science. 2023(04): 1249-1262 .  必应学术
必应学术
5. 张昌民,张祥辉,朱锐,冯文杰,尹太举,尹艳树,Adrian J.HARTLEY. 分支河流体系研究进展及应用前景展望. 岩性油气藏. 2023(05): 11-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张祥辉,张昌民,冯文杰,徐清海,朱锐,刘帅,黄若鑫. 干旱地区分支河流体系沉积特征——以疏勒河分支河流体系为例. 石油勘探与开发. 2021(04): 756-767 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵芸,张昌民,朱锐,冯文杰,赵康. 分支河流体系(DFS)研究进展. 大庆石油地质与开发. 2021(06): 1-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: