Vertical distribution characteristics of light hydrocarbon components in Well SK-2 and its implications for deep oil and gas
-
摘要:
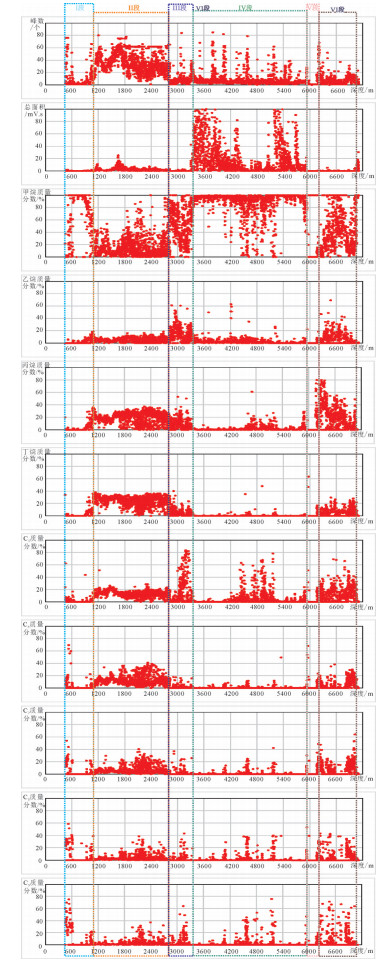
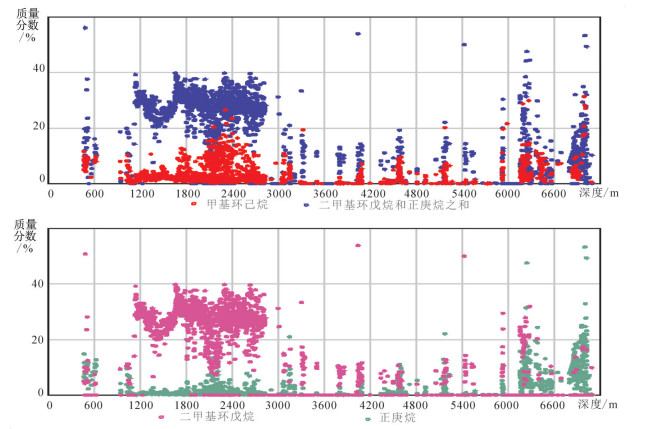
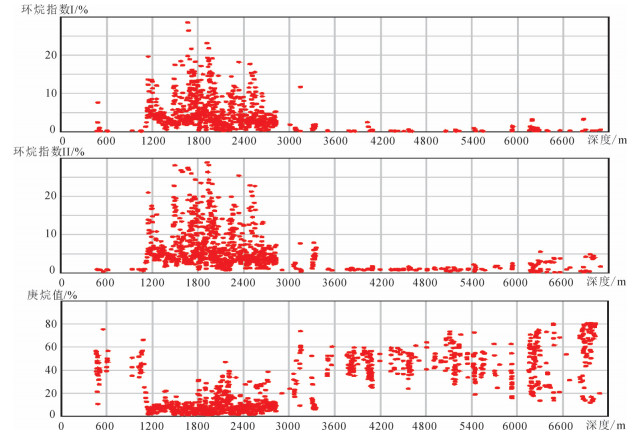
松辽盆地深部油气已成为今后油气战略性接替领域的一个重要方向,松科二井连续取样的6042组103种单体的轻烃组分数据显示,轻烃组分垂向分布特征呈现明显的分段性,整体可划分为6个区段:Ⅰ段(井段470~1000 m)罐顶气峰面积小,出峰个数少,主要以甲烷为主,重烃较低,为浅层低熟油气段。Ⅱ段(井段1000~2800 m)罐顶气峰面积小,出峰个数多;甲烷含量中等,重烃含量普遍较高;有机质类型以Ⅰ型为主,处于成熟阶段,为常规油气段。Ⅲ段(井段2800~3320 m)罐顶气峰面积小,出峰个数较少、零散;甲烷含量整体较高,重烃含量与Ⅳ段相似,表明该段气源可能来源于Ⅳ段。Ⅳ段(井段3320~5940 m)罐顶气峰面积大,集中分布在3400~3800 m和5200~5400 m井段,明显高于Ⅲ段和Ⅴ段;为Ⅲ型烃源岩,处于高成熟-过成熟阶段。Ⅴ段(井段5940~6200 m)罐顶气峰面积、出峰个数低;甲烷和重烃含量较低。Ⅵ型(井段6200~7018 m)出峰个数、罐顶气峰面积低;甲烷含量较高,重烃含量中等,其总体特征与Ⅳ和Ⅴ段不同,推测深部可能存在气源。上述垂向分布特征反映了白垩系、侏罗系和前侏罗系在油气成因类型、成熟度和含气性及其油气来源等具有不同的特征,为松辽盆地深部非常规天然气探索拓展提供了重要依据。
Abstract:With the maturation of oil and gas exploration and development in Songliao basin, it is urgent to expand strategic replacement areas for oil and gas storage and production. In this task, deep oil and gas seem to be an important direction. Roof gas logging with continuous sampling in the whole well section of Well SK-2 obtained 6042 groups of light hydrocarbon composition data containing 103 monomers, and fully demonstrated vertical variation characteristics of light hydrocarbon components in the deep part of Well SK-2, which shows obvious segmentation. As a whole, it can be divided into 6 sections:section Ⅰ (470-1000 m in well section), which has a small peak area, a small number of peak outfalls, and a low heavy hydrocarbon content, showing the characteristics of shallow and low-mature oil and gas; Section Ⅱ (well section 1000-2800 m) has a large peak area, a large number of peaks and a high heavy hydrocarbon content. It is a mature type Ⅰ source rock and a conventional oil and gas section dominated by oil generation; Section Ⅲ (2800-3320 m in well section) has fewer and scattered peaks, low content of heavy hydrocarbon and no hydrocarbon source rocks, which are characteristic of reservoirs; Section Ⅳ (3320-5940 m in well section) is the upper unconventional gas section of Shahezi Formation, with a large peak area and a large number of peak outputs, high content of heavy hydrocarbon, being Type Ⅲ source rocks with large thickness in the maturation-over-maturation stage, and sandstone interbeds can form various types of unconventional natural gas, suggesting an important section for future exploration; Section Ⅴ (5940-6200 m in well section) is the lower part of Shahezi Formation and Huoshiling Formation, and the peak area and peak number of roof gas are scattered within the section which is considered to be in the stage of over-maturation; Section Ⅵ (6200-7108 m in well section) is volcanic rock and basement segment, and the peak area and number of peaks are generally low. However, the peak area of top gas in 7000-7100 m well segment shows that the light hydrocarbon parameters are different from those of section Ⅴ, and it is inferred that there may be gas sources of type Ⅱ-Ⅲ organic matter in the deep part. These characteristics show that the vertical distribution of light hydrocarbon components reflects the different characteristics among Jurassic, Cretaceous and the basal formations in oil and gas formation, maturation, gas content and oil and gas sources. The results obtained by the authors reveal the potential of deep unconventional gas resource, and provide an important foundation for Songliao Basin's exploration shift from conventional oil and gas exploration and tight conglomerate gas exploration at the edge of fault depression to deep trough zone for the exploration and expansion of unconventional natural gas.
-
1. 引言
层序地层的概念自Sloss(1963)在对比与划分北美克拉通前寒武纪晚期至全新世地层单元时提出后,20世纪70年代以来,在被动大陆边缘盆地油气勘探研究实践中不断得以发展完善,先后建立了地震地层学和层序地层学的理论方法体系(Vail et al,1977;Vail,1987;Haq et al,1988;Jervey,1988;Posamentier et al,1988;Van Wagoner et al,1990;Posamentier and Allen, 1993),在油气勘探中发挥着重要作用。但与海相盆地相比,陆相湖盆发育规模小、物源多、相变快、控制地层发育的因素复杂等特点(徐怀大, 1991, 1997;谢渊等,2002)决定了源于被动大陆边缘海盆的经典层序地层学理论并不完全适合陆相湖盆的层序地层学研究。Cross(1993)提出的通过地层基准面分析实现高分辨率陆相层序地层格架构建的高分辨率层序地层学摆脱了经典层序地层学关于海平面变化控制层序形成这一思想对陆相层序地层研究的束缚,在中国部分中、新生代陆相含油气盆地层序地层研究中得到较为成功的应用和发展(杨勇强等,2011;刘犟等,2015;郑荣才等,2015)。目前,特别是随着油气勘探的不断深入,较易找到的较大型构造油气藏大多已被发现,而隐蔽性强、成藏规律更复杂的岩性-地层油气藏成为高成熟探区油气增储上产的主体时,作为岩性-地层油气藏勘探研究核心技术的层序地层学发挥着越来越重要的作用(贾承造等, 2004, 2008)。
白音查干凹陷的油气勘探研究主要起始于中原油田获得其勘探权之后的1993年。2000年之前,白音查干凹陷的油气勘探主要是围绕井位部署而进行的区块评价,而综合性的基础研究不多。有关白音查干凹陷层序地层的研究也较少,只有张万选等❶对其西部次凹进行过层序地层的初步研究,将下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组划分为5个层序,分别对应于阿尔善组一段(简称阿一段)、阿尔善组二段(简称阿二段)、腾格尔组、都红木组一段(简称都一段)、都红木组二段(简称都二段)—都红木组三段(简称都三段),认为各层序界面均为不整合面。在探明达尔其地区都一段和桑合地区腾格尔组2个小规模稀油油藏,以及控制达尔其地区达9块都一段稠油油藏之后,认为白音查干凹陷油气分布分散、油藏规模小、富集程度低而停止了勘探工作量的投入❷。为打破白音查干凹陷油气勘探的被动局面,2000年中国石化集团总公司下达了为期两年半的油气勘探“十五”重大科技攻关项目“白音查干凹陷石油地质综合研究”,在构造、沉积、地球化学等方面对白音查干凹陷开展了较系统的研究。以此为契机,白音查干凹陷的层序地层研究也得以开展(李金良,2002;张福顺等,2003;许书堂等,2004;李金良等,2007;闫玉英等,2008),其划分方案与之前的划分方案❶基本相同,也认为各层序界面均为不整合面,其划分层序的级别也仍主要为Vail(1977,1987)的经典Ⅲ级层序及体系域。
随着2006年白音查干凹陷锡林好来地区腾格尔组中、下部油藏的勘探成功,特别是锡26井腾格尔组-都一段缝洞型泥质白云岩岩性油藏的发现,拉开了白音查干凹陷岩性-地层油气藏勘探的序幕。至2012年,白音查干凹陷的油气勘探重点已转为地层-岩性油气藏(高红灿等,2015a)。基于层序地层学在地层-岩性油气藏勘探中的重要作用和指导意义,本文在前人研究成果基础上,对白音查干凹陷(主要是西部次凹)油气勘探的主要目的层下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组的层序发育特征进行再认识,对层序界面的性质进行重新厘定,并进行超长期—长期层序地层的划分和等时地层格架的建立,为白音查干凹陷的构造-沉积演化、沉积充填序列和生储盖组合,以及油气运移和成藏等研究提供基础地质资料。
2. 地质背景
早白垩世,由于库拉—太平洋板块向欧亚板块俯冲导致地下深部地幔物质快速向上运移而产生的弧后区域性伸展作用,形成了位于地幔物质隆升中心、张开幅度较大的松辽裂谷盆地,以及不在地幔物质隆升中心、张开幅度较小的二连断陷盆地群(吴福元等,1995;肖安成等,2001)。白音查干凹陷位于二连断陷盆地西缘的川井坳陷西北部,是一个以下白垩统陆源沉积为主的中生代断陷盆地,长约127 km,宽12~33 km,呈NE-SW向的狭长梭形,面积约3200 km2。白音查干凹陷总体上具东西分区、南北分带的构造格局,以翁特—毛呼一带近南北向的毛呼低凸起构造转换带为界将凹陷分割为三部分——西部次凹、毛呼低凸起和东部次凹(图 1)。东部次凹以双断断槽式结构为主,面积约740 km2,发育较晚,沉积厚度薄,勘探程度也较低;西部次凹整体呈北断南超的单断箕状结构,面积约2200 km2,发育较早,沉积厚度大,是白音查干凹陷的主体。
白音查干凹陷的基底为下古生界变质岩,其沉积充填主要为下白垩统巴彦花群和厚度较小的上白垩统二连达布苏组,局部发育新生界,总沉积厚度大于5000 m。其中,下白垩统巴彦花群自下而上进一步划分为阿尔善组(阿一段、阿二段)、腾格尔组、都红木组(都一段、都二段、都三段)和赛汉塔拉组(图 2)。
3. 地层划分沿革
在各盆地的油气勘探开发中,其地层的划分与对比都普遍存在或多或少的分歧,所以,在对各盆地进行研究时,首先要了解其各研究阶段的地层划分与对比方案,以避免在借鉴前人研究成果及开展实际生产和科研工作时,由于地层单位名称相同但所指地层不同或地层相同但地层单位名称不同而造成理解上的偏差及由此造成的困扰。
白音查干凹陷的地层研究也主要是从1993年中原油田获得其勘探权之后开始的。到目前为止,由蒋飞虎等分别于1995、1997、2002年进行过3次较系统的研究❸❹❺,形成了两套地层划分方案(1995和1997年的地层划分方案❸❹相同)(表 1)。这两套地层划分方案的主要差别是下白垩统腾格尔组的顶、底界线划分不一致——不仅在白音查干凹陷内不一致,而且与二连盆地科研分层的腾格尔组(蔡志国等,1990)或生产分层的腾格尔组一段❻(简称腾一段)的顶、底界线也不一致(表 1)。
表 1 二连盆地和白音查干凹陷下白垩统划分对比Table 1. Division correlation of Lower Cretaceous strata between Baiyinchagan Sag and Erlian Basin
关于白音查干凹陷腾格尔组的顶界划分,目前主要是依据地震剖面解释将其划分在“红层细脖子段”之底❺,与二连盆地科研分层的腾格尔组或生产分层的腾一段的顶界不一致(表 1)。但同时蒋飞虎等❺又通过古生物和岩性等资料与二连盆地的对比,以及由地层倾角测井所反映出的“梳状白云质泥岩段”与“红层细脖子段”之间存在一地层界线等来分析,认为将白音查干凹陷腾格尔组的顶界划分在“红层细脖子段”的顶界较合适。本文根据白音查干凹陷的构造演化、古生物和岩性等方面的特征所反映出的“红层细脖子段”顶界面为一不整合面(详见后面的论述),从层序地层的角度也建议将白音查干凹陷腾格尔组顶界划分在“红层细脖子段”的顶界(表 1)。
关于白音查干凹陷腾格尔组的底界划分,目前主要是依据白音查干凹陷和二连盆地的构造-沉积演化特征,将其划分在相当于二连盆地科研分层的阿尔善组上段与中段之间或生产分层的阿尔善组三段(简称阿三段)与阿二段之间❺(表 1),其中,白音查干凹陷中相当于二连盆地生产分层的阿尔善组四段(简称阿四段)与阿三段的岩性均为“高阻砂砾岩”不易区分,但与下伏的阿二段“泥岩发育段”的岩性差别明显,反映期间构造-沉积环境的较大变化,本文也采用这种地层划分方案(表 1),具体将腾格尔组底部划分在目前白音查干凹陷生产上标注的腾格尔组第13#标志层之上的砂岩底部(高红灿等, 2015b, 2017)。
4. 层序地层特征
不同于受海平面变化控制的被动大陆边缘盆地层序的形成机制(Vail et al,1977;Vail,1987;Haq et al,1988;Jervey,1988;Posamentier et al,1988;Van Wagoner et al,1990;Posamentier and Allen,1993),陆相断陷盆地层序的形成主要受构造沉降作用控制(解习农和李思田,1993;池英柳等,1996;解习农等,1996;冯有良等,2000),层序地层划分的关键是不同级别层序界面的识别(李思田等,1993;郑荣才等, 2000, 2001)。构造演化阶段的区域构造应力场转换是形成陆相断陷盆地超长期层序的主控因素,构造幕的脉动性强弱变化是形成陆相断陷盆地长期层序的主控因素(郑荣才等,2000)(表 2)。
表 2 层序划分方案和基本特征(据郑荣才等,2000修改)Table 2. Classification and basic characteristics of sequences stratigraphy(modified from Zheng Rongcai et al., 2000)
通过研究区200多口钻井的精细地层对比和33口井759.42 m岩心的详细观察,以及区域构造-沉积演化分析,综合运用构造、古生物、岩性、测井和地震等5个方面的特征,以郑荣才等(2000)的层序级次划分和命名原则为基础(表 2),同时考虑界面性质、界面级次、层序结构和叠加样式等,将白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组划分为2个超长期层序(分别对应于阿尔善组—腾格尔组和都红木组)和5个长期层序(分别对应于阿一段、阿二段、腾格尔组、都一段和都二段—都三段)(图 2)。
4.1 超长期层序
4.1.1 构造特征
二连盆地白垩系包含着3个裂陷—构造反转旋回,分别为生产分层上的阿尔善组—腾一段、腾格尔组二段(简称腾二段)和赛汉塔拉组(梁宏斌等,2010),对应于白音查干凹陷内的阿尔善组—腾格尔组、都红木组和赛汉塔拉组。即在早白垩世阿尔善组—都红木组沉积期,在白音查干凹陷内由构造应力场的反转而形成了3个超长期层序(构造层序)界面——阿尔善组底、都红木组底和赛汉塔拉组底。
(1)晚侏罗世末期,二连盆地的构造背景由早—中侏罗世的伸展断陷转变为挤压抬升,形成了二连盆地构造演化的第一次构造应力场反转,造成了二连盆地内普遍存在下白垩统角度不整合于下伏地层之上。该期构造应力场反转对整个内蒙古东部均普遍造成影响(内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1993;朱坤玉,1997)。该构造应力场反转的原因可能与西伯利亚和布列亚地块的碰撞俯冲及由此引起的蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋的闭合有关(肖安成等,2001)。在白音查干凹陷内表现为侏罗系的缺失和阿尔善组直接以角度不整合覆盖于下古生界变质岩基底之上,形成了白音查干凹陷内的第一个超长期层序(构造层序)界面。
(2)在早白垩世晚期的腾一段(生产分层)沉积期与腾二段(生产分层)沉积期之间,二连盆地的构造演化又发生了第二次构造应力场反转——由伸展断陷转变为挤压抬升,该期构造应力场反转所产生的冲断作用导致腾一段(生产分层)褶皱抬升,从而造成腾一段与腾二段(生产分层)的不整合接触,在邻区的海拉尔盆地和松辽盆地也均有响应(肖安成等,2001)。其原因可能与由太平洋板块运动方向变化所导致的中国东部乃至日本及朝鲜地区产生区域性的左旋剪切走滑作用有关(Otoh,1996),即太平洋板块中生代向欧亚板块汇聚的运动方向在110 Ma(早白垩世晚期)左右从NW向转变为正N向(肖安成等,2001)。该期构造应力场反转在白音查干凹陷内表现为较大幅度的抬升,致使腾格尔组沉积末期红层普遍发育,造成腾格尔组与都红木组的不整合接触,形成了白音查干凹陷内的第二个超长期层序(构造层序)界面。
(3)对应于二连盆地腾二段(生产分层)与赛汉塔拉组沉积之间的第三次构造应力场反转,白音查干凹陷在早白垩世晚期的都红木组沉积之后整体挤压抬升,湖盆收缩,其北部控凹边界断层发生构造反转❼。一方面表现为凹陷边部抬升剥蚀,之后在局部地区沉积了少量上白垩统和新生界;另一方面表现为边界断层下降盘地层加厚与倾向方向相反,即下白垩统上部地层向北加厚而区域产状却为南倾。该期构造反转形成的赛汉塔拉组下部的“灰白色厚层砂砾岩段”(表 1,图 2),与下伏都红木组深灰色泥页岩细粒沉积形成鲜明的对比,造成赛汉塔拉组与都红木组的不整合接触,形成了白音查干凹陷内的第三个超长期层序(构造层序)界面。
对应于二连盆地及白音查干凹陷内的这三期构造应力场反转形成的阿尔善组底、都红木组底和赛汉塔拉组底的3个超长期层序界面,可将白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组划分为2个超长期层序,分别对应于阿尔善组—腾格尔组和都红木组(图 2)。
4.1.2 古生物特征
二连盆地下白垩统巴彦花群介形类化石属种丰富,共12属86种,主要产于阿三段—腾格尔组(生产分层)(李宏容,1989)。白音查干凹陷下白垩统巴彦花群介形类化石也很丰富,共11属54种,主要产于都红木组,其次为腾格尔组,与二连盆地介形类化石发育的层位基本相当(蒋飞虎等, 1996, 2000)。
二连盆地的阿一段—阿二段(生产分层)(相当于白音查干凹陷的阿尔善组)不含介形类化石(李宏容,1989)。阿三段—腾一段(生产分层)(相当于白音查干凹陷的腾格尔组)介形类化石属种在巴彦花群中最多(共11属47种),且在二连盆地内广泛稳定分布,以Cypridea为主,富含Cypridea(Cypridea)badalahuensis、Timiriasevia polymorpha、Dryelba krystofovitschi等,称为Cypridea(Cypridea)badalahuensis—Timiriasevia polymorpha—Dryelba krystofovitschi组合(李宏容,1989)。自下而上可划分为3个亚组合:阿三—阿四段(生产分层)(相当于白音查干凹陷腾格尔组下部)的Cpridea(C.)badalahuensis—Djungarica saidovi亚组合代表该阶段介形类的初生期,腾一段(生产分层)下部(相当于白音查干凹陷腾格尔组中部)的C.(C.)badalahuensis—Timiriasevia polymorpha— Darwinula contracta亚组合代表该阶段介形类的发展期,腾一段(生产分层)上部(相当于白音查干凹陷腾格尔组上部)的C.(C.)masjacini giganta subsp. Nov.—Dryelba krystofovitschi亚组合代表该阶段介形类的繁盛期,各亚组合之间介形类具继承性和连续性(李宏容,1989)。
与二连盆地阿尔善组—腾一段(生产分层)沉积期介形类演化特征相似,白音查干凹陷阿尔善组介形类化石含量极少,仅在其上部零星发现适应性强的Limnocypridea minuta和Lycoptercypris infantilis,化石分异度很低。白音查干凹陷腾格尔组介形类化石属种和数量远不及二连盆地主体丰富,共8属17种,主要产于腾格尔组上部,为白音查干凹陷巴彦花群介形类初生期的产物,以Rhinocypris nomugenensis、Cypridea(Cypridea)delnovi、C.(C.)unicostata、C.(C.)prognata、C.(C.)sulcata和Timiriasevia为标志性分子,称为Cypridea(Cypridea)unicostata—Cypridea(Cypridea)delnovi—Rhinocypris nomugenensis组合(蒋飞虎等,1996,2000)。其中所含的Cypridea(Cypridea)delnovi和Rhinocypris nomugenensis等介形类分子也是二连盆地主体腾一段(生产分层)上部C.(C.)masjacini giganta subsp. Nov. —Dryelba krystofovitschi亚组合的特征分子,两者层位相当(蒋飞虎等,1996)。
二连盆地都红木组(科研分层)介形类化石面貌与下伏腾格尔组(科研分层)介形类化石组合明显不同,为二连盆地巴彦花群介形类的一个新发展期。以发育Ilyocyprimorpha、Limnocypridea、Cypridea和Cypridea(Ulwellia)为主要特征,称为Limnocypridea grammi—Ilyocyprimorpha erlianensis —Cypridea(U.)copulenta组合(李宏容,1989)。其中绝大部分介形类属种为二连盆地都红木组(科研分层)中新出现的分子,在该组的9属43种中,仅有6属13种是由下伏地层延续上来的,其余30种均产自都红木组,约占总种数的70%(李宏容,1989),特别是在下伏阿三段—腾一段(生产分层)Cypridea(Cypridea)badalahuensis—Timiriasevia polymorpha —Dryelba krystofovitschi组合(李宏容,1989)中很兴盛的优势分子Cypridea(Cypridea)badalahuensis、C.(C.)masjacini、C.(C.)accommodata、Timiriasevia polymorpha和Djungarica saidovi已全部绝迹,Dryelba也基本绝迹,Mongolianella偶见。
与二连盆地都红木组(科研分层)沉积期介形类演化特征相似,白音查干凹陷都红木组介形类化石面貌与下伏腾格尔组相比也发生了明显的变化,代表介形类的发展进入了一个新的阶段。在其10属50种介形类化石(蒋飞虎等,2000)中,除12种从腾格尔组延续上来外,其余38种均为都红木组中新产生的,占总种数的76%。其介形类属种类型及数量从都一段(9属31种,其中从腾格尔组继承12种)开始发展,都二段(10属45种,其中从都一段继承29种)—都三段(6属17种,其中从都二段继承15种)达到繁盛。按介形类属种不同,白音查干凹陷都红木组介形类化石可划分为两个组合:都一段—都二段介形类化石个体较大、属种丰富,为白音查干凹陷介形类的繁盛期,其优势分子为Limnocypridea、Clinocypris和Cypridea(Yumenia),称为Limnocypridea trapeazoidea—Clinocypris ventriconcava—Cypridea(Yumenia)subremota组合。其中的Limnocypridea分子繁盛的情况与二连盆地主体都红木组(科研分层)下部Limnocypridea grammi富集情况相对应,特别是其主要分子Limnocypridea tapezoidea与二连盆地主体Limnocypridea grammi形态很接近(蒋飞虎等,1996);都三段以个体小、壳饰简单的Limnocypridea minuta的高度富集为特点,还产有大量的Paralimnocythere chuanjingensis和Paralimnocythere impolita,称为Limnocypridea minuta富集组合。其中的次要分子Cypridea(Cypridea)xisuensis、Rhinocypris jurassica spinosa和R. potanini均分布于二连盆地主体都红木组(科研分层)中,Ilyocyprimorpha cf. erlianensis与二连盆地主体都红木组(科研分层)上部的富集分子Ilyocyprimorpha erlianensis可对比(蒋飞虎等,1996)。
二连盆地赛汉塔拉组介形类化石属种与下伏都红木组相比截然不同,除少数种(如Cypridea(Ulwellia)copulenta)从下伏地层都红木组(科研分层)延续上来外,基本上都为新出现的分子,以Cypridea为主,称为Cpridea(Morinina)subtuberculisperga — Cpridea(Pseudocypridina)infidelis — Cpridea(Cypridea)unicostata组合。
与二连盆地赛汉塔拉组沉积期介形类演化特征相似,在都红木组沉积末期,白音查干凹陷绝大多数介形类分子也基本绝灭而未进入赛汉塔拉组,赛汉塔拉组介形类仅见少量Limnocypridea和Cypridea等,分异度很低。
白音查干凹陷与二连盆地的介形类化石演化特征相似,发育层位基本相同,各化石组合基本可以对比。白音查干凹陷阿尔善组中介形类化石含量很少,进入腾格尔组后逐渐增多以致繁盛,至腾格尔组沉积末期,介形类发生了第一次大绝灭,都红木组中新出现的介形类分子大于70%,介形类发展进入了一个新阶段;至都红木组沉积末期,介形类又发生了第二次大绝灭,绝大部分介形类未进入赛汉塔拉组,赛汉塔拉组发育的介形类基本上都为新出现的分子。腾格尔组(二连盆地的科研分层)沉积末期和都红木组(二连盆地的科研分层)沉积末期介形类的两次大绝灭,反映了二连盆地及白音查干凹陷当时的沉积环境发生了巨大变化,也与前述二连盆地及白音查干凹陷白垩纪构造应力场反转(梁洪斌等,2010)相对应。所以,从古生物演化的角度也将白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组划分为2个超长期层序(构造层序),分别对应于阿尔善组—腾格尔组和都红木组(图 2)。
4.2 长期层序
4.2.1 构造特征
白音查干凹陷发育有3条主控断层——塔拉断层、塔拉南断层和白音—翁特断层(图 1),对凹陷的形成演化、沉积-沉降中心的迁移等起主要控制作用。其中,控制凹陷发育的Ⅰ级断层塔拉断层的垂直活动量最大,为几百至2000多米(图 3),而控制凹陷内构造带发育的Ⅱ级断层塔拉南断层和白音—翁特断层的垂直活动量较小,分别为几十至400多米和多小于200 m❼(图 4,图 5)。东部次凹内发育的断层大多为Ⅲ级和Ⅳ级,对凹陷的构造和沉积控制不明显。根据地质平衡剖面分析❼,白音查干凹陷的断陷活动主要发生在都红木组沉积之前,可分为阿一段沉积期、阿二段沉积期和腾格尔组沉积期3个幕式断陷构造旋回。腾格尔组沉积之后白音查干凹陷的构造演化开始由断陷向拗陷转换,其中都一段沉积期为断—拗转换构造旋回,而都二段—都三段沉积期主要为拗陷构造旋回。都红木组沉积之后,白音查干凹陷便进入了萎缩抬升阶段。
(1)初始断陷期(阿一段沉积期):该期白音查干凹陷北部边界的塔拉断层与西部次凹北部的塔拉南断层开始发育并强烈活动,顺断层延伸方向差异沉降明显,在西部次凹形成了以桑合、古尔东横向凸起分割的3个次洼——霍恩次洼、呼热—敖伦次洼和冬屋次洼,其中,呼热—敖伦次洼沉降幅度最大(大于2000 m),霍恩和冬屋次洼沉降幅度较小(1000~1500 m)❼(图 3,图 4)。次洼中主要充填了厚度近400 m的杂色砂砾岩,说明当时白音查干凹陷尚未形成汇水盆地。东部次凹的东达断层和查干断层该期也相继发育,形成了与走向一致的狭长断槽,并充填了一套厚度远小于西部次凹的砂泥岩沉积。相应于该期断层的垂向活动,白音查干凹陷也开始发生水平伸展,其不同部位的总水平断距生长速率变化为0.23~0.54 km/Ma,平均为0.37 km/Ma❼(图 6)。
(2)稳定断陷期(阿二段沉积期):该期是白音查干凹陷的主裂陷期与扩张期。塔拉断层及塔拉南断层活动强度及顺断层延伸方向差异沉降作用均较阿一段沉积期减弱,冬屋次洼向西扩展并与呼热—敖伦次洼基本连为一体,其间的古尔东横向凸起收缩明显(图 3,图 4)。该期白音查干凹陷南坡的白音—翁特断层虽有活动,但其活动速率及垂直下降幅度比塔拉断层小得多,一般在100~300 m的范围内,多数地区小于100 m❼(图 5),对凹陷的构造格局影响不大。东部次凹的断层于阿二段沉积期再次活动,但总体沉积特征仍是充填夷平,阿二段沉积后,东部次凹断裂活动趋于平静,断槽已基本夷平,并由断槽沉积型转化为湖盆沉积型。该期凹陷的总水平断距生长速率也不断增大,但不同部位的差别较大,其变化范围为0.26~0.79 km/Ma,平均为0.47 km/Ma❼(图 6)
(3)震荡断陷期(腾格尔组沉积期):该期白音查干凹陷曾发生回返抬升,断陷活动强度在有所减弱后逐渐加强。该时期塔拉断层的活动有两个突出特点:一是断层的活动量相对于阿二段沉积期有所减弱,除霍恩—桑合、冬屋地区维持较高的沉降幅度(超过1000 m)外,大多数地区断层的活动量在600~700 m❼(图 3);二是顺断层延伸方向的差异性活动增强,断层活动量曲线表现为大起大落。呼热—古尔地区向上抬升使阿尔善组沉积期形成的呼热—敖伦次洼转变为横向凸起,霍恩次洼和冬屋次洼则继承性扩展(图 3)。该期白音查干凹陷的总水平断距生长速率进一步扩大,但不同部位的差别较之前变小,其变化范围为0.27~0.65 km/Ma,平均为0.50 km/Ma❼(图 6)。
(4)断—拗转换期(都一段沉积期):该期白音查干凹陷也呈现出两个明显的特点:一是塔拉断层的垂向活动仍较强烈,垂直下降幅度为500~1400 m,顺断层延伸方向的差异沉降也十分突出,形成该期的次洼分布格局与腾格尔组有明显的不同——3个次洼分别分布于霍恩、桑合—呼热和冬屋地区,冬屋次洼最大,霍恩次洼最小(图 3);二是白音查干凹陷的总水平断距生长速率不仅在整个西部次凹各处的差异性较之前明显减小而趋于一致,而且其在白音查干凹陷各构造旋回中也较小(变化范围为0.28~0.51 km/ Ma,平均为0.41 km/Ma❼)(图 6),说明白音查干凹陷的构造演化已开始从断陷向拗陷转换。
(5)拗陷期(都二段—都三段沉积期):该期断裂活动相对较弱并逐渐停止,东西次凹连成一体,白音查干凹陷的构造演化进入了拗陷阶段,以稳定厚层泥岩沉积为主,成为覆盖全区的良好区域性盖层。在西部次凹,南坡有少量断层仍有继承性活动,但活动强度变弱,以稳定泥页岩沉积为主;北坡的断层基本停止活动,桑合等构造停止发育。相应于该期白音查干凹陷的构造演化由断陷逐渐转化为拗陷,其水平伸展作用也基本停止❼。都红木组沉积之后,白音查干凹陷便进入了萎缩挤压抬升期,全区面貌发生较大改观。
对应于构造演化的5个幕式构造旋回,白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组可划分出5个长期旋回层序(相当于Vail的Ⅲ级层序),分别对应于阿一段、阿二段、腾格尔组、都一段和都二段—都三段(图 2)。
4.2.2 岩性特征
阿一段沉积期是白音查干凹陷的构造初始断陷期,凹陷内主要发育杂色砂砾岩(图 7a)、灰白色-浅灰色含砾砂岩、砂砾岩,夹薄层浅灰色泥岩、粉砂岩和紫红色泥岩等,主要为陆上氧化环境下冲积扇快速堆积的产物,说明当时凹陷尚未形成汇水盆地,大面积均处于暴露剥蚀的水上氧化环境。
![]() 图 7 白音查干凹陷下白垩统岩性特征a—杂色砂砾岩,达56井,3394.6 m,阿一段;b—暗棕红色泥岩中发育的不规则状钙质结核,达5井,501.8 m,腾格尔组顶部;c—灰色泥页岩中的黄铁矿集合体,达9井,476.5 m,都一段;d—灰色砂砾岩(含原油),锡14井,413.4 m,都一段;e—灰色砂砾岩,锡40井,1230.3 m,腾格尔组底部Figure 7. Lithologic features of Lower Cretaceous in Baiyinchagan Sag, Erlian Basina -Mottled sandstone and conglomerate, Well Da56, 3394.6 m, the 1st member of Aershan Formation; b-Irregularly shaped calcareous concretions from dark brownish red mudstone, Well Da5, 501.8 m, the top of Lower Cretaceous Tenggeer Formation; c-Pyrite accumulations from grey mudstone and shale, Well Da9, 476.5 m, the 1st member of Duhongmu Formation; d-gray sandstone and conglomerate (including crude oil), Well Xi14, 413.4 m, the 1st member of Duhongmu Formation; e-Gray sandstone and conglomerate, Well Xi40, 1230.3 m, the bottom of Lower Cretaceous Tenggeer Formation
图 7 白音查干凹陷下白垩统岩性特征a—杂色砂砾岩,达56井,3394.6 m,阿一段;b—暗棕红色泥岩中发育的不规则状钙质结核,达5井,501.8 m,腾格尔组顶部;c—灰色泥页岩中的黄铁矿集合体,达9井,476.5 m,都一段;d—灰色砂砾岩(含原油),锡14井,413.4 m,都一段;e—灰色砂砾岩,锡40井,1230.3 m,腾格尔组底部Figure 7. Lithologic features of Lower Cretaceous in Baiyinchagan Sag, Erlian Basina -Mottled sandstone and conglomerate, Well Da56, 3394.6 m, the 1st member of Aershan Formation; b-Irregularly shaped calcareous concretions from dark brownish red mudstone, Well Da5, 501.8 m, the top of Lower Cretaceous Tenggeer Formation; c-Pyrite accumulations from grey mudstone and shale, Well Da9, 476.5 m, the 1st member of Duhongmu Formation; d-gray sandstone and conglomerate (including crude oil), Well Xi14, 413.4 m, the 1st member of Duhongmu Formation; e-Gray sandstone and conglomerate, Well Xi40, 1230.3 m, the bottom of Lower Cretaceous Tenggeer Formation阿二段沉积期是白音查干凹陷的构造稳定断陷期,白音查干凹陷发育规模逐渐扩大,开始形成汇水盆地并逐渐向凹陷南、北斜坡超覆,水域面积也逐渐扩大。白音查干凹陷内主要沉积暗色泥页岩,形成了凹陷内的第一套烃源岩层。代表受构造断陷作用的影响,凹陷内的沉积环境由阿一段沉积期以陆上暴露的氧化环境为主转变为阿二段沉积期较稳定的半深湖—深湖还原环境。
腾格尔组沉积期是白音查干凹陷的构造震荡断陷期,其基本沉积特征为下粗上细,下灰上红,自下而上发育3个沉积单元:底部为灰—灰白色砂砾岩、含砾砂岩、砂岩、粉砂岩与灰色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩等呈互层,与下伏阿二段暗色泥页岩呈突变接触,表明腾格尔组沉积初期构造运动使白音查干凹陷发生一定幅度的抬升,造成阿二段沉积期较稳定的半深湖—深湖环境变为腾格尔组沉积期较动荡的湖泊三角洲浅水环境;向上腾格尔组变为暗色砂岩、含砾砂泥岩互层段,砂岩或泥岩中含有白云质;最上部含暗棕红色砂泥岩互层,整体上从凹陷西部向东部红层含量逐渐增多,暗棕红色泥岩中发育有较多不规则状的钙质结核(图 7b),反映当时沉积环境为暴露于地表的氧化环境,也反映腾格尔组沉积末期白音查干凹陷为较干旱的气候环境,与由孢粉化石资料所得出的白音查干凹陷腾格尔组沉积期为干旱热带—亚热带型气候(李寿军,2009)相一致。
都红木组沉积期是白音查干凹陷的断拗转换期—拗陷期,其沉积环境由腾格尔组沉积期的湖泊三角洲浅水沉积为主转变为半深湖—深湖的深水沉积为主,白音查干凹陷东、西次凹连为一体,都红木组以暗色泥岩广泛发育为基本特征,形成了白音查干凹陷较稳定的区域性盖层。都一段俗称“梳状白云质泥岩段”(表 2),以浅-深灰色泥岩、白云质泥岩、灰黄色泥质白云岩为主,夹浅灰色粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩和粉砂质泥岩等,其中,泥岩中含黄铁矿(图 7c),白云质含量由西往东逐渐减少。在凹陷边缘,都一段底部发育灰色含砾泥岩(图 7d),与下伏腾格尔组顶部的红色砂泥岩地层呈突变接触。不仅反映出白音查干凹陷的沉积环境由腾格尔组沉积末期的氧化环境变为都一段沉积期的还原环境,而且也指示都红木组与腾格尔组的分界面为不整合面,油气正是经由该不整合面从凹陷内部向边缘运移,在凹陷南部斜坡带形成了都一段底部规模较大的砂砾岩稠油油藏。
都二段—都三段岩性相似,以暗色泥页岩发育为特征。都二段主要为深—浅灰色页岩与泥岩的等厚或不等厚互层,偶夹浅灰色粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,俗称“页岩细脖子段”(表 2);都三段主要为厚层灰色泥岩,有时夹浅灰色粉砂质泥岩、粉砂岩、砂岩等,俗称“泥岩细脖子段”(表 2)。
都红木组各段虽均以泥页岩等细粒沉积为主,但都一段泥质白云岩发育,而都二段—都三段不发育。近年来的研究表明(郭强等, 2012, 2014;钟大康等,2015),白音查干凹陷腾格尔组—都一段发育的泥质白云岩为深部热液经由地下深大断裂进入盆地而形成的热水沉积白云岩,与前述白音查干凹陷都二段沉积之前以裂陷为主,而都一段沉积之后以拗陷为主的构造背景相对应。此外,热水沉积白云岩呈现出异常高的自然伽马值(GR=700~ 1100API),为正常泥质岩的2~4倍(郭强等,2014),具异常高的自然伽马的环境对介形类动物的发展可能产生不利的影响❺,致使白音查干凹陷都一段介形类化石的属种和数量均不丰富,而都二段—都三段介形类化石则十分丰富(为白音查干凹陷介形类化石最富集的层位)。地层中介形类化石的丰度大致能反映其沉积期介形类动物群的丰度,而沉积期介形类动物群的丰度主要受当时沉积环境所控制,所以,从古生物的角度也进一步印证了白音查干凹陷都一段与都二段—都三段由沉积环境的较大差别造成其岩性的较大差别。
赛汉塔拉组下部以厚层-块状灰白色砾状砂岩、含砾砂岩、粗砂岩为主,夹薄层灰色泥岩或含砾泥岩,俗称“灰白色厚层砂砾岩段”(表 2),与下伏的都三段暗色泥岩细粒沉积呈突变接触,反映了都红木组沉积末期受构造运动影响沉积环境的较大变化。
白音查干凹陷阿尔善组—都红木组中各组段岩性变化明显,均呈突变接触,与该沉积阶段白音查干凹陷的5个幕式构造演化阶段也相对应,反映了受构造运动的影响,白音查干凹陷阿尔善组—都红木组各组段的沉积环境的较大变化。据此可将白音查干凹陷阿尔善组—都红木组划分为5个长期层序,分别对应于阿一段、阿二段、腾格尔组、都一段和都二段—都三段(图 2)。
4.2.3 地震反射特征
根据地震反射层特征及过井剖面层位标定,在白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组可划分出7个地震反射界面(图 8),即Tg、T8、T7、T6、T5、T4和T3,分别对应于下古生界基底、阿一段、阿二段、腾格尔组、都一段、都二段和都三段的顶界面。
Tg地震反射界面相当于白音查干凹陷下古生界基底顶界面的反射,其内部具杂乱地震反射特征。在坳陷南部斜坡带地震剖面上,Tg表现为2个相位、低频、连续性较好的反射,在凹陷中部及北部陡坡带基底反射不清。该地震反射界面为一区域性角度不整合面,在全凹陷内基本可追踪对比。T8地震反射界面相当于阿一段顶界面,其内部具中—高频、弱连续的地震反射特征,主要与其岩性以砂砾岩为主、成层性较差且埋藏深度较大有关。在地震剖面上T8多表现为单相位、中—弱振幅、连续性相对较差的反射,在全凹陷内基本可追踪对比。T7地震反射界面相当于阿二段顶界面,其内部具中频、连续—弱连续的地震反射特征。在地震剖面上T7表现为多相位、中频、强振幅、连续性较好的反射,在全凹陷内可追踪对比。T6地震反射界面相当于腾格尔组顶界面,其内部具中频、连续—弱连续的地震反射特征。在地震剖面上T6表现为单相位、中振幅、连续性较好的反射,为一区域性不整合面,在全凹陷内可追踪对比。T5地震反射界面相当于都一段顶界面,其内部具中频、弱连续、弱反射的地震反射特征。在地震剖面上T5表现为1~2个强相位组合、强振幅、连续性好,在全凹陷内极易追踪对比。T4地震反射界面相当于都二段顶界面,其内部具中低频、连续、弱反射的地震反射特征。在地震剖面上T4表现为3~4个强相位组合、低频、连续性好的反射,在全凹陷内可较易追踪对比。T3地震反射界面相当于都红木组顶界面,其内部具中低频、连续—较连续的地震反射特征。在地震剖面上T3表现为2~3个强相位组合、低频、连续性好的反射。该地震反射界面层为一区域性角度不整合面,在全凹陷内可较易追踪对比。
以上各地震反射界面特征明显,在白音查干凹陷内基本可追踪对比,其中Tg、T8、T7、T6、T5和T3与白音查干凹陷阿尔善组—都红木组沉积期由5个幕式构造运动所形成的6个长期层序界面及其岩性突变面相对应,可划分为5个长期层序,分别对应于阿一段、阿二段、腾格尔组、都一段和都二段—都三段。
5. 讨论——腾格尔组长期层序底界面性质
从前述构造、古生物、岩性、地震反射等方面的特征,可明显判断出白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组所发育的5个长期层序所对应的6个层序界面中的阿一段底、阿二段底、都一段底、赛汉塔拉组底的4个层序界面为不整合面,而都二段底的层序界面为整合面。关于腾格尔组底的层序界面性质,前人均认为是不整合面,但通过本文进一步研究认为该界面为一整合面,即腾格尔组与阿尔善组为连续沉积、整合接触。
从地层沉积特征方面分析,阿二段沉积期,白音查干凹陷处于构造稳定断陷期,凹陷内水体较深,阿二段主要为非常稳定的暗色泥页岩沉积,而凹陷边缘,特别是南部缓坡带的大部分地区均处于暴露地表的剥蚀夷平状态。至阿二段沉积末期,水域已扩展至凹陷边缘,特别是凹陷南部缓坡带已被水淹没,普遍沉积有厚度不大的阿二段暗色泥页岩。腾格尔组沉积期,白音查干凹陷处于构造震荡断陷期,水体变浅,腾格尔组沉积呈现出明显的下部砂岩发育而上部泥岩发育的下粗上细特点,与下伏阿二段暗色泥页岩的分界较明显。凹陷内腾格尔组与阿尔善组分界面之下的阿二段顶部为稳定的砂泥岩薄互层沉积,其GR测井曲线表现为连续5~6个起伏较大的尖刀状,在凹陷内稳定发育,具有很好的可对比性(图 9),反映其沉积环境较稳定,也表明阿尔善组与腾格尔组为连续无间断的沉积。在凹陷边缘南部缓坡带局部地区(如锡40井—锡43井区),虽然腾格尔组底部发育有含砾砂岩、砂砾岩以及泥质砂砾岩等粗碎屑沉积(图 7e),但其下仍均发育有厚度不大的阿二段暗色泥页岩(图 10),而不是粗碎屑沉积直接覆盖在下古生界变质基底之上,而且粗碎屑沉积均呈灰色,研究认为其主要为水下弱还原—还原条件下形成的水下扇沉积(高红灿等,2015a),反映即使是在凹陷边缘,腾格尔组与阿尔善组分界处的沉积均处于较深的水下环境,也表明腾格尔组与阿尔善组为连续沉积,即白音查干凹陷腾格尔组与阿尔善组为整合接触。由此也说明腾格尔组与阿尔善组的分界面不能构成油气运移的良好通道,在生产上也解释了在腾格尔组底部,即使圈闭条件良好,如锡40井—锡43井区腾格尔组底部的砾质滩坝岩性圈闭(高红灿等,2015a),但也会因缺乏良好的油气运移通道致使圈闭中供油不足而不能成藏的现象。
此外,地层倾角测井能够反映地层产状的变化,可识别一些较高级别的层序地层界线。白音查干凹陷腾格尔组与阿尔善组分界面上下的地层倾角测井所反映出的地层产状基本一致(图 11),也指示其地层应为较稳定的连续沉积,即腾格尔组与阿尔善组为整合接触。
6. 结论
(1)白音查干凹陷下白垩统阿尔善组—都红木组可划分为2个超长期层序(分别对应于阿尔善组—腾格尔组和都红木组)和5个长期层序(分别对应于阿一段、阿二段、腾格尔组、都一段和都二段—都三段),其长期层序界面所对应的阿一段底界面、阿二段底界面、都一段底界面、赛汉塔拉组底界面为不整合面,都二段底界面为整合面。
(2)白音查干凹陷下白垩统腾格尔组长期层序的底界面为一连续沉积的整合面而不是不整合面,不能构成油气运移的良好通道,所以,在腾格尔组底部即使圈闭条件良好(如锡40井—锡43井区),但也会因缺乏良好的油气运移通道致使圈闭中供油不足而不能成藏。
注释
❶张万选, 池英柳, 唐连文. 1995.二连盆地白音查干凹陷西部洼陷层序地层学研究[R].中国石化中原油田勘探开发研究院.
❷张亚敏, 张放东, 司淑平. 2005.白音查干凹陷西部油气精细勘探及目标评价[R].中国石化中原油田勘探开发研究院.
❸蒋飞虎, 林桂芳, 杨静. 1995.白音查干凹陷地层划分与对比[R].中国石化中原油田勘探开发研究院.
❹蒋飞虎, 范迎风, 杨静. 1997.白音查干凹陷、二连盆地地层对比研究[R].中国石化中原油田勘探开发研究院.
❺蒋飞虎, 杨静, 张放东. 2002.白音查干凹陷地层研究[R].中国石化中原油田勘探开发研究院.
❻陶明华. 1994.二连、赤峰盆地地层对比研究[R].中国石油华北油田勘探开发研究院.
❼库国正, 邓已寻, 张放东. 2002.白音查干凹陷构造及发育演化特征研究[R].中国石化中原油田勘探开发研究院.
致谢: 本项研究得到二级项目所属的工程首席科学院吕庆田研究员大力支持并提出了富有建设性建议,深部中心首席科学家董树文研究员、乔德武研究员和朱永宜教授级高级工程师提供了不可或缺的指导和帮助,郝梓国、王学明两位老师给予了精心指导和大力帮助,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
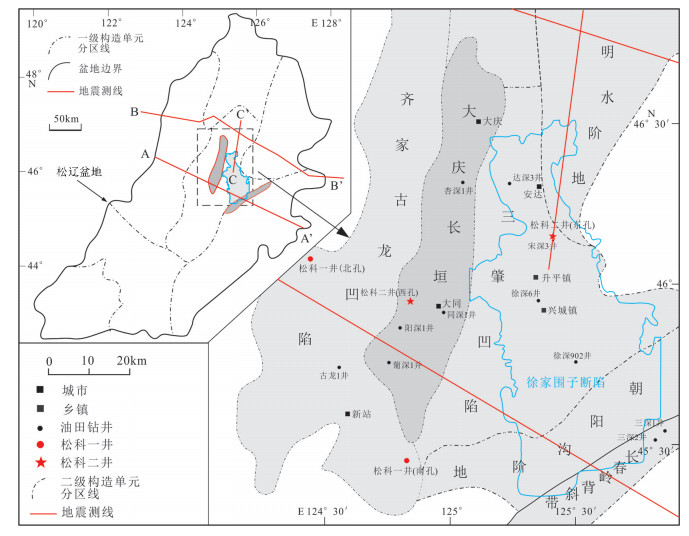
图 1 松辽盆地大陆深部科学钻探工程钻孔分布图(据王璞珺等, 2017, 侯贺晟等,2018)
Figure 1. Borehole distribution of deep continental scientific drilling engineering in Songliao Basin (modified after Wang et al., 2017; Hou et al., 2018)
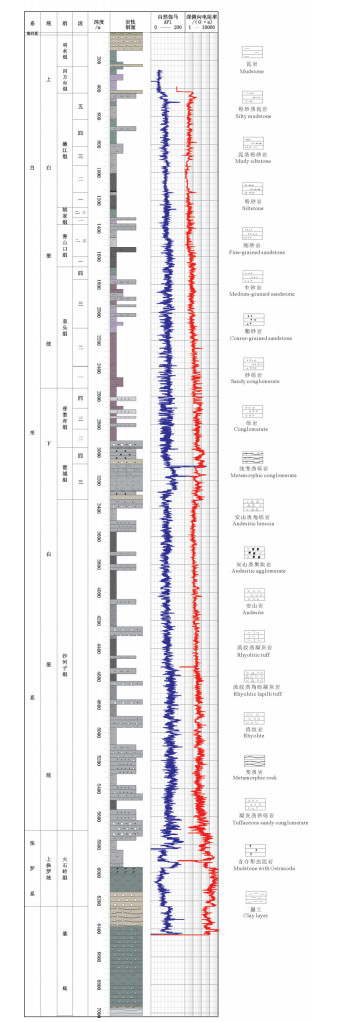
图 2 松科二井岩性综合柱状图(侯贺晟等,2018)
Figure 2. Integrated core histogram of Well SK-2 (after Hou et al., 2018)
-
Chen Haifeng, Wang Fengqi, Wang Min. 2018. Characteristic and resource potential of tight sandy conglomerate gas reservoir in Shahezi formation of Xujiaweizi Depression[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 49(1):141-149(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201801019
Chen Huanqing, Hu Yongle, JinJiuqiang, Ran Qiquan. 2011.Researches on flow unit of the volcanic reservoir in 1st Member of lower Cretaceous Yingcheng Formation, Xudong area, Songliao Basin[J]. Geology in China, 38(6):1430-1439(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201106003
Ding Hongsheng, Sun Zhaolin, ZhangXiaotong. 2004. Analysis of hydrocarbon group composition of light crude oil by capillary gas chromatography[J].Journal of Petrochemical Universities, 4:9-11, 98-99(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syhggdxx200404003
Duan Yi, Zhao Yang, YaoJingli, Zhang Boxiang, Wu Yingzhong, Cao Xixi, Xu Li. 2014. Research advance and tendency of light hydrocarbon geochemistry[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(12):1875-1887(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201412001
Feng Zihui, Yin Changhai, Lu Jiamin, Zhu Yingkang. 2013. Formation and accumulation of tight sandy conglomerate gas:A case from the Lower Cretaceous Yingcheng Formation of Xujiaweizi fault depression, Songliao Basin[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(6):650-656(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SKYK201306003.htm
Gao Lili, Zhang Min, Zhao Hongjing. 2011. Geochemical characteristics of light hydrocarbon in natural gas from Lishu Fault Depression in Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 22(4):709-714(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201104020
Gao Youfeng, Qu Xuejiao, Jiang Lijun, Wang Shuxue, Wang Pujun. 2017. Lithology and stratigraphic interfaces prediction of the Continental Scientific Drilling Project of Cretaceous Songliao Basin (SK2)[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 24(1):242-256(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201701016
Gao Xiang, Gao Youfeng, Qu Xuejiao, Li Honghao, Chen Tong, Wang Pujun. 2017. Volcanic-sedimentary succession description of the Lower Cretaceous Yingcheng Formation based on the ICDP scientific drilling borehole in the Songliao Basin (SK-2)[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 24(1):265-275(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201701018
Ge Rongfeng, Zhang Qinglong, Wang Liangshu, XieAiguo, Xu Shiyin, Chen Juan, Wang Xiyong. 2010. Tectonic evolution of Songliao Basin and the prominent tectonic regime transition in eastern China[J]. Geological Review, 56(2):180-195(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201002004
Guo Wei, Liu Zhaojun, Dong Huimin, Zhao Yujun. 2004. The sequence stratigraphic features and hydrocarbon accumulation of Songliao Basin[J].Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 34(2):216-221(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200402010
He Dian, LiJianghai, Liu Shoujie, Han Liang. 2008. Discovery of a giant caldera in the Yingcheng Formation in the Xujiaweizi fault depression, northern Songliao basin[J].Geology in China, 35(3):463-471(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200803010
Hou Hesheng, Wang Chengshan, Zhang Jiaodong, Ma Feng, Fu Wei, Wang Pujun, Huang Yongjian, Zou Changchun, Gao Youfeng, Gao Yuan, Zhang Laiming, Yang Jin, Guo Rui. 2018. Deep continental scientific drilling engineering in Songliao Basin:Resource discovery and progress in earth science research[J]. Geology in China, 45(4):641-657(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu Guoyi, Luo Xia, Li Zhisheng, Zhang Ying, Yang Chun, Li Jin, Ni Yunyan, Tao Xiaowan. 2010. The geochemical characteristics and origin of light hydrocarbons in biogenic gas[J]. Science China Earth Science, 40(4):426-438(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bfaec2a784a68ac5d12b85a671c532bd
Huang Zhilong, Wang Bin, Zhang Xiuxin, Tang Zhenxing, He Junlin, Lu Xiaoyu. 2013. Evaluation on gas generation potential of Upper Paleozoic source rock in Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 35(3):55-65(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xagcxyxb201303005
Jiang Qigui, Zhang Zhirong, Song Xiaoying, Rao Dan. 2005. Analysis of light hydrocarbon fingerprints and its application[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 24(1):61-64(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb200501012
Li Honghao, GaoYoufeng, WangPujun, Qu Xuejiao, Gao Xiang, Chen Haichao. 2018. Characteristics of top boundary of Shahezi Formation in Xujiaweizi fault depression, northern Songliao Basin:Illustrated by continental scientific drilling borehole SK2[J].Global Geology, 37(3):838-849(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjdz201803015
Li Ning, Zou Changchun, Peng Cheng, Zhao Jinhuan, Niu Yixiong. 2017. Core spatial Position restoring of the CCSD-SK-2 east borehole in the Songliao Basin of Northeast China[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 36(4):271-276(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201704037
Li Yan, Zhang Xiuqi, Lu Xiaoyu, Cui Yang, Tang Zhenxing, Wang Bin, He Junlin, Huang Zhilong. 2013. Characteristics and validity analysis of hydrocarbon source rocks of Upper Paleozoic in Songliao Basin[J].Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 35(4):39-48(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xagcxyxb201304005
Li Yuhuan, Liu Jianying, Liu Huiying. 2010. The theoretic basis and the application principle for light hydrocarbon technology[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 21(1):1-5(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lujgc201001001
Lian Chengbo, Zhang Jianhua, Qu Fang, Wang Zhikun, Yang Jun. 2011. Main factors controlling hydrocarbon accumulation mode of Quan4 Formation in Longxi area, Songliao Basin[J].Geology in China, 38(1):161-169(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201101017
Liang Qianyong, Xiong Yongqiang, Fang Chenqhen, Li Yun. 2015.Geochemical feature of head-space gas components of drill well and its application to petroleum reservoir identification[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 39(4):704-714(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtyht201504008
Liu Bo, LüYanfang, Ran Qingchang, Dai Chunlei, Li Mei, Wang Meng. 2014. Geological conditions and exploration potential of shale oil in Qingshankou Formation, Northern Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 35(2):280-285(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201402018
Liu Wenhui, Wang Xiaofeng, Tenger, Zhang Dianwei, Wang Jie, Tao Cheng, Zhang Zhongning, Zhang Zhongyu, Lu Longfei. 2013.Research progress of gas geochemistry during the past decade in China[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(3):279-289(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201303001
Mango F D. 1997. The light hydrocarbons in petroleum:A critical review[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 26(7):417-440. doi: 10.1016-S0146-6380(97)00031-4/
Qi Shuai, Li Xianqing, He Kun, Zhang Guangwu, Chen Jinming, Gao Wenjie, Liang Wanle. 2017. Comparativeresearch on the yields and chemical compositions of light hydrocarbons derived from pyrolysis of organic matters with different types[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 28(6):975-986(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201706017
Ren Shoumai, QiaoDewu, Zhang Xingzhou, Liu Yongjiang, Wang Nan, Sun Yuewu, Tang Zhenxing, Cui Yongqian. 2011. The present situation of oil & gas resources exploration and strategic selection of potential area in the Upper Paleozoic of Songliao Basin and surrounding area, NE China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(2):197-204(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren Zhanli, Xiao Deming, Chi Yuanlin, Ren Yanguang, Liang Yu. 2011. Restoration of thermal history of the Permo-Carboniferous basement in the Songliao Basin[J].Oil & Gas Geology, 32(3):430-439(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201103016
Shuai Yanhua, Song Nana, Zhang Shuichang, Feng Zihui, Zhu Guangyou, Wang Xue, Huang Haiping. 2011. Gas of biodegradation origin and their pooling characteristics in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 32(5):659-670(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201105004
Wang Min, Sun Yefeng, Wang Wenguang, Wang Yan, Shi Lei. 2014.Gas generation characteristics and resource potential of the deep source rock in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression, northern Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(7):1011-1018(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201407006
Wang Peirong, Xu Guanjun, Zhang Dajiang, Xiao Tingrong, Ren Donglin. 2010. Problems with application of heptane and isoheptane values as light hydrocarbon parameters[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 37(1):121-128(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201001020
Wang Pujun, Liu Haibo, Ren Yanguang, Wang Xiaoqiao, Wang Shuxue, ZhaiXuejiao, Meng Qi'an, Huang Yongjian, Huang Qinghua, Gao Youfeng. 2017. How to choose a right drilling site for the ICDP Cretaceous Continental Scientific Drilling in the Songliao Basin (SK2), Northeast China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(1):216-228(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201701014
Wang Zhihong, Li Jian, Xia Li. 2014. Distribution forecast of source rocks and gas generation potential of Shahezi Formation in deep fault depressions of Songliao Basin[J].Global Geology, 33(3):630-639(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SJDZ201403015.htm
Wu Changjin, Ma Changwei, Zhang Kecao. 2012. Application of light hydrocarbon analysis logging in Hailar Basin[J].Engineering Sciences, 14(4):49-57(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zggckx201204011
Wu Zhenwei, Zeng Zhaofa, Li Jing, Zhao Xueyu, Xu Tianfu. 2015.Distribution of basement lithology in the Songliao Basin derived from gravity and magnetic anomalies[J].Geology and Exploration, 51(5):939-945(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201505014
Xia Yongjiang, Wang Yanbin, Wang Xiaobo, Zhang Ying, Wang Dongliang, Li Zhisheng, Yang Chunxia. 2012. Main controlling factors in the shallow-gas reservoir formation and its favorable exploration area in the northern Songliao Basin[J].Acta PetroleiSinica, 33(6):961-969(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201206006
Zhang Junfeng, Xu Hao, Zhao Junlong, Ren Pengfei. 2018. Geological characteristics and exploration potential of oil and gas in the northeast area of China[J]. Geology in China, 45(2):260-273(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201802004
Zhang Min, Zhang Jun. 1998. Development and application of Mango's light hydrocarbon parameters[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 25(6):43-45, 5-6, 12(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800522003
Zhang Shuxia, Zou Changchun, Peng Cheng, Zhao Jinhuan, Li Ning, Zhang Xiaohuan, Ma Huolin, NiuYixiong. 2018. Abnormally high natural radioactivity zones in the main borehole of the Continental Scientific Drilling Project of Cretaceous Songliao Basin:Geophysical log responses and genesis analysis[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(11):4712-4728(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xiaodong, Yu Jing, Zhang Dazhi, Lu Jiamin, Xiao Limei, Li Guozheng. 2014. Accumulation conditions and exploration prosopects for Shahezi-Formation tight sandstone gas in Xujiaweizi fault depression[J].Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 33(5):86-91(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zang Zhili, Cai Xiyao, Zang Ming, Li Jingchang, Zhang Ying. 2014.An analysis of the relationship between types of ostracoda shell ornaments and shell shapes and the environment from Late Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation to 1st Member of Nenjiang Formation in Songliao Basin[J].Geology in China, 41(1):135-147(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201401010
Zhao Zehui, Xu Shujuan, Jiang Xiaohua, Lin Changsong, Cheng Honggang, Cui Junfeng, Jia Li. 2016. Deep strata geologic structure and tight sandy conglomerate gas exploration in Songliao Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration & Development Online, 43(1):13-23(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zou Changchun, Xiao Liang, NiuYixiong, HouJie, Peng Cheng. 2016.General design of geophysical logging of the CCSD-SK-2 East Borehole in the Songliao Basin of Northeast China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(3):279-287(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201603031
Zou Changchun, Zhang Xiaohuan, Zhao Jinhuan, Peng Cheng, Zhang Shuxia, Li Ning, Xiao Liang, NiuYixiong, Ding Yujiao, Qin Yuxing, Lin Feng. 2018. Scientific results of geophysical logging in the Upper Cretaceous strata, CCSD SK-2 east borehole in the Songliao Basin of Northeast China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(6):679-690(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201806005
陈海峰, 王凤启, 王民. 2018.徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密砂砾岩气藏特征与资源潜力[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 49(1):141-149. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zngydxxb201801019 陈欢庆, 胡永乐, 靳久强, 冉启全. 2011.松辽盆地徐东地区下白垩统火山岩储层流动单元研究[J].中国地质, 38(6):1430-1439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.003 丁洪生, 孙兆林, 张晓彤. 2004.毛细管气相色谱法分析轻烃族组成[J].石油化工高等学校学报, 17(4):9-11, 98-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-396X.2004.04.003 段毅, 赵阳, 姚泾利, 张伯祥, 吴应忠, 曹喜喜, 徐丽. 2014.轻烃地球化学研究进展及发展趋势[J].天然气地球科学, 25(12):1875-1887. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.12.1875 冯子辉, 印长海, 陆加敏, 朱映康. 2013.致密砂砾岩气形成主控因素与富集规律——以松辽盆地徐家围子断陷下白垩统营城组为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 40(6):650-656. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201306002 高丽丽, 张敏, 赵红静. 2011.松辽盆地南部梨树断陷天然气轻烃地球化学研究[J].天然气地球科学, 22(4):709-714. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201104020 高有峰, 瞿雪姣, 蒋丽君, 王树学, 王璞珺. 2017.松辽盆地白垩系大陆科学钻探松科二井钻遇地层界面及岩性剖面预测[J].地学前缘, 24(1):242-256. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201701021.htm 高翔, 高有峰, 瞿雪姣, 李宏浩, 陈桐, 王璞珺. 2017.松辽盆地松科二井下白垩统营城组火山-沉积序列精细刻画[J].地学前缘, 24(1):265-275. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201701023.htm 葛荣峰, 张庆龙, 王良书, 解国爱, 徐士银, 陈娟, 王锡勇. 2010.松辽盆地构造演化与中国东部构造体制转换[J].地质论评, 56(2):180-195. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201002004 郭巍, 刘招君, 董惠民, 赵羽君. 2004.松辽盆地层序地层特征及油气聚集规律[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 34(2):216-221. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb200402010 贺电, 李江海, 刘守偈, 韩亮. 2008.松辽盆地北部徐家围子断陷营城组大型破火山口的发现[J].中国地质, 35(3):463-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.03.010 侯贺晟, 王成善, 张交东, 马峰, 符伟, 王璞珺, 黄永建, 邹长春, 高有峰, 高远, 张来明, 杨瑨, 国瑞. 2018.松辽盆地大陆深部科学钻探地球科学研究进展[J].中国地质, 45(4):641-657. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180401&flag=1 胡国艺, 罗霞, 李志生, 张英, 杨春, 李瑾, 倪云燕, 陶小晚. 2010.生物气中轻烃分布特征及其成因[J].中国科学:地球科学, 40(4):426-438. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7260064 黄志龙, 王斌, 张秀颀, 唐振兴, 贺君玲, 逯晓喻. 2013.松辽盆地上古生界烃源岩生气潜力评价[J].地球科学与环境学报, 35(3):55-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.005 蒋启贵, 张志荣, 宋晓莹, 饶丹.2005.轻烃指纹分析及其应用[J].地质科技情报, 24(1):61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2005.01.012 李宏浩, 高有峰, 王璞珺, 瞿雪姣, 高翔, 陈海潮. 2018.松辽盆地徐家围子断陷沙河子组顶界面特征研究——基于松辽盆地大陆科学钻探松科二井[J].世界地质, 37(3):838-849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2018.03.015 李宁, 邹长春, 彭诚, 赵金环, 牛一雄. 2017.松辽盆地科学钻探工程松科二井东孔岩心空间归位[J].地质科技情报, 36(4):271-276. 李艳, 张秀颀, 逯晓喻, 崔洋, 唐振兴, 王斌, 贺君玲, 黄志龙. 2013.松辽盆地上古生界烃源岩特征及有效性分析[J].地球科学与环境学报, 35(4):39-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.04.005 李玉桓, 刘建英, 刘慧英. 2010.轻烃录井技术的理论基础和应用原理[J].录井工程, 21(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9803.2010.01.001 连承波, 钟建华, 渠芳, 王志坤, 杨军.2011.松辽盆地龙西地区泉四段油气成藏主控因素及模式[J].中国地质, 38(1):161-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.01.017 梁前勇, 熊永强, 房忱琛, 李芸. 2015.钻井罐顶气组分地球化学特征及其在储层辨识中的应用[J].物探与化探, 39(4):704-714. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201504008 刘波, 吕延防, 冉清昌, 戴春雷, 李梅, 王猛. 2014.松辽盆地北部青山口组页岩油形成地质条件及勘探潜力[J].石油与天然气地质, 35(2):280-285. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201402018 刘文汇, 王晓锋, 腾格尔, 张殿伟, 王杰, 陶成, 张中宁, 卢龙飞. 2013.中国近十年天然气示踪地球化学研究进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(3):279-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.03.001 祁帅, 李贤庆, 何坤, 张光武, 陈金明, 高文杰, 梁万乐. 2017.不同类型有机质热演化轻烃产率及组成特征对比[J].天然气地球科学, 28(6):975-986. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201706017 任收麦, 乔德武, 张兴洲, 刘永江, 王楠, 孙跃武, 唐振兴, 崔永谦. 2011.松辽盆地及外围上古生界油气资源战略选区研究进展[J].地质通报. 30(2):197-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.02.003 任战利, 萧德铭, 迟元林, 任延广, 梁宇.2011.松辽盆地基底石炭-二叠系热演化史[J].石油与天然气地质, 32(3):430-439. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201103016 帅燕华, 宋娜娜, 张水昌, 冯子辉, 朱光有, 王雪, 黄海平. 2011.松辽盆地北部生物降解成因气及其成藏特征[J].石油与天然气地质, 32(5):659-670. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201105004 王民, 孙业峰, 王文广, 王岩, 石蕾. 2014.松辽盆地北部徐家围子断陷深层烃源岩生气特征及天然气资源潜力[J].天然气地球科学, 25(7):1011-1018. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201407006 王培荣, 徐冠军, 张大江, 肖廷荣, 任冬苓. 2010.常用轻烃参数正、异庚烷值应用中的问题[J].石油勘探与开发, 37(1):121-128. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201001020 王璞珺, 刘海波, 任延广, 万晓樵, 王树学, 瞿雪姣, 蒙启安, 黄永建, 黄清华, 高有峰.2017.松辽盆地白垩系大陆科学钻探"松科二井"选址[J].地学前缘, 24(1):216-228. 王志宏, 李剑, 夏利. 2014.松辽盆地深层断陷沙河子组烃源岩分布预测与生气潜力[J].世界地质, 33(3):630-639. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjdz201403014 吴长金, 马昌伟, 张可操. 2012.轻烃分析录井技术在海拉尔盆地的应用[J].中国工程科学, 14(4):49-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.04.011 吴真玮, 曾昭发, 李静, 赵雪宇, 许天福. 2015.基于重磁场特征的松辽盆地基底岩性研究[J].地质与勘探, 51(5):939-945. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201505014 夏永江, 王延斌, 王晓波, 张英, 王东良, 李志生, 杨春霞. 2012.松辽盆地北部浅层气成藏主控因素及勘探有利区[J].石油学报, 33(6):961-969. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201206006 张君峰, 许浩, 赵俊龙, 任鹏飞. 2018.中国东北地区油气地质特征与勘探潜力展望[J].中国地质, 45(2):260-273. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180204&flag=1 张敏, 张俊. 1998. Mango轻烃参数的开发与应用[J].石油勘探与开发, 25(6):43-45, 5-6, 12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800522003 张淑霞, 邹长春, 彭诚, 赵金环, 李宁, 张小环, 马火林, 牛一雄. 2018.松科二井东孔营城组高放射性异常层测井响应特征及成因初探[J].地球物理学报, 61(11):4712-4728. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0210 张晓东, 于晶, 张大智, 陆加敏, 肖利梅, 李国政. 2014.徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密气成藏条件及勘探前景[J].大庆石油地质与开发, 33(5):86-91. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2014.05.014 张智礼, 蔡习尧, 张铭, 李京昌, 张莹. 2014.松辽盆地晚白垩世青山口组-嫩江组一段介形类壳饰、壳形类型与环境关系分析[J].中国地质, 41(1):135-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.010 赵泽辉, 徐淑娟, 姜晓华, 林畅松, 程宏岗, 崔俊峰, 贾丽. 2016.松辽盆地深层地质结构及致密砂砾岩气勘探[J].石油勘探与开发, 43(1):12-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201601002 邹长春, 肖亮, 牛一雄, 侯颉, 彭诚. 2016.松辽盆地科学钻探工程松科二井东孔测井设计[J].地学前缘, 23(3):279-287. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201603036.htm 邹长春, 张小环, 赵金环, 彭诚, 张淑霞, 李宁, 肖亮, 牛一雄, 丁娱娇, 秦宇星, 林峰. 2018.松辽盆地科学钻探工程松科二井东孔上白垩统地球物理测井科学成果[J].地球学报, 39(6):679-690. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201806005 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 张京,王玮莹. 地下水中偏硅酸测定的两种常用方法研究. 山西化工. 2024(02): 53-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李哲,王力娜. 不同水文地质条件对城市地下水资源污染的影响研究. 环境科学与管理. 2024(06): 120-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王波,赵莉,陈晓梅,朱广毅,张高引. 洱海流域天然出露矿泉水资源特征及远景评价. 中国岩溶. 2024(06): 1275-1286 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵德杨,周晓成,何苗,天娇,李静超,董金元,颜玉聪,欧阳澍培,刘峰立,姚炳宇,王昱文,曾召君,陈曲菲,张晓明,杨耀,罗志鑫. 大凉山断裂带温泉水文地球化学特征. 地震研究. 2023(01): 26-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周长松,李军,邹胜章,林永生,卢丽,樊连杰,王佳,吴树诚. 乌蒙山区“地质调查+”经济发展模式研究——以昭觉县为例. 中国地质调查. 2023(06): 120-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李状,苏晶文,董长春,叶永红,杨洋. 安徽马鞍山市当涂地区地下水水化学特征及演化机制. 中国地质. 2022(05): 1509-1526 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 吴丽霞,曾彩璇. 广东典型山区县地下水化学特征与水质评价研究. 地下水. 2022(06): 57-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: