Characteristics of stratigraphic sedimentary in the south-north continental margin basin of the South China Sea and its differential control on hydrocarbon accumulation
-
摘要:
南海作为西太平洋最大的边缘海,油气资源丰富,油气赋存规律的南北差异性大。本文在系统梳理南海中—新生代地层、沉积相发育特征的基础上,对南海南北典型含油气盆地的石油地质条件进行了对比分析。结果认为南海打开过程对古南海沉积地层的改造,使得现有残余地层南北分离,主要分布于北部的珠江口盆地—台西南盆地和南部的礼乐盆地中,推测发育“自生自储”、“新生古储”或“古生新储”的中—新生界油气成藏模式。南海新生代油气藏在“北张、南挤”的构造应力背景下,古近纪以来的古水系控制了大型碎屑岩油气藏的分布;区域构造运动和海平面变化控制了中新世碳酸盐岩油气藏的发育;早新生代以来的古地貌控制的深水峡谷、深海扇、扇三角洲沉积体系孕育了潜在深水油气藏。总之,南海南北地层沉积各有特色,油气成藏条件各有优势,但均有良好的油气勘探前景,本文以期为未来南海油气勘探战略部署和选区提供参考。
Abstract:As the largest marginal sea in western Pacific, the South China Sea is rich in oil and gas resources, and the difference in hydrocarbon occurrence laws between the north and south is large. On the basis of the systematic analysis of the MesozoicCenozoic strata and sedimentary facies development characteristics of the South China Sea, the petroleum geological conditions of the typical petroliferous basins in the south and north of the South China Sea were compared and analyzed. The results show that the reconstruction of the sedimentary strata of the ancient South China Sea by the opening process of the South China Sea causes the existing residual strata to separate from north to south, mainly distributed in the Pearl River Mouth Basin and the Tainan Basin in the north, and in the Lile Basin in the south. It is inferred that there are Mesozoic-Cenozoic hydrocarbon accumulation models of "selfgeneration and self-storage", "new-generation and paleo-storage" or "paleo-generation and new-storage". The Cenozoic oil and gas reservoirs in the South China Sea are under the tectonic stress background of "north extension and south extrusion". The distribution of large clastic reservoirs has been controlled by the paleo-water system since Paleogene. Regional tectonic movements and sea level change controlled the development of Miocene carbonate reservoirs. The deep-water canyons, deep-sea fans, and fan-delta sedimentary systems controlled by paleo-geomorphology since the early Cenozoic have spawned potential deep-water reservoirs. In a word, the south and north sedimentary strata of the South China Sea have their own characteristics, and the hydrocarbon accumulation conditions have their own advantages, but they all have good prospects for oil and gas exploration. This paper is expected to provide reference for future strategic deployment and selection of oil and gas exploration in the South China Sea.
-
1. 引言
中国是世界上煤炭开采历史悠久、开采量最大的国家,2022年中国原煤产量45.6亿t(国家统计局,2023)。多年来形成的采空区体积达300×108 m3以上,而且以每年近20×108 m3的速率在增加(李凤明等,2004;梁永平等,2021)。由于能源结构优化调整,截止2022年底,新时代十年来全国煤矿数量由1.3万处减少到4400处以内(中国煤炭工业协会,2023)。煤矿关闭后,废弃坑道、采空区将成为地下水循环、蓄积空间,特定条件下将形成劣质的酸性“老窑水”。近年来,中国山西阳泉、山东淄博、贵州凯里等多地相继发现了煤矿“老窑水”对地表、地下水体的污染(梁永平等,2014;张秋霞等,2016;刘强,2018;梁浩乾等,2019;梁永平等,2021;韩双宝等,2021),成为中国生态文明建设的重要制约因素。
目前国内外学者对废弃煤矿酸性水的研究主要集中于酸性水的地球化学特征(pH、硫酸根、铁锰、多环芳烃、重金属等)(张建立等,2000;赵峰华,2005;张秋霞等,2015;Juliana et al.,2016;高波,2019)及对地表水、地下水(Powell et al.,1988;钟佐燊等,1999;Zhang et al.,2016)等的影响,而关于水量及其与水质相互关系的研究以及野外原位长系列研究较少。山底河流域位于山西省娘子关泉域内,其煤矿“老窑水”是泉域内流量最大、污染程度最高的污染源(梁永平等,2021),它集地表水、露天矿坑积水、现采煤矿矿坑水、生活污水和煤矿老窑水于一体,是一个完整、独立的水循环系统,具有开展煤矿“老窑水”防治深入研究的“示范性”价值。本文基于对山底河煤矿“老窑水”的长系列监测,分析煤矿“老窑水”水循环系统演化特征,评估对娘子关泉域岩溶水的污染影响,可为流域煤矿“老窑水”治理及娘子关泉域生态修复提供科学依据,为中国同类地区的地下水保护与生态修复提供参考。
2. 研究区概况
山底河流域处于娘子关泉域内,行政区划属阳泉市河底镇及盂县青城乡,流域面积58 km2(图 1)。由于国家政策调整,流域内大部分小型煤矿被关闭。2009—2010年,闭坑煤矿“老窑水”开始溢出,在山底村柳沟一带形成了流域“老窑水”的集中排泄区,老窑水出流后进入娘子关泉域碳酸盐岩渗漏段(梁永平等,2021)。渗漏段分为2段,第一段为山底河下游,从监测点(F05)向下游约0.5 km进入碳酸盐岩后到温河入口处(监测点G03),渗漏长度1.8 km;第二段为山底河汇入温河后至娘子关泉群,渗漏长度35.89 km(图 1b)。研究区属于大陆型干旱、半干旱气候区,根据距流域最近的盂县气象站资料多年平均降水量551.98 mm,最大日降水151.8 mm;多年年平均气温9.14℃,极端日均气温21.6℃,最高24.5℃。雨热同期、四季分明,降水主要集中于6—9月,占全年降水总量75%以上。
山底河流域内主要出露的地层有奥陶系、石炭系、二叠系以及第四系(图 1),其中石炭系太原组及二叠系山西组为含煤层位,分布于流域上游,由砂岩、页岩、灰岩夹层和煤层构成,分布面积占流域总面积的90%以上。东北部出露奥陶系碳酸盐岩。流域区域上位于沁水向斜东北翘起端,地层总体由北东向南西倾斜(图 1),北部发育东西向红土岩背斜,与燕龛一带相比,地层抬升约40 m,其对煤矿“老窑水”的储存运移有控制性作用。
山底河流域发育有2套含水岩组,分别是上部石炭系—二叠系煤系地层砂页岩夹碳酸盐岩含水岩组(煤系地层含水岩组)和下部奥陶系碳酸盐岩含水岩组,两含水岩组间为石炭系中部本溪组铝土质泥岩区域隔水层。
(1)上部煤系地层地下水。煤系地层发育有多层砂岩(如图 1c中K1)和灰岩夹层(图 1c中K2和K3)。各含水层间以细砂岩、页岩、煤层为相对隔水层,受采煤活动影响,采空区各含水层间已全部沟通,构成了具有同一流场的含水系统。地下水从燕龛向东北方向径流,山底河柳沟一带是地势最低处,汇集形成了流域煤矿“老窑水”的集中排泄区(图 1c;石维芝,2022)。
(2)下部岩溶水。流域内深层岩溶地下水属于娘子关泉域岩溶地下水系统的一部分,其地下水由北西向东南渗流。因碳酸盐岩裸露区出露面积不大,降雨入渗补给量有限;岩溶地下水主要接受山底河的渗漏补给。
3. 采样与测试
2014年6月—2020年12月,对山底河流域煤矿老窑水循环系统进行了系统的长期监测(图 1a)。主要监测内容为:(1)雨量站3处,编号Y01、Y02、Y03,监测期为2014—2020年,监测频率3次/日,监测降水量、气温。(2)流量3处,分别为流域煤矿“老窑水”主排泄点柳沟泉(G01)、山底河总出口(F05)和位于F05下游约2.3 km山底河汇入温河入口处的温河口(G03)。F05监测期为2014—2020年,G01和G03监测期为2017—2020年,监测频率3次/月,除监测流量外,还现场测试水温、pH值、氧化还原电位(Eh)、电导率、溶解氧。(3)煤系地层不同类型的水化学监测点5处,其中庙沟泉(F01)发育于太原组K3灰岩之上的砂页岩中,该泉补给区分布有开采煤层,属于上层滞水,采集样品76组;小沟(F02)为露天矿积水,采集样品73组;榆林垴孔(F03)为煤矿老窑水钻孔,该孔水位埋深125 m,开口为石炭系太原组,底部揭穿K1砂岩并进入石炭系本溪组,利用采样桶从井下提水,共采集样品45组;跃进煤矿(F04)主要为跃进煤矿排水,采集样品76组;山底河总出口(F05)为流域总出口监测断面,该断面汇集了流域内闭坑煤矿老窑水出流水、流域地表水、跃进煤矿排水等,采集样品78组。监测期除榆林垴孔(F03)为2017年2020年,其余均为2014—2020年,监测频次1月/次,但受疫情等影响,部分月份缺测。共采集样品348组。
野外现场利用德国WTW Cond 340i水质测试仪测试水温、pH、氧化还原电位(Eh)、溶解氧(DO)等参数,待现场测试各参数稳定后再进行取样。样品采集前先用采集的水样清洗采样瓶3遍。样品分析测试由国土资源部太原矿产资源监督检测中心采用A-130原子吸收分光光度计、A-37分光光度计等测定。
4. 结果与讨论
4.1 流域“老窑水”流量特征
山底河总出口(F05)平均流量为12424.12 m3/d,变异系数>1.77(表 1);柳沟泉(G01)和温河口(G03)点流量变异系数分别为0.35和1.53,与F05点相比其流量动态变化较稳定。3个监测点流量动态均明显受降水影响;雨季后进入流量衰减阶段(图 2)。电导率G01>F05>G03,pH值与电导率相反。溶解氧主要受气温和水体酸化程度的影响,其溶解氧值G01<F05<G03。氧化还原电位在一定程度上可以代表水体的Fe3+离子浓度,G01>G03>F05,G03大于F05样表明在两点间径流过程中发生了Fe3+离子沉淀反应,在沿途河床底部可见红色沉淀。
表 1 各监测点月平均流量及水质现场测试结果统计表(2017.06—2020.12)Table 1. Statistical table of monthly average flow and water quality field test results of each monitoring point (2017.06—2020.12)
4.1.1 流域流量与降雨量非线性相关
降水作为流域各类水体的总补给来源,对总出口流量动态起着着决定性控制作用。流域总流量与降雨量应存在一定关系(Huang et al.,2016;罗玉等,2019;Wang et al.,2020;Li,2020;成艺等,2022)。但日流量与日降雨量或月累计流量与月累计降雨量之间却不存在明显的线性相关关系(图 3),说明流域系统对降雨量的调节时间大于一个月,尝试对流量与降雨量进行累计滑动平均处理,流域流量与半年降雨量间呈指数相关,相关系数为0.94(图 3),其主要原因为流域产流滞后、各种水体调节时间不一致、地表水及地下补给、降水等多种因素叠加影响。各产流因素错综复杂,相互间叠加影响,尚未建立完备的统计关系,但随着监测序列的加长,能够建立二者间符合其补排关系的统计模型。
4.1.2 流量与电导率呈指数相关
电导率与流量间一般存在负相关关系,即:雨季大量低矿化度雨水混合稀释,电导率降低。地表水体由于水的总体电导率较低,雨水等的混入对电导率变化不明显,但对山底河这种矿化程度很高的煤矿“老窑水”,低矿化度新鲜降水补给的稀释将对“老窑水”的电导率变化造成显著影响。因此,可将电导率作为同时表征系统水量与水质的关联性指标(郭芳等,2018;张涛等,2018;朱彪等,2019)。
流量-电导率曲线的曲率半径代表了数据变化的剧烈程度,曲率半径越小,数据的稳定性越差。从图 4中可以看出,小流量下的曲率半径较大,而大流量下的曲率半径较小。显然,F05和G03在流量 < 2000 m3/d和电导率>2000 μs/cm时,具有线性关系,说明小流量时老窑水来源较为单一。
流域内3个监测点流量和电导率间均存在较为显著的指数相关性(图 4),表明电导率与流量间存在一定的内在关联,并不能用简单的稀释作用的线性关系解释。分析认为这是多种因素共同叠加形成的,一是采空区积水区水位与采空区接触面积(或体积)间为非线性关系,如榆林垴孔(F03)的采空积水区水位一般在15#煤采空区以下(图 1c),但雨季来临时,水位上升进入采空区,地下水呈面状(或体状)向采空区扩散并与其中残留煤中的黄铁矿发生氧化反应,从而形成水位与水化学浓度间的非线性关系;二是由流域水文地质条件可知,F05和G02的流量是由流域内地表水、地下水以及煤矿老窑水等共同组成,不同来源的水对雨水的转换量以及影响滞后期各不相同,最后叠加的结果可能造成流量对电导率的非线性效应(图 4);三是不同来源水量的混合不仅是一个物理过程,同时也将发生各种复杂的水化学反应。
4.1.3 电导率与化学组分浓度间关系
电导率与酸性煤矿“老窑水”最主要的特征产物SO42-具有显著的相关性(图 5)。F01、F04和F05的SO42-浓度与电导率间均为线性相关,在一定程度上可认为SO42-浓度在水中占主导性地位;F03与其他3个点的函数类型不同应该与其SO42-浓度变化的控制因素不同有关,而非线性关系的成因应该与多种控制因素有关,主要原因是由于在高电导率区间(也即高SO42-浓度区间)控制SO42-浓度的主要因素是水位上升进入15#煤层采空区后强烈氧化黄铁矿的结果。而F02有几个低电导率的样点偏差较大(可能受融雪或其他因素影响),因此影响了其相关性的建立。综合以上分析,也说明流量与SO42-浓度呈非线性相关。
4.2 流域“老窑水”水化学特征
山底河“老窑水”与国内外其他矿区老窑水一样,具有低pH值、高SO42-、高TFe、高Mn和高TDS等特征(表 2;岳梅等,2004;赵峰华,2005;Sun et al.,2018;冯海波等,2019)。
表 2 流域水化学组分统计特征表(mg/L)Table 2. Statistical characteristics of hydrochemical components in the Shandi River Basin (mg/L)
庙沟泉(F01)的SO42-、TFe、Mn、TDS等主要特征组分浓度均最大,其平均值F01> F02>F05>F04> F03,与pH值呈负相关(表 2)。各监测点氧化还原电位(Eh)平均值F02>F01>F05>F04>F03。这主要与各点所处的环境有关。庙沟泉(F01)发育于与大气交换作用强烈的包气带,为开放氧化环境,多年平均氧化还原电位为444.04 mV,开放、强氧化环境是导致各特征组分浓度偏高的主要原因。小沟(F02)露天矿长期处于半暴露状态,其平均氧化还原电位最大为476 mV,由于在雨季大气降雨混入露天矿坑中,Eh变幅较大,其特征组分浓度次之。山底河总出口(F05)是多种来源水的混合断面,其Eh处于中值位置(平均222.07 mV)。跃进煤矿为正在开采的煤矿,其矿坑排水(F04)Eh平均为141.26 mV,虽然低于前3个各样点,但远高于闭坑的榆林垴孔(F03)矿坑水,仍然处于氧化环境。榆林垴孔(F03)的采空区位于水位季节变动带,其氧化还原电位均值为−46.56 mV,总体处于半封闭的还原环境,因此其总体的水化学特征浓度最低。榆林垴孔平均水温19.89℃且较稳定,平均pH值7.26,是有利于硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)生长的良好环境(赵宇华等,1997),在此水化学条件下,可采取微生物方法原位修复矿坑水。流域煤矿“老窑水”主排泄点柳沟泉(G01)的Eh值为346.8~428.6 mv,平均值为401.57 mV,较接近于F01和F02露天矿积水的数值。综上分析,表明煤系地层中黄铁矿的强氧化作用是造成老窑水特征浓度变化的主要原因,其氧化作用主要发生在地下水位季节变动带、包气带和地表,这些地带应作为煤矿“老窑水”源头治理的重点区。因此可通过回填流域内小沟露天矿以及覆盖地面煤渣、煤矸石等治理措施(梁永平等,2021)。
4.2.1 SO42-和TDS浓度特征
SO42-和Fe是煤系地层黄铁矿氧化的直接产物(肖有权,1982;Evangelou et al.,1995;Egon et al., 2016;Dogramaci et al., 2017;张玉卓等,2021;张春潮等,2021)。SO42-更具稳定性,与TDS、总硬度(HB)和Fe组分间存在显著的正相关关系,与pH呈负相关关系(图 6),是水中主要水化学成分的综合体现,对酸性煤矿水具有重要的指征意义。
庙沟泉(F01)的SO42-、TDS浓度最大(图 7),其雨季浓度大,枯季浓度低,且从枯季到雨季,浓度缓慢升高,这与F05显著不同,如2016年7月19日发生一次60年一遇特大暴雨降雨过程(24 h降水量129.80 mm),7月29日TDS值达到了最大51640 mg/L。从水文地质和地球化学背景分析,F01主要发育于采空区上部,为一上层滞水泉,下伏老窑积水水位低于15#煤层标高,在特大暴雨后,地下水位迅速上升至采空区,长时间溶滤的高浓度老窑水补给F01泉,导致离子浓度和TDS迅速增加;雨后地下水位迅速下降,高浓度老窑水补给量减少,泉口浓度降低。小沟(F02)的浓度极大值出现在雨季之前,主要与其氧化和蒸发浓缩作用有关。F01和F02两个监测点的极低值多出现在冬、春季,推测可能与融雪稀释或低温天气有关。
榆林垴孔(F03)和跃进煤矿(F04)监测点的SO42-、TDS浓度较为接近(图 7)。其动态变化与降水表现出一定的相关性,具有一定“水文型”补给特征;但两个监测点的浓度与降雨响应时间不同。F04浓度在雨季前增大至极大值,雨季浓度缓慢降低,受降雨影响较大。F03的SO42-、TDS浓度则在雨季达到最大,雨季多处于快速衰减阶段,监测数据中有浓度与降水的波峰与波谷型相对应的状况,这种动态特征与F03特殊的采空区地质结构有关(图 1c)。山底河总出口(F05)的SO42-、TDS浓度最小值一般出现在雨季或雨季后期(图 7),冬春季为浓度升高期;而个别雨季监测数据SO42-含量大于4000 mg/L,如2017年雨季浓度增大到极大值(SO42-为11153 mg/L,TDS为13990 mg/L),主要与其涌出地表的高浓度矿坑老窑水量增大有关,而导致SO42-与HB和Fe的相关性偏离线性关系曲线(图 6);其浓度总体呈现趋势性下降的特点,推测由于老窑水更新加快,水岩作用时间短,污染浓度逐渐降低。
4.2.2 TFe和Mn浓度特征
庙沟泉(F01)的TFe和Mn浓度最大(表 2,图 8),一般在雨季浓度最大,枯季浓度最低,最大为5600 mg/L,榆林垴孔(F03)有同样的特征。小沟(F02)、榆林垴孔(F03)和山底河总出口(F05)则是在雨季之前浓度最高。大部分样点的TFe和Mg均不同程度超出《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)限值0.3 mg/L和0.1 mg/L。各监测点的TFe和Mn表现出与SO42-和TDS相同的变化特征,均与降雨量相关。Mn的浓度低于TFe的浓度,这是由于在地质作用过程中,Fe和Mn具有相似的迁移和富集规律,一般水中的Mn比Fe易迁移富集,但受煤矿中黄铁矿氧化的影响,导致水中TFe浓度高于Mn浓度。
酸性矿坑水SO42-中S和TFe存在较为显著的线性相关关系(图 9),且相关曲线斜率和截距远高于纯FeS2的氧化水解,如F05点。一是因为煤系地层中S元素除来源于FeS2外,还有如石膏、单质硫等其他来源;二是因为水中的Fe离子易发生氧化沉淀为Fe(OH)3。山底河老窑水循环系统水循环过程复杂,渗流过程中发生着一系列的氧化、还原、沉淀、混合等诸多水化学作用和生物化学反应过程,均影响到SO42-中S和TFe的浓度分布。
4.2.3 溶解氧浓度特征
溶解氧是水质评价的重要指标(刘胤序等,2019;Oluwatosin et al.,2020;苗得雨和衣鹏,2021)。黄铁矿氧化需要消耗水中的氧,在不同径流路径上水体溶解氧不同(图 10)。柳沟(G01)水样为煤矿老窑水主出口,相对而言黄铁矿的氧化反应最强烈(现场测试平均pH为3.35,平均电导率为65630 μs/cm),耗氧多,水中溶解氧最低;山底河总出口(F05)的水样混合了上游各类水(现场测试平均pH为5.28,平均电导率为4465 μs/cm),其溶解氧高于G01;温河口(G03)的水样经过了天然爆气,溶解氧较G01的值有所增加。清水中饱和溶解氧随水温的升高而减小(美国公共卫生协会等,1978)。水循环过程中受有机物浓度等其他因素的影响,溶解氧存在着一定的偏差,但总体上3个点水样的溶解氧均低于清水。
5. 流域“老窑水”对泉域岩溶水的环境效应
5.1 对岩溶水的渗漏补给
酸性矿坑水径流进入下游碳酸盐岩渗漏段,补给岩溶含水层,是泉域地下水的重要补给源(王桃良等,2015;霍建光等,2015;王志恒等,2020;唐春雷等,2020)。监测期(2017年6月至2020年12月)山底河总出口(F05)平均流量为12424.12 m3/d,同期温河口(G03)平均流量为8632.75 m3/d,在1.8 km渗流段内的平均渗漏量为3791.37 m3/d,平均渗漏率为30.5%。忽略区间产流,参考梁永平等(2011)计算单位公里长的漏失系数方法计算如下:

根据上列数据计算山底河单位公里漏失系数β为0.1831。另外温河单位公里长的漏失系数为0.0156(王桃良等,2015)。
综上,求得山底河煤矿“老窑水”在娘子关泉域内的总渗漏率为: 1-(1-0.1831)1.8 + 1-(1-0.0156)35.89=73.64%
汇总监测期(2014—2020年)F05实测平均流量为10085.66 m3/d,利用渗漏率可计算监测期内的总渗漏量,计算得山底河煤矿“老窑水”出流后两个主要渗漏段的总渗漏补给量为7247.08 m3/d;其中山底河流域内的渗漏为3076.13 m3/d,温河主干流渗漏量为4350.95 m3/d。如此大的渗漏补给量和污染程度如此严重的山底河“老窑水”必将成为娘子关泉域岩溶地下水的重要污染源。
5.2 对泉域岩溶水水质的影响
根据梁永平等(霍建光,2015;梁永平,2021)研究表明,娘子关泉水SO42-含量快速增加和超标的主要原因是受到煤矿“老窑水”的污染。在娘子关泉域岩溶水渗漏段处于山底河煤矿“老窑水”的河底镇岩溶井已经受到了山底河煤矿“老窑水”的污染(石维芝,2022),其SO42-多年平均含量为882.58 mg/L。
按照《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)集中式饮用水地表水源地补充项目标准限值,山底河总出口(F05)水SO42-是标准限值250 mg/L的7.07~14.47倍,平均值是其13.31倍;Fe是标准限值0.3 mg/L的200.73~511.77倍,平均值是其410倍;Mn是标准限值0.1 mg/L的48.43~150.10倍,平均值是其97.5倍。
根据上述研究,渗漏量如此大的山底河煤矿“老窑水”,水质恶劣,入渗补给作为饮用水水源的娘子关泉域岩溶地下水,必将对泉域岩溶水造成严重污染,水质恶化同时引起一系列生态环境问题,河道两侧受老窑水污染地区植被破坏、土壤污染,农作物如已造成周边植被枯死,农作物无法生长等,生态环境持续恶化,急需开展煤矿老窑水污染机理、治理措施研究,开展废弃煤矿老窑水治理和区域生态修复。
6. 结论
(1)山底河流域“老窑水”流量动态主要受降水影响,雨季后为流量衰减阶段;“老窑水”流量对降雨量的调节时间为半年。煤矿“老窑水”的流量与水化学特征指标电导率、SO42-浓度呈非线性相关。山底河流域煤系地层中黄铁矿的强氧化反应主要发生在地下水位季节变动带、包气带和地表,而且煤矿采空积水区的一定深度为还原环境。
(2)山底河煤矿“老窑水”出流后进入下游碳酸盐岩河段渗漏,对娘子关泉域岩溶水的渗漏补给量达7247.08 m3/d。山底河煤矿“老窑水”总出口水SO42-、Fe、Mn已严重超过《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)集中式饮用水地表水源地补充项目标准限值,水质恶劣,急需开展煤矿“老窑水”的治理和废弃煤矿生态修复。
-
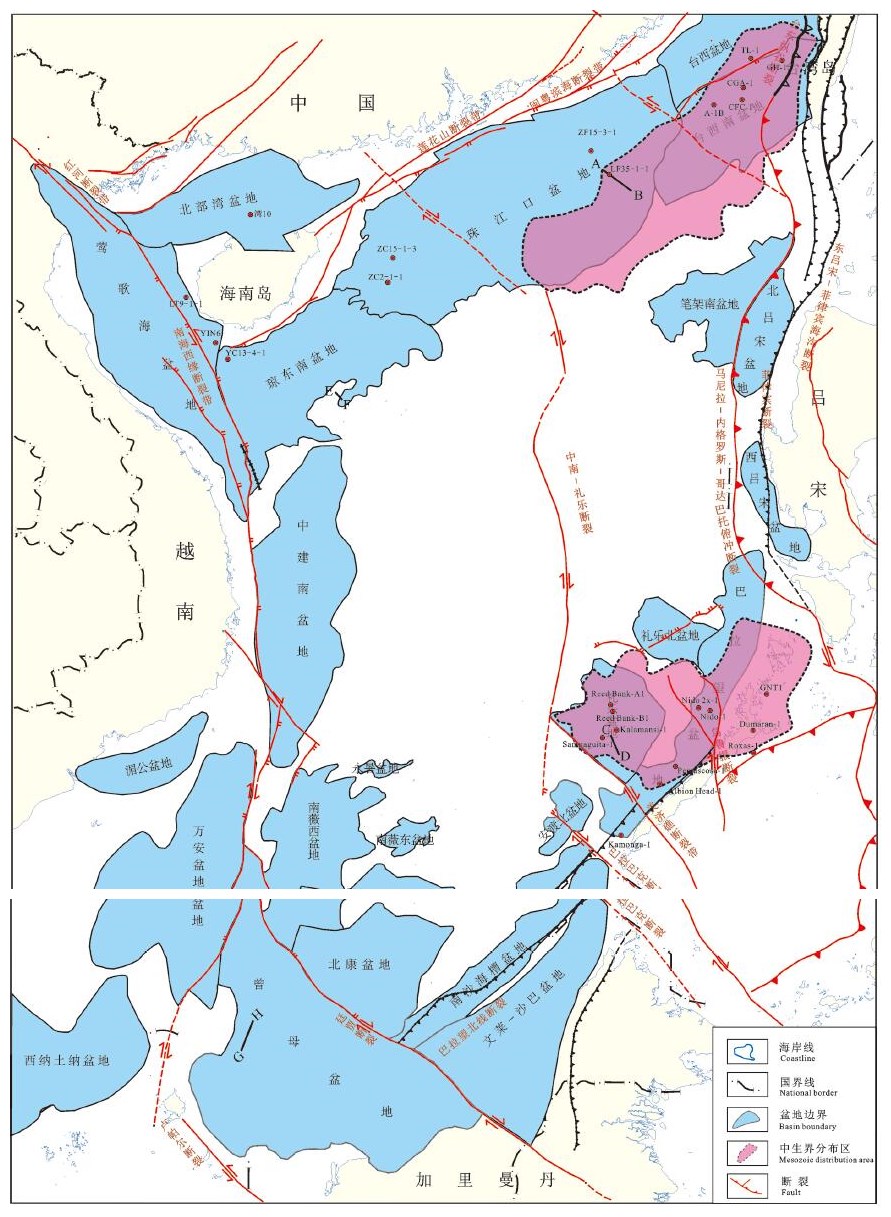
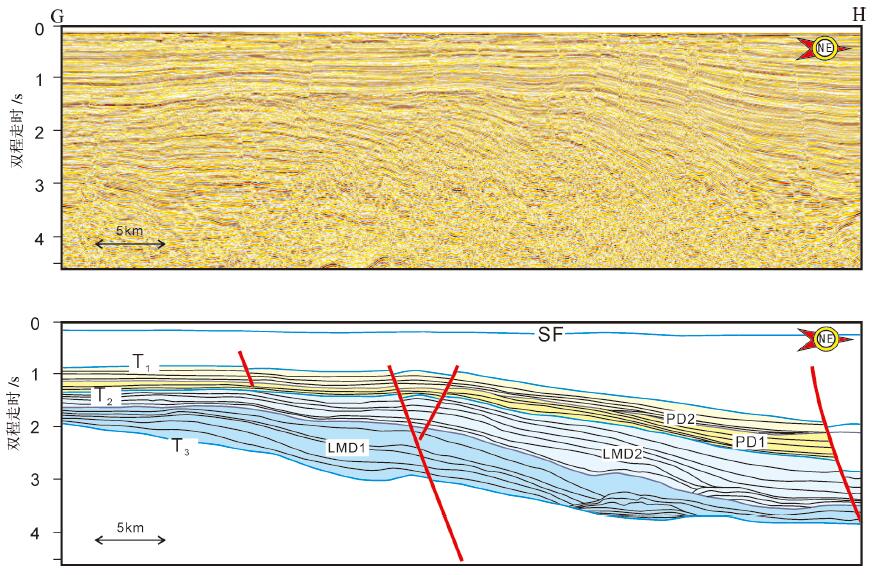
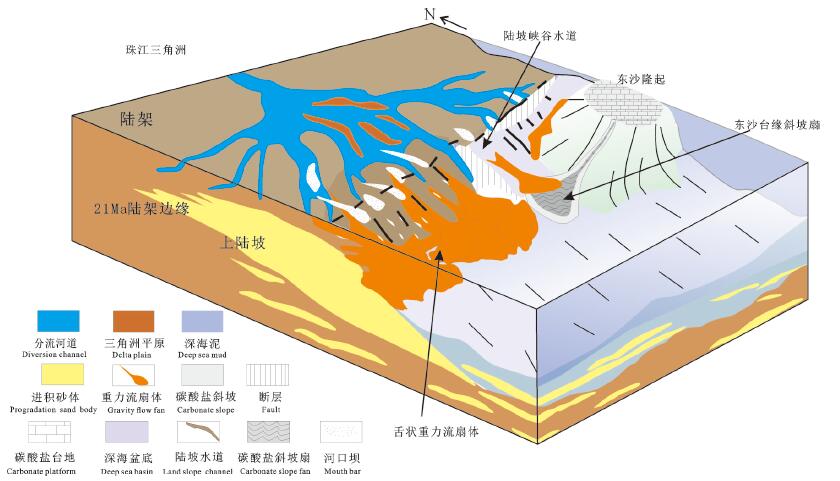
图 5 曾母盆地陆架三角洲模式图(剖面位置见图GH)
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the continental shelf delta in Zengmu Basin(see Fig. 1 for its location)
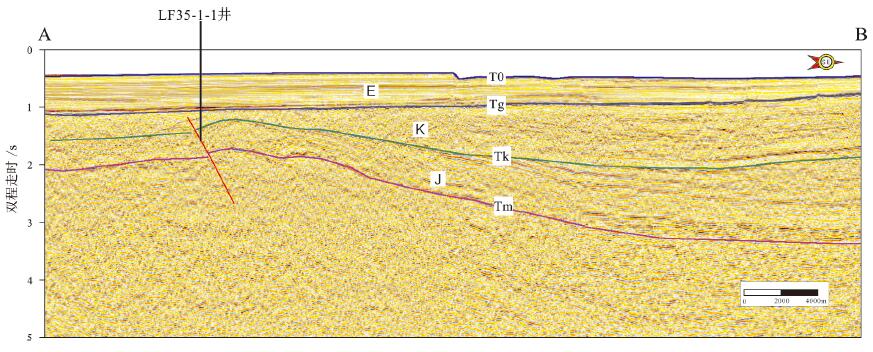
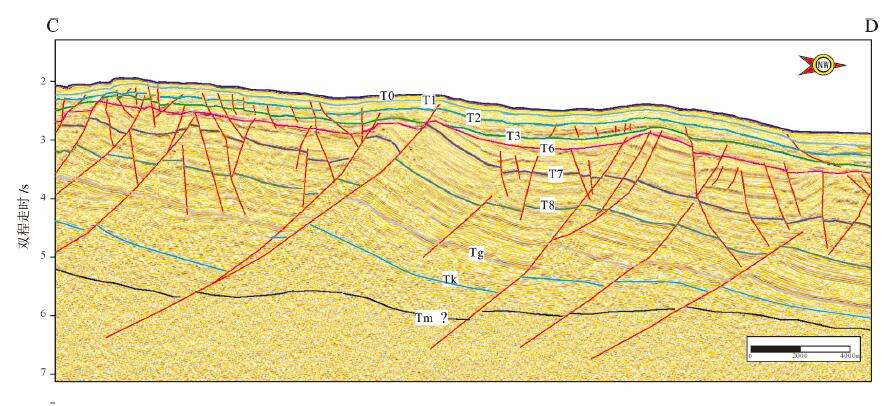
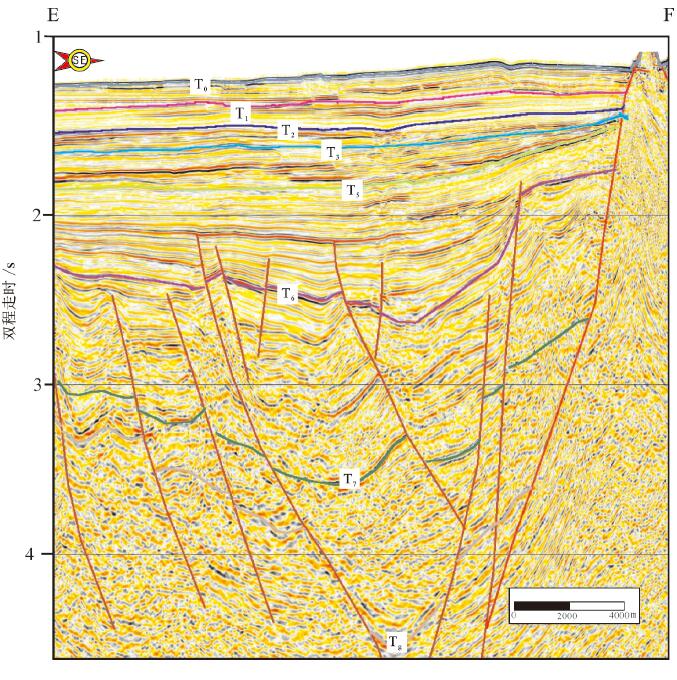
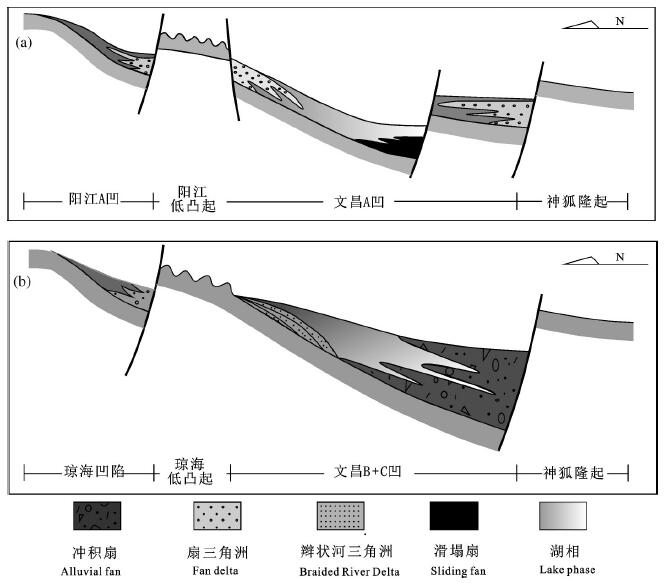
图 8 珠江口盆地珠三坳陷裂陷期古地貌与沉积体系模式据(姜华等,2008)
Figure 8. Paleogeomorphology and sedimentary system model during the rifting period of the Zhusan depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin (afterJiang Hua et al., 2008)
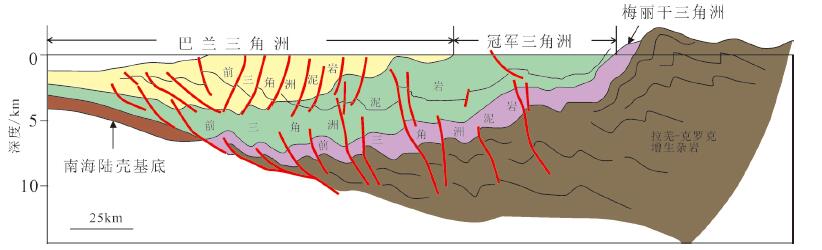
图 9 珠江口盆地白云凹陷陆架边缘三角洲沉积模式(据朱伟林,2012)
Figure 9. Delta sedimentary model of the margin of the continental shelf in Baiyun sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin (afterZhu Weilin, 2012)
图 10 红河沉积体系平面展布(据王英明,2011)
Figure 10. Plane distribution of the Honghe sedimentary system (afterWang Yingming, 2011)
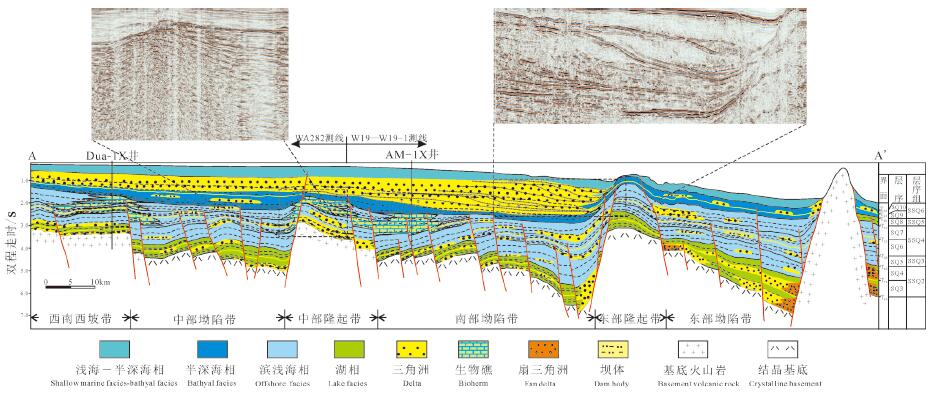
图 11 万安盆地层序充填格架及岩性地层圈闭分布(据杨楚鹏等,2011)
Figure 11. Sequence packing grid and lithologic stratigraphic trap distribution in Wan'an Basin (after Yang Chupeng et al., 2011)
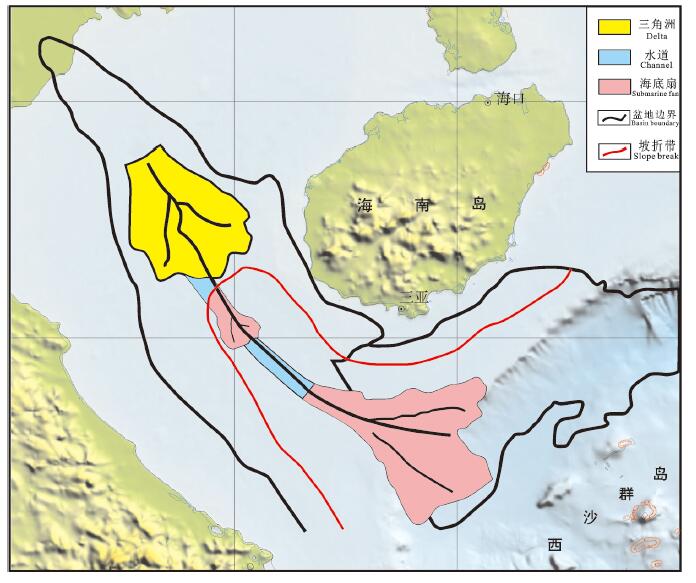
图 12 南海南部文莱—沙巴盆地三角洲演化模式图(据雷志斌等,2016)
Figure 12. Delta evolution pattern of the Brunei-Sabah basin in the southern South China Sea (after Lei Zhibin et al., 2016)
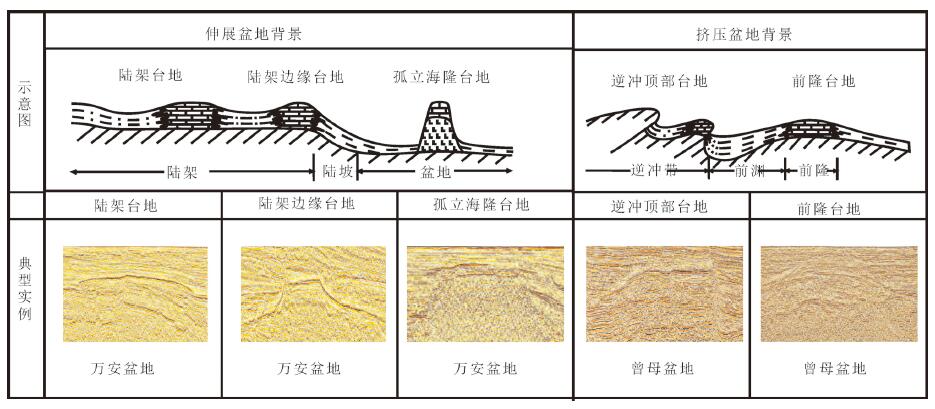
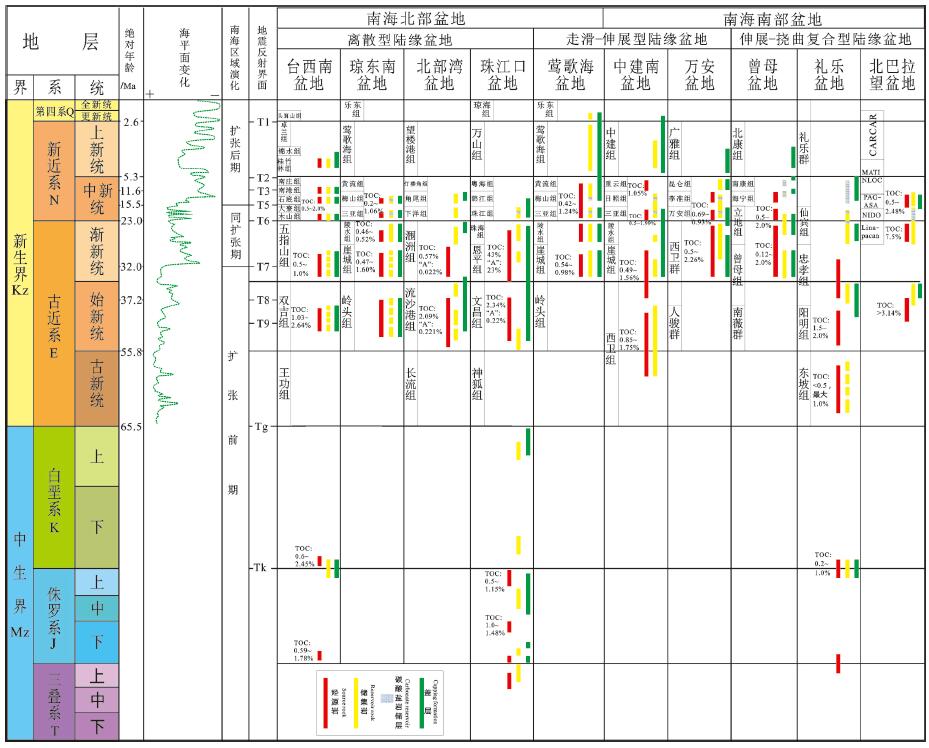
表 1 南海海域新生代沉积盆地分类
Table 1 Classification of Cenozoic sedimentary basins in the South China Sea

表 2 南海及邻区中生代沉积岩生烃参数(鲁宝亮等,2014)
Table 2 Hydrocarbon generation parameters of Mesozoic sedimentary rocks in the South China Sea and adjacent areas (after Lu Baoliang et al., 2014)

-
Ali M Y B, Abolins P. 1999. Charpter 15: Central Luconia Province. In: The Petroleum Geology and Resources of Malaysia[M].Petronas, 369-392.
Franke D, Barckhausen U, Heyde I, Tingay, M, Ramli, N. 2008.Seismic images of a collision zone offshore NW Sabah/Borneo[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 25(7): 0-624. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8845b5b30d41ffc82cc11028ec6396ab
Hao Fang, Zou Huayao, Yang Xusheng, Wang Minfang. 2003. Episodic petroleum accumulation, its driving mechanisms and distinguishing markers[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(3): 403412(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200303015
He Jiaxiong, Chen Shenghong, Liu Hailing, Wan Zhifeng. 2008. Geological characteristics and the law of formation of Hydrocarbon migration on accumulation Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 30(5): 46-52(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnsyxyxb200805010
He Jiaxiong, Yan Wen, Ma Wenhong, Zhu Youhai, Chen Shenghong, Gong Xiaofeng. 2010. Analogy of oil and gas geology between Quasi-passive margin of Northern South China Sea and global oil and gas enriched Areas in deep water[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 21(6): 897-908, 995(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201006004
He Jiaxiong, Zhang Wei, Lu Zhenquan, Li Xiaotang. 2016. Petroleum system and favorable exploration directions of the main marginal basins in the northern South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 27(6): 943-959(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201606001
Holloway N H. 1982. The north Palawan block, Philippines: Its relation to the Asian mainland and its role in the evolution of the South China Sea[J]. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull., 66(9) :13551383. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/aapgbull/article-abstract/66/9/1355/37564/north-palawan-block-philippines-its-relation-to
Hutchison C S. 2004. Marginal basin evolution: the southern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 21(9):1129-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.07.002
Jiang Hua, Wang Hua, Xiao Jun, Chen Shaoping, Lin Zhengliang. 2008. Control of paleomorphology to sedimentary filling in marginal sea basin - by taking ZhuⅢ Depression for example[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 30(1): 10-15, 387(in Chinese with English abstract).Kudrass, H R, Wiedicke M, Cepek P, Kreuzer H, Müller P. 1986. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200801004.htm
Mesozoic and Cainozoic rocks dredged from the South China Sea (Reed Bank area) and Sulu Sea and their significance for platetectonic reconstructions[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 3(1): 1930.
Lei Chao, Ren Jianye, Pei Jianxiang, Lin Haitao, Yin Xinyi, Tong Dianjun. 2011. Tectonic framework and multiple episode tectonic evolution in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Earth science Journal of China University of Geoscience, 36(1): 151-162(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201101016
Lei Zhibin, Yang Minghui, Zhang Houhe, Liao Zongbao, Zhang Shaohua, Luo xiaohua. 2016. Tertiary delta evolution and related hydrocarban accumulation in the Southern Nansha Area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 21(4): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2096249517300297
Li Wenbao, Wang Rujian. 2014. Research of the mechanism of sea level change during the last 100 Ma[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(1): 117- 127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201401013
Liu Baoming, Liu Hailing. 2011. The Mesozoic in the South China Sea and adjacent areas: new targets for hydrocarbon explotation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 31(2): 105- 109(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876380414600653
Liu Botu, Chen Changsheng. 2002. Analysis on the Cenozoic petroleum system in the Wanan Basin, Nansha area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 24(2): 110-114(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225675111_Petroleum_System_in_Deepwater_Basins_of_the_Northern_South_China_Sea
Liu Zhaoshu. 2000. Geotectonics and hydrocarbon resources in the South China Sea[J]. Queternary Sciences, 20 (1): 69- 77(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221462961630322X
Liu Zhenhu. 2005. Distribution of sedmentary basins and petroleum potential in southern South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(3): 410-417(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817208000160
Lu Baoliang, Wang Pujun, Wu Jingfu, Li Wuzhi, Wang Wanyin, Lang Yuanqiang. 2014. Distribution of the Mesozoic in the continental margin basins of the South China Sea and its petroliferous significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(4): 497-503(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201404017
Lu Baoliang, Wang Pujun, Wu Jingfu, Li Wuzhi, Wang Wanyin, Lang Yuanqiang. 2014. Distribution of the Mesozoic in the continental margin basins of the South China Sea and its petroliferous significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(4): 497-503(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201404017
Lu Baoliang, Wang Pujun, Zhang Gongcheng, Zhang bin, Sun Xiaomeng, Li Wuzhi, Lang Yuanqiang. 2011. Basement structures of an epicontinental basin in the northern South China Sea and their significance in petroleum prospect[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 32 (4): 580-587(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201104004
Lu Li, Clift P D, Nguyen H T. 2013. The sedimentary, magmatic and tectonic evolution of the southwestern South China Sea revealed by seismic stratigraphic analysis[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 34 (3/4):341-365. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aa209553f1c415d3fe8bee406756d040
Luo Shuaibing, Zhang li, Zhou Jiangyu, Lei Zhenyu, Shuai Qingwei, Zhou Jiajia, Luo Wei. 2020. Study on the characteristics and development patterns of source rocks in Beikang basin, South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20200420.1404.html(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-6003-y
Qiang Kunsheng, Zhang Guangxue, Zhang Li, Lü Baofeng, Zhong Guangjian, Feng Changmao, Yi Hai. 2018. Paleogeomorphic features and sedimentary facies model of Jurassic strata in Chaoshan sub- basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1251-1258(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201806015
Qiu Yan, Wang Yingmin. 2001. Reefs and paleostructure and paleoenvironment in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 21(1): 65-67, 69-73(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200101011
Qiu Yan. 1996. The interpretation of Carbonate sequence stratigraphy in the Southwestern region of South China Sea[J]. Geological Reasearch of South China Sea, 62- 74(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073897000730
Qiu Yan. 2001. Tertiary reefs of the South China Seas and their oil-gas bearing characters[J]. Gresearch of Eological South China Sea, 4154(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.searchanddiscovery.com/abstracts/pdf/2002/annual/EXTENDED/ndx_46647.pdf
Ren Jianye. 2018. Genetic dynamics of China offshore Cenozic basins[J]. Earth Science, 43(10): 3337- 3361(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912018303729
Sun Longtao, Sun Zhen, Zhan Wenhuan, Liu Hailing, Fan Hao. 2010. Pertoleum potential prediction of the Lile Basin in Nansha[J]. EarthScience——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(1): 137-145(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.014
Sun Longtao, Sun Zhen, Zhou Di, Liu Hailing. 2008. Stratigraphic and structural characteristics of Lile Basin in Nansha area[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 32(2): 151- 158(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200802003
Tongkul F. 1994. The geology of Northern Sabah, Malaysia: its relationship to the opening of the South China Sea Basin[J]. Tectonophysics, 235(1/2): 131-147. http://eprints.ums.edu.my/3385/
Wang Pengcheng, Li Sanzhong, Guo Lingli, Zhao Shujuan, LI Xiyao, Wang Yongming, Hui Gege, Wang Qian. 2017. Opening of the South China Sea(SCS) : A joint effect of dextral strike-slip pullapart and proto-SCS slab pull[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 24(4):294319(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yingmin, Xu Qiang, Li Dong, Han Jianhui, Lü Ming, Wang Yongfeng, Li Weiguo, Wang Hairong. 2011. Late Miocene Red River submarine fan, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(10): 781-787(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2011-56-10-781
Wei Xi, Deng Jinfu, Xie Wenyan, Zhu Yongjun, Zhao Guochun, Li Yuxi, Chen Yihan. 2005. Constraints on biogenetic reef formation during evolution of the South China Sea and exploration potential analysis[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 12(3): 245-252(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200503026
Wu Dong, Zhu Xiaomin, Zhang Houhe, Zhu Mao, Zhao Dongna, Geng Mingyang, Li Wei, Liao Zongbao. 2014. Deposition characteristics and hydrocarbon distribution in medium and large basins of Nansha, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 16(5): 673-686(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201405009
Wu Shimin, Zhou Di, Liu Hailing. 2004. Tectonic framework and evolutionary characteristics of Nansha block, South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 28(1): 23- 28(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200401004
Xie Xinong, Li Sitian, Dong Weiliang, Zhang Minqiang, Yang Jihai. 1999. Trace marker of hot fluid flow and their geological implications——A case study of Yinggehai Basin[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 24(2):75-80(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX902.016.htm
Xie Xinong, Zhang Cheng, Ren Jianye, Yao Bochu, Wan Ling, Chen Hui, Kang Bo. 2011. Effects of distinct tectonic evolutions on hydrocarbon accumulation in northen and southern continental marginal basins of South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(12): 3280-3291(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1002/cjg2.1687
Yan Wei, Zhang Guangxue, Zhang Li, Xia Bin, Yang Zhen, Lei Zhenyu, Lin Zhen, Luo Shuaibing. 2018. Focused fluid flow systems and their implications for hydrocarbon accumulation on the southern margin of South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 45 (1): 39-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801004
Yang Chupeng, Yao Yongjian, Li Xuejie, Chang Xiaohong. 2014. Sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary cycle of Miocene Carbonate buildups in Zengmu basin, the southern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University ofGeoscience, 39(1): 91-98(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.009
Yang Chupeng, Yao Yongjian, Li Xuejie, Liao Zewen. 2010. Oilgenerating potential of Cenozoic coal- measure source rocks in Zengmu Basin, the southern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 31(6): 920-926(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287513659_Oil-generating_potential_of_Cenozoic_coal-measure_source_rocks_in_Zengmu_Baisn_the_southern_South_China_Sea
Yang Chupeng, Yao Yongjian, Li Xuejie, Wan Ling, Han Bin, Wan Rong- sheng. 2011. Cenozoic sequence stratigraphy and lithostratigraphic traps in Wan'an Basin, the Southwestern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 36(5): 845-852(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201105009
Yao Bochu, Liu Zhenhu.2006. Sedimentary basins and petroleum resources in Nansha offshore area, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil And Gas, 18(3): 150-160(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc200603002
Yao Bochu, Wan Ling, Liu Zhenhu. 2004. Tectonic dynamics of Cenozoic sedimentary basins and hydrocarbon resources in the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 29(5): 543-549(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200405007
Yao Yongjian, Jiang Yukun, Zeng Xianghui. 2002. Cenozoic tectonic movements in Nansha area, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil And Gas(Geology), 16(2): 42-46, 53(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-dz200202008
Zhang Gongcheng, Qu Hongjun, Zhang Fenglian, Chen Shuo, Yang Haizhang, Zhaozhao, Zhaochong. 2019. Major new discoveries of oil and gas in global deepwaters and enlishtenment[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinaca, 40(1): 1-34, 55(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0042-6
Zhang Gongcheng, Xie Xiaojun, Wang Wanyin, Liu Shixiang, Wang Yibo, Dong Wei, Shen Huailei. 2013. Tectonic tytps of petroliferous basins and its exploration potential in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(4): 611- 627(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876380418300247
Zhang Li, Li Wencheng, Zeng Xianghui. 2003. Stratigraphic Sequence and hydrocarbon potential in Lile basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 25(5): 469-472, 480(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200305009
Zhang Qiang, Lu Fuliang, He Xiaosu, Wang Bin, Sun Guozhong. 2018. Progress and enlightenment of oil and gas exploration in the South China Sea in recent five years[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 23(1): 54-61(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200305009
Zhu Weilin, Zhang Gongcheng, Gaole. 2008. Geological characteristics and exploration objectives of hydrocarbons in the northern contimental margin basin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 29(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00742.x
Zhu Weilin, Zhong Kai, Li Youchuan, Xu Qiang, Fang Dianyong. 2012. Characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration potential of the northern South China Sea Deepwater Basins[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(20): 1833-1841(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2012-57-20-1833
龚再升, 李思田, 谢泰俊. 1997.南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M].北京:科学出版社, 63–67.郝芳, 邹华耀, 杨旭升, 王敏芳. 2003.油气幕式成藏及其驱动机制和识别标志[J].地质科学, 38(3): 403-412. 何家雄, 陈胜红, 刘海龄, 万志峰. 2008.南海北部边缘区域地质与油气运聚成藏规律[J].西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 30(5): 46-52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnsyxyxb200805010 何家雄, 颜文, 马文宏, 祝有海, 陈胜红, 龚晓峰. 2010.南海北部准被动陆缘深水区油气地质及与世界深水油气富集区类比[J].天然气地球科学, 21(6): 897-908, 995. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201006004 何家雄, 张伟, 卢振权, 李晓唐. 2016.南海北部大陆边缘主要盆地含油气系统及油气有利勘探方向[J].天然气地球科学, 27(6): 943-959. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201606001 姜华, 王华, 肖军, 陈少平, 林正良. 2008.古地貌对边缘海盆地沉积充填特征的控制——以南海珠江口盆地珠三坳陷为例[J].石油天然气学报, 30(1): 10-15, 387. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jhsyxyxb200801003 解习农, 李思田, 董伟良, 张敏强, 杨计海. 1999.热流体活动示踪标志及其地质意义——以莺歌海盆地为例[J].地球科学, 24(2):75-80. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx199902017 解习农, 张成, 任建业, 姚伯初, 万玲, 陈慧, 康波. 2011.南海南北大陆边缘盆地构造演化差异性对油气成藏条件控制[J].地球物理学报, 54(12): 3280-3291. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201112026 雷超, 任建业, 裴健翔, 林海涛, 尹新义, 佟殿君. 2011.琼东南盆地深水区构造格局和幕式演化过程[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 36(1): 151-162. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201101016 雷志斌, 杨明慧, 张厚和, 廖宗宝, 张少华, 罗晓华. 2016.南沙海域南部第三纪三角洲演化与油气聚集[J].海相油气地质, 21(4): 21-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201604004 李文宝, 王汝建. 2014.近100 Ma以来海平面变化机制[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(1): 117-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201401013 刘宝明, 刘海龄. 2011.南海及邻区中生界——新的油气勘探领域[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 31(2):105-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201102013 刘伯土, 陈长胜. 2002.南沙海域万安盆地新生界含油气系统分析[J].石油实验地质, 24(2): 110-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200202003 刘昭蜀. 2000.南海地质构造与油气资源[J].第四纪研究, 20(1): 6977. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200001012 刘振湖. 2005.南海南沙海域沉积盆地与油气分布[J].大地构造与成矿学, 29(3): 410-417. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200503017 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 吴景富, 李伍志, 王万银, 郎元强. 2014.南海陆缘盆地中生界分布特征及其油气地质意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 41(4): 497-503. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201404017 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 张功成, 张斌, 孙晓猛, 李伍志, 郎元强. 2011.南海北部陆缘盆地基底结构及其油气勘探意义[J].石油学报, 32(4):580-587. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201104004 骆帅兵, 张莉, 周江羽, 雷振宇, 帅庆伟, 周佳维, 罗威. 2020.南海南部北康盆地烃源岩特征及发育模式探讨[J].中国地质, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20200420.1404.html. 强昆生, 张光学, 张莉, 吕宝凤, 钟广见, 冯常茂, 易海. 2018.南海北部潮汕坳陷侏罗系古地貌特征及沉积相模式[J].中国地质, 45(6):1251-1258. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201806015 邱燕, 王英民. 2001.南海第三纪生物礁分布与古构造和古环境[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 21(1):65-67, 69-73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200101011 邱燕. 1996.南海西南部主要盆地碳酸盐岩层序地层学解释[J].南海地质研究, 62-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600771290 邱燕. 2001.南海第三纪生物礁及其含油气性[J].南海地质研究, 41-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200201904695 任建业. 2018.中国近海海域新生代成盆动力机制分析[J].地球科学, 43(10): 3337-3361. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201810002 孙龙涛, 孙珍, 詹文欢, 刘海龄, 樊浩. 2010.南沙海域礼乐盆地油气资源潜力[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 35(1): 137-145. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.014 孙龙涛, 孙珍, 周蒂, 刘海龄. 2008.南沙海区礼乐盆地沉积地层与构造特征分析[J].大地构造与成矿学, 32(2): 151-158. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200802003 王鹏程, 李三忠, 郭玲莉, 赵淑娟, 李玺瑶, 王永明, 惠格格, 王倩.2017.南海打开模式:右行走滑拉分与古南海俯冲拖曳[J].地学前缘, 24(4):294-319. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2017-4-3 王英民, 徐强, 李冬, 韩建辉, 吕明, 王永凤, 李卫国, 王海荣. 2011.南海西北部晚中新世的红河海底扇[J].科学通报, 56(10): 781-787. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201110012 魏喜, 邓晋福, 谢文彦, 祝永军, 赵国春, 李玉喜, 陈亦寒. 2005.南海盆地演化对生物礁的控制及礁油气藏勘探潜力分析[J].地学前缘, 12(3): 245-252. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200503026 吴冬, 朱筱敏, 张厚和, 朱茂, 赵东娜, 耿名扬, 李维, 廖宗宝. 2014.中国南沙海域大中型盆地沉积特征与油气分布[J].古地理学报, 16(5): 673-686. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201405009 吴世敏, 周蒂, 刘海龄. 2004.南沙地块构造格局及其演化特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, (1): 23-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200401004 鄢伟, 张光学, 张莉, 夏斌, 杨振, 雷振宇, 林珍, 钱星, 骆帅兵. 2018.南海南部陆缘地质流体类型及其油气成藏意义[J].中国地质, 45(1):39-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801004 杨楚鹏, 姚永坚, 李学杰, 常晓红. 2014.南海南部曾母盆地中新世碳酸盐岩的层序地层[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 39(1): 91-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201401009 杨楚鹏, 姚永坚, 李学杰, 廖泽文. 2010.南海南部曾母盆地新生界煤系烃源岩生油条件[J].石油学报, 31(6): 920-926. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201006008 杨楚鹏, 姚永坚, 李学杰, 万玲, 韩冰, 万荣胜. 2011.万安盆地新生代层序地层格架与岩性地层圈闭[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 36(5): 845-852. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201105009 姚伯初, 刘振湖. 2006.南沙海域沉积盆地及油气资源分布[J].中国海上油气地质, 18(3): 150-160. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc200603002 姚伯初, 万玲, 刘振湖. 2004.南海海域新生代沉积盆地构造演化的动力学特征及其油气资源[J].地球科学, 29(5): 543-549. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200405007 姚永坚, 姜玉坤, 曾祥辉. 2002.南沙海域新生代构造运动特征[J].中国海上油气地质, 16(2): 42-46+53. 张功成, 屈红军, 张凤廉, 陈硕, 杨海长, 赵钊, 赵冲. 2019.全球深水油气重大新发现及启示[J].石油学报, 40(1): 1-34, 55. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbCode=CJFD&filename=SYXB201901001&tableName=CJFDPREP&url= 张功成, 谢晓军, 王万银, 刘世翔, 王一博, 董伟, 沈怀磊. 2013.中国南海含油气盆地构造类型及勘探潜力[J].石油学报, 34(4): 611-627. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201304001 张莉, 李文成, 曾祥辉. 2003.礼乐盆地地层发育特征及其与油气的关系[J].石油实验地质, (5): 469-472+480. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200305009 张强, 吕福亮, 贺晓苏, 王彬, 孙国忠. 2018.南海近5年油气勘探进展与启示[J].中国石油勘探, 23(1): 54-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt201801006 朱伟林, 张功成, 高乐. 2008.南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J].石油学报, 29(1): 1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb200801001 朱伟林, 钟锴, 李友川, 徐强, 房殿勇. 2012.南海北部深水区油气成藏与勘探[J].科学通报, 57(20): 1833-1841. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201220003 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 闫军林. 河道活动坝特性研究与应用——以白杨河为例. 水利科技与经济. 2024(04): 59-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李冰,杜天愉,梅惠杰,吴玥洁,马卿皓,郭玉杰,弋双文,李月丛. 泥河湾盆地油房遗址MIS 5阶段人类活动与气候、植被的关系. 第四纪研究. 2024(05): 1322-1337 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 彭远黔,高武平,冉志杰,王红蕾,朱坤静,张安东,王志胜. 基于浅层地震勘探的滹沱河断裂第四纪活动性研究. 华北地震科学. 2024(04): 35-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郝娇娇,郭雯豪,刘耀徽,陈伟,李鹏为,马小飞,李夫星,袁璟,扶有镜. 基于高分辨率遥感影像的古中山国平原区地面古河道识别研究. 河北师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 628-637 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王燕校,王永,姚培毅,田飞,袁路朋,叶梦旎. 白洋淀漕河全新世早期古洪水事件的沉积特征及气候背景. 岩石矿物学杂志. 2022(05): 916-928 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: