Identification of provenance on uranium-bearing rocks from the Zhiluo Formation in the Nanlinggou uranium deposit, northern Ordos Basin
-
摘要:研究目的
纳岭沟铀矿是鄂尔多斯盆地北部最重要铀矿床之一,识别其含铀岩系物源区对于深化成矿作用和找矿预测具有实际意义。
研究方法笔者通过岩石学、重矿物学、地球化学和沉积相分析等方法,识别了纳岭沟铀矿床中侏罗统直罗组含铀岩系的蚀源区。
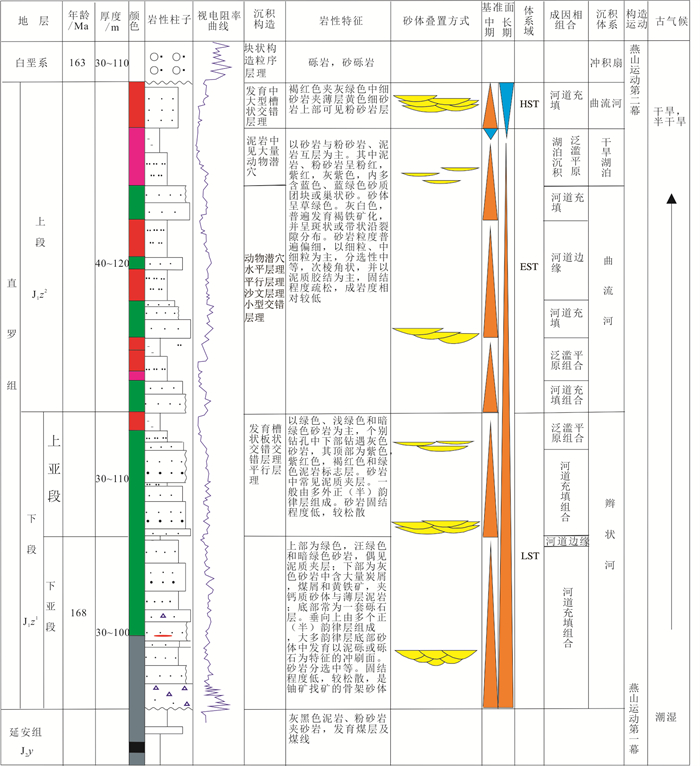
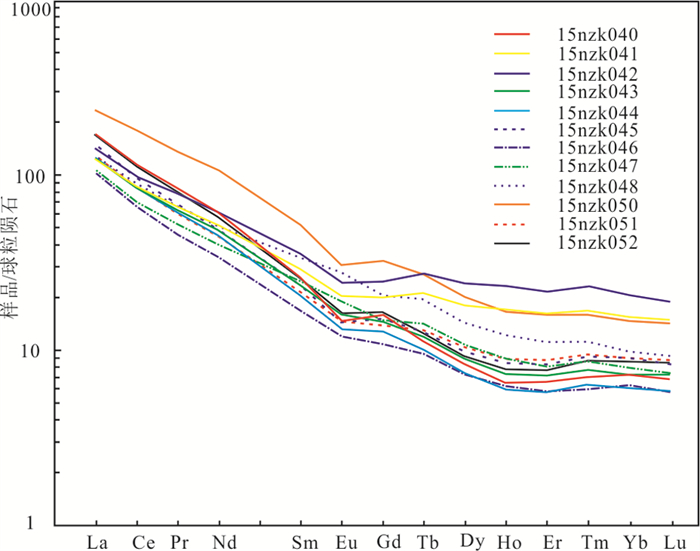
研究结果含铀岩系岩石类型主要为中粗长石砂岩,碎屑成分有长石、石英、黑云母和花岗岩岩屑、变质岩岩屑等,分选中等至差;碎屑多呈棱角状、次棱角状,少数为次滚圆状,磨圆度差至中等。重矿物分布极不均匀,呈棱角状、次棱角状、次滚圆状,磨圆度差至中等;ZTR(锆石+电气石+金红石)指数2%~10%。电气石、尖晶石、锐钛矿、角闪石、碳硅石等呈集簇状分布;碎屑锆石延长系数主要为1~2.2,其次2.2~3.2。稀土元素球粒陨石配分曲线形态相似,ΣREE值104.75×10-6~283.86×10-6,LREE/HREE值0.13~0.47,La/Yb值9.60~32.66,元素含量变化幅度大。纳岭沟地区含铀岩系砾质、砂质辫状河沉积相由矿区北东方向至南西方向延展,与高厚度砂体、高含砂率砂体分布规律一致。
结论纳岭沟铀矿直罗组含铀岩系蚀源区为矿区北东缘的晋蒙交界地带的前中侏罗世隆起区的太古代片麻岩、古元古代孔兹岩、二长花岗岩和古生代岩浆岩、沉积岩和中生代沉积岩、火山岩。
创新点:鄂尔多斯盆地纳岭沟铀矿区中侏罗统直罗组含铀岩系的蚀源区为晋蒙交界处的变质岩、岩浆岩和火山岩。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
ObjectiveThe Nalinggou uranium deposit is one of the most important uranium deposits in northern Ordos Basin. Identification onthe provenance of uranium bearing rocks is of practical significance for deepening mineralization and prospecting prediction.
MethodsBy means of petrology, heavy mineralogy, geochemistry and sedimentary facies analysis, the authors have identified the provenance of the uranium bearing rocks from the Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit.
ResultsThe uranium-bearing rocks are dominantly composed of medium coarse arkose. The clastic components are feldspar, quartz, biotite, debrises of granite and metamorphic rock, etc., with medium to poor sorting. The clasts are mostly angular and sub-angular, and a few are sub-rounded, with poor to medium roundness. The distribution of heavy minerals is extremely uneven, in angular, sub angular and sub rounded shapes, with poor to medium roundness. The ZTR (zircon+tourmaline+rutile) index varies of 2%-10%. The tourmaline, spinel, anatase, amphibole and carbosilica are distributed in clusters.The extension coefficient of detrital zircon is mainly in the range of 1-2.2, followed by the range of 2.2-3.2. The rocks exhibit similar chondrite-normalized patterns with great elemental variations among different samples. The ΣREE, LREE/HREE, and La/Yb values are in the range of 104.75×10-6-283.86×10-6, 0.13-0.47, and 9.60-32.66 respectively. The uranium bearing strata exhibit highly thick sand bodies. In the mining area, the sedimentary facies extend synchronously from the northeast to the southwest.
ConclusionsIn conclusion, it is generally considered that the uranium bearing rocks of the Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit is mainly proximal provenance, with a small amount of distal provenance. The sourced rocks are the pre-Jurassic bedrock area exposed at the boundary between Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia on the northeast edge of the mining area. The rock types include Archean gneiss, Paleoproterozoic Khondalite, magmatic rocks, Paleozoic magmatic rocks, sedimentary rocks and Mesozoic volcanic rocks, of which the khondalite belt provides the most important materials.
-
1. 引言
找矿模型,又称勘查模型,是表述目标矿床及其对一定勘查技术产生预期效应的模拟体系,利用已有地质信息及现有找矿手段,并通过找矿模型来实现成矿的预测。找矿模型的建立不仅需要总结地质直接找矿标志,还需要借助地球物理、地球化学等间接找矿标志识别成矿信息,推断矿体空间位置(陈毓川和朱裕生,1993)。陈毓川和朱裕生(1993)指出找矿模型突出的是某类矿床的基本要素和找矿过程中特殊意义的地质、物化探和遥感影像等特征及其在空间的变化情况,总结发展该类矿床的基本标志和找矿使用的方法手段。找矿模型是矿产勘查工作的实际指导,它是缩小勘查区(或靶区)甚至发现矿床的择优技术。当前,地质找矿已由浅部逐步转变为深部矿、隐伏矿,其找矿难度也逐步增大,对隐伏矿预测定位及找矿模型的建立显得尤为关键。
20世纪80年代以来,中国的地质工作者开始探索建立找矿模型的技术,来处理和分析各类地学资料进行综合分析,为普查和评价矿产资源提供依据,根据所利用的地学数据的不同来源,综合研究成果分别表述为矿田或矿床的地球物理模型、地球化学模型、地质-地球物理-地球化学模型或物理-地质模型。20世纪90年代以来,中国许多研究者对找矿模型的建模技术进行了系统的总结和推广。在寻找隐伏矿床的新方法上,多位研究者也建立了特有的找矿模型,如活动金属离子法、金属活动态法(MOMEO、(MMI) (Mann et al., 1998)、地气法(geogas) (Malmqvistet et al., 1984)。姚金炎(1990)提出综合物探、化探的隐伏矿床预测方法生物地球化学法、离子晕法、电吸附(周奇明,1996)、植物地球化学、地电化学等。
箭猪坡矿床作为五圩矿田矿集区代表性矿床之一,该矿床于20世纪80年代被发现,先后进行了普查和详查工作,经过20多年的开采,矿山资源量已不能满足矿山开采需求,急需开展地质找矿工作,增加储量。前人对该矿床的地质特征、矿床成因,流体特征等方面开展了较多的研究,普遍认为其受构造控制的岩浆期后热液脉状矿床。然而,箭猪坡矿床乃至五圩矿田的同类型矿床至今缺少找矿模式的研究。笔者所在项目组2012—2016年先后对箭猪坡矿床开展了构造控矿规律、矿体定位预测及外围探矿权找矿预测研究等工作,首次在五圩矿田箭猪坡矿床发现了石英脉型锡矿体,矿体呈脉状,倾角70°~75°,矿体平均品位:锡0.65%,铅0.56%、锑0.73%、银46 g/t,锡石主要呈棕褐色,多沿裂隙发育,呈条带状。经锡物相分析,锡以锡石为主。并对紧邻采矿权外围的花洞、板才探矿权开展了土壤地球化学测量、地电化学测量、瞬变电磁测量、可控源测量工作,大大丰富了找矿信息。本文在综合分析箭猪坡矿床地质、物探、化探特征基础上,构建了箭猪坡锑多金属矿地质-物探-化探测量综合信息找矿模型(经验证找矿效果良好),以期为箭猪坡锑多金属矿集区热液脉型矿床及外围同类型矿床找矿勘查和评价工作提供重要参考。
2. 矿床地质特征
五圩矿田位于丹池多金属成矿带南端(图 1)。区内出露的地层为下泥盆统塘丁组(D1t)—中三叠统(T2b);其中赋矿层位为下泥盆统塘丁组条带状绢云母泥岩夹砂岩(箭猪坡矿床),中泥盆统罗富组泥灰岩(三排洞—芙蓉厂矿床),上泥盆统榴江组、五指山组硅质岩。区域构造较为复杂,主要由五圩复式背斜及一系列以NNW向为主的张扭性断裂组成。北北西走向断裂带是五圩矿田内最发育的一组构造形迹,呈帚状构造的形态,向北北西向(箭猪坡—芙蓉厂)逐渐撒开,在花洞南东向成逐渐收敛状态,断裂带控制着区域矿化带的形成与发育。区域上未见岩浆岩出露。
![]() 图 1 五圩矿田区域地质简图T—三叠系(粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、灰岩);P—二叠系(灰岩、凝灰岩、硅质岩);C—石炭系(条带灰岩、微晶灰岩、泥岩);D—泥盆系(泥岩、灰岩、硅质岩); 1—背斜轴;2—向斜轴;3—断裂;4—铅锌锑银矿床;5—砷汞铅锌锑银矿床;6—锑矿点;7—汞矿床(点);8—矿田Figure 1. Regional geologic map of Wuxu mining areaT-Triassic system (silty mudstone, argillaceous siltstone, limestone); P-Permian System (Limestone, Tuff, Siliceous Rock); C-Carboniferous system (banded limestone, microcrystalline limestone, mudstone); D-Devonian System (Mudstone, Limestone, Siliceous Rock); 1-Anticlinal Axis; 2-Syncline axis; 3-Fracture; 4-Pb-Zn-Sb-Ag deposit; 5-Arsenic-mercury-lead-zinc-antimony-silver deposit; 6-Antimony ore site; 7-Mercury deposit (spot); 8-Ore field
图 1 五圩矿田区域地质简图T—三叠系(粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、灰岩);P—二叠系(灰岩、凝灰岩、硅质岩);C—石炭系(条带灰岩、微晶灰岩、泥岩);D—泥盆系(泥岩、灰岩、硅质岩); 1—背斜轴;2—向斜轴;3—断裂;4—铅锌锑银矿床;5—砷汞铅锌锑银矿床;6—锑矿点;7—汞矿床(点);8—矿田Figure 1. Regional geologic map of Wuxu mining areaT-Triassic system (silty mudstone, argillaceous siltstone, limestone); P-Permian System (Limestone, Tuff, Siliceous Rock); C-Carboniferous system (banded limestone, microcrystalline limestone, mudstone); D-Devonian System (Mudstone, Limestone, Siliceous Rock); 1-Anticlinal Axis; 2-Syncline axis; 3-Fracture; 4-Pb-Zn-Sb-Ag deposit; 5-Arsenic-mercury-lead-zinc-antimony-silver deposit; 6-Antimony ore site; 7-Mercury deposit (spot); 8-Ore field箭猪坡矿床范围内出露的地层为下泥盆统塘丁组第一段和第二段,其中以第二段为主,该段为灰黑色条带状及薄层状绢云母泥岩;矿床内发育了两组断裂,一组为北北西向张扭性断裂,第二组为北北东向扭性断裂。在矿区范围内未见到岩浆岩出露。
箭猪坡矿床矿体主要受北北西向构造破碎带和断裂的控制,呈脉状、细网脉状,条带状充填在断裂带中或节理裂隙中,沿矿体走向和倾向分支复合、尖灭再现和尖灭侧现的现象均有出现。矿石中金属矿物主要有硫化物(铁闪锌矿、闪锌矿、辉锑矿)、硫盐矿物(脆硫锑铅矿等),碳酸盐矿物(含锰菱铁矿、含铁菱锰矿),非金属矿物主要有石英、方解石等(刘伟,2013)。箭猪坡矿床成矿阶段划分为3个阶段,即石英-硫化物阶段(Ⅰ)、石英-硫盐矿物-多硫化物阶段(Ⅱ)和锑硫化物-石英-铁锰碳酸盐阶段(Ⅲ),第Ⅱ成矿阶段为主要成矿阶段(刘伟等,2015)。
3. 地球物理特征
本次研究工作选用的物探工作方法有瞬变电磁测量(TEM)、可控源音频大地电磁测深法(CSAMT)。物探测线布置图见图 2。
![]() 图 2 箭猪坡矿床物化探工作测线分布图1—三叠系百逢组中段(细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩); 2—三叠系百逢组下段(含粉砂质泥岩夹凝灰质泥岩); 3—中三叠统罗楼祖上段(粉砂质泥岩夹灰岩); 4—中三叠统罗楼组下段(粉砂质泥岩); 5—下二叠统茅口组(燧石条带灰岩); 6—下二叠统栖霞组(灰岩、泥灰岩、硅质岩); 7—上石炭统南丹组(硅质条带灰岩、微晶灰岩)8—中石炭统大埔组(白云岩、含生物硅质条带灰岩); 9—下石炭统巴平组(泥岩、硅质泥岩); 10—上泥盆统五指山组(灰岩); 11—上泥盆统榴江组(硅质岩、硅质灰岩、灰岩); 12—中泥盆统罗富组上段(泥质灰岩、生物碎屑灰岩); 13—中泥盆统罗富组中段(泥灰岩夹泥岩); 14—中泥盆统罗富组下段(钙质泥岩、泥灰岩); 15—下泥盆统塘丁组四段(泥岩); 16—下泥盆统塘丁组三段(泥岩、粉砂质泥岩); 17—下泥盆统塘丁组二段(泥岩夹砂质泥岩); 18—下泥盆统塘丁组一段(泥岩); 19—实测正断层; 20—实测逆断层; 21—岩层产状; 22—地质界线; 23—大型锑多金属; 24—工作区范围; 25—可控源测量测线及编号; 26—瞬变电磁测量、地电化学测量、土壤地球化学测量测线Figure 2. Distribution of geophysical and chemical detection lines in Jianzhupo Deposit1-Middle of Triassic Baifeng Formation (fine sandstone and argillaceous siltstone); 2-Lower of Triassic Baifeng Formation (silty mudstone mixed with tuffaceous mudstone); 3-Upper of Middle Triassic Luolouzu Formation (silty mudstone mixed with limestone); 4-Lower of Middle Triassic Luolou Formation (silty mudstone); 5-Lower Permian Maokou Formation (flint banded limestone); 6-Lower Permian Qixia Formation (limestone, marl, siliceous rock); 7-Upper Carboniferous Nandan Formation (siliceous banded limestone) Microcrystalline limestone); 8-Middle Carboniferous Dapu Formation (dolomite, siliceous banded limestone); 9-Lower Carboniferous Baping Formation (mudstone, siliceous mudstone); 10-Upper Devonian Wuzhishan Formation (limestone); 11-Upper Devonian Liujiang Formation (siliceous rock, siliceous limestone, limestone); 12-Middle Devonian Luofu Formation upper member (argillaceous limestone, Bioclastic limestone); 13-Middle of Middle Devonian Luofu Formation (marl with mudstone); 14-Lower Devonian Luofu Formation (calcareous mudstone and marl); 15-Lower Devonian Tangding Formation 4 (mudstone); 16-Lower Devonian Tangding Formation 3 (mudstone, Silty mudstone); 17-Member 2 of Lower Devonian Tangding Formation (mudstone mixed with sandy mudstone); 18-Member 1 of Lower Devonian Tangding Formation (mudstone); 19-Measured normal fault; 20-Measured reverse fault; 21-Strata occurrence; 22-Geological boundary; 23-Large antimony polymetallic; 24-Scope of work area; 25-Controlled source measuring line and No; 26-Transient electromagnetic measuring line, geoelectrochemical measuring line and soil geochemical measuring line
图 2 箭猪坡矿床物化探工作测线分布图1—三叠系百逢组中段(细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩); 2—三叠系百逢组下段(含粉砂质泥岩夹凝灰质泥岩); 3—中三叠统罗楼祖上段(粉砂质泥岩夹灰岩); 4—中三叠统罗楼组下段(粉砂质泥岩); 5—下二叠统茅口组(燧石条带灰岩); 6—下二叠统栖霞组(灰岩、泥灰岩、硅质岩); 7—上石炭统南丹组(硅质条带灰岩、微晶灰岩)8—中石炭统大埔组(白云岩、含生物硅质条带灰岩); 9—下石炭统巴平组(泥岩、硅质泥岩); 10—上泥盆统五指山组(灰岩); 11—上泥盆统榴江组(硅质岩、硅质灰岩、灰岩); 12—中泥盆统罗富组上段(泥质灰岩、生物碎屑灰岩); 13—中泥盆统罗富组中段(泥灰岩夹泥岩); 14—中泥盆统罗富组下段(钙质泥岩、泥灰岩); 15—下泥盆统塘丁组四段(泥岩); 16—下泥盆统塘丁组三段(泥岩、粉砂质泥岩); 17—下泥盆统塘丁组二段(泥岩夹砂质泥岩); 18—下泥盆统塘丁组一段(泥岩); 19—实测正断层; 20—实测逆断层; 21—岩层产状; 22—地质界线; 23—大型锑多金属; 24—工作区范围; 25—可控源测量测线及编号; 26—瞬变电磁测量、地电化学测量、土壤地球化学测量测线Figure 2. Distribution of geophysical and chemical detection lines in Jianzhupo Deposit1-Middle of Triassic Baifeng Formation (fine sandstone and argillaceous siltstone); 2-Lower of Triassic Baifeng Formation (silty mudstone mixed with tuffaceous mudstone); 3-Upper of Middle Triassic Luolouzu Formation (silty mudstone mixed with limestone); 4-Lower of Middle Triassic Luolou Formation (silty mudstone); 5-Lower Permian Maokou Formation (flint banded limestone); 6-Lower Permian Qixia Formation (limestone, marl, siliceous rock); 7-Upper Carboniferous Nandan Formation (siliceous banded limestone) Microcrystalline limestone); 8-Middle Carboniferous Dapu Formation (dolomite, siliceous banded limestone); 9-Lower Carboniferous Baping Formation (mudstone, siliceous mudstone); 10-Upper Devonian Wuzhishan Formation (limestone); 11-Upper Devonian Liujiang Formation (siliceous rock, siliceous limestone, limestone); 12-Middle Devonian Luofu Formation upper member (argillaceous limestone, Bioclastic limestone); 13-Middle of Middle Devonian Luofu Formation (marl with mudstone); 14-Lower Devonian Luofu Formation (calcareous mudstone and marl); 15-Lower Devonian Tangding Formation 4 (mudstone); 16-Lower Devonian Tangding Formation 3 (mudstone, Silty mudstone); 17-Member 2 of Lower Devonian Tangding Formation (mudstone mixed with sandy mudstone); 18-Member 1 of Lower Devonian Tangding Formation (mudstone); 19-Measured normal fault; 20-Measured reverse fault; 21-Strata occurrence; 22-Geological boundary; 23-Large antimony polymetallic; 24-Scope of work area; 25-Controlled source measuring line and No; 26-Transient electromagnetic measuring line, geoelectrochemical measuring line and soil geochemical measuring line可控源音频大地电磁法(CSAMT)是在大地电磁法(MT)和音频大地电磁法(AMT)基础上发展起来的一种方法。可控源频率测深方法具有勘探深度范围大(通常可达2 km)、分辨能力强、观测效率高,兼有测深和剖面研究双重特点,是研究深部地质构造和寻找隐伏矿的有效手段,越来越多应用于受构造控制的脉状金属矿床的找矿工作。通过可控源音频大地电磁测深法(CSAMT)测量,探索箭猪坡矿床深部隐伏构造的空间形态。
磁瞬变电磁法(TEM)是基于电性差异,利用不接地回线或接地线源向地下发送一次脉冲电场,利用线圈或接地电极观测二次涡流场或电场的方法。该方法具有穿透低阻覆盖的能力,故探测深度大。在低阻围岩地区地形的起伏仅对早期道有影响,这种影响又是易于分辨的。瞬变电磁法异常响应强,多测道曲线形态简单,分层能力较强。工作效率高,同时完成剖面测量与测深工作。通过瞬变电磁测量(TEM),查明构造和矿(化)体空间展布特征。
3.1 矿区岩(矿)石物性特征
在物探方法工作前,先对矿区内的主要岩矿石进行物性参数取样分析。矿区内出露的主要矿石划分为5类,围岩划分为7类。每类岩(矿)石进行系统的物性参数取样。所采集标本均来自新鲜露头及坑道,大小约10 cm×10 cm×10 cm,使用测试方式为强迫电流法,获得岩矿石标本的电阻率参数,使用GDD型标本测试仪,测定结果如表 1所示。根据表 1,矿区内与低阻因素有关的是断裂破碎带、矿化蚀变及炭质岩层,因此,圈定低阻异常区是本次电法工作的重点。
表 1 五圩铅锌锑矿岩石的物性特征Table 1. Physical properties of Wuxu Pb-Zn-Sb ore and rocks
(1)密度特征
区域出露的地层从下泥盆统塘丁组至中三叠统均有,是高密度层,以泥岩、碳酸盐岩为主,其岩性主要有泥岩、白云质泥灰岩、泥质粉砂岩、炭质泥岩、硅质泥岩、泥灰岩、白云岩、硅质岩、硅质灰岩、生物碎屑灰岩等,以上岩性密度值相对较高且较为稳定,一般为2.71 g/cm3左右。
根据实测及前人的资料,五圩矿区的各类岩石中,以松散的砂岩、砾岩等密度最低,一般为2.48 g/cm3,这些岩层的厚度不大;泥岩、碳酸盐岩建造为主的岩层,其厚度可达数千米,密度平均值为2.71 g/cm3,构成高密度背景;花岗岩类岩石密度平均值为2.61 g/cm3,与泥岩、碳酸盐岩为围岩的密度存在0.1 g/cm3左右的差异,当花岗岩体具有一定规模时,可以引起重力低异常。
(2)电性特征
矿床中岩石在宏观上电阻率ρ与电极化率η呈负相关,即η增大,ρ有减小的趋势。矿床中的炭质泥岩、钙质泥岩具有“低电阻率”特征,电阻率常见为5.2×101~5.1×102 Ω·m,最大为3.9×103 Ω·m,而矿床中方解石、白云岩、硅质泥岩、灰岩具有“高电阻率”特征,电阻率常见为4.1×103~7.3×105 Ω·m,最大为9.8×105 Ω·m。含矿岩石具有低电阻、高极化率、高密度特征。矿床围岩普遍具有中高电阻率、低极化率、中等密度特征。矿区内炭质泥岩普遍发育,其具有低电阻率、高极化率特征,且具有成层出现的特点,其矿石与围岩存在较明显的电性差异,为电磁法测量工作提供了有利条件。
(3)磁性特征
工作区内绝大部分岩石为无磁性或弱磁性,花岗岩呈弱磁性,一些矿石含有少量磁性矿物磁性相对较强,但仍呈弱磁性。
3.2 可控源(CSAMT)特征
结合矿床地质特征,笔者在五圩箭猪坡矿床开展了可控源剖面测量工作(位置见图 2),试验剖面有3条,测量方位线与勘探线方位一致为80°,点距40 m。投入本次工作的仪器为GDP-32II多功能电磁仪。工作选择的是GGT-30大功率(30 kAV)发射机,工作频率:DC~8 kHz;最大输出功率:30 kW;最大输出电流:30 A;最高输出电压:1000 V;关断时间:≤125 μs;稳流精度:0.1%;同时配合工作的是一个ZMG-10(10 kW)发电机。CSAMT资料反演软件是GDP-32II机器所带的带地形平面波反演软件SCS2D。
本次CSAMT工作各技术参数如下:工作频率:1~8192 Hz。发射系统:供电偶极子长度AB=1000 m;方位角117°,偶极子中心与测线中心偏差<15°。收发距R最小为7 km,最大为12.7 km;基本电流大于6 A,1024 Hz以下频率电流大于8 A。供电线使用耐高压、大电流的电缆线,供电极则将大张铝箔置于挖好的坑中埋好,并将盐水浇于其中。接收系统:采用一个磁道带两个电道测量方式。测量电偶极子长度MN=40 m。接收电极使用不极化电极,稳固地置于土中20~30 cm,并浇入盐水。观测数据叠加次数为32~16384次,数据离差SEM < 20时,方可认定为可靠数据,并将其记录。
由图 3(317线CSAMT测深)可以看出,物探CSAMT测深曲线圆滑,其卡尼亚电阻率均方相对误差为5.783%;大于200 mrad的阻抗相位均方相对误差为8.698%,小于200 mrad的阻抗相位均方误差为40.997 mrad,测量结果为Ⅰ级精度。根据测区岩石电性特征,矿区内与低阻因素有关的是断裂破碎带、矿化蚀变及炭质岩层,由此圈定低阻异常区是本次电法工作的重点。根据电阻率剖面结果,反演的低阻异常,对应的阻抗相位高值异常,因此低阻异常可信度高。
以317号勘探线剖面图为例(图 4)。选取该线的3160~4520点号,作为反演剖面,长度1.36 km,317线低阻异常及推断解释见图 4,其特征如下:3840~4080号点范围存在⑤号低阻异常,电阻率低于100 Ω·m,呈带状分布,异常上窄下宽,向东倾斜,延深约1200 m,⑤号低阻异常位于下泥盆统塘丁组第二岩性段(D1t2),主要为灰—深灰色中薄层泥岩夹深灰色中薄层条带状泥岩,局部夹有薄层砂岩透镜体和砂质泥岩,岩石中普遍见有浸染状黄铁矿,该岩性段为矿区主要含矿层位。已知含矿破碎带F3及F7位于⑤号低阻异常边部或异常内,且有钻孔ZK317-1揭露,其破碎带产状与⑤号低阻异常形态一致,推测⑤号低阻异常是由含矿破碎带F3和F7引起。目前钻孔只揭露了含矿破碎带F3及F7浅部垂深200 m范围的情况,从电阻率剖面图看出,⑤号低阻异常往深部延深至标高-700 m,说明含矿破碎带F3及F7往深部仍有延伸,该异常深部仍具有较大的找矿空间。
![]() 图 4 箭猪坡矿床317号勘探线电阻率剖面与推断解释剖面图1—泥盆系下统塘丁组第三段;2—泥盆系下统塘丁组第二段;3—断裂;4—钻孔;5—电阻率异常带Figure 4. Resistivity profile and inferred interpretation profile of 317 geological profile in Jianzhupo Deposit1-Third Member of Tangding Formation of Lower Devonian system; 2-Second Member of Tangding Formation of Lower Devonian system; 3-Fault; 4-Drill holel; 5-Resisttivity anomaly band
图 4 箭猪坡矿床317号勘探线电阻率剖面与推断解释剖面图1—泥盆系下统塘丁组第三段;2—泥盆系下统塘丁组第二段;3—断裂;4—钻孔;5—电阻率异常带Figure 4. Resistivity profile and inferred interpretation profile of 317 geological profile in Jianzhupo Deposit1-Third Member of Tangding Formation of Lower Devonian system; 2-Second Member of Tangding Formation of Lower Devonian system; 3-Fault; 4-Drill holel; 5-Resisttivity anomaly band从以上结果看出,CSAMT法探测深度大,对断裂构造反应较灵敏,在五圩矿田可以取得较好的找矿效果。
3.3 瞬变电磁特征
本次TEM法采用重叠回线装置(接收线圈Rx和发送线圈Tx相重合敷设的装置),发射和接收线圈均为100 m×100 m,网度为100 m×50 m;通过试验应采用1 Hz和4 Hz作为发射基频,观测参数为归一化的感应电动势,单位为μV/A。本次使用仪器为重庆奔腾数控技术研究所研制的WTEM-1瞬变电磁仪。以箭猪坡矿床320号勘探线剖面为例(测线分布见图 2),运用一维电阻率反演(图 5),结合地质特征分析得出:通过320线多测道剖面图可见,在23~34点之间存在凸起异常,与相对低阻异常吻合较好,从形态上看,呈脉状,表明在中深部存在导电性较好的脉状地质体,反映了中深部硫化物矿(化)体的存在。从电阻率反演图中可以得出,标高200~300 m,异常带晕为一个呈现倾向东的低阻带,电阻率值一般小于100 Ω·m,多为0~50 Ω·m,倾角为50~60°,与高阻区域区别明显,且该异常带由近地表往深部有变宽的趋势。该地段构造发育,结合矿区岩矿石物性特征及矿区的地质特征推测为含金属硫化物的岩(矿)石引起的异常。通过在地表实施探槽及钻孔(ZK320-2、ZK320-3、ZK320-4、ZK320-5)验证,均揭露到含黄铁矿化的硅化破碎带或矿(化)体,已知硅化破碎带或矿(化)体,均分布在电阻率低阻区。
4. 地球化学特征
4.1 土壤地球化学特征
在箭猪坡矿区开展了土壤剖面地球化学测量工作,以箭猪坡矿床320号勘探线剖面为例,结果显示矿区土壤地球化学化学主成矿元素Pb、Zn、Sb异常与隐伏矿体(含矿破碎带)的分布范围相一致,各异常同步性较好,并且有很好的重叠性。Pb最高值为97.4×10-6,异常带Pb均值大于65×10-6;Zn最高值为255.9×10-6,异常带均值大于220×10-6;Sb最高值为154.8×10-6,异常带均值大于90×10-6;推测异常由破碎带(含矿)引起,并经钻探工作验证,在钻孔中见到真厚0.71m,Zn品位5.05%的锌矿体(钻孔ZK320-2、J144)。
4.2 地电化学特征
地电化学提取方法是将地球物理、地球化学及电化学综合交叉为一体的综合找矿方法,该方法利用电场作用,选择性提取近地表介质中的电活动态物质,通过研究电提取元素组合、含量分布及异常特征,进而提供找矿信息的一种勘查方法。而大量的找矿勘探实践证明,地电化学勘探新技术、新方法能够发现500 m以下,其中包括150~200 m浮土以下的有色金属矿床、贵金属矿床、稀有金属矿床。在箭猪坡矿床南端开展了6条地电化学剖面测量工作(测线分布见图 2),方位线与勘探线方位一致为80°,点距一般20 m,以320号勘探线剖面地电化学特征为例(图 5):地电化学异常与隐伏矿体或含矿破碎带的分布吻合度高,即矿体的分布范围与地电化学综合异常范围一致,异常分布的规模、强度与含矿破碎带规模呈正比关系。矿体产出均较陡,倾角75°~80°,异常为多个异常点组成的“驼峰”或者“倒钟”形态,在地表矿头对应部位附近有异常峰。Pb、Zn、Sb元素异常规模大、强度高,异常同步清晰,因此Pb、Zn、Sb可以作为本区地电化学方法寻找隐伏锌矿的指示元素。当出现Pb、Zn、Sb为主异常时,则显示深部具有隐伏矿体(矿化)存在的可能性。经钻探验证,ZK320-2、ZK320-4、ZK320-5钻孔均揭露到了含锌锑的矿体及富含黄铁矿的硅化破碎带,亦说明地电化学能很好的圈定金属硫化物异常。
![]() 图 5 箭猪坡矿床320号勘探线地质-物探(TEM)-化探(地电化学)综合剖面图1—构造破碎带;2—铅锌锑矿体;3—下泥盆统塘丁组第二段;4—钻孔Figure 5. Electrogeochemical comprehensive profile of 320 exploration line in Jianzhupo Deposit1-Tectonic fracture zone; 2-Lead-zinc-antimony ore body; 3-Second member of Tangding Formation of Lower Devonian system; 4-Drill hole
图 5 箭猪坡矿床320号勘探线地质-物探(TEM)-化探(地电化学)综合剖面图1—构造破碎带;2—铅锌锑矿体;3—下泥盆统塘丁组第二段;4—钻孔Figure 5. Electrogeochemical comprehensive profile of 320 exploration line in Jianzhupo Deposit1-Tectonic fracture zone; 2-Lead-zinc-antimony ore body; 3-Second member of Tangding Formation of Lower Devonian system; 4-Drill hole5. 综合找矿模型特征
根据箭猪坡矿床地质特征、地球物理特征、地球化学特征,总结了该矿床地质、地球物理,地球化学的找矿标志(表 2),并建立了矿床的地质-化探-物探找矿模型(图 6),实质是反映化探特征、物理特征与地质构造、矿体的空间关系。
表 2 箭猪坡矿床地质-地球物理-地球化学找矿标志Table 2. Geological-geophysical -geochemical prospecting criteria of JianZhuPo Deposit
从矿床成矿条件分析,箭猪坡矿床矿体赋存在断裂构造中,矿体形态呈脉状、透镜体状,空间分布具有斜列状,叠瓦状排列等。区内矿体具有明显的低阻异常,表现为低电阻率特征,且瞬变电磁反演断面图与硅化破碎带及地质内容吻合较好。
模型的地质特征:矿体受层位控制,控矿层位为下泥盆统塘丁组沉积建造,因构造变形,控矿层位位于褶皱翼部,产状一般较陡;近矿围岩蚀变发育范围有限,蚀变类型有硅化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化、绿泥石化等。矿体形态以陡产状脉状、细脉状、透镜状为主,倾角60°~80°,厚度0.1~4.5 m不等,最大10.72 m,矿石类型分致密块状和条带状;矿石以金属硫化物为主,并含硫盐矿物;矿床类型属低温热液充填型。
模型的地球物理特征:以工业矿体为中心的矿化系统,具有低电阻率,稍高密度,高极化率特征。
模型的地球化学特征:常规土壤异常较小或无异常,而地电化学异常能较清晰地反映盲矿体成矿元素的异常,且各元素间连续性较好,异常的分布范围与深部盲矿体的垂直投影基本一致,通过钻孔揭露,能较准确的反映深部埋藏盲矿体(矿化体)的分布范围。
6. 讨论
(1)通过近几年的找矿勘查,在箭猪坡矿床,矿带走向延伸控制总长度为1400 m,并根据物探可控源测量结果,经钻探工程控制,在标高为-300~-400 m)仍能见到矿体, 从而扩大了该区的找矿空间,在该矿带南、北两个延伸方向及东部矿体倾向延深方向都是寻找隐伏矿体的有利部位,勘查平面图、剖面图等资料表明矿体的倾向延深和南北走向延伸还未完全控制,尚有较大找矿空间。而且随着深部石英脉型锡矿体的发现,为该矿区增加了新的找矿方向。
(2)矿区中局部构造陡倾或直立,且构造中有炭质、硅质等围岩,具有极低或极高的电阻率,故引起了CSAMT测量反演结果出现电阻率非常大和非常小的值。
(3)受整个区围岩炭质泥岩背景影响,该区矿化不均匀,极化率值波动较大,矿区未采样激发极化法, 其还难以识别矿异常和非矿异常。
因此,对于箭猪坡矿床成因需要加强研究,勘查模型需要逐步完善,找矿方法手段的选择也需要不断探索。
7. 结论
物化探工作是目前找矿工作中的重要手段。在充分分析、深入研究物化探成果特征,选出与成矿有关的异常范围,尤其是物化探重叠异常范围,再以地质条件为基础,化探信息为先导,选取地质、化探、物探等成矿有关的综合信息标志重叠的地区或地段,是寻找成矿有利地段的保障。
(1)物探研究表明:CSAMT出现的所有低阻异常,均具有找矿意义。这类低阻异常范围、形态大致反映矿(化)脉组在空间的展布特征,为深部勘查工程布置提供了重要依据;CSAMT异常显示该区往南北两端仍具有较大的找矿空间,中深部层状低阻异常出现在较低标高,均具有较大规模,且没有完全控制,这类异常推测与炭质层或新类型矿化有关。瞬变电磁表明:矿(化)体多分布在归一化电位高值区或低电阻率区,已知构造主要分布在归一化电位较高值区域或较低电阻率区和电位值梯度带,已知矿化体与物探异常特征吻合较好。
(2)常规的化探次生晕及地电化学研究表明:地电化学异常在已知矿体上方有比较清晰的Pb、Zn、Sb元素异常,为典型的共生组合元素,它们之间也存在良好的正相关关系,说明这些元素组合可以作为找矿指示元素,在该地区利用地电化学在该地区寻找隐伏矿,方法是可行的。化探次生晕Sb、Pb、Zn等元素套和较好,异常特征相近,可以作为寻找本区矿区的主要指示元素,进而推断矿体存在的大致位置和特征。
综上所述,可控源音频大地电磁法、瞬变电磁法、土壤地球化学、地电化学在异常区和非异常区有效性明显,利用这四种集成方法对深部勘查预测具有良好的找矿效果,达到技术集成示范,值得在类似的矿床中应用。
-
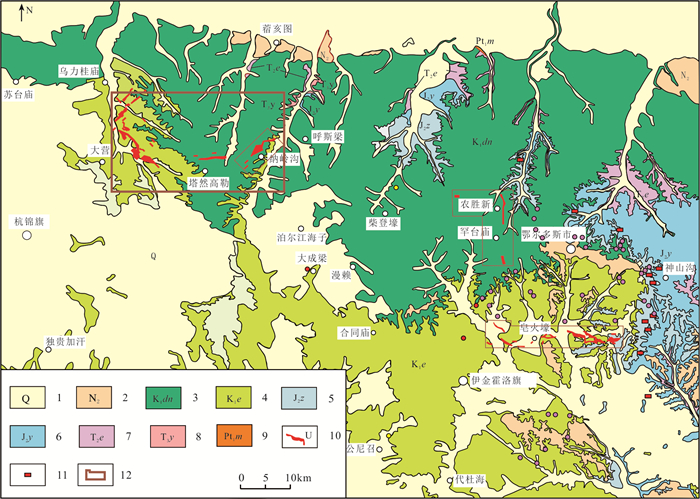
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿区域地质简图
1—第四系;2—新近系;3—下白垩统东胜组;4—下白垩统伊金霍洛组;5—中侏罗统直罗组;6—中侏罗延安组;7—中三叠统二马营组;8—中三叠统二马营组;9—古元古代美岱召岩群;10—铀矿体地表投影范围;11—地表放射性异常点;12—研究区范围
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Dongsheng uranium orefield
1-Quaternary; 2-Neogene; 3-Lower Cretaceous Dongsheng Formation; 4-Lower Cretaceous Yijinhuoluo Formation; 5-Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation; 6-Middle Jurassic Yan'an Formation; 7-Middle Triassic Ermaying Formation; 8-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 9-Paleoproterozoic Meidaizhao Group; 10-Uranium ore bodies; 11-Surface radioactive anomaly; 12-Study area
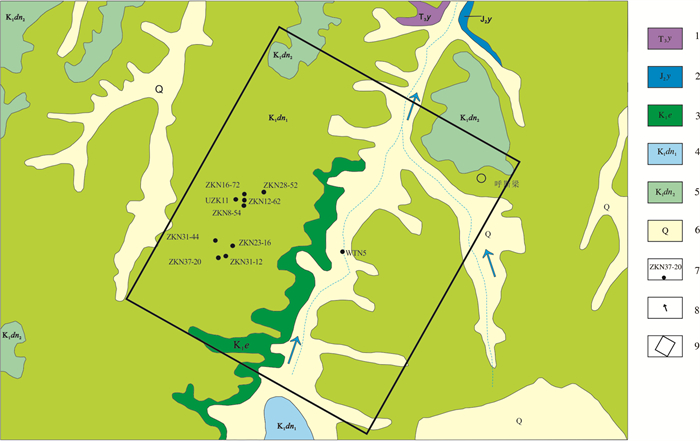
图 3 纳岭沟铀矿地质简图
1—上三叠统延长组;2—中侏罗统延安组;3—下白垩统伊金霍洛组;4—下白垩统东胜组一段;5—下白垩统东胜组二段;6—第四系;7—钻孔;8—水流方向;9—矿区范围
Figure 3. Simplified geological map of the Nalinggou uranium deposit
1-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation; 2-Middle Jurassic Yanan Formation; 3-Lower Cretaceous Yijinhuoluo Formation; 4-The first member of Dongsheng Formation of Lower Cretaceous; 5-The second member of Dongsheng Formation of Lower Cretaceous; 6-Quaternary system; 7-Drill; 8-Current Direction; 9-Mining area
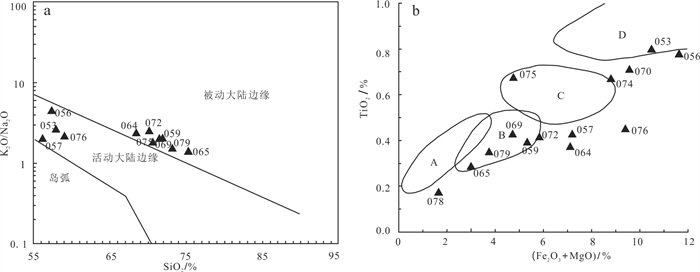
图 4 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZK23-16)SiO2-K2O/Na2O(a)、Fe2O3+MgO-TiO2(b)构造环境判别图
A—克拉通盆地;B—大陆壳内裂谷或弧后盆地;C—大陆边缘弧;D—大洋弧
Figure 4. Discriminant diagrams of tectonic environment on SiO2-K2O/Na2O(a)、Fe2O3+MgO-TiO2(b)for uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16
A-Craton basin; B-Intracontinental rift or back-arc basin; C-Continental margin arc; D-Oceanic arc
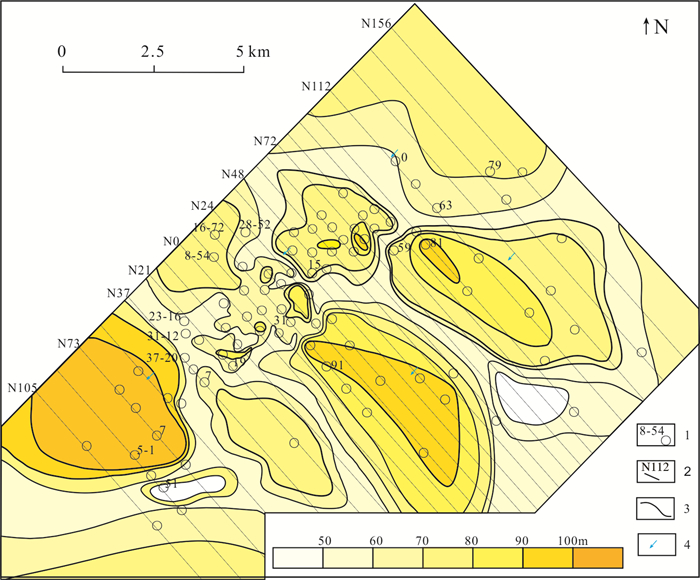
图 6 纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段下亚段砂体厚度等值图(据核工业208大队❶,略改)
1—钻孔及编号;2—勘探线及编号;3—砂体厚度等值线;4—古流向
Figure 6. The sand body thickness contour map of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit(modified from CNNC No.208 Geological Party❶)
1-Drill and number; 2-Survey line and number; 3-Sand body thickness isoline; 4-Ancient flow direction
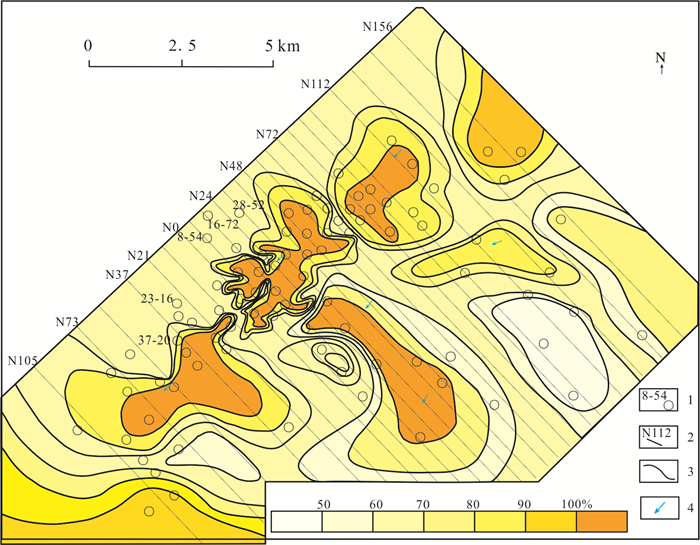
图 7 纳岭沟铀矿床直罗组下段下亚段含砂率等值线图(据核工业208大队❶,略改)
1—钻孔及编号;2-勘探线及编号;3—含砂率等值线;4—古流向
Figure 7. The sand percentage isogram of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit (Modified from CNNC No.208 Geological Party❶)
1-Drill and number; 2-Survey line and number; 3-Sand isoline; 4-Ancient flow direction
图 8 纳岭沟地区直罗组下段下亚段沉积相图
1—蚀源区;2—泛滥平原;3—河间洼地;4—湖泊;5—砾质辫状河道;6—砂质辫状河道;7—辫状河道;8—三角洲平原;9—心滩;10—边滩;11—沙坝;12—分流间湾;13—地理位置;14—河流及流向;15—铀矿体地表投影
Figure 8. The sedimentary facies map of the lower member of the Lower Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou area
1-Erosion source; 2-Flood plain; 3-Gamma herculis depression; 4-Lake; 5-Gravel braided channel; 6-Sandy braided channel; 7-Braided channel; 8-Delta plain; 9-Heart beach; 10-Side beach; 11-Sand bar; 12-Distributary bay; 13-Geographic location; 14-River and flow direction; 15-Projection of Uranium ore body
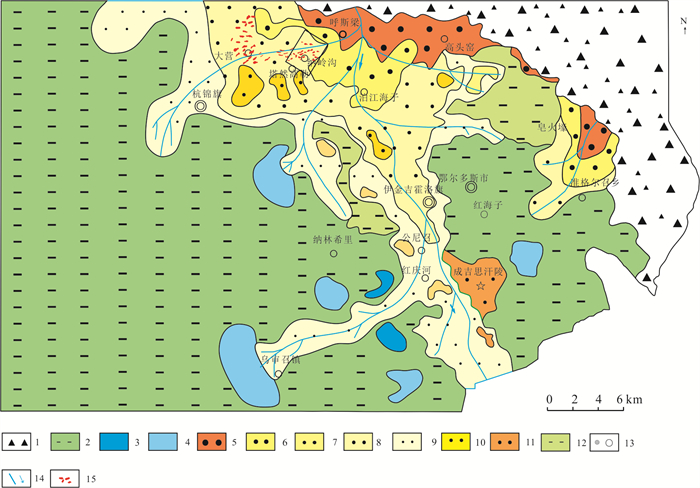
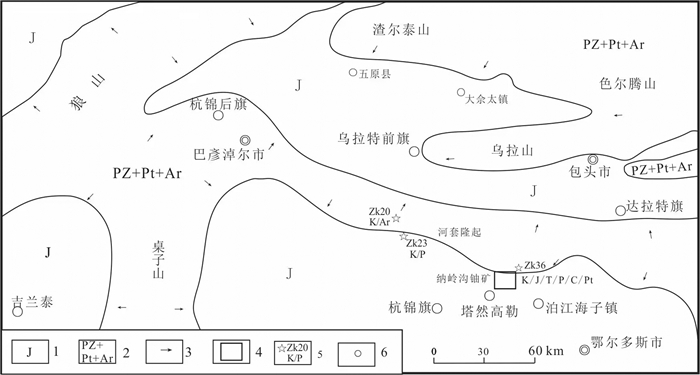
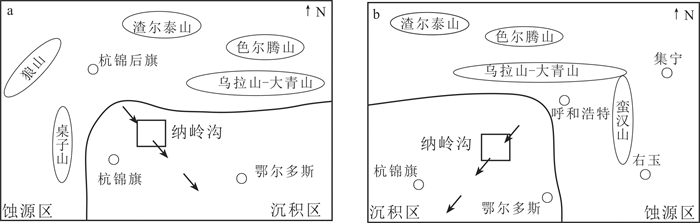
图 9 鄂尔多斯盆地北部早中侏罗世蚀源区分布示意图
1—早中侏罗世沉积区;2—前侏罗纪剥蚀区;3—物源方向;4—纳岭沟矿区;5—钻孔、编号及揭露地层;6—城镇
Figure 9. The distribution diagram of the Early-Middle Jurrassic provenance in the north Ordos Basin
1-Early-middle Jurassic sediment; 2-Pre-Jurassic strata; 3-Source direction; 4-Nalinggou mining area; 5-Drill, number and strata; 6-Cities and towns
表 1 钻孔ZK23-16直罗组下亚段含铀岩系粒度分析
Table 1 Grain size analysis of uraniferous rocks in lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16

表 2 钻孔ZK23-16直罗组下亚段含铀岩系成分成熟度指数
Table 2 Compositional maturity index of uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16

表 3 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系重矿物含量(%)统计
Table 3 Statistics of heavy mineral content (%) of uraniferous rocks in the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation from drill ZK23-16 in the Nalinggou uranium deposit

表 4 直罗组下亚段含铀岩系稳定重矿物磨圆度和延长系数
Table 4 Roundness and elongation coefficient of stable heavy minerals of uraniferous series from the lower segment of Zhiluo Formation

表 5 纳岭沟铀矿直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZKN23-16)主量元素分析结果(%)
Table 5 Major element data (%) of uraniferous rocks (drill ZKN23-16) from the lower member of theZhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposit

表 6 纳岭沟铀矿直罗组下亚段含铀岩系(钻孔ZKN23-16)稀土元素分析结果(10-6)
Table 6 REE(10-6) element data of uraniferous rocks (drill ZKN23-16) from the lower member of the Zhiluo Formation in the Nalinggou uranium deposi

-
Bao Hongping, Shao Dongbo, Hao Songli, Zhang Guisong, Ruan Zhengzhong, LiuGang, Ouyang Zhengjian. 2019. Basement structure and evolution of early sedimentary cover of the Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(1): 33-43(in Chinese with English abstract).
Beverly Z S, Angeline M C, Daniel I H, Federico A, Darin A C. 2022. Lithostratigraphy, chronostratigraphy, and sedimentary environments of the Middle Miocene Quebrada Honda Basin in southern Bolivia and implications for Andean climate and uplift[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 601: 1-14.
Bhatia M R. 1985. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australia Paleozoic Greywacks andmudrock: Provenance and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 45: 97-113. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(85)90025-9
Bradley D R, Brian J D, Tim C. 2001. Early Jurassic extensional basin formation in the Daqing Shan segment of the Yinshan belt, northern North China Block, Inner Mongolia[J]. Tectonophysics, 339(3): 239-258.
Chen Haidong, Wang Zilong, Lu Ning, Yin Hai, He Guoqiang. 2016. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age and their tectonic significance of the garnet granites form Helin-Liangcheng zone of Central Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 43(1): 81-90(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yin, Feng Xiaoxi, Chen Lulu, Jin Ruoshi, Miao Peisen, Sima Xianzhang, Miao aisheng, Tang Chao, Wang Gui, Liu Zhongren. 2017. An analysis of U-Pb dating of detrital zircons and modes of occurrence of uranium minerals in the Zhiluo Formation of northeastern Ordos Basin and their indication to uranium sources[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1190-1206(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Zuyi, Chen Haisheng, Gu Kangheng. 2010. Research and Evaluation of China Uranium Deposit, the Third Volume of Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposits[M]. Beijing: China Nuclear Industry Geology Bureau, 1-360 (in Chinese).
Cheng Xianyu, Zhang Tianfu, Chen Yinhang, Wang Shaoyi, Tian Jian. 2021. Paleosedimentary environment evolution of Zhiluo Formation in Tarangaole area, northern margin of the Ordos Basin-evidence from geochemical characteristics[J]. North China Geology, 44(2): 1-3(in Chinese with English abstract).
David C, Gary O'Sullivan, Caracciolo L, Chris M, Shane T. 2020. Sourcing the sand: Accessory mineral fertility, analytical and other biases in detrital U-Pb provenance analysis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 202: 1-27.
Feng Xiaoxi, Jin Ruoshi, Sima Xianzhang, Li Jianguo, Zhao Hualei, Chen Yin, Chen Lulu, Tang Chao, Ao Cong, Wang Xinhua. 2017. Uranium source analysis and its geological significance to Uranium metallogenic evolution in Dongsheng Uranium Ore Field[J]. Geology in China, 44(5): 993-1005(in Chinese with English abstract).
Feng Xiaoxi, Teng Xueming, He Youyu. 2019. Preliminary discussions on the metallogenesis of Dongsheng uranium orefields in the Ordos basin[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 42(2): 96-108(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.02.003
Fu Xinghui, Zhao Hongge, Zhou Yijun, Peng Zhichao, Jiang Sheng, Zhangsun Xuanqi, Wang Hairan, Li Yanan. 2016. Jurassic detrital zircon U-Pb dating of Langshan area, Inner Mongolia, and its provenance significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(12): 2063-2075(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ge Yuhui, Xi Aihua, Wang Zhigang, Wang Yufen, Sun Chunlin. 2010. A palaeoclimatic analysis of the Middle Jurassic period in Daqinshan area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 37(1): 204-211(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Huiping, Wu Chunying, Bai Qinghua, Chen Peng, Liu Xinshe, Qin Baiping. 2014. Zircon U-Pb dating of clastic sandstone in the Upper Paleozoic from Wushenqi area, Ordos basin and its geological significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 32(4): 643-653(in Chinese with English abstract).
Himadri B, Dandele P S, Srivastava S K. 2021. Sedimentary facies of the Mesoproterozoic Srisailam Formation, Cuddapah basin, India: Implications for depositional environment and basin evolution[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 133: 105242. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105242
Hou Mingcai, Jiang Wenjian, Ni Shijun, Huang Hu, Luo Wen, Shi Xin, Miu Zongli. 2016. Geochemical characteristic of the Lower and Middle Jurassic clastic rocks in the southern margin of the Yili Basin, Xinjiang and its constraints on provenance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(12): 3337-3351(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jaireth S, McKay A, Lambert I. 2008. Association of large sandstone uranium deposits with hydrocarbons[J]. Geoscience Australia Issue, 89: 1-6.
Jiang Xiaojun, Xu Zhongyuan, Liu Zhenghong, Xue Wei, Yan Pengbing, XingYajie. 2016. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the granites in Honggeertu area, central Inner Mongolia: Constraints from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(5): 750-765(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiao Yangquan, Chen Anping, Wang Minfang, Wu Liqun, Yuan Haitao, Yang Qin, Zhang Chengze, Xu Zhicheng. 2005. Genetic analysis of the bottom sandstone of Zhiluo Formation, northeastern Ordos Basin: Predictive base of spatial orientation of sandstone-type uranium deposit[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 23(3): 371-379(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiao Yangquan, Wu Liqun, Pang Yunbiao, Rong Hui, Ji Dongmin, Miao Aisheng, Li Hongliang. 2015. Sedimentary tectonic setting of the deposition type uranium deposits forming in the Paleo-Asian tectonic domain, North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1): 189-205(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jin Ruoshi, Feng Xiaoxi, Teng Xueming, Nie Fengjun, Cao Haiyang, Hou Huiqun, Liu Hongxu, Miao Peisen, Zhao Hualei, Chen Lulu, Zhu Qiang, Zhou Xiaoxi. 2020. Genesis of green san dstone/mudstone from middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation in the Dongsheng uranium orefield, Ordos basin and its enlightenment for uranium mineralization[J]. China Geology, 3(1): 52-64. doi: 10.31035/cg2020002
Lei Kaiyu, Liu Chiyang, Zhang Long, Wu Bollin, Wang Jianqiang, Cun Xiaoni, Sun Li. 2017. Detrital zircon u-pb dating of Middle -Late Mesozoic strata in the northern Ordos basin: Implication for tracing sediment sources[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 91(7): 1522-1541(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Hongyan, Xu Yigang, Huang Xiaolong, He Bin, Luo Zhenyu, Yan Bin. 2009. Activation of northern margin of the North China Craton in Late Paleozoic: Evidence from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from the Upper Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation in the Ningwu-Jingle basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(5): 632-640(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-5-632
Li Xiangbo, Liu Huaqing, Wan Yanrong, Feng Ming, Wei Lihua. 2012. Tectonic properties and post-reformation in Late Triassic, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 34(4): 376-394(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Yanxing, Zhang Ji nghua, Guo Liangqian, Zhang Zhongfu, Zhang Junqing. 2005. Counter clock wise rotation and geodyanmics of Ordos block[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 25(3): 50-56(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Zhenhong, Dong Shuwen, Feng Shengbin, Qu Hongjie. 2015. Sedimentary response to Middle-Late Jurassic tectonic eventsin the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 36(1): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Ziying, Chen Anping, Fang Xiheng, Ou Guangxi, Zhang Ke, Jiao Yangquan, Xia Yuliang, Chen Fanzhen, Zhou Wenbin, Liu Zhonghou, Wu Regui, XiaoXinjian, Sun Ye. 2006. Metallogenic mechanism and superposition metallogenic model of the sandstone type uranium deposits in northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(Z2): 245-248(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Ziruo, Hou Mingcai, Cao Haiyang, Chao Hui. 2020. Elemental geochemistry characteristics of Jurassic and indication of sedimentary environment of Shiguai Basin, Daqingshan, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Chendu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 47(3): 307-317(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Lu, Peng Yunbiao, Dai Mingjian. 2018. Forming conditions of interlayer oxidation zone and uranium mineralization in northeastern Ordos basin[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 35(1): 16-23(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Xiaoxue, Tang Chao, Sima Xianzhang, Zhu Qiang, Li Guangyao. 2016. Major elements geochemical characteristics of sandstone-type uranium deposit in north-east Ordos basin and its geological implactions[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 39(3): 169-183(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu Lu, Chen Shuguang, Li Zhuangfu, Qing Yong, Qu Zhenghui, Shen Yulin. 2022. Sedimentalry evolution and petroleum potential of Cretacous to Paleogene in Linhe depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 22(2): 308-331(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Xinhua, Xing Lisheng, Yang Zhenyu, Xu Shujin, Zhang Jingxin. 1993. Paleomagnetic study since Late Paleozoic in the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 36(1): 68-79(in Chinese with English abstract).
Pawan K R, Angana C, Narage P, Santamu B. 2022. Tracking sources and paleotectonic settings of Mesozoic sandstones in interlinked rift basins of western India: An integrated approach using petrography and heavy mineral chemistry[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 11(2): 173-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jop.2022.02.001
Peng Shenglong, Tian Jiapeng, Guo Xiaoyu, Jin Yunpeng, Sun Bo, Dou Hongxin, Zhang Fan, Hao Jing, Hu Yinglian, Chen Lin, Xu Wei, Tong Ye. 2023. Characteristics and metallogenesis of ore-bearing sandstone in the Tarangaole sandstone type uranium deposit, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 264-276(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qu Hongjun, Han Xing, Chen Shuo, Yang Bo, Du Meiying, Dong Yangyang, Zhao Chong. 2020. U-Pb dating of detrital zircon from the Upper Paleozoic clastic rocks and basin-mountain coupling of the northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 44(3): 501-527(in Chinese with English abstract).
Roser B P, Korsch R J. 1986. Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio[J]. The Journal of Geology, 94(5): 635-650. doi: 10.1086/629071
Si Qinghong, Yu Reng'an, Cai Hongguang, Wang Shangbo, Wang Daohua, Zhang Chao, Zhu Qiang. 2021. Element geochemical characteristics and geological significance of sandstones of Zhiluo formation in uranium-bearing strata in Naimadai area, Ordos basin[J]. North China Geology, 44(2): 49-57(in Chinese with English abstract).
Vanesa B, Gonzalo R, Inés A, Rodrigo J S, Miguel E R, Maximiliano N, Christian S, Matías C G. 2019. Tectonic evolution of the northern Austral-Magallanes basin in the Southern Patagonian Andes from provenance analysis[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 95: 1-17.
Wang Jinping, Min Maozhong, Chen Yuehui, Peng Xinjian. 2005. Study on the relationship between SiO2/Al2O3 ratios and ore-bearing capacity in interstratified oxidized zone: Exemplified by Kujieertai and Wukuerqi uranium deposits[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(1): 77-84(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.01.006
Wang K S, Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Aleksandr A B, Hu L M. 2022. Sediment sources and transport pathways on shelves of the Chukchi and East Siberian Seas: Evidence from the heavy minerals and garnet geochemistry[J]. Polar Science, 100873: 1-12.
Wang Sili, Nie Fengjun, Yan Zhaobin, He Naishuo, Zhang Yuanyuan, Zhang Pengfei. 2018. Lithologic characteristics and modes of occurrence of uranium of the target strata in the Nalinggou uranium deposit of Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(3): 573-590(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Zhengjiang, Zhang Jinquan, Chen Hongde. 2001. Study of the dispositional provenance of the terrigenous detritus in Ordos basin in Late Paleozoic Era[J]. Journal of Chengdu university of technology, 28(1): 7-12(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xie Huili, WuLiqun, JiaoYangquan, RongHui, WangHongqiang. 2016. The quantitative evaluation index system for uranium reservoir heterogeneity in Hantaimiao region, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science, 41(2): 279-292(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Dexiang, Qu Zhenghui, Chen Shuguang, Li Zhuangfu, Wu Jianping, Wang Jianguang, Wu Han. 2020. Determination of Mesozoic tectostratigraphic units and its significance in Jilantai Sag, Hetao Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 26(6): 691-703(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yi Chao, Gao Hewei, Li Xide, Zhang Kang, Chen Xinlu, Li Jingxian. 2015. Study on indicative significance of major elements for sandstone-type uranium deposit in Zhiluo Formation in northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(4): 801-813(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yi Chao, Han Xiaozhong, Li Xide, Zhang Kang, Chen Xinlu. 2014. Study on sandstone petrologic feature of the Zhiluo Formation and its controls on uranium mineralization in Northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 20(2): 185-197(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Reng'an, Zhu Qiang, Wen Sibo, Tu Jiarun, Peng Shenglong, Si Qinghong, Tang Yongxiang. 2020. Tectonic setting and provenance analysis of Zhiluo Formation sandstone of Tarangaole Area in the Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science, 45(3): 829-843(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeh A, Cabral A R. 2021. Combining detrital zircon shape and U-Pb-Hf isotope analyses for provenance studies-An example from the Aquiri region, Amazon Craton, Brazil[J]. Precambrian Research, 364: 1-17.
Zhang Bin, Liu Hongxu, Ding Bo, Yi Chao, Zhang Yan. 2020. Petrological and mineralogical characteristics of Nalinggou uranium deposit in Ordos Basin and its indicative significance for uranium mineralization[J]. Geological Review, 66(2): 410-423(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Bin, Liu Hongxu, Yi Chao, Ding Bo, Zhang Yan. 2020. Petrogeochemical characteristics and provenance indication of the sandstone from lower submember lower Member of Zhiluo Formation in Nalinggou Area Northen Ordos Basin[J]. Uranium Geology, 36(2): 84-95(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Daofeng, Yang Wenjing, Qi Yaling, Yan Xiaoxiong. 2009. Analysis of the material source of Upper Paleozoic Shanxi Formation in Shenmu region of Ordos basin[J]. Natueal Gas Geoscience, 20(9): 902-906(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Hong, Jin Xianglan, Li Guihong, Yang Zhiyuan, Zhang Hui, Jia Jiancheng. 2008. Original features and palaeogeographic evolution during the Jurassic-Cretaceous in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 10(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Long, Wu Bailin, Liu Chiyang, Lei Kaiyu, Hou Huiqun, Sun Li, Cun Xiaoni, Wang Jianqiang. 2016. Provenance analysis of the Zhiluo Formation in the sandstone hosted uranium deposits of the Northern Ordos basin and implications for uranium mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(12): 3441-3453(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.12.012
Zhang Tianfu, Zhang Yun, Cheng Xianyu, SunLixin, Cheng Yinhang, Zhou Xiaoxi, Wang Shaoyi, Ma Hailin, Lu Chao. 2020. Borehole databases and 3D geological model of Jurassic-Cretaceous strata in Dongsheng Area, North Odors Basin[J]. Geology in China, 47(S1): 220-230(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yuanyuan, Zhang Pengfei, Nie Fengjun, Yan Pengbing, Zhang Zhibo, Yan Zhaobin, Zhang Xin. 2021. Distribution characteristics of heavy minerals in the sandstone of Zhiluo Formation of northern Ordos Basin and its implication[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 49(4): 142-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.04.017
Zhang Yun, Zhang Tianfu, Cheng Xianyu, Sun Lixin, Cheng Yinhang, WangShaoyi, Wang Shanbo, Ma Hailin, Lu Chao. 2022. A brief analysis on the three-dimensional geological structure and uranium mineralization of Jurassic uranium-bearing rock series in the northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 66-80(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yuqing, Zhang Ting, Chen Haidong, Zhang Yongqing. 2016. LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of garnet monzonitic granite in the Manhan Mountain of Liangcheng, Inner Mongolia, and its petrogenesis[J]. Geology in China, 43(3): 768-779(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Junfeng, Liu Chiyang, Liang Jiwei, Wang Xiaomei, Yu Lin, Huang Lei, Liu Yongtao. 2010. Restoration of the original sedimentary boundary of the Middle Jurassic Zhiluo Formation-Anding Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(4): 553-569(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Junfeng, Liu Chiyang, Zhao jianshe, Wang Xiaomei. 2008. Sedimentary facies and its evolution of Jurassic Zhiluo Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science edition), 38(3): 480-486(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhong Yan, Chen Yali, Zhai Mingguo, Ma Xudong. 2016. Stratigraphic correlation and lithofacies paleogeography of khondalite series in the western North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(3): 713-726(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/299826257_Stratigraphic_correlation_and_lithofacies_paleogeography_of_khondalite_series_in_the_western_North_China_Craton
Zhou Ke. 2014. Application of the characteristics of major elements and trace elements in provenance analysis[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 43(4): 515-520(in Chinese with English abstract).
包洪平, 邵东波, 郝松立, 章贵松, 阮正中, 刘刚, 欧阳征健. 2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地基底结构及早期沉积盖层演化[J]. 地学前缘, 26(1): 33-43. 陈海东, 王子龙, 鲁宁, 银海, 何国强. 2016. 内蒙古中部和林—凉城一带石榴花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 中国地质, 43(1): 81-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.005 陈印, 冯晓曦, 陈路路, 金若时, 苗培森, 司马献章, 苗爱生, 汤超, 王贵, 刘忠仁. 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部直罗组内碎屑锆石和铀矿物赋存形式简析及其对铀源的指示[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1190-1206. doi: 10.12029/gc20170611 陈祖伊, 陈戴生, 古抗衡. 2010. 中国铀矿床研究评价第三卷砂岩型铀矿[M]. 北京: 中国核工业地质局, 1-360. 程先钰, 张天福, 程银行, 王少轶, 田健. 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘塔然高勒地区直罗组古沉积环境演化——来自地球化学特征的证据[J]. 华北地质, 44(2): 1-3. 冯晓曦, 金若时, 司马献章, 李建国, 赵华雷, 陈印, 陈路路, 汤超, 奥琮, 王心华. 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿田铀源示踪及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 44(5): 993-1005. doi: 10.12029/gc20170511 冯晓曦, 滕雪明, 何友宇. 2019. 初步探讨鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿田成矿作用研究若干问题[J]. 地质调查与研究, 42(2): 96-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.02.003 付星辉, 赵红格, 周义军, 彭治超, 蒋盛, 张孙玄琦, 王海然, 李亚男. 2016. 内蒙古狼山地区侏罗系LA-ICP-MS碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源意义[J]. 地质通报, 35(12): 2063-2075. 葛玉辉, 郗爱华, 汪志刚, 王玉芬, 孙春林. 2010. 内蒙古大青山地区中侏罗世古气候分析[J]. 中国地质, 37(1): 204-211. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/cn/article/id/20100124 韩会平, 武春英, 白清华, 陈鹏, 刘新社, 秦百平. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地乌审旗地区上古生界砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 32(4): 643-653. 侯明才, 江文剑, 倪师军, 黄虎, 罗文, 石鑫, 缪宗利. 2016. 伊犁盆地南缘中下侏罗统碎屑岩地球化学特征及对物源制约[J]. 地质学报, 90(12): 337-3351. 蒋孝君, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 薛伟, 剡鹏兵, 邢亚杰. 2016. 内蒙古中部红格尔图地区花岗岩的成因及构造背景——LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学的制约[J]. 地质通报, 35(5): 750-765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.011 焦养泉, 陈安平, 王敏芳, 吴立群, 原海涛, 杨琴, 张承泽, 徐志诚. 2005. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部直罗组底部砂体成因分析——砂岩型铀矿床预测的空间定位基础[J]. 沉积学报, 23(3): 371-379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.001 焦养泉, 吴立群, 彭云彪, 荣辉, 季东民, 苗爱生, 里宏亮. 2015. 中国北方古亚洲构造域中沉积型铀矿形成发育的沉积-构造背景综合分析[J]. 地学前缘, 22(1): 189-205. 雷开宇, 刘池洋, 张龙, 吴柏林, 王建强, 寸小妮, 孙莉. 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部中生代中晚期地层碎屑锆石U-Pb定年与物源示踪[J]. 地质学报, 91(7): 1522-1541. 李洪颜, 徐义刚, 黄小龙, 何斌, 罗震宇, 燕滨. 2009. 华北克拉通北缘晚古生代活化: 山西宁武-静乐盆地上石炭统太原组碎屑锆石U-Pb测年及Hf同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 54(5): 632-640. 李相博, 刘化清, 完颜容, 冯明, 魏立花. 2012. 鄂尔多斯晚三叠世盆地构造属性及后期改造[J]. 石油实验地质, 34(4): 376-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2012.04.006 李延兴, 张静华, 郭良迁, 张中伏, 张俊青. 2005. 鄂尔多斯的逆时针旋转与动力学[J]. 大地测量与旋转动学, 25(3): 50-56. 李振宏, 董树文, 冯胜斌, 渠洪杰. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地中—晚侏罗世构造事件的沉积响应[J]. 地球学报, 36(1): 22-30. 李子颖, 陈安平, 方锡珩, 欧光习, 张珂, 焦养泉, 夏毓亮, 陈法正, 周文斌, 刘忠厚, 吴仁贵, 肖新建, 孙晔. 2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部砂岩型铀矿成矿机理和叠合成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 25(Z2): 245-248. 梁子若, 侯明才, 曹海洋, 晁晖. 2020. 内蒙古大青山石拐盆地侏罗系元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 47(3): 307-317. 刘璐, 彭云彪, 戴明建. 2018. 鄂尔多斯盆地北东部区域大规模叠合氧化形成条件与铀成矿作用[J]. 世界核地质科学, 35(1): 16-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2018.01.003 刘晓雪, 汤超, 司马献章, 朱强, 李光耀, 陈印, 陈路路. 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部砂岩型铀矿常量元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质调查与研究, 39(3): 169-183. 陆鹿, 陈树光, 李壮福, 秦勇, 屈争辉, 沈玉林. 2022. 河套盆地临河坳陷白垩纪—古近纪沉积环境演化及油气地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 22(2): 308-331. 马醒华, 邢历生, 杨振宇, 徐树金, 张景鑫. 1993. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚古生代以来古地磁研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 36(1): 68-79. 彭胜龙, 田家鹏, 郭晓宇, 靳云鹏, 孙波, 窦洪鑫, 张帆, 郝静, 胡英莲, 陈琳, 许伟, 佟野. 2023. 鄂尔多斯盆地塔然高勒地区砂岩型铀矿含矿层砂岩特征及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 264-276. doi: 10.12029/gc20200814001 屈红军, 韩星, 陈硕, 杨博, 杜美迎, 董阳阳, 赵冲. 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部上古生界碎屑锆石测年及盆山耦合探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 44(3): 501-527. 司庆红, 俞礽安, 蔡洪广, 王善博, 王道华, 张超, 朱强. 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地乃马岱地区直罗组砂岩元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 华北地质, 44(2): 49-57. 王金平, 闵茂中, 陈跃辉, 彭新建. 2005. 砂岩型铀矿床中SiO2/Al2O3比值与含矿性的关系研究: 以库捷尔太和乌库尔其铀矿床为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 11(1): 77-84. 王思力, 聂逢君, 严兆彬, 何乃烁, 张媛媛, 张鹏飞. 2018. 鄂尔多斯盆地纳岭沟铀矿床目的层岩石学及铀存在形式[J]. 中国地质, 45(3): 573-590. doi: 10.12029/gc20180311 汪正江, 张锦泉, 陈洪德. 2001. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚古生代陆源碎屑沉积源区分析[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 28(1): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2001.01.002 谢惠丽, 吴立群, 焦养泉, 荣辉, 汪洪强. 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地罕台庙地区铀储层非均质性定量评价指标体系[J]. 地球科学, 41(2): 279-292. 杨德相, 屈争辉, 陈树光, 李壮福, 吴健平, 王建广, 武函. 2020. 河套盆地吉兰泰凹陷中生代构造层划分及意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 26(6): 691-703. 易超, 韩效忠, 李西得, 张康, 陈心路. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部直罗组砂岩岩石学特征与铀矿化关系研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 20(2): 185-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.003 易超, 高贺伟, 李西得, 张康, 陈心路, 李静贤. 2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部直罗组砂岩型铀矿床常量元素指示意义探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 34(4): 801-813. 俞礽安, 朱强, 文思博, 涂家润, 彭胜龙, 司庆红, 唐永香. 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地塔然高勒地区直罗组砂岩源区构造背景与物源分析[J]. 地球科学, 45(3): 829-843. 张宾, 刘红旭, 丁波, 易超, 张艳. 2020a. 鄂尔多斯盆地纳岭沟铀矿床岩石学、矿物学特征及其对铀成矿作用的指示意义[J]. 地质论评, 66(2): 410-423. 张宾, 刘红旭, 易超, 丁波, 张艳. 2020b. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部纳岭沟地区直罗组下段下亚段砂岩岩石地球化学特征及对物源的指示[J]. 铀矿地质, 36(2): 84-95. 张道锋, 杨文敬, 漆亚玲, 闫小雄. 2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地神木地区上古生界山西组物源分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 20(9): 902-906. 张泓, 晋香兰, 李贵红, 杨志远, 张慧, 贾建称. 2008. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪-白垩纪原始面貌与古地理演化[J]. 古地理学报, 10(1): 1-11. 张龙, 吴柏林, 刘池洋, 雷开宇, 侯惠群, 孙莉, 寸小妮, 王建强. 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部砂岩型铀矿直罗组物源分析及其铀成矿意义[J]. 地质学报, 90(12): 3441-3453. 张天福, 张云, 程先钰, 孙立新, 程银行, 周小希, 王少轶, 马海林, 鲁超. 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部东胜地区侏罗系—白垩系钻孔数据库与三维地质模型[J]. 中国地质, 47(S1): 220-230. doi: 10.12029/gc2020Z120 张媛媛, 张鹏飞, 聂逢君, 剡鹏兵, 张治波, 严兆彬, 张鑫. 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部直罗组砂岩重矿物分布特征及其指示意义[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 49(4): 142-152. 张云, 张天福, 程先钰, 孙立新, 程银行, 王少轶, 王善博, 马海林, 鲁超. 2022. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部侏罗纪含铀岩系三维地质结构与铀成矿规律浅析[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 66-80. doi: 10.12029/gc20220105 张玉清, 张婷, 陈海东, 张永清. 2016. 内蒙古凉城蛮汗山石榴石二长花岗岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及成因讨论[J]. 中国地质, 43(3): 769-779. doi: 10.12029/gc20160306 赵俊峰, 刘池洋, 梁积伟, 王晓梅, 喻林, 黄雷, 刘永涛. 2010. 鄂尔多斯盆地直罗组—安定组沉积期原始边界恢复[J]. 地质学报, 84(4): 553-569. 赵俊峰, 刘池洋, 赵建设, 王晓梅. 2008. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系直罗组沉积相及其演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 480-486. 钟焱, 陈雅丽, 翟明国, 马旭东. 2016. 华北克拉通西部古元古代孔兹岩系的地层对比、岩相古地理特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 32(3): 713-726. 周科. 2014. 常量元素与微量元素特征在物源分析中的应用[J]. 辽宁化工, 43(4): 515-520. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 王学阳,杨言辰,刘志宏,张继武,戴台鹏. 长江中下游成矿带大金山地区综合信息找矿效果及深部找矿潜力分析. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2025(01): 125-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谭杰,徐文杰,赵毅,罗达,赵俊宏,钟玉龙,陶明荣. 广西五圩矿田多金属矿成矿模式及找矿预测. 中国矿业. 2024(S1): 508-514 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李双飞,黄鹂,陈建,朱伟,孙丽莎,王欣,彭永和,商祥鸿,邹占春,唐名鹰,高远,赵家强. 山东省五莲七宝山金铜矿床成矿模式与找矿勘查模型——来自综合物化探的证据. 地质与勘探. 2023(05): 961-973 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李玉坤,王兴龙,廖阿托,李科. 东天山梧桐沟钨矿区综合信息找矿模型. 新疆地质. 2023(04): 530-537 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: