Genesis and paleoenvironment of the iron ooids from the Ganxi prolife of the Devonian Yangmaba Formation in Beichuan County, Longmenshan Area
-
摘要:
龙门山区中泥盆统养马坝组底部发育丰富的铁质鲕粒。为分析该铁质鲕粒成因,本文以甘溪石沟里剖面精细实测为基础,通过详细的薄片和扫描电镜等分析,对铁质鲕粒的特征进行了研究,分析结果表明:龙门山区北川甘溪泥盆系养马坝组鲕粒类型多样,鲕粒核心包括石英碎屑颗粒、海百合碎片、黑色赤铁矿和方解石等4种类型,鲕粒圈层可分为明暗相间圈层、颜色均匀圈层和绿泥石圈层等3种类型。根据鲕粒核心和外部圈层的组合,可将甘溪泥盆系养马坝组的铁质鲕粒划分为粉砂质鲕粒、铁化鲕粒和绿泥石薄皮鲕粒等3种类型。龙门山区北川甘溪泥盆系养马坝组铁质鲕粒对古环境具有重要的指示意义,粉砂质鲕粒形成于开放近岸浅海氧化环境,而铁化鲕粒和绿泥石薄皮鲕粒则指示浅海滨岸中相对封闭的泻湖与残积鲕粒滩环境。
Abstract:There exist abundant iron ooids at the bottom of the Middle Devonian Yangmaba Formation in the Longmenshan area. In order to analyze the genesis of the iron ooids, their characteristics were studied by means of thin section and scanning electron microscope based on the detailed measurement of the Shiligou Profile in Ganxi village. The analysis results show that there are various types of ooids in Middle Devonian Yangmaba Formation of Longmenshan area. The ooidal cores include four types:quartz clastic particles, crinoid fragments, black hematite and calcite. The outer laminas of ooids can be divided into three types:alternate dark and bright one, uniform-colored one and chlorite-fragmented one. The iron ooids of Middle Devonian Yangmaba Formation in the Longmenshan area have an important significance to the ancient environment. The silty ooids were formed in the open environment nearshore shallow water under oxidation condition, and iron ones and chlorite ones with thin layers were deposited in the relatively closed lagoon and residual ooids beach of shallow seashore.
-
1. 研究目的(Objective)
尼玛盆地构造上位于班公湖—怒江缝合带中部,是发育在侏罗系—白垩系海相地层之上的古近系陆相裂谷盆地,北接羌塘地块,南邻冈底斯地块,近东西向展布,面积约3000 km2。本次研究目的是初步查明尼玛盆地东部冻土发育特征,调查盆地东部古近系地层层序,获取古近系烃源岩、储盖层等关键评价参数,进一步评价盆地油气资源潜力。
结合新获取的大地电磁测深、地表地质调查及藏尼地1井资料,通过对盆地东部石油地质条件的进一步论证,中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心在盆地东部赛布错坳陷部署实施了藏双地1井,该井的实施对于西藏高原陆相盆地的油气勘探具有重要意义。
2. 研究方法(Methods)
通过资料的收集和重新处理解释,建立了尼玛盆地基础资料数据库,结合之前在尼玛盆地东部发现的油气显示带及最新的大地电磁测深和藏尼地1井资料,优选井位。藏双地1井完钻井深1206.78 m,全井段进行了取心、录井和测井,共有岩心407箱,岩心总长1108.88 m,收获率95.9%。在古近系牛堡组选取烃源岩样品进行地球化学分析测试,通过分析有机质丰度、有机质类型、热演化成熟度来评价烃源岩生烃潜力;使用荧光分析仪对岩石进行荧光分析,主要进行干照和滴照实验,来检测岩石、岩屑中的沥青、烃类等有机物质。
3. 结果(Results)
藏双地1井从上到下钻遇地层依次为第四系+ 新近系—牛堡组三段—牛堡组二段(未穿),气测录井有3处气测异常段,总烃最高为0.159%,岩性为棕红色粉砂岩、灰色细砂岩。含气量解析取样井段527.90~1206.78 m,共取样54个,现场解析在标准大气压下最高含气量为0.213 m3/t;共做浸水试验20个,拍摄视频20个,其中井深744.40 m、752.08 m、767.30 m、774.66 m、797.20 m、832.43 m均有气泡冒出,以井深752.08 m最为明显。
荧光录井井段0~1206.78 m,对全井岩心按设计逐包进行荧光直照、拍照、氯仿浸泡,定级;全井共录取荧光资料421个点,其中井深1024.23~1026.23 m牛二段灰绿色泥岩断面处,可见黑色薄膜状干沥青,具荧光显示,干照下呈黄色、淡黄色,产状为星点状、带状,用氯仿滴照可呈片状;井深1077.46~1077.76 m牛二段见油迹;井深1078.16~1078.76 m牛二段见点状干沥青;井深1078.76~1079.16 m牛二段层理间见油斑;井深1079.16~1080.16 m牛二段顶部断面处见油迹,都具有荧光显示,呈黄色、淡黄色,产状为星点状、带状(图 1)。
4. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)藏双地1井全井取心,获得了尼玛盆地东部古近系地层层序、烃源岩及储层等相关参数,分别在牛三段418.43~422.00 m、牛二段890.00~898.00 m及1068.16~1087.00 m发现3处气测异常段,总烃最高为0.159%,现场解析含气量值最大为0.213 m3/t,并在牛二段1077~1080 m处发现不同级别的油气显示,首次实现了尼玛盆地地下油气的重要发现,对盆地下一步的勘探部署具有重要意义。
(2)本井是继藏尼地1井后在西藏尼玛盆地部署实施的第2口地质调查井,通过对藏双地1井的钻井技术攻关,进一步总结出了适合高寒缺氧、地表及地下地质条件复杂的高原钻井施工工艺和设备参数,为下一步在该区钻井施工提供了重要的技术支撑。
尼玛盆地平均海拔近4800 m,由于其高海拔的特殊性,具有高寒缺氧、气候恶劣、生态脆弱等特征,在野外施工过程中与其他地区有着很大的不同,通过藏尼地1井、藏双地1井的钻探,克服了高寒条件下冻土发育钻井技术难题和高原缺氧条件下深井取心难题,基本形成了一套安全、环保、高效的作业技术体系,为高原地区的钻探施工工程积累了丰富的经验。
5. 致谢(Acknowledgement)
感谢李韬、李显亮等同志的交流和启发。
-
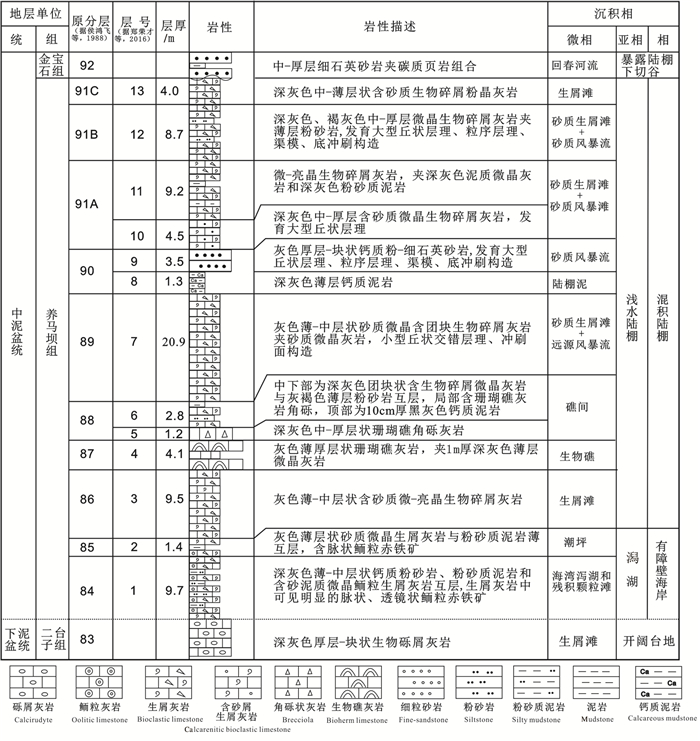
图 2 龙门山区石沟里养马坝组沉积综合柱状图(据侯鸿飞等,1988;郑荣才等,2016等文献修编)
Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Yangmaba Formation in the Shigouli profile, Longmenshan area, Sichuan Basin (modified from Hou et al., 1988; Zheng et al., 2016)
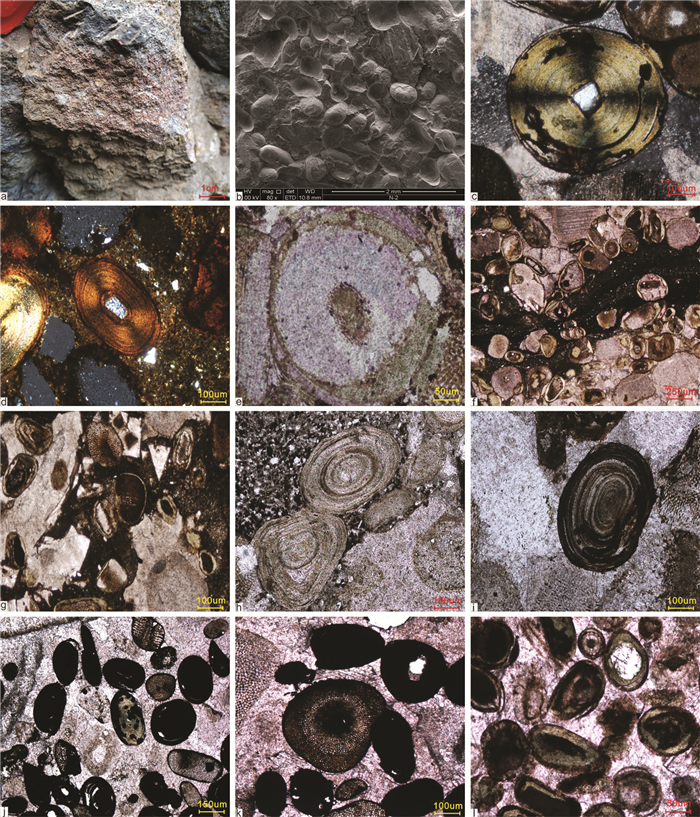
图 4 龙门山区石沟里养马坝组铁质鲕粒岩石特征照片
a—铁质鲕粒灰岩,野外宏观照片,可见红色鲕粒赤铁矿呈透镜状分布于生屑灰岩,第7层;b—鲕粒生屑灰岩,鲕粒呈球状、椭球状,SEM,N-2;c—鲕粒生屑灰岩,真鲕,核心为单晶石英颗粒,少量铁质,沿鲕粒纹层分布,N-2;圆形鲕粒,N-1;鲕粒形态,SEM,N-2;d—粉砂质鲕粒生屑灰岩,真鲕,核心为多晶石英颗粒,基质中分布石英颗粒,正交偏光下鲕粒呈十字消光,N-1;e—鲕粒生屑灰岩,海百合核心,绿泥石纹层,薄皮鲕,B1-2;f—生屑鲕粒灰岩,鲕粒核心为海百合碎片,薄皮鲕,纹层成分绿泥石质,基质为黑褐色赤铁矿,N-4;g—生屑鲕粒灰岩,鲕粒核心为海百合碎片和赤铁矿,薄皮鲕,纹层成分绿泥石质,基质为黑褐色赤铁矿,N-4;h—生屑鲕粒灰岩,真鲕,鲕粒核心不明显,B1-3;i—生屑鲕粒灰岩,铁质含量丰富,沿鲕粒纹层分布,B1-3;j—生屑鲕粒灰岩,铁质鲕粒,海百合内充填铁质,B1-3;k—生屑鲕粒灰岩,铁质鲕粒,海百合内充填铁质,B1-3;l—生屑鲕粒灰岩,鲕粒核心为海百合碎片和赤铁矿,薄皮鲕,纹层成分绿泥石质,基质为黑褐色赤铁矿,B2-2-1
Figure 4. Photos of rocks with iron ooids from the Shigouli profile in the Yangma Formation, Longmenshan area
a- Ferric oolitic limestone. In the field macroscopic photos, it can be seen that red oolitic hematite is distributed lenticular in bioclastic limestone, the 7th layer; b-Bioclastic oolitic limestone, globular and ellipsoidal oolitic, SEM, N-2; c-Bioclastic oolitic limestone, true oolite, core is single crystal quartz grain, a small amount of iron distributed along oolitic striatum, N-2; Round oolite, N -1; Oolite morphology, SEM, N-2; d-Silt-bioclastic oolitic limestone, true oolite, core is polycrystalline quartz grain, quartz grain distribution in the matrix, cross extinction under orthogonal polarization, N-1; e- o Bioclastic oolitic limestone, core of crinoids, chloritic stromatolite, thin-skinned oolite, b1-2; f-Bioclastic oolitic limestone, oolitic core is fragments of crinoids, thin-skinned oolitic, striatum composition is chloritic, matrix is black brown hematite, n-4; g- Bioclastic oolitic limestone, oolitic core is crinoids fragments and hematite, thin crust oolitic, striatum composition is chloritic, matrix is black brown hematite, N-4; hBioclastic oolitic limestone, true oolite, oolitic core is not obvious, B1-3; i-Bioclastic oolitic limestone, rich in iron, distributed along oolitic striatum, B1-3; j- Bioclastic oolitic limestone, ferric oolitic, ferric fill in crinoids, B1-3; k-Bioclastic oolitic limestone, ferruginous oolitic, ferric fill in crinoids, B1-3; l- Bioclastic oolitic limestone, oolitic core consists of crinoids fragments and hematite, thin-skinned oolitic, striatum composition is chloritic, matrix is black brown hematite, B2-2-1
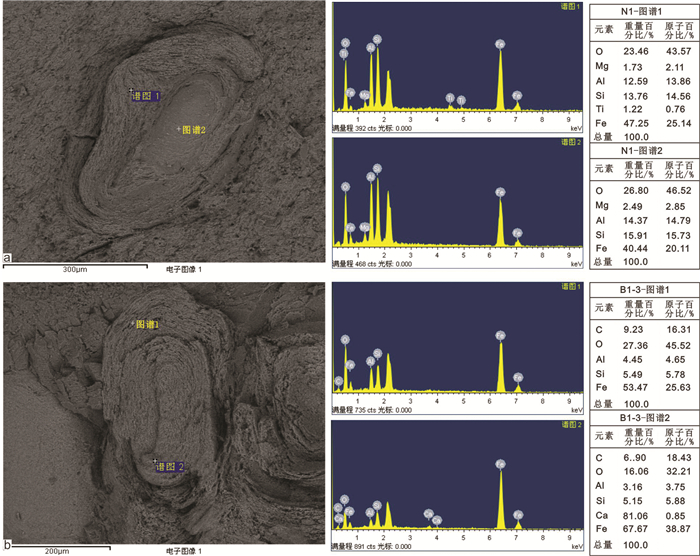
图 5 龙门山区石沟里养马坝组铁质鲕粒能谱分析
a—鲕粒能谱分析位置图,在鲕粒核心和外部圈层中铁的赋存形式是Fe2O3(赤铁矿),N-1;b—鲕粒能谱分析位置图,在鲕粒核心和外部圈层中铁的赋存形式是FeCO3(菱铁矿),B1-3
Figure 5. Energy spectrum analysis of iron ooids from the Shigouli profile of the Yangma Formation, Longmenshan area
a-Energy spectrum analysis location diagram, in the oolite core and the outer ring, the occurrence of iron is Fe2O3 (hematite), N-1; b-Energy spectrum analysis location diagram, the occurrence form of iron in the oolite core and outer ring is FeCO3 (siderite), B1-3
-
Dai Yongding, Song Haiming, Shen Jiying. 2003. Iron fossil bacterial from the Xuanlong area, Hebei Province[J]. Science in China(Series D), 33(8):751-759(in Chinese).
Franceschelli M, uxeddu M, Carta M. 2000. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Late Ordovician phosphate-bearing oolitic ironstones from NW Sardinia, Italy[J]. Mineralogy & Petrology, 69(3/4):267-293. doi: 10.1007/s007100070024
Greensmith J T. 1989. Ferruginous deposits[M]//Petrology of the Sedimentary Rocks. Springer Netherlands, 165-181.
Gygi R A. 1981. Oolitic iron formations:marine or not marine[J]. Eclogae. Geol. Helv., 74:233-254. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284386684_Oolitic_iron_formations_Marine_or_not_marine
Jing Xigui, Li Fengjie, Cheng Xiaoyu, Yang Xiaoqi, Zhang Hao, Shen Fan. 2018. Trace fossils of hybrid facies from Early-Middle Devonian strata in Longmenshan area, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 45(2):377-391(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/328850820_Trace_fossils_of_hybrid_facies_from_Early-Middle_Devonian_strata_in_Longmenshan_area_Sichuan_Province
Joachimski M M, Breisig S, Buggisch W. 2009. Devonian climate and reef evolution:Insights from oxygen isotopes in apatite[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 284:599-609. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.05.028
Hou Hongfei, Wan Zhengquan, Xian, Siyuan. 1988. Devonian Stratigraphy, Paleontology and Sedimentary Facies of Longmenshan, Sichuan[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-100(in Chinese).
Hou Kui, Chen Zhiming, Yu Hao. 1983. Ore fabric and effect of blue algae on iron richment in Xuanlong ironmine, Hebei[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, (3):246-250(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX198303005.htm
Houten, F B V. 1992. Review of Cenozoic ooidal ironstones[J]. Sediment. Geol., 78:101-110. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(92)90115-8
Hu Ning, Xu Anwu. 1998. Horizon, Lithofacies and genesis of the Ningxiang-tape iron deposit in western Hubei, China[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 13(1):40-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzzk801.004.htm
Hui Bo. 2014. The Sedmentary Characteristics and Genesis of the Ningxiang-type Iron Ore in the West of Hubei Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1-134(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Xianghui, Liu Wenjun, Zheng Rongcai. 1997. Hybird facies and mechanism for the formation of the mixed Devonian carbonate-siliciclastic sediments in the Longmen Mountain area, Sichaun[J]. Facies Paleogeogr., 17(3):339-344(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/291970579_Hybrid_facies_and_Mechanism_to_the_formation_of_mixed_carbonate_and_siliciclastic_sediments_in_the_Devonian_in_the_Longmen_Mt_area_Sichuan_in_Chinese_with_English_abstract
Li Xianghui, Liu Wenjun, Zheng Rongcai. 1998. Frequency, amplitude, and pattern of sea-level changes in Devonian in Longmen mountains, western Yangtze[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 25(4):495-502(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG804.003.htm
Liao Shifan, Wei Lianghong, Liu Chengde, Zhang Xueshou, Ran Chongyin, Shi Qingqin. 1993. Sedimentary environments and origin of the Devonian oolitie ironstones in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 11(1):93-102(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Baojun, Yang Zhihua. 1990. Devonian sedimentary environments and basin evolution in Zhashui-Zhen'an district, East Qinling, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 8(4):3-12(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199004000.htm
Liu Wenjun, Chen Yuanren, Zheng Rongcai. 1996. Devonian sequence stratigraphy and relative sea-level changes in Longmenshan area, Sichuan[C]//Liu Wenjun, Chen Yuanren, Zhong Rongcai. Sequence Stratigraphy. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract).
Rahiminejad A H, Zand-Moghadam H. 2018. Synsedimentary formation of ooidal ironstone:an example from the Jurassic deposits of SE central Iran[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 95:238-257. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.02.028
Simon L, Goddéris Y, Buggisch W, Strauss H, Joachimski M M. 2007. Modeling the carbon and sulfur isotope compositions of marine sediments:Climate evolution during the Devonian[J]. Chemical Geology, 246:19-38. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.08.014
Sorby H C. 1894. On the structure and origin of limestones[J]. GeolSoc London, 35:56-95. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/240675777_Structure_and_origin_of_limestones
Wu Xiangfeng, Yi Haisheng, Hui Bo, Yang Wei, Du Qiuding. 2010. Genesis and sedimentary environments of the ferruginous ooids from the Majiaoba Formation in northern Longmen Mountains, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 30(1):25-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201001004.htm
Xu Antao, Li Fengjie, Liu Kui, Xiang Pengfei, Zhao Chenyuan, Hu Peng. 2018. The characteristics and sedimentary model of Storm deposits in the Lower Devonian strata of Beichuan[J]. Geology in China, 45(5):1049-1062(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201805013.htm
Young T P. 1989. Phanerozoic ironstones: an introduction and review[C]//Young T P, Taylor W E G(eds.). Phanerozoic Ironstones. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., 46: ix-xxv.
Zhang Yang, Xi Wenkun, Li Yilong, Zhang Xionghua. 2009. Carboniferous oolitic hematite in Longmenshan area of Sichuan Province and its paleoenvironmental significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 28(1):51-57(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz200901007
Zhao Yiming, Bi Chengsi. 2000. Time-space distribution and evolution of the Ningxiang type sedimentary iron deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 19(4):350-362(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200004007.htm
Zheng Rongcai, Wen Huaguo, Wang Changyong, Chang Hailiang. 2016. Guide to the Field Practice of the Devonian in Longmen Mountain[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-262(in Chinese).
Zhou Jiayun, Zheng Rongcai, Zhang Yushu, Zhu Zhimin, Li Xiaoyu, Luo Liping, Zhou Mangeng. 2009. Constraints of South China Devonian Ningxiang palaeogeography on the temporal and spatial distribution of iron ore deposits and their characteristics[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 28(1):93-98(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Shixing. 1980. Ferreous stromatolite and its significance in the Xuanlong area, Heibei province[J]. Bulletin of the Tianjin Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1(1):70-88(in Chinese with English abstract).
戴永定, 宋海明, 沈继英. 2003.河北宣龙铁矿化石细菌[J].中国科学(D辑), 33(8):751-759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200308005.htm 荆锡贵, 李凤杰, 成晓雨, 杨晓琪, 张昊, 沈凡. 2018.四川龙门山地区早-中泥盆世混积相遗迹化石及其环境分析[J].中国地质, 45(2):377-391. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180212&flag=1 侯鸿飞, 万正权, 鲜思远. 1988.四川龙门山地区泥盆纪地层古生物及沉积相[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-100. 侯奎, 陈志明, 于浩. 1983.宣龙铁矿矿石组构特征及蓝藻对铁的富集作用[J].地质科学, (3):246-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198303005.htm 胡宁, 徐安武. 1998.鄂西宁乡式铁矿分布层位岩相特征与成因探讨[J].地质找矿论丛, 13(1):40-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK801.004.htm 惠博. 2014.鄂西宁乡式铁矿沉积特征及成因[D].成都理工大学, 1-134. 李祥辉, 刘文均, 郑荣才.1997.龙门山地区泥盆纪碳酸盐与硅质碎屑的混积相与混积机理[J].岩相古地理, 17(3):339-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD199703002.htm 李祥辉, 刘文均, 郑荣才. 1998.龙门山地区泥盆纪海平面升降规程、频幅及对比[J].成都理工学院学报, 25(4):495-502. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG804.003.htm 廖士范, 魏梁鸿, 刘成德, 张学寿, 冉崇英, 史清琴. 1993.中国泥盆纪鲕铁石沉积环境、成因[J].沉积学报, 11(1):93-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199301010.htm 刘宝珺, 杨志华. 1990.东秦岭柞水-镇安地区泥盆纪沉积环境和沉积盆地演化[J].沉积学报, 8(4):3-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199004000.htm 刘文均, 陈源仁, 郑荣才. 1996.龙门山地区泥盆纪层序地层划分、对比和海平面相对变化[C]//刘文均, 陈源仁, 郑荣才.层序地层[C].成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1-11. 武向峰, 伊海生, 惠博, 杨伟, 杜秋定.2010.四川龙门山马角坝组铁质鲕粒成因及沉积环境[J].沉积与特提斯地质, ,30(1):25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201001004.htm 许安涛, 李凤杰, 刘奎, 向鹏飞, 赵晨圆, 胡鹏.2018.北川甘溪下泥盆统风暴岩沉积特征及其沉积模式[J].中国地质, 45(5):193-205. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180512&flag=1 张扬, 郄文昆, 李益龙, 张雄华. 2009.四川龙门山石炭纪鲕状赤铁矿及其古环境意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 28(1):51-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2009.01.007 赵一鸣, 毕承思. 2000.宁乡式沉积铁矿床的时空分布和演化[J].矿床地质, 19(4):350-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2000.04.008 郑荣才, 文华国, 王昌勇, 常海亮. 2016.龙门山泥盆系野外实习指南[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-262. 周家云, 郑荣才, 张裕书, 朱志敏, 李潇雨, 罗丽萍, 周满耿. 2009.华南泥盆纪古地理环境对宁乡式铁矿床时空分布、矿石特征的制约[J].地质科技情报, 28(1):93-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.01.015 朱世兴. 1980.河北宣龙区的铁质叠层石及其意义[J].中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所所刊, 1(1):70-88. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198012001007.htm -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张云,张天福,程先钰,孙立新,程银行,王少轶,王善博,马海林,鲁超. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部侏罗纪含铀岩系三维地质结构与铀成矿规律浅析. 中国地质. 2022(01): 66-80 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 庞康,吴柏林,孙涛,郝关清,雷安贵,杨松林,刘池阳,傅斌,权军明,王苗,郝欣,刘明义,李琪,张效瑞. 鄂尔多斯盆地砂岩型铀矿碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素及其天然气-水混合流体作用特征. 中国地质. 2022(05): 1571-1590 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 林兆民,张嘉冕. 甘肃省207铀矿及富铀岩体特征研究. 甘肃地质. 2022(04): 42-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. Reng-an Yu,Shan-bo Wang,Qiang Zhu,Qing-hong Si,Xue-ming Teng,Xiao-xue Liu,Hou-ning Liu,Yong-xiang Tang. Zircon U-Pb ages and provenance characteristics of the Zhiluo Formation sandstones and the formation background of the uranium deposit in Huangling area, Ordos Basin, China. China Geology. 2021(04): 600-615 .  必应学术
必应学术
5. 张天福,张云,金若时,俞礽安,孙立新,程银行,奥琮,马海林. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘侏罗系层序界面特征对砂岩型铀矿成矿环境的制约. 中国地质. 2020(02): 278-299 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 张云,张天福,孙立新,程银行,张祺,王少轶,程先钰,周小希. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘黄陵地区煤铀兼探钻孔数据集成与三维地质模型构建. 中国地质. 2020(S1): 231-254 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 张天福,张云,程先钰,孙立新,程银行,周小希,王少轶,马海林,鲁超. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部东胜地区侏罗系-白垩系钻孔数据库与三维地质模型. 中国地质. 2020(S1): 220-245 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 田亮,赵天林,尹永朋,李名,叶阳. 内蒙古二连盆地额仁淖尔地区铀成矿水文地质条件分析. 矿产勘查. 2020(11): 2424-2429 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: