Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil nutrients in cultivated land in Renhuai, Guizhou Province
-
摘要:研究目的
为仁怀市农业生产中土壤养分的合理利用、农业结构调整及土地利用价值的提升等提供科学依据。
研究方法本文利用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法、容量法及电位法获取了5486件表层土壤样品氮磷钾(全量和有效态)及有机质的含量,系统研究了其地球化学特征及含量影响因素。
研究结果仁怀市耕地土壤氮、磷、钾、有机质、碱解氮、速效磷及速效钾的平均值分别为1.74 g/kg、0.75 g/kg、19.90 g/kg、30.90 g/kg、100.28 mg/kg、10.40 mg/kg和101.03 mg/kg。其中,氮、碱解氮、磷、钾及有机质的含量及分布与地层关系密切;速效磷及速效钾的含量及分布与地层关系较差。仁怀市耕地土壤肥力较好,以较丰富等级为主,较丰富及丰富等级占比为57.6%。其中,氮、磷及钾皆处于丰富水平;碱解氮及有机质处于中等水平;速效磷及速效钾处于缺乏水平。
结论仁怀市耕地土壤养分的含量及分布不仅受地质背景、土壤类型、海拔高度、酸碱度及土壤深度等自然因素影响,还与土地利用方式等人为活动有关。
创新点:系统统计了仁怀市耕地土壤氮磷钾(全量和有效态)及有机质的含量,对其地球化学等级开展了评价,并系统分析了它们的含量影响因素。耕地土壤养分的含量及分布不仅受地质背景、土壤类型等自然因素影响,还与土地利用方式等人为活动有关。
Abstract:This paper is the result of agricultural geochemical survey engineering.
ObjectiveThe research aimed to provide a scientific basis for the rational use of soil nutrients in agricultural production, adjustment of agricultural structure and improvement of land use value in Renhuai.
MethodsTotal and available nitrogen (phosphorus and potassium) content and organic matter content of 5, 486 topsoil samples were obtained using inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry, volumetric method, and potentiometric method. Their geochemical characteristics and influencing factors were systematically studied.
ResultsThe average values of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, organic matter, available nitrogen, rapidly available phosphorus, and rapidly available potassium were 1.74 g/kg, 0.75 g/kg, 19.90 g/kg, 30.90 g/kg, 100.28 mg/kg, 10.40 mg/kg, and 101.03 mg/kg, respectively. The contents and distributions of nitrogen, available nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and organic matter were closely related to the stratum, whereas those of rapidly available phosphorus and rapidly available potassium were not. Cultivated land in Renhuai had a relatively high soil fertility rating, which was mainly dominated by relatively rich soil grades, with the share of relatively rich and rich grades reaching 57.6%. Rich nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels were found, along with medium available nitrogen and organic matter levels. However, rapidly available phosphorus and rapidly available potassium were at deficient levels.
ConclusionsThe content and distribution of soil nutrients in cultivated land are not only affected by natural factors such as geological background, soil type, altitude, pH, and soil depth, but also related to human activities, such as land use patterns.
-
1. 引言
耕地土壤是农业生产的物质基础,是人类生存重要的自然资源(黄昌勇,2000)。而土壤养分指植物所必需的且主要由土壤提供的营养元素(刘国栋等,2008),是土壤肥力的重要物质基础,是评价土壤肥力水平的重要指标(沈其荣,2001),能供应和协调植物生长的营养条件与环境条件,是耕地地力的重要标志,对土地的可持续利用具有重要作用(童倩倩等,2011),其含量的高低直接影响作物的生长发育及产量与品质(袁杭杰,2020)。土壤养分是自然因子和人为因子共同作用的结果(孔祥斌等,2003),其含量、分布、形态及迁移转化不仅受成土母质、气候等自然因素影响,还与耕作方式、土地利用方式等人为活动有关(梁玉峰等,2018)。作为土壤肥力三要素的氮、磷、钾主要来自于土壤(张凤禹等,2010),有机质是土壤养分的主要来源(付嵩等,2018)。碱解氮、速效磷及速效钾则是土壤中可被植物吸收利用的有效组分(陈均玲等,2017;祁桥伟,2018;吴晨媛,2018)。因此,通过对氮磷钾(全量和有效态)及有机质的分析,对了解耕地土壤养分状况具有十分重要意义。
仁怀市耕地土壤养分状况一直颇受关注,金晓亮(2009)对仁怀市茅台酒原料基地表层土壤养分进行研究,涉及19个乡镇,样品共计329件;王维(2017)对仁怀市五马镇三元村表层土壤养分进行评价,样品共计24件;邵代兴等(2017)分别对仁怀市耕地土壤有机质、氮、碱解氮、速效磷和速效钾的平均含量进行了统计(样品采集时间为2009年以前)。但前人的研究主要存在两个问题:(1)基于少量土壤样品对大面积区域得出结论;(2)测试数据距今时间较长。因此,2017年,贵州省人民政府明确由省自然资源厅牵头,以县为单位开展全省耕地质量地球化学调查评价工作。本次开展的1∶5万尺度耕地质量地球化学调查,是迄今为止针对仁怀市耕地土壤较为全面、系统的专业调查。以仁怀市2015年度土地利用现状图图斑为基础,涵盖全市耕地、园地(果园、茶园)、裸地等土地利用类型。共采集耕地表层土壤样5486件(不含重复样)。
本文以仁怀市耕地质量地球化学调查评价项目的数据资料为依据,对仁怀市耕地土壤氮磷钾(全量和有效态)及有机质的地球化学特征、含量影响因素开展研究,为仁怀市耕地土壤养分含量调控管理、科学施肥、农业结构调整、提升土地利用价值等提供科学依据,进一步为仁怀市的现代山地特色高效农业全面、高效、持续发展提供基础成果支撑。
2. 研究区概况
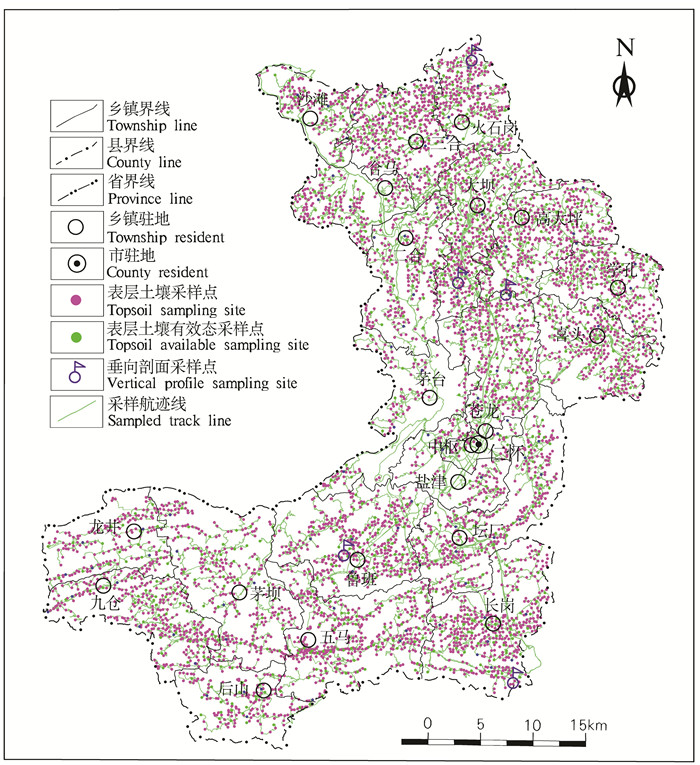
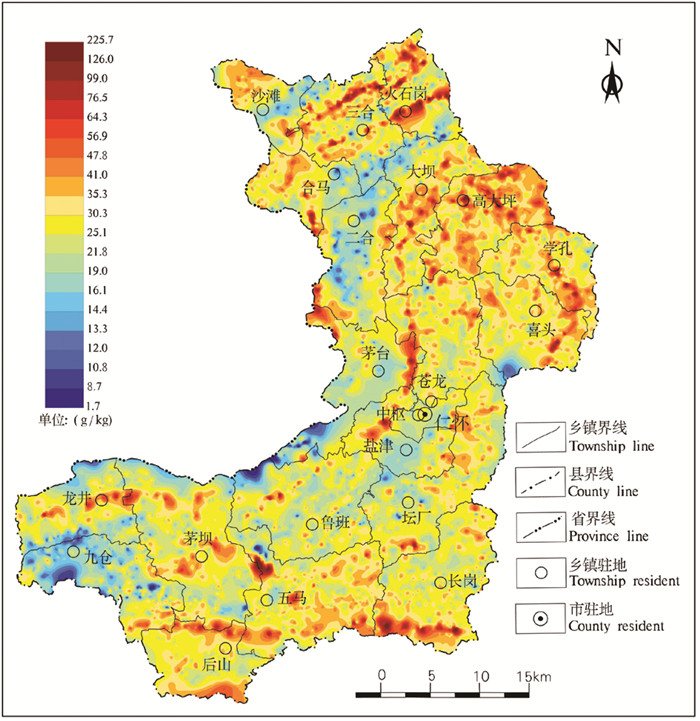
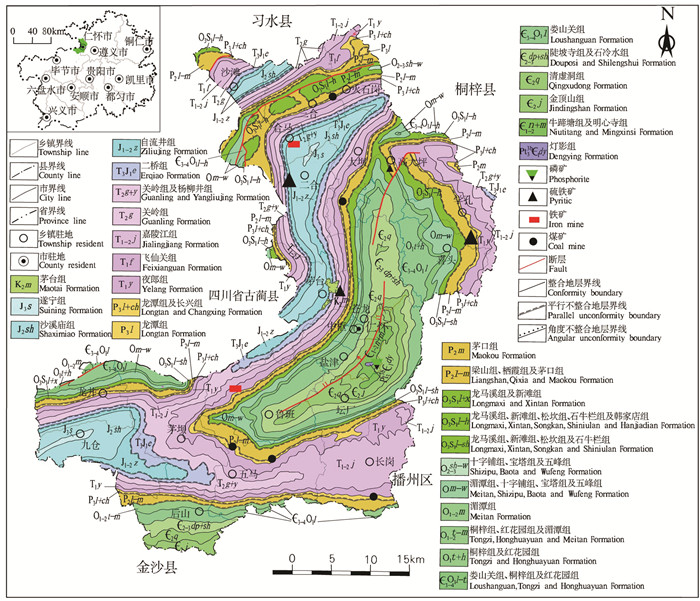
仁怀市位于贵州省西北部,是黔北经济区与川南经济区的连接点,是驰名中外的茅台酒的故乡。其南东与遵义市播州区,西南与金沙县,西北与四川省古蔺县,北与习水县,东北与桐梓县相连。区内交通便利,现有公路网是以S208省道、G4215高速公路为骨架,通过县道、乡村道连接全市21个乡镇街道。全市幅员面积为178991.52 hm2,地形起伏大,地貌类型复杂。海拔高度在全国地势第二级阶梯上。地势东南高西北低,呈弧状三级台阶。气候属中亚热带湿润季风气候,垂直差异较大,小气候明显。河流均属长江流域赤水河水系,河网密度0.476 km/km2。主要粮食和经济作物有红高粱、蔬菜、玉米、小麦、水稻、油菜等。根据贵州省仁怀市地方志编纂委员会(2013)可知,仁怀市土壤类型为石灰土、黄壤、紫色土、水稻土、黄棕壤。其中,石灰土为64149.6 hm2,占土壤总面积的40.7%;黄壤为58857.6 hm2,占37.3%;紫色土为20299.2 hm2,占12.9%;水稻土为14003.3 hm2,占8.9%;黄棕壤为298.3 hm2,占0.2%。土地利用类型以耕地和林地为主,林地面积大于耕地面积,耕地主要以旱地和水田为主。出露地层主要为震旦系、寒武系、奥陶系、二叠系、三叠系、侏罗系、白垩系。其中,震旦系为20 hm2;寒武系为44080 hm2;奥陶系为13700 hm2;志留系为20800 hm2;二叠系为37300 hm2;三叠系为45100 hm2;侏罗系为17300 hm2;白垩系为20 hm2。岩性主要有黏土岩、粉砂岩、砂岩、灰岩、白云岩等。矿产资源有煤矿、铁矿、硫铁矿、磷矿等10余种(图 1)。
3. 样品采集与分析测试
3.1 样品采集
以约9个点/km2的采样密度采集耕地表层土壤样品共5846件,其中有效态样品698件(图 2)。以主采样点为中心,在距离其20~50 m范围内向四周辐射,确定3~5个分样点,每个分样点采样深度均为0~20 cm,用铁锹先挖好坑后,然后用竹片去除与铁锹接触的土壤,再用竹片采集20 cm的土壤。尽量挑出根系、秸秆、石块等杂物,每个点从表至下均匀采取不低于300 g的土壤样品,等份组合成一个混合样,样品重量均在1500 g以上,有效态样均在2500 g以上,装入干净的棉布样品袋中,潮湿样品再用自封袋装袋保存。每件样品采集后,应将采样工具上的泥土清除干净,再采集下一件样品。采样时避开沟渠、田埂、道路、旧房基、粪堆等无代表性或代表性差的地段。野外采用便携式GPS或者贵州耕调APP终端采集各采样点坐标及航迹。土壤样品在自然条件下风干,过2 mm孔径筛,以对角线缩分法称取200 g以上(有效态样为500 g以上)样品送实验室分析。
3.2 分析测试
土壤样品分析测试按照《贵州省耕地质量地球化学调查评价总体设计》、《多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250000)》(DZ/T0258-2014)、《生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求》(DD2005-03)等执行,测试工作由具备地质实验测试甲级资质的自然资源部贵阳矿产资源监督检测中心(贵州省地质矿产中心实验室)承担。不同元素或指标的分析方法及检出限见表 1。2019年9月25—26日,实验室通过贵州省耕地质量地球化学调查评价办公室组织的验收,并有相应的分析检测验收意见书。土壤全量、有效态样品分析的质量监控严格遵照“设计”、“规范”和“技术要求”进行,分析质量达到相应规定要求。
表 1 各项元素或指标分析方法及检出限Table 1. The analysis method and detection limit of various elements or indicators
3.3 数据处理
地球化学图或等值线图的绘制采用实测原始数据,以0.5%、1.2%、2%、3%、4.5%、8%、15%、25%、40%、60%、75%、85%、92%、95.5%、97%、98%、98.5%、99.5%、100%分级间隔对应的含量进行等量线勾绘,土壤有效态以0.5%、1.5%、4%、8%、15%、25%、40%、60%、75%、85%、92%、95%、98.5%、99.5%、100%分级间隔对应的含量进行等量线勾绘。以冷色调(蓝色)作为低值区,随着数据的增大,颜色变暖,即由蓝—黄—红变化,各色区内不同等量线间隔用过渡色阶表示,由制图软件Geo Chem Studio2.5.7及MapGIS 6.7联合处理完成。土壤质量地球化学等级图以仁怀市2015年度土地利用现状图图斑为底图,由中国地质调查局发展研究中心“土地质量地球化学评价管理与维护(应用)子系统”及ArcGIS 10.2、MapGIS 6.7软件联合处理完成。
此外,运用Geo Chem Studio2.5.7软件完成测试数据的地球化学参数统计,相关性分析(Pearson相关系数)采用SPASS 21软件进行统计分析。
4. 结果与分析
4.1 元素或指标地球化学参数
对仁怀市表层土壤样品氮磷钾(全量和有效态)及有机质含量进行统计(表 2),氮的平均值为1.74 g/kg,磷为0.75 g/kg,钾为19.90 g/kg,有机质为30.90 g/kg,碱解氮为100.28 mg/kg,速效磷为10.40 mg/kg,速效钾为101.03 mg/kg。通过与遵义市、贵州省耕地土壤平均值以及全国A层土壤背景值对比可知,仁怀市耕地表层土壤中氮的平均值低于贵州省及遵义市,但高于全国;磷及钾平均值高于全国及贵州省;有机质平均值低于全国、贵州省,但高于遵义市;碱解氮、速效钾及速效磷背景值远低于贵州省及遵义市。
表 2 仁怀市耕地土壤养分元素或指标地球化学特征值Table 2. Geochemical characteristic values of soil nutrient elements or indicators in cultivated land in Renhuai
氮的变异系数为32%,磷为41%,钾为37%,有机质为55%,碱解氮为26%,速效磷为80%,速效钾为62%。变异系数的大小能够反映土壤特性空间变异性大小,通常认为变异系数CV≤10%时为弱变异,10%≤CV≤100%时为中等变异性,CV≥100%时为强变异性(秦占飞和常庆瑞,2012),7个元素或指标变异系数范围为26%~80%,属于中等变异,变异系数大小依次为速效磷>速效钾>有机质>磷>钾>氮>碱解氮。速效磷变异系数较大,与施用磷肥量的差异、土壤中磷元素固定难移动性和成土母质等都有关(李小刚等,2014)。
4.2 元素或指标地球化学特征
4.2.1 氮与碱解氮
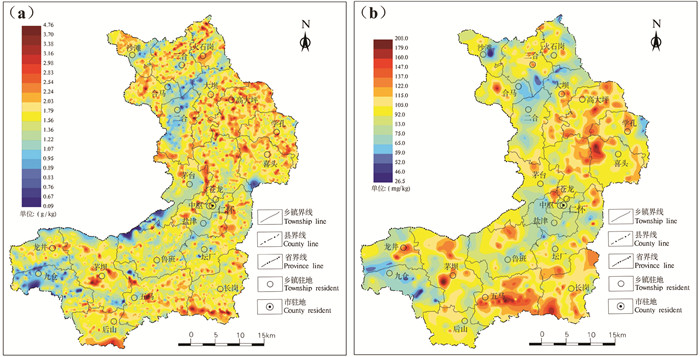
耕地土壤氮的含量及分布与地层关系较为密切,氮的高值区主要在二叠系、三叠系、奥陶系及部分寒武系分布区,特别是二叠系龙潭组、长兴组地层分布区,低值区主要在侏罗系自流井组、沙溪庙组等地层分布区,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市北部、北东部及南部含量较高。其中,茅坝、高大坪学孔、长岗等乡镇高含量带较集中(图 3)。
而碱解氮的高值区亦主要在二叠系、三叠系、奥陶系及部分寒武系分布区,低值区主要在侏罗系自流井组、沙溪庙组等地层分布区,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市南部及北东部含量较高,在五马长岗、喜头等乡镇高含量带较集中。低含量地区主要在九仓、二合—火石岗等乡镇(图 3)。
4.2.2 磷与速效磷
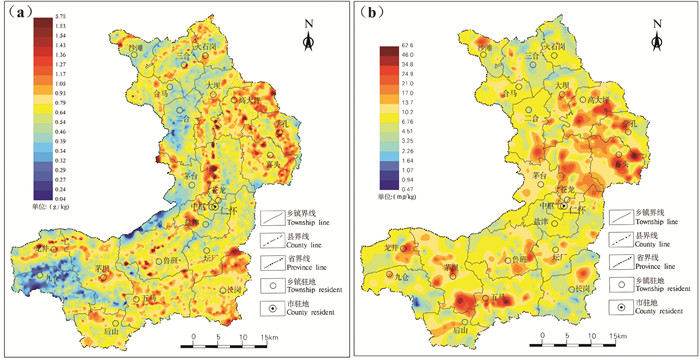
耕地土壤磷的含量及分布与地层关系密切,磷的高值区主要在三叠系夜郎组及奥陶系桐梓组及红花园组等地层分布区,低值区在侏罗纪地层分布区,特别是自流井组、沙溪庙组,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市北东部及中部含量较高。其中,高大坪—学孔、苍龙等地区高含量带较集中(图 4)。
而速效磷的含量及分布与地层关系较差,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市南部及北东部含量较高,在茅坝—五马、高大坪—学孔—喜头等乡镇高含量带较集中。低含量地区主要在长岗、三合、火石岗等乡镇(图 4)。
4.2.3 钾与速效钾
耕地土壤钾的含量及分布与地层关系密切,钾的高值区主要在奥陶系及寒武系分布区,特别是桐梓组、红花园组、湄潭组及娄山关组分布区,此外,位于长岗镇的三叠系嘉陵江组局部区域含量也较高。低值区主要在二叠系分布区,特别是梁山组、栖霞组及茅口组分布区,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市北东部及南部含量较高。其中,长岗中部、喜头、龙井北部等地区高含量带较集中(图 5)。
而速效钾的含量及分布与地层关系较差,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市西南部含量较高,在五马、鲁班、茅坝等乡镇高含量带较集中。低含量地区主要在火石岗、三合、学孔东部等地区(图 5)
4.2.4 有机质
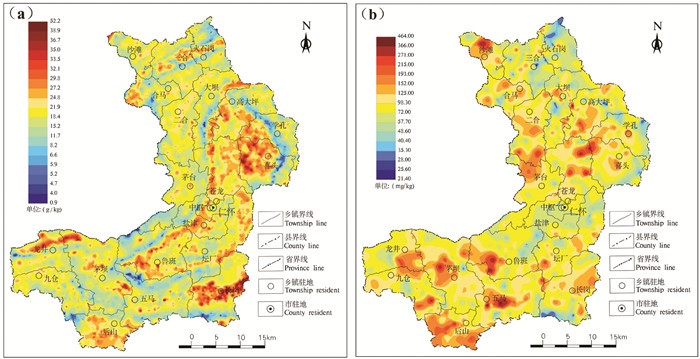
耕地土壤有机质的含量及分布与地层关系密切。有机质的高值区主要在二叠系龙潭组、长兴组、梁山组、栖霞组及茅口组分布区,低值区主要在侏罗系自流井组、沙溪庙组等地层分布区,从地理位置上分析,仁怀市北部、北东部及南部含量较高,西部边缘相对较低。其中,火石岗、高大坪—学孔、长岗等乡镇高含量带较集中(图 6)。
4.3 元素或指标地球化学等级
4.3.1 氮与碱解氮
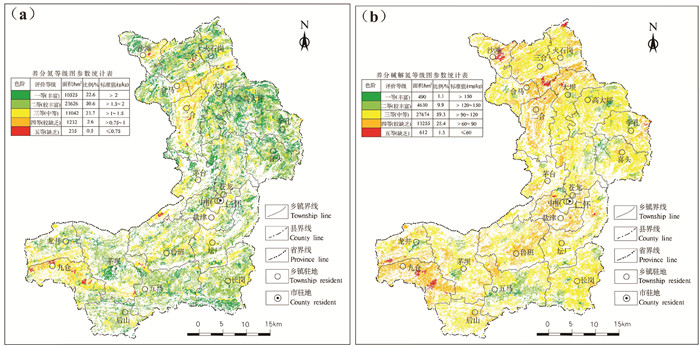
氮是农作物生长必需的元素之一。氮充足则作物生长快,株高叶茂,光合作用强,合成有机质多,产量高。氮缺乏则作物叶绿素和酶合成减少,从而导致株小叶黄,光合作用弱,合成有机质少,产量低(李佳等,2019)。仁怀市耕地土壤氮为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为10525 hm2、23626 hm2、11042 hm2、1232 hm2、235 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的22.6%、50.6%、23.7%、2.6%、0.5%。氮以较丰富等级为主,较丰富及丰富等级占比为73.2%,遍及全市。中等等级占比为23.7%,主要分布于九仓、二合等乡镇。较缺乏及缺乏等级占比为3.1%,零星分布在九仓、二合等乡镇(图 7)。
碱解氮是土壤中可被植物直接吸收利用的氮素(祁桥伟,2018),是表征近期内土壤氮素动态与供氮能力的重要指标,土壤氮素含量过低会导致水稻叶片发黄、产量下降,氮素过多则会引起环境污染等农业问题(黄仕辉等,2020)。仁怀市碱解氮为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为490 hm2、4630 hm2、27674 hm2、13255 hm2、612 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的1.1%、9.9%、59.3%、28.4%、1.3%。碱解氮以中等等级为主,较缺乏等级次之,中等等级占比为59.3%,遍及全市。较丰富及丰富等级占比为11.0%,五马镇较为集中,其余零星分布全市。较缺乏等级占比为28.4%,主要集中在九仓、二合等乡镇。缺乏等级占比为1.3%,零星分布于九仓、三合、沙滩等乡镇(图 7)。
4.3.2 磷与速效磷
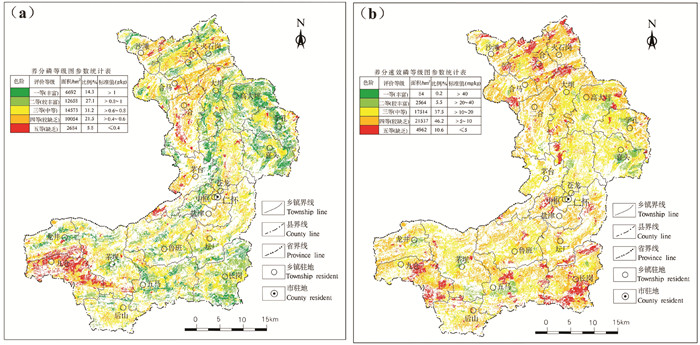
磷作为农作物生长必需的元素之一,能参与作物体内蛋白质等有机物的代谢,可以加强作物对土壤养分的吸收能力,促进作物的发育,增强抗寒和抗干旱性,以及加速作物成熟、增加产量等,缺磷则作物体内代谢失调,引起发育不良、成熟期推迟、产量大幅降低等(李佳等,2019)。仁怀市耕地土壤磷为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为6692 hm2、12658 hm2、14573 hm2、10054 hm2、2684 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的14.3%、27.1%、31.2%、21.5%、5.8%。磷以中等等级为主,占比为31.2%,遍及全市;较丰富及丰富等级面积为19350 hm2,占比为41.4%,主要分布在高大坪、学孔、长岗等乡镇。较缺乏及缺乏等级面积为12736 hm2,占比为27.3%,主要分布在九仓、二合等乡镇(图 8)。
速效磷是土壤中可被植物吸收的磷组分,是土壤磷素养分供应水平高低的指标,在农业生产中一般采用速效磷的指标来指导施用磷肥(陈均玲等,2017)。仁怀市速效磷为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为84 hm2、2564 hm2、17514 hm2、21537 hm2、4962 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的0.2%、5.5%、37.5%、46.2%、10.6%。速效磷以较缺乏等级为主,占比为46.2%,遍及全市;缺乏等级面积为4962 hm2,占比为10.6%,零星分布在长岗、火石岗、九仓、三合等乡镇;较丰富及丰富等级面积为2648 hm2,占比为5.7%,主要零星分布在五马、茅坝、喜头等乡镇(图 8)。
4.3.3 钾与速效钾
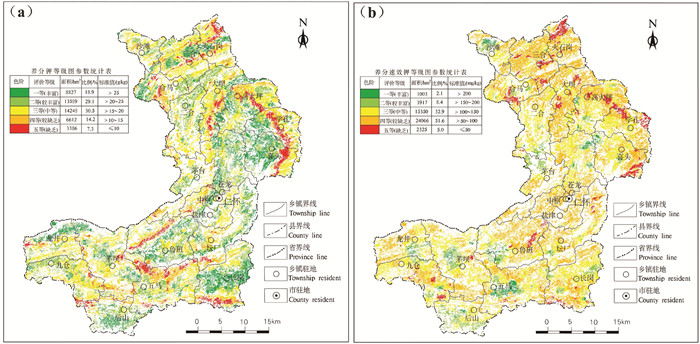
钾也是农作物所必需的营养元素之一。它能促进糖分的转移和淀粉的形成,能促进作物吸收养分,增强抗倒伏能力和耐寒与对病害的抵抗能力,能显著提高作物的产量(李佳等,2019),其缺乏与否对植物的光合作用、生长发育,都有明显影响,并进而影响到其生理过程与物质生产过程(李娟,2007)。仁怀市耕地土壤钾为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为8827 hm2、13589 hm2、14248 hm2、6612 hm2、3386 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的18.9%、29.1%、30.5%、14.2%、7.3%。钾以中等等级为主,面积为14248 hm2,占比为30.5%,主要分布在三合、火石岗、学孔东部、五马北部;较丰富及丰富等级面积为22416 hm2,占比为48%,集中分布在喜头、坛厂、鲁班、长岗、后山等乡镇;较缺乏及缺乏等级面积为9998 hm2,占比为21.5%,主要分布在学孔及喜头东部、高大坪中部(图 9)。
速效钾是作物可吸收利用的钾,可促进作物的多种代谢,促进有机物质的合成,增强作物抗性等(吴晨媛,2018)。仁怀市速效钾为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为1003 hm2、3917 hm2、15350 hm2、24066 hm2、2325 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的2.1%、8.4%、32.9%、51.6%、5.0%。速效钾以较缺乏等级为主,面积为24066 hm2,占比为51.6%,遍及全市;缺乏等级面积为2325 hm2,占比为5.0%,零星分布在高大坪、火石岗、三合等乡镇;较丰富及丰富等级面积为4902 hm2,占比为10.5%,主要零星分布在五马、茅坝、后山、沙滩一带(图 9)。
4.3.4 有机质
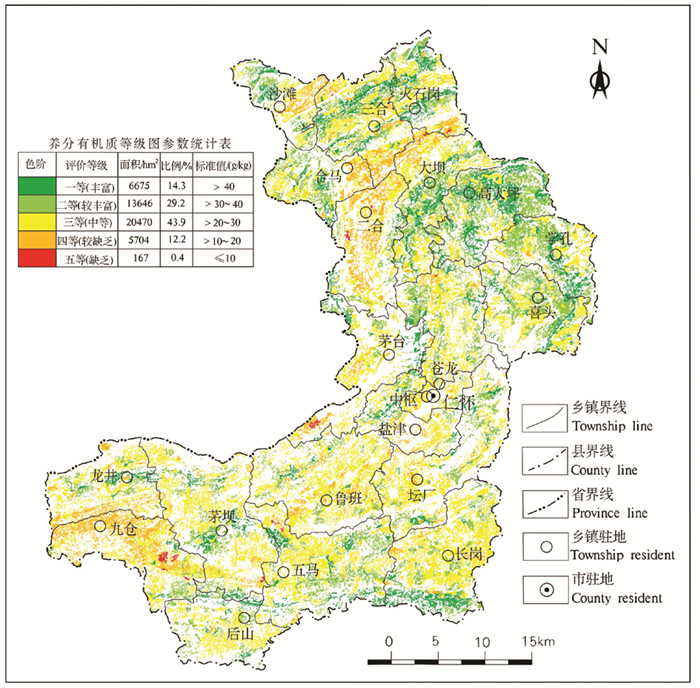
土壤有机质是土壤质量的核心,维系着土壤肥力(汪景宽等,2019),它在腐殖化过程中可以释放被作物吸收的养分,也可改良土壤的性状(李佳等,2019)。仁怀市耕地土壤有机质为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为6675 hm2、13646 hm2、20470 hm2、5704 hm2、167 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的14.3%、29.2%、43.9%、12.2%、0.4%。有机质以中等等级为主,占比为43.9%,遍及全市。较丰富及丰富等级耕地占比为43.5%,北部主要集中在大坝、高大坪、学孔等乡镇,南部主要集中在五马、长岗南部等地区,较缺乏及缺乏等级耕地占比为12.6%,主要分布在二合、合马、九仓等乡镇(图 10)。
4.4 土壤养分地球化学综合等级
依据《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295-2016),对耕地土壤养分丰缺状况进行单指标评价,在氮、磷、钾土壤单指标养分地球化学等级划分基础上,按照下面公式计算土壤养分地球化学综合得分/养综:

式中:f养综—土壤氮、磷、钾评价总得分1≤f养综≤5;ki—氮、磷、钾权重系数,分别为0.4,0.3和0.3;fi—土壤氮、磷、钾的单元素等级得分,单指标评价结果为五等、四等、三等、二等、一等时所对应的fi得分分别为1分、2分、3分、4分、5分。
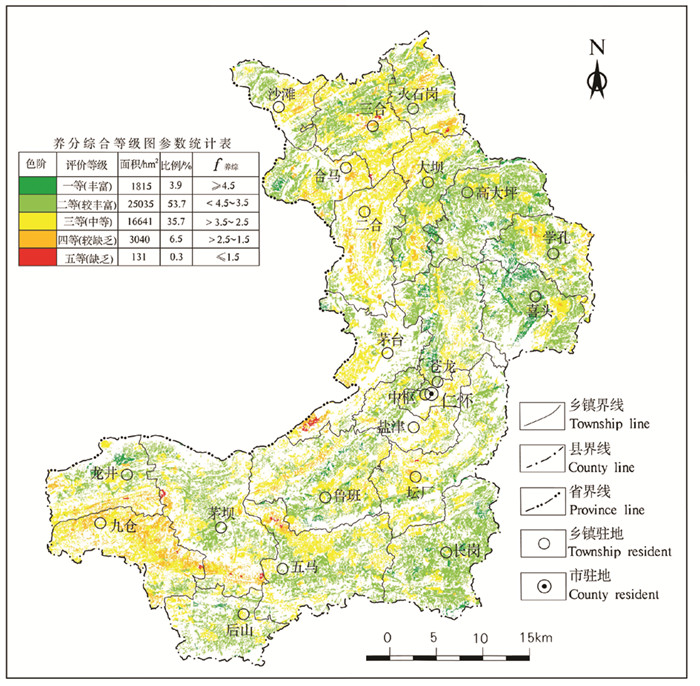
仁怀市耕地土壤养分综合等级为一等(丰富)、二等(较丰富)、三等(中等)、四等(较缺乏)、五等(缺乏)的面积分别为1815 hm2、25035 hm2、16641 hm2、3040 hm2、131 hm2,分别占调查评价面积的3.9%、53.7%、35.7%、6.5%、0.3%。耕地土壤肥力较好,以较丰富等级为主、中等等级次之,较丰富及丰富等级面积为26850 hm2,占比为57.6%,主要分布在长岗、后山、喜头、高大坪、茅坝及五马等乡镇;中等等级面积为16641 hm2,占比为35.7%,主要分布在九仓、二合、茅台等乡镇;较缺乏及缺乏等级面积为3171 hm2,占比为6.8%,主要分布在九仓、茅坝南部等地区(图 11)。
4.5 土壤养分相关性
相关性分析结果(表 3)显示,土壤氮与磷、有机质、碱解氮、pH、速效钾及速效磷呈显著正相关,而与钾呈显著负相关;磷与氮、钾、有机质、碱解氮、速效钾及速效磷均呈显著正相关,而与pH没有相关性;钾与磷、pH及速效钾均呈显著正相关,而与氮、有机质、碱解氮呈显著负相关,与速效磷没有相关性;有机质与氮、磷、碱解氮及速效磷呈显著正相关,而与钾呈负相关,与pH、速效钾无相关性;碱解氮与氮、钾、有机质、速效钾及速效磷均呈显著正相关,而与磷呈显著负相关,与pH无相关性;速效磷与除磷以外的6个元素或指标均呈显著正相关,与磷无相关性;速效钾与除有机质以外的6个元素或指标均呈显著正相关,与有机质无相关性。
表 3 仁怀市耕地土壤养分间的相关系数Table 3. Correlation coefficients of soil nutrients in cultivated land in Renhuai
5. 土壤养分的影响因素
5.1 地质背景
不同地层单元中,岩石组合即成土母岩差别较大。成土母质是形成土壤的物质基础和大多植物矿质养分元素的最初来源,其元素含量是决定土壤元素含量的重要因素,而由于成土母质成因及其化学组成的差别,土壤中部分元素含量存在显著的差异性(杨立国等,2019)。贵州省内的土壤多在原地基岩基础上风化形成(邓军等,2019)。从地球化学图(图 3~图 6)可知:仁怀市耕地土壤氮及有机质的高值区主要在二叠系龙潭组及长兴组分布区,磷的高值区主要在三叠系夜郎组及奥陶系桐梓组及红花园组分布区,且氮、磷、碱解氮及有机质的低值区皆为侏罗系分布区。钾的高值区主要在奥陶系及寒武系分布区,钾的低值区主要在二叠系分布区。分别对二叠系、三叠系及侏罗系等地层单元土壤养分的平均值进行了统计分析(表 4)。结合仁怀市地质矿产略图(图 1),对部分地层单位进行了归并处理。由表 4可知,氮的平均含量大小顺序为:P3l+ch>O1t+h>T1-2j>T2g+y>P2l- m>Є3-4O1l>T1y>T1f>T3J1e>J1-2z>J3s>J2sh;磷:O1t+h>P3l+ch>T1y>T1f>T1-2j>Є3-4O1l>T2g+y>P2l-m>J1-2z>T3J1e>J3s>J2sh;钾:O1t+h>T1-2j>Є3-4O1l>J2sh>T2g+y>J3s>T1f>T1y>J1-2z>T3J1e>P3l+ch>P2l-m;有机质:P3l+ch>P2l-m>O1t+h>T1y>T1f>T1-2j>T2g+y>Є3-4O1l>T3J1e>J3s>J1-2z>J2sh;碱解氮:P3l+ch>T2g+y>T1-2j>P2l-m>Є3-4O1l>T1y>O1t+h>T1f>T3J1e>J1-2z>J3s>J2sh;速效磷:T2g+y>O1t+h>Є3-4O1l>J3s>P2l-m>J1-2z>T1y>T1-2j>T3J1e>P3l+ch>T1f>J2sh;速效钾:T2g+y>Є3-4O1l>J3s>O1t+h>T1-2j>J1-2z>J2sh>P3l+ch>T3J1e>T1y>P2l-m>T1f。综上,氮、磷、碱解氮及有机质在侏罗系自流井组、沙溪庙组及遂宁组中含量较低,在二叠系龙潭组及长兴组分布区含量较高。因为侏罗系分布区成土母岩主要为紫红色碎屑岩,有机质含量较低。紫色地层岩石物理风化强烈,而化学风化过程缓慢,风化发育的土壤无论在基本理化性质和物质组成上,均易长期继承母岩的特点,是一种典型的初育土壤(童建川,2016)。而龙潭组及长兴组分布区主要以黏土岩及碳酸盐岩为主,且有煤层分布,其有机质含量较高。根据养分元素相关性分析(表 3),氮、磷、碱解氮与有机质呈明显正相关,对应的龙潭组及长兴组分布区耕地土壤中氮、磷及碱解氮含量亦较高,侏罗系分布区较低。而钾与有机质呈负相关,则龙潭组及长兴组分布区耕地土壤钾含量较低。
表 4 仁怀市主要地层单元耕地土壤养分平均值Table 4. Average value of soil nutrients in cultivated land of main stratigraphic unit in Renhuai
5.2 土壤类型
不同成土因素可形成不同的土壤类型,许多土壤质量指标受土壤类型的影响(章明奎和徐建民,2002;蒋云舞等,2013),土壤类型不同不仅影响土壤中微量元素有效含量(刘强和杨东,2017),而且影响着土壤养分元素或指标,受到许多学者关注(张小琴和郭晔红,2002;章明奎和徐建民,2002;姚光琴,2016;蔡能等,2017)。仁怀市土壤类型有石灰土、黄壤、紫色土、水稻土、黄棕壤五大类。按土壤类型分别统计养分平均含量(表 5)。从表 5可知,不同土壤类型的养分指标差异显著。氮平均含量大小顺序为:石灰土>水稻土>黄壤>黄棕壤>紫色土;磷:黄棕壤>石灰土>黄壤>水稻土>紫色土;钾:黄棕壤>石灰土>水稻土>黄壤>紫色土;有机质:石灰土>黄壤>水稻土>黄棕壤>紫色土;碱解氮:石灰土>黄壤>黄棕壤>水稻土>紫色土;速效磷:黄棕壤>黄壤>石灰土>水稻土>紫色土;速效钾为:石灰土>黄壤>黄棕壤>紫色土>水稻土。综上,石灰土中氮、磷、钾、有机质、碱解氮及速效钾含量较高,紫色土中氮、磷、钾、有机质、碱解氮及速效磷含量最低。贵州石灰土中氮含量较高,且一般情况下,钾磷含量普遍高于黄壤(郑永春和王世杰,2002),紫色土中有机质含量较低,矿质元素除钾外一般都偏低(聂明华,2008)。王晖等(2006)认为贵州烟草区紫色土相对于其他土壤类型,其有机质、氮、磷、速效磷及速效钾含量偏低,钾含量偏高。而仁怀市紫色土中钾偏低可能与紫色土的pH有关,紫色土pH平均值为6.64,pH偏低。占丽平等(2012)认为,土壤钾的固定量一般随土壤pH的升高而升高。申玲等(2015)认为贵州毕节地区紫色土的pH为6.29,其钾的含量低于石灰土及粗骨土。
表 5 仁怀市各土壤类型耕地土壤养分平均值Table 5. Average value of soil nutrients in cultivated land of soil types in Renhuai
5.3 不同土地利用方式
土地利用方式与土壤养分有着密切的联系(马云等,2009;赵瑞芬等,2011)。土地利用方式的改变往往会引起土壤理化性质的变化(郑华等,2008),同时也会引起土壤养分的变化(马云等,2009)。与本次研究相关的土地利用方式主要为旱地、水田、园地、水浇地及裸地。按土地利用方式分别统计养分平均含量(表 6)。从表 6可知,氮平均含量大小顺序为:水田>水浇地>旱地>园地>裸地;磷:水浇地>旱地>园地>水田>裸地;钾:旱地>水田>水浇地>裸地>园地;有机质:水田>水浇地>旱地>园地>裸地;碱解氮:水浇地>水田>旱地>裸地>园地;速效磷:水浇地>水田>旱地>裸地>园地;速效钾:水浇地>旱地>水田>园地>裸地。综上,水田中氮、碱解氮及有机质含量较高,因为由于水田淹水条件下,土壤长期处于还原状态,有利于有机质和氮素的积累,此外还受到秸秆还田及施肥等因素的影响,加之淹水条件下土壤微生物活动受到抑制,有机质分解慢(郑华等,2008)。旱地中磷、钾含量相对较高,可能因为旱地受耕作的影响,成土母质的物理、化学风化加深,含磷、钾矿物被分解,土壤磷、钾含量增加(廖晓勇等,2005)。裸地由于受到人为干扰小,特别是农业施肥,所以养分含量均较低。
表 6 仁怀市各土地利用方式耕地土壤养分平均值Table 6. Average value of soil nutrients in cultivated land of land uses in Renhuai
5.4 海拔
海拔高度是影响作物生长发育的重要生态因子之一,土壤养分的有效性常常和海拔高度有一定关系(尹梅等,2012),高程变化导致水热资源在空间分布上存在差异,这些差异会影响土壤养分的矿化、降解、迁移和累积,进而导致不同高程下土壤养分含量存在较大空间异质性(林建平等,2019)。此外,不同海拔高度的耕地,有着不同的种植制度,这些人为因素也一定程度上影响着土壤的熟化过程(梁涛等,2015)。本次选取了6个海拔区间对仁怀市土壤养分进行分析(表 7),从表 7可知,不同土壤养分的平均含量随着海拔的增加表现出不同的变化趋势。总体上,土壤磷、钾和碱解氮呈现出随海拔增加而增加的趋势;而当海拔在360~1160 m区间,土壤有机质、氮呈现出随海拔增加而增加的趋势,但当海拔大于1160 m,呈现减少趋势;土壤速效钾、速效磷随海拔的变化趋势不明显。一般而言,在低海拔地区,水热条件优越,土壤物质循环加速,养分的利用率高而沉积较少;在高海拔地区,气温下降,微生物分解速度减慢,造成有机质以及氮、钾等养分含量累积较多(林建平等,2019)。但当海拔达到一定高度时,土壤有机质及氮略有变化,呈现出先降低后升高的趋势(鲜娅等,2014)。
表 7 仁怀市不同海拔下耕地土壤养分变化Table 7. The variation of soil nutrients in cultivated land at different elevations in Renhuai
5.5 酸碱度
土壤pH是土壤酸碱度的反映,是土壤物理化学性质的综合反映(孙朝等,2010),对土壤生态系统的稳定性起着至关重要的作用,也是影响土壤肥力、农作物吸收的一个重要因素(李佳等,2019)。本次选取了5个酸碱度区间对土壤养分进行分析(表 8),从表 8可知,不同土壤养分的平均含量随着pH值的增加表现出不同的变化趋势,当土壤由强酸性至碱性时,氮、钾、碱解氮及有机质呈现出随pH增加而增加的趋势,至强碱性又降低;而土壤磷、速效钾、速效磷随pH的变化趋势不明显,当土壤为中性时,磷及速效磷平均含量最高,而当土壤为碱性时,速效钾含量最高。
表 8 仁怀市不同酸碱度下耕地土壤养分变化Table 8. The variation of soil nutrients in cultivated land at different pH in Renhuai
5.6 土壤深度
土壤养分在垂直空间上具有分异现象,不同的土壤类型、土地利用方式、施肥方式都会对土壤养分的垂直分布产生影响(邓小华等,2018),长期施肥不仅影响着土壤中养分数量的变化,而且由于养分的向下移动也影响土壤中养分的垂直分布。这种垂直分布在生产上有两个方面的意义:一是养分下移超过根系所能吸收的范围,将造成养分的淋失,进而影响水体质量;二是养分适度下移,可以丰富底土养分数量,这对于培育土壤肥力异常有利(鲁如坤等,2000)。因此,对土壤养分空间变异的充分了解是管理好土壤养分和合理施肥的基础(吴晓磊等,2010),是调整各项管理措施和各项物质投入量、获得最大经济效益的基础(郭家文等,2007)。为探讨仁怀市表、深层土壤中养分元素的分布规律,本次选取5条土壤垂向剖面对土壤养分进行分析,实际采样位置见图 2。从表 9可知,土壤中氮、磷、有机质、碱解氮、速效磷在表土含量相对较高,随深度增加表现为含量降低,而钾表层含量低,随深度增加表现为含量增加,速效钾垂向变化无明显规律性。有机质是土壤中的各种含碳有机化合物的总称,包括动植物残体、微生物体和生物残体在不同分解阶段的产物,以及由分解产物合成的腐殖质等(黄春雷等,2013;周墨等,2018)。表层土壤有机质高,随着深度增加,有机质含量下降(尚斌等,2014;李卫东等,2018),但不同剖面从表层向下有机质含量变化趋势不同(李龙波等,2012)。根据养分元素相关性分析(表 3),氮、磷、碱解氮及速效磷与有机质呈正相关,且有机质中氮含量也很高。其次,氮、磷可能受人为施肥作用的影响,导致表层土壤富集明显。而钾与有机质呈明显负相关,随有机质含量增加而降低。且钾迁移性强,受淋溶作用影响大,随着土壤深度增加,黏土矿物含量增加,而钾离子易于被黏土矿物所吸附富集(徐传奇等,2016)。
表 9 仁怀市不同深度下耕地土壤养分变化Table 9. The variation of soil nutrients in cultivated land at different depths in Renhuai
6. 结论
(1)仁怀市耕地土壤氮、磷、钾、有机质、碱解氮、速效磷及速效钾的平均值分别为1.74 g/kg、0.75 g/kg、19.90 g/kg、30.90 g/kg、100.28 mg/kg、10.40 mg/ kg和101.03 mg/kg。
(2)仁怀市耕地土壤氮、碱解氮、磷、钾及有机质的含量及分布与地层关系密切,速效磷及速效钾的含量及分布与地层关系较差。
(3)仁怀市耕地土壤肥力较好,以较丰富等级为主,较丰富及丰富等级占比为57.6%。其中,氮、磷及钾处于丰富水平,碱解氮及有机质处于中等水平,速效磷及速效钾处于缺乏水平。
(4)仁怀市耕地土壤养分的含量及分布不仅受地质背景、土壤类型、海拔高度、酸碱度及土壤深度等自然因素影响,还与土地利用方式等人为活动有关。
致谢: 本文所有数据、成果均基于《贵州省仁怀市耕地质量地球化学调查评价》项目,参加该项目的还有张厚松、樊洪富、刘奎勇、赵来、杨育慎、谢亚林等同仁。野外工作中,得到仁怀市自然资源局相关领导的大力支持,笔者一并表示衷心感谢! -
表 1 各项元素或指标分析方法及检出限
Table 1 The analysis method and detection limit of various elements or indicators

表 2 仁怀市耕地土壤养分元素或指标地球化学特征值
Table 2 Geochemical characteristic values of soil nutrient elements or indicators in cultivated land in Renhuai

表 3 仁怀市耕地土壤养分间的相关系数
Table 3 Correlation coefficients of soil nutrients in cultivated land in Renhuai

表 4 仁怀市主要地层单元耕地土壤养分平均值
Table 4 Average value of soil nutrients in cultivated land of main stratigraphic unit in Renhuai

表 5 仁怀市各土壤类型耕地土壤养分平均值
Table 5 Average value of soil nutrients in cultivated land of soil types in Renhuai

表 6 仁怀市各土地利用方式耕地土壤养分平均值
Table 6 Average value of soil nutrients in cultivated land of land uses in Renhuai

表 7 仁怀市不同海拔下耕地土壤养分变化
Table 7 The variation of soil nutrients in cultivated land at different elevations in Renhuai

表 8 仁怀市不同酸碱度下耕地土壤养分变化
Table 8 The variation of soil nutrients in cultivated land at different pH in Renhuai

表 9 仁怀市不同深度下耕地土壤养分变化
Table 9 The variation of soil nutrients in cultivated land at different depths in Renhuai

-
Chen Xuhui. 2001. Variations of soil nutrient content and fertilization in Guizhou[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 7(2): 121-128(in Chinese with English adstract).
Chen Junling, Sun Zhiming, You Yong, Tang Jianzhou. 2017. Paddy soil available phosphorus content change and influential factors in Pingnan County[J]. Journal of Changsha Uinversity, 31(5): 14-16(in Chinese with English adstract).
Cai Neng, Qiao Zhongquan, Zeng Huijie, Li Yongxin, Wang Xiaoming. 2017. Nutrient status of different soil types in Hunan forest land[J]. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 44(3): 24-29(in Chinese with English adstract).
Deng Xiaohua, Li Yuanhuan, Zhou Miliang, Zhao Jiongping, Tian Feng, Jian Panfeng, Liu Zhaoying, Li Hailin. 2018. Vertical distribution characteristics of main nutrients and acid parameters of tobacco-planting soils in wuling mountains[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 39(3): 48-58(in Chinese with English adstract).
Deng Jun, Shi Huading, Zhao Jian, Han Xiaobin, Peng Yulong, Liu Jing, Ma Jin. 2019. Soil selenium distribution and its influencing factors in Zunyi City[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 3: 49-55(in Chinese with English adstract).
Fu Song, Ding Yujin, Zhang Xinyuan, Wang Wei, Li Shehong. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of soil nutrients in Xinmin-Lierbao Area of Minhe County, Qinghai Province[J]. Geoscience, 32(5): 1103-1108(in Chinese with English adstract).
Guo Jiawen, Zhang Yuebin, Liu Shaochun, Ma Zhihe. 2007. Vertical distribution of soil nutrients in sugarcane field in Changning, Yunnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 38(6): 1072-1075(in Chinese with English adstract).
Gao Xue, Chen Haiyan, Tong Qianqian. 2013. Nutrient status of surface soil of cultivated land in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 41(12): 87-91(in Chinese with English adstract).
Guizhou Renhuai Local Chronicles Compilation Committee. 2013. City Local Records of Renhuai[M]. Beijing: Local Records Press, 1-806(in Chinese).
Huang Changyong. 2000. Edaphology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1-310(in Chinese).
Huang Chunlei, Song Mingyi, Wei Yingchun. 2013. Study on selenium contents of typical selenium-rich soil in the middle area of Zhejiang and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 34(11): 4405-4410(in Chinese with English adstract).
Huang Shihui, Fang Bin, Li Xin, He Shasha. 2020. Study on spatial heterogeneity of alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen in paddy fields at the county scale[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 36(2): 179-185(in Chinese with English adstract).
Jin Xiaoliang. 2009. Relationship between Soil Nutrient Spatial Characteristics and Crop Yield and Quality in Moutai Raw Material Base[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 1-91(in Chinese).
Jiang Yunwu, Wang Jianxin, Lu Yao, Yang Jinghua, Zhou Min. 2013. Analysis of farmland soil nutrient content of diferent models planting patterns and soil types[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 41(5): 2063-2066(in Chinese with English adstract).
Kong Xiangbin, Zhang Fengrong, Qi Wei, Xu Yan. 2003. The influence of land use change on soil fertility in intensive agricultural region: A case study of Quzhou County, Hebei[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58(3): 15-24(in Chinese with English adstract).
Lu Rukun, Shi Zhengyuan, Lai Qingwang. 2000. The characteristics of nutrient downshift under long-term fertilization in red soil[J]. Soils, 32(1): 27-29(in Chinese).
Liao Xiaoyong, Chen Zhijian, Liu Xiaoquan, Wang Haiming. 2005. Effects of land use types on soil fertility in small watershed in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Ecology and Environment, 14(1): 99-101(in Chinese with English adstract).
Nie Minghua. 2008. Characteristics and improving measure of purple soil-A case of purple soil in wuyi mountain[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 3: 60-62(in Chinese with English adstract).
Li Juan. 2007. Advances in research on potassium, calcium and magnesium nutrition of plants[J]. Fujian Science and Technology of Rice and Wheat, 25(1): 39-42(in Chinese).
Liu Guodong, Cui Yujun, Tan Fucheng, Wang Enbao, Wen Dan. 2008. Evaluation of soil fertility and environment health in the Wuchang Area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 22(6): 1010-1014(in Chinese with English adstract).
Li Longbo, Liu Taoze, Li Xiaodong, Liu Wenjing, Liu Congqiang. 2012. Vertical distribution patterns of organic carbon and its isotopic composition in typical soil types in Guizhou karst areas of Southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31(2): 3-9(in Chinese with English adstract).
Li Xiaogang, Ma Youhua, Wang Qiang, Guo Cuijin. 2014. Spatiotemporal variations of soil nutrients and regional fertilization on county land-A case study of Feidong County[J]. Soils, 46(6): 976-983(in Chinese with English adstract).
Liang Tao, Gao Xingren, Xu Yidan, Wen Shu, Zhou Ling, Chen Yan. 2015. Analysis of relationship between soil nutrient status and elevation in two regions of Chongqing[J]. South China Agriculture, 9(1): 28-30(in Chinese).
Liu Qiang, Yang Dong. 2017. Study on the contents of available trace elements in different soils——A case study in Linze Area, Zhangye City[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 24(6): 205-215(in Chinese with English adstract).
Liang Yufeng, Tan Changyin, Cao Xueying, He Qihui, Zhu Shangyou, Xie Yucheng, Dai Bing. 2018. Vertical distribution of soil nutrient and heavy metals in soil under different land use[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 12(6): 1792-1799(in Chinese with English adstract).
Li Weidong, Chen Yongbo, Huang Guangyu, Zhang Chaoyang, Hu Baishun, Qin Bang, Liu Shuqin, Chen E, Xiong Qian. 2018. Physicochemical characteristics and nutrient profile distribution of cultivated lands in Enshi Prefecture[J]. Soils, 50(6): 1134-1138(in Chinese with English adstract).
Li Jia, Fang Yuan, Li Zhenglong, Ding Xinke, Zheng Xiaowei, Xu Zhenghua, Guan Kaiping. 2019. Geochemical characteristics of cultivated soil nutrients in the Wuxing District, Zhejiang[J]. Mineral Exploration, 10(10): 2711-2718(in Chinese with English adstract).
Lin Jianping, Deng Aizhen, Zhao Xiaomin, Jiang Yefeng, Han Yi, Xie Yu. 2019. Variation characteristics of soil nutrients of cultivated land in different elevation fields in typical hilly areas of southern mountains[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 50(5): 300-309(in Chinese with English adstract).
Ma Yun, He Binghui, Chen Xiaoyan, Shi Zhimin, He Jianlin. 2009. Distribution characteristics of the soil fertility in a slope under different land use[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(6): 118-122(in Chinese with English adstract).
Qin Zhanfei, Chang Qingrui. 2012. Analysis on spatial variability of soil nutrients at county level-A case study in Pucheng County[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 30(1): 30-35(in Chinese with English adstract).
Qi qiaowei. 2018. Distribution of Soil Organic Matter, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Nutrition in Cultivated Land of Xi'an City[D]. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, 1-33(in Chinese with English adstract).
Shen Qirong. 2001. General Theory of Soil Fertilizer[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1-308(in Chinese).
Sun Zhao, Hou Qingye, Yang Zhongfang, Yang Xiaoyan, Huang Yong, Chen Enke. 2010. Factors controlling the transport and transformation of selenium in typical soil environments: A case study of the Chengdu economic zone in Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 37(6): 1760-1768(in Chinese with English adstract).
Shang Bin, Zou Yan, Xu Yimin, Song Wenjing, Wang Chengdong, Meng Lin, Liu Xiaobin, Chu Zhiguo. 2014. Relationship between SOM contents of tobacco fields and elevation and parent materials in central region of Guizhou Province[J]. Soils, 46(3): 446-451(in Chinese with English adstract).
Shen Ling, Yu Jianlong, Yang Yongkui, Hu Hui, Yang Bo, Liang Yanfei. 2015. - Soil-nutrients-content- and- soil-C/N-value- of- four- different- soil-types- in-Bijie-[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 10: 61-64(in Chinese with English adstract).
Shao Daixing, Zhou Kaifang, Liu Hong, Lin Li. 2017. Contents and change trends of soil nutrients in cultivated land in Zunyi City[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 45(5): 62-65(in Chinese with English adstract).
Tong Qianqian, He Tengbing, Gao Xue, Peng Zhiliang, Han Feng, Zhao Zeying, Yang Li, Yuan Chengjun, Yang Liu. 2011. Soil nutrients of arable land in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 39(2): 82-84(in Chinese with English adstract).
Tong Jianchuan. 2016. On distribution of selenium in purple soil region of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 41(3): 170-175(in Chinese with English adstract).
Wei Fusheng, Yang Guozhi, Jiang Dezhen, Liu Zhihong, Sun Benmin. 1991. Basic statistics and characteristics of background values of soil elements in China[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 7(1): 3-8(in Chinese).
Wang Hui, Ding Wei, Xu Zicheng, Shi Junxiong, Zhang Changyun. 2006. Difference of nutrients between purple soil and other soil types in Guizhou tobacco-growing areas[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 34(3): 22-25(in Chinese with English adstract).
Wu Xiaolei, Wang Daqing, Xu Bo, Nie Ying, Wang Hongyan. 2010. Spatial variability of black soil nutrients in hilly land[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 41(4): 825-829(in Chinese with English adstract).
Wang Wei. 2017. Evaluation of Soil Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in the Middle and Upper Reaches of Chishui River: A case study of Sanyuan Village, Wuma Town, Renhuai City[D]. Master Degree Thesis. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 1-53(in Chinese).
Wu Chenyuan. 2018. Study on relationship between soil organic matter and available potassium in lushan mountain[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 11: 186-187(in Chinese with English adstract).
Wang Jingkuan, Xu Yingde, Ding Fan, Gao Xiaodan, Li Shuangyi, Sun Liangjie, An Tingting, Pei Jiubo, Li Ming, Wang Yang, Zhang Weijun, Ge Zhuang. 2019. Process of plant residue transforming into soil organic matter and mechanism of its stabilization: A review[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56(3): 528-540(in Chinese with English adstract).
Xian Ya, Meng Guangtao, Zhao Yanan, Wang Mian. 2014. Vertical distribution patterns of soil organic matter and total nitrogen contents in different altitudes of eastern slope of gaoligong mountain[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 26(5): 6-10(in Chinese with English adstract).
Xu Chuanqi, Liao Fuqiang, Jia Yulian, Huang Siyuan, Lian Licong, Ling Chaohao, Long Jin. 2016. Element geochemical characteristics of the reticulate red clay in southern China and its significance for the formation proccess of reticulated mottles[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 18(5): 865-878(in Chinese with English adstract).
Yin Mei, Hong Lifang, Fu Libo, Chen Hua, Wang Jinsong, Su Fan. 2012. Nutrient plentiful-lack index of maize on red soil at different altitudes in east of Yunnan[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, (3): 39-43(in Chinese with English adstract).
Yao Guangqin. 2016. Nutrient status and countermeasures of different soil types in Mengban, Jinggu[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2: 215-217(in Chinese).
Yang Liguo, Ma Zhichao, Wang Xin. 2019. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in the soil of Horqin District, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 28(4): 383-388(in Chinese with English adstract).
Yuan Hangjie, Yang Wenye, Li Dan, Wang Jingwen. 2020. Evaluation of cultivated soil nutrients in upland in suburb of Hangzhou[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 61(1): 147-149(in Chinese).
Zheng Yongchun, Wang Shijie. 2002. Geological cause of calcareous soil erosion and land rocky desertification in karst area, Guizhou Province[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, (5): 69-73(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zhang Mingkui, Xu Jianmin. 2002. Effects of land use and soil type on selected soil fertility quality indicators[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Agricuture and Life Sciences), 28(3): 277-282(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zhang Xiaoqin, Guo Yehong. 2002. The fertilizer analysis of different soil types in Linze County[J]. Journal of Gansu Forestry Science and Technology, 27(2): 9-11(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zheng Hua, Su Yirong, He Xunyang, Huang Daoyou, Wu Jinshui. 2008. Effects of land use on soil nutrient in peak-forest valley——A case study in dacai village of Huanjiang County, Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 27(2): 177-181(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zhang Fengyu, Zhu Yan, Wang Xikuan, Kang Hongzai. 2010. Analysis and evaluation of soil nutrient of tuoketuo area in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 24(5): 1022-1028(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zhao Ruifen, Zhang Yigong, Zhang Qiang, Cheng Bin, Zhang Jianjie. 2010. Effects of different land use types on soil nutrients conditions in cultivated land——A case study of Taiyuan[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(14): 262-266(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zhan Liping, Li Xiaokun, Lu Jianwei, Wang Jin, Liao Zhiwen. 2012. Research advances on influence factors of soil potassium movement[J]. Soils, 44(4): 548-553(in Chinese with English adstract).
Zhou Mo, Chen Guoguang, Zhang Ming, Zhan Long, Liang Xiaohong, Zhang Jie, Sun Zhongcong, Yong Taijian, Tang Zhimin. 2018. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of south Jiangxi Province: A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 32(6): 1292-1301(in Chinese with English adstract).
陈旭晖. 2001. 贵州土壤养分含量的变化与施肥管理[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 7(2): 121-128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2001.02.001 陈均玲, 孙智明, 游勇, 唐建洲. 2017. 平南县水田土壤有效磷含量变化及影响因素[J]. 长沙大学学报, 31(5): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4681.2017.05.003 蔡能, 乔中全, 曾慧杰, 李永欣, 王晓明. 2017. 湖南省林地不同土壤类型养分状况分析[J]. 湖南林业科技, 44(3): 24-29. 邓小华, 李源环, 周米良, 赵炯平, 田峰, 菅攀锋, 刘朝营, 李海林. 2018. 武陵山地植烟土壤养分和酸度垂直分布特征[J]. 中国烟草科学, 39(3): 48-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYV201803007.htm 邓军, 师华定, 赵建, 韩小斌, 彭玉龙, 刘京, 马瑾. 2019. 遵义市土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 3: 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRFL201903008.htm 付嵩, 丁玉进, 张新远, 王伟, 李社宏. 2018. 青海省民和县新民-李二堡地区土壤养分地球化学特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 32(5): 1103-1108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201805024.htm 郭家文, 张跃彬, 刘少春, 马志和. 2007. 云南昌宁蔗区不同耕层土壤养分的垂直分布[J]. 土壤通报, 38(6): 1072-1075. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2007.06.007 高雪, 陈海燕, 童倩倩. 2013. 贵州耕地耕层土壤养分状况评价[J]. 贵州农业科学, 41(12): 87-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2013.12.022 贵州省仁怀市地方志编纂委员会. 2013. 仁怀市志[M]. 北京: 方志出版社, 1-806. 黄昌勇. 2000. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1-310. 黄春雷, 宋明义, 魏迎春. 2013. 浙中典型富硒土壤区土壤硒含量的影响因素探讨[J]. 环境科学, 34(11): 4405-4410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201311043.htm 黄仕辉, 方斌, 李欣, 何莎莎. 2020. 基于县域尺度的稻田土壤碱解氮空间异质性研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(2): 179-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCST202002006.htm 金晓亮. 2009. 茅台原料基地土壤养分空间特性与作物产量及品质的关系[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 1-91. 蒋云舞, 王建新, 鲁耀, 杨景华, 周敏. 2013. 不同典型作物种植模式和土壤类型农田养分含量现状分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 41(5): 2063-2066. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.05.068 孔祥斌, 张凤荣, 齐伟, 徐艳. 2003. 集约化农区土地利用变化对土壤养分的影响——以河北省曲周县为例[J]. 地理学报, 58(3): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB200303001.htm 鲁如坤, 时正元, 赖庆旺. 2000. 红壤长期施肥养分的下移特征[J]. 土壤, 32(1): 27-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA200001005.htm 廖晓勇, 陈治谏, 刘邵权, 王海明. 2005. 三峡库区小流域土地利用方式对土壤肥力的影响[J]. 生态环境, 14(1): 99-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2005.01.021 聂明华. 2008. 紫色土的特性及改良措施——以武夷山紫色土为例[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 3: 60-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJN200803024.htm 李娟. 2007. 植物钾、钙、镁素营养的研究进展[J]. 福建稻麦科技, 25(1): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9799.2007.01.022 刘国栋, 崔玉军, 谭福成, 王恩宝, 温丹. 2008. 黑龙江五常地区土壤肥力及环境健康评价[J]. 现代地质, 22(6): 1010-1014. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.06.018 李龙波, 刘涛泽, 李晓东, 刘文景, 刘丛强. 2012. 贵州喀斯特地区典型土壤有机碳垂直分布特征及其同位素组成[J]. 生态学杂志, 31(2): 3-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201202003.htm 李小刚, 马友华, 王强, 郭粹锦. 2014. 县域耕地土壤养分的时空变化及区域施肥研究——以肥东县为例[J]. 土壤, 46(6): 976-983. 梁涛, 高兴仁, 徐毅丹, 文殊, 周玲, 陈艳. 2015. 重庆2个区土壤养分状况与海拔高度关系分析[J]. 南方农业, 9(1): 28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-890X.2015.01.016 刘强, 杨东. 2017. 不同土壤类型有效微量元素的空间特征——以张掖市临泽县为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 24(6): 205-215. 梁玉峰, 谭长银, 曹雪莹, 何其辉, 朱上游, 谢雨呈, 代兵. 2018. 不同土地利用方式下土壤养分和重金属元素垂直分布特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 12(6): 1792-1799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201806027.htm 李卫东, 陈永波, 黄光昱, 张朝阳, 胡百顺, 秦邦, 刘淑琴, 陈娥, 熊倩. 2018. 恩施州耕地土壤剖面理化特征及养分分布变化规律[J]. 土壤, 50(6): 1134-1138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806012.htm 李佳, 方园, 李政龙, 丁心科, 郑晓伟, 徐正华, 官开萍. 2019. 浙江吴兴区耕地土壤养分地球化学特征[J]. 矿产勘查, 10(10): 2711-2718. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.10.033 林建平, 邓爱珍, 赵小敏, 江叶枫, 韩逸, 谢雨. 2019. 南方典型丘陵山区不同高程耕地土壤养分变化特征分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 50(5): 300-309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJX201905034.htm 马云, 何丙辉, 陈晓燕, 史志民, 何建林. 2009. 不同土地利用方式下坡面土壤养分分布特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 23(6): 118-122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.06.027 秦占飞, 常庆瑞. 2012. 县域土壤养分空间变异分析——以蒲城县为例[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 30(1): 30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7601.2012.01.006 祁桥伟. 2018. 西安市耕地土壤有机质及氮磷钾养分分布特征[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 1-33. 沈其荣. 2001. 土壤肥料学通论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1-308. 孙朝, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 杨晓燕, 黄勇, 陈恩科. 2010. 典型土壤环境中硒的迁移转化影响因素研究——以四川省成都经济区为例[J]. 中国地质, 37(6): 1760-1768. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.023 尚斌, 邹焱, 徐宜民, 宋文静, 王程栋, 孟霖, 刘晓冰, 褚智国. 2014. 贵州中部山区植烟土壤有机质含量与海拔和成土母质之间的关系[J]. 土壤, 46(3): 446-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201403010.htm 申玲, 于健龙, 杨永奎, 胡辉, 杨波, 梁燕菲. 2015. 毕节地区4大类型土壤的养分含量及土壤C/N值分析[J]. 湖南农业科学, 10: 61-64. 邵代兴, 周开芳, 刘红, 林莉. 2017. 遵义市耕地土壤的养分含量及其变化趋势[J]. 贵州农业科学, 45(5): 62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2017.05.017 童倩倩, 何腾兵, 高雪, 彭志良, 韩峰, 赵泽英, 杨莉, 袁成军, 杨柳. 2011. 贵州省耕地土壤的养分状况[J]. 贵州农业科学, 39(2): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2011.02.027 童建川. 2016. 重庆紫色土区硒分布特征研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 41(3): 170-175. 魏复盛, 杨国治, 蒋德珍, 刘志红, 孙本民. 1991. 中国土壤元素背景值基本统计量及其特征[J]. 中国环境监测, 7(1): 3-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB199101000.htm 王晖, 丁伟, 许自成, 石俊雄, 张长云. 2006. 贵州烟区紫色土与其它土壤类型养分特点的差异[J]. 贵州农业科学, 34(3): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2006.03.008 吴晓磊, 王大庆, 徐博, 聂颖, 王宏燕. 2010. 漫岗丘陵区黑土村级农田土壤养分空间变异研究[J]. 土壤通报, 41(4): 825-829. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201004014.htm 王维. 2017. 赤水河中上游土壤养分及重金属污染评价--以仁怀市五马镇三元村为例[D]. 硕士学位论文. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 1-53. 吴晨媛. 2018. 庐山土壤有机质与速效钾的关系[J]. 现代农业科技, 11: 186-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANHE201811117.htm 汪景宽, 徐英德, 丁凡, 高晓丹, 李双异, 孙良杰, 安婷婷, 裴久渤, 李明, 王阳, 张维俊, 葛壮. 2019. 植物残体向土壤有机质转化过程及其稳定机制的研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 56(3): 528-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201903003.htm 鲜娅, 孟广涛, 赵亚男, 王勉. 2014. 高黎贡山东坡不同海拔梯度土壤有机质和全氮的垂直分布规律[J]. 江西农业学报, 26(5): 6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8581.2014.05.002 徐传奇, 廖富强, 贾玉连, 黄思源, 连丽聪, 凌超豪, 龙进. 2016. 中国南方网纹红土元素地球化学特征及其对网纹化过程的指示意义[J]. 古地理学报, 18(5): 865-878. 尹梅, 洪丽芳, 付利波, 陈华, 王劲松, 苏帆. 2012. 滇东红壤区不同海拔高度带玉米的土壤养分丰缺指标研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 3: 39-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRFL201203008.htm 姚光琴. 2016. 景谷县勐班乡不同土壤类型养分现状及对策[J]. 现代农业科技, 2: 215-217. 杨立国, 马志超, 王鑫. 2019. 内蒙古通辽市科尔沁区土壤硒地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 28(4): 383-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.04.012 袁杭杰, 杨文叶, 李丹, 王京文. 2020. 杭州市郊旱地耕作土壤养分评价[J]. 浙江农业科学, 61(1): 147-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNX202001044.htm 郑永春, 王世杰. 2002. 贵州山区石灰土侵蚀及石漠化的地质原因分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 5: 69-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2002.01.016 章明奎, 徐建民. 2002. 利用方式和土壤类型对土壤肥力质量指标的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 28(3): 277-282. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-9209.2002.03.010 张小琴, 郭晔红. 2002. 临泽县不同土壤类型肥力分析[J]. 甘肃林业科技, 27(2): 9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0960.2002.02.003 郑华, 苏以荣, 何寻阳, 黄道友, 吴金水. 2008. 土地利用方式对喀斯特峰林谷地土壤养分的影响——以广西环江县大才村为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 27(2): 177-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.02.013 张凤禹, 祝艳, 王喜宽, 康红在. 2010. 内蒙古托克托地区土壤养分状况评价[J]. 现代地质, 24(5): 1022-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.05.026 赵瑞芬, 张一弓, 张强, 程滨, 张建杰. 2010. 不同土地利用方式对土壤养分状况的影响——以太原市为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(14): 262-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201114055.htm 占丽平, 李小坤, 鲁剑巍, 王瑾, 廖志文. 2012. 土壤钾素运移的影响因素研究进展[J]. 土壤, 44(4): 548-553. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.04.004 周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 湛龙, 梁晓红, 张洁, 孙众从, 雍太健, 唐志敏. 2018. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究: 以青塘-梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 32(6): 1292-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm -
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 贺军奇,拜寒伟,王金泉,徐轶玮,倪莉莉. 黄土区不同地貌类型耕地土壤养分空间格局及驱动因素. 水土保持研究. 2024(05): 221-231 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 潘有良,费光春,张钟华,杨恩林,王小洪,刘浩,肖波,吴鹏,肖玉. 贵州省桐梓县耕地表层土壤钾元素分布特征及生态环境评价. 中国地质. 2024(04): 1304-1318 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李民军,杜健. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析的刚察县耕地土壤肥力综合评价. 中国农学通报. 2023(26): 51-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 罗荣鹏,刘佳君,王雨薇,李耀. 仁怀市土壤主要理化性状及特征分析. 山地农业生物学报. 2023(06): 18-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘思佳,常森,吴红梅,文雪峰. 仁怀市地质多样性特征及价值分析. 山地农业生物学报. 2023(06): 1-8+31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 息朝庄,刘开坤,吴林锋,范云飞. 耕地土壤养分元素调查与评价:以贵州惠水涟江高效农业园区为例. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 43-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 吴生华,兰安军. 赤水河流域白酒产业空间分布特征及影响因素——以仁怀市为例. 农业与技术. 2022(03): 169-173 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杜国强,陈富荣,邢润华,梁红霞,陶春军,李明辉,史春鸿,严明疆. 皖江经济带耕地土壤养分丰缺地球化学评价及科学施肥研究. 安徽农业科学. 2022(07): 150-154+183 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 曹雨,房莉,余健,水恒涛,黄振华. 长江下游沿江丘岗圩田地形区土壤养分空间分布特征及影响因素. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(05): 453-461 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: